Textiles for interior designers
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
what is a shower-head like tool that viscose is forced through to form synthetic fibers?
A spinneret
Name 2 cellulose fibers
cotton and linen
name 2 protein fibers
wool and silk
cellulose fibers
A natural fiber made from plant cellulose, commonly used in textiles. Examples include cotton and linen.
protein fibers
Natural fibers made from protein, often sourced from animal hair or plant proteins. Examples include wool and silk.
textiles
Flexible materials made from fibers, used for making clothing, upholstery, and other fabric products.
Fibers
Raw materials that produce yarns & fabrics.
Yarns
Continuous strands made from fibers, used to create fabrics and textiles.
Fabrics
When fibers and yarns go through a weaving or knitting process to create a material.
cotton
A natural fiber derived from the seed fibers of the cotton plant, commonly used in textiles due to its softness and breathability.
linen
A natural fiber made from the flax plant, known for its durability, breathability, and ability to wick moisture.
wool
A natural fiber obtained from the fleece of sheep and other animals, valued for its warmth, elasticity, and moisture-wicking properties.
silk
A natural fiber produced by silkworms, prized for its luxurious texture, sheen, and ability to regulate temperature.
Mineral an metallic
Created from naturally occurring minerals including the metals gold, sliver, and copper.
manufactured fibers
Derived from synthetic chemicals, natural solutions are chemically treated.
viscose
Organic liquid regenerated into fibers for the making of textiles.
microfiber
manufactured fibers that are finer than all natural fibers, including silk.
cellulose
plant and wood fibers
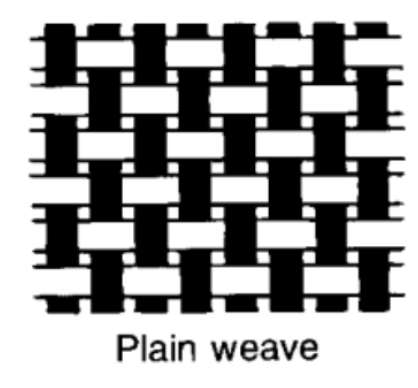
plain weave
made by the simple interlocking of warp threads and weft threads. (simple over under).
warp threads
vertical or lengthwise
weft
horizontal or crosswise
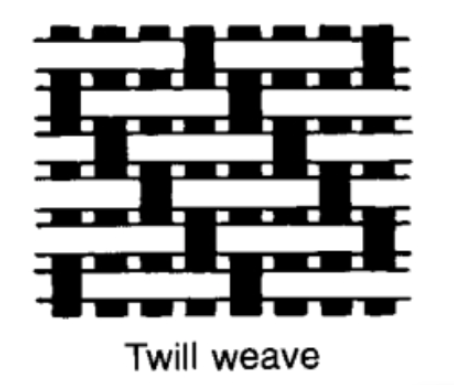
Twill weave
Two or more threads pass over or under another set of threads. skips at regular intervals to create a diagonal effect.
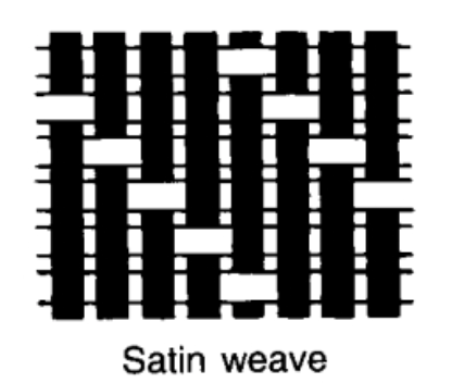
satin weave
floats one warp warn over four or more weft yarns. This makes the fabric really soft.
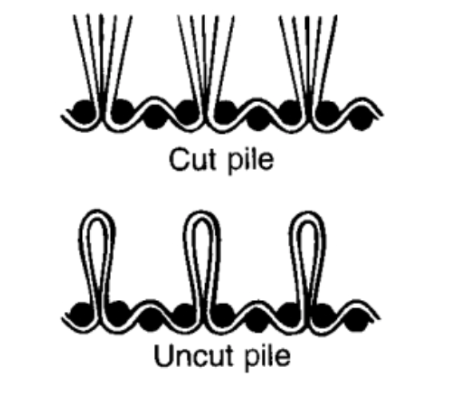
Pile Weave
produced by additional threads in weft or warp that form loops or tufts of yarn that stand out from service of the fabric. Loops can be cute or uncut.
