Osmosis Note Flashcards
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Describe Osmosis
The movement of water from an area of high concentration to low concentration depending on the solute concentration
passive transport
can be both simple and facilitated (aquaporins)
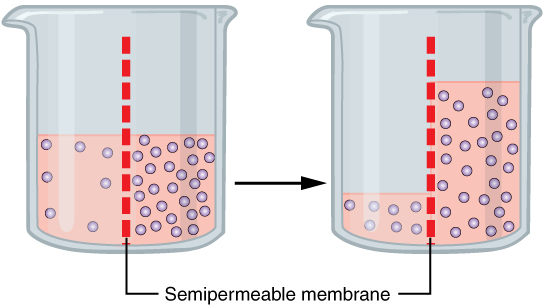
The left side of the jar has 5% NaCI and the right has 15% NaCI. Why would water move towards the right side instead of the left over time?
Because there is a high concentration of water on the left and a low concentration of water on the right, the water will diffuse through the membrane from a high to low concentration
high concentration of water = low solute concentration
low concentration of water = high solute concentration
Osmotic Particles
the dissolved solutes that are separated from a solvent (typically water) by a semipermeable membrane
ex. salts, sugars, and ions
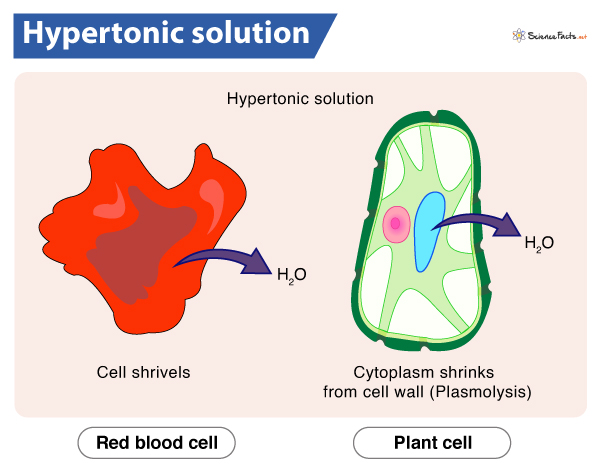
Hypertonic Solutions
an external solution with a higher concentration of solutes and a lower concentration of H2O compared to the inside of a cell
animal cells in a hypertonic solution will shrivel, causing it to shrink and die
plant cells in a hypertonic solution will also shrink and will loose its rigidity, causing it to wilt (plasmolysed)
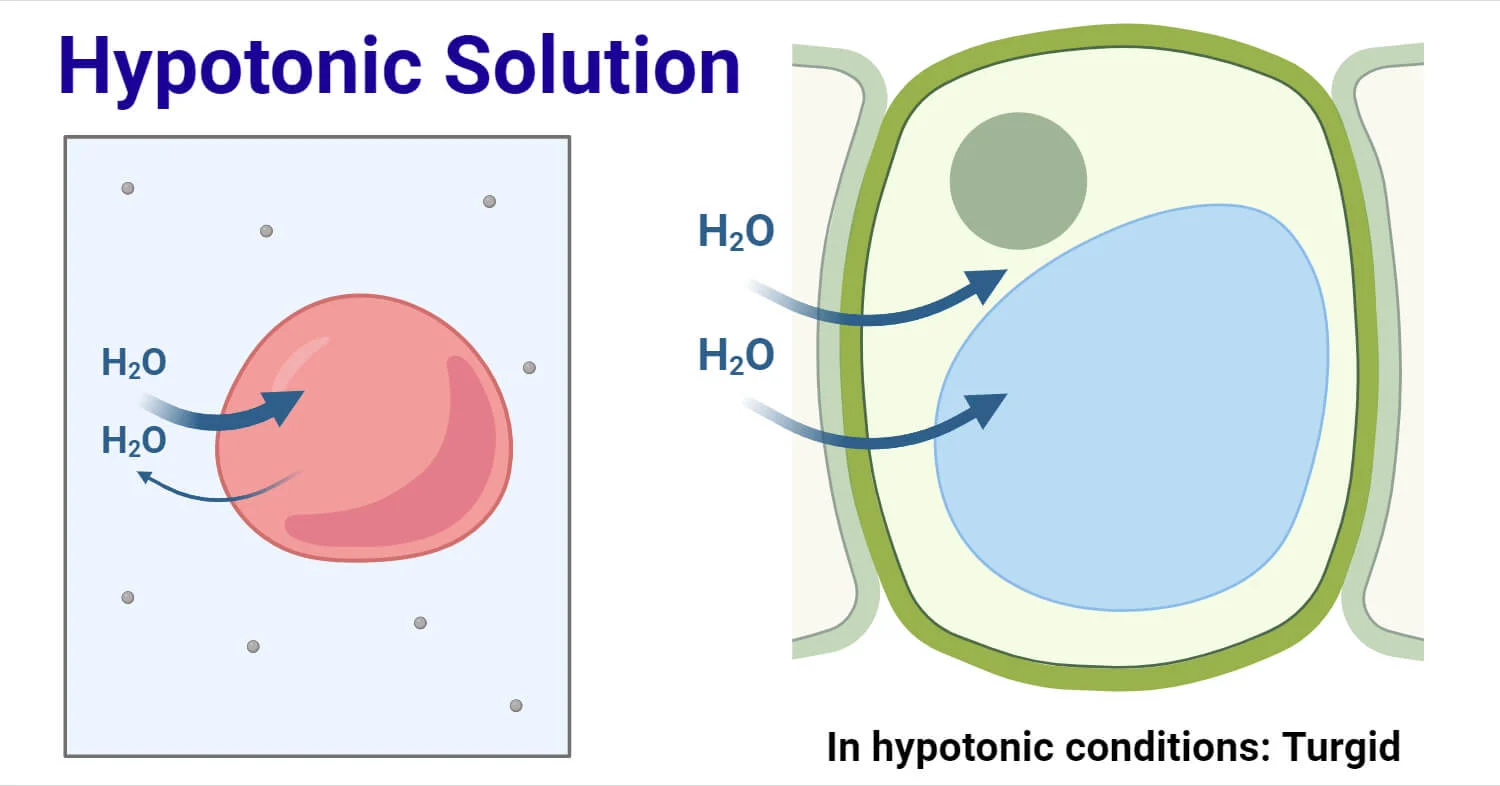
