Embalming II - Final
1/250
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
251 Terms
Tiny structures that connect arterioles to venules
Capillaries
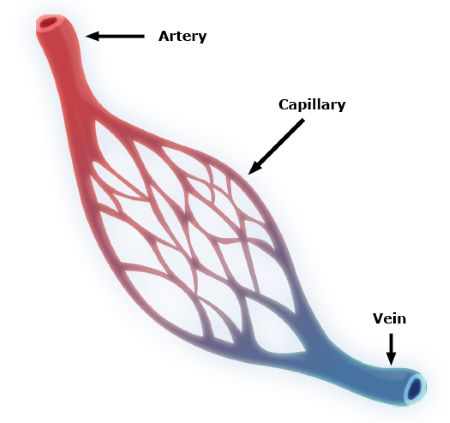
What is the smallest and most abundant form of blood vessel in the human body?
Capillary
The movement of embalming solution from intravascular to extravascular locations:
Fluid diffusion
Steps of fluid diffusion:
Hint: There are 3 steps
Embalming solution passes from the capillaries to the body tissues
The preservatives in the embalming solution come in contact with proteins in the body cells
The proteins of body cells are stabilized and the body is temporarily preserved
Consists of blood, tissue fluids, lymph, and some of the arterial solution:
Drainage
As much as what % of drainage can be arterial solution?
50%
The embalming solution that passes through the pores or walls of the capillaries and eventually embalms the cells
Stabilizes the body proteins and brings about temporary preservation
Retained arterial solution
What happens to arterial solution that remains in the body system?
It is pushed ahead into the venules and veins and is eventually drained from the body serves only to clear the vascular system of blood and can only embalm the walls of the vascular system.
Examples of embalming physical processes:
Filling the arterial system by forced injection under pressure
Control of drainage
Filtration through capillaries via pressure, passive transport processes of osmosis and dialysis
Examples of embalming chemical processes:
The arterial fluid itself
Preservatives that stabilize and produce new compounds (chemical preservation, sanitation)
Resistance within the blood vessels:
Intravascular resistances
Resistance outside the blood vessels
Extravascular resistance
This is needed to overcome resistances that interfere with arterial solution distribution:
Pressurized injection
The amount of pressure produced by an injection device to overcome initial resistance within the vascular system
Injection pressure
The amount of embalming solution injected in a given period, or the speed at which the embalming solution enters the body (usually measured by ounces per minute)
Rate of flow
The pressure needed to overcome vascular resistances of the body to distribute solution to all body areas
Ideal pressure
The rate of flow needed to achieve uniform distribution without distention of tissues
Ideal rate of flow
This book suggests a rate of - gallon(s) of solution over a — to —minute period, under a pressure of — to — pounds
1 gallon
10 to 15 minute
2 to 10 pounds
What is the center of arterial distribution?
The ascending aorta and the arch of the aorta
Supplies the right side of the head and right arm
Brachiocephalic artery
Supplies the left side of the head and face
Left common carotid
Supplies the left arm:
Left subclavian artery
The process where one substance takes up another substance:
Absorption
Assimilation of gas, vapor, or dissolved matter by the surface of a solid or liquid:
Adsorption
Concentrated, preservative embalming chemical:
Arterial fluid
The in-use solution composed of the concentrated embalming fluid:
Arterial solution
The movement of arterial solution from inside the vascular system:
Arterial solution diffusion
The movement of arterial solution from the point of injection throughout the arterial system and into the capillaries:
Arterial solution distribution
Small solutes that can pass through a semi-permeable membrane:
Crystalloid
Separation of substances in solution by the difference in their rates of diffusion through a semipermeable membrane:
Dialysis
Passage of some components of the injected embalming solution from an intravascular to a extravascular location:
Diffusion
Extravascular settling of fluids by gravitational force to the dependent areas of the body:
Gravity filtration
Solution having a greater concentration of a dissolved solute then the solution with which it is compared:
Hypertonic solution
Solution having a lesser concentration of a dissolved solute then the solution with which it is compared:
Hypotonic solution
Fluid in the supporting connective tissue surrounding body cells:
Interstitial fluid
Passage of solvent from a solution of lesser to one of greater solute concentration:
Osmosis
Method by which solutes and/or solvents cross through a membrane with no energy provided by the cells of the membrane:
Passive transport system
Passage of embalming solution through the capillary wall to diffuse with the interstitial fluids by application of positive intravascular pressure:
Pressure filtration
Dilution attained as the embalming solution is mixed in the embalming machine:
Primary dilution
Leftover embalming fluid that remains within a body after the embalming process:
Retained embalming solution
Dilution of the embalming fluid by the fluids of the body, both vascular and interstitial:
Secondary dilution
Separation of substances in solution by the difference in their rates of diffusion:
Semipermeable membrane
Substance that is dissolved in a solution:
Solute
Liquid holding another substance in solution:
Solvent
The treatment of disease with chemical agents and drugs:
Chemotherapy
Where did the Chemotherapy Era originate from?
