My BIO230 Section1
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
177 Terms
Prokaryotic Organisms
它是Single-celled的,没有核和细胞器(nucleus and organelles),多为Eubacteria, and archaea
Eukaryotic Organisms
它是Single-celled or multicellular,有核和细胞器(nuclei and organelles),多为Plants, fungi, animals, humans
Plasma membrane
Semi permeable membrane surround all cells.
Cell wall
它是一个Tough and protective的外膜,不是所有的Prokaryotic都有!
flagellum鞭毛
它是prokrayotic的,用来移动,不是所有都有
Eukaryotic Cell
它拥有membrane bond organelles
microbiome
它是combined genomes of a microbiota
microbiota
这是一种特殊的Biota,包括bacteria, archaea, fungi, protists, and viruses.
驻留(reside)在 skin, lungs, mouth, gastrointestinal tract, etc
The Microbial Cell : Human Cell 比率最低为1 :1
人体内微生物基因的数量比人类基因多达200倍。
Operon
它是原核生物内的一段DNA region, 在单个启动子(single promoter)的控制下,1个以上的基因被转录为单个RNA
Genome
大多数 genomes由DNA组成
except some viruses have RNA genomes(virus are not living things)
释放 biological information stored in the genome requires genome expression
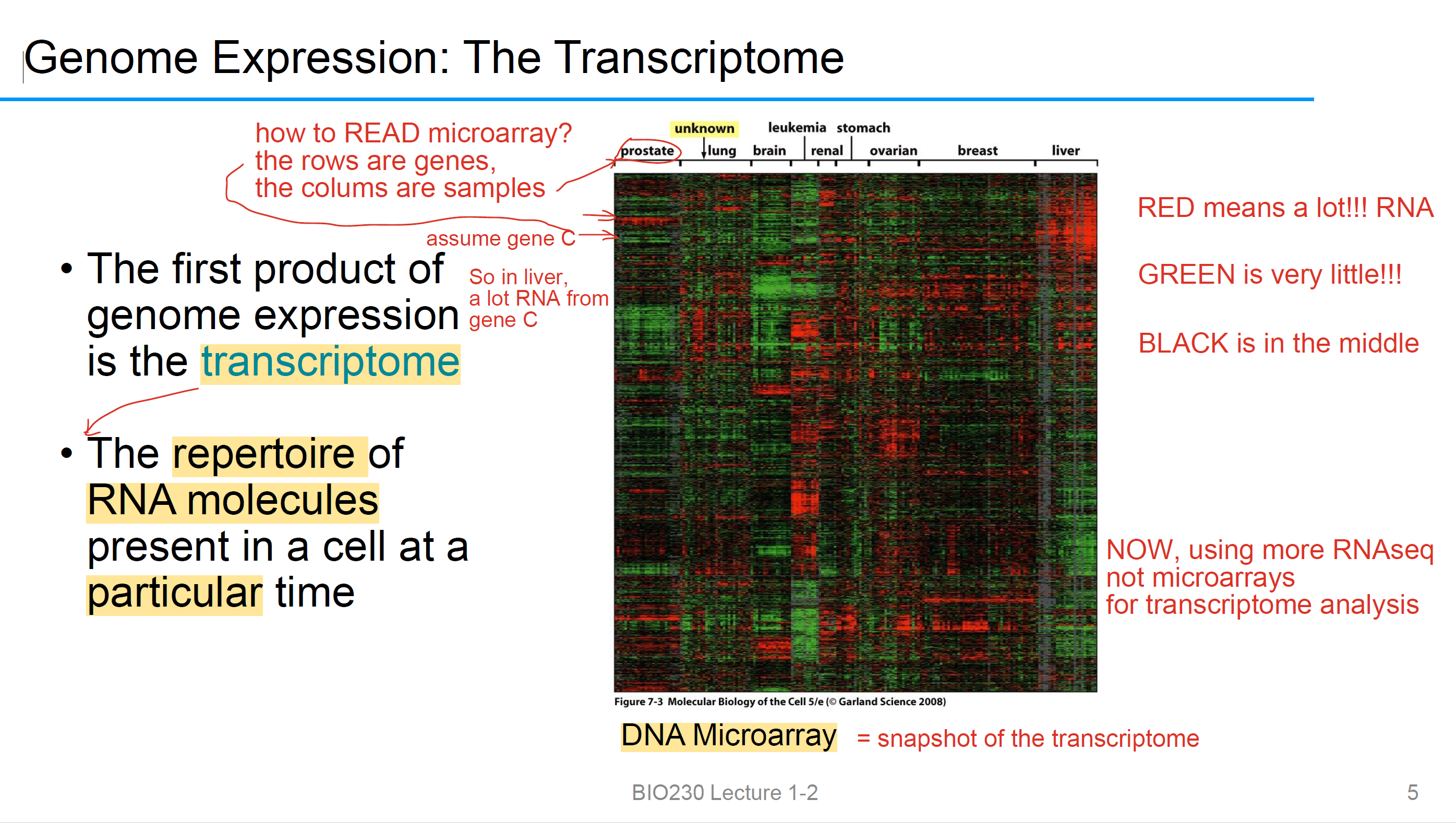
Transcriptome
基因表达的第一个产物
The repertoire of RNA molecules 在特定时间存在于细胞中
DNA Microarray
它是snapshot of the transcriptome, NOT DNA
RED = a lot, Green= little
竖轴gene,横行sample
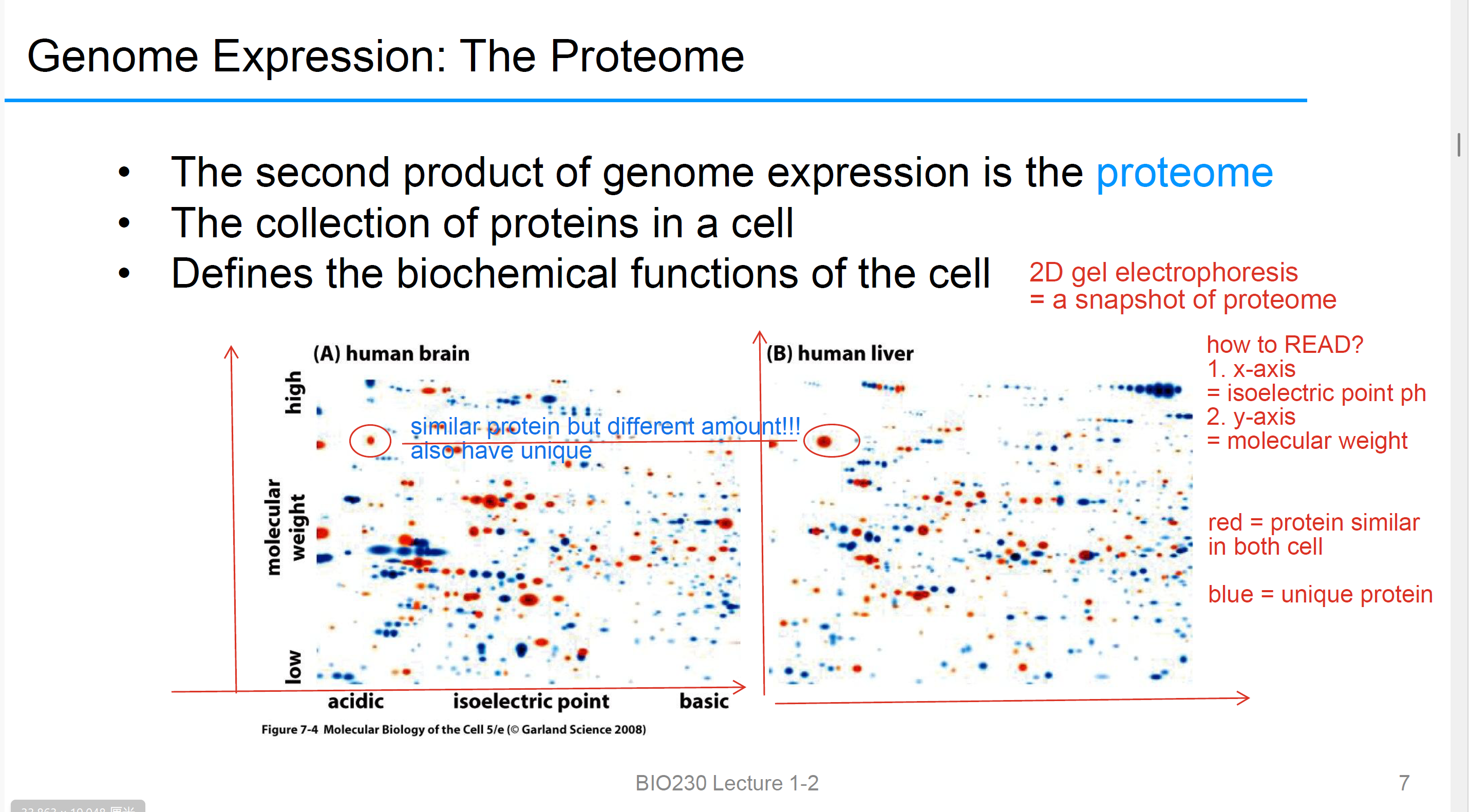
proteome
基因表达的第二个产物
是所有Protein in the cell
2D gel electrophoresis
1. x-axis= isoelectric point ph
2. y-axis= molecular weight
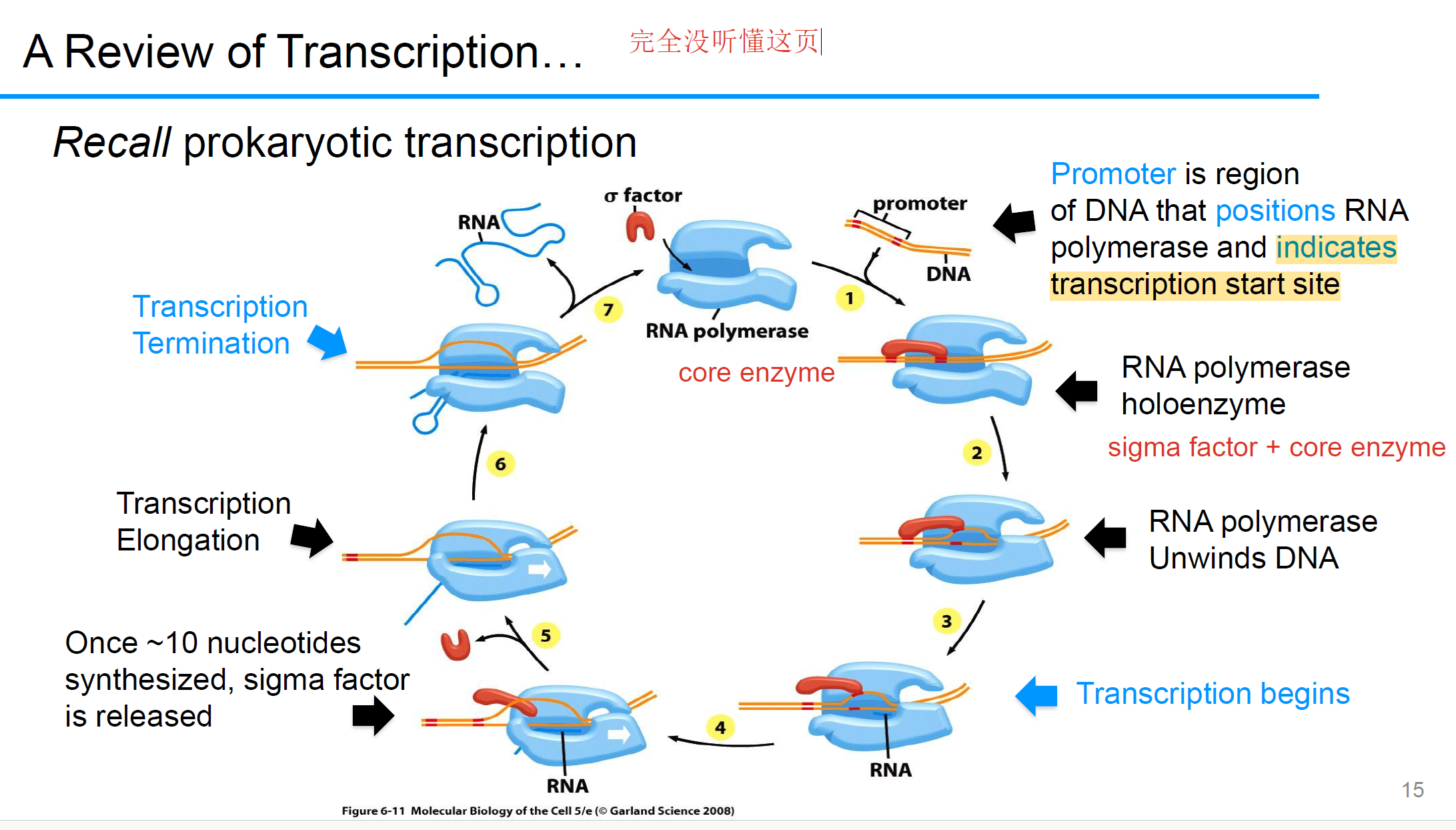
Recall of prokaryotic transcription
σ factor bind 启动子promoter; RNA Polymerase holoenzyme(polymerase core enzyme 加上σ factor)开始组装; 然后RNA Polymerase 打开(unwind) the DNA, 转录开始; 一旦 RNA polymerase 生成大概 10 个核苷酸 of RNA, 释放 σ factor; 然后RNAP and DNA goes to Elongation; 当遇到Termination signal,释放新转录的RNA; 这些信号通过形成 RNA hairpin来导致RNA polymerase不稳定(destabilizes)
cis element
DNA sequences on the same double helix
gene regulatory proteins (transcription factors)
Regulate Gene expression in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes
分为activator(turn on)和represso(off)两种
E.coli
unicellular prokaryote 单细胞原核生物
环状DNA 染色体 chromosome一条
编码约4300 proteins
transcriptionally regulated by food availability食物供应情况
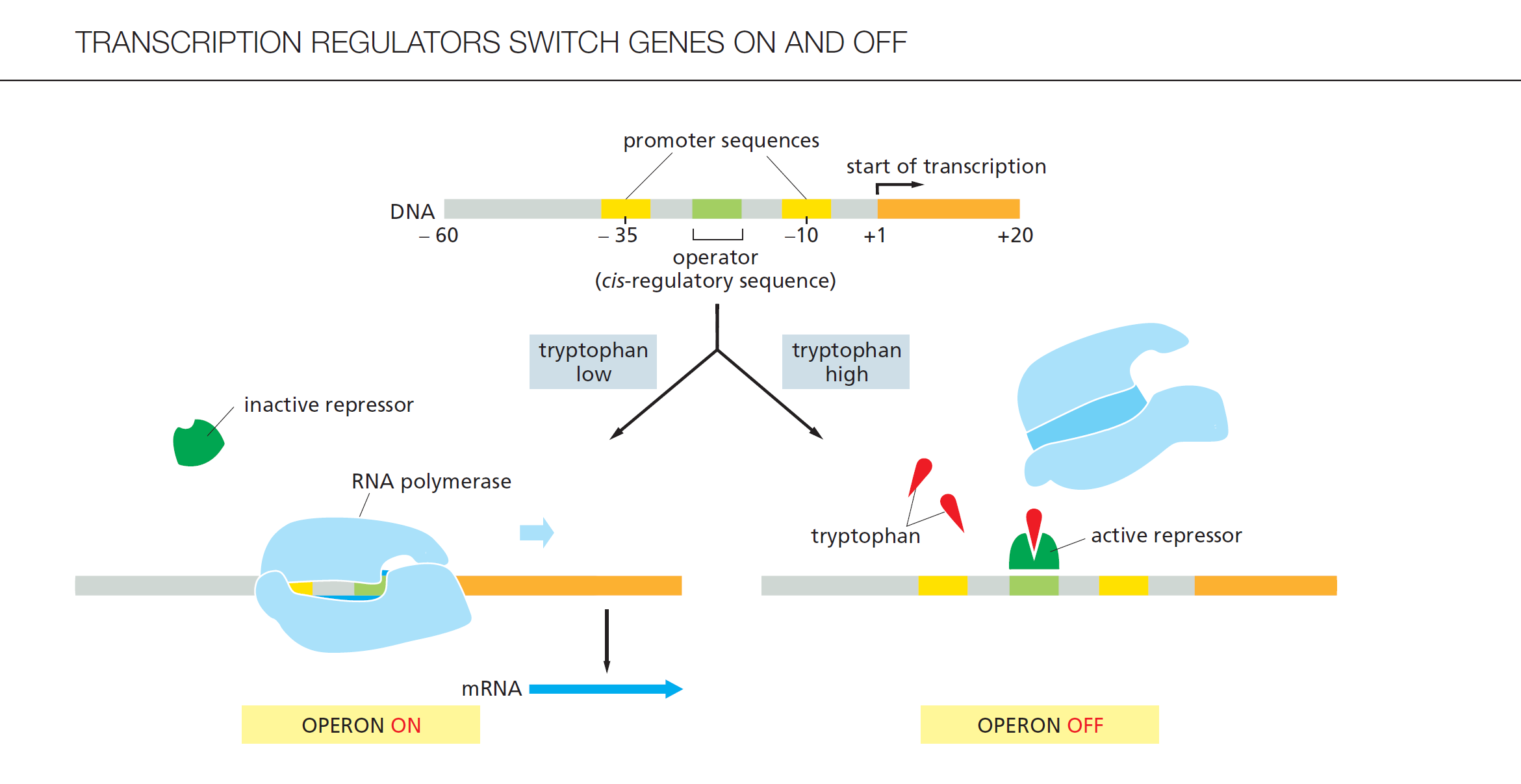
Trp Operon
能 codes 5 genes
每一个基因都编码一个不同的酶for 色氨酸tryptophan biosynthesis (5 enzymes)
转录被一个单启动子调控(single promoter)
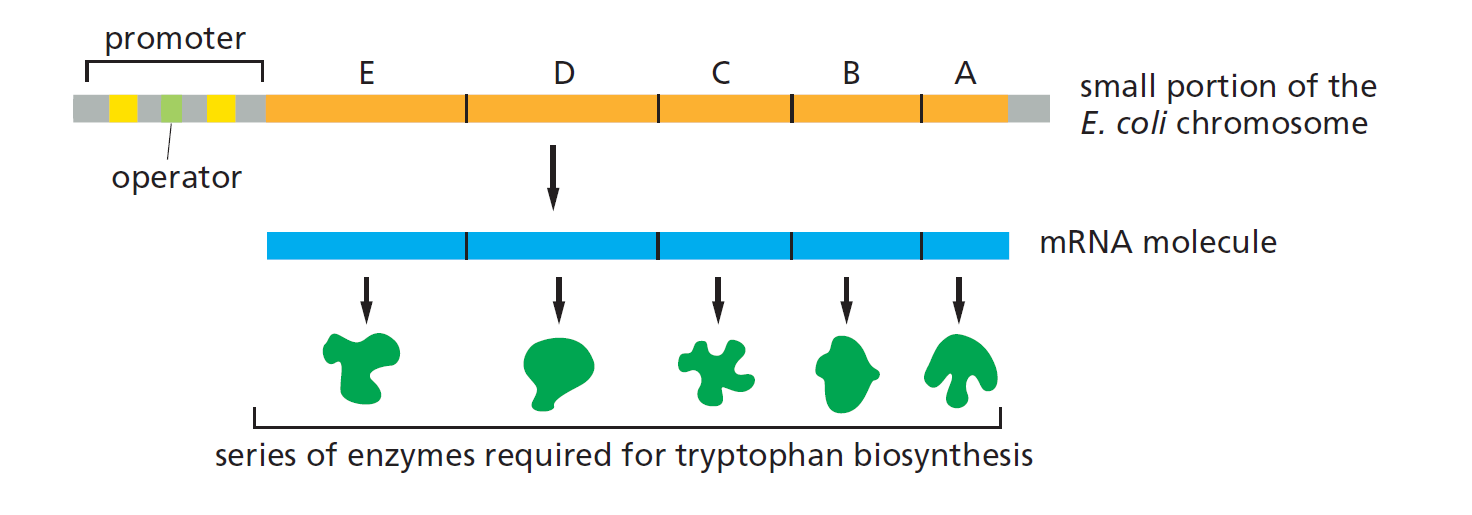
protein-bound states of Trp Operon
1) Trp 低,结合RNA polymerase
➢ Trp 基因表达开启
2) Trp 高,结合tryptophan repressor protein
(must bound to 2 trp)
➢ Trp 基因表达关闭
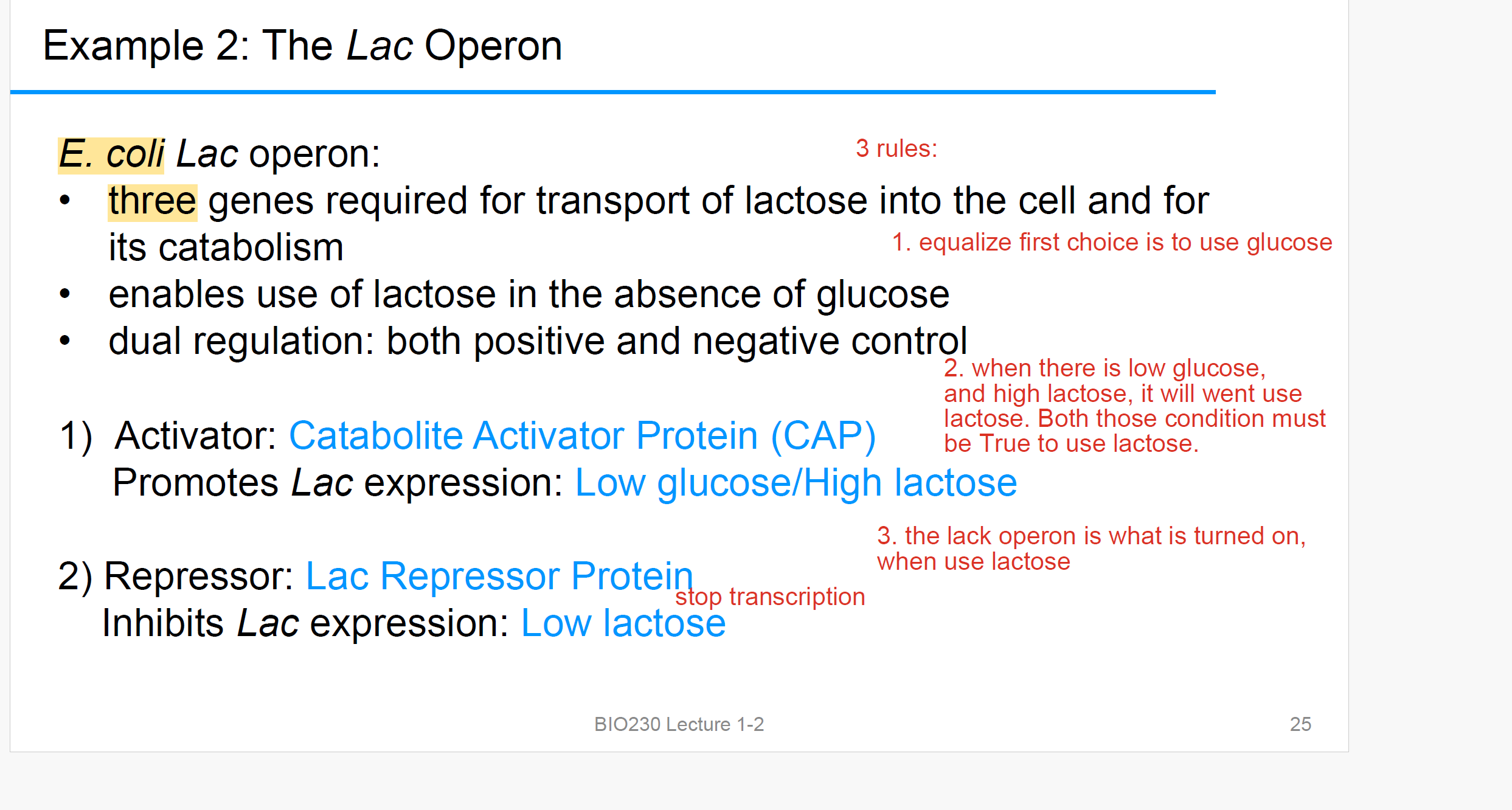
Lac Operon
3个基因负责运输乳糖L进入细胞并分解代谢
在没有葡萄糖g的情况下利用乳糖L
双重dual regulation: 正向和负向调控
Lac operon as an activator
Glucose 低, cAMP 高, cAMP binds CAP protein:
➢构象改变
➢CAP bind DNA
Then, CAP 招募 RNA polymerase to the Lac promoter.
