Anatomy and Physiology - Respiratory System
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
What is the overall function of the respiratory system?
To exchange gases between the air and the body
How does the structure and function of the pleural membrane support efficient lung function?
Lungs are attached to the surface of the thoracic cavity by the pleural membrane and surfactant allows the lungs to stick to the ribs. This allows the lungs to expand to take air in.
How does the drop in pH relate to the body’s respiratory response?
A drop in pH occurs when there is more carbon dioxide present. This causes the medulla oblongata to send signals to increase respiration rate.
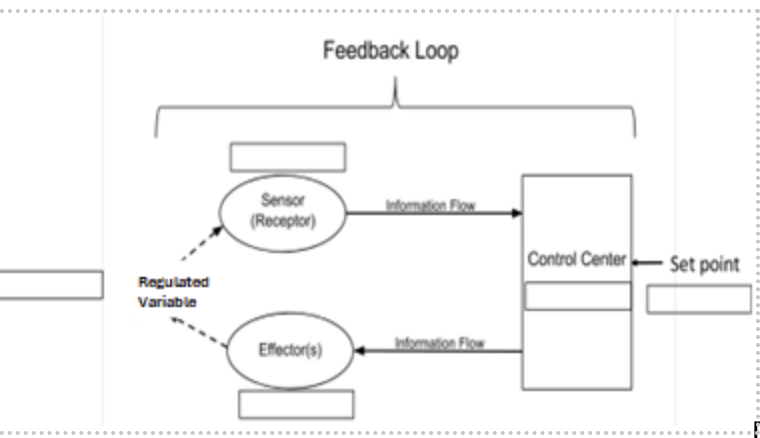
Regulated Variable:
Amount of CO2