Hypotonic Solution
an external solution with a lower concentration of solutes and a higher concentration of H2O compared to the inside of a cell
animal cells in a hypotonic solution will swell up, causing it to burst and die
plant cells in a hypotonic solution will also swell up, but will not burst due to the cell wall preventing that to happen (turgid)
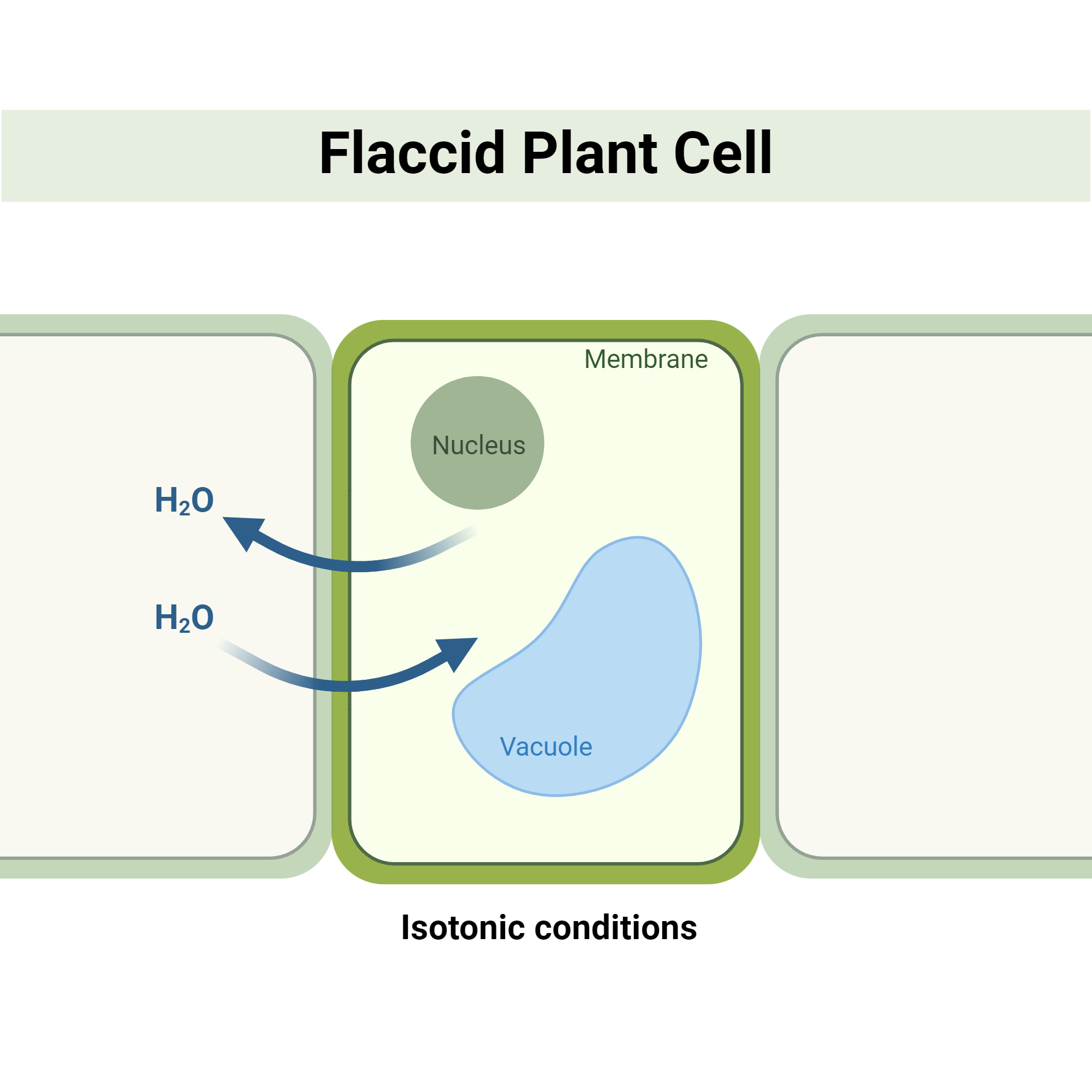
Isotonic Solution
an external solution with the same concentration of solutes and H2O compared as the inside of a cell
both animal and plant cells will remain the same
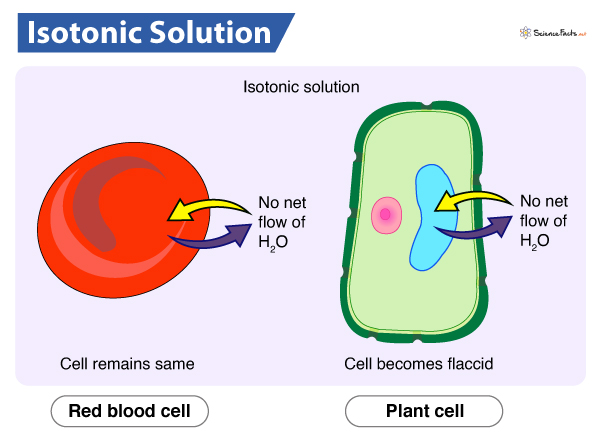
What is always true about the movement of water?
