week seven: conservativism and fascism as theories of IR
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is conservativism IR
Conservatism is not a rigorously developed and cohesive school of thought but a constellation of ideas, attitudes, and thinkers revolving around a series of historically situated rejections of liberal and socialist ideas. As Karl Mannheim argues, conservatism ‘is a counter-movement, and this fact alone already makes it reflective: it is, after all a response, so to speak, to the “self-organization” and agglomeration of “progressive” elements in experience and thinking’.
What are the key strands of conservativism and fascism within IR?
Traditional Conservativism
Conservative Internationalism
Fascist IR Theory
Who was the key proponent of Traditional Conservativism?
1. Edmund Burke (Traditional Conservatism)
│ • Emphasis on order, tradition, stability
│ • Gradualism in foreign affairs
│ • Skepticism of radical change
│ • Morality rooted in inherited practices
Who is the key proponent of conservative internationalism?
Henry Nau (Conservative Internationalism)
│ • Diplomacy backed by force
│ • Democracy promotion
│ • Competition of ideas over balance of power
│ • Belief in moral clarity in foreign affairs
Who is the key proponent in Fascist IR theory?
Benito Mussolini (Fascist IR Theory)
• Imperial expansion as central aim
• Rejection of liberal internationalism
• State power and violence legitimized
• War as a mechanism for national vitality
How does liberalism differ from conservativism?
Believes in human progress, cooperation, and global institutions. Values universal rights and democracy.
Conservatives critique liberalism as utopian and naive.
How does liberalism differ from fascism?
Rejects authoritarianism, racism, and expansionist nationalism. Supports inclusive international order.
Fascism rejects liberal values entirely, seeing them as weak or corrupt. Liberals critique both for undermining peace and individual rights.
How does realism differ from conservativism>
Shares some overlap (pessimism, focus on power and sovereignty), but lacks Conservatism’s moralism and emphasis on tradition.
Conservatives critique realism for being amoral.
How does fascism differ from realism?
Fascism is more ideological and aggressive than realism’s pragmatic statecraft.
Realists critique fascism as reckless and destabilizing.
How does Marxism/critical theory differ from conservativism
Fundamentally opposed to Conservatism’s defense of tradition and existing hierarchies. Focuses on class struggle and systemic change.
Conservatives reject Marxism as radical and utopian.
How does realism differ from fascism?
Sees fascism as a capitalist tool of repression. Strongly anti-fascist and anti-authoritarian
Marxists critique conservatism as preserving elite rule; fascism as violent repression of the working class. Sees fascism as a capitalist tool of repression. Strongly anti-fascist and anti-authoritarian.
How does post-colonialism differ from conservativism?
Critiques Conservatism for Eurocentrism and support of imperial legacy. Challenges the celebration of Western tradition.
Post-colonial scholars expose the colonial logic within both theories. Conservatives push back, defending historical legacy;
How does post-colonialism differ from fascism?
Identifies fascism as an extension of racialized imperial domination. Strongly opposes it. fascists actively embody colonial power structures.
What is the normative position of conservativism?
- Emphasizes moral order, tradition, prudence, and sovereignty.
- Skeptical of universal ideals, abstract theories, and utopianism.
- Believes freedom must be defended (not assumed), and values restrained but principled international engagement.
- Argues that IR must be grounded in historical continuity, national interest, and cultural particularism.
What is the normative position of fascism?
- Anti-universalist, anti-democratic, and often racist.
- Normatively seeks strength, unity, and hierarchy through authoritarian rule and expansionist nationalism.
- Views international relations as a space for struggle between civilisations or races.
- Rejects liberal values and embraces a vision of order based on power and identity.
What are some examples of conservativism and fascism?
