Topic 2: Molecular Biology (2.1-2.4)
1/36
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
molecular biology
the study of explaining life processes in terms of the chemical substances involves
list the four main elements found in organic compounds
hydrogen
oxygen
nitrogen
carbon
HONC!
explain the importance of carbon
all living things are composed of organic compounds, compounds containing carbon
carbon has 4 electrons on its outer ring, allowing 4 bonds to be created
covalent bonds
the bonds that hold two or more atoms together by sharing electrons
can be single, double, or triple
relatively strong
intermolecular forces
relatively weaker bonds that hold molecules together
hydrogen bond
an intermolecular bond that can form between the positive pole of one water molecule to the negative pole of another
the bond between one, slightly positive, hydrogen atom of a water molecule to the, slightly negative, oxygen atom of another water molecule
polarity
the consequence of the nucleus of one atom being attracted to the electrons of another
part of the molecule will have a slight positive charge and another part has a slight negative charge
explain polarity in a water molecule
the hydrogen nuclei are less attracted to electrons oxygen
the two hydrogen atoms have a slight positive charge
the oxygen atom has a slight negative charge
metabolism
all enzyme-catalyzed reactions in a cell or organism; it is a function of life
anabolism
the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler molecules; involves condensation reactions
catabolism
the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules; involves hydrolysis reactions
macromolecules
large molecules
monomers
the building blocks of macromolecules
polymer
a chain of monomers
explain the thermal properties of water
ice melts at a higher temperature (0 degrees Celsius); heat is needed to stop h-bonds from preventing the movement of water molecules
water has a high boiling point (100 degrees Celsius)
water has a high heat capacity
water has a much higher heat of vaporization
hydrophilic
substances attracted to water
form intermolecular bonds with water
ionic compounds + substances with polar molecules
most dissolve as their electrons are more attracted to those of water rather than each other
soluble
hydrophobic
substances ‘repelled’ by water
it’s just because the hydrophobic substance is more strongly attracted to each other
insoluble
what property of water demonstrates the strength of h-bonds?
adhesive property
molecules will stick to other surfaces
cohesive property
molecules will stick to each other
as shown through capillary action in xylem vessels
what are the four main classes of large biological molecules that life is based on?
carbohydrates
lipids
nucleic acids
proteins
which of life’s organic compounds are polymers?
carbohydrates
proteins
nucleic acids
NOT LIPIDS!
carbohydrates
sugars and the polymers of sugars
what are the monomers of carbohydrates?
monosaccharides
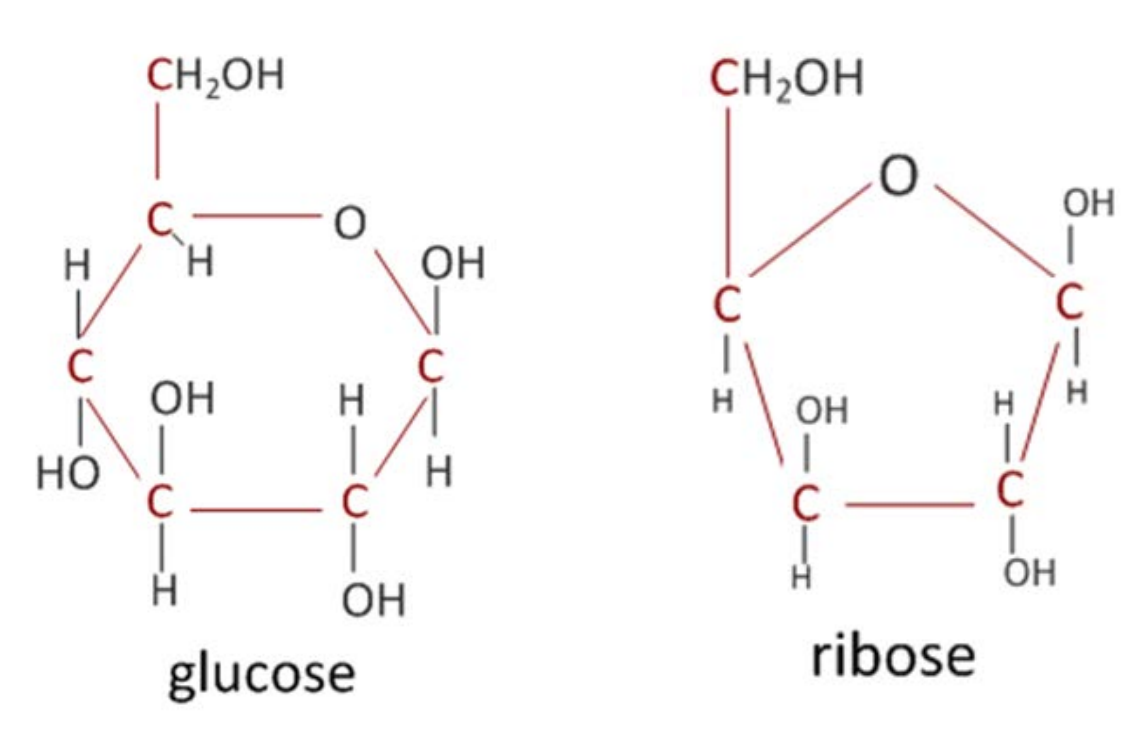
give two examples of monosaccharides and draw their molecular structure
glucose
hexose (6-carbon) sugar
C6H12O6
ribose
pentose (5-carbon) sugar
C5H10O5
give an example and function of one of each type of saccharide (-mono, -di, -poly)
monosaccharide
glucose: used in cell respiration
disaccharide
lactose: easily broken down and digested
polysaccharide
glycogen: stored in the liver to be used in low blood glucose conc.
what type of bond is created during condensation of two saccharides to form a disaccharide?
glycosidic bond
lipids
insoluble compounds identified by their hydrocarbon chains; there are three types
what are the three types of lipids?
triglycerides
phospholipids
steroids
triglycerides
contain three fatty acids and one glycerol
synthesized through condensation reactions creating ester linkages
includes fats and oils
phospholipids
contain a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails
essential components of cell membranes; create the bilayer
steroids
composed of four fused rings of carbons
functional groups can be attached to change the function
list the types of fatty acids
saturated: all are connected by single covalent bonds
unsaturated: contains one or more double bonds between atoms in the chain
monounsaturated: contains only one double bond
polyunsaturated: contains two or more double bonds
proteins
what are the six main functions of proteins?
transport
enzymatic activity
signal transduction
cell-cell recognition
intercellular joining
attachment to the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix
what are the monomers of proteins?
amino acids
identify the three component groups that make up an amino acid
R group
Carboxylic group (-COOH)
Amino group (-NH2)
along with the carbon and hydrogen atom
what are the four structures of a protein?
primary: single polypeptide chain
secondary: coils and folds of a polypeptide chain held together by different types of bonds
tertiary: 3D shape is created as bonds form between R groups
quaternary: interaction between multiple protein subunits.
enzymes
biological catalysts; proteins that help speed up reactions by lowering activation energy needed to kickstart a reaction