m2 biological molecules
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
draw molecules of water with the hydrogen bonding between it and what type of bonding are the darker lines
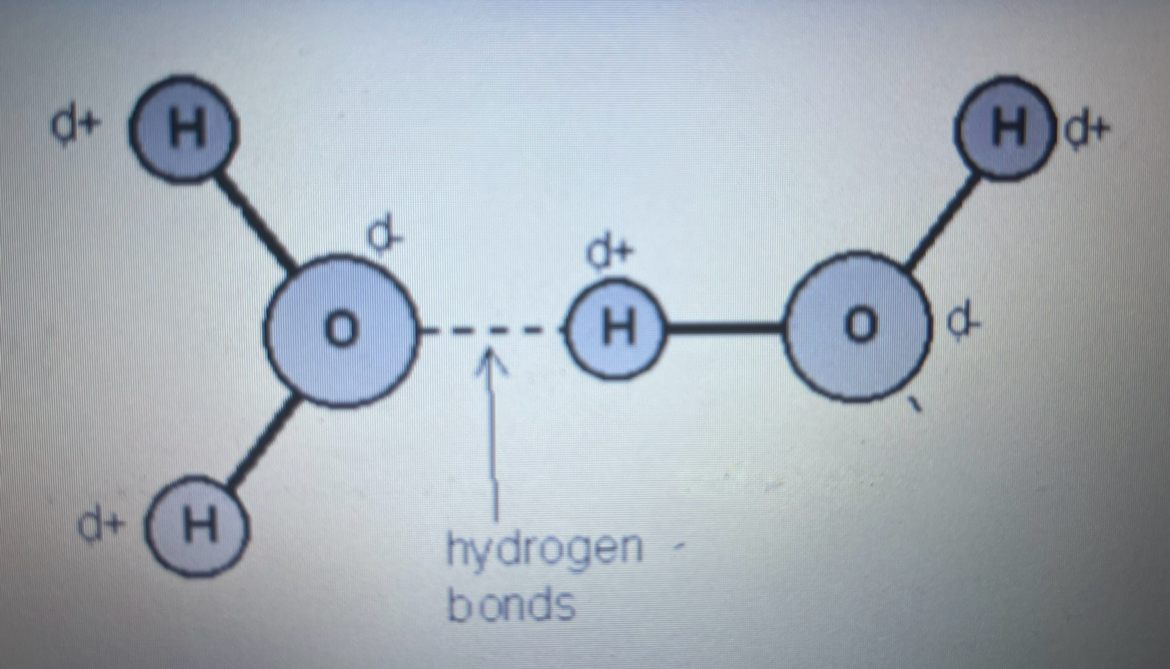
how does a hydrogen bond form
hydrogen bonds form when a slightly negatively oxygen of one molecule comes close to a slightly positively charged hydrogen in another molecule
describe how water has a high boiling point
a lot of energy needed to break hydrogen bonds
creates stable water temp for aquatic animals
less energy spent on temp control
describe how ice is less dense than water
creates insulating barrier
water below doesn’t freeze
allowing organisms to move under water
creates habitat for animals
describe cohesion and adhesion in water
cohesion happens through hydrogen bonding in water and creates high surface tension for insects
adhesion happens through attraction of water molecules to other surfaces
describe how water acts as a solvent
allows mineral ions to be transported around plants and animals
describe how water acts as a transport medium
allows transport of soluble substances
describe how water acts as a coolant
from evaporation and takes heat away from body
describe how water has high specific heat capacity
takes a lot of energy to heat up water by one degrees
creates stable temp
enzymes can work at their optimum temp ,
gases can remain soluble for aquatic organisms
describe how water has high latent heat of vaporisation
takes a lot of energy to change water from liquid to gas form
important for metabolic reactions
