Biomolecules - Carbohydrates
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
12-Pro Biology '24-'25 Learn > Settings > Answer with Definiton ON > Flashcards ON
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What are Micronutrients?
Essential Elements/Small molecule chains required by organisms in Varying amounts
What are Vitamins?
Organic Micronutrients consumed in small amounts
Either Water-soluble (taken w/ water) or Fat-soluble (taken w/ food)
What are Minerals?
Inorganic elements on earth & in food
Needed by body to develop and function normally
What defines being organic?
Possessing C-H bonds
What are Macromolecules or Biomolecules?
4 Groups of molecules that make up the building blocks of life
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
How are Macromolecules made? What are their common components?
Formed by Polymerization: joining small monomers together
Mainly made of Carbon, also H, O, N, P, S
CHONPS
How is Polymerization done?
Condensation/Dehydration Synthesis, where monomers are covalently linked producing water
How is Depolymerization done?
Hydrolysis, where covalent bonds between monomers are broken by the addition of water
What are Carbohydrates?
Fuel and Building material
Main source of immediate energy
Used for energy storage, cell structure, and energy source
What is the general structure of Carbohydrates?
Made of C-H-O bonds
Polymers made of monosaccharides
Monomer: Monosaccharides
What are Monosaccharides?
Simplest form of Carbohydrates
Energy stored in chemical bonds broken during Cellular Respiration
What is the structure of Monosaccharides?
Simple chain of carbon bonded to hydrogen and oxygen C-OH
One Carbonyl group; C=O
What are the types of Monosaccharides?
Glucose, Fructose, and Galactose
What are Disaccharides?
2 Monosaccharides joined by a Glycosidic Linkage:
covalent bond formed by condensation reaction
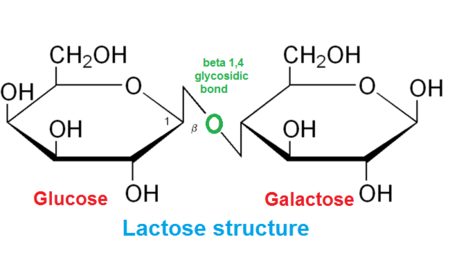
What are the types of Disaccharides?
Sucrose (table sugar) - Glucose + Fructose
Lactose (in milk) - Galactose + Glucose
Maltose (in beer) - Glucose + Glucose
What are Polysaccharides?
Sugar polymers made by long chain of monosaccharides
Function as storage or structural support
What are the types of Structural Polysaccharides?
Cellulose - plant cell walls
Chitin - forms exoskeleton of arthropods and cell walls of some fungi, containing N
What are Storage Carbohydrates?
Polysaccharides used for energy harvest in Hydrolysis
Types: Starch and Glycogen
What is Starch?
Storage carbohydrate of plants
Stored as granules within plastids
Broken down by Animals for nutrition through digestion enzymes
Amylose: One chain of carbohydrates
Amylopectin: Highly branched chain of carbohydrates
What is Glycogen?
Storage carbohydrates of animals
Large Glucose polymer more highly branched than amylopectin
Stored in muscle and liver
May be turned into fats
What are Glycoproteins?
Proteins w/ carb grps attached to its polypeptide chain
Occurs on cell membranes and blood
Serve as receptors for chemical interactions
What are Glycolipids?
Lipids w/ carb grps attached by a glycosidic bond
Occurs on cell membrane: less diverse than Glycoprotein
Facilitate cellular recognition