Chemistry - Chapter 6: Thermochemistry
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Types of Energy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
joules (J)
Because of the direct connection between energy and work, energy is measured in the same unit as work: ____
Thermodynamics
branch of physics that studies the relationship between heat, work, temperature, and energy.
Thermochemistry
specifically focuses on the heat energy involved in chemical reactions and changes.
open system
exchanges mass and energy
closed system
exchanges energy but not mass
isolated system
exchanges neither mass nor energy
exothermic reaction
condensation is an example of which reaction?
exothermic reaction
combustion is an example of which reaction?
First Law of Thermodynamics
“Energy cannot be created nor destroyed.” By Rudolf Clausius
Yield
is the mass of a product made in a chemical reaction
actual yield
is the mass that is made in the chemical reaction.
it is the amount of product obtained when the reaction takes place.
theoretical yield
maximum mass that is possible to make from a given mass of reactants.
the maximum amount of product calculated using the balanced equation.
percent yield
calculated by comparing the theoretical yield with the actual yield in the chemical reaction.
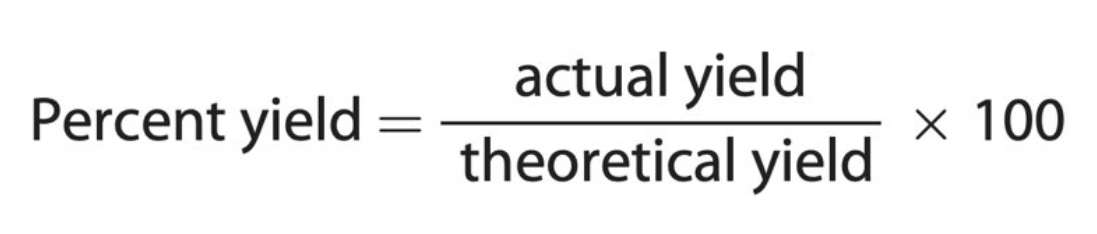
PY = (AY/TY) * 100
formula for percent yield
Energy
capacity to do work or transfer heat
Mechanical Energy
When work is done to an object, it requires energy. That required energy is called ____
Thermal Energy
Internal motion of the atoms is called _______, because moving particles produce heat.
Thermal Energy
____ causes changes in temperature and phase of any form of matter.
Friction
Thermal Energy can be produced by ____
Chemical Energy
is the energy that is stored in chemical bonds.
absorbed
When chemical bonds are broken, energy is ____
released
When new chemical bonds are formed, energy is ___
Exothermic Reaction
reaction where energy is released from the system to the surroundings
Endothermic Reaction
reaction where energy is absorbed from the surroundings to the system
fuel
___ and food are forms of stored chemical energy.
Electrical Energy
____ results from moving charges; depending on whether the charges are moving or stored it can be a form of kinetic or potential energy.
Radiant Energy
____ results from the motion of the particles within atoms and usually travels in waves.
Sound Energy
____ is given off by a vibrating object. This energy travels through matter in the form of waves.
Energy Transformation
Changes in the form of energy are called ___
Mechanical Energy
In an electric motor, electromagnetic energy is converted to ____
Electromagnetic Energy
In a battery, chemical energy is converted into ___
Mechanical Energy
The ___ of a waterfall is converted to electrical energy in a generator.