Examples
Empirical
Theoretical
Reagan's Anti-Communist Policies
Armed Diplomacy and Moral Clarity
• Military buildup confronting Soviet Union
• Support for anti-communist forces in Central America
• 30,000 deaths in Nicaragua's Contra War
• Framing conflict as moral struggle between freedom and tyranny
• Demonstrates conservative internationalism's willingness to use force
• Illustrates conservative emphasis on ideological competition
• Shows prioritization of anti-communism over human rights concerns
• Reflects Manichean worldview dividing states into good and evil
George W. Bush's Iraq War
Neoconservative Democracy Promotion
• Invasion justified as promoting democracy and security
• Unilateralism and "coalition of the willing" instead of UN approval
• Nation-building attempt in Iraq
• Destabilization of regional order and rise of insurgency
• Exemplifies neoconservative belief in transformative power of force
• Shows rejection of multilateral constraints on American power
• Demonstrates faith in universal applicability of Western democracy
• Illustrates consequences of conservative military interventionism
Trump's "America First" Policy
Conservative Nationalism in Practice
• Withdrawal from international agreements (Paris Climate Accord, Iran Deal)
• Skepticism of NATO and traditional alliances
• Tariffs and trade wars with allies and competitors
• Anti-immigration policies and border wall construction
• Demonstrates prioritization of perceived national interest over global commitments
• Shows conservative nationalist skepticism of multilateralism
• Reflects belief that international relations should directly benefit domestic constituency
• Illustrates transactional approach to foreign relations
USAID Budget Cuts Under Trump
Conservative Anti-Internationalism
• 83% of agency programs canceled
• 2,900 USAID workers losing jobs
• Significant reduction in global health funding, including HIV/AIDS
• Humanitarian consequences in developing nations
• Exemplifies conservative skepticism toward foreign aid
• Shows prioritization of domestic spending over global concerns
• Reflects belief that development assistance is ineffective or counterproductive
• Demonstrates preference for bilateral over multilateral engagement
Fascist Italy's Invasion of Ethiopia (1935)
Fascism's Imperial Expansionism
• Mussolini's campaign for a new Roman Empire
• Use of chemical weapons against Ethiopian forces
• Rejection of League of Nations condemnation
• Racial hierarchy justifying colonial conquest
• Illustrates fascism's glorification of imperial conquest
• Demonstrates rejection of international law and norms
• Shows how racial ideology informed fascist foreign policy
• Exemplifies the militaristic nationalism central to fascist IR
What is conservativism?
- Corey Robin: conservatism is defined by being reactionary and often counterrevolutionary in response to changes promoted by liberal and
left politics and social movements.
- Robin: defence of hierarchy and getting lower classes to support that; victimhood crucial; slave owning and colour consciousness crucial in the US;
- The importance of complacency, status anxiety and dominance o one’s personal realm
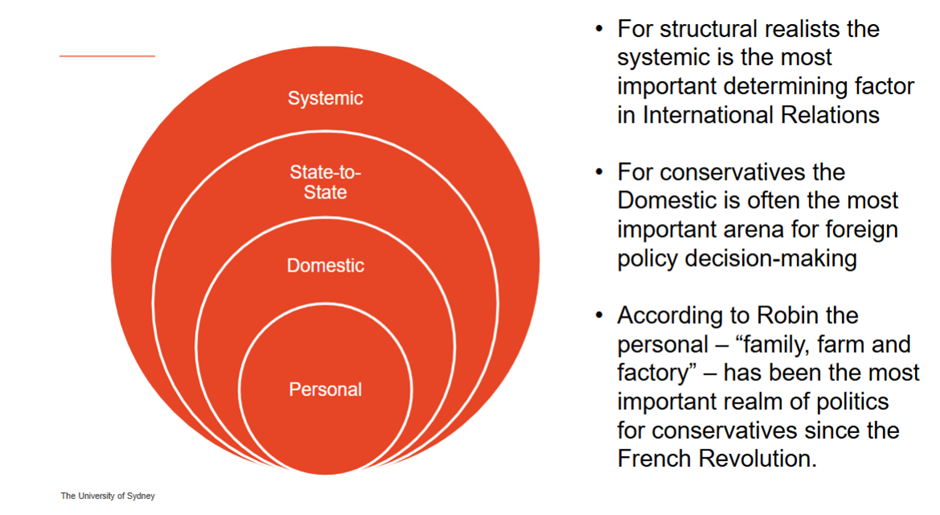
è Conservativism – often reactionary, built around traditional beliefs of family, kings and queens, etc. Usually reacting against change, hence defence of hierarchy and sense you can co-opt lower classes into supporting it through claims of victimhood- white men and white people. Perfectionism, utopianism etc is not appreciated.
