T1 Integumentary System
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
components of dermis layer
ct, dense, fibrous, blood vessel, nerves
components of hypodermis
subcutaneous, ct
skin layer injections are injected into and why
hypodermis because fat absorbs well
functions of the skin
maintain homeostasis, site of Langerhans (APC), produce vitamin D
epidermis characteristics
keratinized stratified squamous, basement membrane, no vasculation
thick skin locations
palm, sole
what component is in thin skin that isn’t in thick skin
hair
epidermis layers starting from basement membrane
stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, stratum corneum
cell types of epidermis
keratinocyte (majority), melanocyte, langerhans, merkel
what cell junction is present in stratum basale
hemidesmosome
stratum basale characteristics
single layer with mitosis (stem cell), keratinocytes rest on basement membrane
stratum spinosum characteristics
spikes from cell surface (prickle cells), langerhans
function of tonofibrils
bind to desmosome for cohesion and resistance to abrasion
stratum granulosum characteristics
keratohyalin granules (cysteine), lamellar granules (lipid coats), more purple
stratum lucidum characteristics
lack nucleus, only in thick skin, contain keratin filaments and eleidin
stratum corneum characteristics
lack nucleus, contain keratin, shed every 25 days
melanocyte location
stratum basale
dermal papilla
invaginations of dermis into epidermis
epidermal ridge
invaginations of epidermis into dermis
keratinocyte characteristics
originate from stratum basale, mitosis
melanocyte characteristics
originate from neural-crest cells, round nucleus with space around it, in basale, no desmosome
langerhans cell morphology
resemble melanocyte but in spinosum
melanin pigment formation