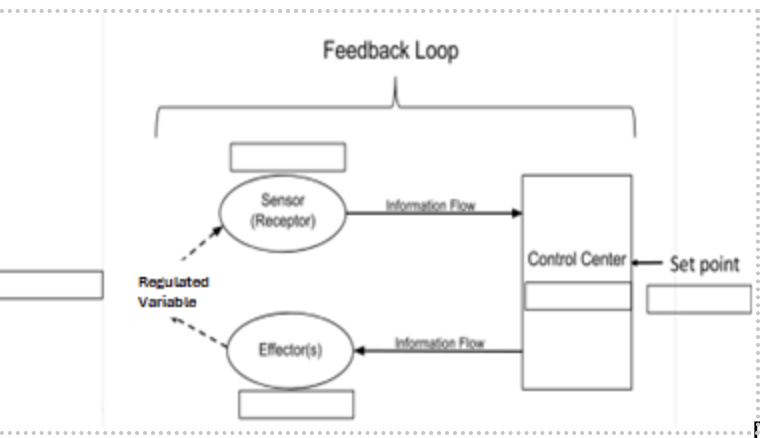
Sensor (receptor):
Cell receptors in medulla
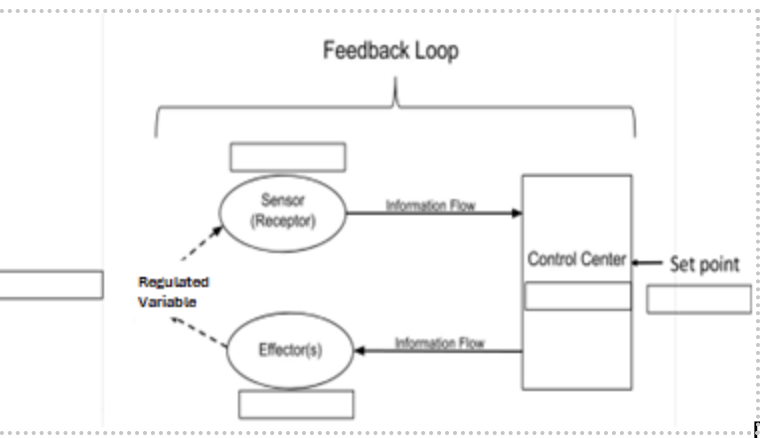
Control Center:
Medulla Oblongata
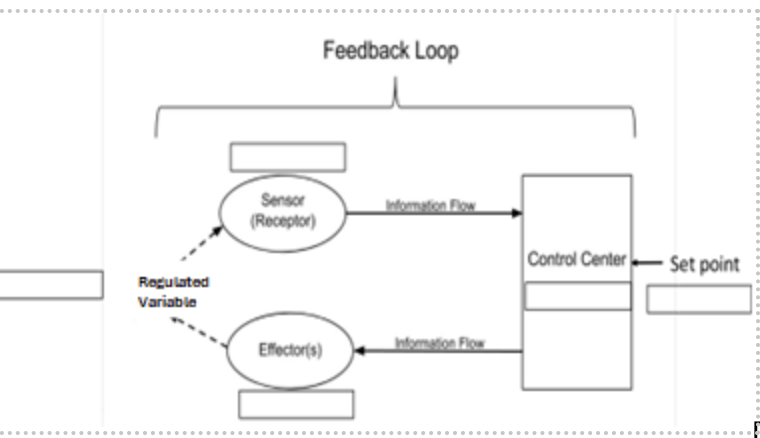
Effector(s):
Diaphragm and intercostal muscles
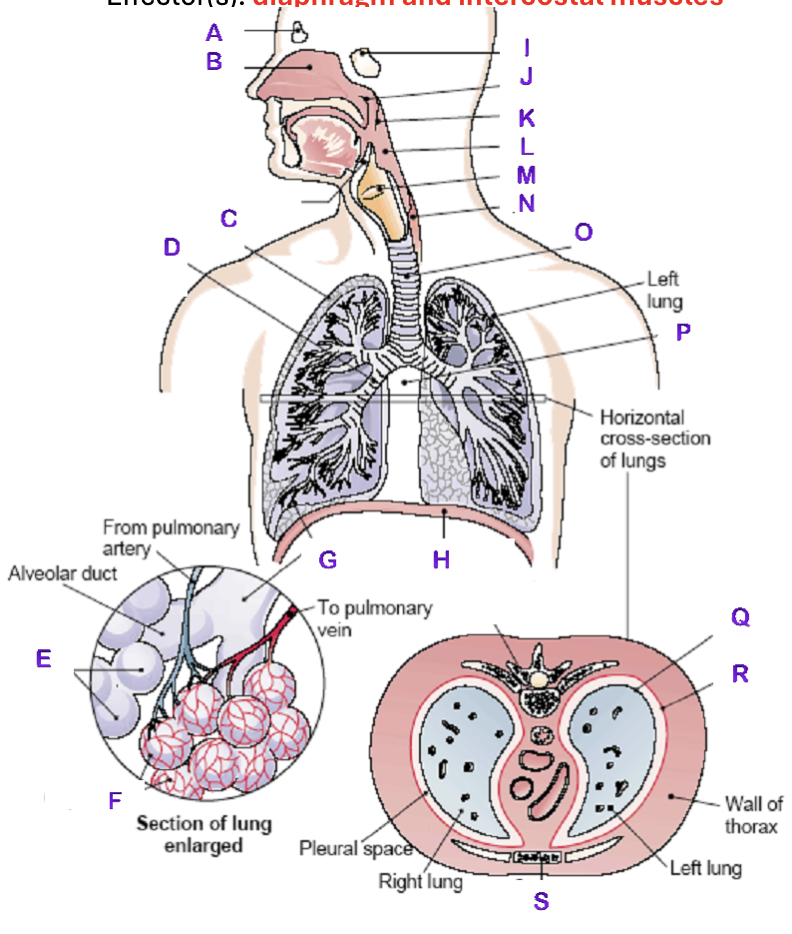
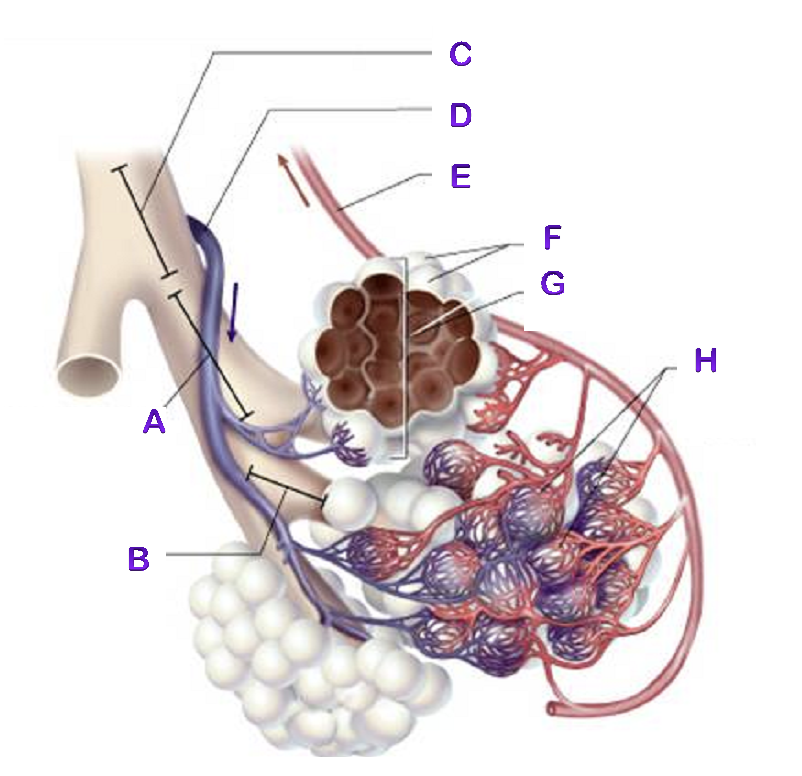
A?
Frontal Sinus
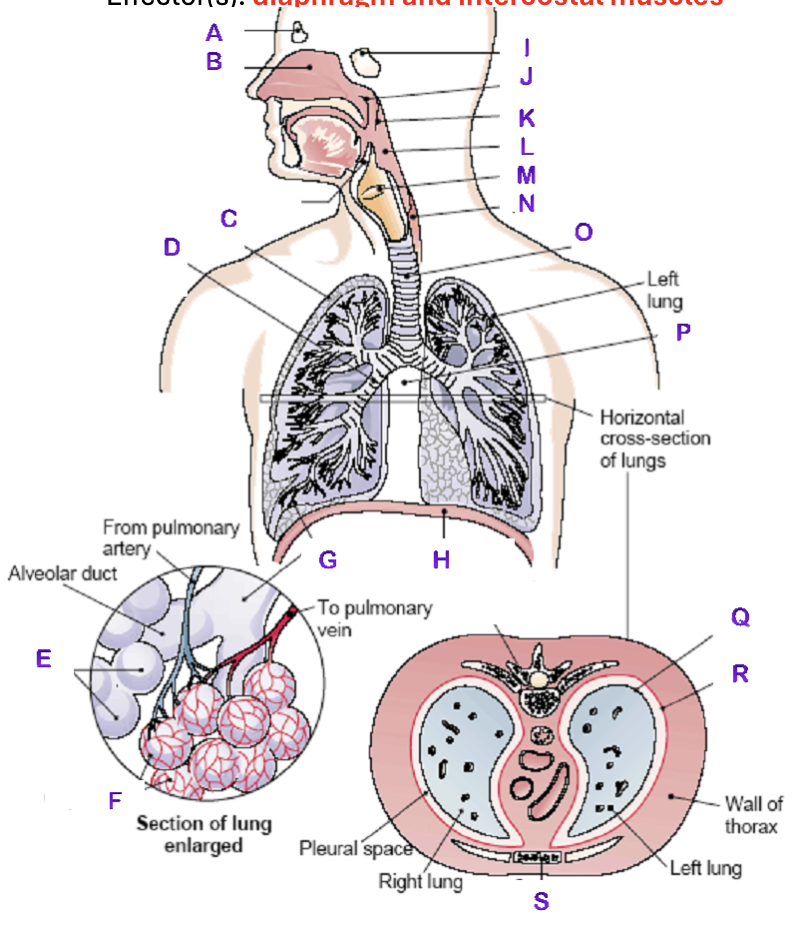
B?