Lactose 高, 转为使用 lactose, lac operon turn on.
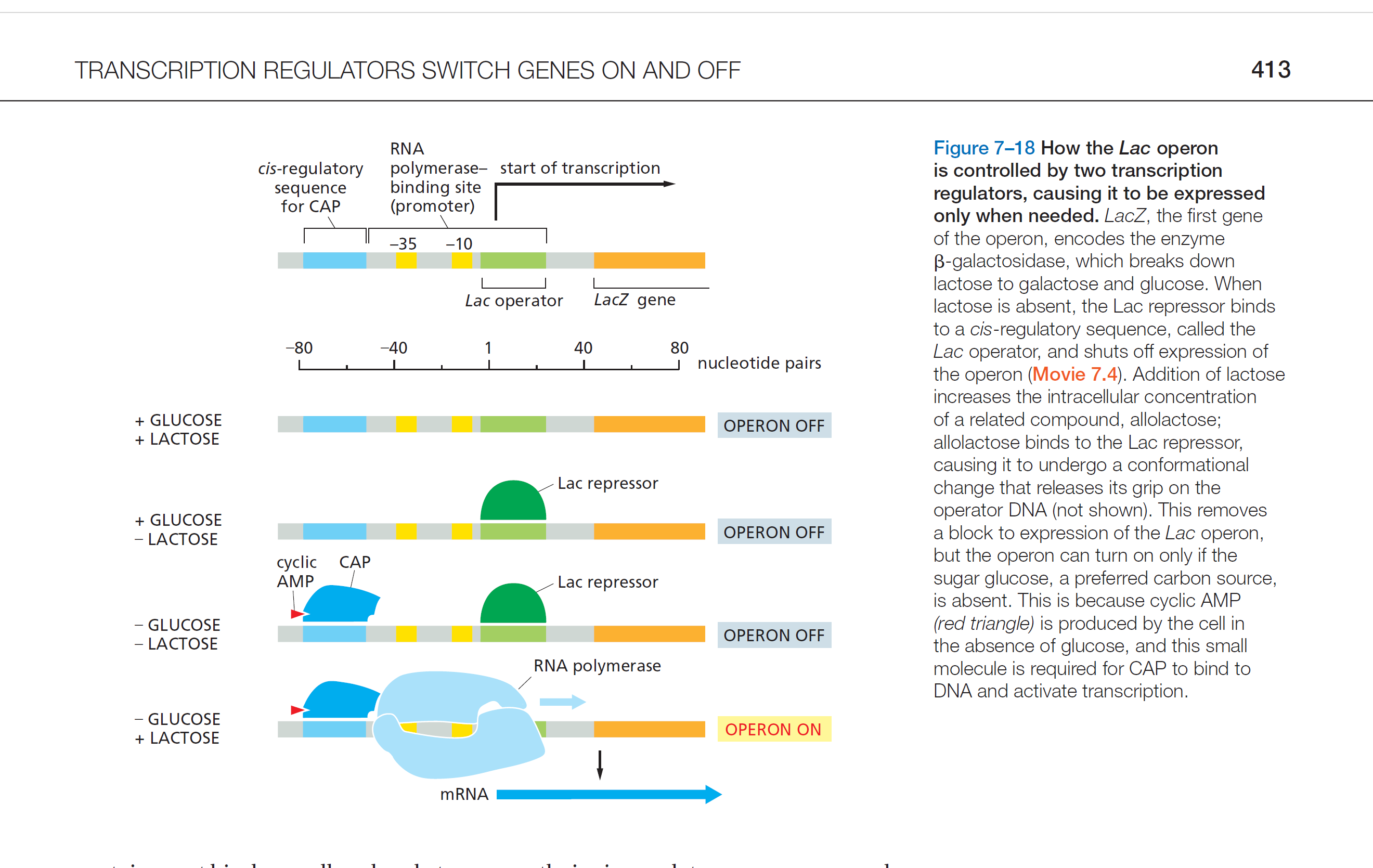
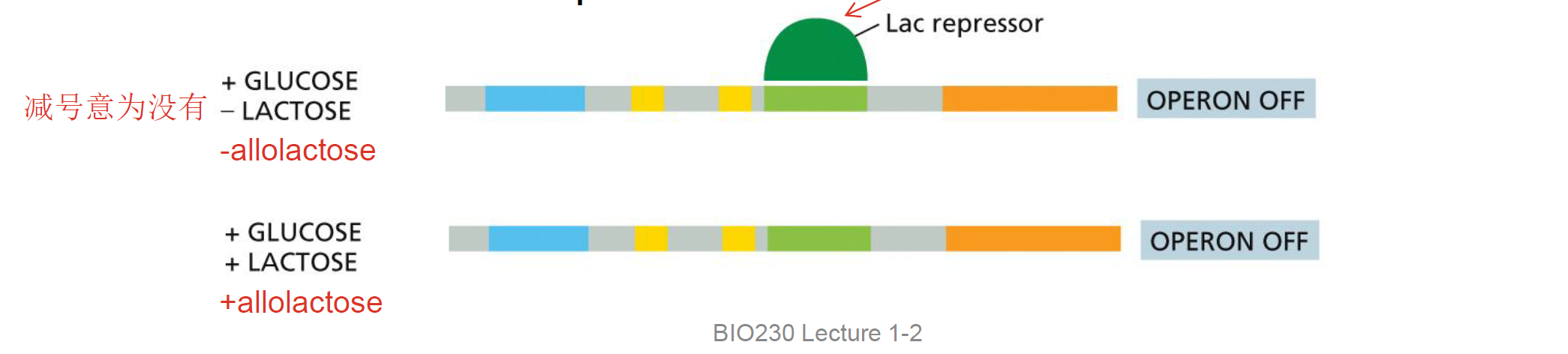
Lac operon as a repressor
lactose⬇, lac repressor结合operator, 转录关闭
Increases⬆ lactose, 导致 allolactose⬆(β-galactosidase 将lactose转换成allolactose), Allolactose 结合Lac repressor; repressor构象改变,DNA-binding activity(affinity)⬇; repressor Release from the operator; operon 开启
一句话就是lactose高⬆将repressor释放。
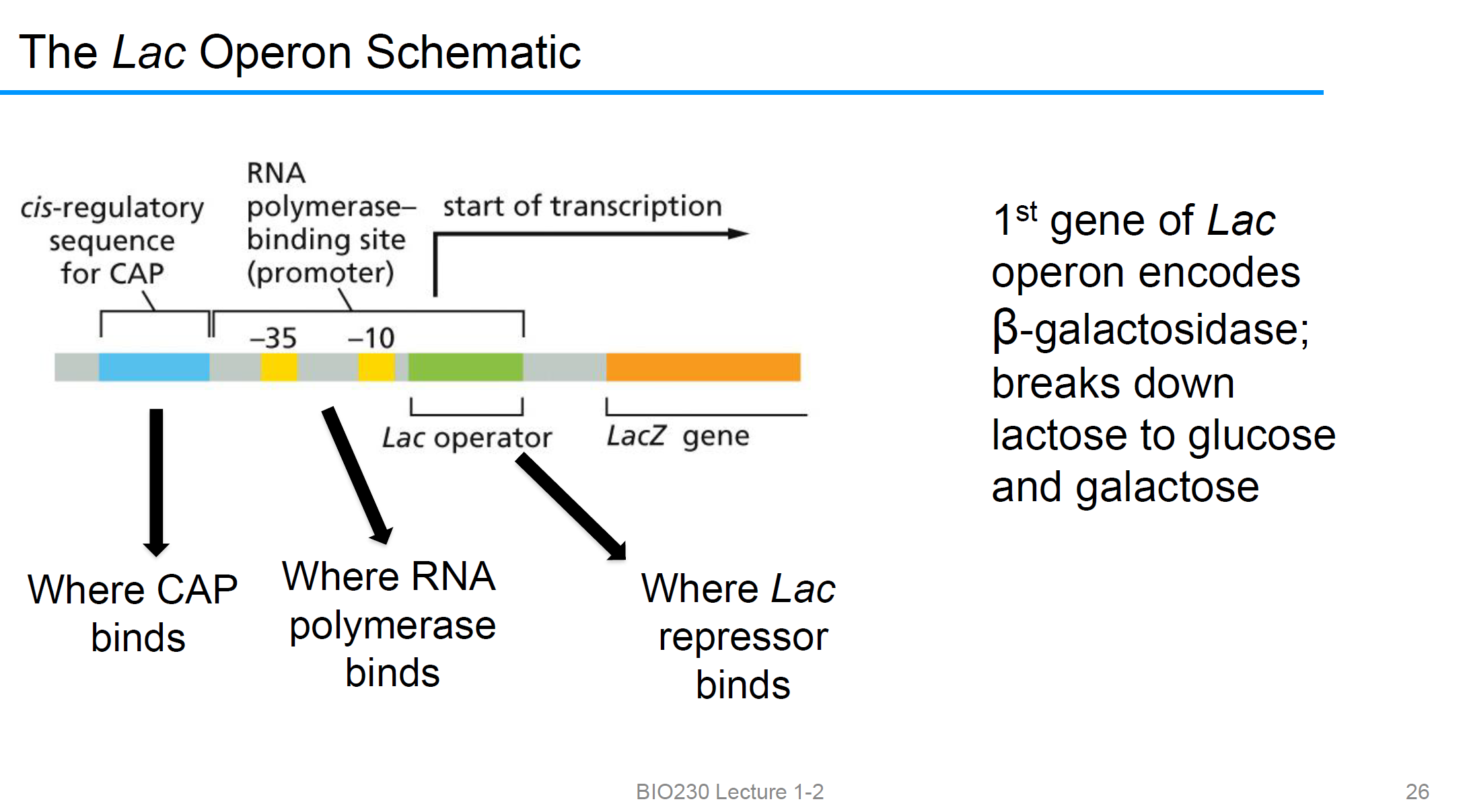
The Lac Operon Schematic
CAP结合cis regulatory sequence
promoter结合 RNAP
LAC operator 结合lac repressor
regulatory elements can be found in
transcriptional start site of prokaryotic genes;
Far upstream of gene(超级negative的那方向)
Downstream of gene (eukaryotes)
Within gene (introns; eukaryotes) 原核细胞没有introns
How Ntrc protein works as transcriptional protein?
