RS212 sim positions/questions
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
hand, wrist, fingers // forearm, humerus, elbow // clavicle, joints, scapula, shoulder
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
what demonstrates the pisiform AND triquetral (triquetrum) free of superimposition?
PA oblique (wrist)
what best demonstrates the pisiform free of superimposition?
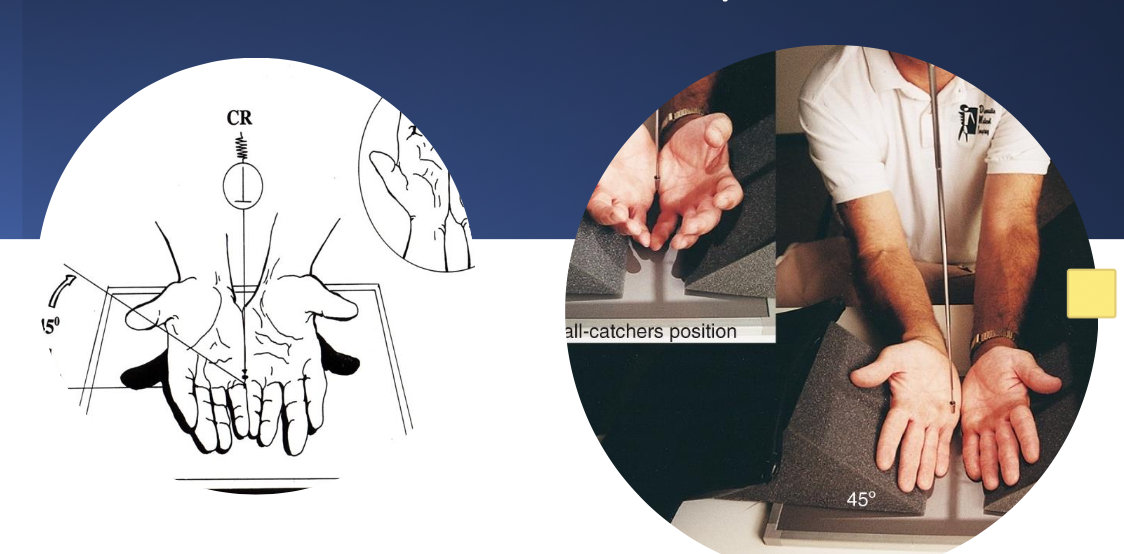
ball catchers (AP oblique) OR carpal canal
how do you diagnose a Bennetts vs Rolandos fracture?
Roberts projection
hand 15° medially/towards thumb
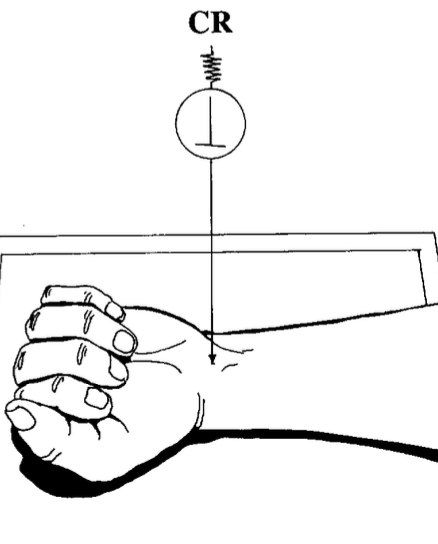
what best demonstrates the proximal and distal radioulnar joints with minimum superimposition?
AP wrist
fist clenched
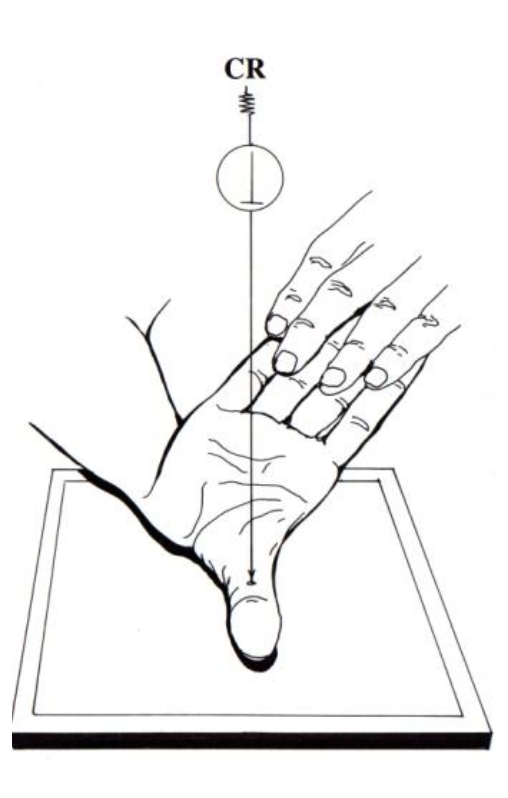
what projection best demonstrates the proximal scaphoid, capitate, and hamate free of superimposition?
PA wrist
hand in light fist

where are the 3rd-5th metacarpals free of superimposition?
PA hand
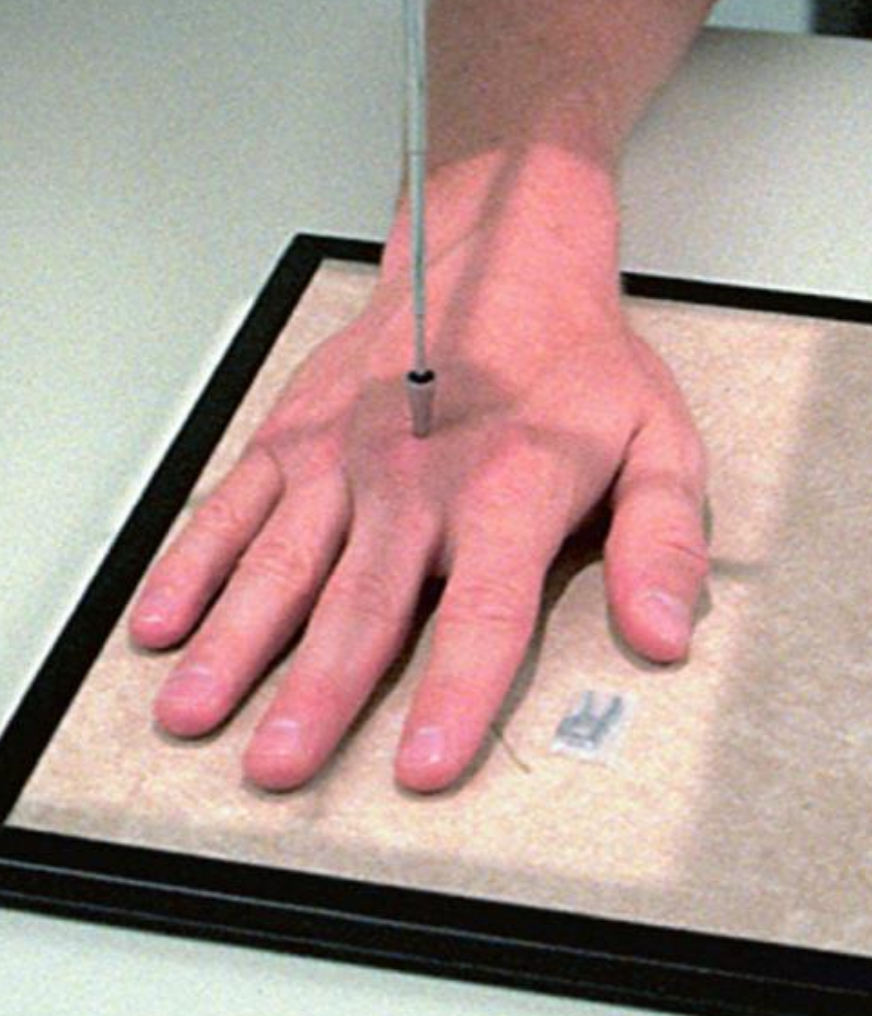
what best demonstrates the trapezium free of superimposition and the 3rd-5th metacarpal bones superimposed?
AP oblique (wrist)
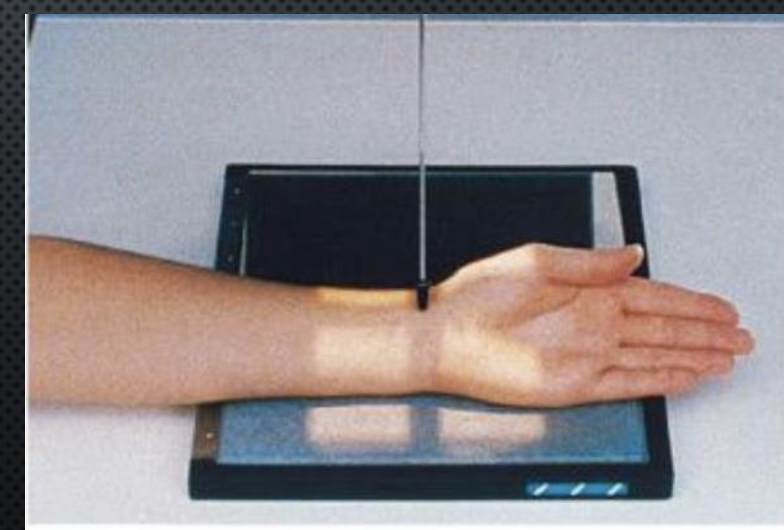
What best demonstrates impingement on the [left] median nerve?
carpal canal
hand held back
CR rotated 30°
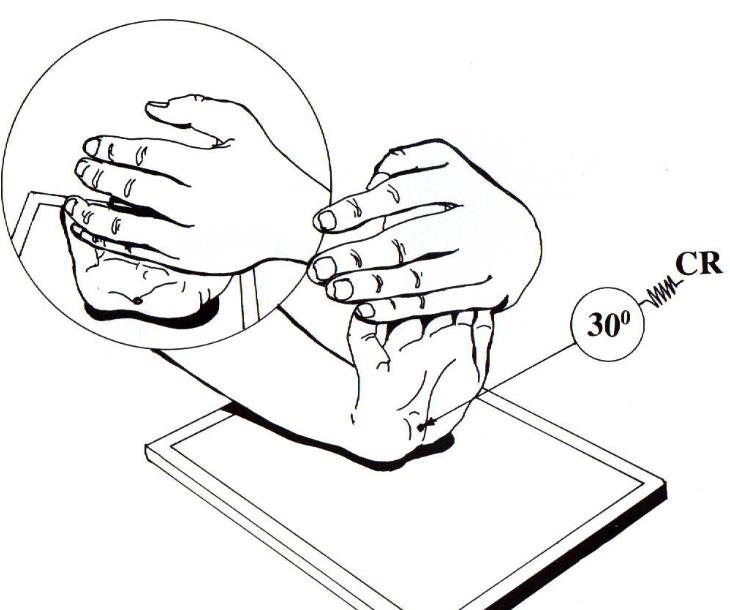
what best demonstrates anterior vs posterior displacement when the patient suffered [left] hand trauma?
Lateral (wrist)

what best demonstrates anterior vs posterior displacement of the [right] wrist?
Lateral (wrist)

