water
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
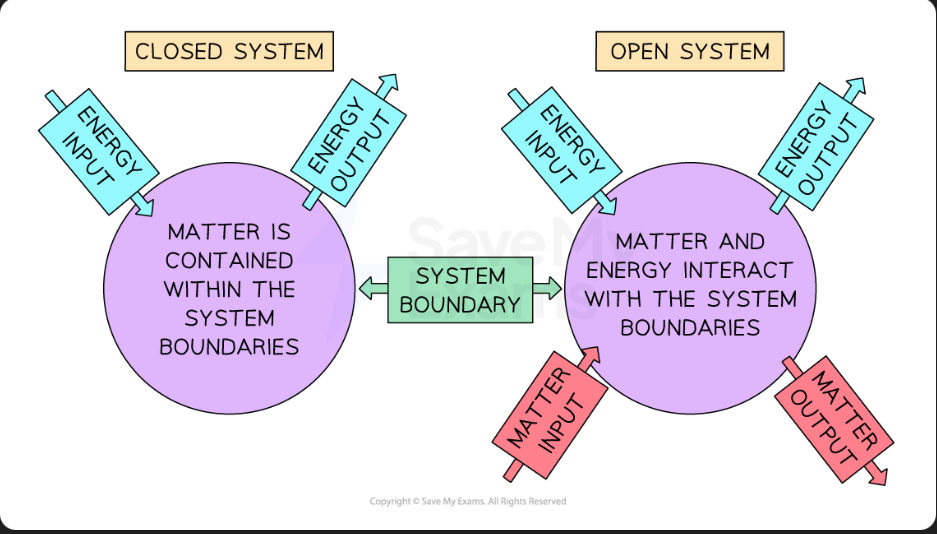
What are open systems?
Have external inputs and outputs of energy and matter exchange at its boundaries
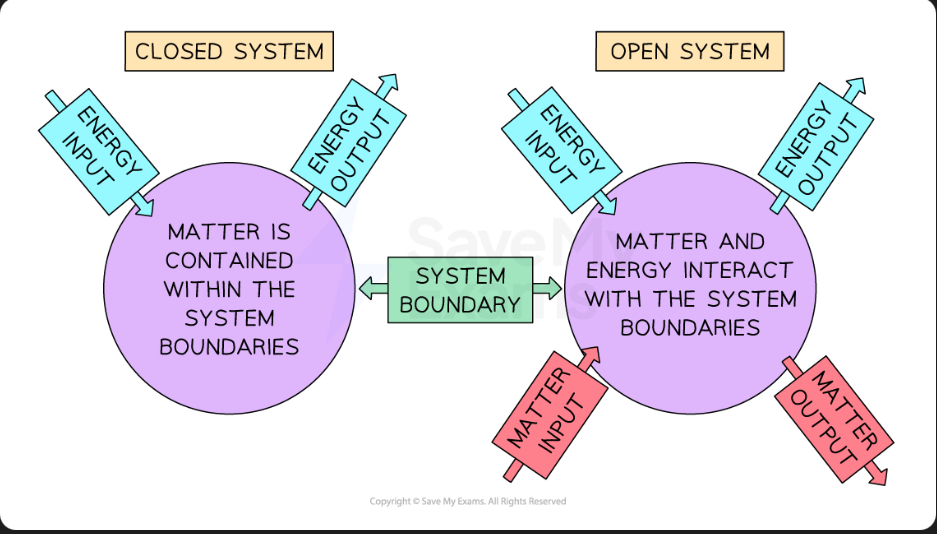
What are closed systems
No inputs occur from outside and nothing is lost. Only energy as its input and output and matter is contained within system boundary
What is the global hydrological system?
The continuous movement of water on above and below the Earths surface. It’s a closed system so no external inputs or outputs, no water lost or gained
Explain how water is recycled in the global hydrological system
The sun evaporates surface water into water vapour
The water vapour condenses to form clouds
Moisture is transported around the globe which drives atmospheric circulation and returns to surface as precipitation
When water reaches the ground, some water will evaporate back into atmosphere whilst some water may percolate the ground to form groundwater.
How does the hydrological cycle lead to local temperature fluctuations
Water evaporates using energy form its surrounding to do this process, which cools the environment. When water condenses, heat is released.
How is gravitational potential energy involved in the hydrological system
When a water droplets falls from high above sea level to the ground it has a high amount of gravitational potential energy. When it’s in motion GPE turn into KE so allows water to move over the surface.
