ULTIMATE ANAPHY QUIZ HAHAHAHAHAHAHHA (3,4,5,6,7)
1/395
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
396 Terms
Tissue
It is a group of cells with similar structure and function.
It contributes to the functioning of the organs in which it is found.
epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous
4 types of tissue
Epithelial Tissues
Found on surfaces as either coverings (outer surfaces) or linings (inner surfaces).
blood supply of the connective tissue beneath them
Because epithelial tissues have no capillaries of their own, they tend to receive oxygen and nutrients from the ___.
glandular epithelium
Also known as glands
squamous cells
these cells are flat (shape)
cuboidal cells
these cells are cube shaped (shape)
columnar cells
the cells are tall and narrow (shape)
simple
it is the term for a single layer of cells (number of cells)
stratified
it means that many layers of cells are present (number of cells)
squamous
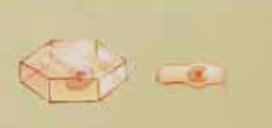
cuboidal

columnar
simple squamous
one layer of flat cells

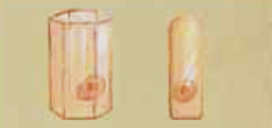
simple cuboidal
One layer of cube-shaped cells
simple columnar
one layer of columnar-shaped cells

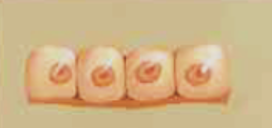
stratified squamous
Many layers of cells; surface cells flat; lower cells rounded; lower layer undergoes mitosis

