Fundamentals of Computer Systems
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This will skip actual Boolean Algebra prep and only include like the definition of De Morgans Law because F*** BOOLEAN ALGEBRA. AQA if you're reading this and put it on the gawdamn 2024 paper I will do something.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
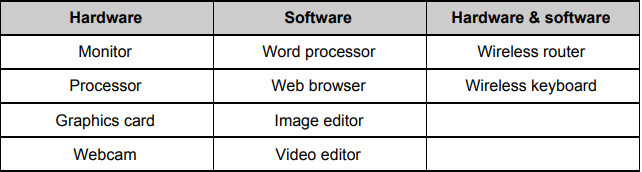
What is Hardware?
Something physical that you can feel and touch and embrace.
Can be both Internal AND EXTERNAL hardware (Mice, Keyboards etc. count)
What is software?
Something virtual, online, untouchable
What is the difference between System and Application software?
The same difference between Vital and Extra. Between System 32 and Google Chrome.
One works for the system one is simply just for the user.
What are the 4 types of system software?
OS (Operating System)
Utility Programs (Example: Speccy)
Libraries
Translators (Compilers, Interpreters, assemblers)
What is the Role of the OS?
To act as a platform for software to run free
To handle operations between Hardware and Software so that they can speak in unison
What does OS stand for?
Operating System
What is counts as both Hardware & Software combined?
Bluetooth, wireless hardware makes use of both Hardware and Software.
What are library programs?
Libraries provide helpful functions which can be used by a program with this being incredibly helpful as instead of the programmer having to write their own simply it can be called via the installed library.
What is a translator?
A translator is what makes it possible to ‘translate‘ (hence the name) between different programming languages.
With a different tool for each job:
Compilers
Assemblers
Interpreters
What is the difference between High-Level and Low-Level languages?
High-Level refers to legible human coding languages while Low-Level is things like:
Machine Code
Assembly Language
(Which personally I think it should probably be the other way round with probably a much Higher level of skill is required to write in machine or assembly language but y’know the rules are the rules.)
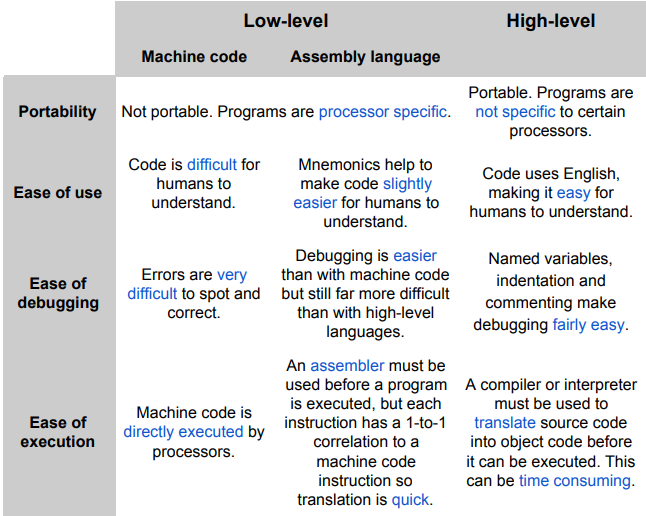
What are the 2 categories of low-level languages?
Machine Code
Assembly Language
What is the difference between Machine Code and Assembly Language?
There is a reason why Machine Code is titled as code and not a language because it literally only makes use of 1’s and 0’s whereas Assembly Language at-least features human level commands
What are some examples of High-Level Languages?
C#,C++,C
Java
Pascal
Python
What makes High-Level languages different to Low-Level?
Not just the difficulty but also that considering High-Level Languages they must be translated so that the computer can understand as well.
This can be done through use of a compiler or interpreter.
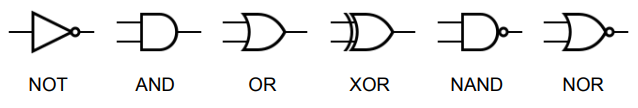
What are the 6 Logic Gates?
NOT
AND
OR
XOR
NAND
NOR
NOT Truth Table?
0 = 1
1 = 0
AND Truth Table?
0 0 = 0
0 1 = 0
1 0 = 0
1 1 = 1
OR Truth Table?
0 0 = 0
0 1 = 1
1 0 = 1
1 1 = 1
XOR Truth Table?
0 0 = 0
0 1 = 1
1 0 = 1
1 1 = 0
NAND Truth Table?
0 0 = 1
0 1 = 1
1 0 = 1
1 1 = 0
NOR Truth Table?
0 0 = 1
0 1 = 0
1 0 = 0
1 1 = 0
What is an Adder?
A logical circuit which adds Boolean values together
How many types of Adders are there?
2
What are the two types of Adders?
Half Adder
Full Adder
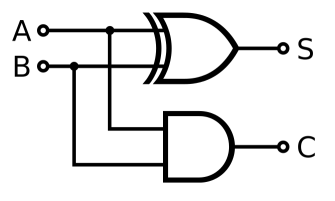
What is a Half Adder?
A type of adder which accepts two inputs and returns two outputs with the overall job of adding two Boolean values.
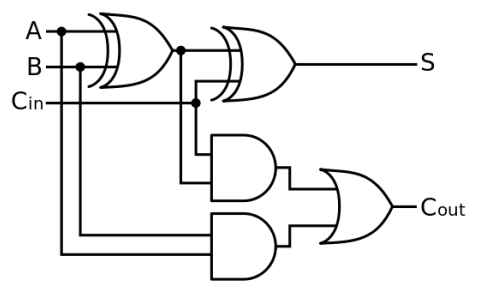
What is a Full Adder?
A type of adder which accepts three inputs and returns two outputs with the overall job of adding two Boolean values and a carry bit.
What is the job of the “Edge-Triggered D-Type Flip-Flop“?
Its job is to act as a memory unit storing a single bit.
It accepts two inputs and returns a single output.
Accepts Data and clock ticks.
What do Assemblers do?
translates assembly language into machine code.
Each assembly has a 1-to-1 relation with machine code making it quick and snappy.
Platform-specific with different CPUs making use of different architecture.
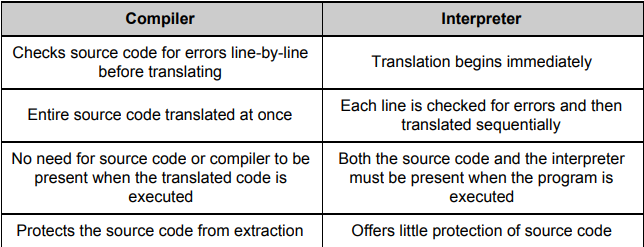
What does compilers do?
Compilers are able to translate high-level languages into machine code.
Compiler takes the source code checking for errors
then translates the entire program at once to be run
Compiled programs don’t require extra software unlike interpreters.
What do Interpreters do?
Interpreters like Compilers convert high-level languages to machine code but instead they do it line by line as well as their error checking procedure also doing it line by line.
This however requires both the interpreter as well as the code being present together. Less Secure compared to compilers.
What is the difference between Compilers and Interpreters?
Compilers will compile the whole thing while interpreters will interpret everything line by line.
What is meant by source code?
The name given to the input to one of the translators
What is meant by Object code?
A translators output is titled object code being then made form source code