Biochemistry 2 Week 5
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
The following molecules participate in oxidation-reduction reactions EXCEPT
FADH2
NAD+
plastoquinone
ATP
ATP
Which of the following is true for an open system?
It allows for free exchange of matter and energy with the surroundings.
Which of the following is correct concerning the first law of thermodynamics in biological systems?
Pressure and volume do not change
Which of the following would be an example of decreasing entropy?
flow of ions through a channel from higher ionic concentration to lower ionic concentration
catabolic pathway
anabolic pathway
ice melting
anabolic pathway
For the reaction: A + B ↔ C + D, which of the following is correct?
Keq = [C][D]/[A][B]
Which of the following differentiates the biochemical standard state from the standard state when discussing standard free energy changes?
1M concentration for all reactants and products
Temperature of 298 K
pH of 7
Constant pressure of 1 atm
pH of 7
In which case will a reaction be spontaneous only above a certain temperature according to the Gibbs free energy equation?
ΔH > 0; ΔS > 0
Which of the following statements is correct?
an endergonic reaction drives an exergonic reaction in living systems
an exergonic reaction drives an endergonic reaction in living systems
ATP is rarely used in coupled reactions
the overall free energy of a coupled reaction is the difference of the free energies for the individual reactions
An exergonic reaction drives an endergonic reaction in living systems
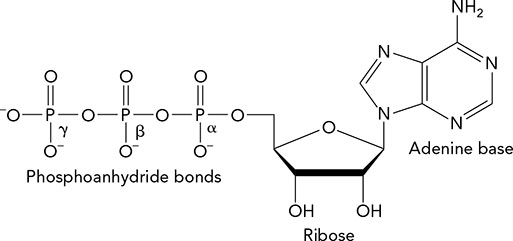
For ATP (shown below), cleavage of the bond between __________ has the largest ΔG°′.
α phosphate and β phosphate
Reduced molecules become _____ upon donating an electron in a redox reaction
oxidized
Photosynthesis reactants
sunlight
CO2
water
Photosynthesis products
glucose
O2
Which of the following statements about redox reactions is correct?
A reduced compound becomes oxidized only when it acquires an electron from an oxidized compound
An oxidized compound has fewer protons than its reduced counterpart
A reduced compound has more carbon atoms than its oxidized counterpart
A reduced compound becomes oxidized only when it transfers an electron to an oxidized compound
A reduced compound becomes oxidized only when it transfers an electron to an oxidized compound
The energy change in a system is related to the amount of heat transferred and work done. If there is no heat transferred, what is the magnitude of work in a system equal to?
energy change in the system (ΔE = Efinal – Einitial)
Given the following reactions or reaction conditions, determine which are spontaneous.
The hydrolysis of ATP under standard conditions: ATP ⇔ ADP + Pi
ΔGº' > 0
ΔH < 0 and ΔS > 0
Keq = 10,000
ΔGº' = +12.0 kJ/mol
The hydrolysis of ATP under standard conditions: ATP ⇔ ADP + Pi
ΔH < 0 and ΔS > 0
Keq = 10,000
Which of the following biochemical reactions are endergonic?
Glutamate + NH4+ + ATP ⇒ Glutamine + ADP + Pi ; ΔG∘ΔG∘ = −16.3 kJ/mol
ATP ⇒ ADP + Pi ; ΔG∘ΔG∘ = −30.5 kJ/mol
L-Malate + NAD+ ⇒ Oxaloacetate + NADH + H+ ; ΔG∘ΔG∘ = +29.7 kJ/mol
Acetyl-CoA + Oxaloacetate + H2O ⇒ Citrate + CoASH + H+ ; ΔG∘ΔG∘ = –32.2 kJ/mol
Glutamate + NH4+ ⇒ Glutamine; ΔG∘ΔG∘ = +14.2 kJ/mol
L-Malate + NAD+ ⇒ Oxaloacetate + NADH + H+ ; ΔG∘ΔG∘ = +29.7 kJ/mol
Glutamate + NH4+ ⇒ Glutamine; ΔG∘ΔG∘ = +14.2 kJ/mol
Which statement best describes the relationship between anabolic and catabolic pathways?
Catabolic pathways convert energy-rich compounds into energy-depleted compounds and are generally associated with breakdown, whereas anabolic pathways use compounds high in chemical energy for biosynthesis.
Which of the following reactions is anabolic?
ATP ⇒ AMP + PPi
GTP ⇒ GDP + Pi
sucrose ⇒ fructose + glucose
glycerol + fatty acids ⇒ a triacylglycerol
glycerol + fatty acids ⇒ a triacylglycerol
The thermodynamic parameter entropy is a measure of
disorder
What are the units of entropy?
joule/mol*K
Given equal masses (the same number of moles of a compound), which phase of matter has the greatest entropy?
gas
At 25 °C, what is the Keq for a reaction where ΔH∘ΔH∘ = –9.3 kJ/mol and ΔS∘ΔS∘ = 75.5 J/mol·K?
375000
How are changes in enthalpy (H) and entropy (S), related to changes in free energy (G)?
ΔG=ΔH−TΔS
Given the following common reactions, which are entropically favored?
2 pyruvate ⇒ glucose
6CO2 + 6H2O ⇒ C6H12O6 + 6O2
glucose6P ⇒ fructose6P
ATP ⇒ ADP + Pi
ATP ⇒ ADP + Pi
At standard conditions, a biochemical reaction has a Keq of 4,000. The reaction favors the
products
What is the change in free energy of this reaction, which has Keq = 4,000?
-20.5 kJ/mol
Given the following reaction,
fructose-6-phosphate ⇔ fructose + Pi ΔG° = –15.9 kJ/mol
What is the equilibrium constant under standard conditions?
614
A reaction is always spontaneous if
the change in free energy, ΔG, is negative
Of the three thermodynamic quantities, ΔG, ΔH, ΔS, which is most useful for determining spontaneity of a reaction?
ΔG
At standard conditions, the equilibrium lies toward products for a given biochemical reaction. What is known about the change in free energy?
ΔG° is less than 0
The sodium–potassium ATPase hydrolyzes ATP to pump two K+ ions inside the cell and three Na+ ions out. This is an example of energy conversion in which the energy from ATP is converted to
a chemical gradient across the cell membrane
an electrical potential across the cell membrane
The ΔG°of ATP hydrolysis is –30.5 kJ/mol. Which of the following reactions are not spontaneous and could be driven by being coupled to hydrolysis of ATP (one ATP molecule per individual reaction)?
dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) ⇔ glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (GAP) (+7.5 kJ/mol)
glucose + Pi ⇔ glucose-6-phosphate (+13.8 kJ/mol)
If a typical person hydrolyzes 100.0 mol of ATP per day, how much does this ATP weigh? (The molecular weight of ATP is 507 g/mol.)
50.7 kg