tyrosine > DOPA > dopaquinone > phenomelanin, eumelanin > transfer from melanocyte to keratinocyte
skin brightening mechanism blocks
tyrosinase
albinism
melanocytes can’t synthesize melanin
langerhans characteristics
found in all layers (especially spinosum), no desmosome
merkel (tactile) cells
derived from neural crest, found in stratum basale, in fingertips
carotene
yellow pigment from egg and vegetables
melanin accumulate where
keratinocytes of S. basale and S. spinosum
dermis characteristics
ct with fibers, contains glands and nerve endings
dermis layers and which is majority
papillary, reticular (majority)
papillary layer
loose ct, vascularized, dermal papillae
reticular layer
dense irregular ct, glycoaminoglycan for skin hydration
bullous pemphigoid
autoimmune blistering of dermis-epidermis junction
hypodermis
superficial fascia (subcutaneous), loose ct with adipose, contain sweat glands and hair
skin aging in epidermis, melanocytes, collagen and elastin, oil, subcutaneous fat, sweat
epidermis thinning but same number of cell layers, melanocytes increase in size but less amount, changes in collagen and elastin, less oil produced, thinner subcutaneous fat, less sweat produced
1st degree burn
epidermis, sun burn
2nd degree burn
blisters, epidermis and dermis
3rd degree burn
all layers of skin, fire
4th degree burn
all layers + muscle
cutaneous wound healing
blood clot vessels bleed into wound, blood clot and leukocytes clean wound, blood vessels regrow, granulation tissue forms, epithelium regenerates and fibrosis occurs
squamous cell carcinoma
originate from keratinocyte in sun exposed areas
basal cell carcinoma manifestations
white nodules or waxy bumps
epidermal derivative groups
pilosebaceous apparatus (hair and sebaceous), sweat glands (eccrine and apocrine)