What amount does freshwater make up in all of Earths water
2.5%
What amount of freshwater is locked away and how
1.6% is locked away and 68.7% of this is locked away as ice within cryosphere and the remaining 30.1% is groundwater.
How much of Earths freshwater is accessible to humans
1%
Why’s water stored unevenly around the globe
Water is stored unevenly because of the uneven spread of land to sea and permeable or porous rock which enables aquifers to form.
What are fluxes
Transfers of water in the hydrological cycle
What are annual fluxes
Variations in flows due to to temperature, seasons and location. Flows like evaporation will be greatest in warmer areas so higher rates of precipitation. Store like ice caps will get smaller due to climate change but ocean stores will increase.
What is global water budget
Difference between the inputs and outputs from the different stores
What is residence times?
Time water is held in a store.
What factors affect size of stores and water residence times
Flows or transfers like evaporation
Global factors like climate change
Local factors like human activity on a hill slope
How do transfers affect size of water store and water residence time
More precipitation increases availability of water for storage. Or surface flow increases,allowing more infiltration.
What’s cryosphere
Water stored in solid form like glaciers and ice sheets
What’s hydrosphere
Water stored in liquid form like rivers and lakes, groundwater.
How has climate change affected how water is stored
During last ice age, third of earths surface was ice sheets and glaciers so increased cryosphere stores
This reduced hydrospheres stone and sea levels where 100m lower.
What’s the Inter tropical Convergence Zone
Area of low pressure that forms due to action of the Had,ey Cell, where the Northeast Trade Winds meets the Southeast Trade near the equator.