what best demonstrates anterior vs posterior displacement of the [right] hand? (YOU CAN SEE ALL OF THE DIGITS IN THIS VIEW)
lateral fan (hand)
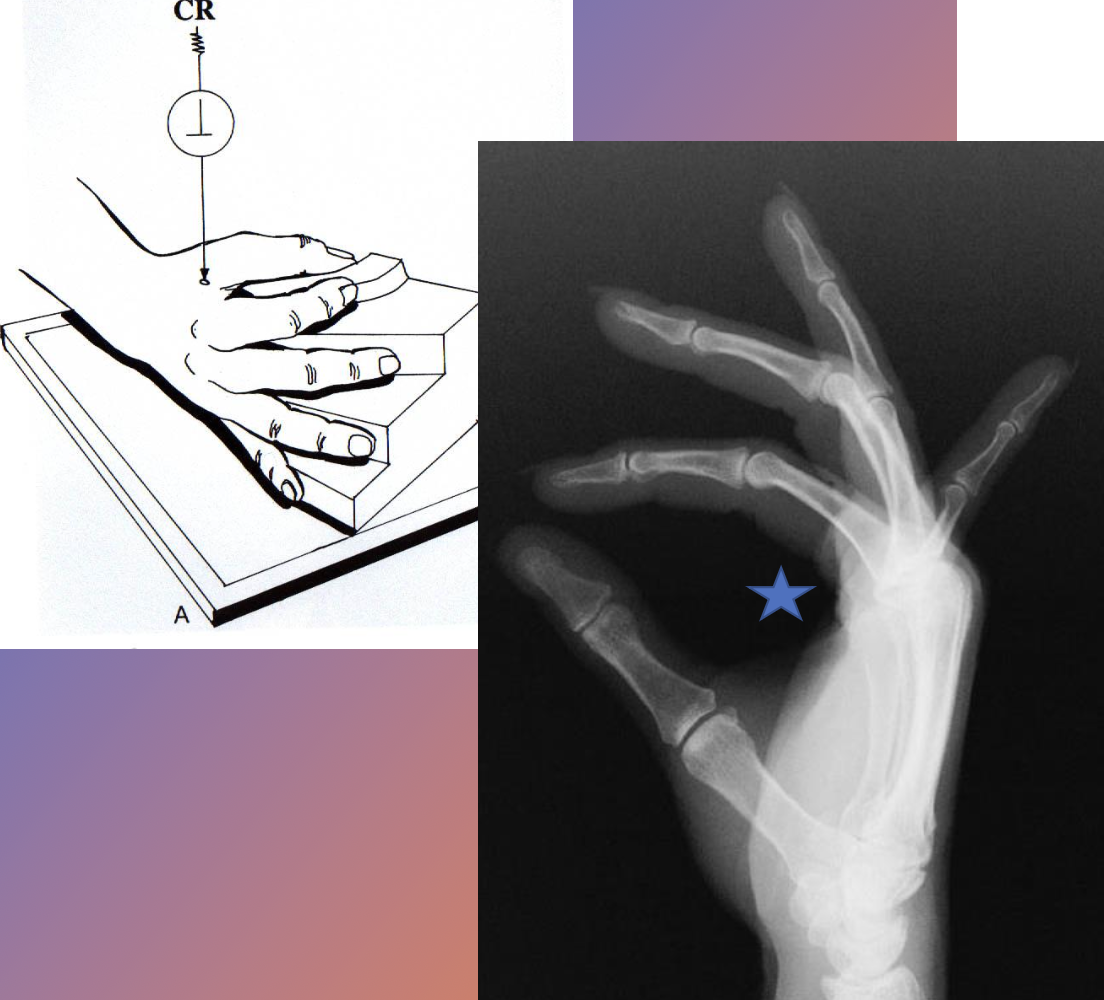
what is used to visualize a colles vs smiths fracture?
Lateral (wrist)

what projection best demonstrates anterior vs posterior displacement of the 2nd phalanx?
Lateral (finger)
what best demonstrates a [right] scaphoid fracture?
true OR modified stretchers (wrist)
true: hand elevated
modified: CR at 20°
what best demonstrated the scaphoid using a perpendicular CR?
true stretchers (wrist)
hand elevated
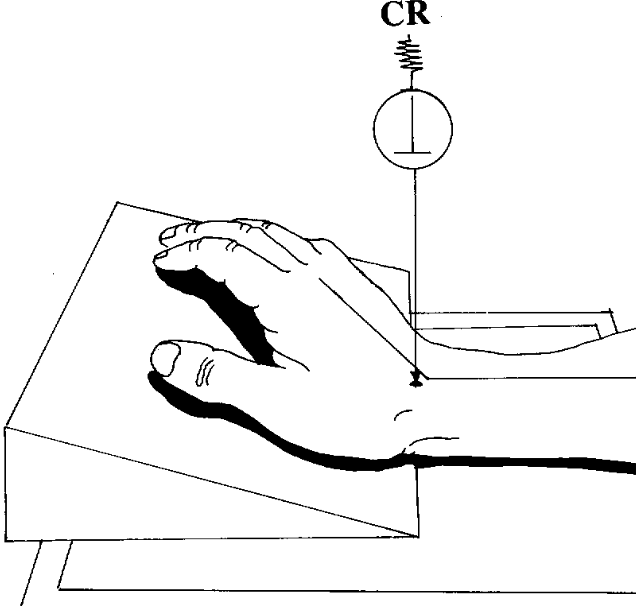
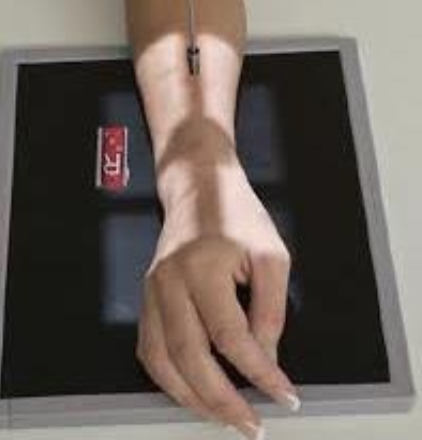
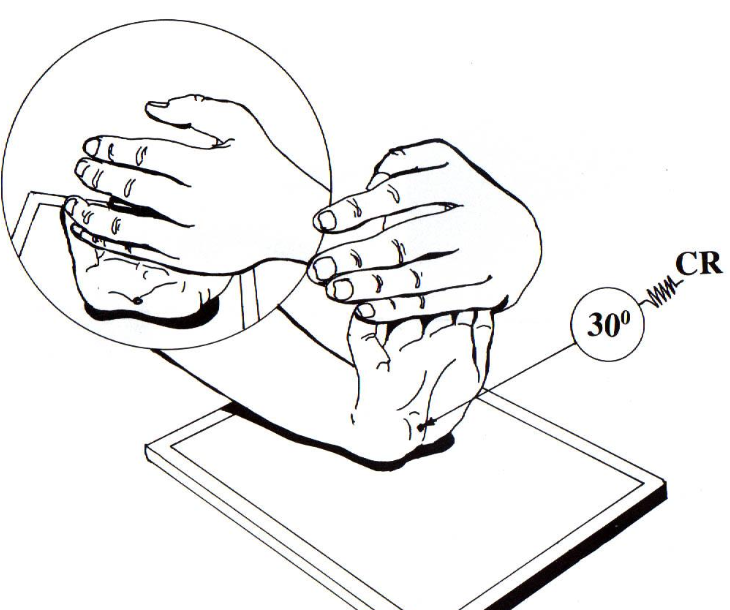
what best demonstrates carpal tunnel syndrome?
carpal canal
hand held back
CR rotated 30°
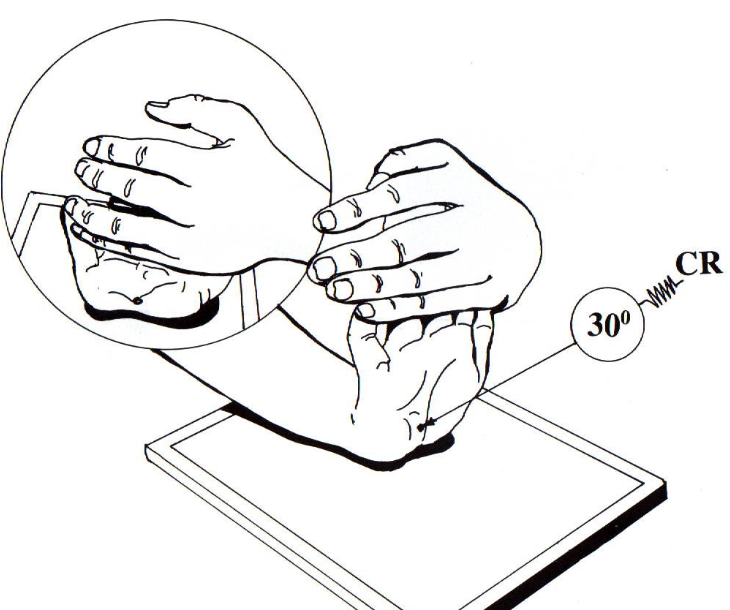
what best demonstrates early arthritic changes and both pisiforms free of superimposition?
ball catchers (AP oblique) OR carpal canal
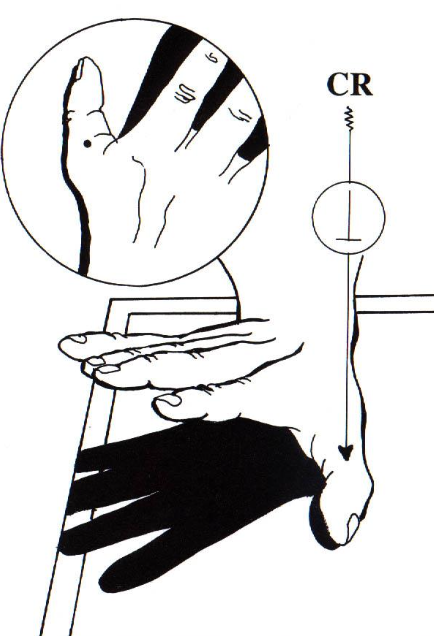
what best demonstrates posterior displacement of the 1st digit?
lateral thumb
hand PA then fist with thumb out
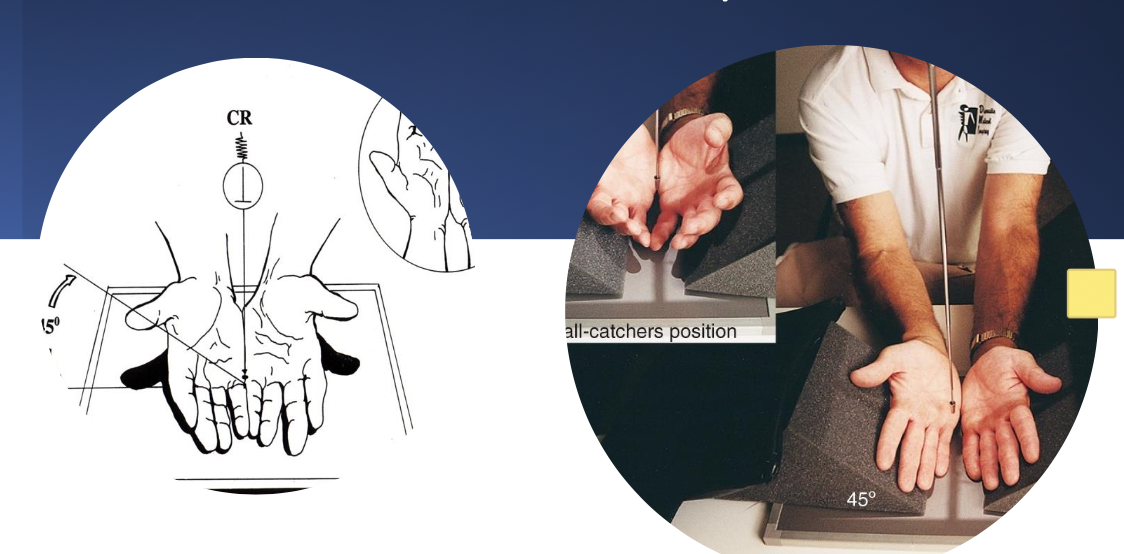
what best demonstrates both the hamulus and pisiform free of superimposition?
carpal canal
hand held back
CR rotated 30°
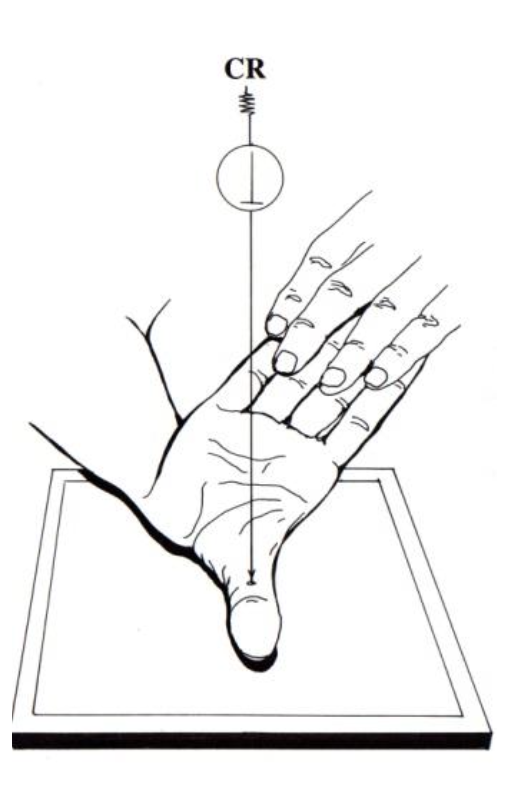
best projection for a lateral view of the distal radioulnar joint?
lateral (wrist)

