Unit 7 Diseases of GB- Colangitis & Pneumobilia ~ Elie
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is the definition of Choledocholithiasis?
Stones in Common Bile Duct
Where does Choledocholithiasis originate from?
•Usually from GB
•Calculous cholecystitis
What are the lab values that are increased with Choledocholithiasis?
•Increased Direct Bilirubin,
• Alk Phos, WBC’s,
• Abnormal liver enzymes
What are the differential diagnosis for Choledocholithiasis?
Cystic Duct remnant,
Surgical clips
What are the potential causes of shadowing?
Calcifications in HA
Calcification in pancreatic head
Air or gas in duodenum
Watch for peristalsis
Changes over time
Air in biliary tree
What is a Pneumobilia?
Air within biliary tree
A pneumobilia is secondary to:
Intervention
Emphysematous cholecystitis
Inflammation from impacted stone in CBD
Prolonged acute cholecystitis
With Pneumobilia, Emphysematous cholecystitis can have:
Air in GB
Air in ducts
May be from bacteria or other bowel process
Pneumobilia US findings: What is the echogenicity description?
Bright, echogenic linear structures following portal veins, dirty shadows, reverberation artifacts
Pneumobilia US findings: What should you look for?
Look for movement of tiny air bubbles when change patient position
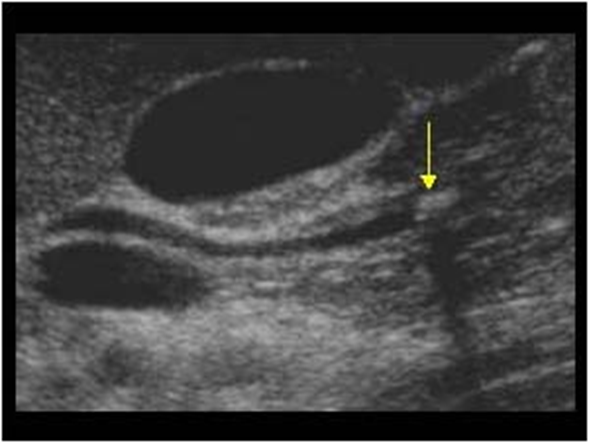
What is this image demonstrating?
Choledocholithiasis
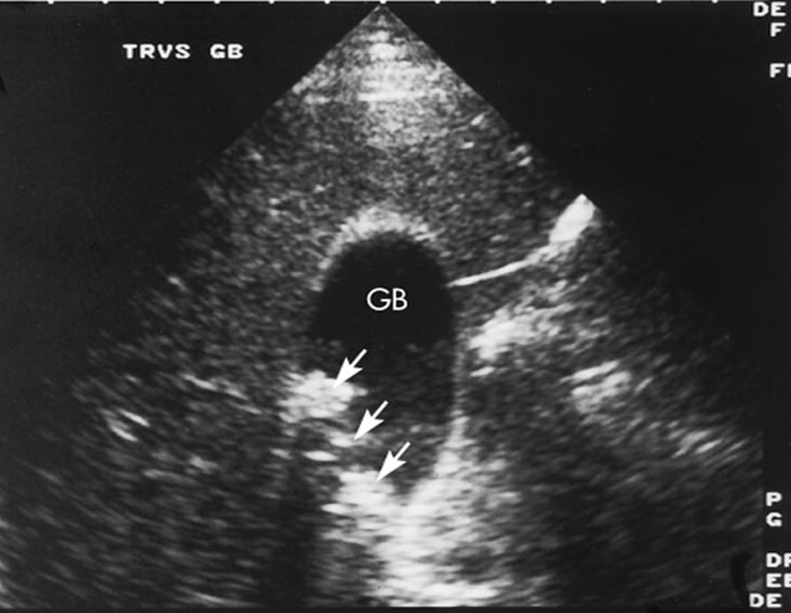
What is being shown in this image?
Pneumobilia
With pneumobilia, what can gas within the duodenum or GB be misinterpreted as?
Stones
What is hemobilia described as?
Biliary trauma secondary to percutaneous biliary procedures or liver biopsy
What are some common symptoms of hemobilia?
Pain
Bleeding
Jaundice
What is the definition of hemobilia?
Blood in the biliary tree
What can the appearance of hemobilia be like?
Depends on the length of time
Acute: fluid with low-level internal echoes
Look for blood clots that may move in the duct with extension into GB
What is the definition of cholangitis?
Inflammation of bile ducts
With cholangitis, the infected bile can either be _______ or ________ _______
Severe or prolonged infection
What are the symptoms of cholangitis?
Malaise
Fever
RUQ pain
Jaundice
Lethargic
Shock
Pus in CBD
Cholangitis US findings:
CBD thickened & dilated
Especially at Ampulla of Vater
What are the specific lab values tested for Cholangitis?
Leukocytosis
Elevated
Serum Alk Phos & Bilirubin
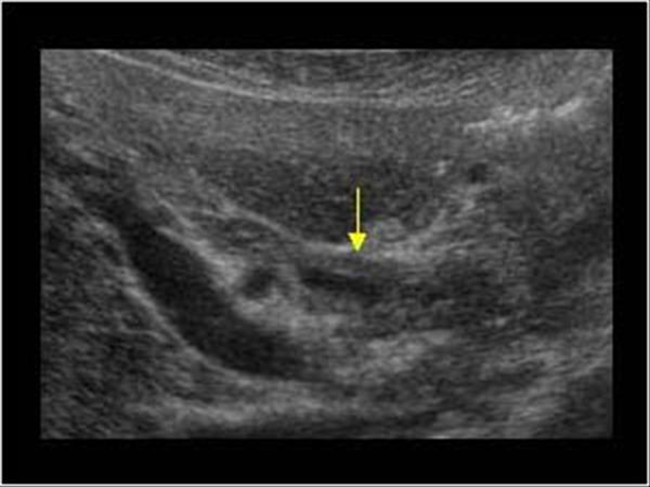
What is the arrow above demonstrating?