By DNA looping, Ntrc will directly interact with RNA polymerase to activate transcription.(like a short kiss)
Bacteriophage Lambda 噬菌体λ
it is a virus infect bacterial cells,
Prophage pathway
Virus grows when bacterial grows well(DNA Polymerase replicated both them)
Lytic pathway
it will happens when host cell damaged because of virus rapidly replication and synthesis RNA, protein. finally virus released from the cell
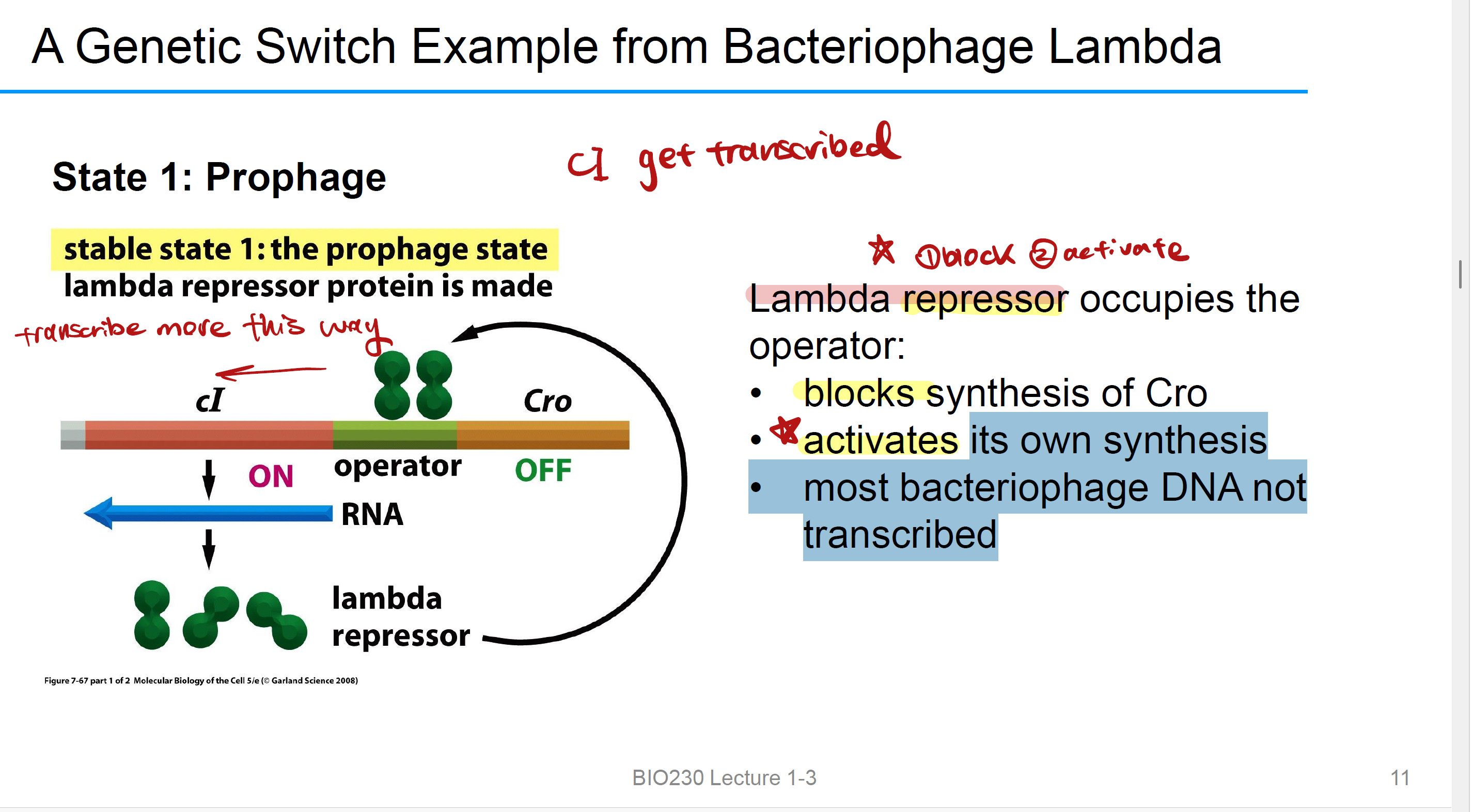
Lambda repressor protein cl (at prophage pathway)
it will bind to the operator and then 2 things happens:
阻止Cro
促进its own synthesis
note: most bacteriophage DNA not transcribed
Cro protein (at lytic pathway)
it gets transcribed and then gets translated, then come back to BLCOK cI. Most bacteriophage DNA is extensively transcribed to 制造大量新病毒并最终导致宿主裂解。
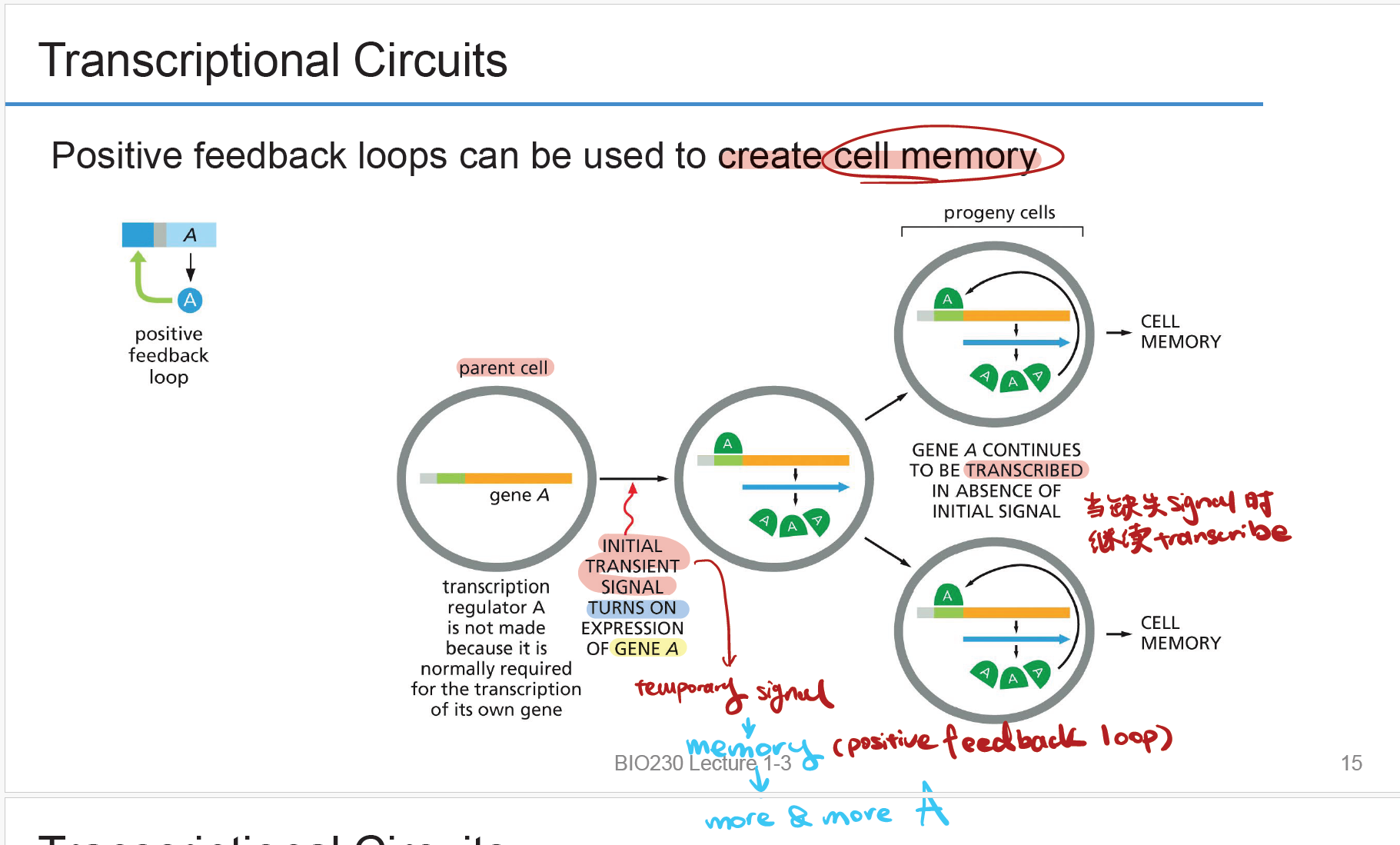
Positive feedback loop
细胞产生 cell memory的方式. The initial 临时信号开启gene expression of A, gene A will continue be transcribed in progeny cells.子代细胞
flip-flop device
A与B互相抑制,不能同时产生。
feed-forward loop
feed forward 是一种积累,需要 both A and B to get Z, 它可以降低 sensitivity (which means need enough input A to get output Z)
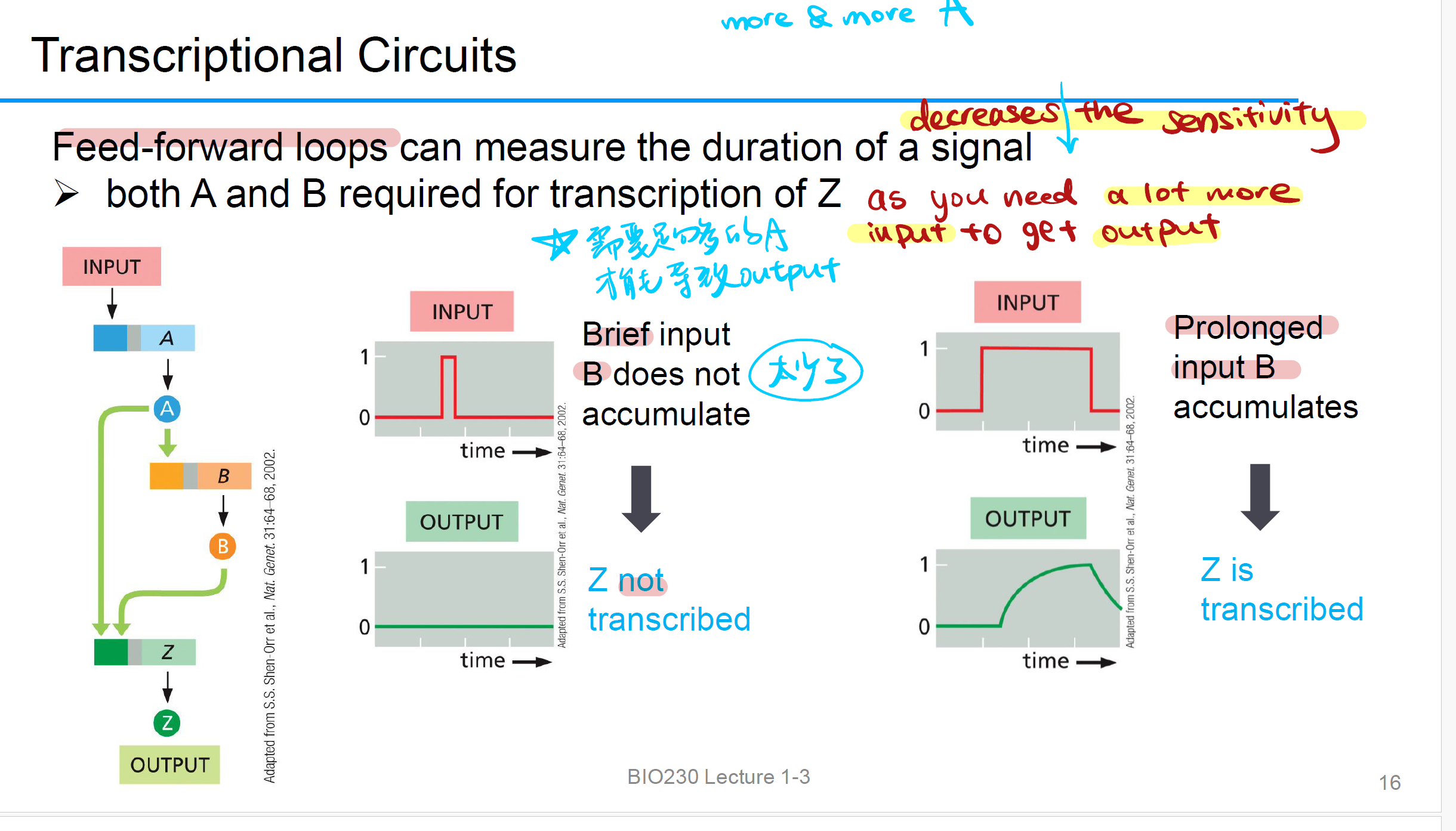
Repressilator
Scientists created a simple gene oscillator(基因振荡器) using a delayed negative feedback circuit. It is the Proof of Principle experiment, which means 人工的一堆repressor的共同作用的组合,为了看到 delayed negative feedback loop.
Transcriptional Attenuation转录衰减
一种提前终止转录的调控机制,premature termination of transcription,can occur in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
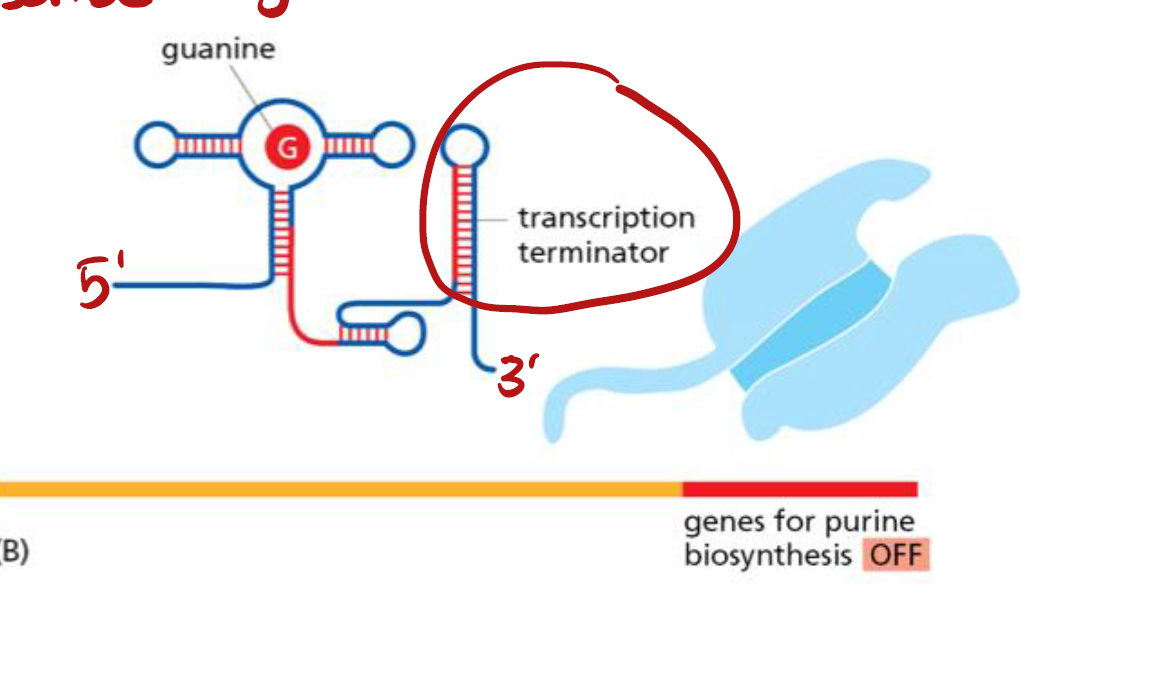
Riboswitches核糖开关
一段短RNA sequences that change conformation when bound by a 小分子
eg. prokaryotic riboswitch that regulates purine biosynthesis: 高guanine level → guanine bind riboswitch → riboswitch undergo conformational change → RNAP terminate transcription → 转录停止
primidine一个环(CUT)
purine两个环(AG)
mRNA
it is messenger RNA, code for proteins. 在真核细胞中pre mRNA由DNA 转录产生,随后切除内含子,就成为成熟的mRNA, 进入到cytoplasm,然后与ribosome结合,mRNA作为翻译的模板。
rRNA
it is ribosomal RNA, 核糖体RNA就是把rRNA运来的amino acid连接成polypeptide chains,form the basic structure of ribosome and catalyze protein synthesis.
tRNA
it transfer RNA, 根据mRNA的编码序列运送氨基酸到ribosome, central to protein synthesis, as the adaptation between mRNA and amino acids
Different RNA Polymerase
RNAP1: transcribed rRNA genes.
RNAP2: All protein coding genes
RNAP3: tRNAs
TATA Box
RNA Polymerase 2,转录的起点,与TBP结合让DNA弯曲,聚集其他因子。
Eukaryotic transcription begin need factors:
General transcriptional factor