best view of a lateral of the metacarpals and the 2nd-5th digits?
fan lateral (hand)
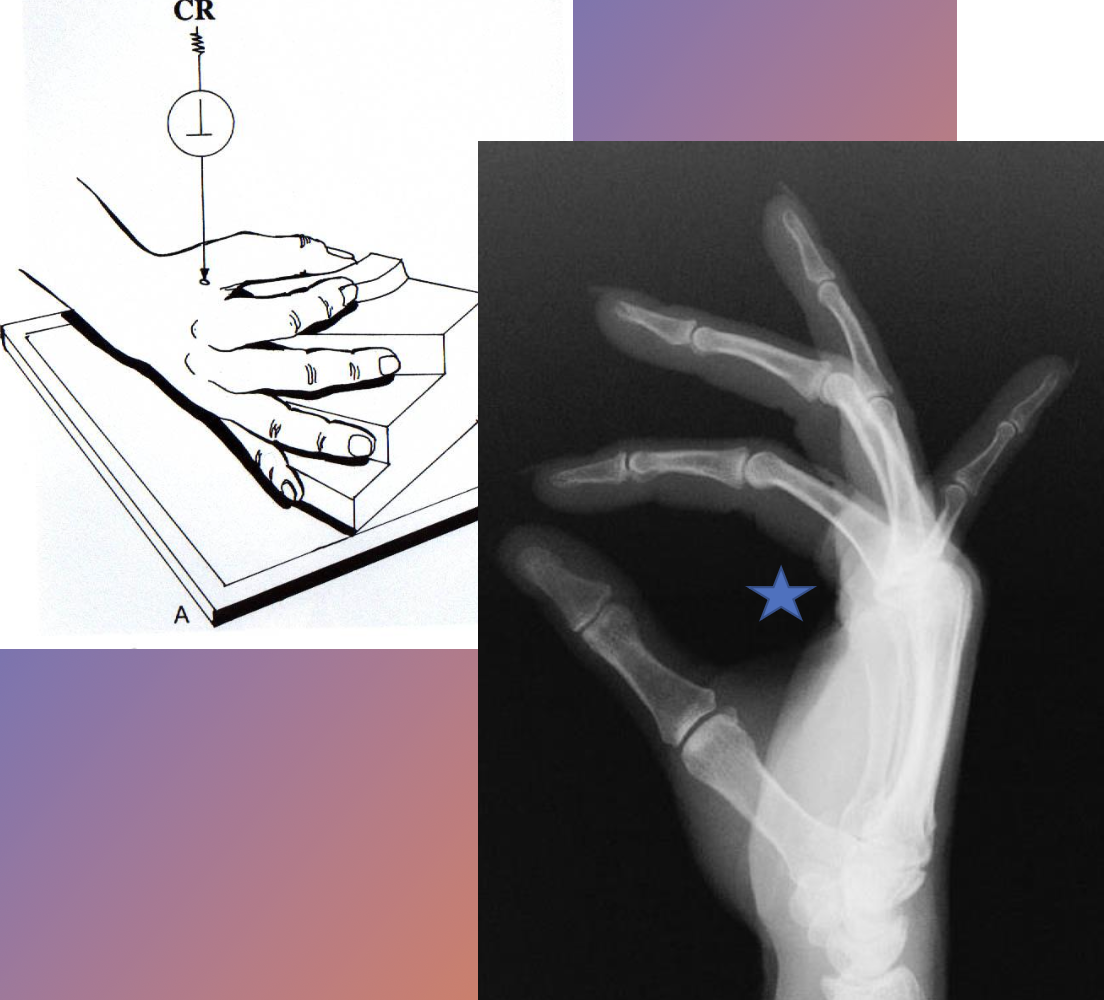
what projection best demonstrates a foreign body in the [left] hand?
full extension lateral (hand)
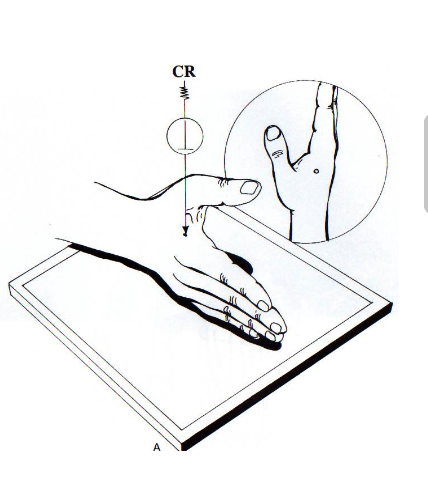
what projection shows elongation of the 1st metacarpal and the CMC joint open?
Roberts (AP thumb)
roberts: hand 15° medially/towards thumb
what projection best demonstrates the 1st CMC joint?
roberts (AP thumb)
Roberts: hand 15° medially/towards thumb
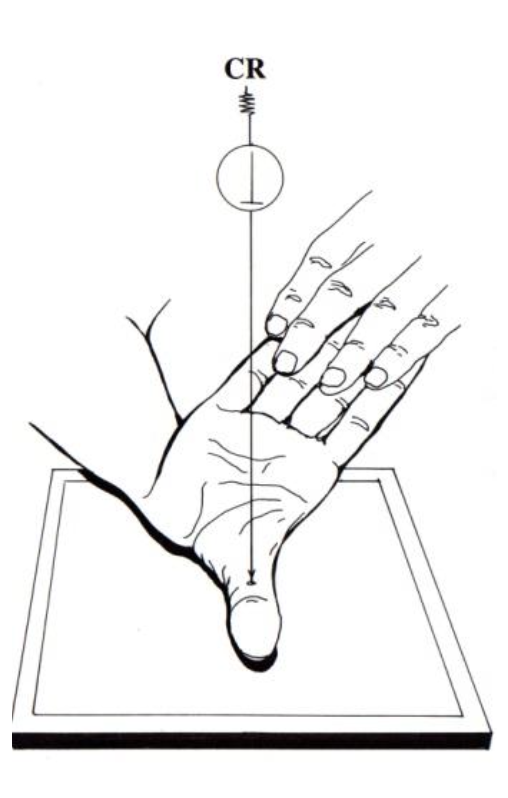
what projection shows the truest lateral of the metacarpals?
relaxed lateral (hand)
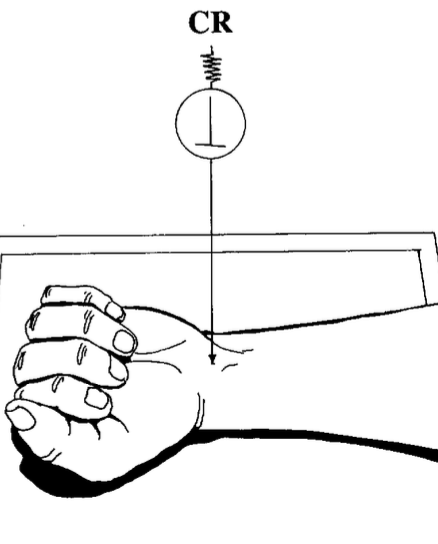
best demonstrates elongation of the scaphoid?
stetchers
true: hand elevated
modified: CR at 20°
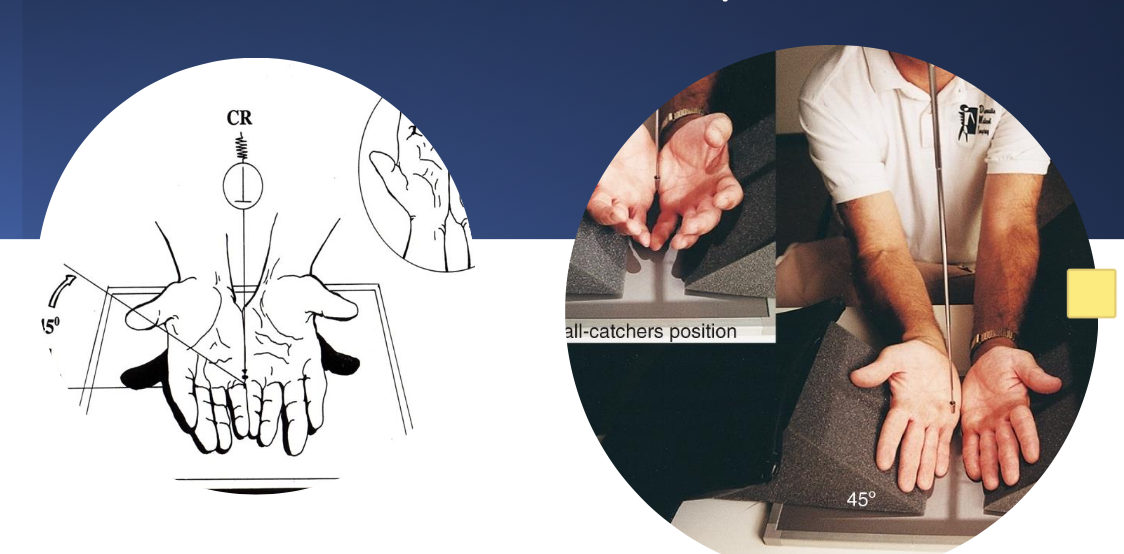
projection used to rule out early arthritic changes in the hand(s)?
ball catcher (AP oblique)
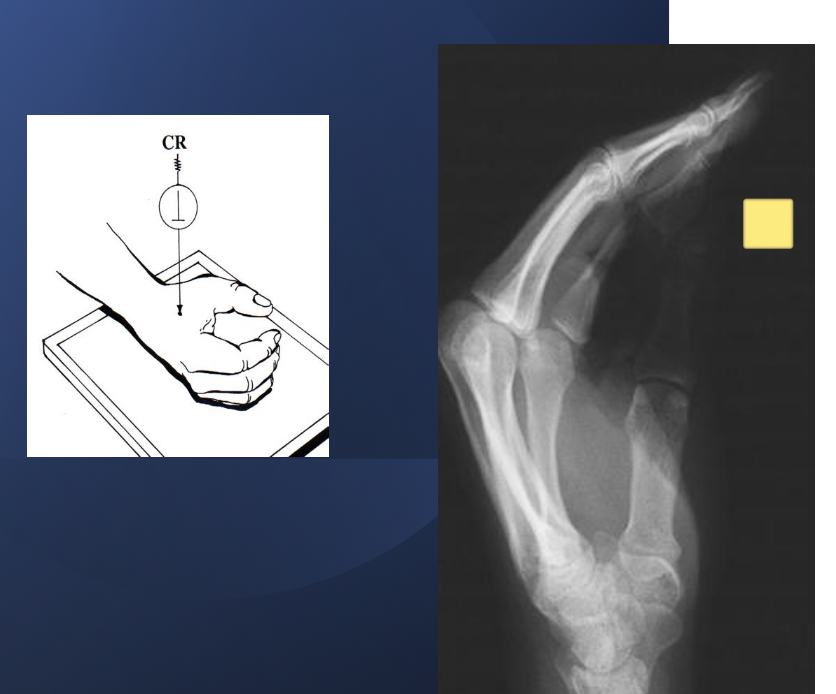
what projection best demonstrates ligament disruption in the wrist?
AP wrist
fist clenched
what projection best demonstrates the bases of the 1st and 2nd metacarpals free of superimposition?
PA oblique (hand)
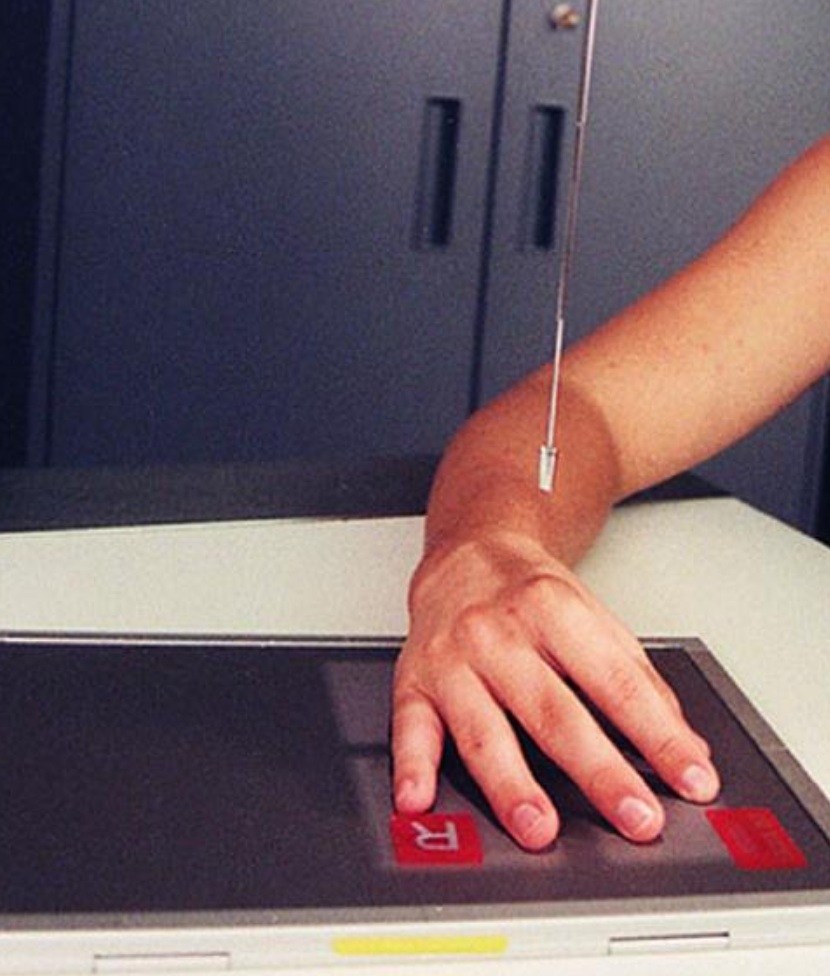