Explain what happens at the Inter tropical convergence zone
The equator receives more insulation so higher temperatures which leads to more evaporation
Warm moist air rises, cools and condenses and forms banks of towering clouds with heavy rainfall
Low pressure zone created called ITCZ
How is a positive feedback created when cryospheres melt
Melting of ice sheets adds water to hydrosphere like oceans. Ice shelves are destabilised so ice breaks off so they melt and hydrosphere store increases . This is positive feedback loop
What are drainage basins
Area of land drained by a river and its tributaries with a boundary known as the watershed composing of hills and mountains. An open subsystem in hydrological system
What’s a catchment area
An individual drainage basin is the area drained by a river and its tributaries
What features do drainage basin features have
Watershed, source, confluence, tributary,mouth
What’s confluence
Point where two rivers meet
What’s tributary
A smaller stream or river flowing into a larger stream or river
What’s the mouth and source of a river
Mouth- where river meets ocean or sea
Source-furthest point from mouth where river starts
What is orographic(relief) rainfall
Warm moist air formed by evaporation and carried by prevailing wind is forced to rise over high ground like mountains. Air cools, condenses , forming clouds so leads to precipitation. In the rain shadow,Dry air descends and warms so more moisture held in atmosphere.
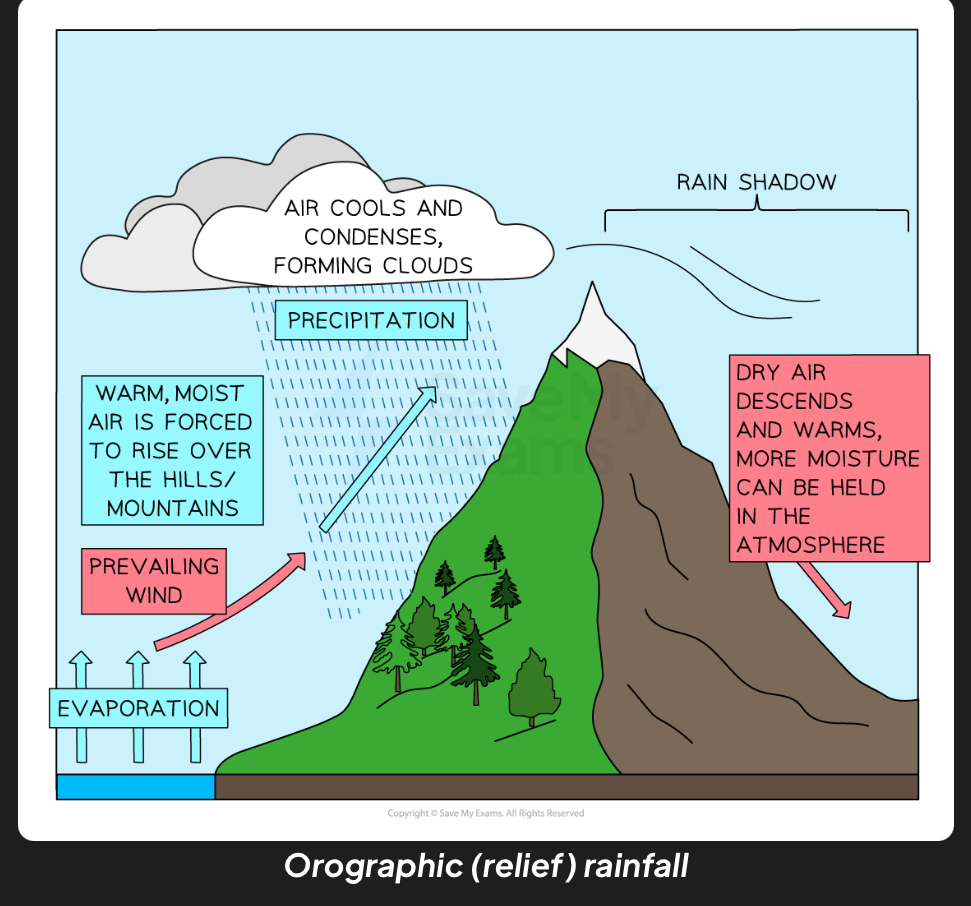
What is a rain shadow
Region with little rainfall because it’s sheltered from prevailing winds by mountains
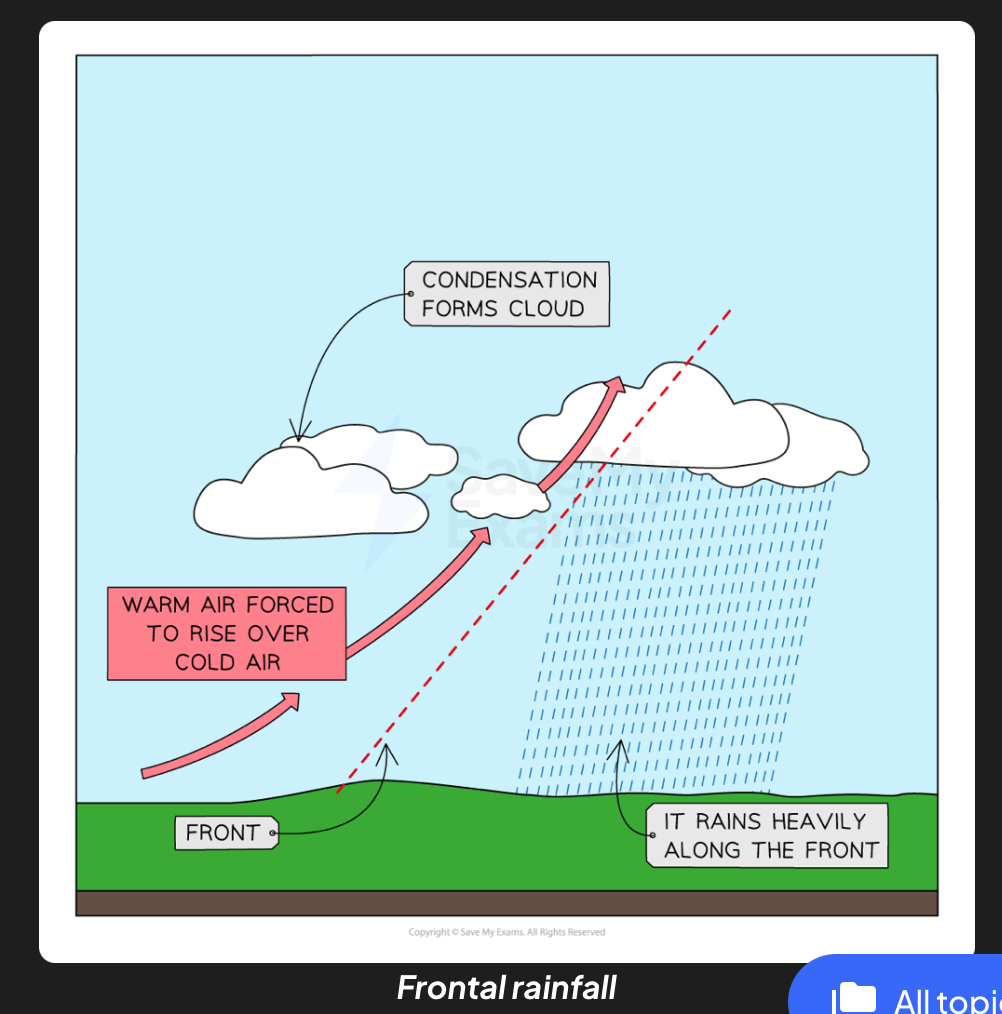
What frontal rainfall
Warm and cold air masses meet and warm air rises over cold air. Warm air cools and condenses to form clouds creating precipitation.