transitional
Many layers of cells; surface cells change from rounded to flat
simple squamous
Location:
Alveoli of the lungs-thin to permit diffusion of gases
Capillaries-thin to permit exchanges of materials;
stratified squamous
Location:
Epidermis-surface cells are dead; a barrier to pathogens
Lining of esophagus, vagina-surface cells are living; a barrier to pathogens
transitional
Location:
Lining of urinary bladder-permits expansion without tearing the lining
simple cuboidal
Location:
Thyroid gland-secretes thyroxine
Salivary glands-secrete saliva
Kidney tubules-permit reabsorption of useful materials back to the blood
simple columnar
Location:
Lining of stomach-secretes gastric juice
Lining of small intestine-secretes enzymes and absorbs end products of digestion (microvilli present)
ciliated
Location:
Lining of trachea-sweeps mucus and dust to the pharynx
Lining of fallopian tube-sweeps ovum toward uterus
glands
cells or organs that secrete something
they produce a substance that has a function either at that site or at a more distant site.
unicellular glands
one cell
Their secretion is mucus
unicellular glands
goblet cells are examples of this: Lining of the respiratory and digestive tracts.
multicellular glands
made of many similar cells, or of a variety of cells with their secretions mingled into a collective secretion.
exocrine glands.
endocrine glands.
multicellular glands is divided into two major groups:
exocrine glands
have ducts (tubes) to take the secretion away from the gland to the site of its function.
salivary glands
(exocrine) secrete saliva that is carried by ducts to the oral cavity.
sweat glands
(exocrine) secrete sweat that is transported by ducts to the skin surface, where it can be evaporated by excess body heat.
gastric glands of the stomach
(exocrine) produce hydrochloric acid and the enzyme pepsin.
Both of these secretions are part of gastric juice
endocrine
ductless glands
hormones
the secretions of endocrine glands are a group of chemicals called ___.
connective tissues
presence of a matrix in addition to cells
structural network or solution of nonliving intercellular material.
bones
(ct) primarily of calcium salts, which are hard and strong
blood
Plasma (matrix) and red blood cells,
white blood cells, and platelets
areolar (loose)
Fibroblasts and a matrix of tissue
fluid, collagen, and elastin fibers
adeposine
Adipocytes that store fat (little matrix)
Fibrous
Mostly collagen fibers (matrix) with
few fibroblasts
elastic
mostly elastin fibers (matrix) with few fibroblasts
bone
Osteocytes in a matrix of calcium
salts and collagen
cartilage
Chondrocytes in a flexible protein
matrix
blood
Location: (ct) Within blood vessels
Plasma-transports materials
RBCs-carry oxygen
WBCs-destroy pathogens
Platelets-prevent blood loss
areolar (loose)
Location: (ct) Subcutaneous
Connects skin to muscles; WBCs destroy pathogens Mucous membranes (digestive, respiratory, urinary, reproductive tracts)
adipose
Location: (ct) Subcutaneous
Stores excess energy
Produces chemicals that influence appetite, use of nutrients, and inflammation
Cushion
fibrous
Location: (ct)
Tendons and ligaments (regular)
Strong to withstand forces of movement of joints
Dermis (irregular)
The strong inner layer of the skin
elastic
Location: (ct) Walls of large arteries
Helps maintain blood pressure Around alveoli in lungs
Promotes normal exhalation
bone
Location: (ct) Bones
Support the body
Protect internal organs from mechanical injury
Store excess calcium
cartilage
Location: (ct)
Wall of trachea
Keeps airway open
On joint surfaces of bones
Smooth to prevent friction
Tip of nose and outer ear
Support
Between vertebrae
Absorb shock
muscle tissue
specialized for contraction.
when ___ cells contract, they shorten and bring about some type of movement.
smooth, skeletal, cardiac
types of muscle tissue
skeletal
Large cylindrical cells with striations and several nuclei each
smooth
Small tapered cells with no striations and one nucleus each
cardiac
Branched cells with faint striations and one nucleus each
skeletal
Attached to bones
• Moves the skeleton and produces heat
smooth
Walls of arteries
• Maintains blood pressure
Walls of stomach and intestines
• Peristalsis
Iris of eye
• Regulates size of pupil
cardiac
Walls of the chambers of the heart
• Pumps blood
skeletal
(effects on nerve impulses) Essential to cause contraction (voluntary)
smooth
(effects on nerve impulses) Bring about contraction or regulate the rate of contraction (involuntary)
cardiac
(effects on nerve impulses) Regulate only the rate of contraction
nerve tissues
consists of nerve cells called neurons and some specialized cells found only in the nervous system.
neurons
nerve tissues consists of nerve cells called ___ and some specialized cells found only in the nervous system.
central and peripheral nervous system
two division of the nervous system
central nervous system
The brain and spinal cord are the organs of the ___.
central nervous system
They are made of neurons and specialized cells called neuroglia.
neuroglia
Specialized cells in the central nervous system, Form myelin sheaths and other functions
peripheral nervous system
consists of all of the nerves that emerge from the CNS and supply the rest of the body.
peripheral nervous system
These nerves are made of neurons and specialized cells called Schwann cells.
peripheral nervous system
The Schwann cells form the myelin sheath to electrically insulate neurons.
schwann cells
Specialized cells in the peripheral nervous system, Form the myelin sheaths around neurons
cell body
Neuron (nerve cell) Contains the nucleus, Regulates the functioning of the neuron
axon
Neuron (nerve cell) Cellular process (extension), Carries impulses away from the cell body
dendrites
Neuron (nerve cell) Cellular process (extension), Carry impulses toward the cell body
synapse
Space between axon of one neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the next neuron
synapse
Transmits impulses from one neuron to others
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals released by axons
Neurotransmitters
Transmit impulses across synapses
Membranes
sheets of tissue that cover or line surfaces or that separate organs or parts (lobes) of organs from one another.
epithelial and connective membranes
2 major categories of membranes
serous and mucous
2 types of epithelial membranes
Thoracic cavity
partial pleura lines chest wall; visceral pleura covers the lungs.
Pericardial sac
parietal pericardium lines fibrous pericardium; visceral pericardium (epicardium) covers the heart muscle.
Abdominal cavity
peritoneum lines the___; mesentery covers the abdominal organs.
mucous membrane
line body tracts that open to the environment:
respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive.
mucus
keeps the living epithelium wet;
mucus
provides lubrication in the digestive tract;
mucus
traps dust and bacteria in the respiratory tract.
Superficial fascia
• Between the skin and muscles; adipose tissue stores fat
Periosteum
• Covers each bone; contains blood vessels that enter the bone
• Anchors tendons and ligaments
Perichondrium
• Covers cartilage; contains capillaries, the only blood supply for cartilage
Synovial
• Lines joint cavities; secretes synovial fluid to prevent friction when joints move
Deep fascia
• Covers each skeletal muscle; anchors tendons
Meninges
• Cover the brain and spinal cord; contain cerebrospinal fluid
Fibrous pericardium
• Forms a sac around the heart; lined by the serous parietal pericardium
cellular level
aging takes place at the ___, but of course is apparent in the groups of cells we call tissues.
aging in muscle tissue
the proteins that bring about contraction deteriorate and are not repaired or replaced.
aging in Connective tissue
collagen and elastin of the dermis of the skin.
Skin
Largest organ of the body, 15-20% of body weight