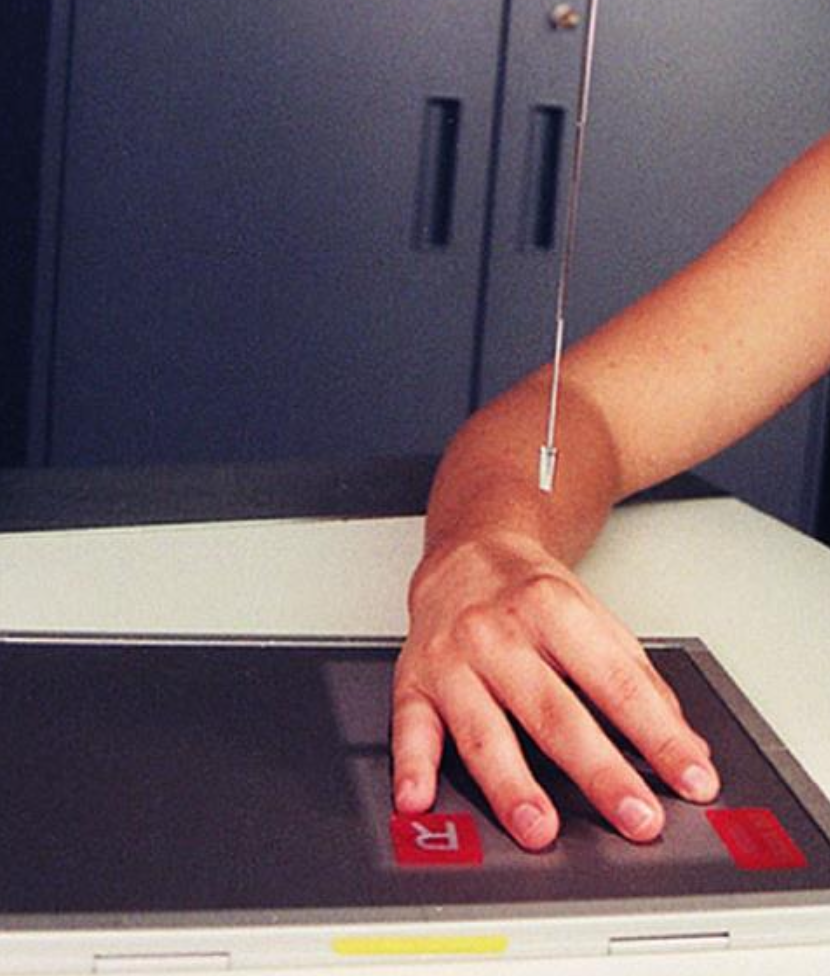
what position best demonstrates the 1st and 2nd MCP joints?
PA oblique (hand)

best demonstrates radial head, neck, and tubercle
external/lateral oblique (elbow)
entire body/arm is rotated laterally
elbow at 45°
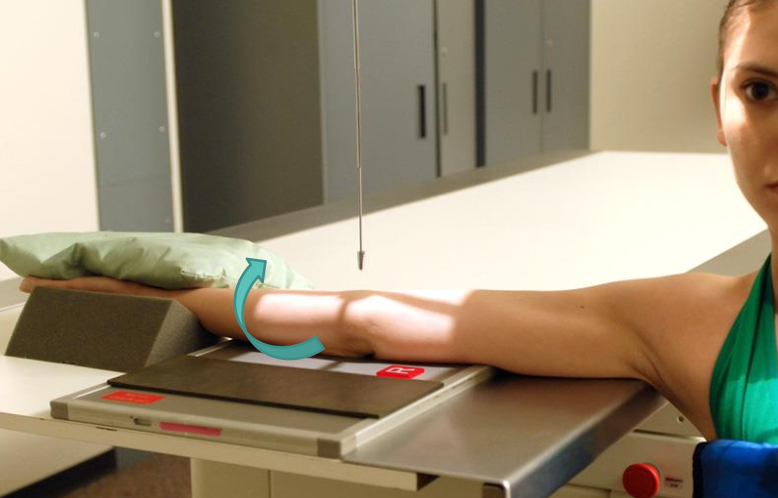
best demonstrates fat pads in elbow
lateral elbow
elbow and humerus in same plane
wrist and forearm are aligned/rotated
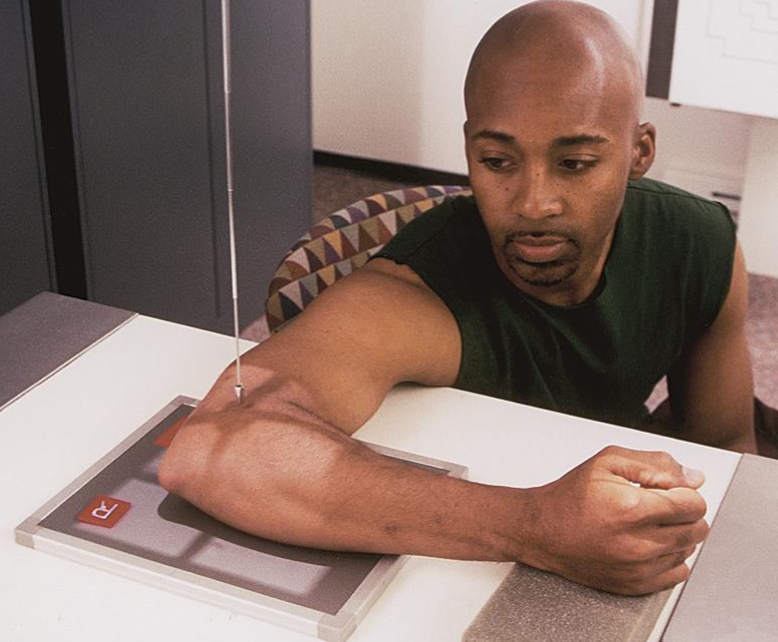

best demonstrates the olecranon process and trochlear notch with superimposed epicondyles
lateral elbow
elbow and humerus in same plane
wrist and forearm are aligned/rotated
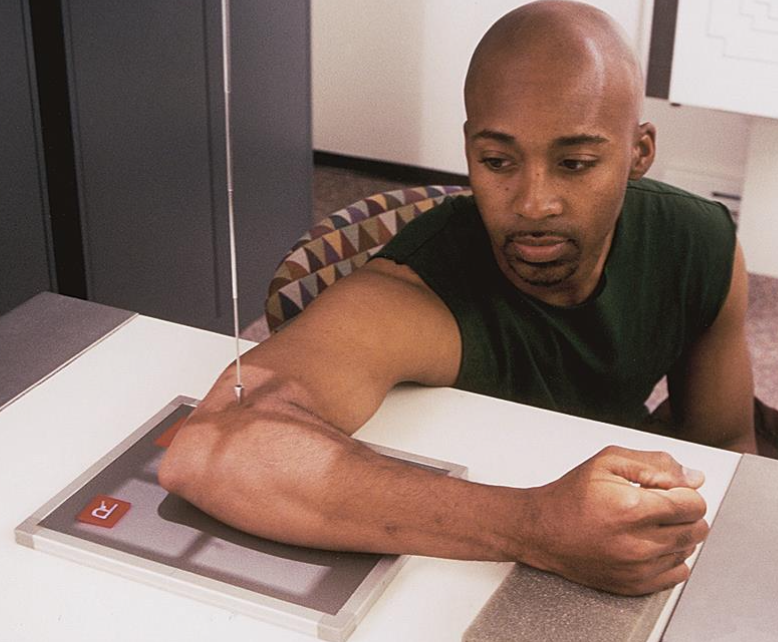

projection used to access olecranon process
tangential: acute flexion (aka jones position) (elbow)
CR 2in distal from olecranon
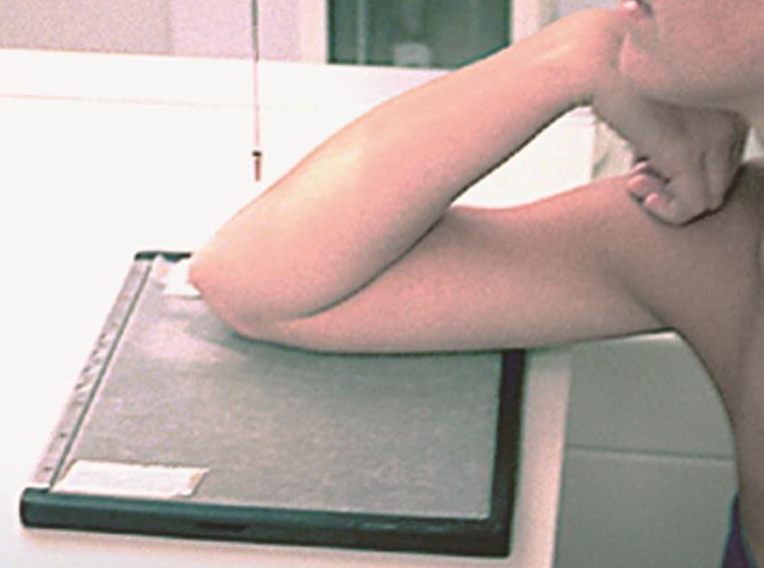
projection used for “avulsion” fracture off coronoid and when bone is broken off
axiolateral: coronoid (elbow)
CR 45° towards ELBOW
elbow is at 80°
arm is in lateral
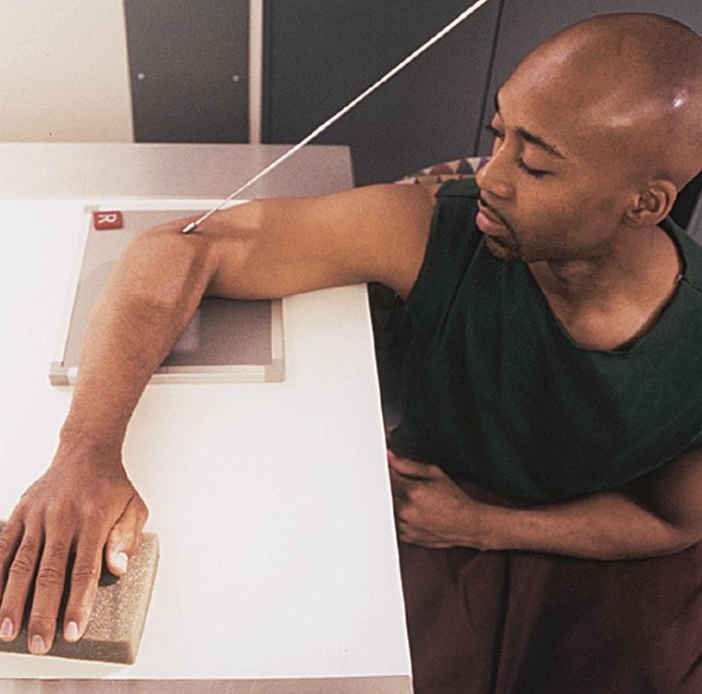