location of hair root
dermis
sebaceous gland secrete into
hair follicle
merocrine sweat gland secrete into
epidermis
apocrine sweat gland secretes into
hair follicle
arrector pilli
smooth muscle attach to hair, involuntary (ANS)
primary hair
lanugo
secondary hair
vellus
hair is
filamentous keratinized epidermal invaginations
structures of hair from outside to inside
ct sheath, root sheath, cuticle, cortex, medulla
types of sweat glands
apocrine, merocrine
sebaceous gland characteristics
flask-shaped with short ducts containing sebocyte cells
merocrine (eccrine) gland secretes ______ into ______
secrete water, nacl, ammonia, urea, uric acid; skin
apocrine gland
secrete thicker and oilier, when poor hygiene it smells
morphology of secretory vs duct portions
secretory more pale
apocrine sweat gland morphology
larger ducts, empty into hair follicle
nail characteristics
keratinized plates of s. corneum containing eponychium (cuticle), lunular (white crescent), matrix (nail growth)
sensory nerve ending types
encapsulated (wrapped in myelin), non-encapsulated
non-encapsulated receptor examples
free nerve ending, merkel’s disc
encapsulated receptors
meissner’s, pacinian, ruffini
meissner’s corpuscle
found at dermal papillae, for light touch
cutaneous plexus
supplies hypodermis, hair follicles
superficial plexus
papillary loops
outer epidermis derived from
ectoderm
deeper dermis derived from
mesoderm
layer that is only present in thick skin
stratum lucidum
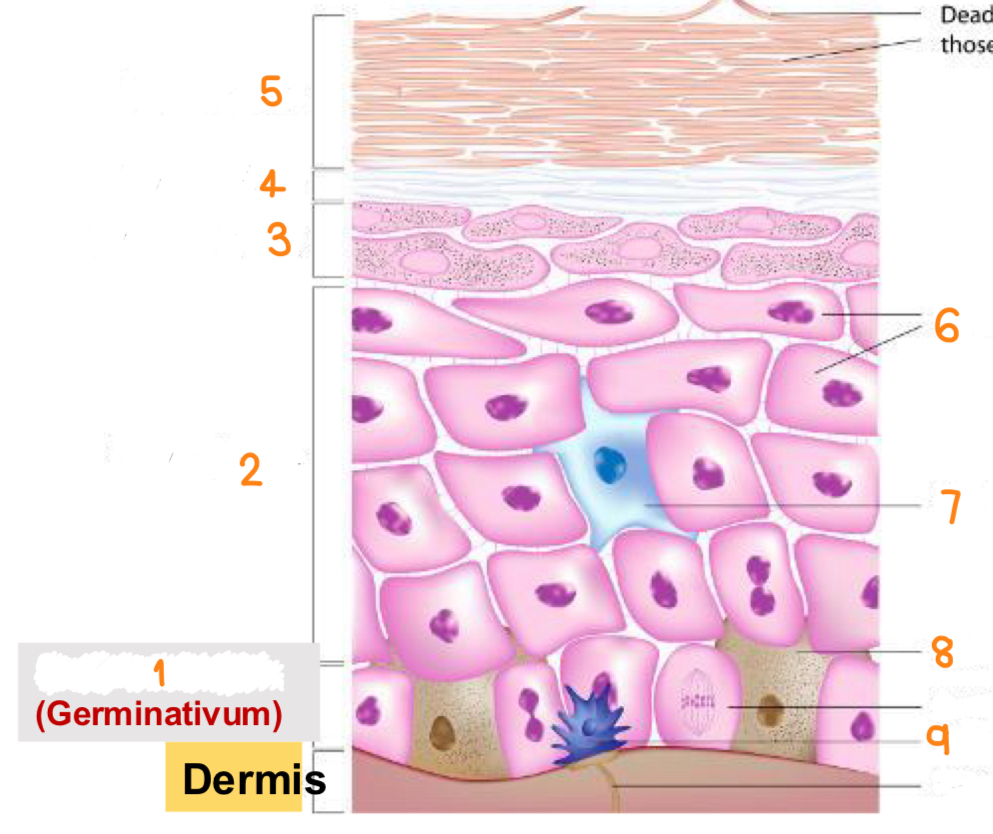
what is 1
stratum basale
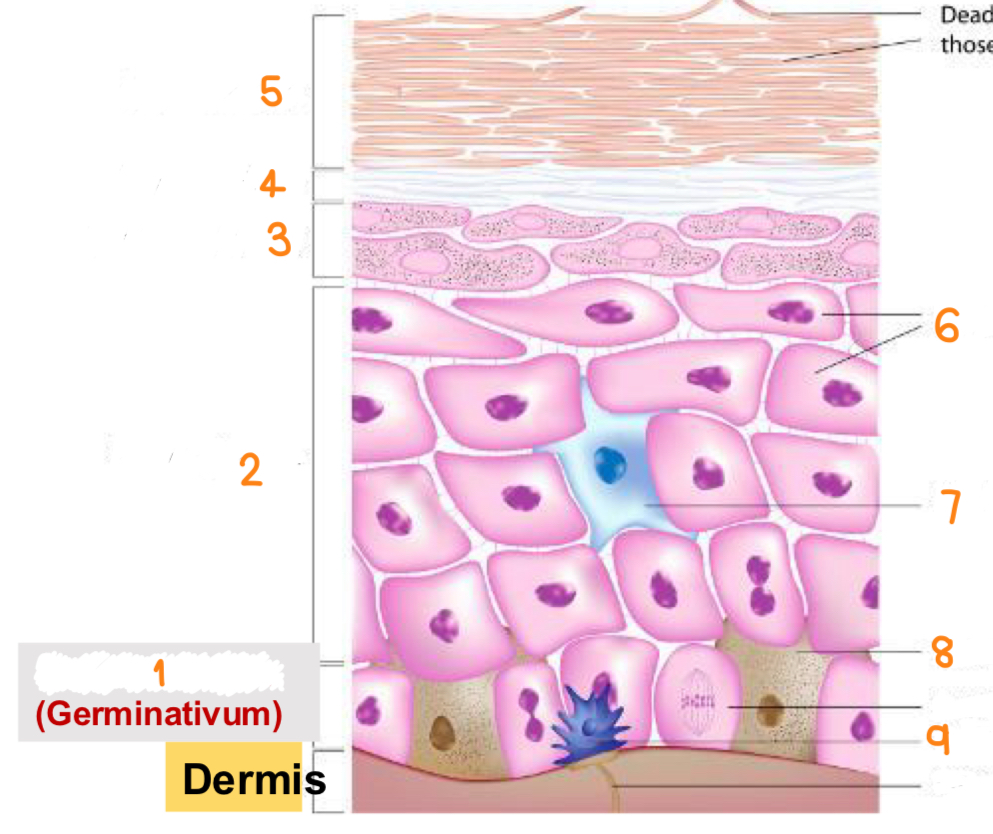
what is 2
stratum spinosum
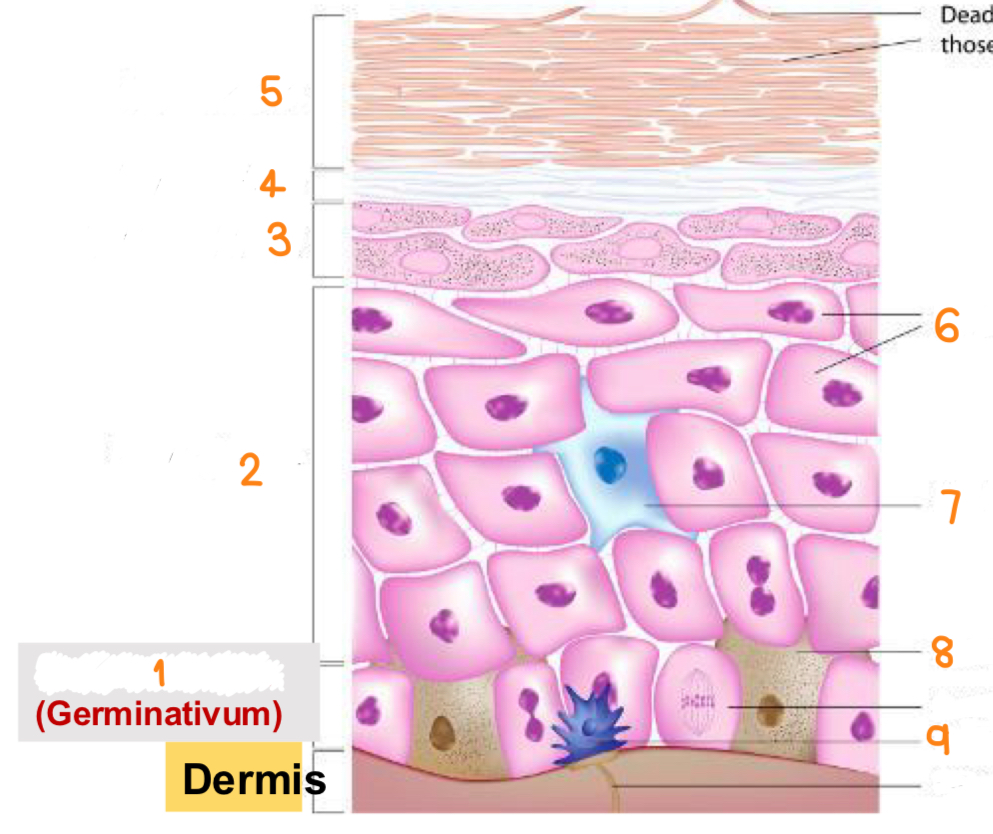
what is 3
stratum granulosum
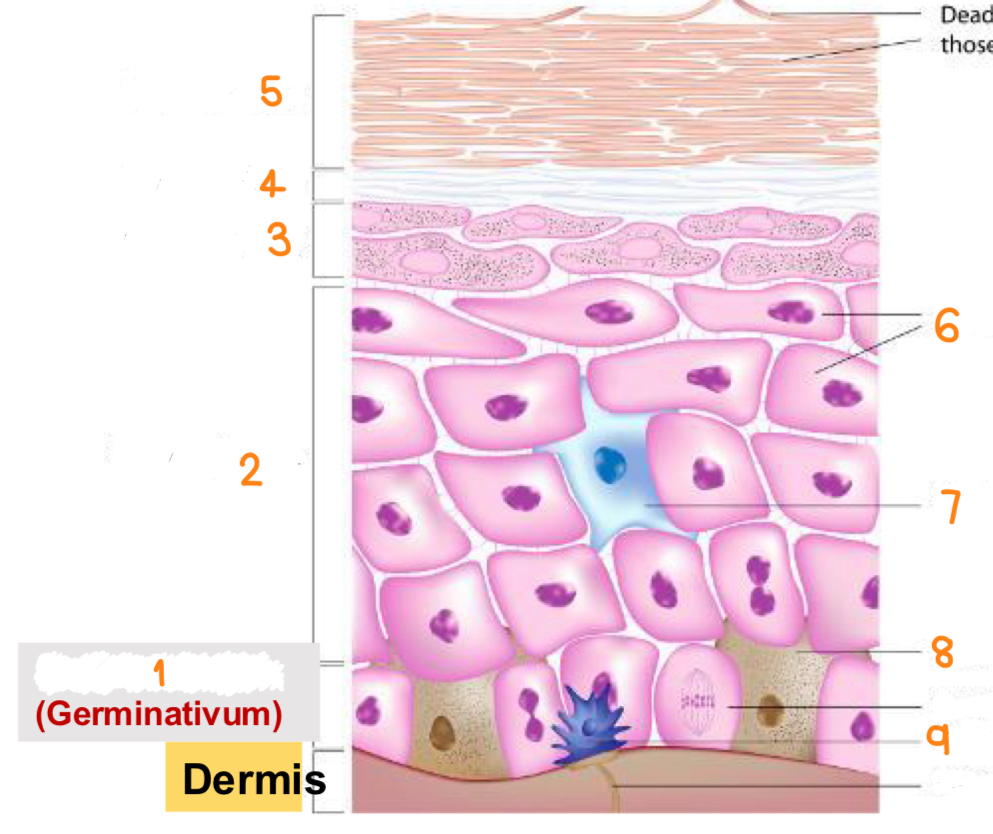
what is 4
stratum lucidum
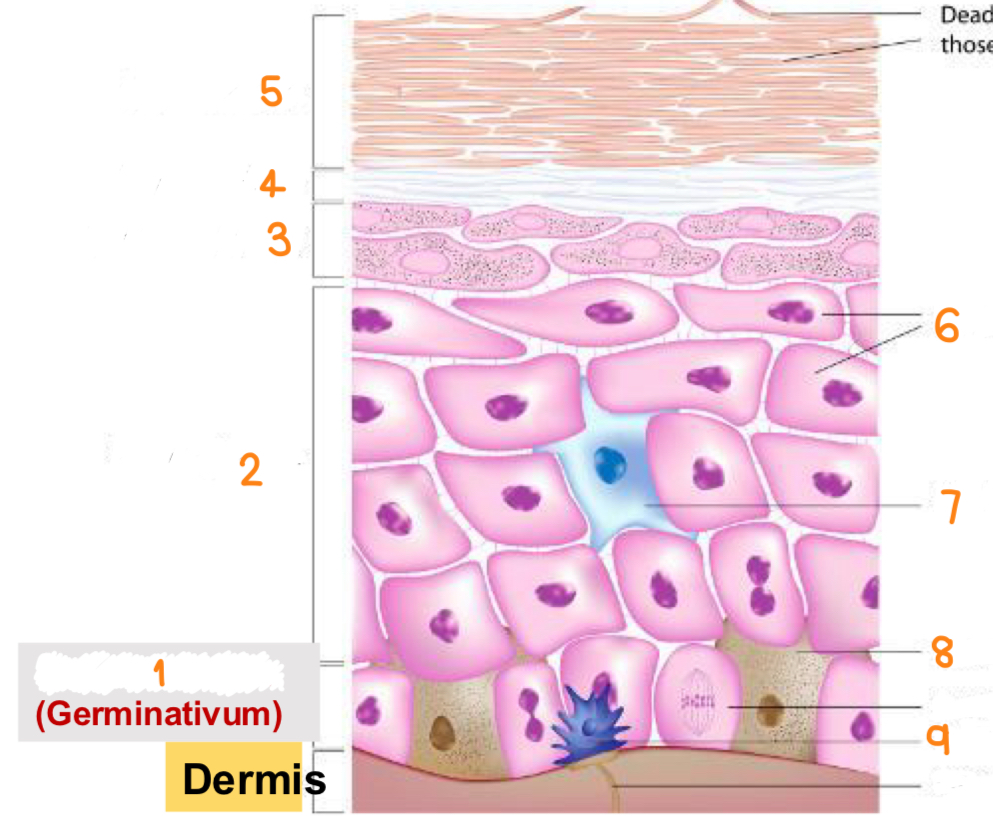
what is 5