è Conservatives prioritise the interpersonal, they prioritise the sense that it’s our proximate relations in the factory, family and field that are most important
è These abstract ideas of global power etc.
o Overlaps with feminism = the personal is political. The level of analysis is interesting to ponder with feminism.
What are the core beliefs of American conservatives?
- The first is an unwavering promotion of capitalism (anti-welfarism and anti-socialism)
- The second is moral opposition to abortion rights, LGBTQ+ rights and so-called
“permissive” culture.
- The third is a zealous advocacy of certain rights and freedoms: gun ownership, free
speech (particularly speech considered to be politically incorrect by liberal
academics), and freedom from economic, environmental and even health regulations.
- American conservatives are largely consumed by promoting and defending these
commitments, thus generally relegating foreign affairs to a secondary concern for
them.
- What do the “conservative internationalists” believe?
1. That “diplomacy must be ‘armed’ to push back against nondemocracies outside
common institutions”
2. “The world works through a competition of ideas more so than a balance of power,
as realists believe...”
3. “there is no moral equivalence or 'peaceful coexistence' among ideas, as realists
accept”.
4. “The moral struggle informed the military struggle. Right made might, not might makes right as the realist dictum goes.” Values and interests can be aligned.
5. Nau contends that President Reagan was “the quintessential conservative
internationalist.”
What are the 11 core commitments of Conservative International Relations Theory?
- Unbridled Nationalism: a willingness to try to turn nationalist rhetoric into policies. This nationalism is often exceptionalist or promoting American greatness.
- Power Maximization: a strong determination to maintain American primacy
- Instinctive Militarism: a prioritizing of military strength and seeing the military as a problem- solving tool.
- Reductive framing of issues and conflicts: Manichean view of enemies and a constant
projection of “toughness” toward threats and suggestion that liberals are too “soft” towards America’s adversaries
- Significant opposition to multilateralism and legalism, and preference for unilateralism or “coalitions of the willing”
- A strong tendency to see foreign policy as principally serving domestic electoral aims
- Lack of knowledge, interest in, and at times even a lack of empathy for, the rest of the world
- A focus on the ability of individual leaders to achieve transformations and greatness in world affairs
- Religion as a guide and motivator of foreign policies
- A patriarchal worldview
- Racialist or Civilizational view of the world
What level does conservativism take place, in terms of analysis?
What are the core tenets of fascism as an IR theory?
- Madeleine Albright: “Fascism should perhaps be viewed less as a political ideology
than as a means for seizing and holding power.”
- As a historical movement Mussolini's Fascist Party and Hitler’s NAZI Party represented
the “last” iteration of European imperialism
- As an ideology: ultra-nationalist; racist; scapegoat oriented; symbiotic relationship
between the leader and their supporters; state and supporter (mob) violence as
necessary and even inspiring; intolerance to alternative views or rivals; searches for
lost past glorious (renewed greatness) in the face of proclaimed “national decline”.
- Fascism as IR theory is profoundly nationalist, imperialist (but potentially isolationist),
and militarist. It is an extreme version of conservatism
Is Trump a fascist?

• January 6, 2021 and the pardons
• Threats of deporting and jailing opponents
• Immigration policies
• Arresting student protesters
• Secretary of Defense Pete Hegseth
• Anti-American museum declaration