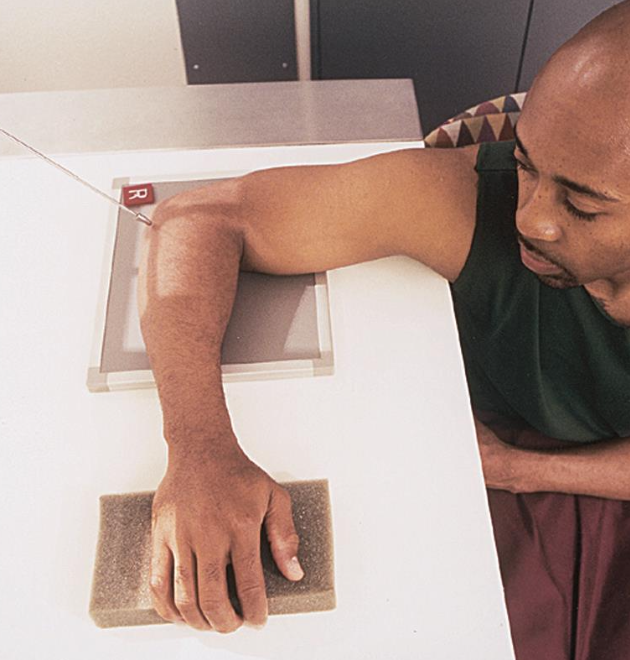
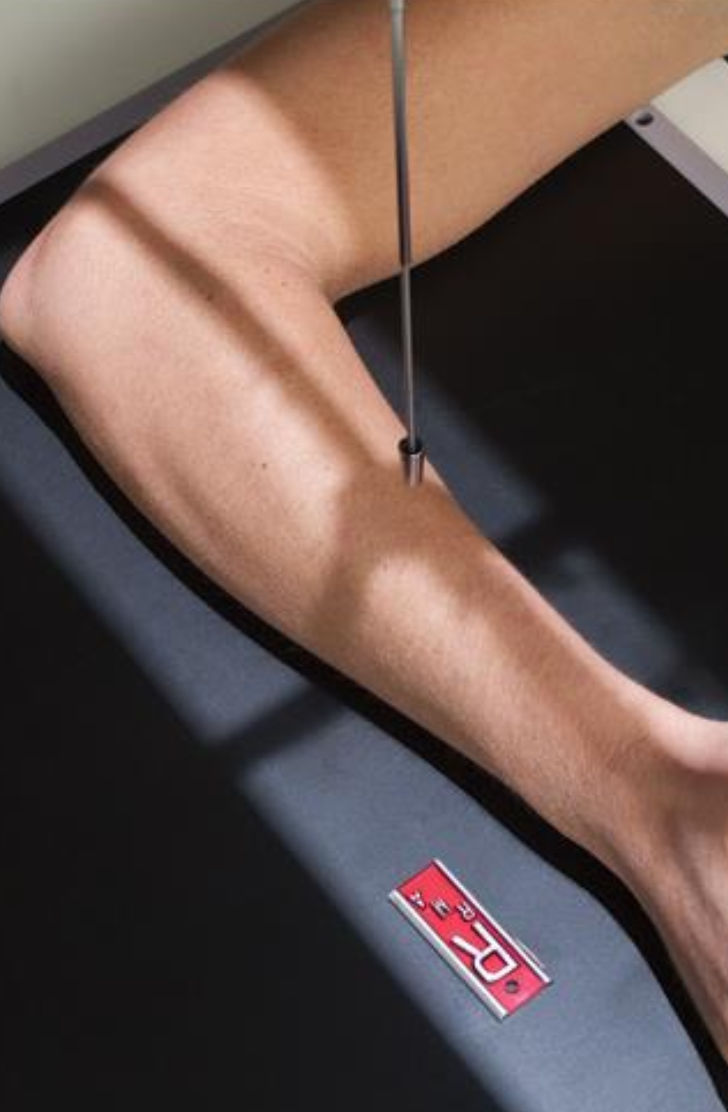
projection used as an alternate for occult intra-articular fracture
axiolateral: radial head (elbow)
CR 45° towards SHOULDER
arm is in lateral
what best demonstrates a general overview of the (elbow) joint with no rotation
AP elbow
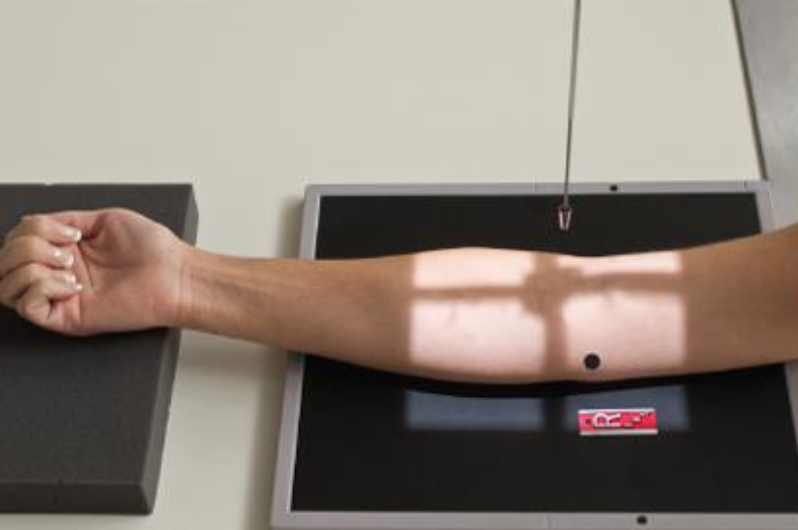
what best demonstrates the epicondyles of the elbow
AP elbow
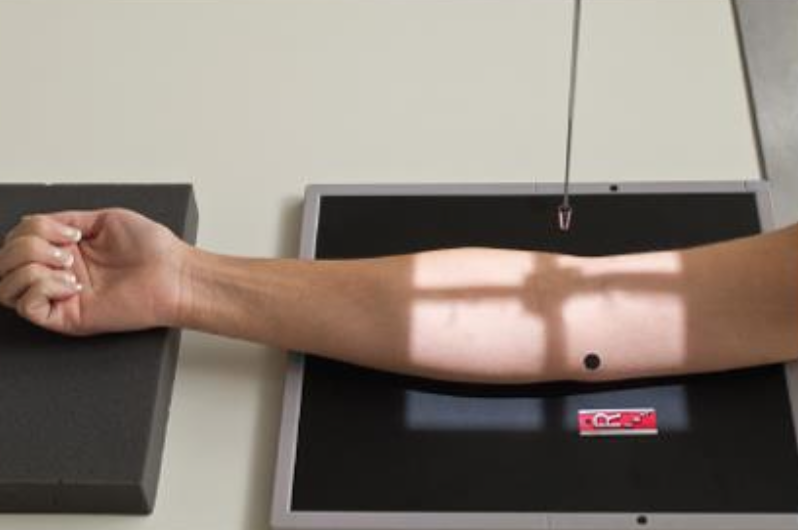
Projection that best shows the medial anatomy of the elbow
internal/medial oblique (elbow)
arm placed AP → palm is turned flat on table
elbow is 45°
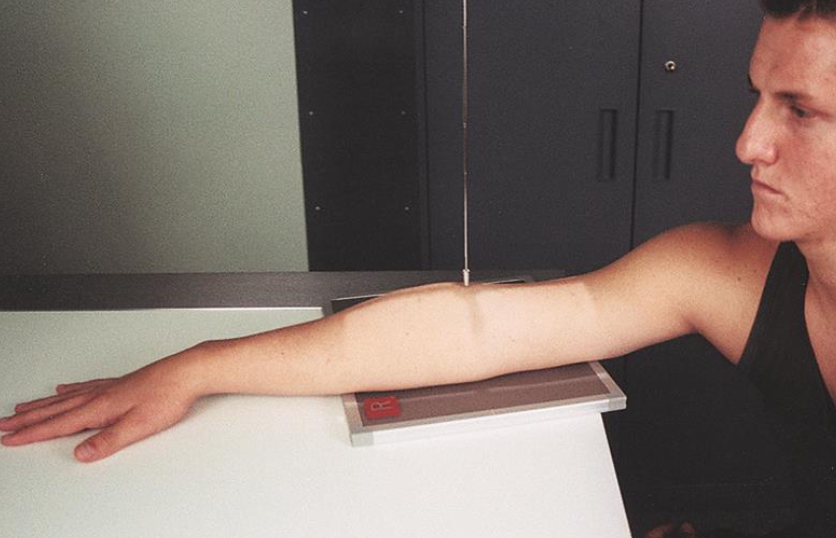
best demonstrates the coronoid process, trochlea, and medial epicondyle (in profile)
internal/medial oblique (elbow)
arm placed AP → palm is turned flat on table
elbow is 45°
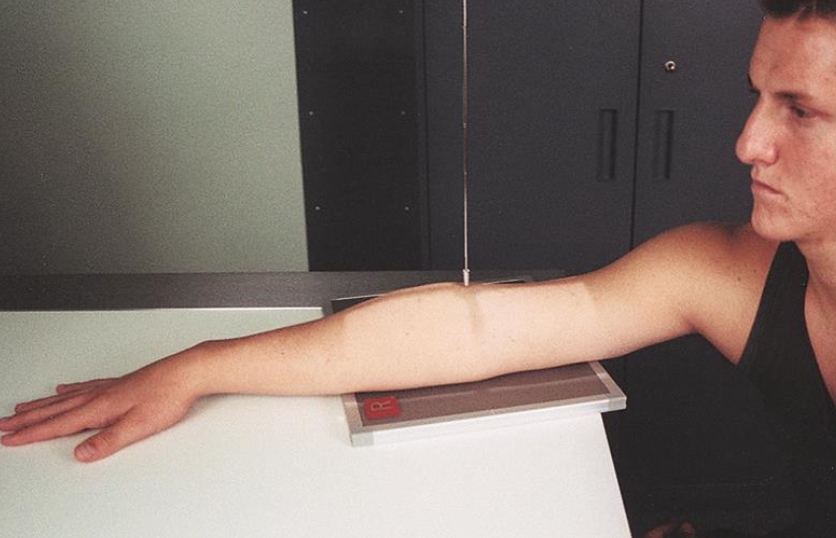
best demonstrates separation of the radius and ulna
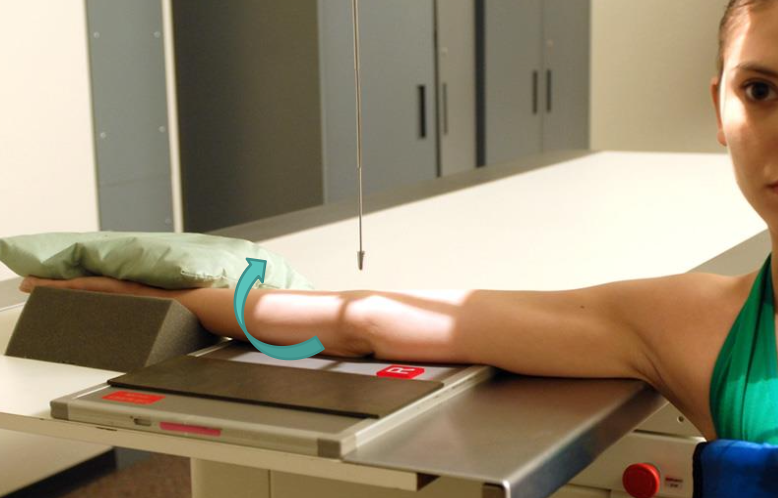
external/lateral oblique (elbow)
entire body/arm is rotated laterally
elbow at 45°
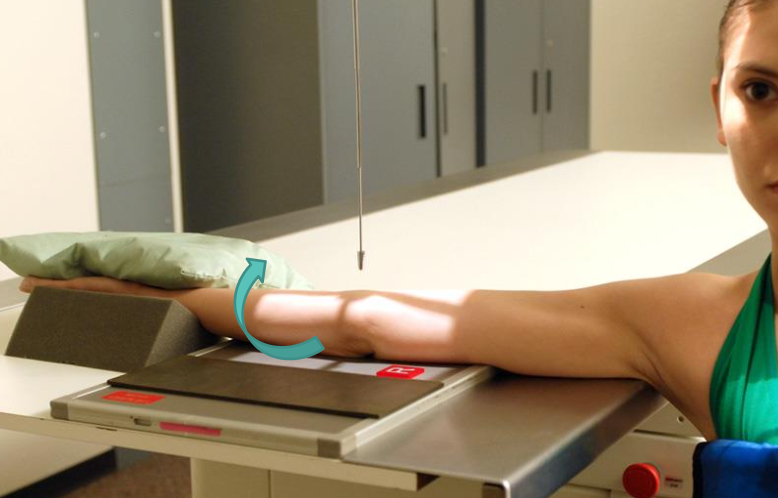
projection that best demonstrates the proximal radio-ulnar joint
external/lateral oblique (elbow)
entire body/arm is rotated laterally
elbow at 45°
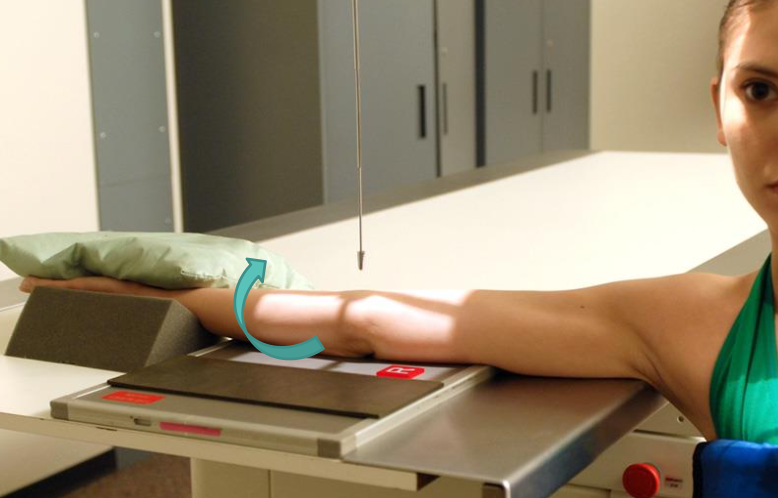
best demonstrates the lateral epicondyle and capitulum (in profile)
external/lateral oblique (elbow)
entire body/arm is rotated laterally
elbow at 45°
what is this projection
AP humerus
abduct arm slightly
palm foward