A.) Germ theory
B.) Magic bullet
C.) Spontaneous general
D.) Binary fission
Magic bullet
Many chemical agents are nephrotoxic and therefore can cause the breakdown of what organ function?
(Remember what organ relates with the term nephron?)
Kidney
These are the main organs responsible for elimination of nitrogenous wastes:
A.) Lungs
B.) Ovaries
C.) Kidneys
D.) Spleen and gallbladder
Kidneys
A large proportion of the formaldehyde in the embalming fluid will be — when it encounters the nitrogenous wastes in the body:
A.) Neutralized
B.) Reduced
C.) Oxidized
D.) Diluted
Neutralized
All chemotherapeutic agents are…
A.) Tasty
B.) Phagocytic
C.) Nephrotoxic
D.) Toxic
Toxic
What is the main detoxification center of the body?
A.) Heart
B.) Liver
C.) Brain
D.) Urinary bladder
Liver
What is is called when formaldehyde is neutralized?
A.) Hexamethylene
B.) Sodium phosphate
C.) Methanal
D.) Methyl glycerin
Hexamethlyene
This term means having an affinity for metallic ions:
A.) Saponification
B.) Catabolism
C.) Calcinification
D.) Chelating
Chelating
When a enzyme reacts with a substrate what does it release?
A.) Phosphate
B.) Lipids
C.) Amino acids
D.) Calcium
Phosphate
These drugs decrease the permeability of the cell membrane:
A.) Cytotoxic
B.) Kanamycin
C.) Corticosteroids
D.) Gentamicin
Corticosteroids
These drugs act directly on the tumor cells to bring about their death:
A.) Antimetabolite
B.) Cytotoxic
C.) NKCs
D.) Penicillin
Cytotoxic
These drugs substitute for an essential metabolite required by the cancer cell for growth:
A.) Growth hormone drugs
B.) Saline
C.) Heparin
D.) Antimetabolite
Antimetabolite
The average body contains how many liters of blood?
6 liters
How many liters of LIQUID is estimated to be in the average body?
41 liters
A body that was treated with antibodies may have a lot of this present:
A.) Bacteria
B.) Fungi
C.) Prions
D.) Protozoa
Fungi
A body presents small wads of greenish “cotton” in its drainage what type of medication could cause these?
A.) Tranquilizers
B.) Sedatives
C.) Antibiotics
D.) Stimulants
Antibiotics
The postmortem evacuation of any substance from any external orifice of the body as a result of pressure:
Purge
True tissue gas is caused by:
(Hint: It’s a bacteria)
Clostridium perfringens
The postmortem loss of moisture occurs as body fluids gravitate to dependent areas and the elevated regions have reduced moisture
Surface dehydration
What does HCHO do to tissues?
Dries them
When trying to contain moisture content? Should you use hypotonic or hypertonic solution?
Hypotonic
(Hypo is going to make the cells swell)
Warm water — fluid reaction
Increases or decreases?
Increase
Abnormal collection of fluid in the tissue spaces, serous cavities, or both
edema
Does edema of the cavities dilute arterial solution?
No
Does edema of the cavities dilute cavity fluid?
Yes
What injection type is recommended for edematous tissues?
Restricted cervical injection
Edema of the abdominal cavity:
Ascites
Edema present in the space between the wall of the thoracic cavity and the lungs:
Hydrothorax
Edema of the scrotum:
Hydrocele
When edematous fluid fills the cranial cavity during fetal development:
Hydrocephalous
Inner lining of the arteries:
A.) Tunica advetitia
B.) Tunica media
C.) Tunica intima
D.) Lumen
Tunica intima
This is the middle lining of the arteries:
A.) Tunica media
B.) Tunica intima
C.) Tunica adventitia
D.) Lumen
Tunica media
This is the outer lining of the arteries:
A.) Tunica media
B.) Tunica intima
C.) Tunica adventitia
D.) Lumen
Tunica adventitia
What is the cavity of the artery?