describe capillary action in water
allows water to move up narrow vessels
what’s a condensation reaction
when water is removed to form covalent bond
what’s a hydrolysis reaction
when water is added to break covalent bond
what elements are in the molecules carbohydrates,lipids,proteins,nucleic acids
C H O for carbohydrates
C H O for lipids
C H O N S for proteins
C H O N P for nucleic acids
what’s a monomer and polymer
monomer is a single unit
polymer is several monomers joined together
draw and state the difference between alpha glucose and beta glucose
the difference is the OH and H side on the carbon 1 right hand side have switched sides
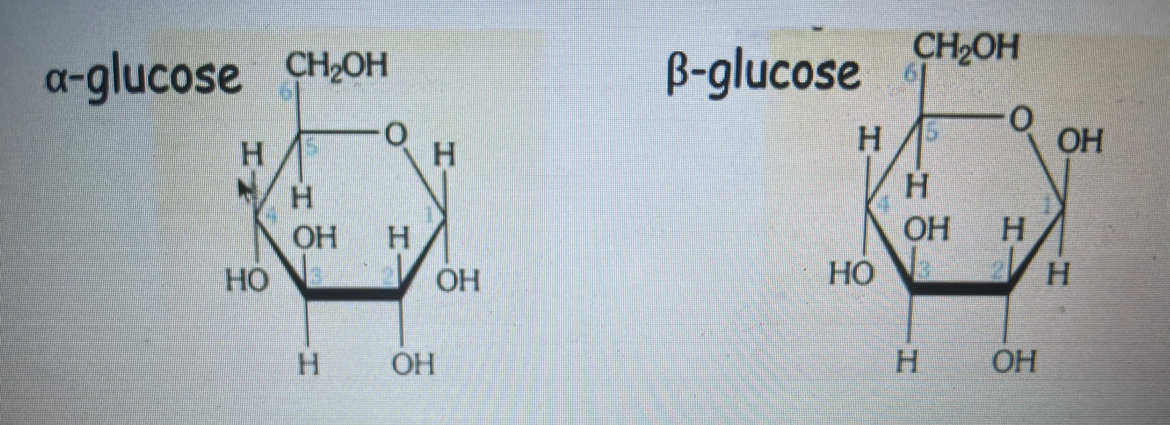
describe features of glucose
glucose is a hexose sugar it contains 6 carbon atoms
glucose is a reducing sugar , when it is in solution it can reduce other chemicals
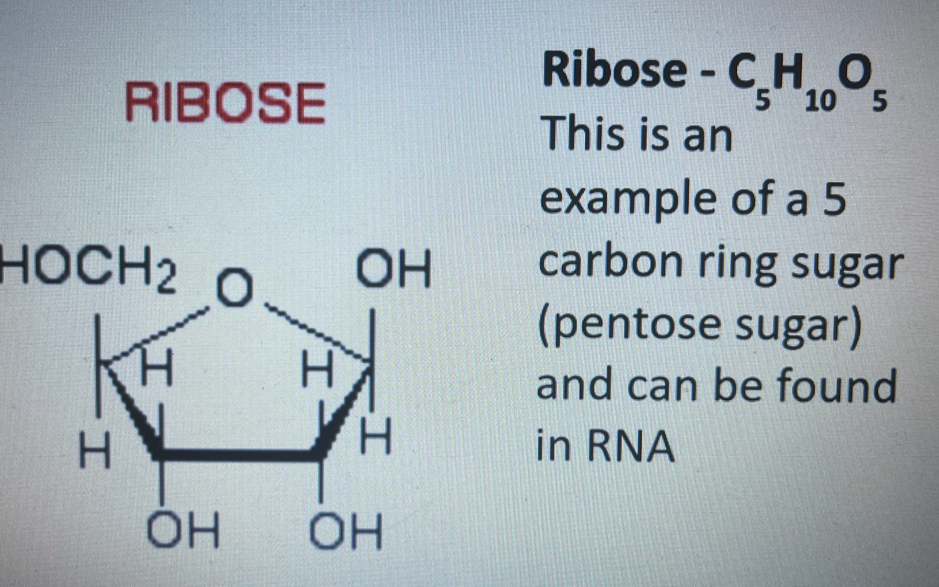
draw ribose
state which monosoccharides join to make each disaccharide maltose,lactose and sucrose
alpha glucose+alpha glucose=maltose
beta glucose+galactose=lactose
alpha glucose+fructose=sucrose
describe structure and function starch including amylose and amylopectin
mixture of amylose and amylopectin , both insoluble so doesn’t affect water potential , holds glucose in chains so it can easily be broken off from ends and used as glucose for respiration
amylose has alpha 1 4 glycosidic bonds which create a coiled structure , compact good for storage ,
amylopectin alpha 1 4 and alpha 1 6 glycosidic bonds , created branched structure , allows hydrolysis of the ends by enzyme to create monosaccharides available for aerobic respiration