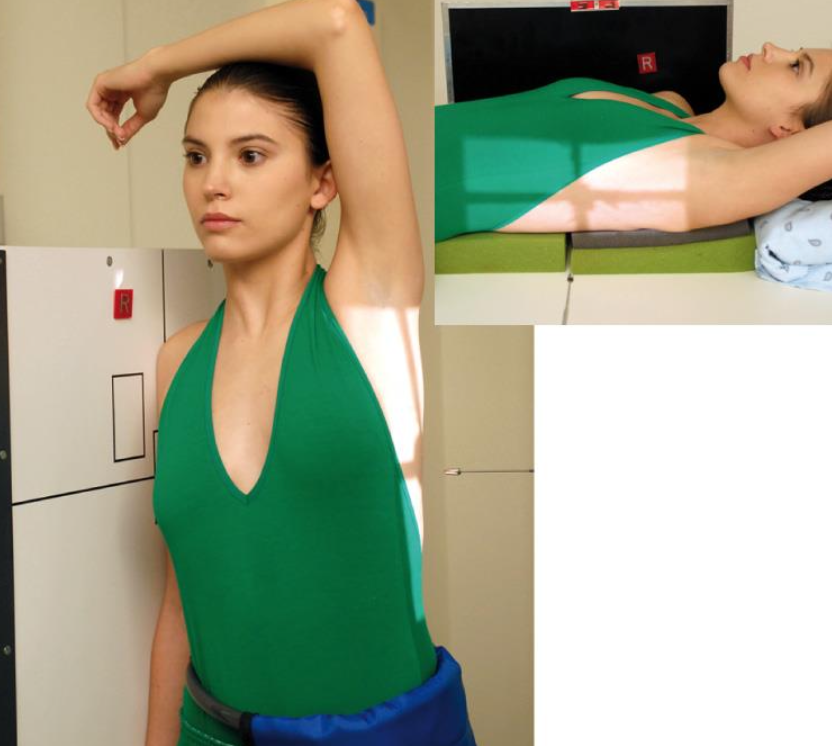
what is this projection
lateral humerus
arm internally rotated
palm facing laterally
what is this projection
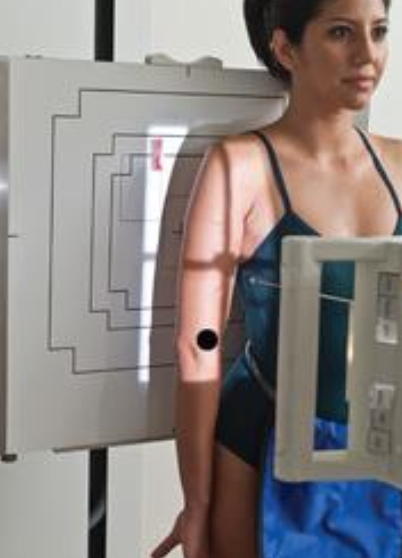
lateral mid and distal humerus trauma position (horizontal beam)
positioned like lateral forearm
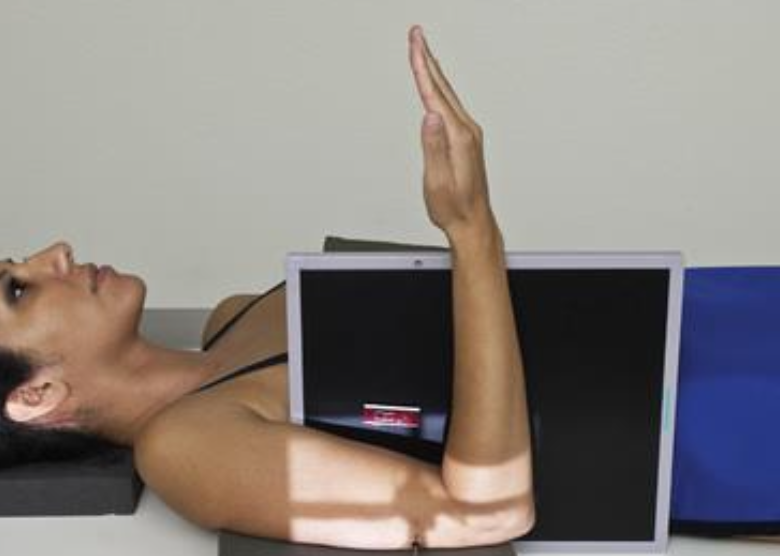

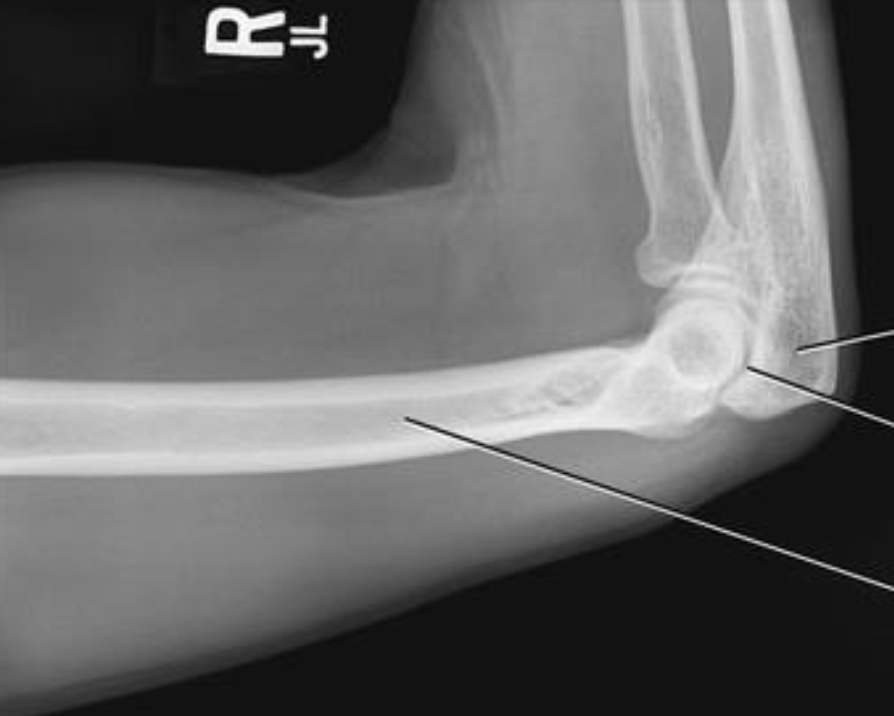
what is this projection
horizontal beam transthoracic lateral humerus
UNAFFECTED limb over head
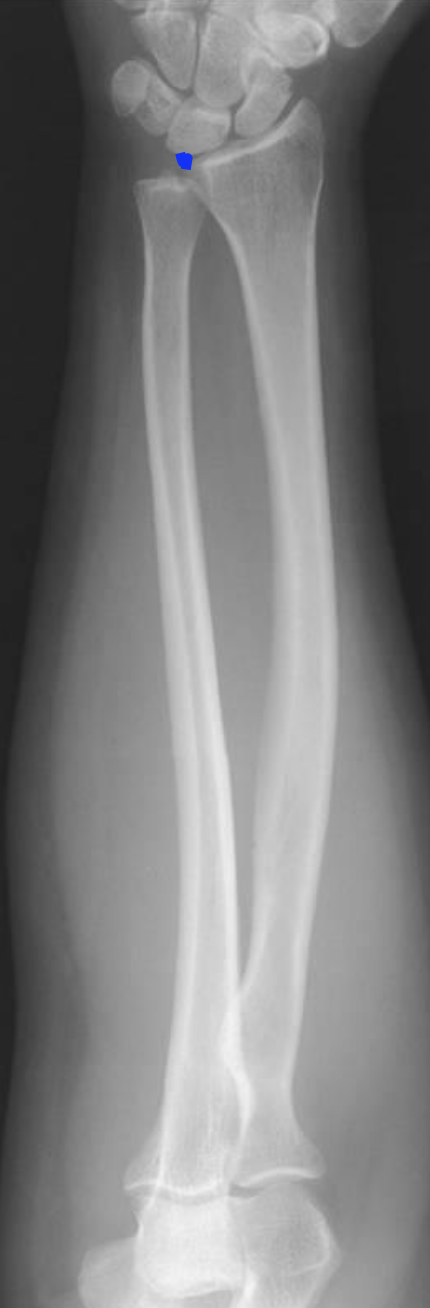
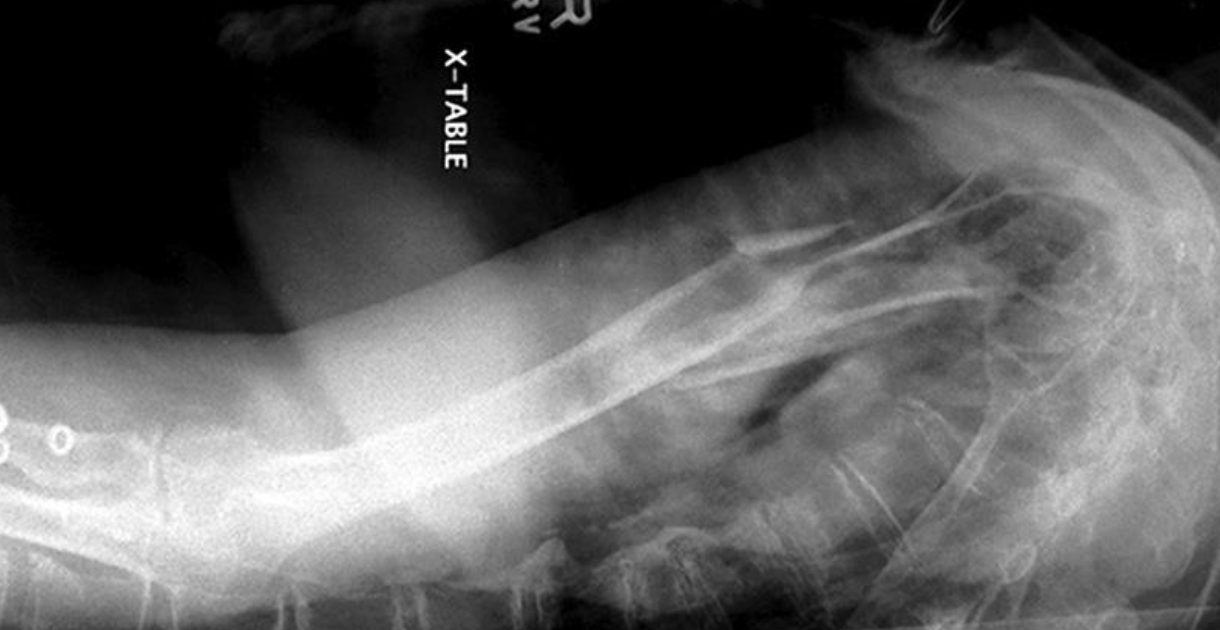
what is this projection
AP forearm
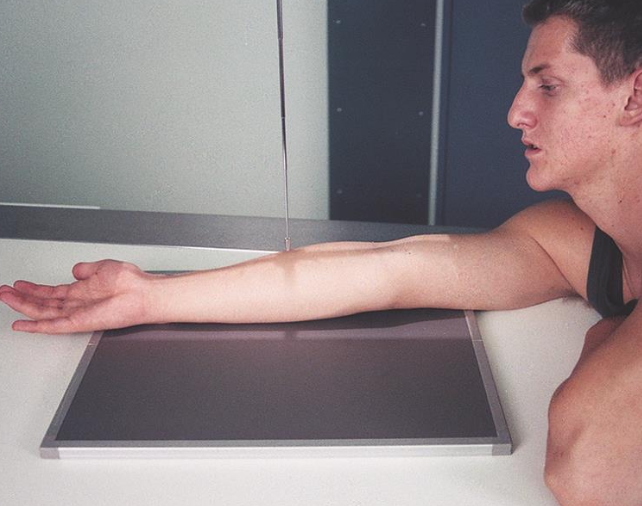