A.) Tunica media
B.) Tunica intima
C.) Tunica adventitia
D.) Lumen
Lumen
What artery is usually affected by atherosclerosis:
Femoral artery
An abnormal color in or on the skin of the human body:
Discoloration
In embalming, how are discolorations classified?
Time at which they appeared and cause
What are the two classifications of discolorations?
Antemortem and postmortem
A discoloration that was present during life and remains after death is classified as a…
Antemortem discoloration
This type of discoloration results from changes in the blood composition, content, and location
Blood discoloration
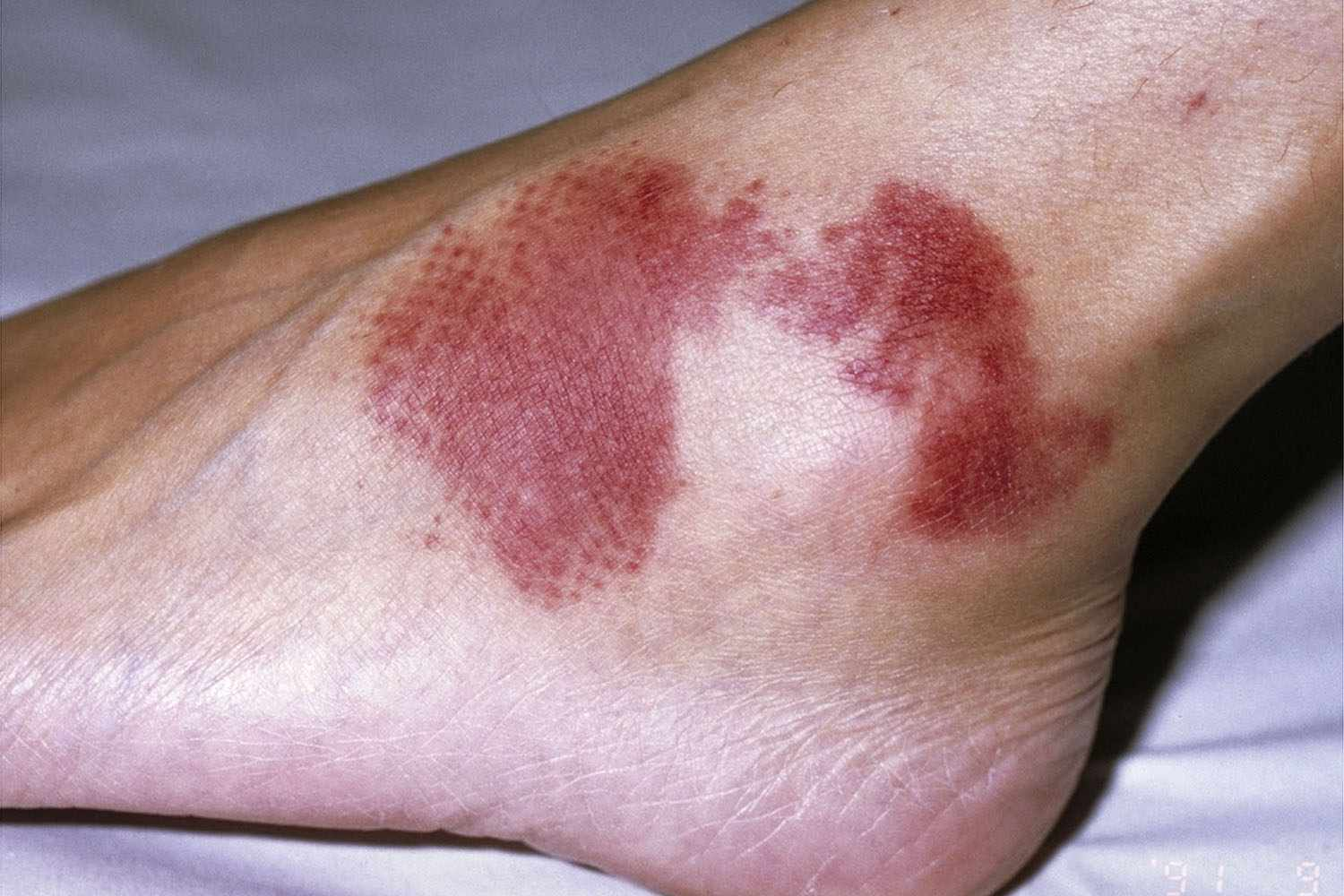
This type of discoloration is an antemortem discoloration resulting from administration of drug or chemotherapeutic agents:
Drug/therapeutic discoloration
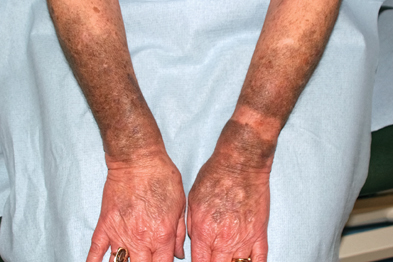
Antemortem discolorations that occur during the course of certain diseases:
Pathological discoloration
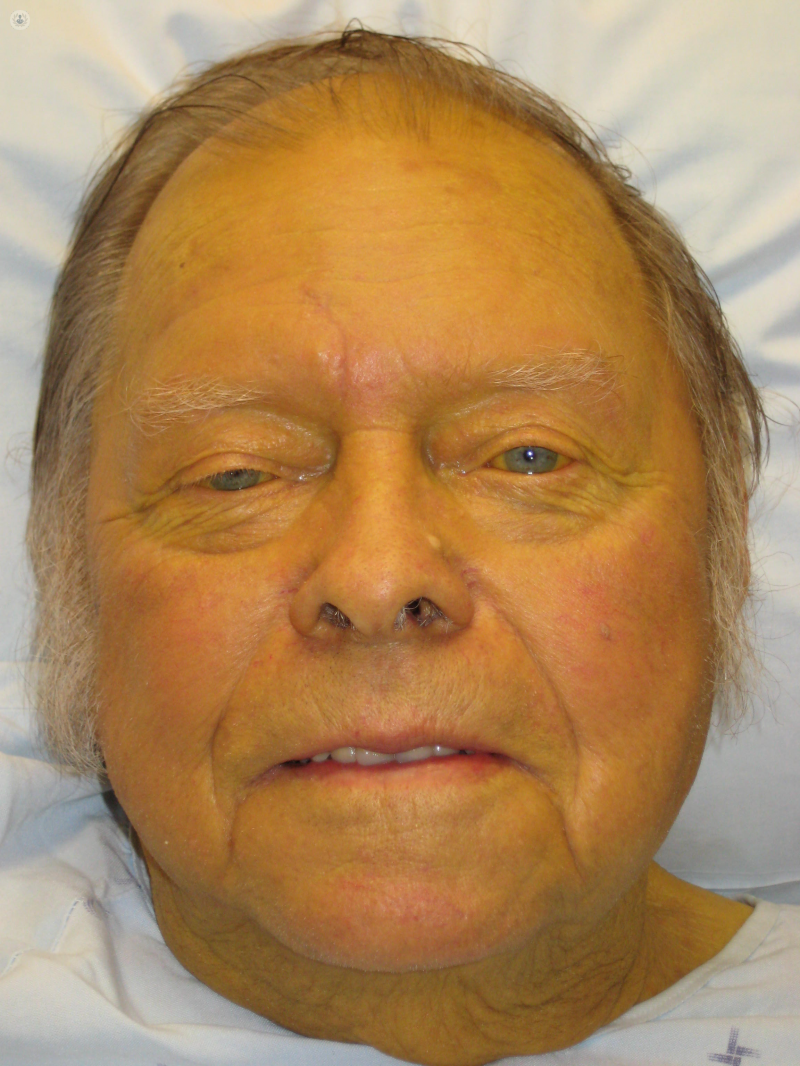
This discoloration can be antemortem or postmortem that can occur prior to or during embalming as the result of the deposit matter on the body surface:
Surface discoloration
This is a postmortem discoloration brought about by the action of bacterial enzymes on the body tissues:
Decomposition discoloration
What color is hypostasis of the blood?
blue-black
What color is carbon monoxide poisoning?
Cherry red
When dealing with discolorations cause by drugs, these vessels breakdown and cause ecchymosis and purpura:
Capillaries
Wet gangrene brings on this color of discoloration:
red to black
Dry gangrene brings on this color of discoloration:
Dark red-brown to black
What color discoloration does Addison’s Disease bring about?
Bronze
What discoloration does leukemia bring about?
A.) Gangrene
B.) Hypostasis
C.) Petechiae
D.) Hyperemia
Petechiae
Intravascular blood discolorations respond best to what embalming treatments?
Hint: There’s two
Arterial injection and blood drainage
How long does livor mortis begin to take place?
20 minutes after death
How long does postmortem stain take to set in?
6 hours after death
What color discoloration can formaldehyde cause?
Gray