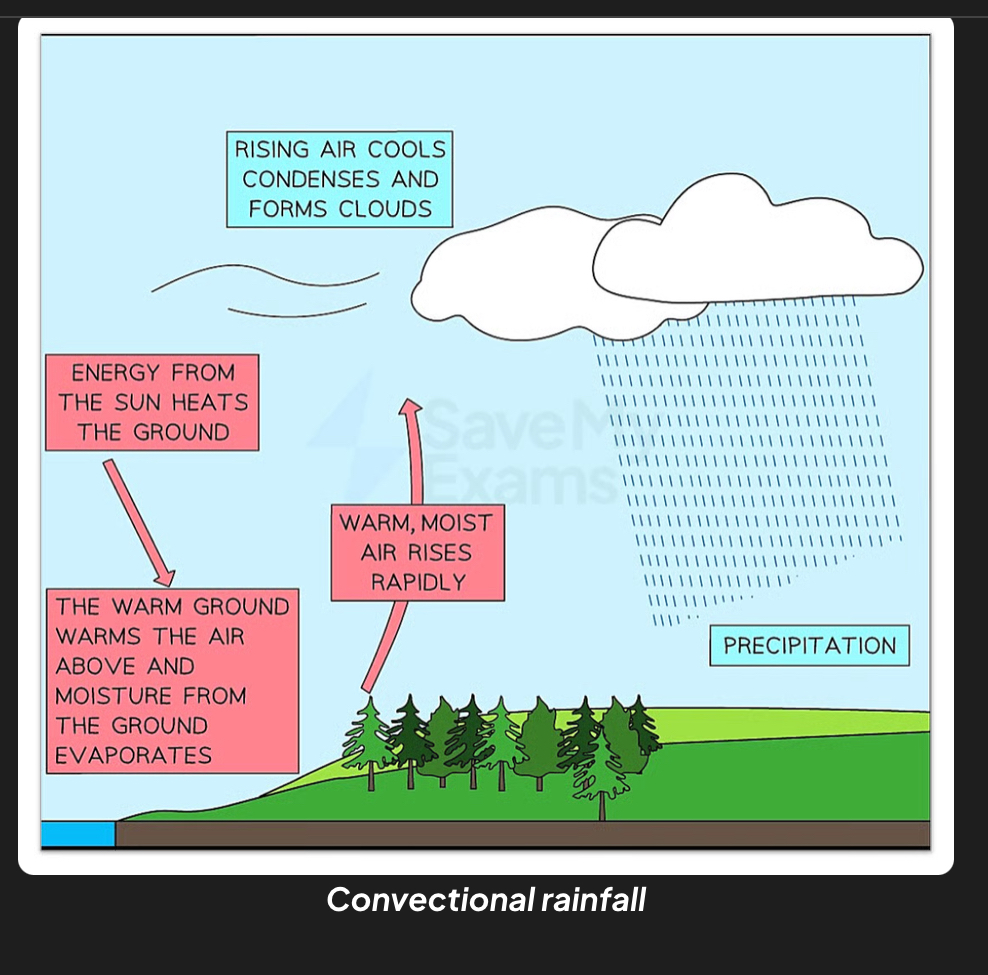
What’s conventional rainfall
Ground heats air above it and moisture from ground evaporates. Warm moist air rises rapidly which cools,condenses to form clouds so that precipitation occurs.