Gene regulatory protein
Eukaryotic DNA is packaged into chromatin so it can?
provides an additional mode of regulation
Mediator
it is acts as an intermediate between regulatory proteins and RNA polymerase
Coactivators and corepressors
they assemble on DNA-bound gene regulatory proteins,不直接结合DNA
DNA binding domain (DBD)
recognizes specific DNA sequence
Activation domain (AD)
accelerates frequency/rate of transcription
How do activator proteins activate transcription?
Attract, position, and modify:
General transcription factors
Mediator
RNA polymerase II
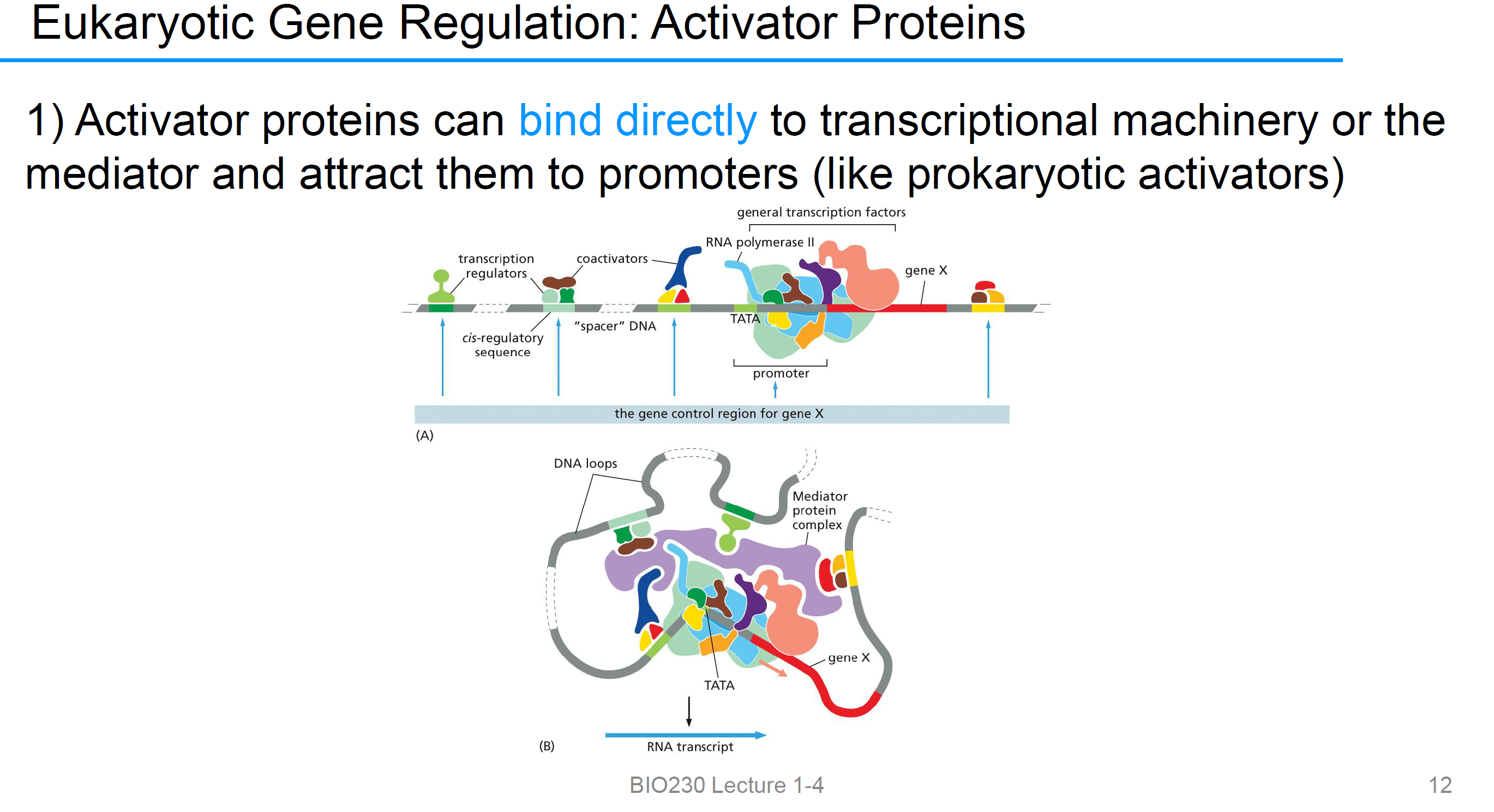
Activator proteins can bind directly to
transcriptional machinery or the mediator and attract them to promoters (like prokaryotic activators)
Activator proteins can
改变chromatin structure and 增加启动子promoter accessibility
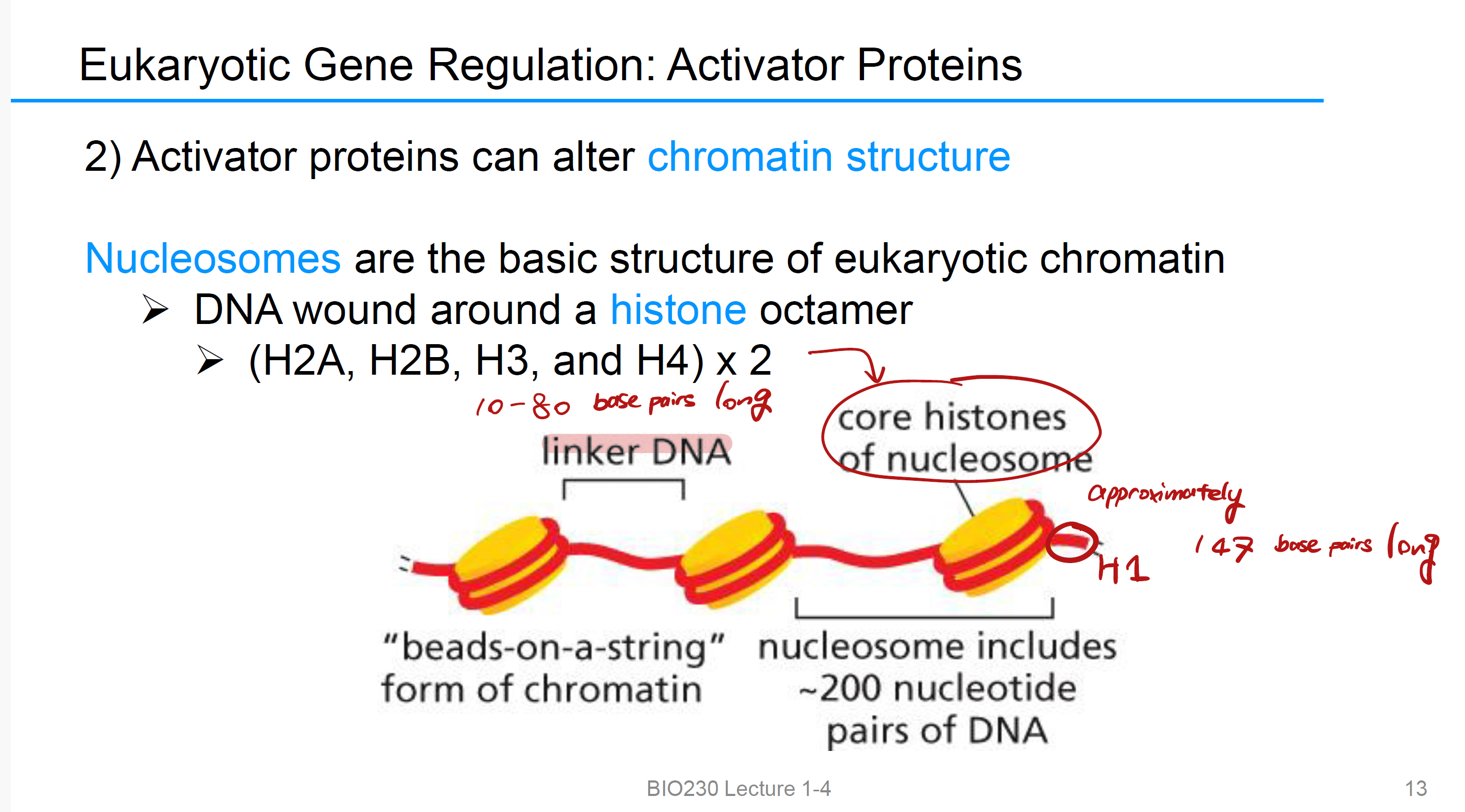
Nucleosomes
eukaryotic chromatin染色质的基础结构
➢ DNA wound around 组蛋白八聚体 histone octamer(8 proteins)
➢ (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4) x 2
Nucleosome sliding核小体滑动
Nucleosome structure 可以被 chromatin remodeling complexe改变,由ATP供能,重新定位核小体的位置。因为核小体会覆盖启动子,导致阻碍transcription。
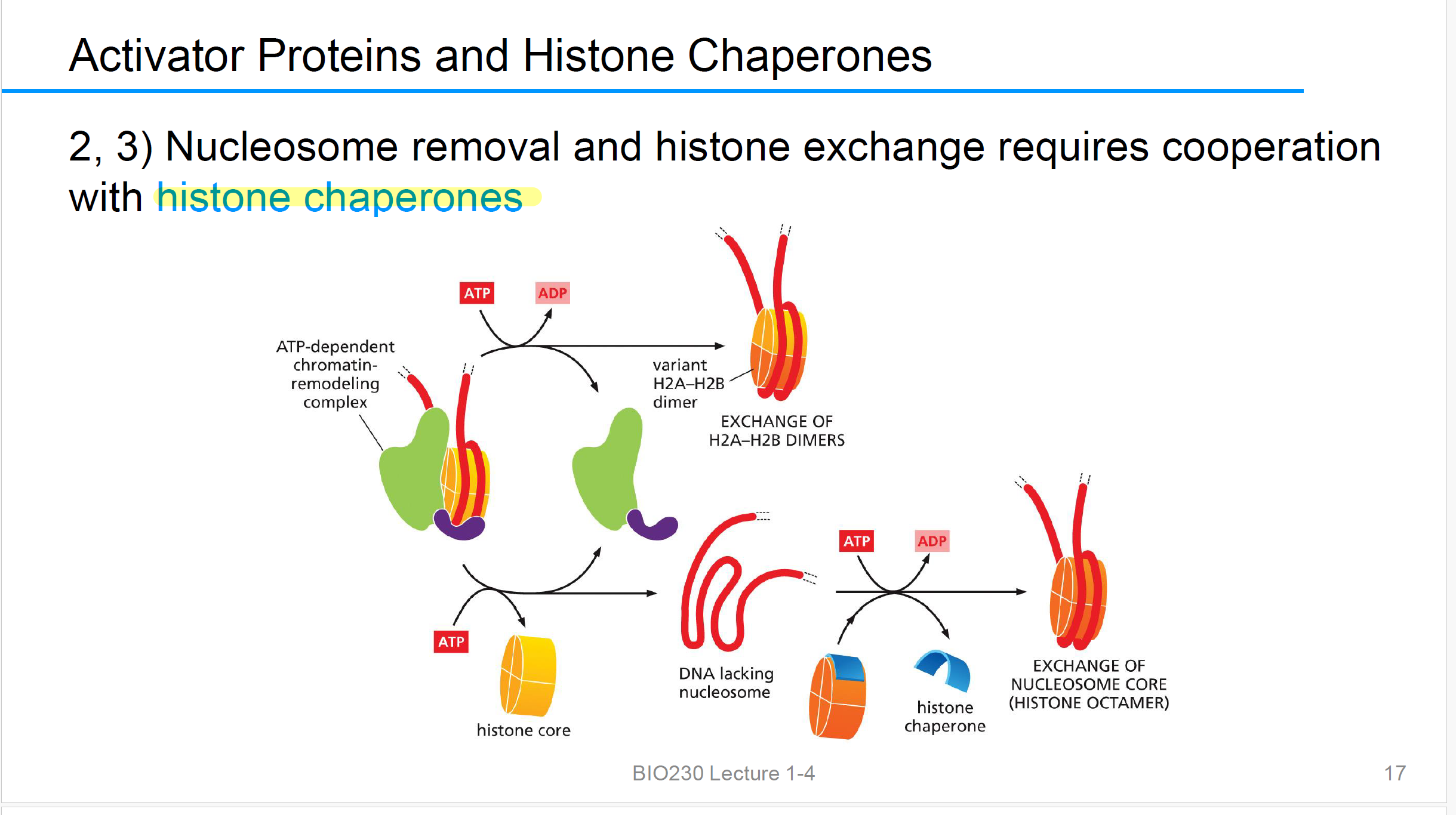
Nucleosome removal
Nucleosome removal and histone exchange 需要cooperation with histone chaperones组蛋白伴侣
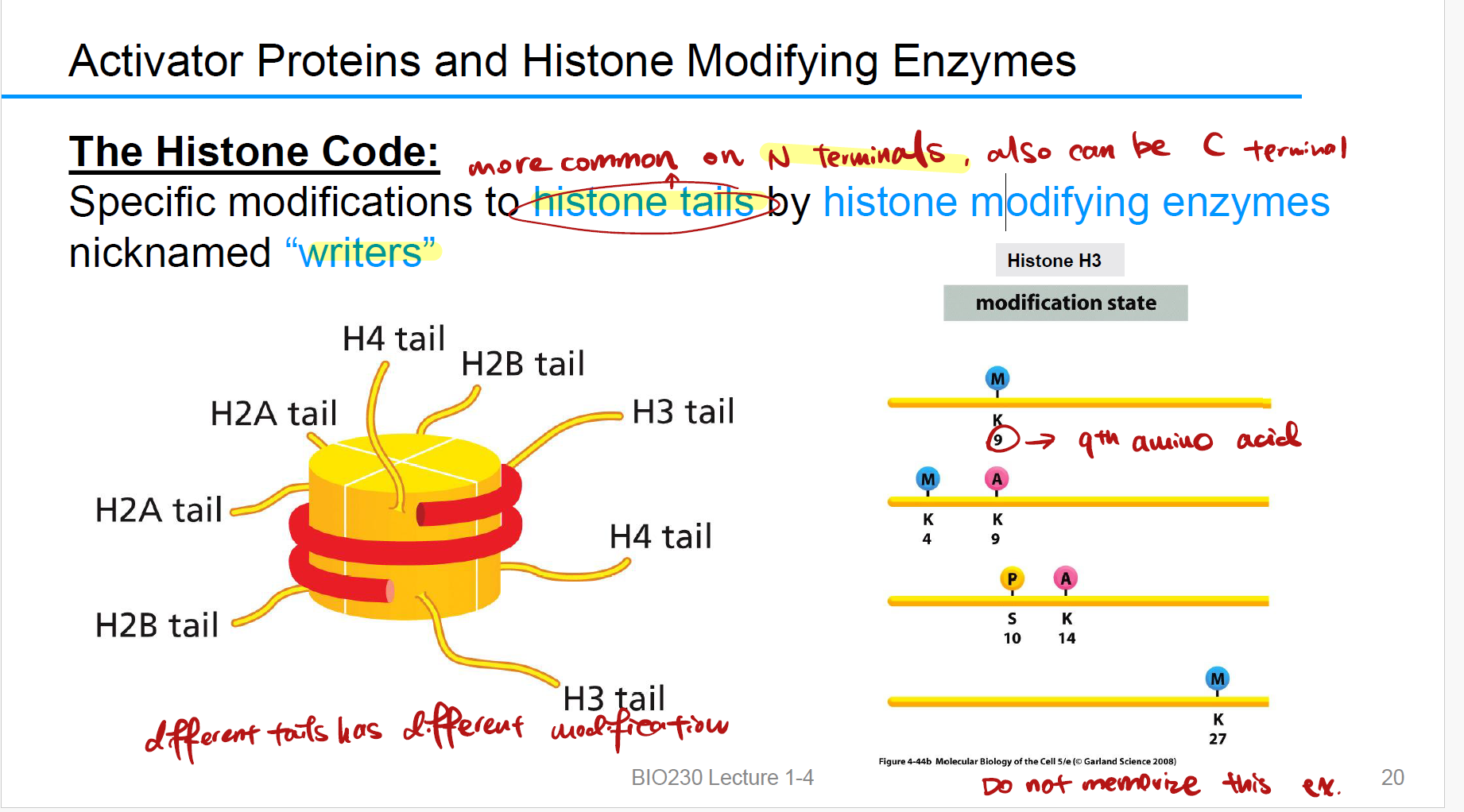
Histone code “writer”
Histone modifying enzymes produce 核小体中组蛋白的尾部修饰
Code “reader” proteins
recognize specific modifications and provide meaning to the code
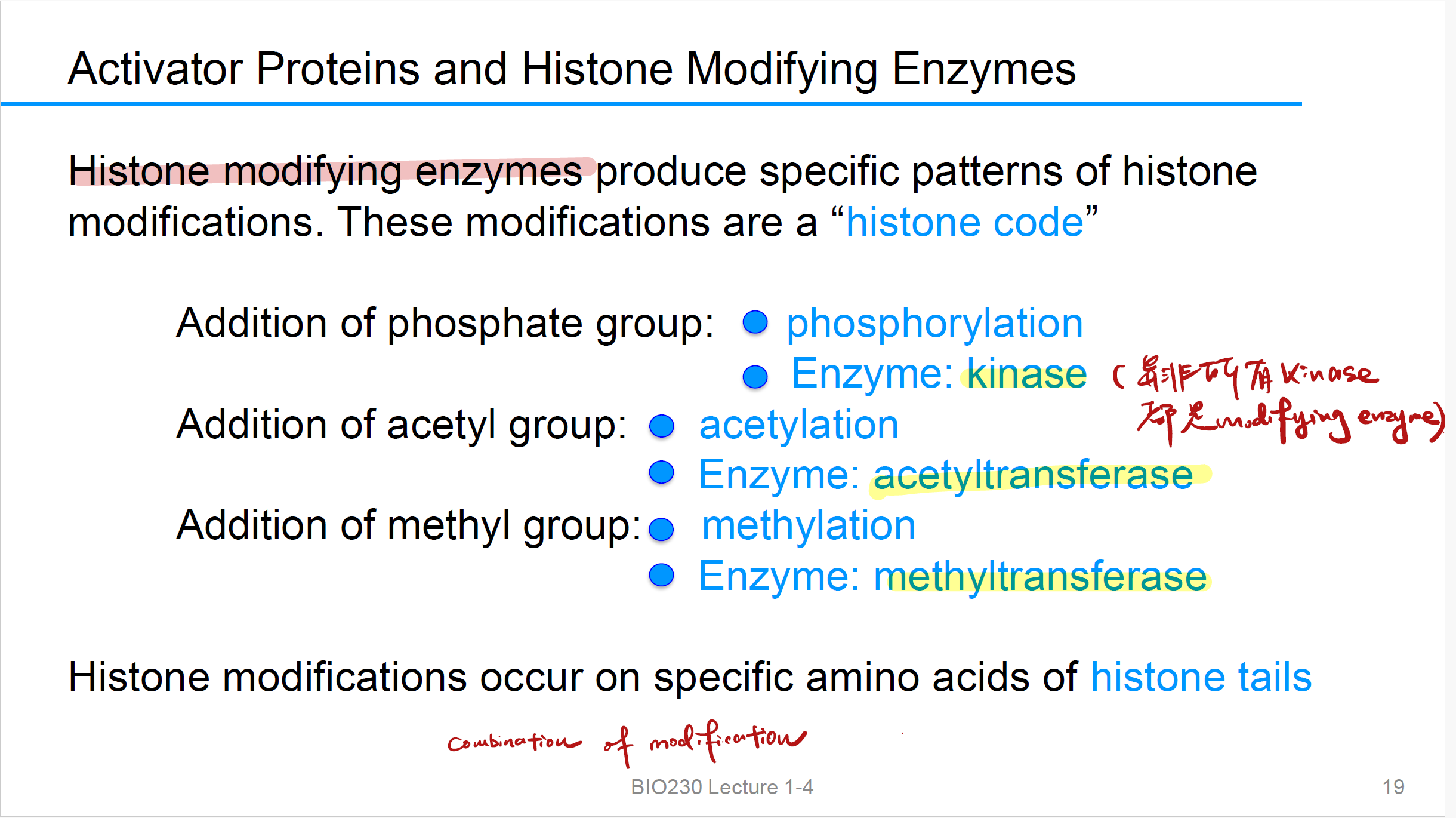
Addition of phosphate group (Histone code)
phosphorylation 磷酸化
Enzyme: kinase 激酶
Addition of acetyl group (Histone code)
acetylation 乙酰化
Enzyme: acetyltransferase 乙酰转移酶
Addition of methyl group (Histone code)
methylation 甲基化
Enzyme: methyltransferase 甲基转移酶
HOW Histone Code works(只有真核细胞)
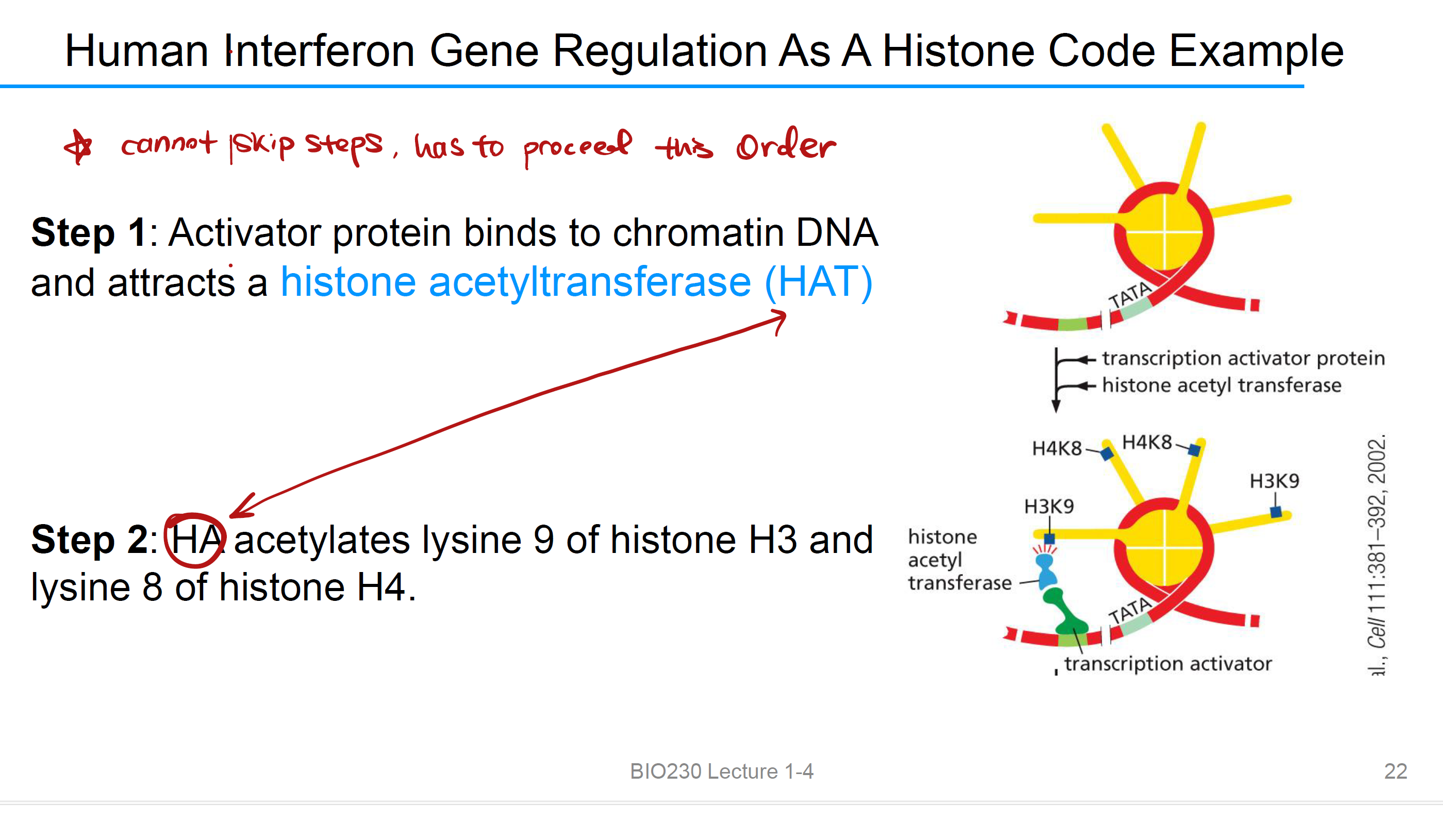
Step 1: Activator protein binds to chromatin DNA and 吸引 histone acetyltransferase (HAT)
Step 2: HA acetylates乙酰化 lysine 9 of histone H3 and lysine 8 of histone H4
Step 3: Activator protein 吸引 histone kinase (HK)
Step 4: HK 磷酸化 serine 10 of histone H3. 只有在上一步acetylation of lysine 9之后才会发生
Step 5: Serine modification signals the acetyltransferase to 乙酰化 lysine 14 of histone H3. 写出了转录起始的histone code
Step 6: TFIID and a chromatin remodeling complex bind to modified histone tails,转录开启
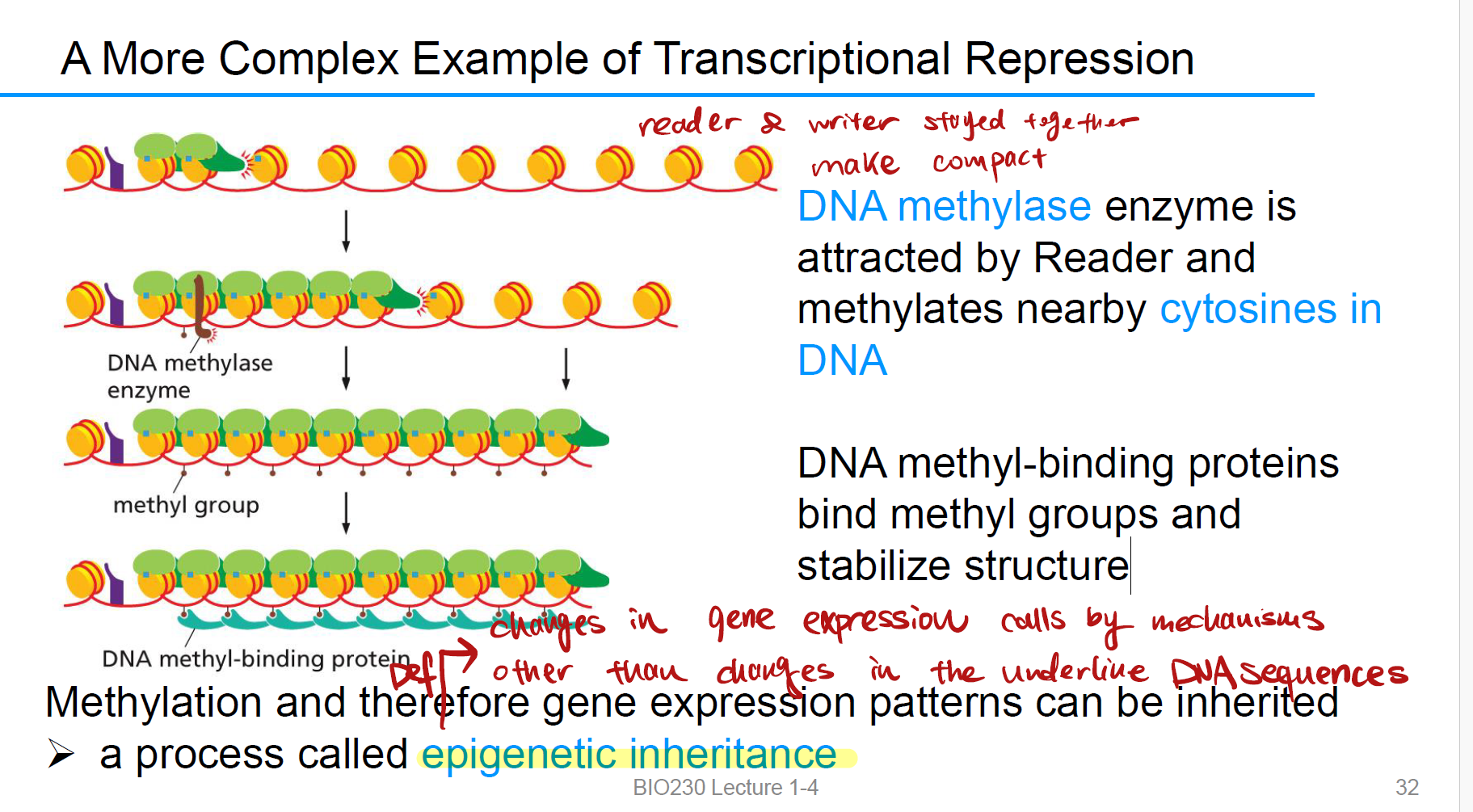
epigenetic inheritance
基因的可遗传变化by mechanisms, 例如甲基化。
repression spread
DNA methylase enzyme is attracted by Reader and methylates nearby cytosines in DNA.