Nasal Cavity
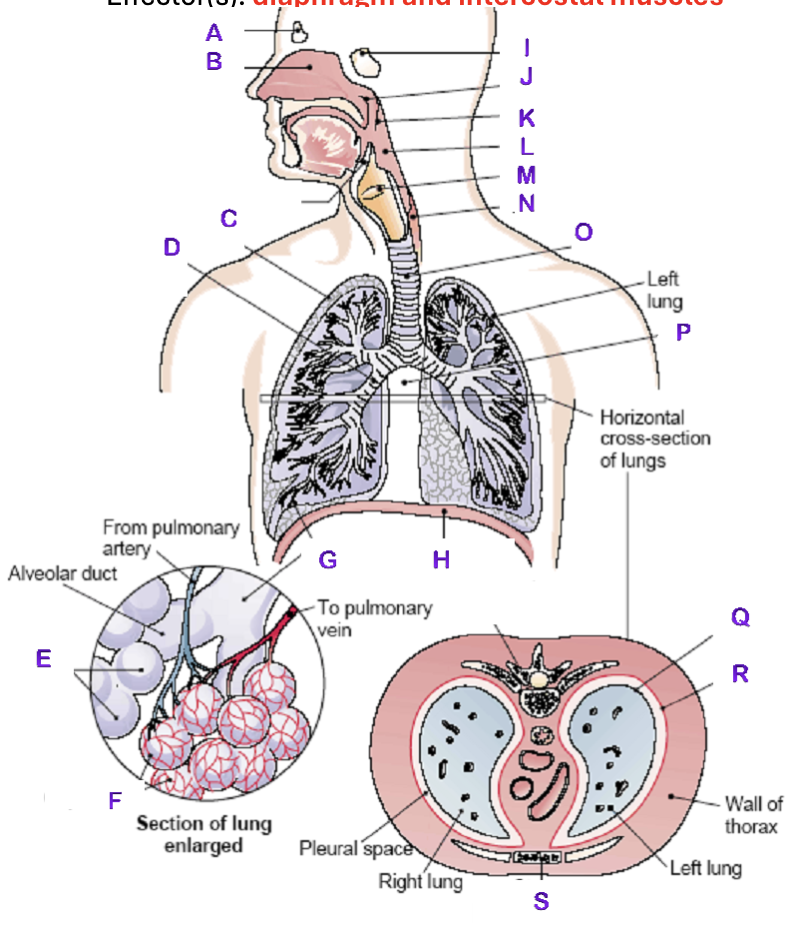
C?