H2O will always move from a hypotonic solution to a hypertonic solution
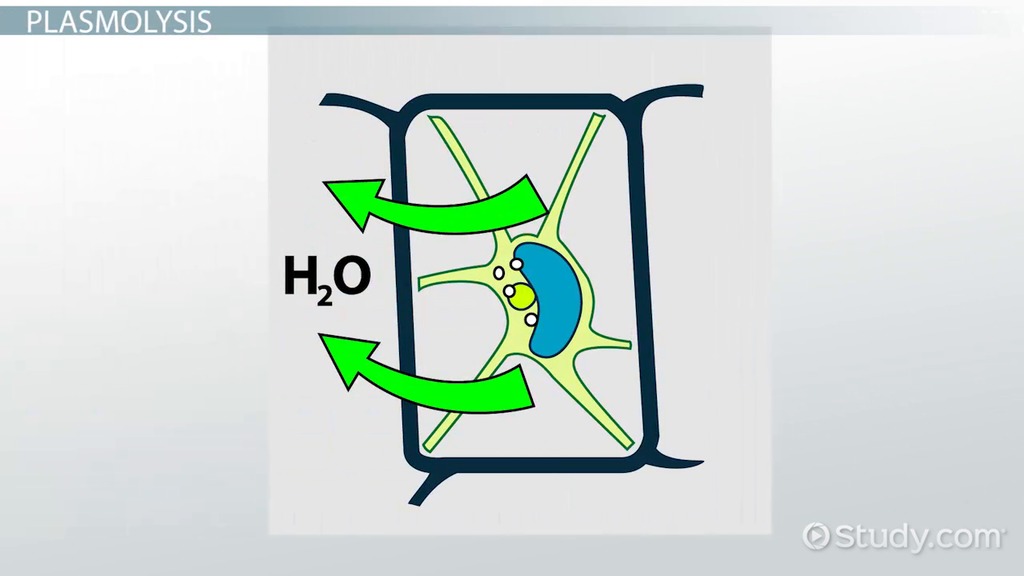
Plasmolysed/Flaccid Plant Cell
a plant cell that is in a hypertonic solution, causing the membrane to shrink and pull away from the rigid cell wall due to excessive water loss
causes it to wilt
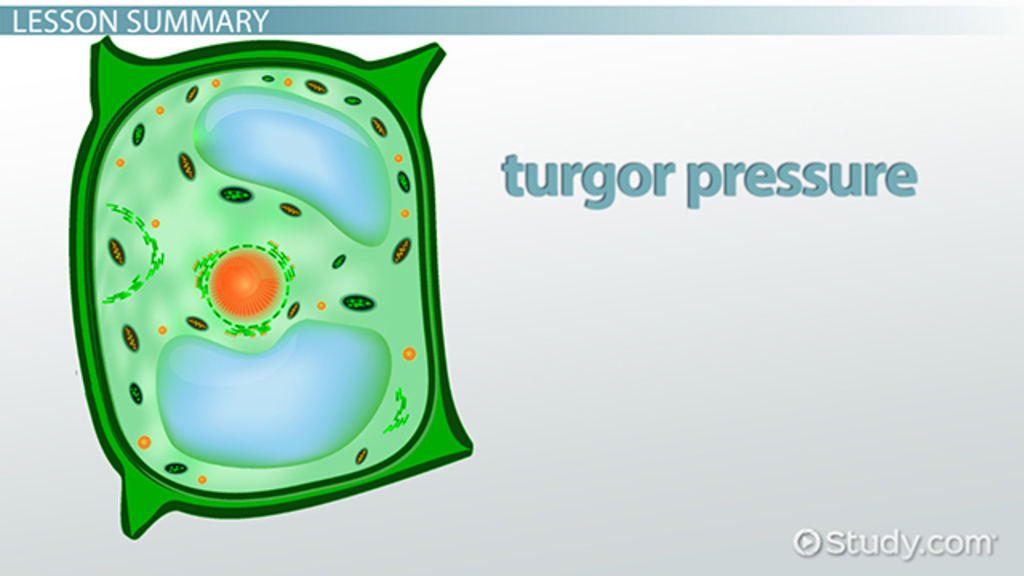
Turgid Plant Cell
a plant cell that is in a hypotonic solution, causing it to be firm and swollen with water as the high turgor pressure pushes outwards against its cell wall
Flaccid Plant Cell
a plant cell that is in a isotonic solution, causing the water to move in and out of the cell at equal rates. This results in a lack of net water movement and the loss of turgor pressure against the cell wall, making the cell limp.