DNA methyl-binding proteins bind methyl groups and stabilize structure. 先甲基化,后结合甲基结合蛋白,稳定染色质的紧密结构,导致RNAP无法进入。
Undifferentiated
model cell line, 确保证明 primary AML是正常的。例如白血病的Undifferentiated 就是标准的白血病病人该有的样子
Chemical treated
to find which chemical will change abnormal to normal
Primary cells from patients
cells comes straight from the patients.
IC50
Concentration of compound required to inhibit cell proliferation by 50%。 数值越小,药效越强
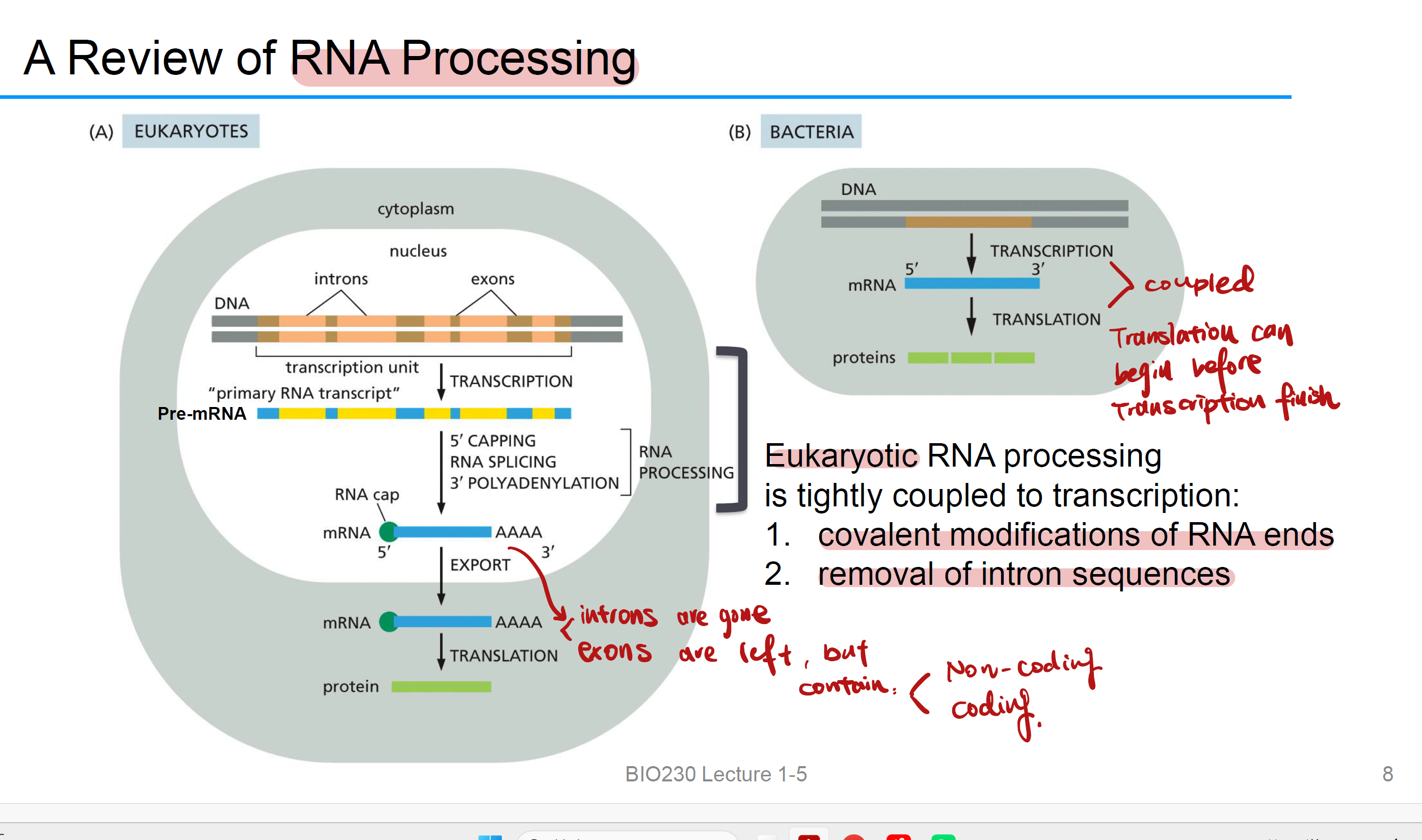
Eukaryotic RNA processing
it is 和transcription分开发生:Eukaryotic RNA processing is initiated before transcription is complete
1. covalent modifications of RNA ends
2. removal of intron sequences
(5 capping, splicing introns, 3′ Polyadenylation)
RNA Capping
Addition of a modified guanine nucleotide to 5’端 pre-mRNA (3 enzymes involved),与cap-binding complex (CBC)结合
Functions:
1. 协助RNA加工和从细胞核中输出
2. 在细胞质中mRNA的翻译中发挥重要作用
3. 保护mRNA免于降解
RNA Splicing
it is a process that Both introns and exons are transcribed into RNA, but the introns are removed
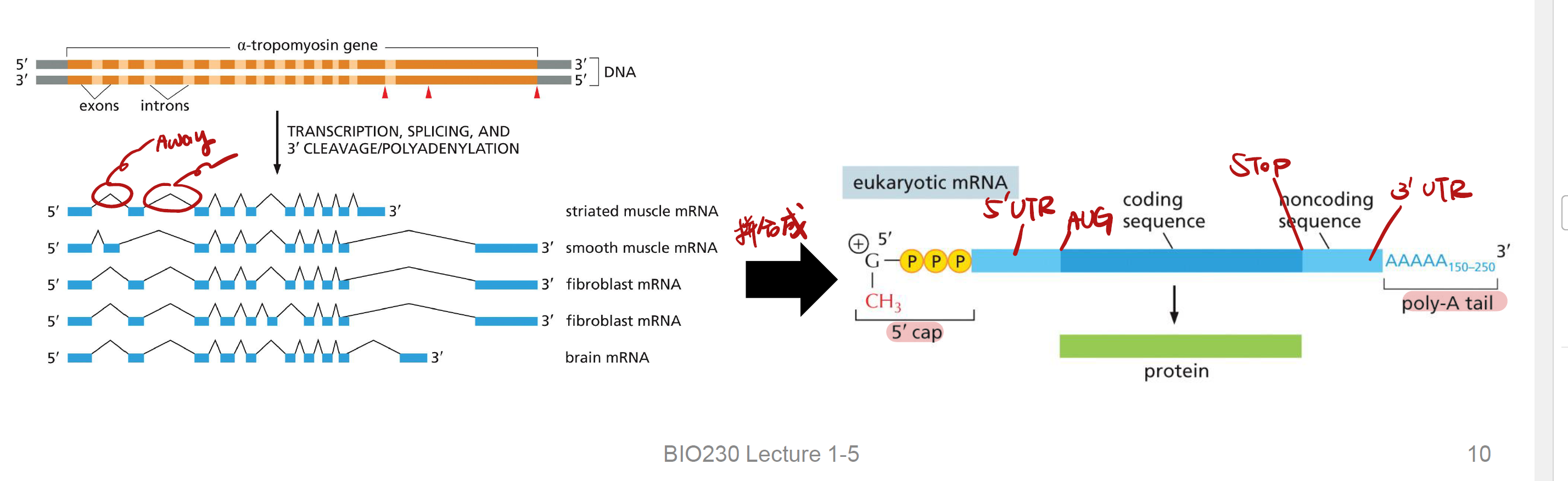
alternative splicing
Different cells can splice an RNA transcript differently to make different
proteins from the same gene
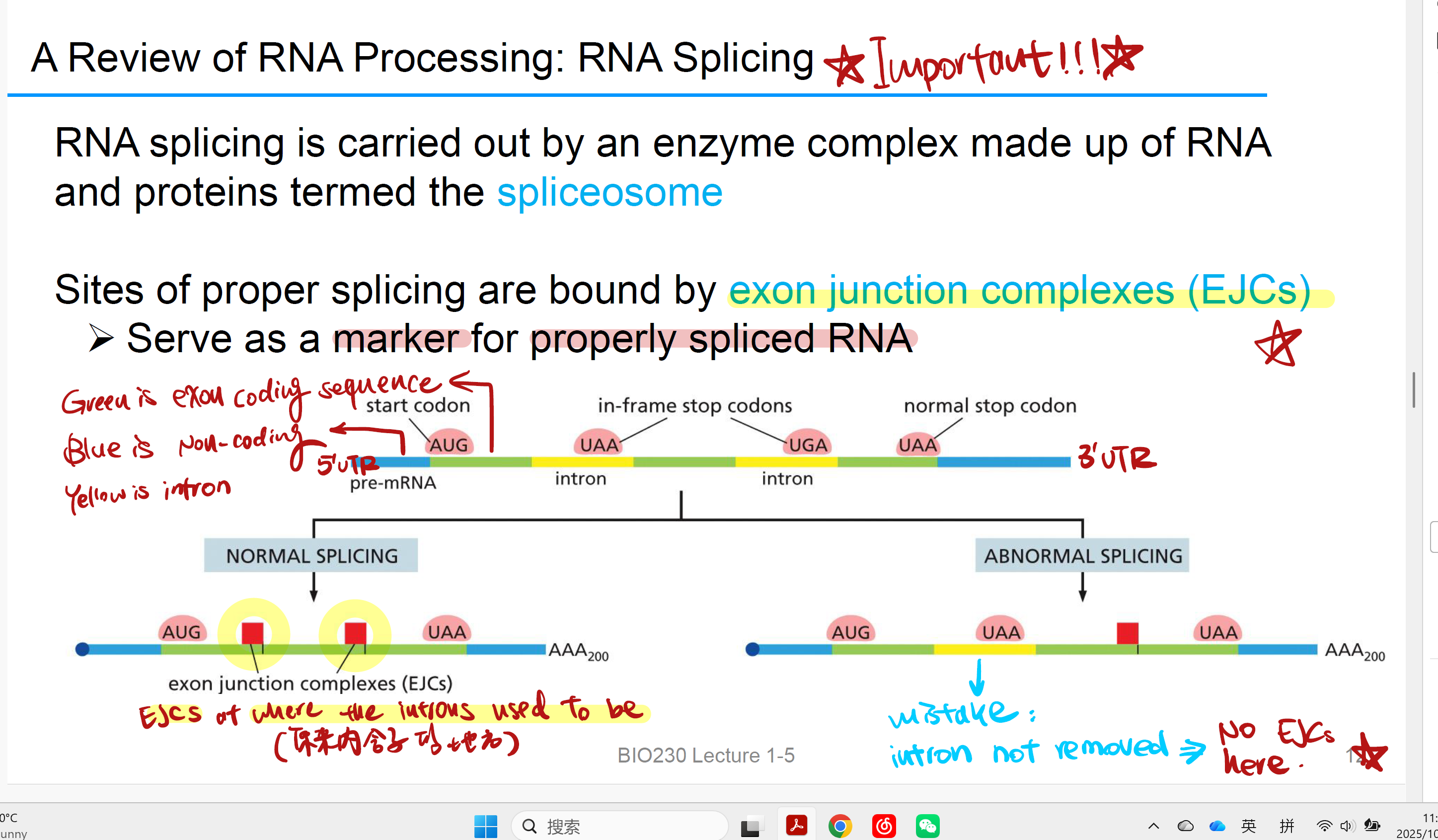
spliceosome
RNA splicing is carried out by an enzyme complex made up of RNA and proteins
exon junction complexes (EJCs)
EJCs bind 在Introns切除位点,引导splicing切除introns,没有EJC就不能切除该intron!
➢ marker for properly spliced RN
并且刺激 translation ensuring proper splicing(at translation initiation)
Splicing regulated
