Lecture 13 - Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What are the five cellular roles of nucleotides?
Precursors for RNA and DNA
Energy carriers (ATP, GTP)
Regulatory signals (e.g., cAMP)
Coenzymes (e.g., FAD, NAD, NADP)
Metabolic intermediates (e.g., UDP-glucose, CDP-acylglycerol)
What are the two main types of nucleic acids and their roles?
DNA: stores genetic information
RNA: carries genetic info, has catalytic and regulatory roles
What sugars are found in DNA and RNA, respectively?
DNA: 2′-deoxy-D-ribose —> lacks O at C2, is reduced
RNA: D-ribose
What are the components of a nucleoside?
A sugar (pentose) and a nitrogenous base.
What are the components of a nucleotide?
A nucleoside (sugar + base) plus one or more phosphate groups.
What are the purine and pyrimidine bases?
Purines: Adenine (A), Guanine (G)
Pyrimidines: Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), Uracil (U in RNA)
Which base is found in RNA but not in DNA?
Uracil replaces thymine in RNA.
How are bases linked to the sugar in nucleotides?
Purines: N9 to C1′ of sugar
Pyrimidines: N1 to C1′ of sugar
(via β-glycosidic linkage)
What are cyclic nucleotides and their role?
cAMP, cGMP
They are second messengers involved in signal transduction.
What are nucleoside di- and triphosphates?
Diphosphate: nucleoside + pyrophosphate
Triphosphate: nucleoside + three phosphate groups (e.g., ATP)
What is the structural backbone of nucleic acids?
Alternating sugar-phosphate units connected by phosphodiester bonds.
What ends do nucleic acid strands have?
A 5′ end (with phosphate) and a 3′ end (with hydroxyl group)
What are Chargaff’s rules?
%A = %T and %G = %C in DNA
What are key features of B-DNA structure?
Right-handed helix, antiparallel strands
Bases on the inside, sugar-phosphate on outside
hydrophobic base pairs can stack one on top forming a hydrophobic interior interacting via vdW and weak dipole:dipole
bases can H-bond
0.34 nm between bases
3.6 nm per full helical turn
10.5 base pairs per turn
What stabilizes DNA besides H-bonds?
Base stacking via hydrophobic and van der Waals interactions, as well as dipole-dipole interactions
helps to minimize contact of bases with water (hydrophobic effect)
What are the major and minor grooves in DNA?
Grooves where proteins can bind specific sequences without disrupting base pairing.
What are the three major forms of DNA?
A-DNA, B-DNA (most common), Z-DNA
How is DNA flexible compared to proteins?
DNA has 7 flexible torsion angles vs. 2 in proteins, enabling complex secondary/tertiary structures.
What causes DNA denaturation (melting)?
Heat
Extreme pH
Enzymatic activity
These disrupt base pairing and stacking interactions.
What is the hypochromic effect in DNA?
Base stacking reduces UV absorbance at 260 nm; melting increases absorbance.
What is Tm in DNA melting?
The temperature at which half the DNA is denatured (half double-stranded, half single-stranded)
Why does GC content affect Tm?
GC pairs have 3 H-bonds and stronger stacking than AT pairs, raising Tm.
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
DNA → RNA → Protein (information flow in cells)
What is the role of DNA polymerases?
Enzymes that replicate DNA by synthesizing a complementary daughter strand with high fidelity.
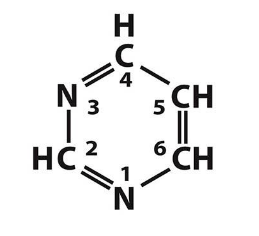
pyrimidine
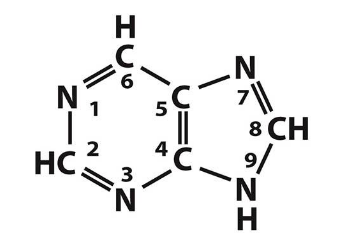
purine
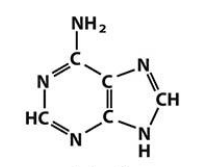
adenine
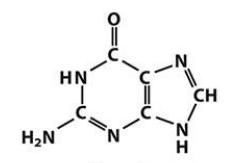
guanine
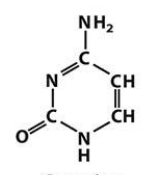
cytosine
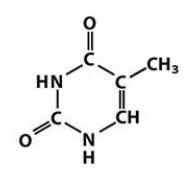
thymine
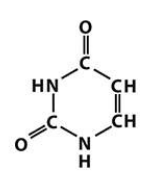
uracil