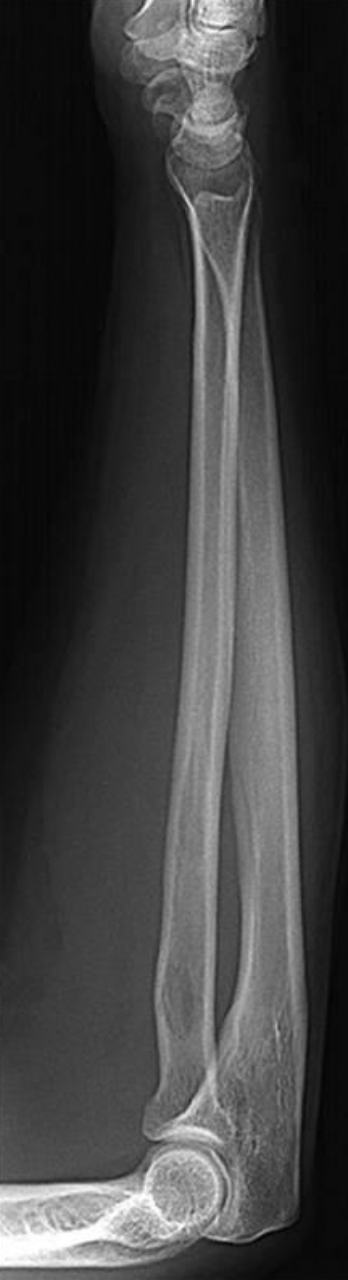
what is this projection
lateral forearm

best demonstrates Lesser tubercle profiled medially
AP with internal rotation (shoulder)
hand and arm turned internally where palm is lateral
CR directed to 1” inferior to coracoid
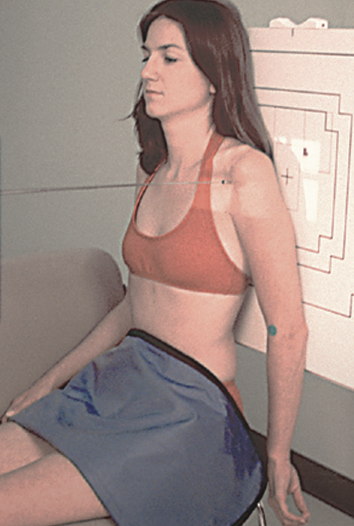
best visualizes the Proximal humerus, scapula, clavicle and SC joint
AP with internal OR external rotation (shoulder)
best demonstrates Greater tubercle profiled laterally
AP with External Rotation (shoulder)
hand and arm rotated externally
CR directed to 1” inferior to coracoid

best demonstrates Glenoid cavity profiled AND the Scapulohumeral joint centered
Grashey method
AP oblique
patient 35-45° toward affected side
CR 2” inferior and medial from superlateral border of humerus
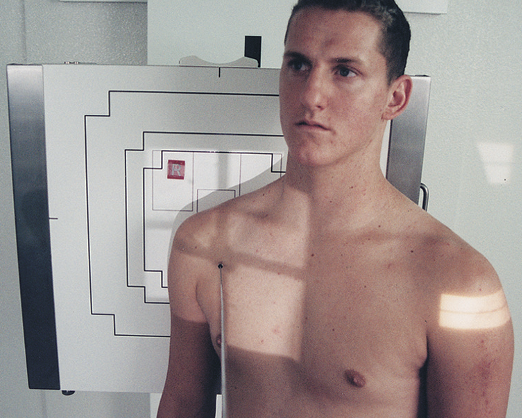
projection that Opens the subacromial space, elongates the humeral head & neck AND open glenohumeral joint
Garth Method
Apical oblique axial
45/45
IR is vertical
CR towards feet (caudal)
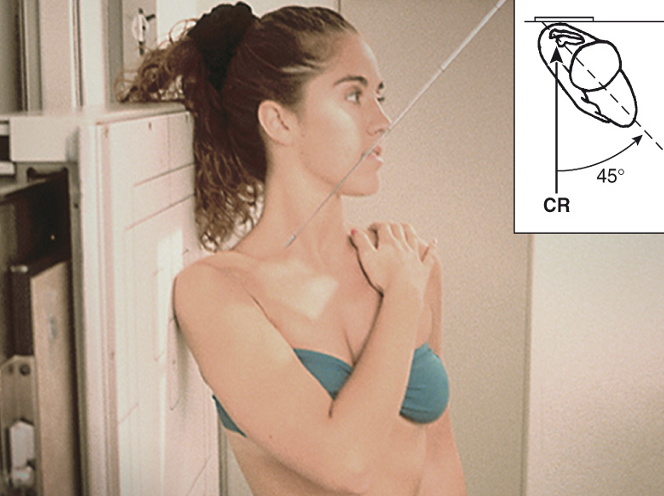
projection that best demonstrates Humeral head, glenoid cavity, and neck free of superimposition
Garth Method
Apical oblique axial
45/45
IR is vertical
CR towards feet (caudal)
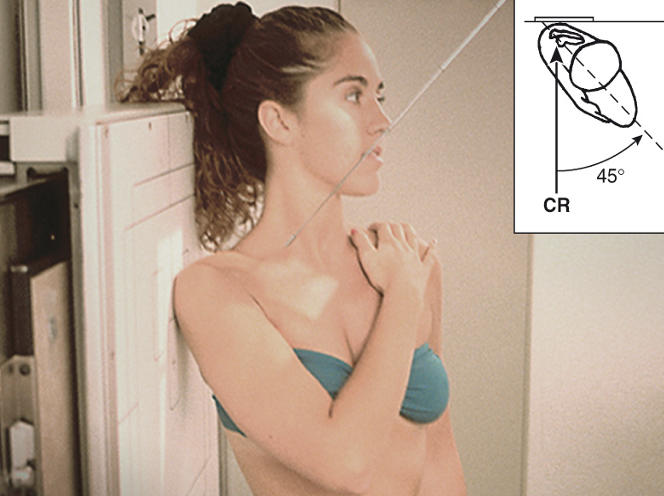
best demonstrates Acromion and coracoid processes in profile
Scapular Y view
PA with affected side towards IR
Oblique shoulder 30° - 45° towards IR
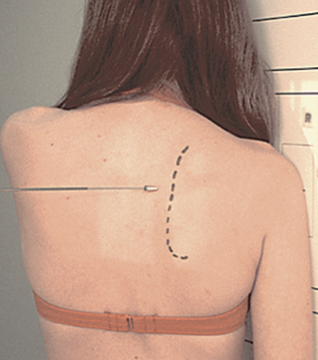
best demonstrates Humeral head Body of scapula and glenoid cavity superimposed
Scapular Y view
PA with affected side towards IR
Oblique shoulder 30° - 45° towards IR
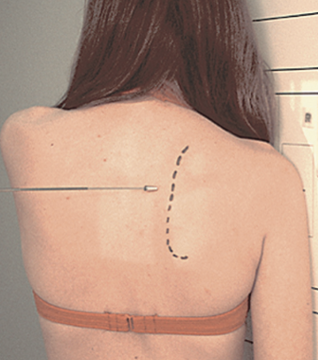
best demonstrates anterior and posterior placement of the scapula
Scapular Y view
PA with affected side towards IR
Oblique shoulder 30° - 45° towards IR
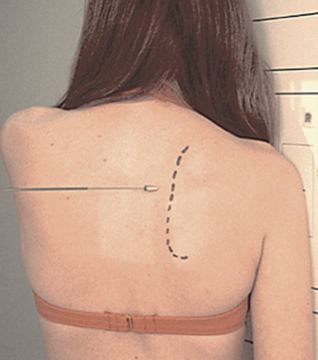
best visualizes Subacromial space and Anterioinferior aspect of acromion
Apical AP axial (shoulder)
Patient is positioned AP with arm in neutral position
CR 30° caudal angle (towards feet)
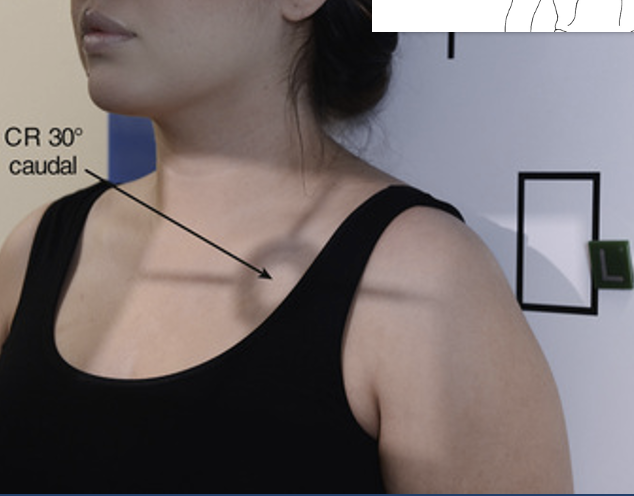
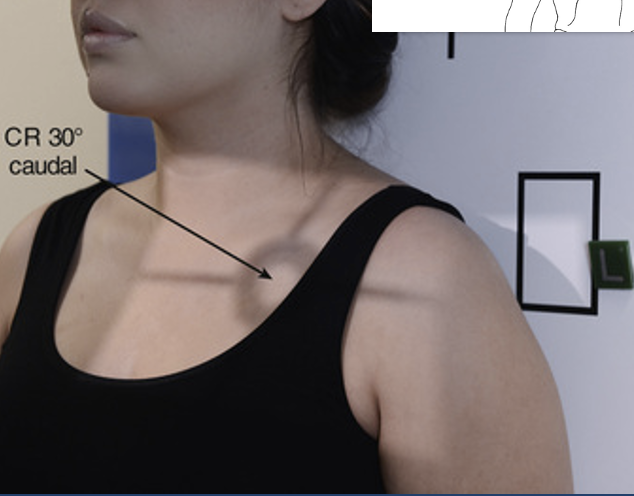
best demonstrates SC joint to proximal humerus and entire scapula seen
Apical AP axial (shoulder)
Patient is positioned AP with arm in neutral position
CR 30° caudal angle (towards feet)
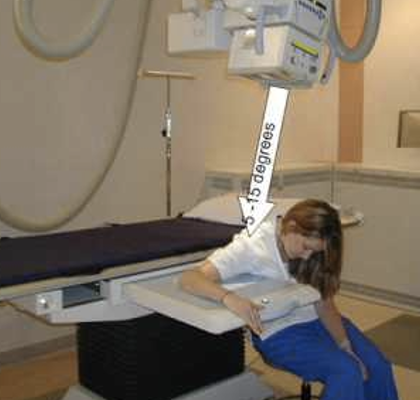
best demonstrates the relationship between the glenoid cavity and humeral head, showing suspected dislocations *****
Superioinferior Axillary
CR 5-10° angle toward the distal humerus
patient seated
best demonstrates Supraspinatus outlet and Coracoacromial arch open and in profile with Humerus superimposed over body of scapula
Neer method
10° - 15° caudal angle (towards feet)
Patient is positioned same as PA Scapular “Y”
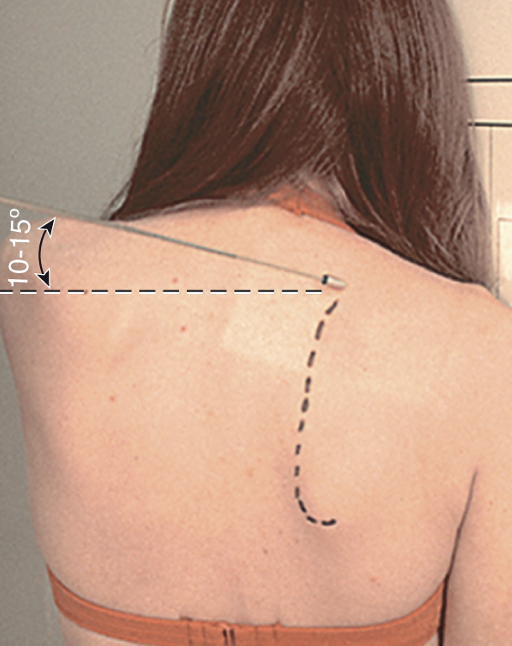
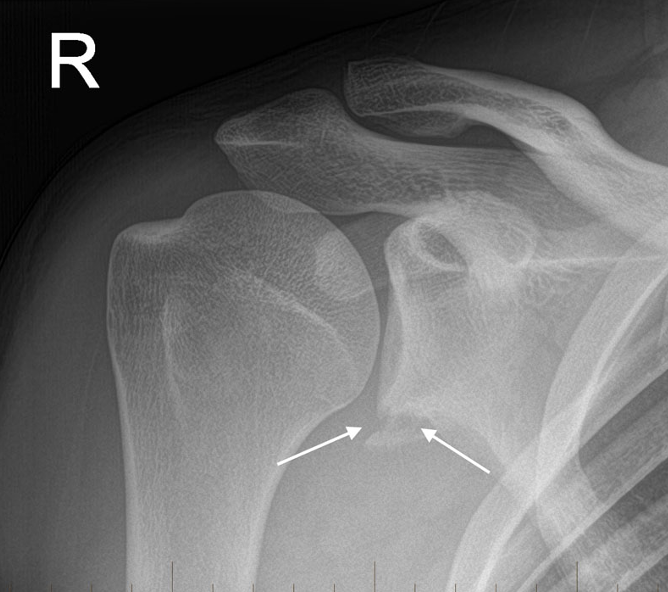
what projection best demonstrates a bankarts lesion
AP with external rotation (shoulder)
hand and arm rotated externally
CR directed to 1” inferior to coracoid