这个词的意思就是是否有repressor或者activator在作用?
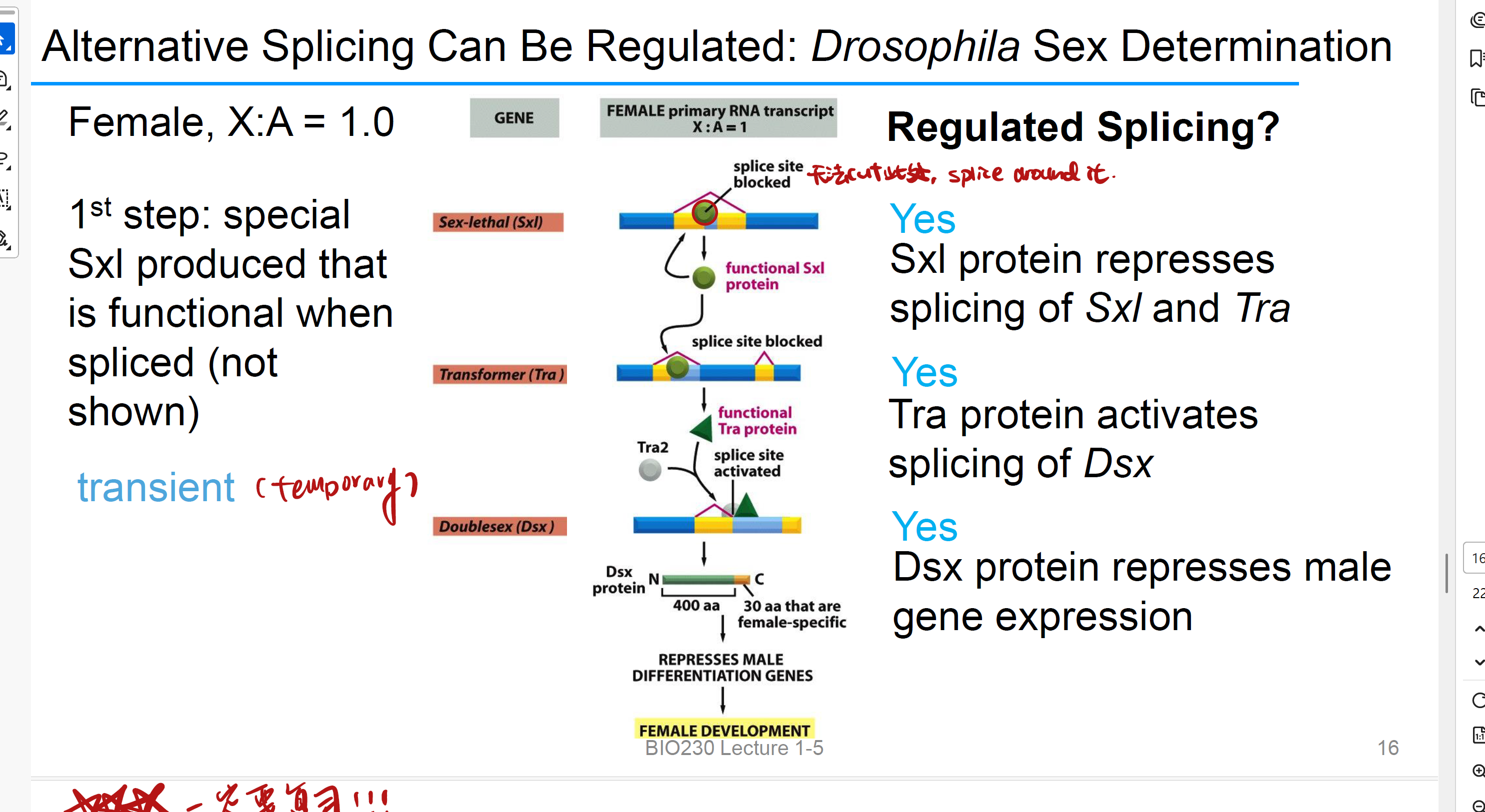
sex-lethal protein 性致死蛋白 sxl
this protein represses splicing of Sxl and Tra. 告诉splicesome这里你不能剪
it is a positive feedback loop
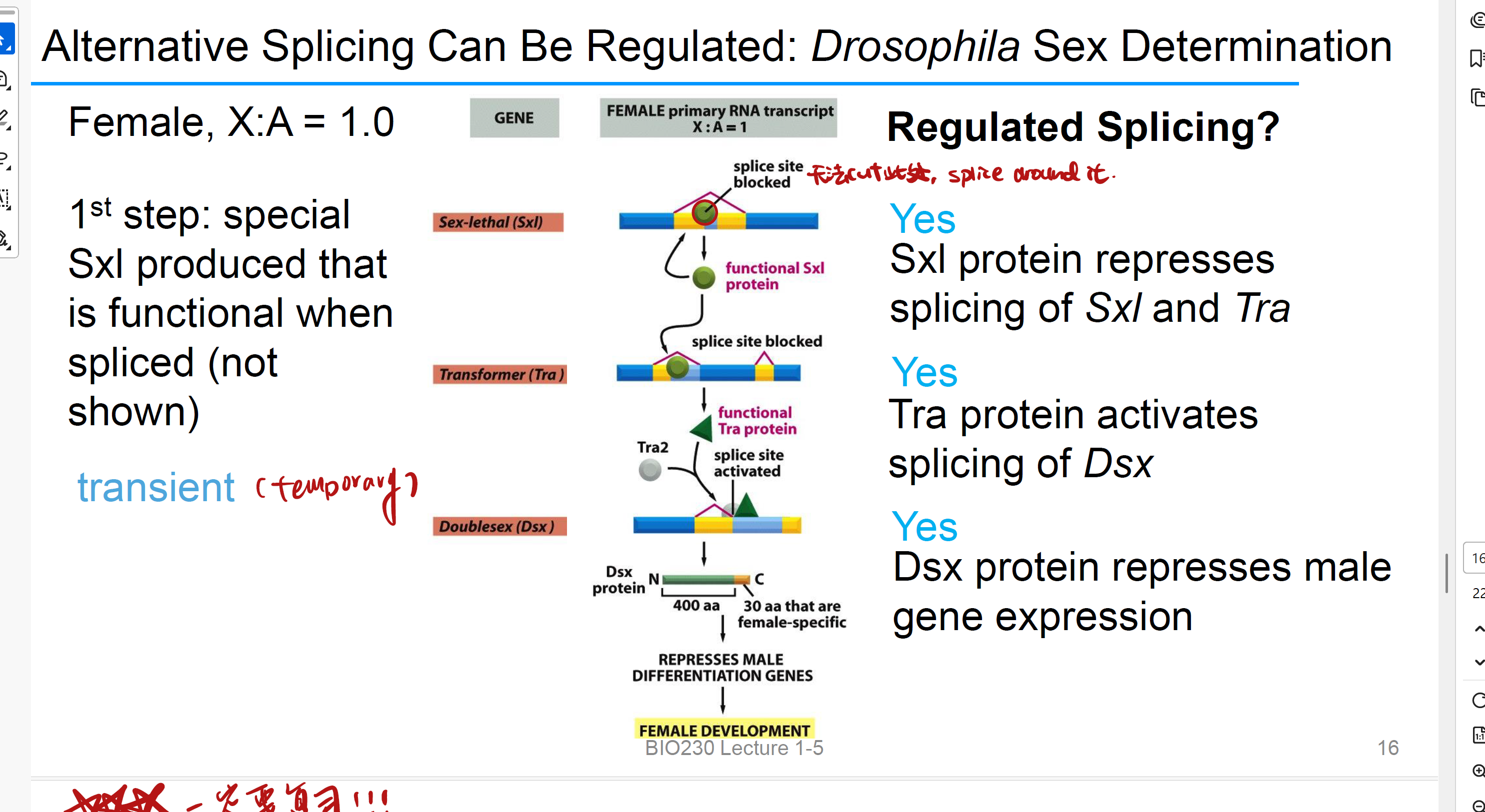
Transformer 转化蛋白 Tra
it is a splicing activator, it activates splicing of Dsx
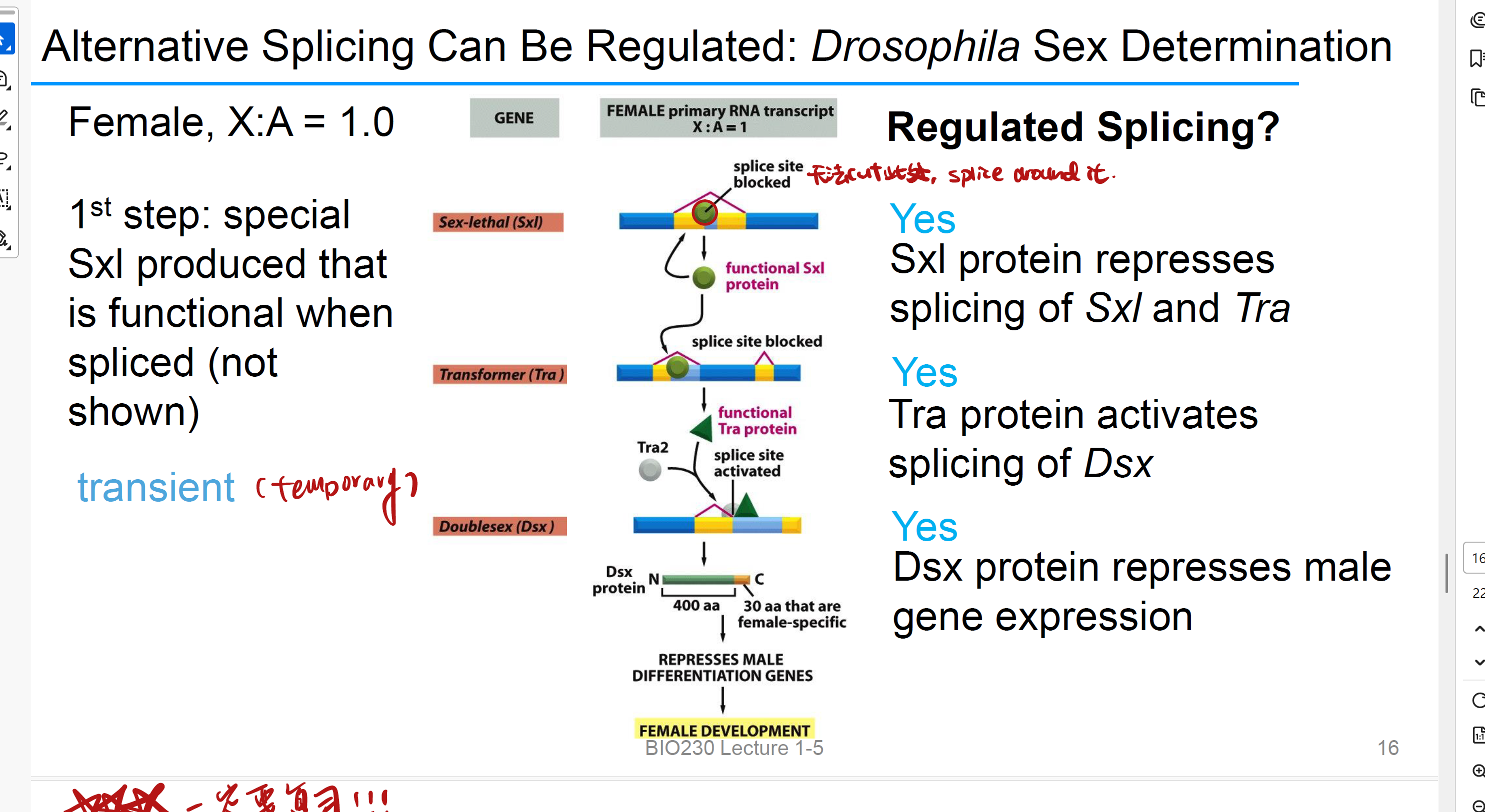
Doublesex 双性蛋白 Dsx
it Regulates sex gene expression, represses male gene expression
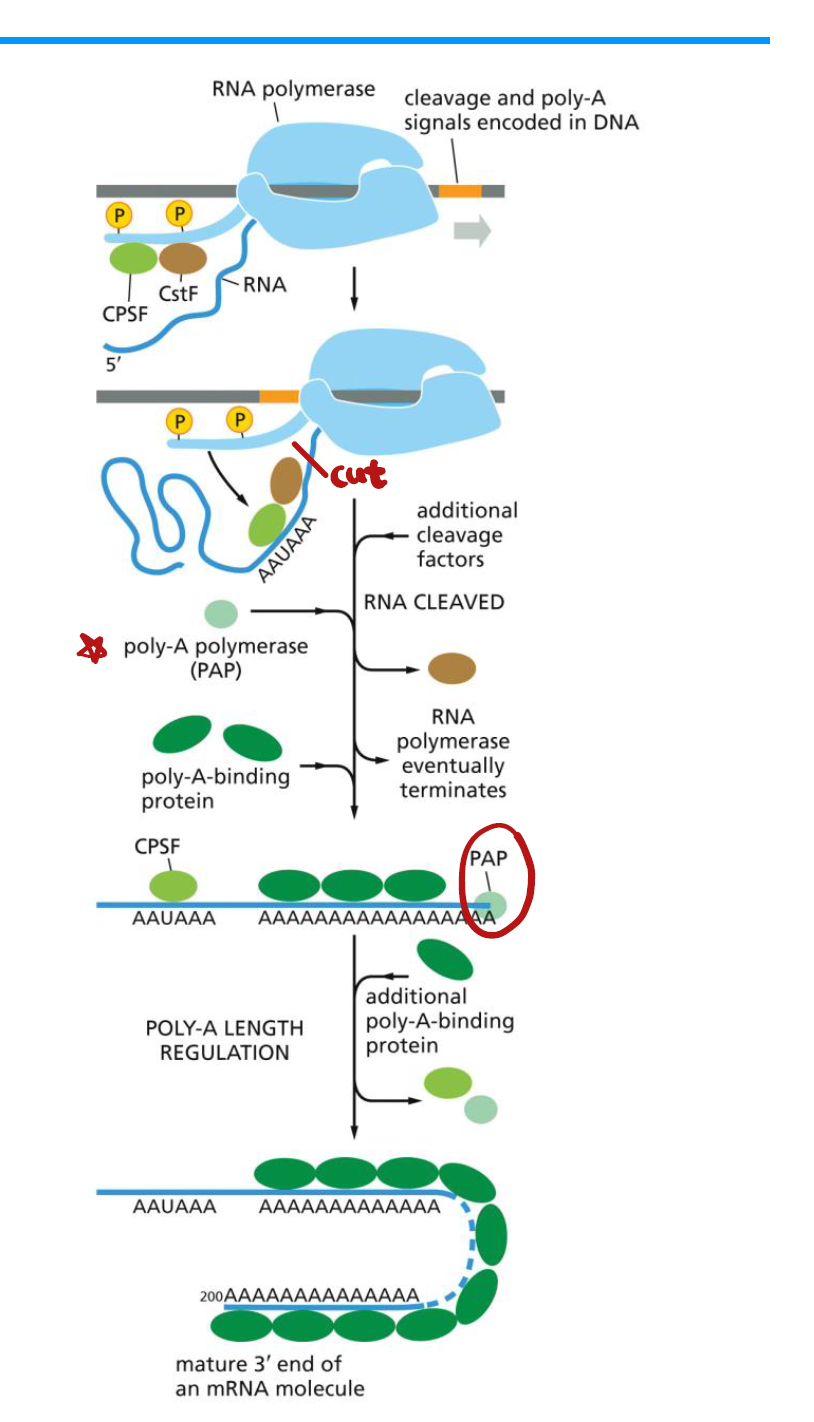
3’ Polyadenylation and Termination
信号被RNAP2识别,立刻转移CstF和CPSF到C端domain,
切下先前生成的所有mRNA,
• Transcription terminates
• Poly-A polymerase (PAP) 添加~200 A nucleotides到RNA 3‘端 from ATP
➢ not genome encoded
• poly-A binding proteins立即与尾部结合,保护mRNA, 帮助后续翻译和输出核。
CstF
(cleavage stimulating factor)
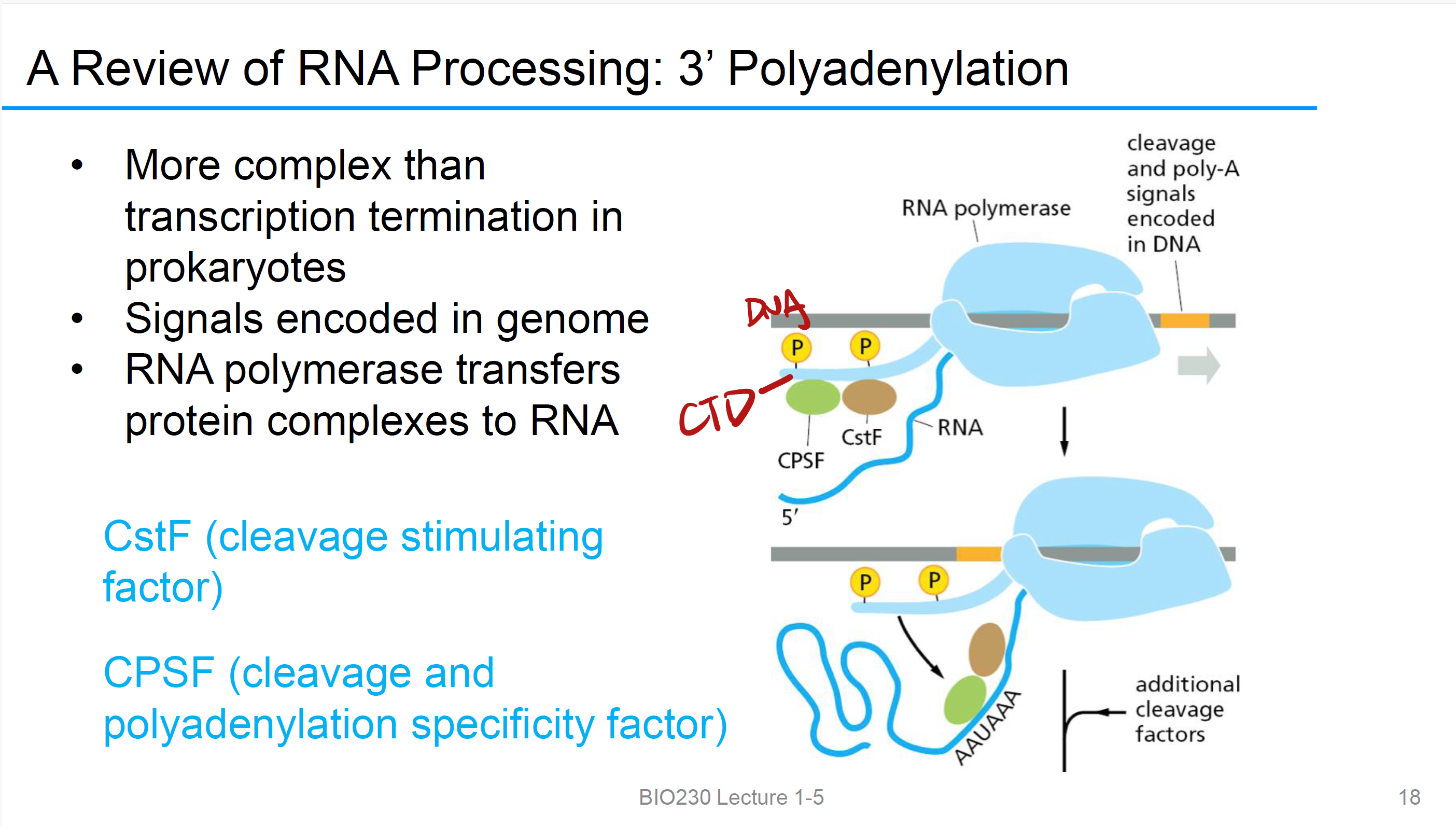
CPSF
(cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor)
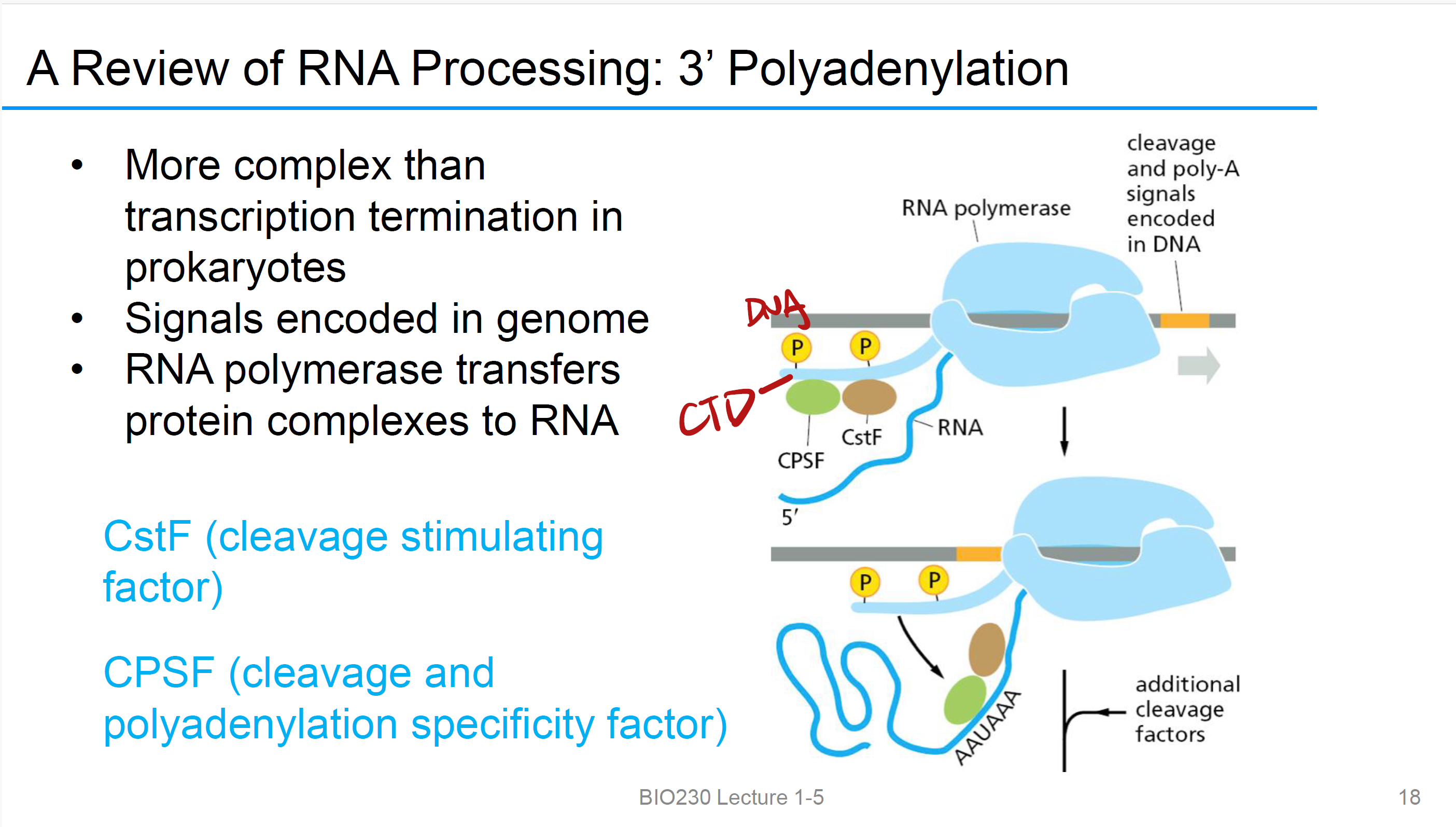
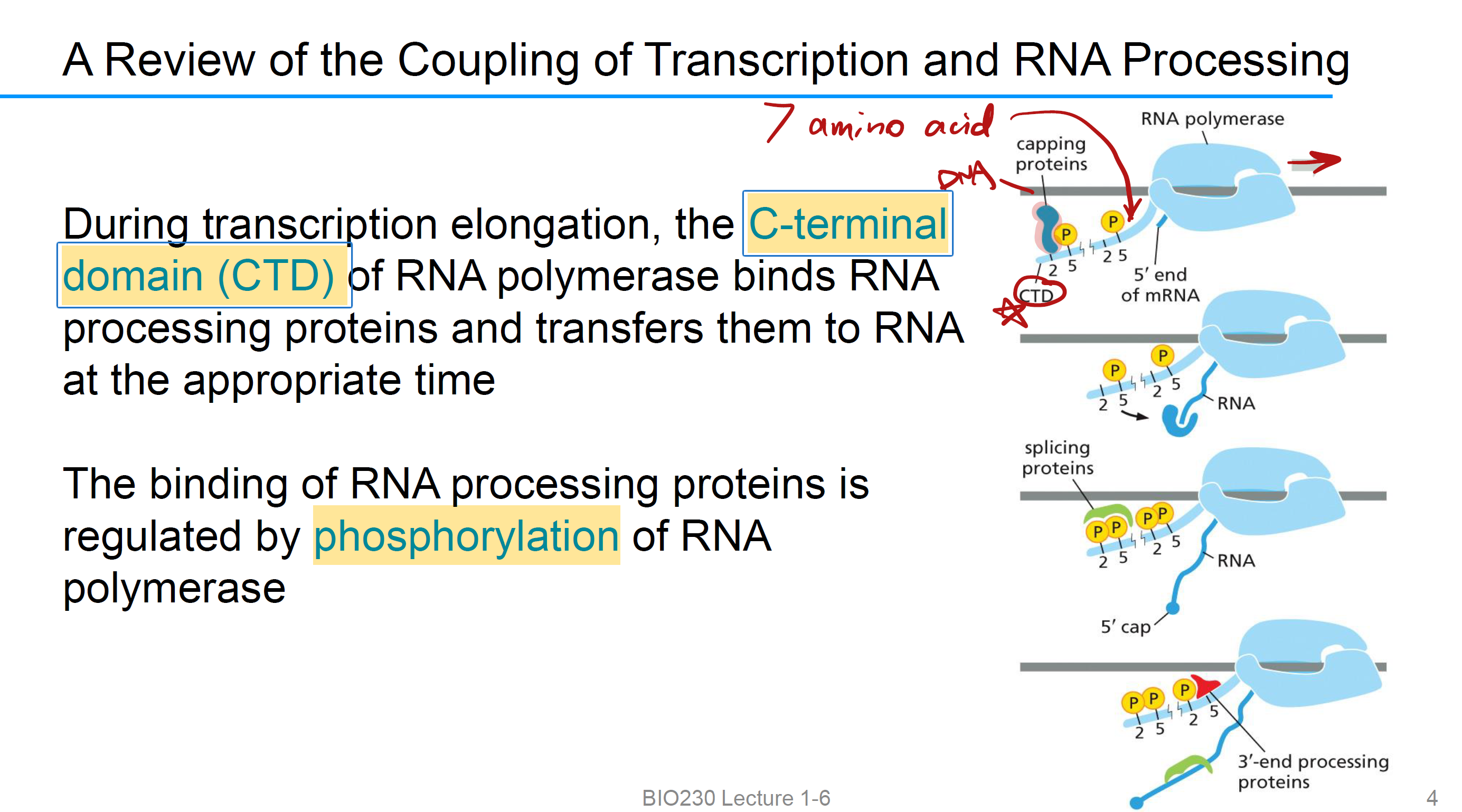
CTD (C-terminal domain)
RNA polymerase 开始合成RNA, CTD phosphorylation, 招募不同的加工蛋白,当RNA的5’端出来的时候,CTD 把 capping proteins(加帽酶) 递过去,继续延伸之后,CTD 把 splicing proteins递过去剪切Introns 拼接exons,到快结束时,CTD 把 3′-end processing proteins 递上去,完成 poly(A) 加尾并结束转录。
Markers of mature RNA
Export的t时候被需要的3个通行证:
Cap binding complex (CBC):结合在 5′ cap上表示已加帽
Exon junction complexes (EJC):在exons拼接处表示已完成剪接
Poly-A-binding proteins:结合在 3′ poly-A 尾巴上表示已加尾
Markers of immature mRNA
RNA上的还带有剪接用的蛋白,如snRNPs。将不会被export
exosome
Improperly processed mRNAs will eventually be degraded in the nucleus by it.