Double cloth weave
woven in two attached in quilted appearance and gives off a quilted affect.
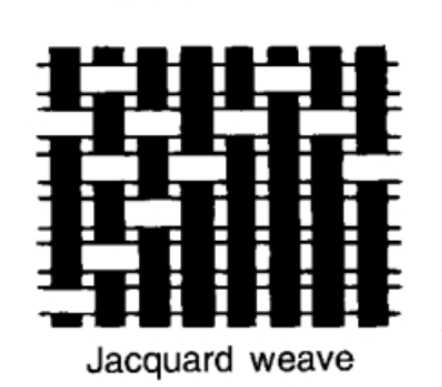
Jacquard weave
Requires an intricate series of hole-punched cards that tell the machine which threads to raise and which threads to drop.
Knitting
Knitting is a method of creating fabric by interlocking loops of yarn with blunt needles.
What is twisting?
Twisting is the process of interlocking and knotting yarn.
Felting
Process of subjecting a mass of fibers to moisture, heat, and pressure. Produces a compact sheet that doesn’t fray, absorbs sounds, provides insulation, and has high resistance to fire.
Bonding
results when two fabrics are adhered chemically or by heat.
Coloring
The process of adding color to materials, including textiles, through various means such as printing ad painting.
Dyeing
The method of applying color to fibers or fabrics using dyes allowing for uniform color throughout the material.
solution dyeing
coloring agent added to viscous l
Stock Dyeing
Dye applied to the fibers BEFORE processed into yarn.
Yarn dyeing
Skeins of yarn dyed BEFORE woven into fabric.
piece Dyeing
Dyeing the fabric AFTER its been woven.
Dye lot
Each time a new batch of color is mixed to dye fabric, it may slightly vary in color from the last one. This is why we have dye lots. It is IPERITIVE to make sure that all the fabric ordered for a job comes from the same dye lot, or else the colors might not match up exactly how me want them.
beetling
gives luster
bleach
whitens
calendering
Provides a smooth finish and tightens weave
chemical finishing
to improve flammability
Heat setting
Add stability, especially for permanent pleating.
Mercerizing
Soaking in caustic soda to cause fibers to swell, which results in improved luster and strength.
Peaching
produces a soft feel.
Pre-shrinking
Make it ready for finishing & prevent fiber contraction when exposed to moisture.
Raising
Produces a flannel like texture.
scouring
removes natural wax & non-fibrous impurities
Singeing
Removes surface fuzz or lint.
Antimicrobial finish
Help prevent mold and mildew.
Antistatic finish
Help guard against static.
Carefree finish
Help resist creasing or wrinkling.
Flame retardant finish
improve insulation qualities.
insulation finishes
improve insulation qualities.
moth proofing finishes
help prevent damage from insects.
soil repellent finish
help resist soiling.
water repellant finishes
helps resist against water and moisture.
hand printing
normally happens after woven and requires manual labor.
Batik printing
section of cloth are colored with wax, dipped into dye, then the wax is removed leaving a pattern.
Hand block printing
A hard wooden block is carved, lined with ink, and stamped onto fabric to create the design.
Tie dye
fabric is wrapped in string and knots, covered in dye, once strings are removed it creates a design.
silk screen
fabric screen resists the color except in desired areas.
machine printed
unlimited styles
roller printing
transfer of color from an engraved copper roller onto fabric.
embossing
engraved rollers produced a pressed high-low design into the fabric.
hand
the feel of the fabric.
wyzenbeek test
a test to count the number of times you can rub a fabric before it starts to wear.
commercial fabrics
25,000 rubs or more
residential fabrics
3,000 rubs per year
colorfastness
measure fabrics resistance to fading from the sun’s rays and from various cleaning methods.
crocking
the color rubbing off onto another fabric or skin.
flammability