stratum corneum
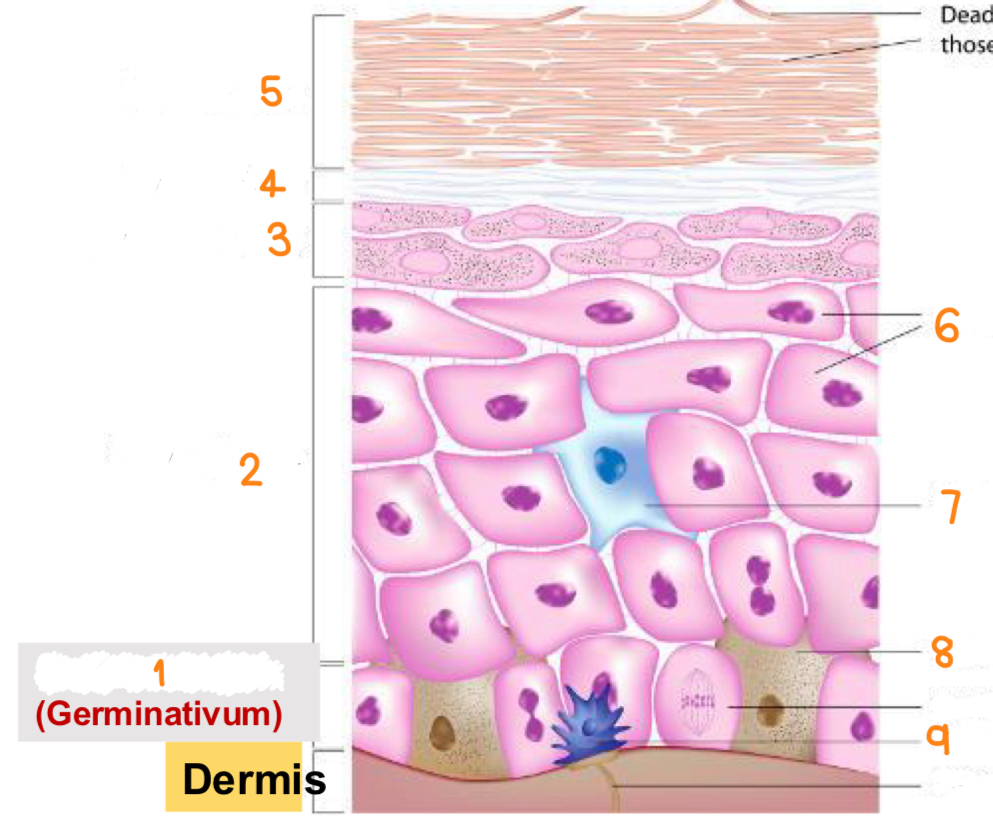
what is 6
keratinocytes
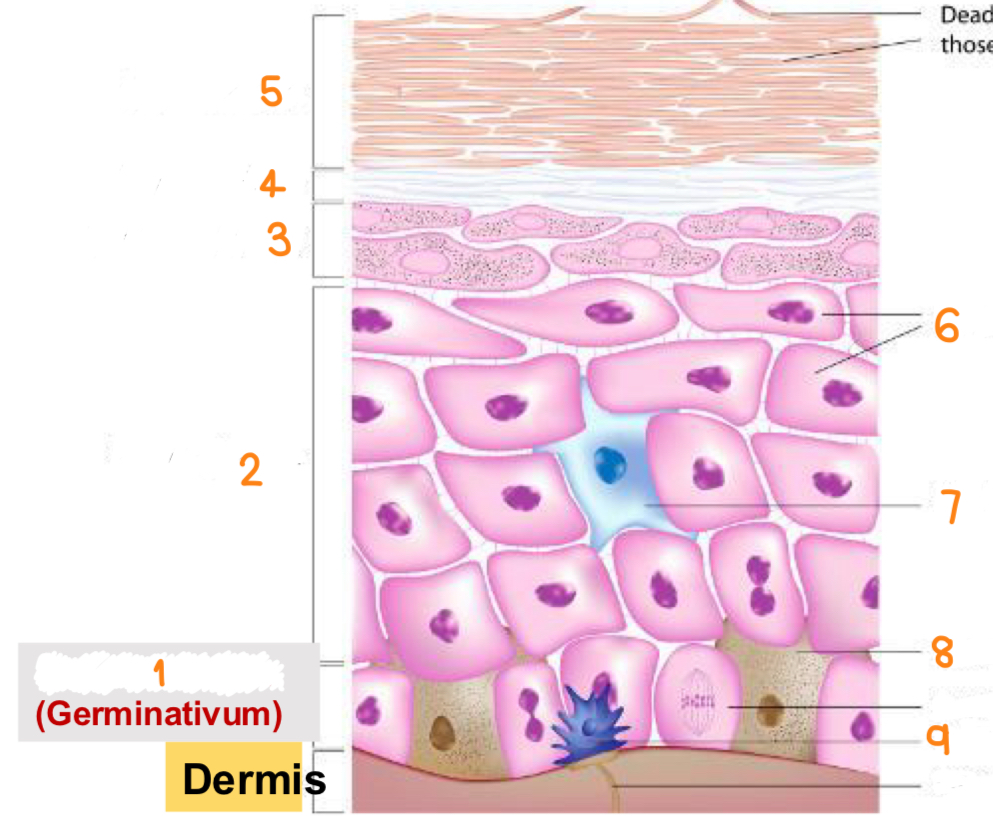
what is 7
dendritic cell
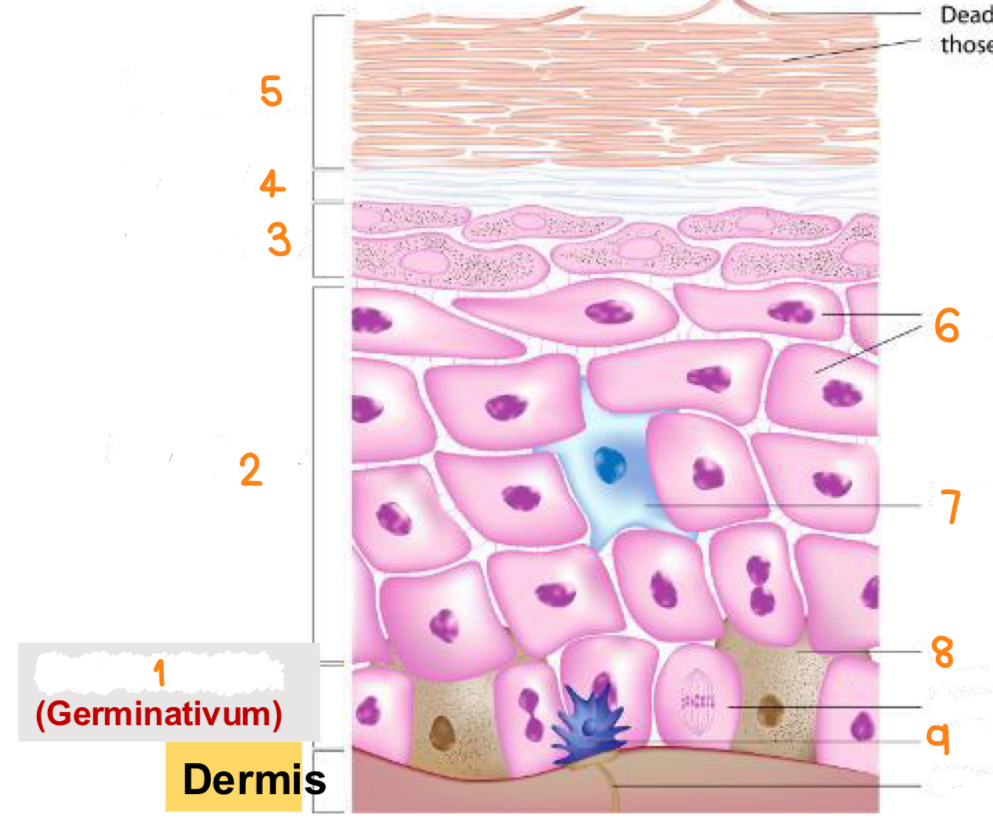
what is 8
melanocyte
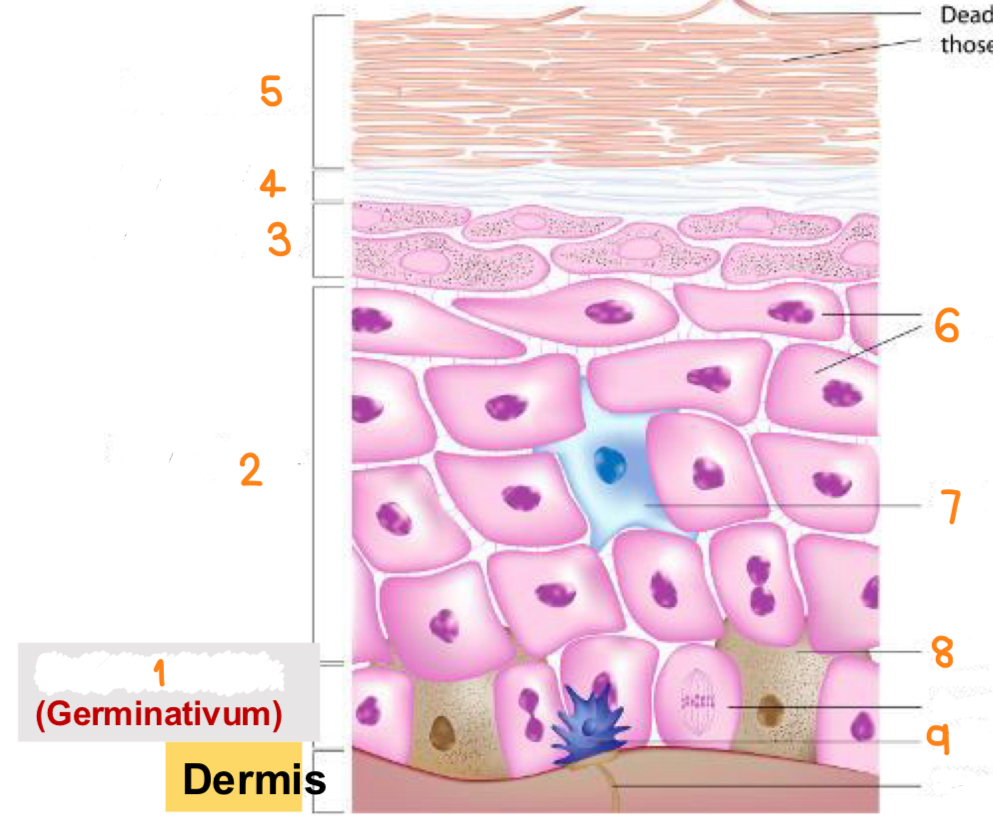
what is 9
tactile cell
stratum basale function
actively divide to produce keratinocytes and repair damage, produce intermediate keratin filaments
stratum spinosum functions
synthesize intermediate filaments called cytokeratins and tonofibrils
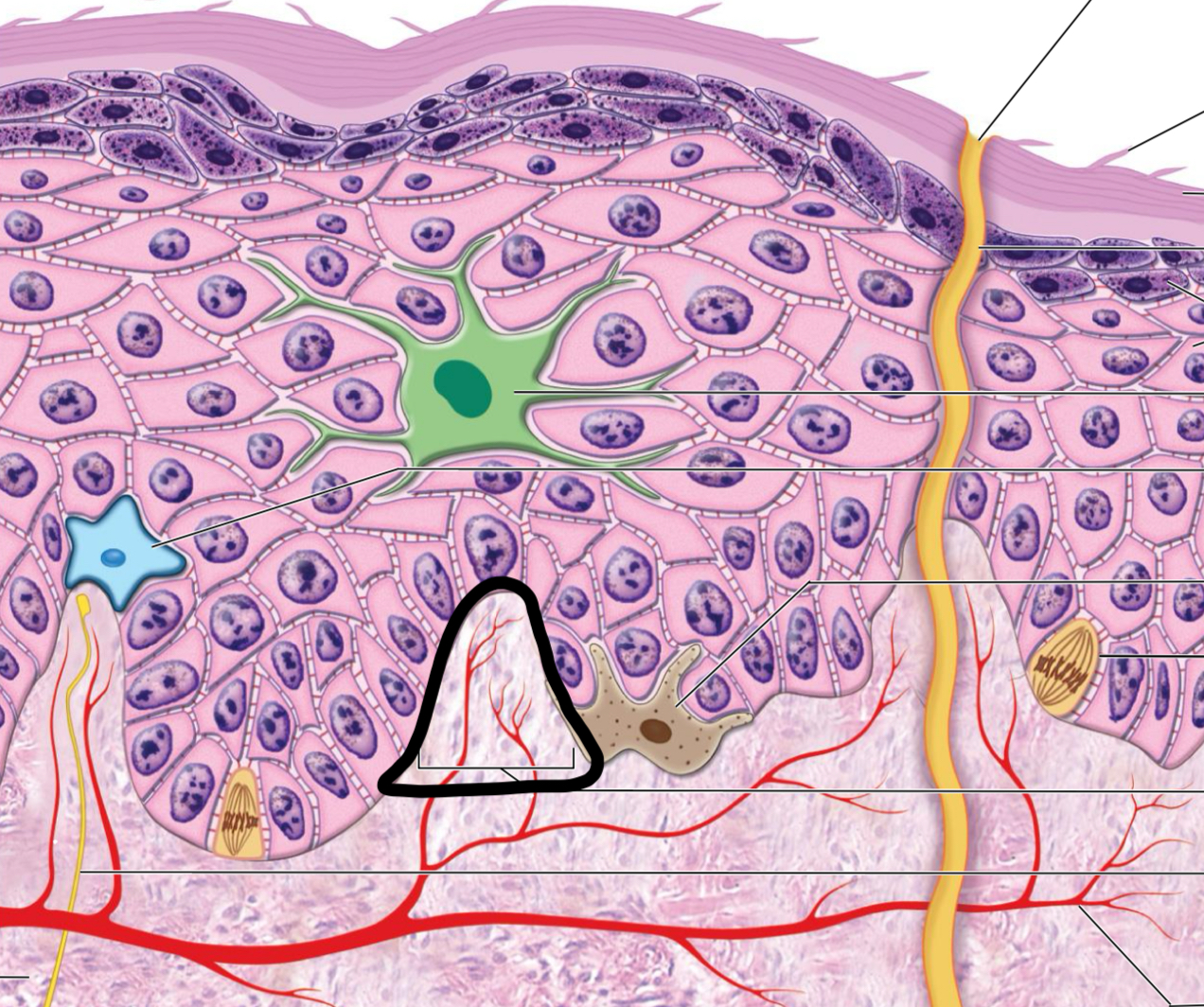
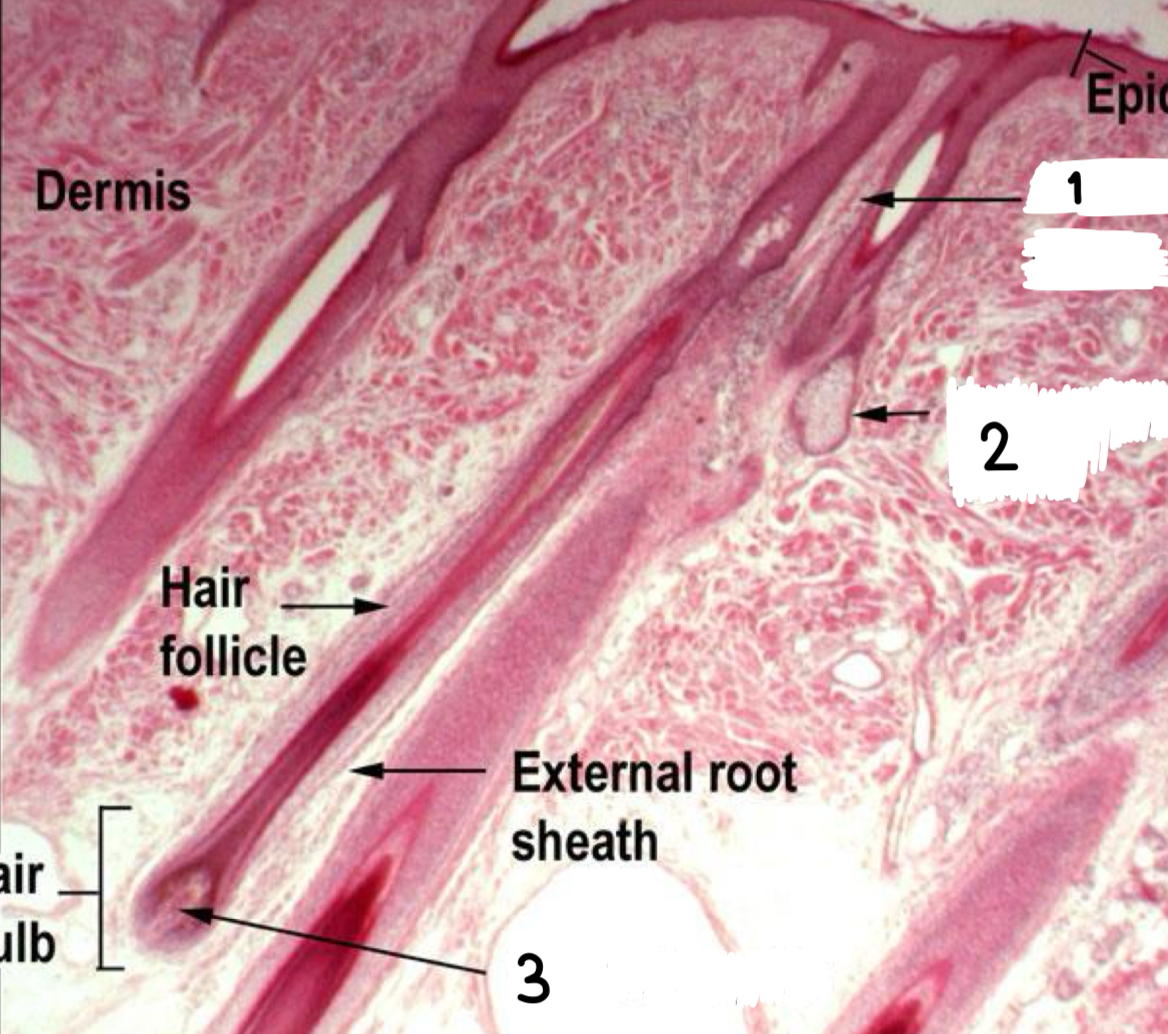
what is circled
dermal papilla
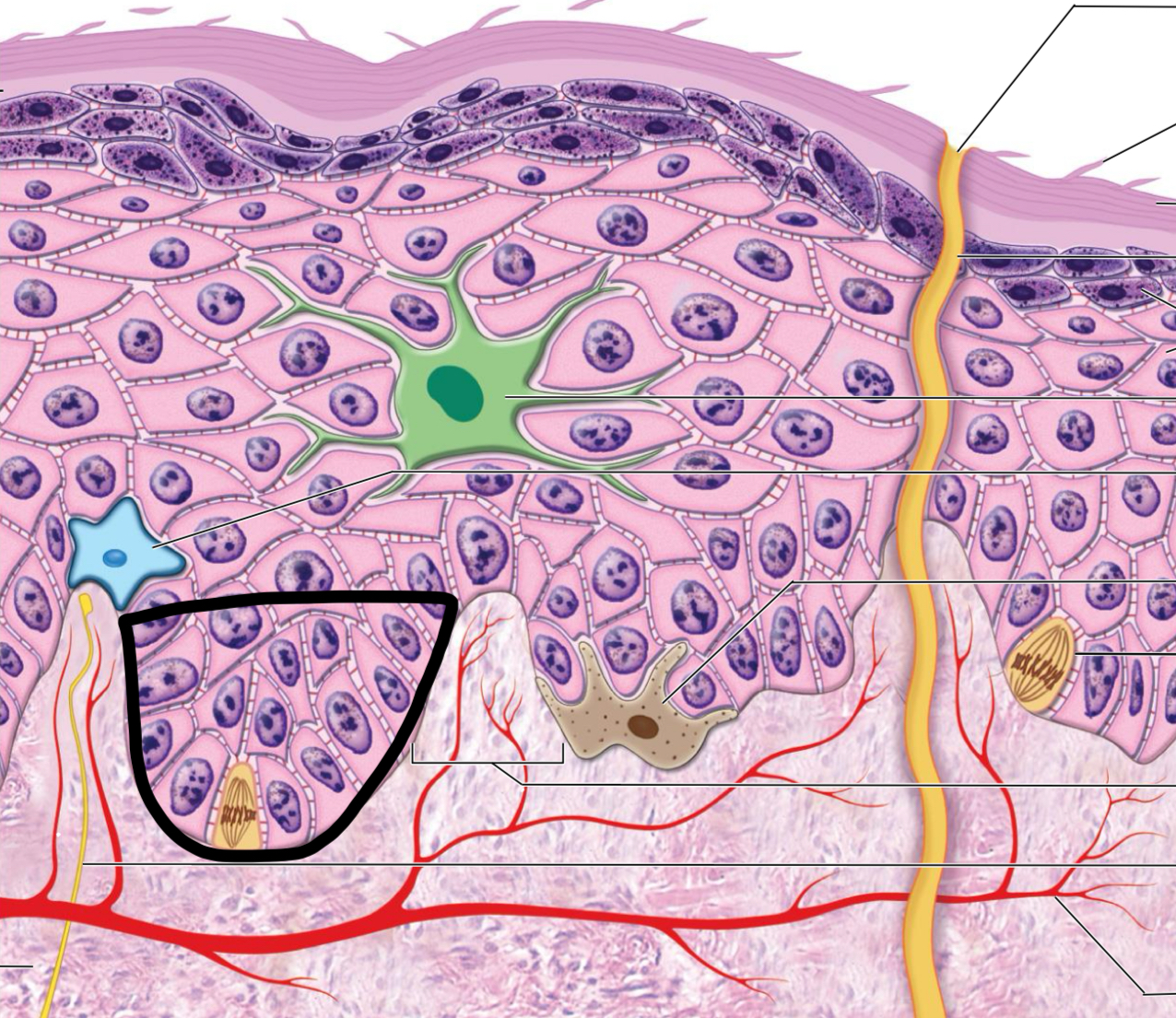
what is circled
epidermal ridge
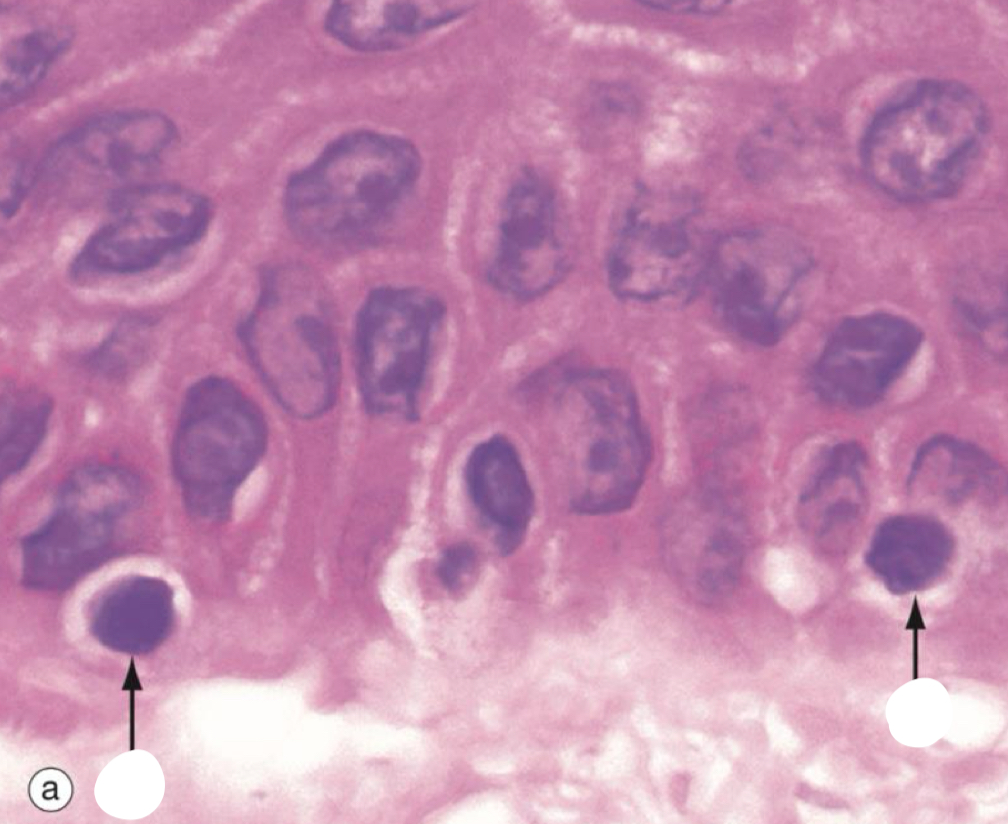
what is pointed to
melanocyte
langerhans cell function
APC, contact hypersensitivity
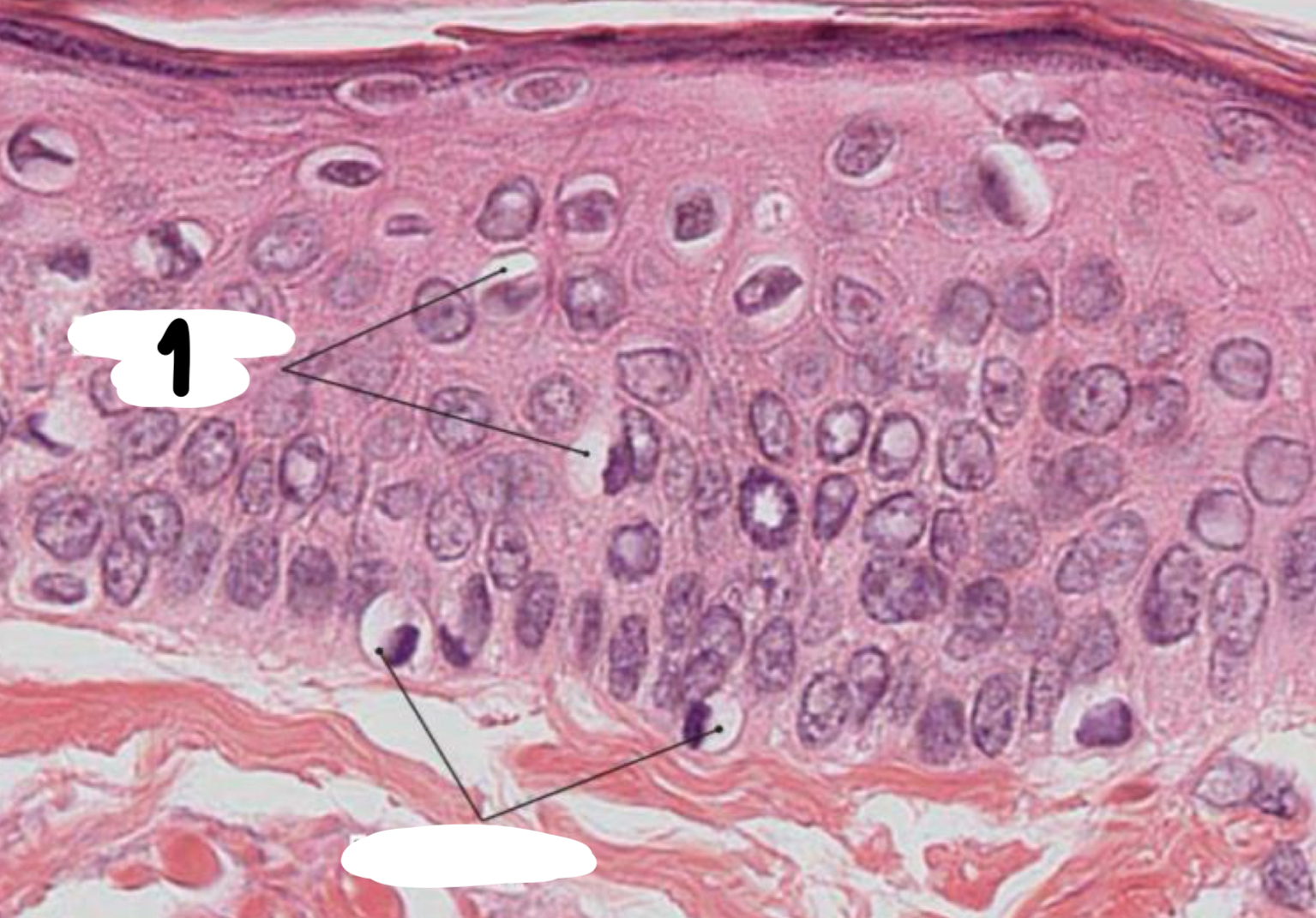
what is labeled as 1
langerhans cells
function of merkel (tactile) cells
