L10 Patterns of Selection and Side Effects
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Balancing selection
occurs when no single allele has a distinct advantage
consequence: selecting on different alleles is balanced
ex:
Negative frequency dependent selection
heterozygote advantage (overdominance)
balancing selection does what to genetic diversity
maintains genetic diversity
Negative frequency dependent selection
occurs when the fitness of alleles change depending on their own frequencies - rare alleles are the most fit
selects for the least frequent - it is most fit but eventually after generations of selection it becomes less beneficial and the other allele that is now the rare one is the most beneficial
increases in frequency and then is no longer rare - the other allele is now most frequent
Heterozygote advantage or overdominance
occurs when the heterozygote has higher fitness than both homozygote
when overdominance alleles reach
a polymorphic equilibrium
polymorphic equilibrium
both alleles are maintained an equilibrium
how does overdominance maintain genetic variation
heterozygote disadvantage - underdominance
occurs when heterozygotes are the least fit of all genotypes
with underdominance if the beneficial allele starts below certain threshold
they will be lost
with underdominance if the beneficial allele starts above certain threshold
they will fix
artificial selection
a selection by humans of a specific trait in another organism (sometimes called selective breeding)
this is different from natural selection in that survival and reproduction (fitness) is dependent on human preference for a chosen trait
the trait may not be beneficial in the wild
genetic correlations
occur when two traits tend to be inherited together
genetic correlation occur through
pleiotropy
evolutionary trade-offs
genetic hitchiking
direct response
selecting for
indirect response
selection of - side effect
pleiotropy
a single mutation affects multiple traits
generates a genetic correlation between traits
epistasis
interactions of multiple loci to produce a single phenotype
Allele A1 is pleiotropic. Individuals with the A1 allele have pink fur and purple eyes. Purple eyes are advantageous, they allow individuals to see better at night. Pink fur is neither beneficial nor deleterious. As the A1 allele spreads through the pop
a. purple eyes only will fix
b. pink fur only will fix
c. purple eyes and pink fur will fix
d. pink fur will increase but not fix, purple eyes will fix
purple eyes and pink fur will fix
evolutionary trade-off
occurs when one trait has fitness benefits and fitness costs
ex. frogs with the loudest mating call attract the most mates and the most predators
evolutionary trade-off can occur as a side effect of pleiotropy
a single allele increases fitness through one trait and the same allele decreases fitness through another trait
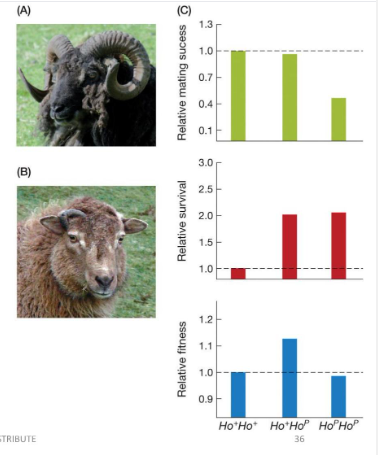
Bighorn sheep with the dominant Ho+ allele have increased mating success. However, sheep with the recessive Hop allele have increased survival. Use this information and the information in the figure to determine if genetic variation at this locus will
a. decrease over time
b. increase over time
c. be maintained over time
be maintained over time
polymorphic equilibrium - overdominance
hitchhiking
occurs when an allele at one locus spreads by natural selection acting on a linked allele at a second locus
hitchhiking is a consequence
of linkage disequilibrium
when a beneficial allele spreads to fixation it can eliminate polymorphism nearby
this is a signature of selective sweep