What’s interception
Precipitation that doesn’t reach soil because it’s intercept by vegetation and the forest floor. Reduces surface runoff and so reduces soil erosion and flooding
What’s infiltration
water on the ground soaking into the soil and porous rocks
What’s throughflow
Flowing of water within soil moving towards the river
What’s percolation
Movement of water through soil or underlying porous rocks
What’s groundwater flow
Flow of water through rocks towards river
What are the flows in a drainage basin
Throughflow, groundwater flow, infiltration,percolation, interception
What is river discharge
Volume of water passing a point in the river channel at a hives unit of time and expressed as cubic metres per second or cumecs
What are outputs of drainage basins
Evaporation, transpiration and channel flow
How does climate affect drainage basins
It’s affect type and amount of precipitation
Extent of evaporation
Amount and type of vegetation
How does soil affect drainage basins
Infiltration and through flow- the pores in soil affects rate of infiltration and through flow
Impermeable , saturated or compacted or frozen soil means low infiltration rates and high surface runoff
How does vegetation affect drainage basins
Amount and type of vegetations affects interception, infiltration
Less or no vegetation means more surface runoff off and reduced interception and more infiltration
How does geology affect drainage basins
Impermeable rocks reduces percolation so reduces groundwater flow
Geology affects type of soil which impacts flows
How does relief affect drainage basins
Flatter slopes means more infiltration so reduces surface runoff off , steeper slopes means infiltration is reduced and surface runoff is increased
Upland areas experience more precipitation so affect flows in drainage basins
How does deforestation impact drainage basins
Clearance of trees reduces interception and infiltration rates. Increases surface runoff o, reduces evapotrAnspiratipn which reduces precipitation
How does urbanisation affect drainage basins
Tarmac and concrete are impermeable so reduce infiltration and increase surface runoff. Drainage system move water to rivers more rapidly so increases risk of flooding
How does agriculture impact drainage basins
Reduces amount of large vegetation so decreases interception and increases runoff
How does livestock farming impact drainage basins
Compaction of soil due to livestock trampling so soil is less porous so less permeable so reduces infiltration
How does abstraction affect drainage basins
Over abstraction leads to reduced through flow and groundwater flow in river and reduces groundwater storage
How do reservoirs affect drainage basins
Dams and reservoirs reduce water flow downstream. Increases evaporation as there’s greater surface area of water
What are water budgets
Annual balance between inputs like rain and outputs like evaporation and their impacts on soil water availability
What’s the water budget equation
Precipitation (P) = total runoff (O) + evapotranspiration(E)±changes in storages (S)
How do west seasons impact water budget
Precipitation greater than evapotranspiration which creates water surplus. Groundwater stores fill with water which increases surface runoff o, higher discharge and higher river levels. So positive water balance
How do drier seasons affect water budget
Evapotranspiration exceeds precipitation, plants absorb water so groundwater stores depleted so negative water balance
What’s the soil water budget
Shows the balance between impure and outputs of a soil store over a year. Dependent on soil depth, type, texture, and permeability
What is discharge
Volume of water moving past a point in a river per given time
How is discharge calculated
Q(discharge in cumecs)= A(cross sectional area in m2) x V(velocity m/s)
What factors influence discharge
Rate of precipitation snd how fast water transfers to the river across the drainage basin.
What are hydrographs
Used to measure discharge and they can be annual or storm hydrographs
What are annual hydrographs
Also called a rivers regime, shows the pattern of seasonal variation that takes places through a drainage basin to river discharge over a year. Measured in cumecs.
What are storm hydrographs
Shows changes in a rivers discharge during and after a storm. Drawn to show a river reacts to a storm. They compare to variables, rainfall during storm in mm and river discharge in cumecs
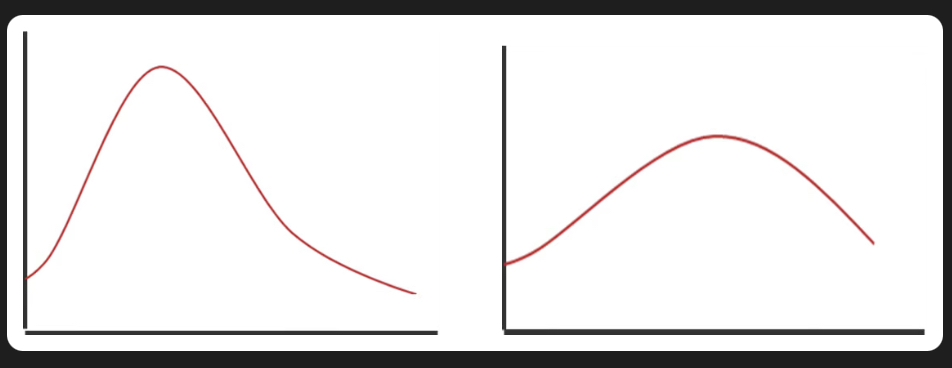
Describe the difference between how a flashy and a flat hydrograph is drawn
Flashy hydrographs have a short lag time with high peak discharge, steep rising limb. Flat hydrograph have longer lag time , low peak discharge and gentle rising limb.