mechanoreceptor
psoriasis
chronic inflammatory skin disorder with demarcated plaques and white scales
cause of psoriasis
excess proliferation of keratinocytes
pemphigus
autoimmune blistering due to disrupted desmosomes
carotene accumulate where
S. corneum and subcutaneous
dermis functions
maintain body temperature, strength and flexibility
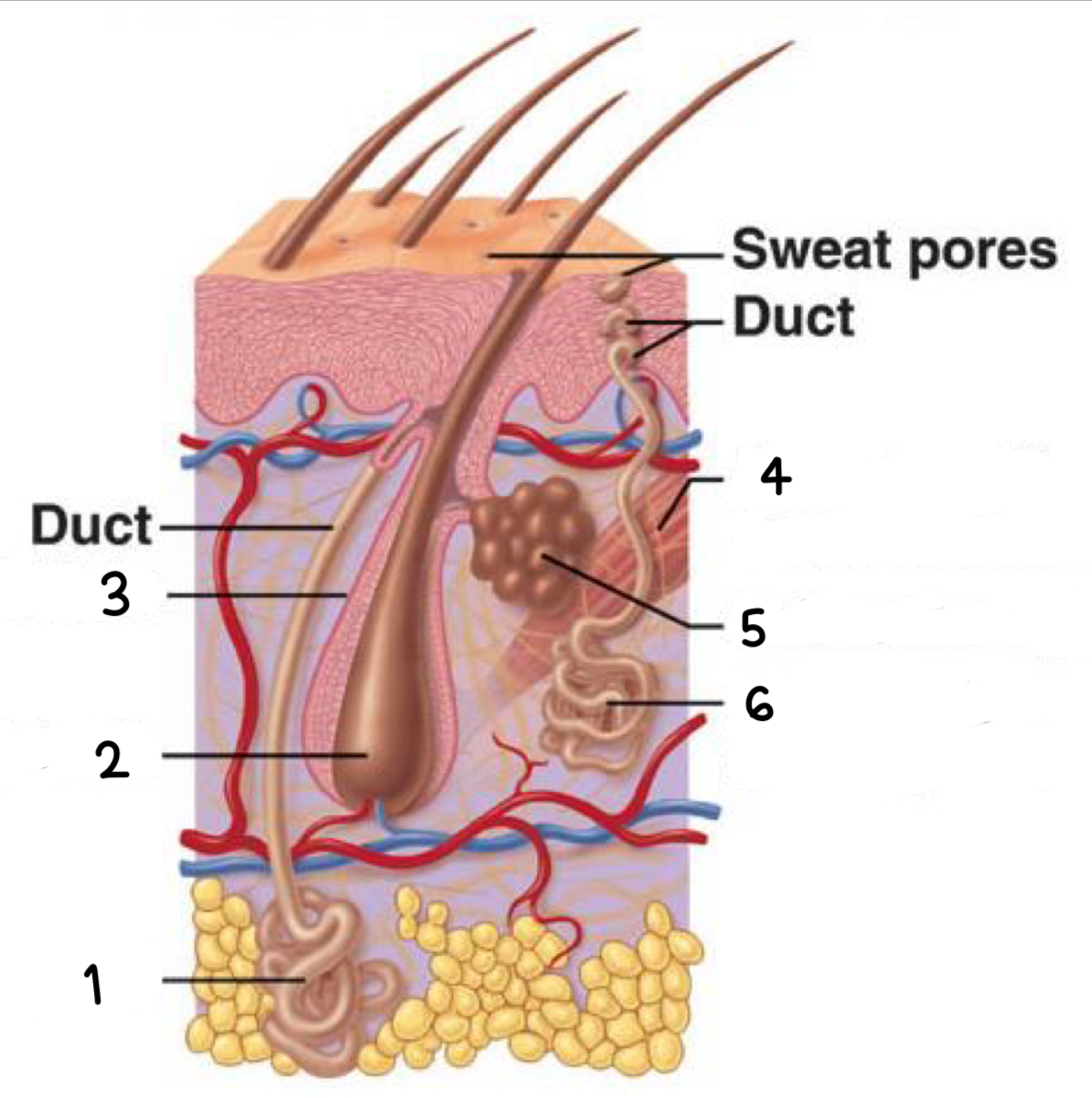
what is 1
apocrine sweat gland
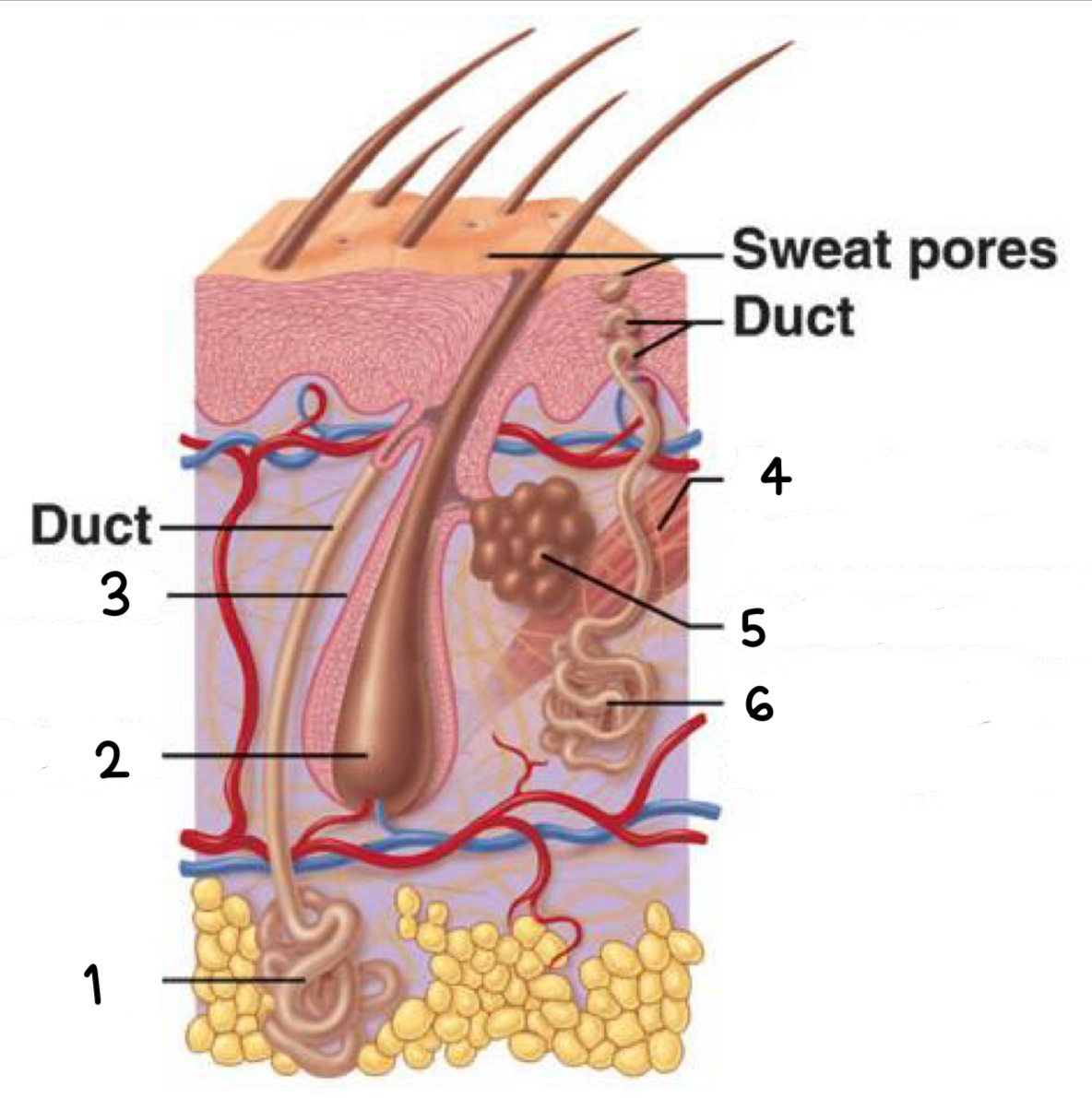
what is 2
hair bulb
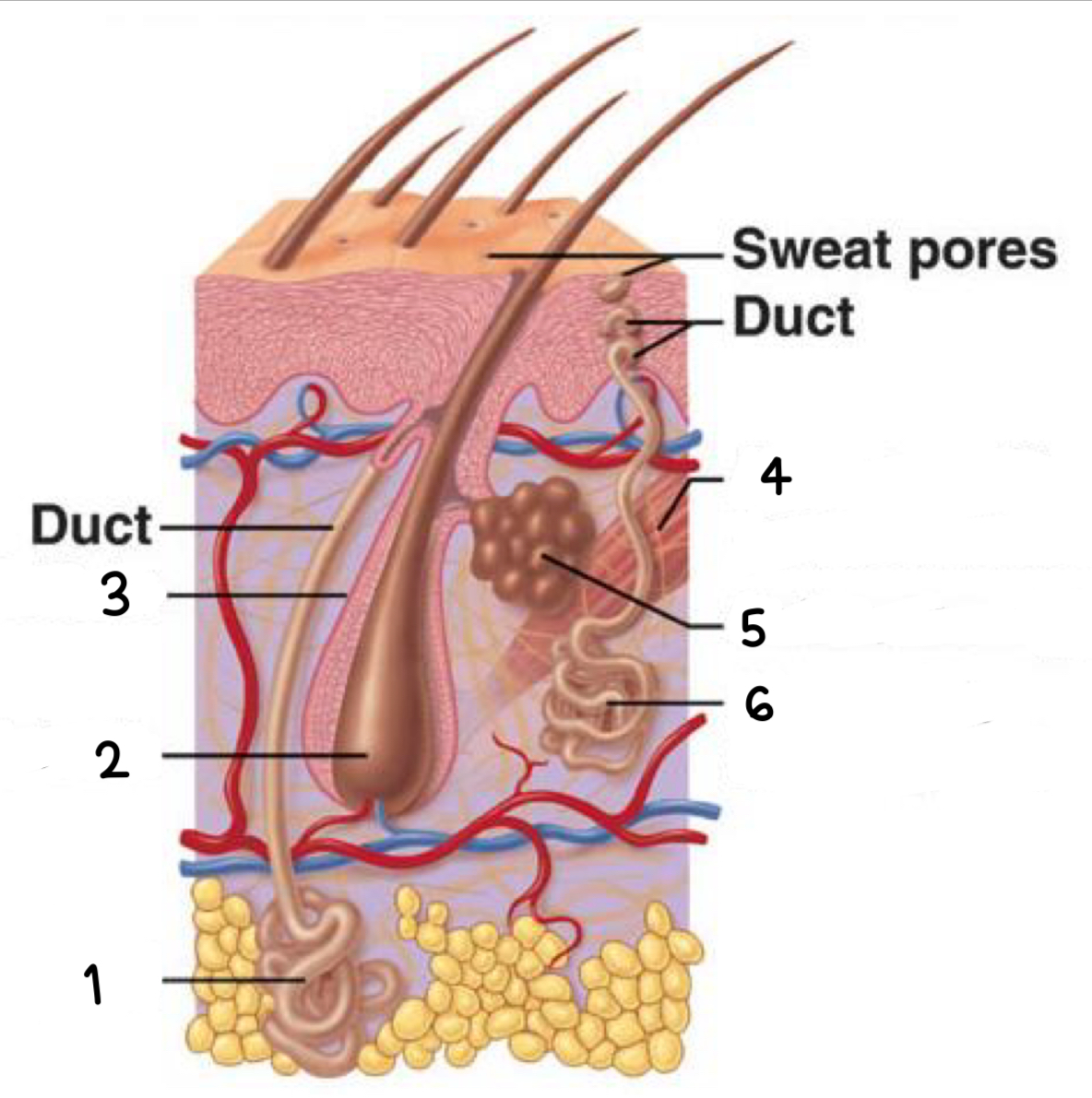
what is 3
hair follicle
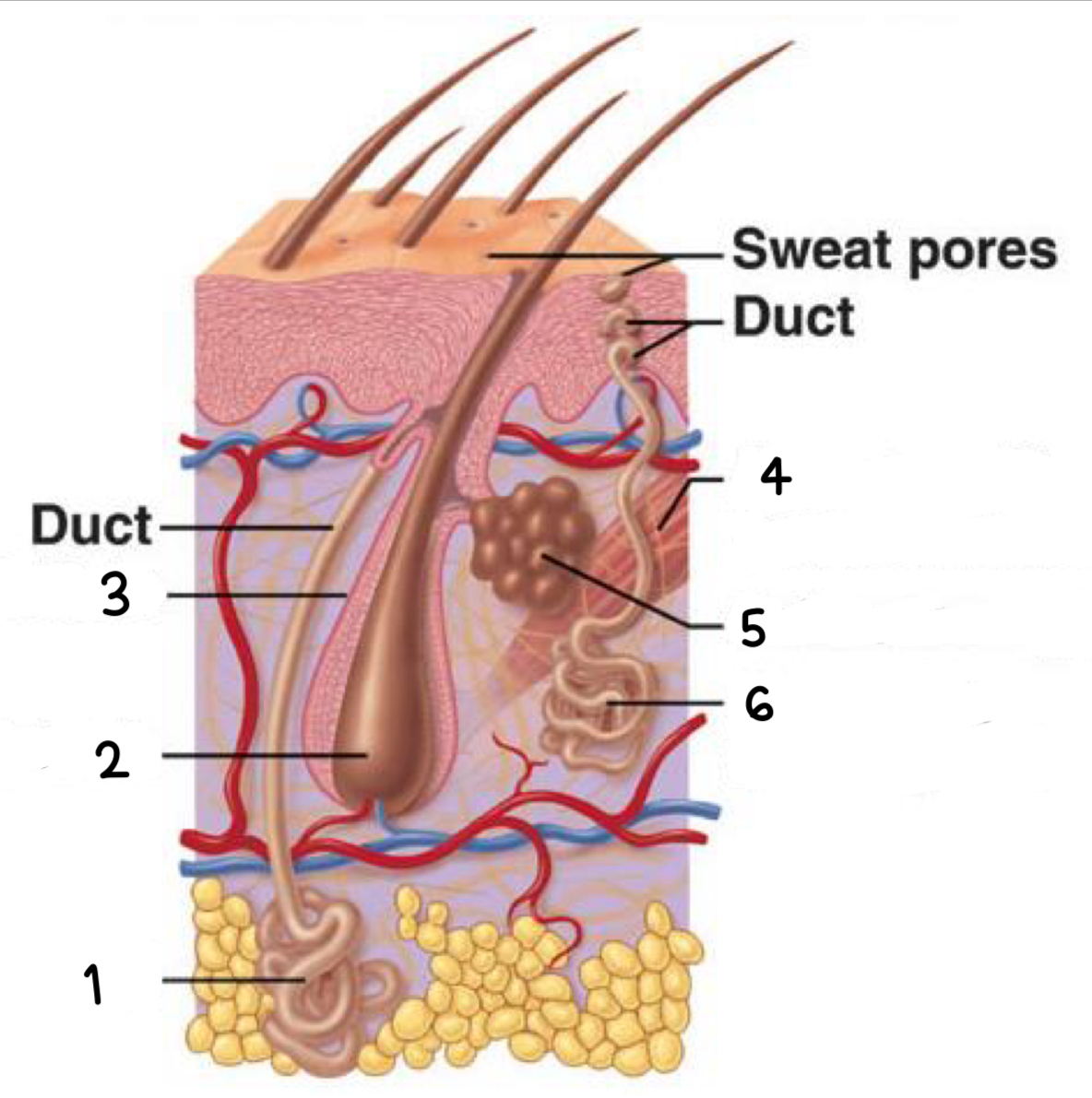
what is 4
arrector pili (smooth muscle)
what is 5
sebaceous gland
what is 6
merocrine sweat gland
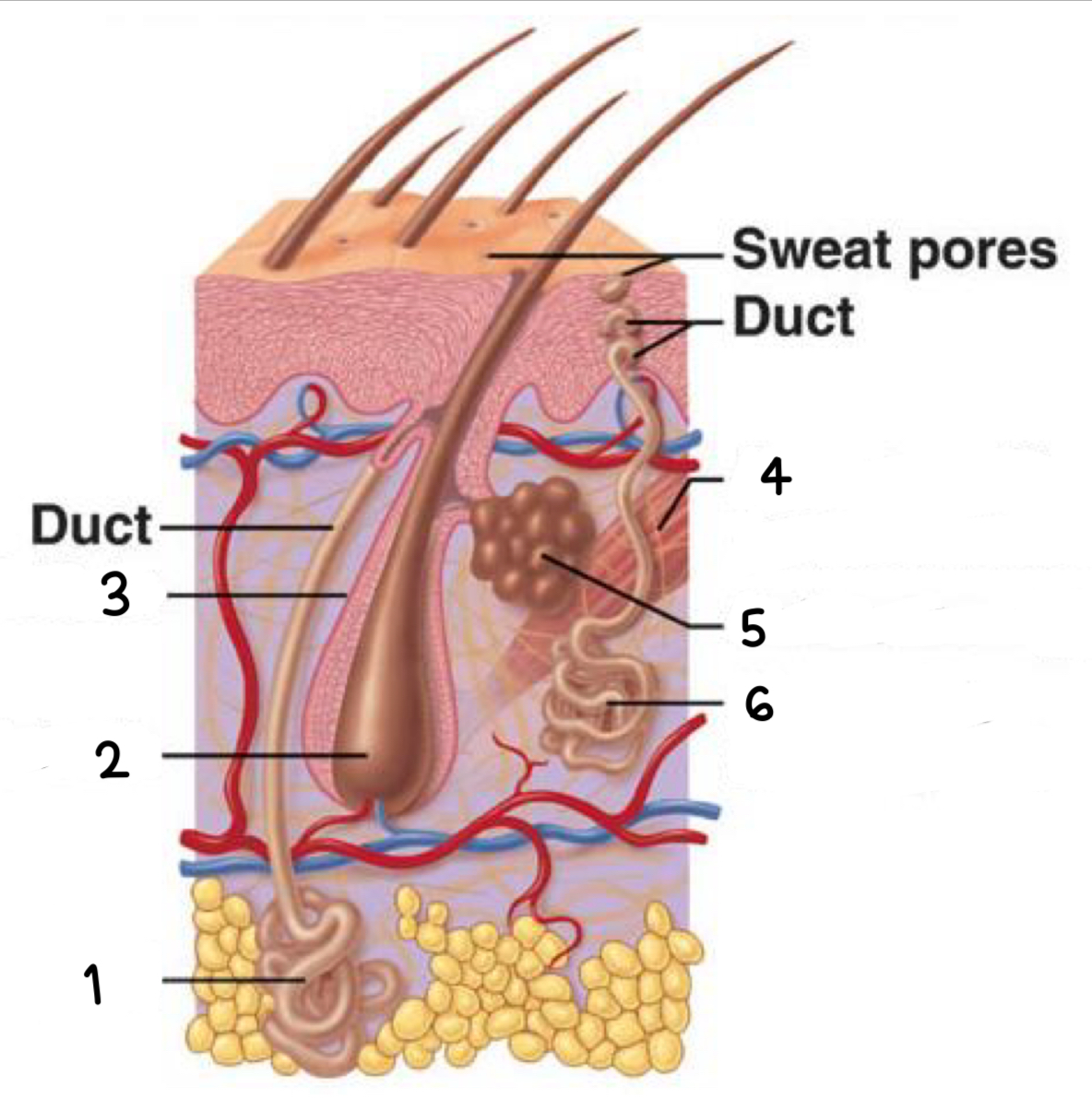
what is 1
arrector pili (smooth muscle)
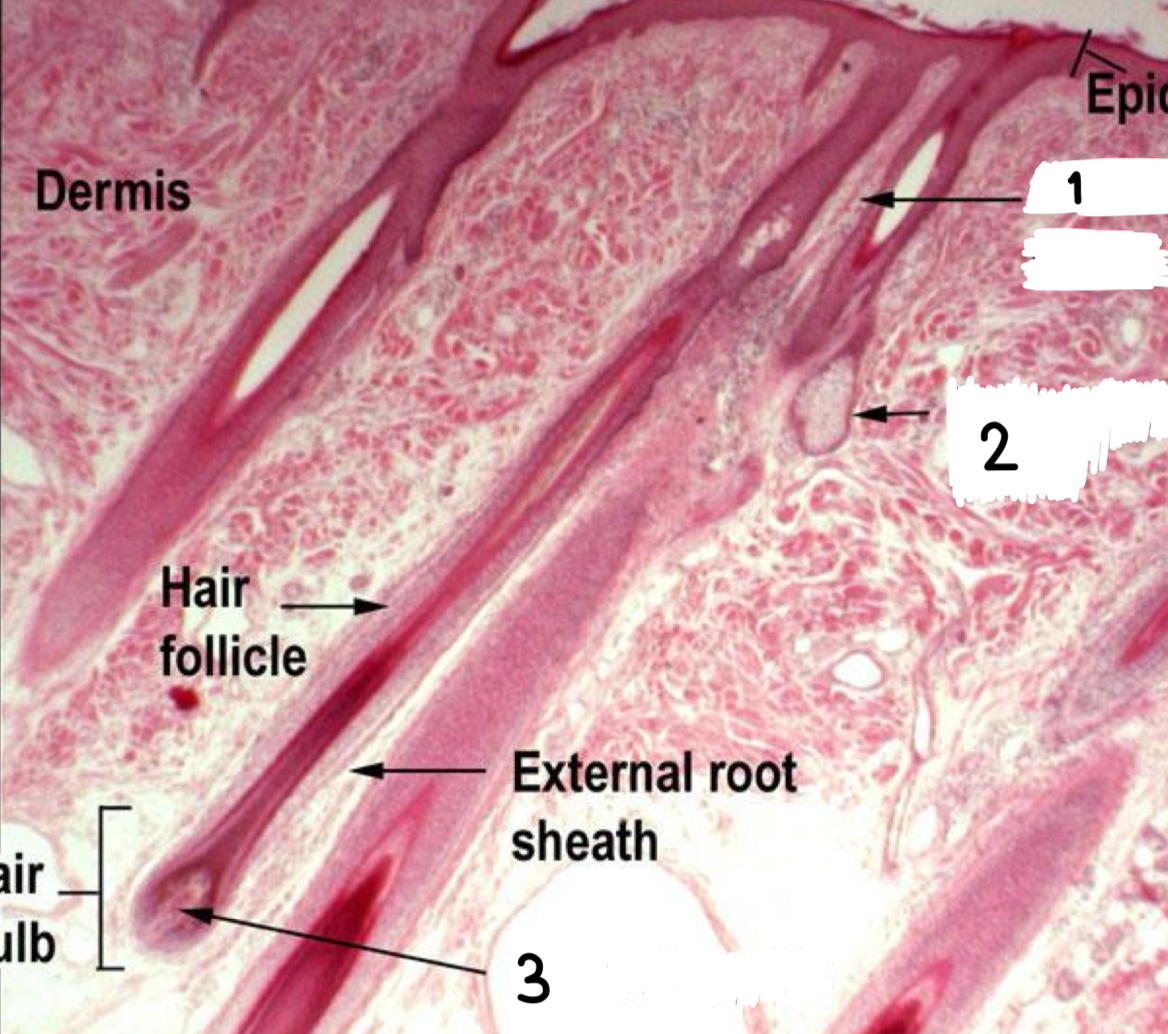
what is 2
sebaceous gland
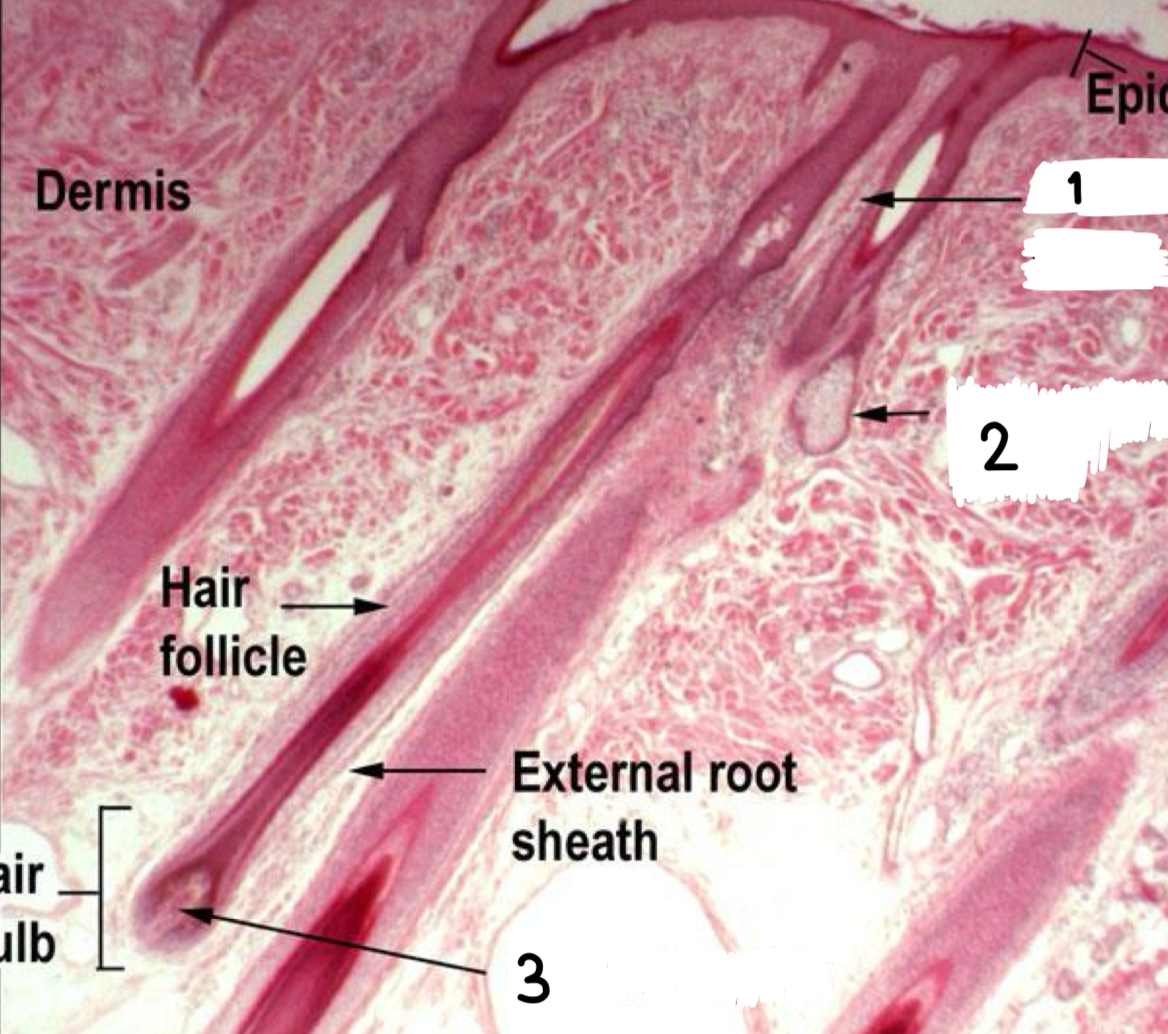
what is 3
dermal papilla