describe structure and function of glycogen
made of alpha 1 4 and 1 6 glycosidic bonds
insoluble , compact , doesn’t affect et water potential
many ends so hydrolyse by enzymes to create aloha glucose again available for respiration
describe structure and function of cellulose
beta glucose , beta 1 4 glycosidic bonds to make long chain
form beta pleated sheets between which hydrogen bonds form cross links to form bundles called microforms , larger bundles called macrofibrils
provides high tensile strength ,prevents cell from bursting , doesn’t affect water potential
draw amino acid structure
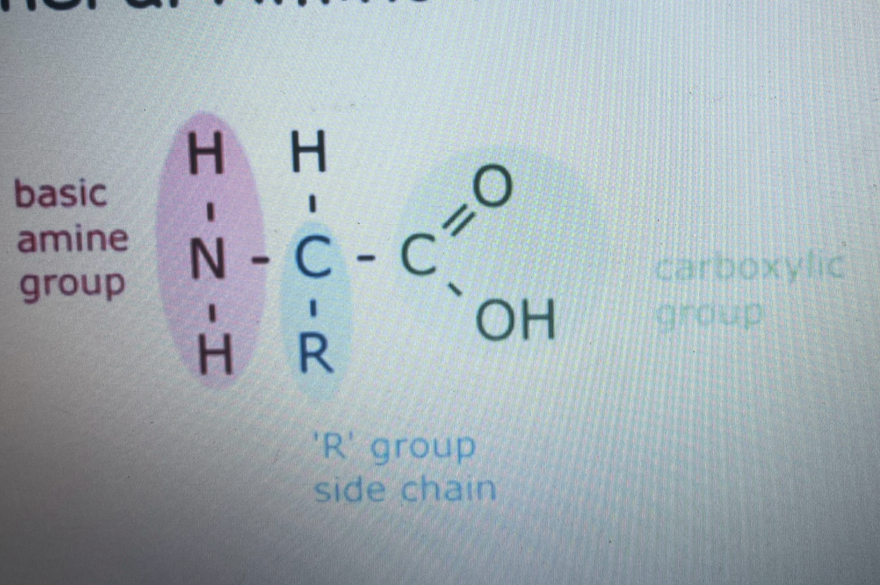
what’s a dipeptide
a dipeptide is two amino acids joining together to form a dipeptide
primary structure of proteins
sequence of amino acids bonded by peptide bonds
secondary structure of proteins
folding of polypeptide chain
held in place with hydrogen bonds
either alpha helix or beta pleated sheets
tertiary structure of proteins
further folding of polypeptide chains
held in place with hydrogen bonds , disulphide bridges , ionic bonds
amino acids with hydrophobic R groups orientate towards center of protein
hydrophilic r groups will orientate toward outside of protein
quartenary structure of proteins
more than one polypeptide chain
describe fibrous proteins
provide structural role
insoluble in water ( lots of amino acids with hydrophobic R groups )
very strong and tough ( many cross bridges between polypeptide chains )
give examples of fibrous proteins