1个amino acid =
3个 nucleotides = 1 个 codon
ribosomes
it is consist of >50 different proteins and several RNA molecules. mRNA message is decoded in it.
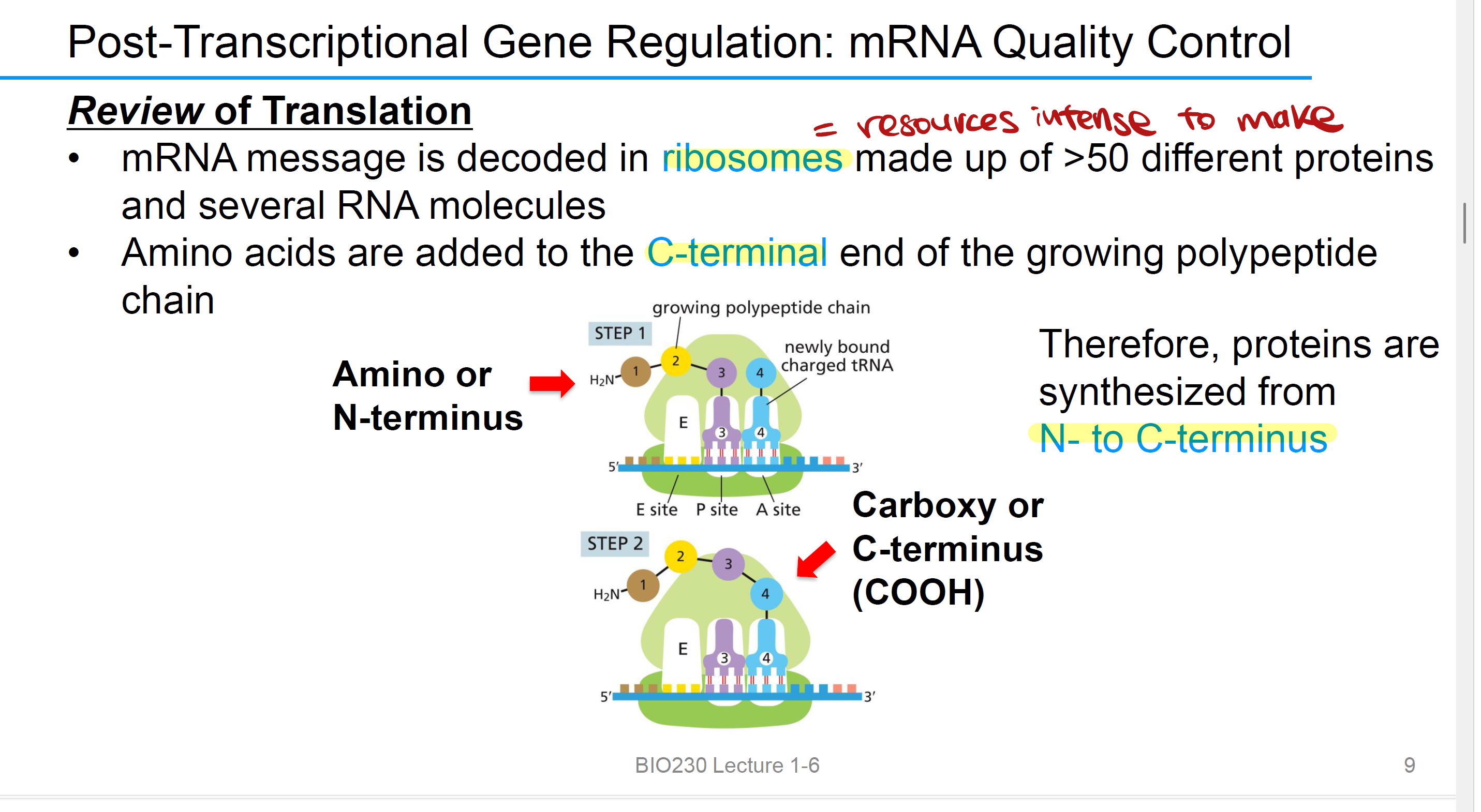
In what direction are proteins translated, and why?
Proteins are synthesized from the N-terminus (amino end) to the C-terminus (carboxyl end) because new amino acids are always added to the C-terminal end of the growing polypeptide chain.
euk翻译开始之前检查,防止错误的第一道坎
5’-cap:5’ cap bound by eIF4E
poly-A tail:poly-A binding protein bound by eIF4G
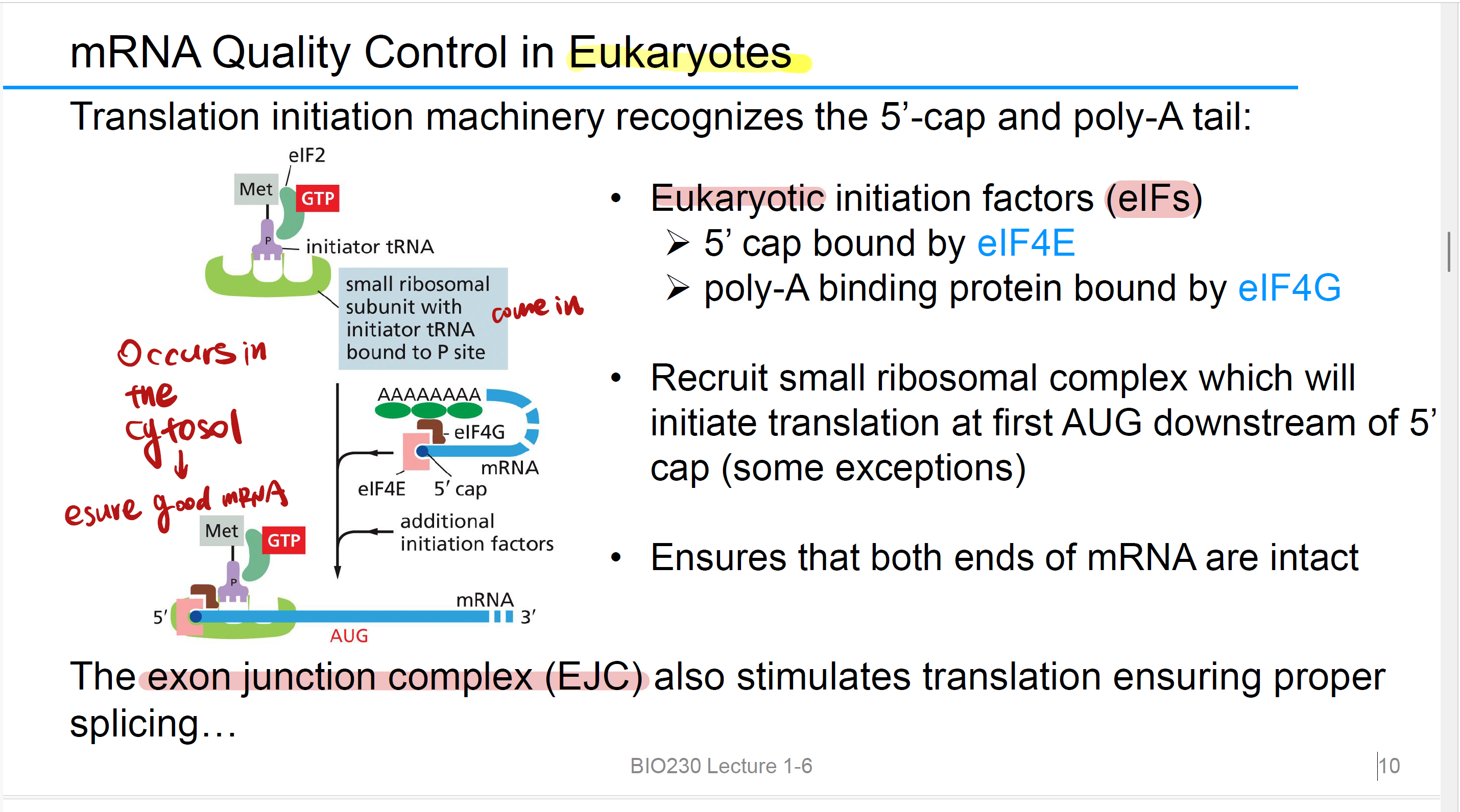
small ribosomal subunit
it will initiate translation at first AUG downstream of 5’ cap (some exceptions)
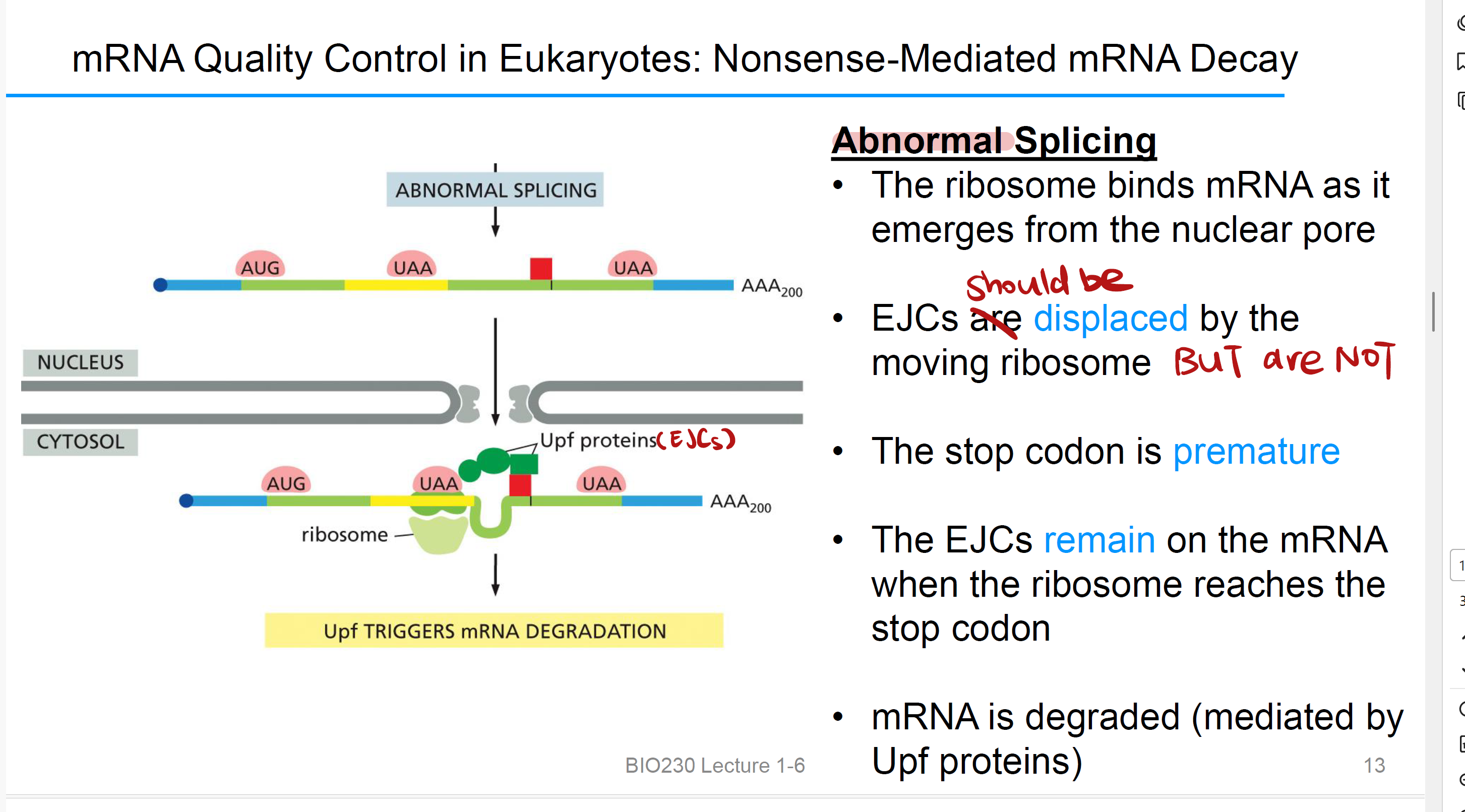
Ribosome 回收当 Abnormal Splicing In Eukaryotic
• when mRNA emerges from the nuclear pore, ribosome binds to it.
• EJCs本该被 moving ribosome取代,然而并未所以导致终止密码子提前达到(stop codon is premature)
• 当ribosome reaches the stop codon, EJCs 仍在mRNA上
• mRNA trigger by Upf Protein, it is degraded.
tmRNA(transfer-messenger RNA),在pro翻译错误时候
mRNA Quality Control in Prokaryotes
当核糖体卡在断裂或异常的 mRNA 上,tmRNA 被招募到核糖体的 A 位点。
tmRNA 自身携带一个 丙氨酸(alanine, Ala),所以它能像 tRNA 一样提供一个氨基酸。
然后核糖体转移到 tmRNA 自带的“假 mRNA 区段”上继续翻译,
在多肽链尾部加上一个特定的“标签序列”。从而被识别并标记为“要降解的蛋白”,同时核糖体被释放出来重新利用。
如假包换,狸猫换太子
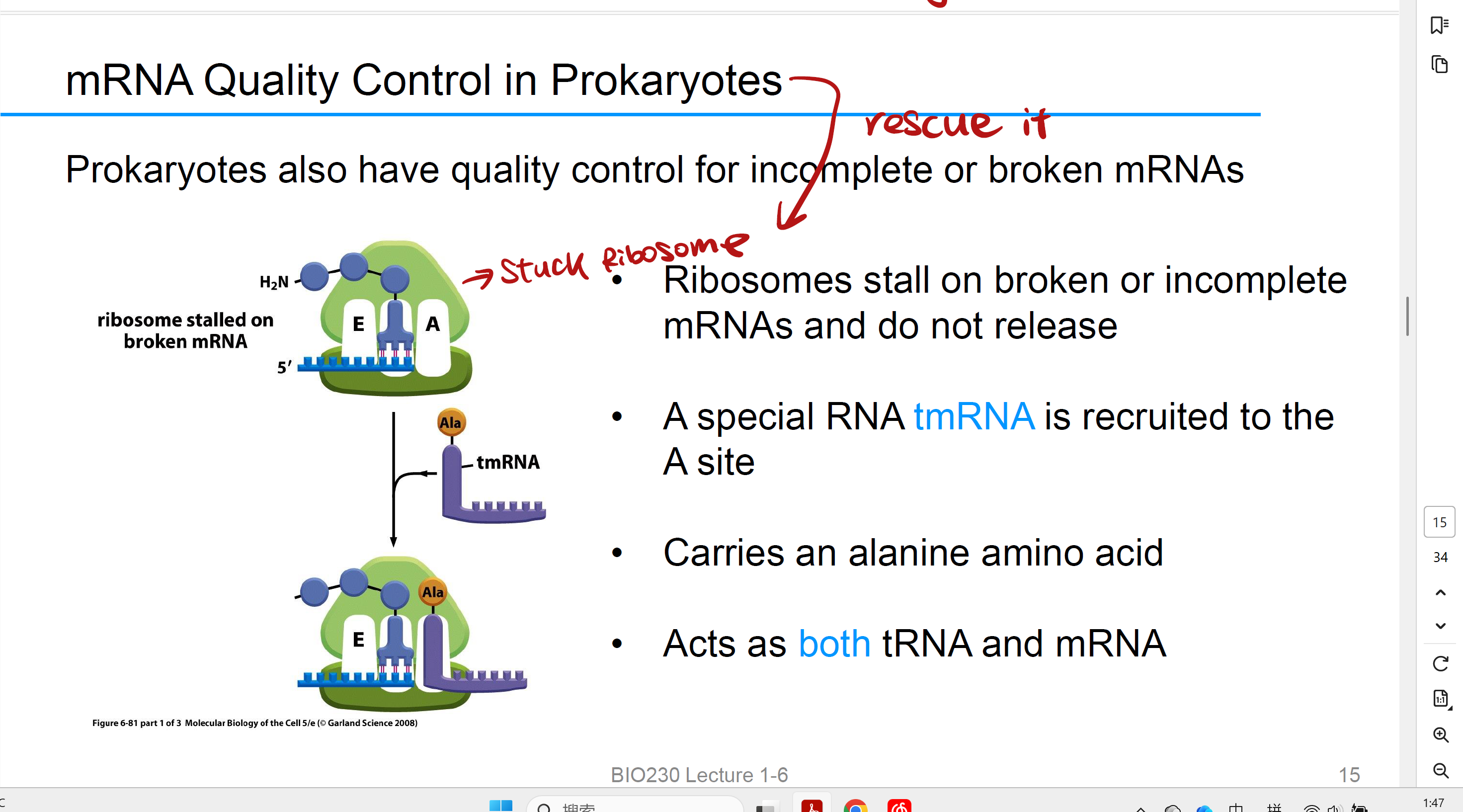
proteases
recognize 11th amino acid and degrade the entire protein(fake mRNA in prokaryotic)
Decapping
当PolyA tail 逐渐被deadenylase越剪越短,就会去除Cap,从而degradation from 5’ to 3’
(Post-Transcriptional Gene Regulation in EUK)
exonucleases
it rapidly degrade most mRNAs in prokaryotes
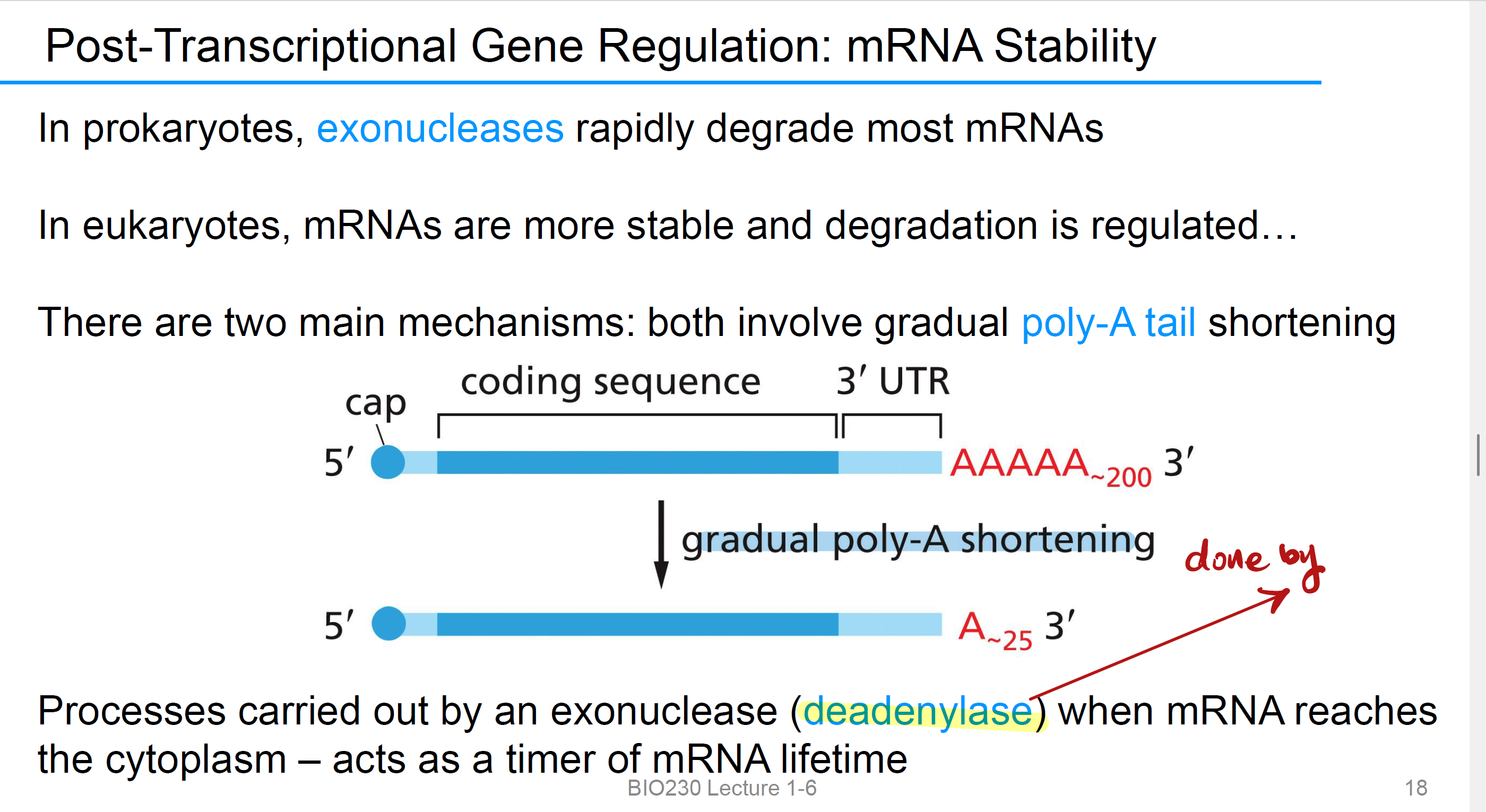
NO Decapping
degradation from 3’-5’.