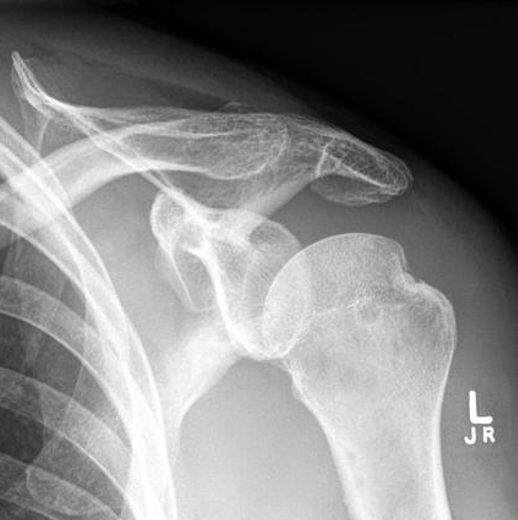
what projection best demonstrates the hill sachs defect
AP with internal rotation (shoulder)
hand and arm turned internally where palm is lateral
CR directed to 1” inferior to coracoid
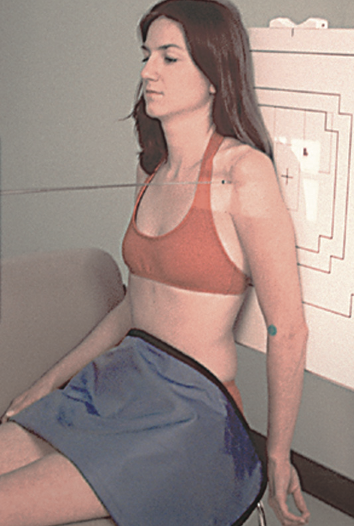
best demonstrates Reduced superimposition of the thorax with the Entire scapula seen
AP scapula
AP shoulder position
Affected arm is abducted 90°, with hand in supination
orthostatic breathing -(3 sec) or full exhalation to improve visibility
best demonstrates the Scapula seen in truest lateral position
Lateral scapula
affected side closest to receptor
patient to place forearm & hand over posterior waist
patient PA and oblique
best demonstrates a Visible “Y” and the Humerus not superimposed over the scapular body
Lateral scapula
affected side closest to receptor
patient to place forearm & hand over posterior waist
patient PA and oblique
best demonstrates the Entire clavicle seen with Slight superimposition on medial end by thorax
PA and AP clavicle
overall view of the clavicle with reduced OID
PA clavicle
affected side closest to receptor
must include SC and AC joints
full exhalation
overall view of the clavicle with increased OID
AP clavicle
posterior aspect closest to receptor
patient erect
full inhalation
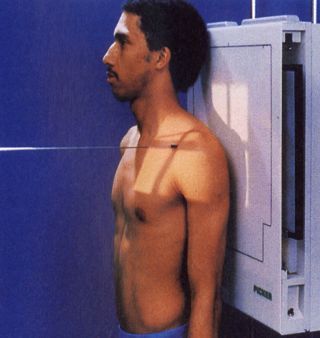
best demonstrates Clear visual of clavicle and separation***
AP and PA axial (clavicle)
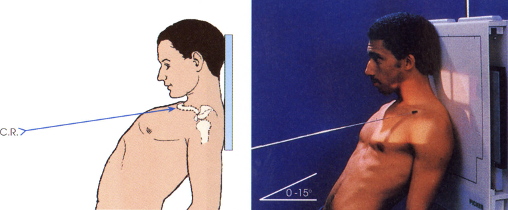
what projection best demonstrates the clavicle superior to the ribs and scapula
AP axial (clavicle)
CR directed 25° – 30° cephalic (towards head)
AP erect with only shoulders against IR, leaning awkwardly against it
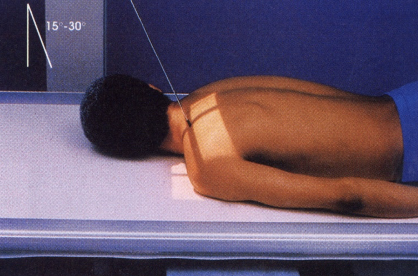
best demonstrates clavicle superior to ribs and scapula with horizontal placement
PA axial (clavicle)
CR directed caudal, 25° – 30°
full inhalation
positioned PA erect
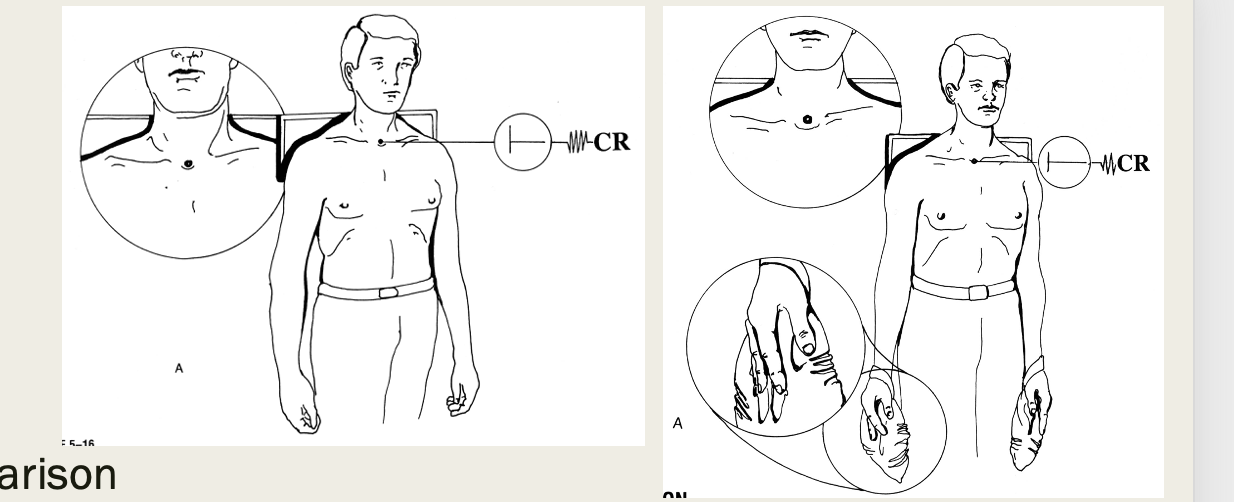
best demonstrates separation and/or dislocation of the AC joint
AP with/without weights (AC joints)
AP shoulder position
minimum 10lb weights
72in SID
include both shoulders
CR 1in above jugular notch
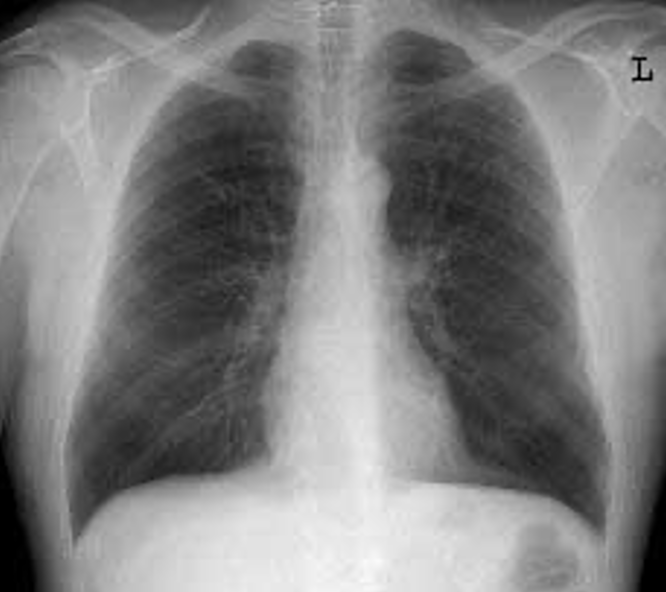
what is this projection
pa chest
72 SID
shoulders rolled forward
double inhalation
CR middle below scapula
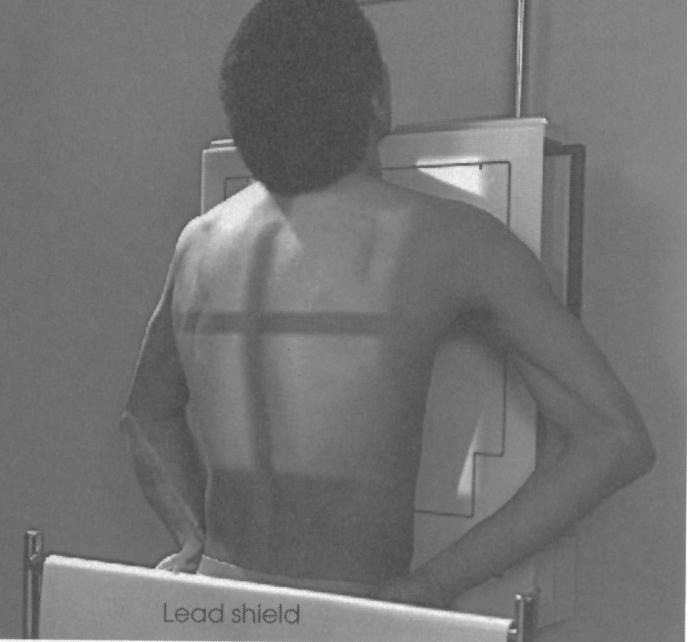
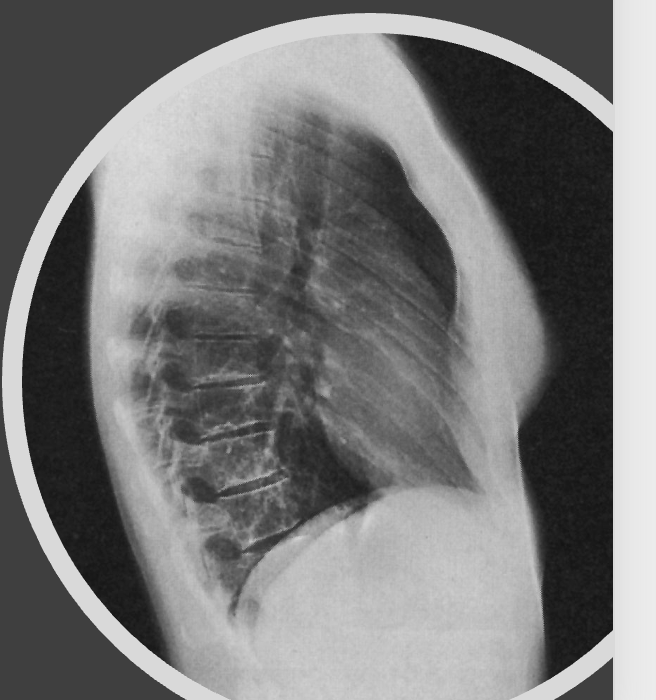
what is this projection
lateral chest
72 SID
hands above head
affected side towards IR
double inhalation
CR middle below scapula
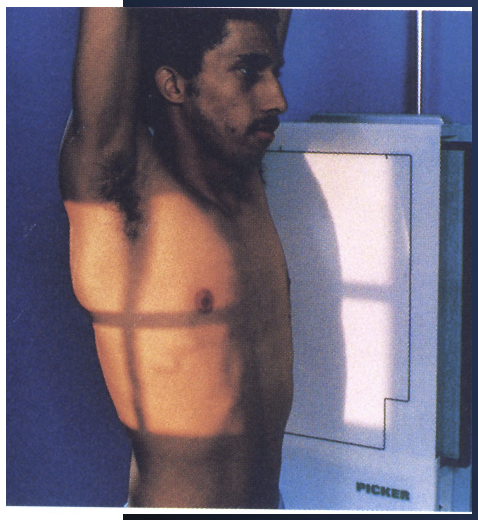
best demonstrates anterior vs posterior dislocation (of a humerus) in a trauma setting
transthoracic horizontal
best demonstrates anterior vs posterior dislocation (of the humerus) shot through the thorax
transthoracic hand over head