How does rock type affect shape of hydrographs
Impermeable rocks decreases percolation and increases surface runoff so flashy hydropgraph
Permeable rocks allow percolation so lower surface runoff so flat hydrograph
How does soil types affect shale of hydrographs
Clay soils means less infiltration sp increases surface runoff so flashy hydrographs
Sandy soils have a high infiltration rate so decreases surface runoff so flat hydrograph
How does weather and climate affect shape of hydrograph
Heavy or prolonged rainfall and rapid snow melt exceeds soil capacity so increased surface runoff so flashy hydrographs
Steady rainfall and slow snow melt don’t exceed infiltration capacity of soil so flat hydrograph. High evaporation means less surface runoff off so flat shape
How does antecedent conditions affects shape of hydrographs
Saturates soil so infiltration is low and surface runoff is greater so flashy shape
Unsaturated soils so infiltration is high and surface runoff is low so flat
How does vegetation affect shape of hydrographs
Deciduous plants and trees means less interception in winter as they shed leaves so flashy
Trees means high levels of interception so flat
How does drainage basin size affect shape of hydrographs
Smaller basins have steep rising limbs and short lag time as water reaches rivers more quickly
Large basins have longer lag times and gentle rising limbs as water takes longer to flow through basin
How does deforestation affect shape of hydrographs
Deforestation reduces interception, urbanisation increases impermeable surfaces, agriculture increases compaction of soil so increases surface runoff off so flashy shapes
Afforestation increases interception so flat.
What are droughts
Extended period of time when there’s below average rainfall
What are meteorological droughts
Occurs when there’s a rainfall deficit and caused by changes in atmospheric circulation leading to lack of rain from short term or long term changes , lack of rainfall combined with high temperatures so increases evaporation
What is agricultural drought
Water deficiency in soil leading to crop failure and reduced biomass
What is hydrological droughts
Lack of water stored on surface and underground in lakes, rivers, reservoirs and aquifers
What’s socio economic drought
Water demand for socioeconomic means exceeds water supply e.g for crop irrigation and hydroelectric power. Could be because of lack of rainfall or overuse of available water.
What’s the El Niño Southern Oscillation(ENSO) cycle
Movement of warm water mass in the equatorial Pacific Ocean, due to changes in trade winds m atmospheric circulation and ocean currents. It includes phases El Niño and La Niña
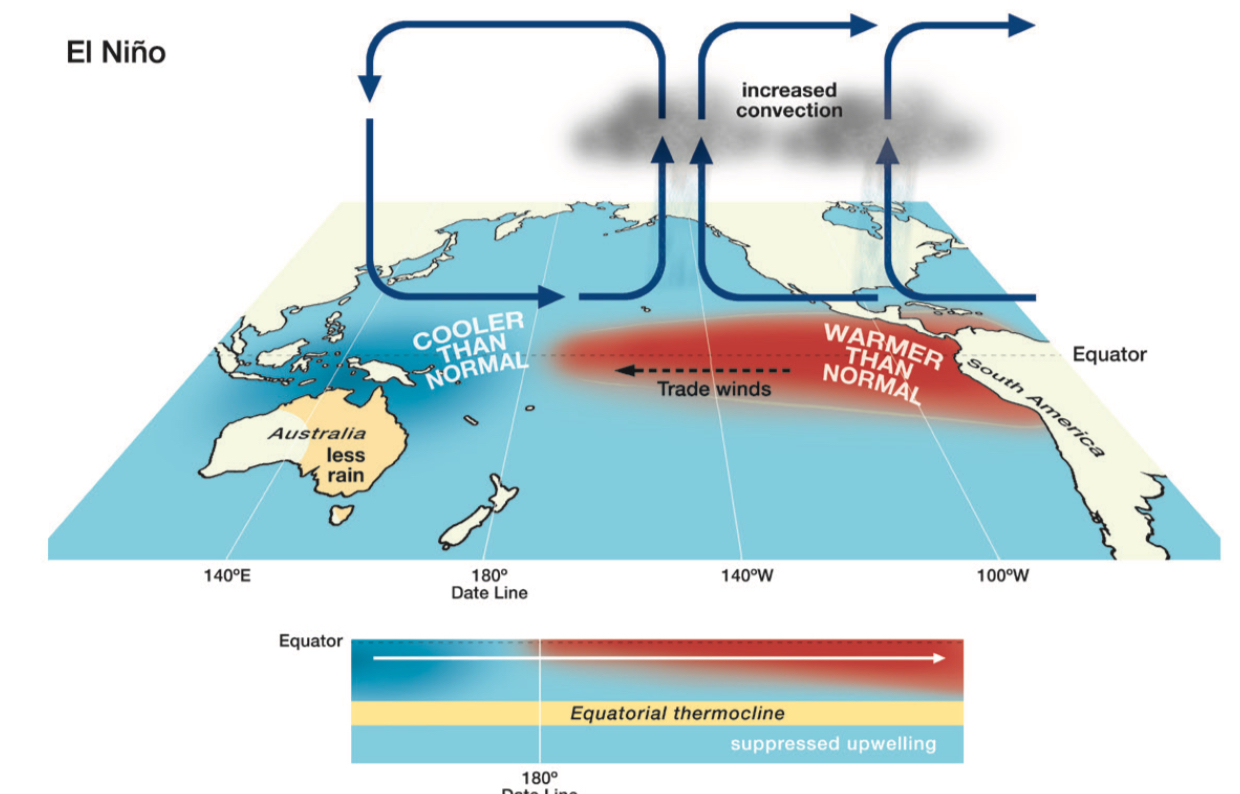
What’s the El Niño phase?