这两种机制可以在同一条 mRNA 上同时发生。
相反地,细胞也能通过 poly-A elongation(延长尾巴) 来稳定 mRNA
Cytosolic aconitase
When iron starvation, 该酶 binds 3’UTR in Post-Transcriptional Gene Regulation,结合到 transferrin receptor mRNA 的 3′UTR 区域, 这会“盖住”降解酶的结合位点(保护poly-A tail);receptor protein gets made,正常translation
这是mRNA stabilize的途径,degrade是stabilize的反义词
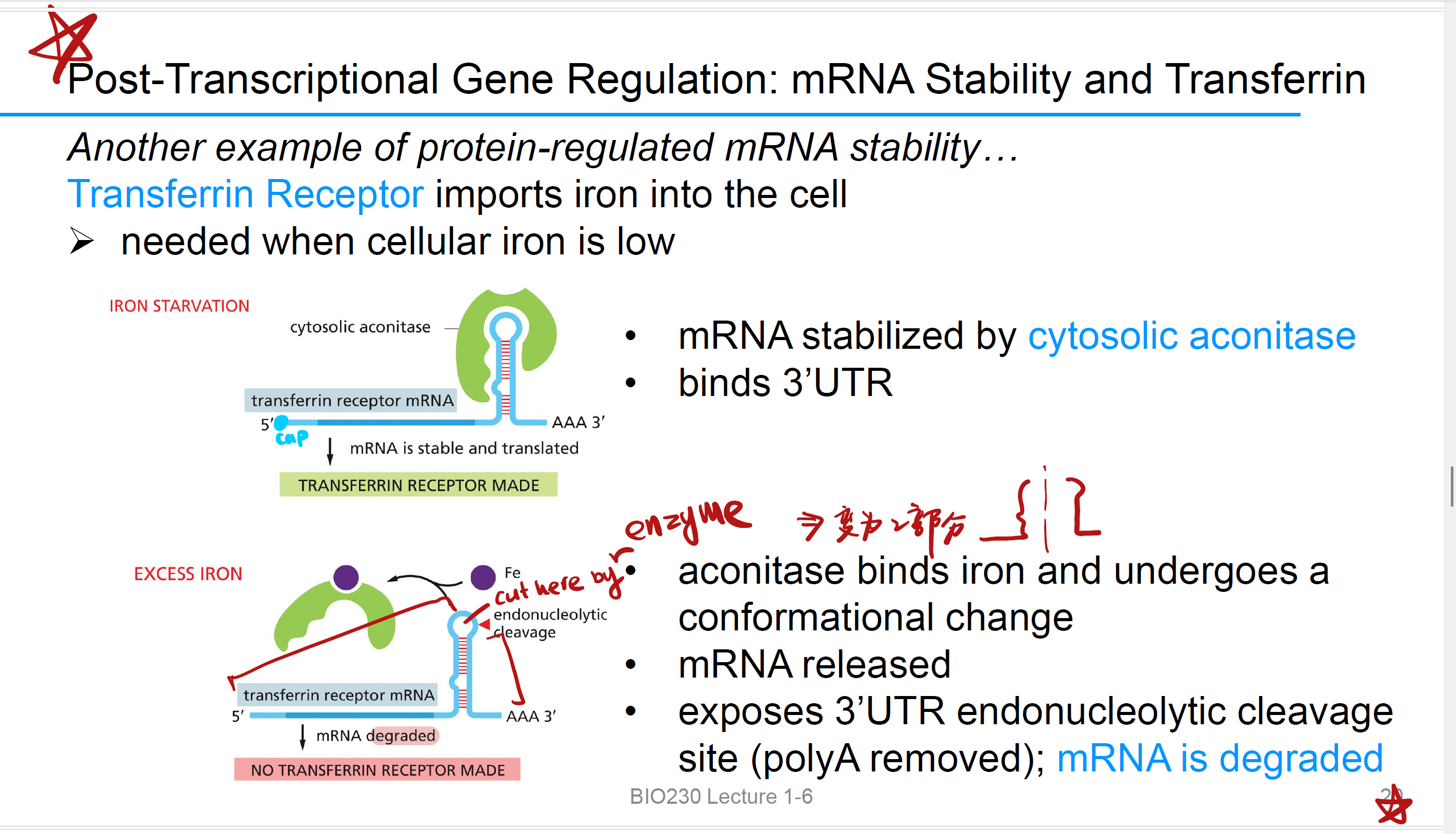
Endonucleolytic cleavage site
过量iron, aconitase binds iron 并构象改变,释放 mRNA
暴露 3’UTR 内切位点 endonucleolytic cleavage site (polyA 被去除); endonuclease 将mRNA 切成两部分,mRNA 成功降解。
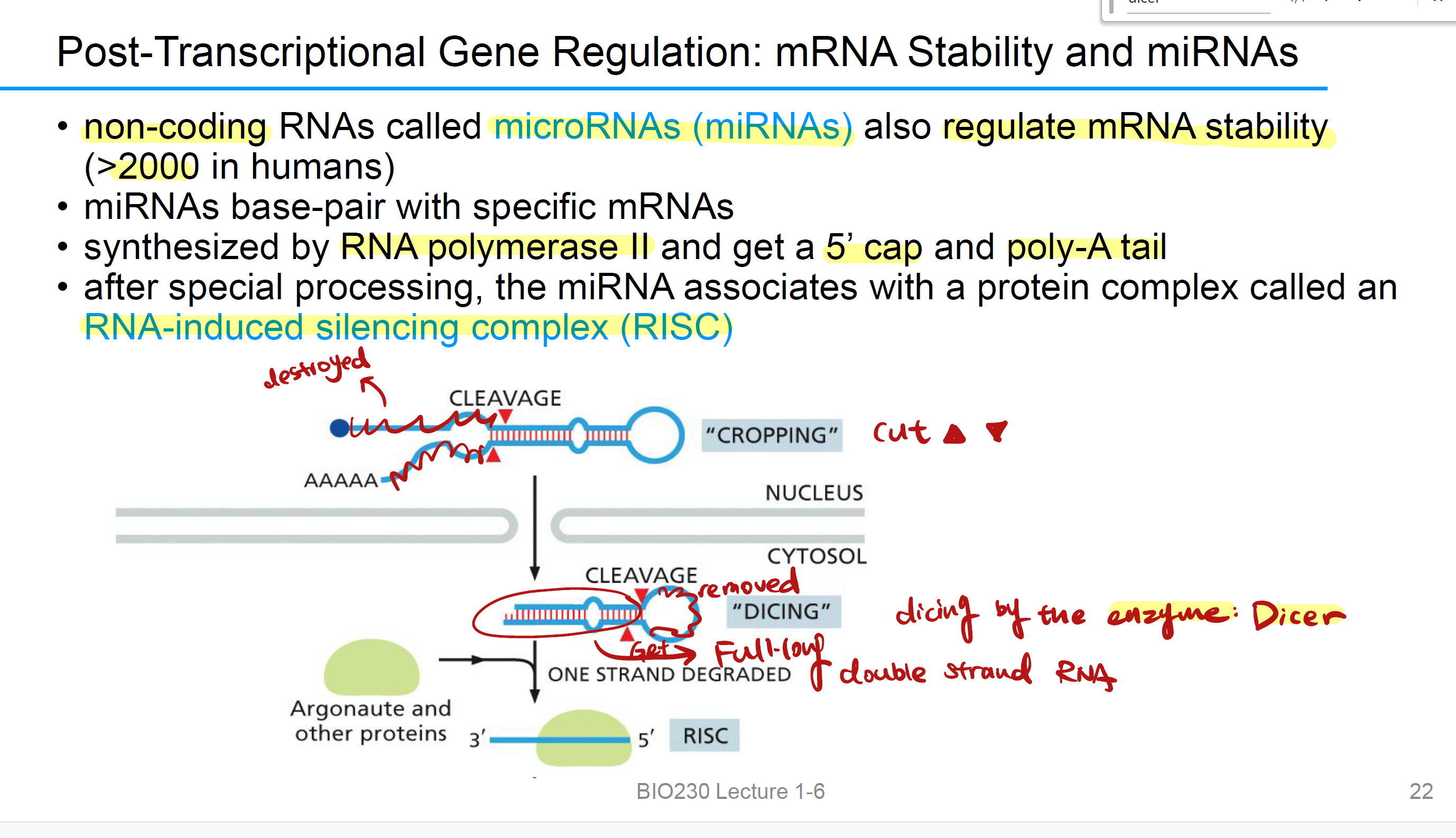
microRNAs (miRNAs)
which also called 非编码区 RNAs(non coding), also regulate mRNA 稳定性(>2000 in humans)
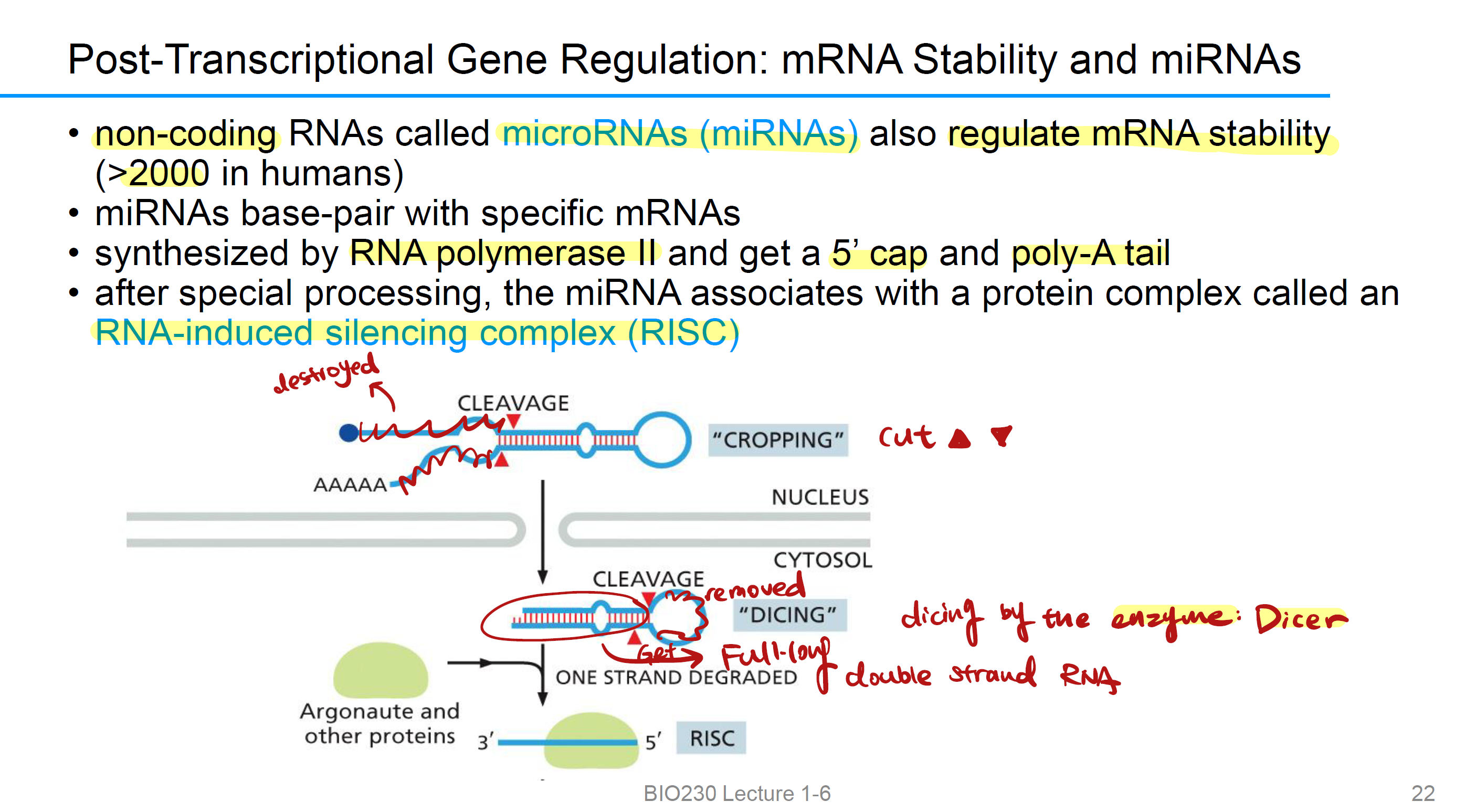
miRNAs base-pair with
specific mRNAs
miRNAs synthesized by
RNA polymerase II and get a 5’ cap and poly-A tail,就像mRNA一样被加工
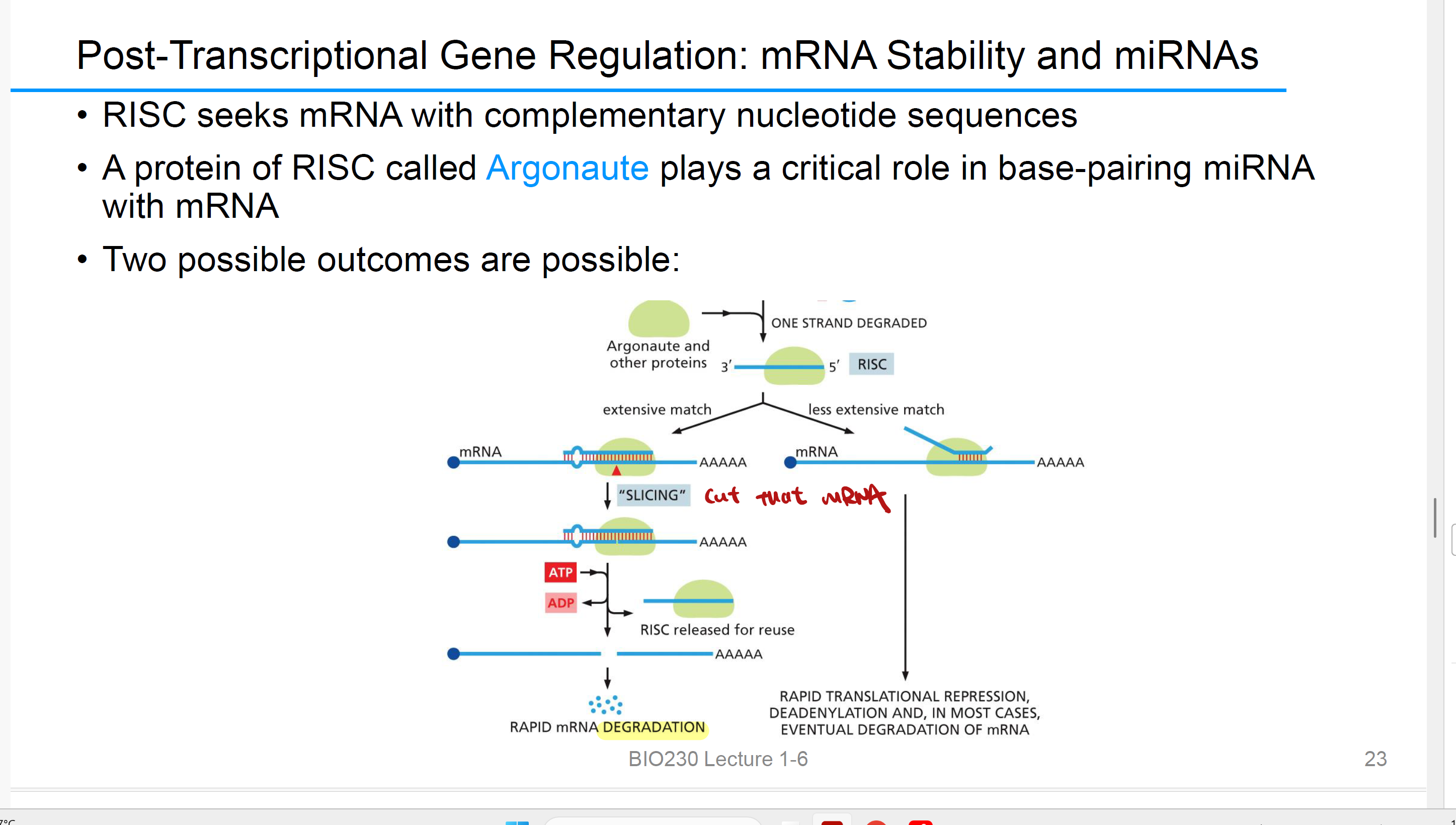
After special processing, the miRNA associates with
a protein complex called an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC).
miRNA的主要功能是引导RISC结合特定的信使RNA(mRNA), 从而阻断翻译或者促进靶向mRNA的降解,抑制基因表达。