Cholangitis
Why is Cholangitis a medical emergency?
It develops increasing pressure in the biliary tree with PUS accumulation.
DECOMPRESSION of CBD is necessary!
What is sclerosing?
Inflammatory response leading to a fibrotic process
What are the early symptoms of sclerosing cholangitis?
Itching
Fatigue
Sclerosing Cholangitis can have dialed ducts with ________ ____?
Thickened walls
In patients who have sclerosing cholangitis, what can occur?
Severe or prolonged infections
In patients who have sclerosing cholangitis, how many have ulcerative colitis?
½
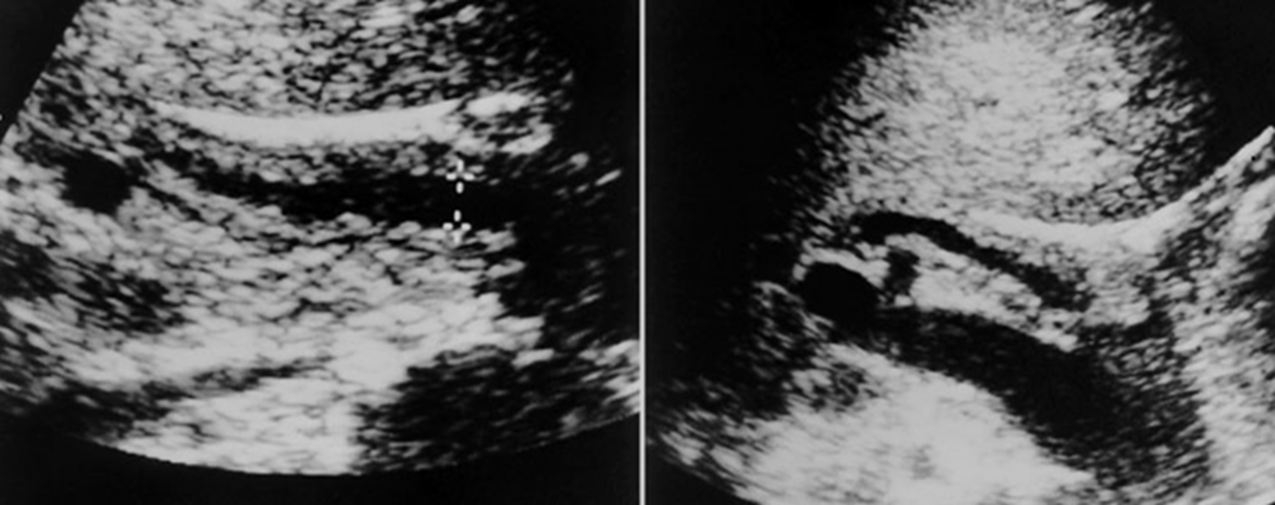
What is being shown in the image above?
Sclerosing Cholangitis
What is common to have while having sclerosing cholangitis?
AIDS
What is Ascariasis?
A parasitic roundworm
Where does the parasitic grow in ascariasis?
In the small bowel before entering biliary tree thru ampulla of Vater
What does the parasitic worm cause in ascariasis?
Acute biliary obstruction
Clinically, what are the symptoms of ascariasis?
•Asymptomatic
•Biliary colic, pancreatitis, biliary symptoms
Ascariasis US findings: It is an enlarged duct with a
Moving tube
Ascariasis US findings: What is the echogenicity in the ducts?
Parallel echogenic lines
Ascariasis US findings: What is the appearance in trans?
Worm is surrounded by duct walls
Target appearance
Ascariasis US findings: What should the sonographer do?
Hold still and watch for movement
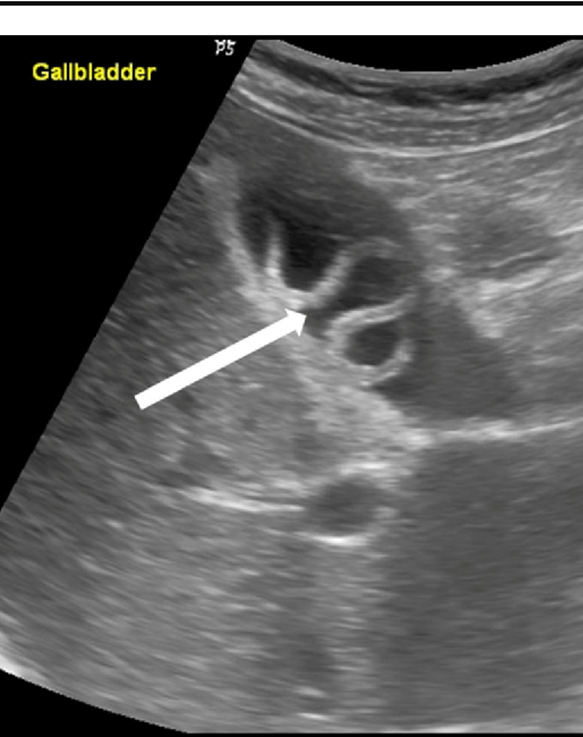
What is this image showing?
Ascariasis