occurs when sea temp is 0.5 degrees above average so warmer average weather in eastern Pacific
Peaks usually in December and occurs 2-7 years
Can cause thermal expansion and sea level rise
Trade winds from East to west are weakened, so warm water travels east increasing sea temp in central and eastern pacific. Warm water heat air above so rainfalls occurs. Low pressure formed as air rises.Dry air travels west and sinks causing high pressure. Clear skies increases temp and lack of moisture causes droughts.
What is a La Niña event
Trade winds from east to west strengthen so warm water pushed to western Pacific. Warn water heats air causing thick clouds and heavy rainfall. Dry air moves east , cools and skunks in eastern Pacific. The sinking of dry air creates high pressure so drought in east.
What happens In the tropical Pacific during a normal year?
Tropical pacific experiences trade winds which pushes warm water from east ( South America ) to west ( Asia and Australasia) . In South America, cold water rises from ocean depth to replace warm water. This is called upwelling, creating a temp difference across the pacific. Warm ocean heat air above it which cools, condenses forming rain clouds. The dry air travels east in upper atmosphere which descends in eastern Pacific.
How does drought risk increase from human activities
Over abstraction from rivers and groundwater
Reducing downstream supply of water by building reservoirs and water transfers
Deforestation and overgrazing reduces vegetation cover so reduces evapotranspiratipn rates which reduces atmospheric moisture and precipitation
Vegetation removal means less organic matter so reduces soils moisture retention. Organic matter like earthworms create pores for water drainage
Compaction of soil so less porous so reduces soil moisture retention so reduces infiltration and increase surface runoff
Case study: Sahel Africa, drought back ground info
Semi arid region.
Since 1960s there’s been a decline in annual rainfall
What were the causes and impacts of Sahel droughts in late 20th century?
Caused by air pollution made from Europe and North America, which led to atmospheric cooling, changing global NEA budget and atmospheric circulation so that the tropical rains associated with the ITCZ didn’t arrive causing drought
A study showed that the droughts could have been from higher sea surface temperature caused by anthropogenic climate change . The rain bearing clouds seem to fall when sea surface temperature in the tropical Atlantic is warmer than usual.
What social factors are increasing the impacts of droughts in Sahel region?
Sahel as one if the worlds highest poverty rates
lowest development levels
Annual population growth rates of 2.5 to 4 %
What are the environmental factors that increase the risk and impacts of drought in Sahel region?
Population growth means greater demand for food and fuel wood so more natural ecosystems converted to farmland.
Land being over cultivated and overgrazed causing desertification
Reduced rainfall causes reduced vegetation and soil moisture.
What’s the Millennium Drought in Australia
Longest uninterrupted years with below median rainfall.
Annual rainfall between 1997- 2009 was 12.4 % below 20th century mean
What was the physical cause of Millennium drought in Australia
El Niño events - strengthening of high pressure belts known as sub tropical ridge accounts for 80% of rainfall decline. This ridge blocks storm tracks(depression) forcing them towards higher latitudes and thereby reducing frontal rainfall.
What is the human cause of Millenium drought in Australia
Climate models used suggest that high pressure belts are intensifying with increases in global temp due to greenhouse gas emissions. Anthropogenic climate change could be reducing temperature gradients between Equator and the Pole which reduces energy for mid latitude storm systems and polar front jet stream. Though insufficient evidence to support this theory.
How does drought impact wetland ecosystems?
Droughts reduce areas of open water so habitats are lost. Soil moisture is reduces which leads to soil erosion for example by the wind and a reducing ability to store water which increase risk of floods. Organic soils may oxidise releasing carbon into atmosphere . Water supply reduced so concentration of nutrients and pollutants increase.
How do droughts affect species?
Can remove species from food webs allowing other species to establish themselves in their place. Droughts destroy habitats while kills species. Species like snipe will be affected as they depend on soil invertebrates and droughts decrease soil moisture so soil will be less penetratabke to receive invertebrates.
How does droughts affect forest ecosystem
Foliage loss, impairment growth of drought stressed trees, increase in pests and diseases , damage to vascular tissues in trees which impacts water transport.
What is an example of droughts affects a forest ecosystem?
Piñon pines dying off in Mexico. Hot dry condition means the pine trees are more vulnerable to pine bark beetle attacks, contributed to warmer winters because beetles are able to survive through winter and reproduce.
Some areas had 90% of piñon die
How much carbon do forests hold?
0.73 tonnes of carbon per hectare per year
how much of the world is affected by freshwater flooding?
One third of the worlds land area
What’s flooding?
Result of surplus water in hydrological system
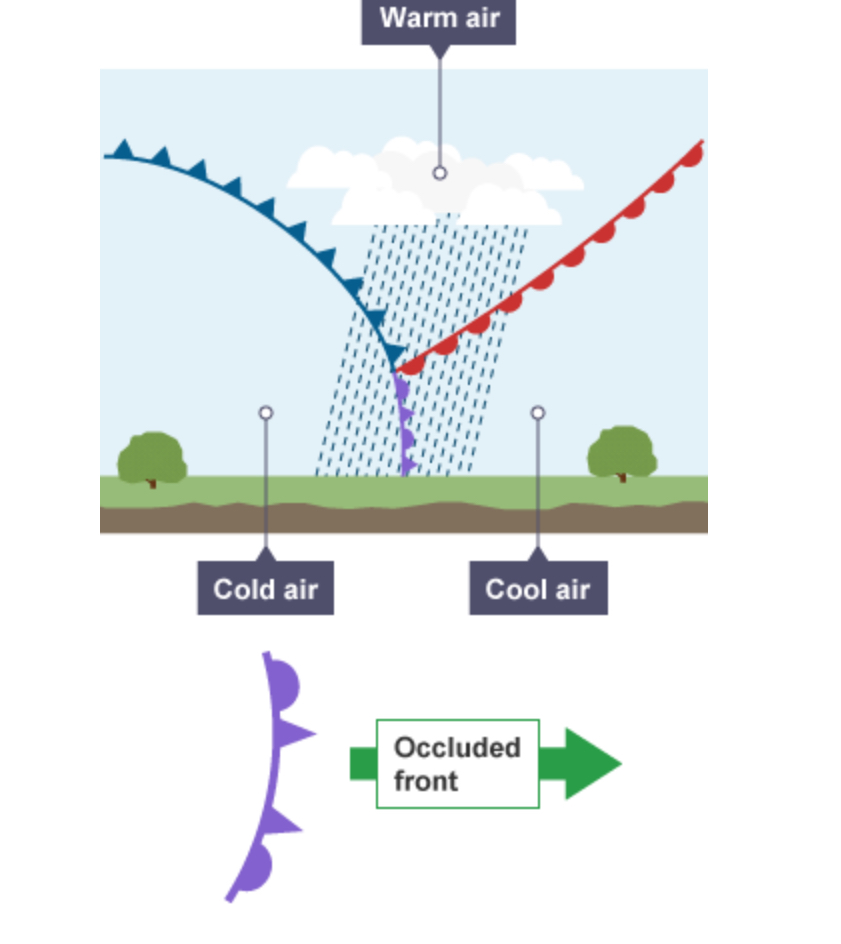
what’s a mid latitude depression.
Mid latitude depression - weather systema low atmospheric pressure. Each depression has two bands of rain, a warm front and cold front. Warm fronts are the first to pass over in a low pressure system. This is when warm air rises above cold air when they meet. Warm fronts bring steady continuous rain. Cold front passes over which brings heavy rains and . When cold fronts catches up with warm fronts it creates an occluded front which brings heavy rains.
What causes most river flooding
Mid latitude depression. Soil absorbs rainfall but when throughflow and groundwater flow can’t transfer water quickly enough, soil becomes saturated which increases surface runoff. This increases river discharge and when river capacity is exceeded , water flood floodplain
What’s a monsoon
Seasonal change in direction of prevailing winds of a region
How does snowmelt lead to flooding
Sudden rise in air temp increases snowmelt. Snow melts faster than water can infiltrate, surface runoff increases which can be due to frozen soil.
Example of snowmelt causing flooding
2008 in North Dakota 2009 foods
How does urbanisation increase flood risk?
Urbanisation- increase in impermeable surfaces like roads increases surface runoff. River lag times are reduced via urban drainage system which transfers water away from streets and into rivers. Bridges and culverts which are underground channels that are made to divert water under infrastructure which reduces river capacity