Right Lung
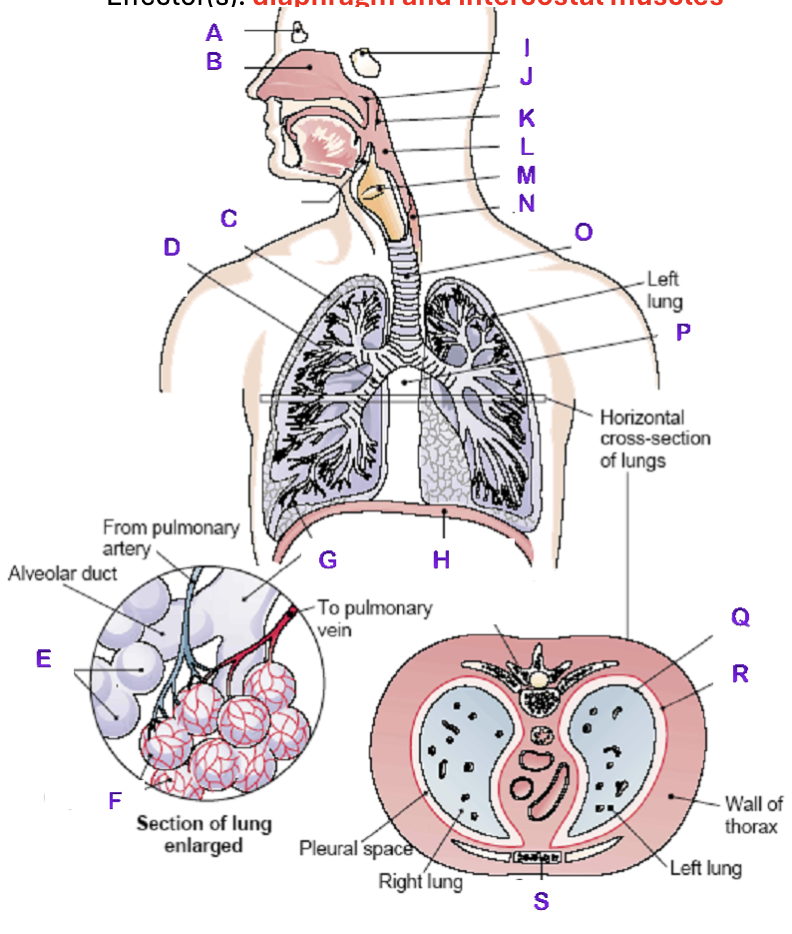
D?
Right Bronchial tree
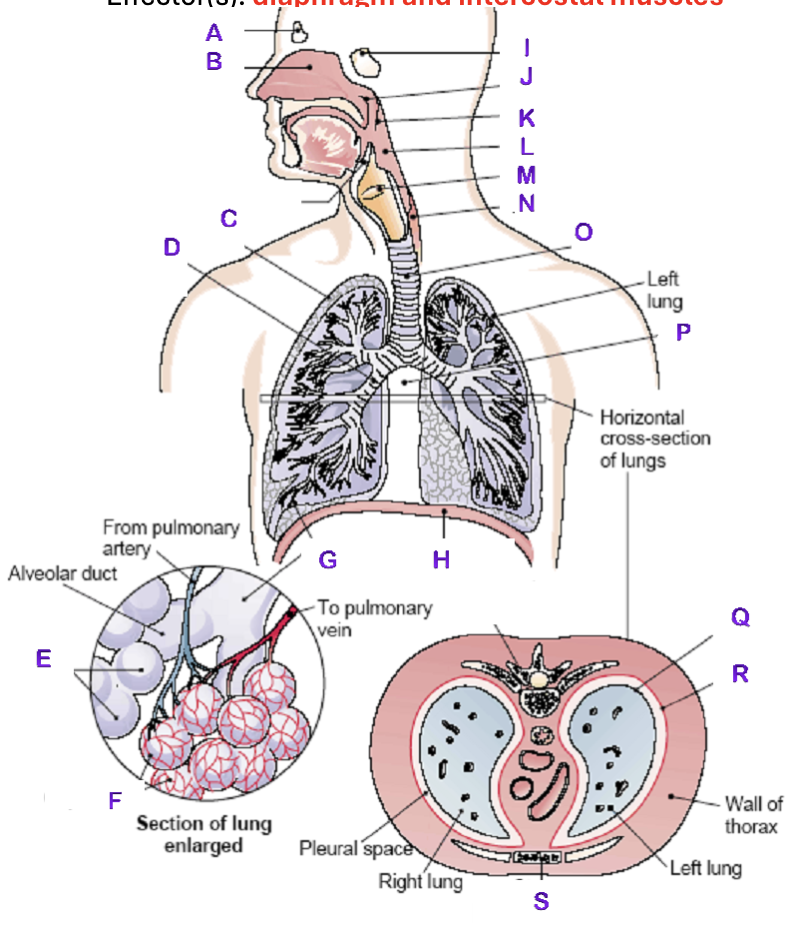
E?
Alveoli
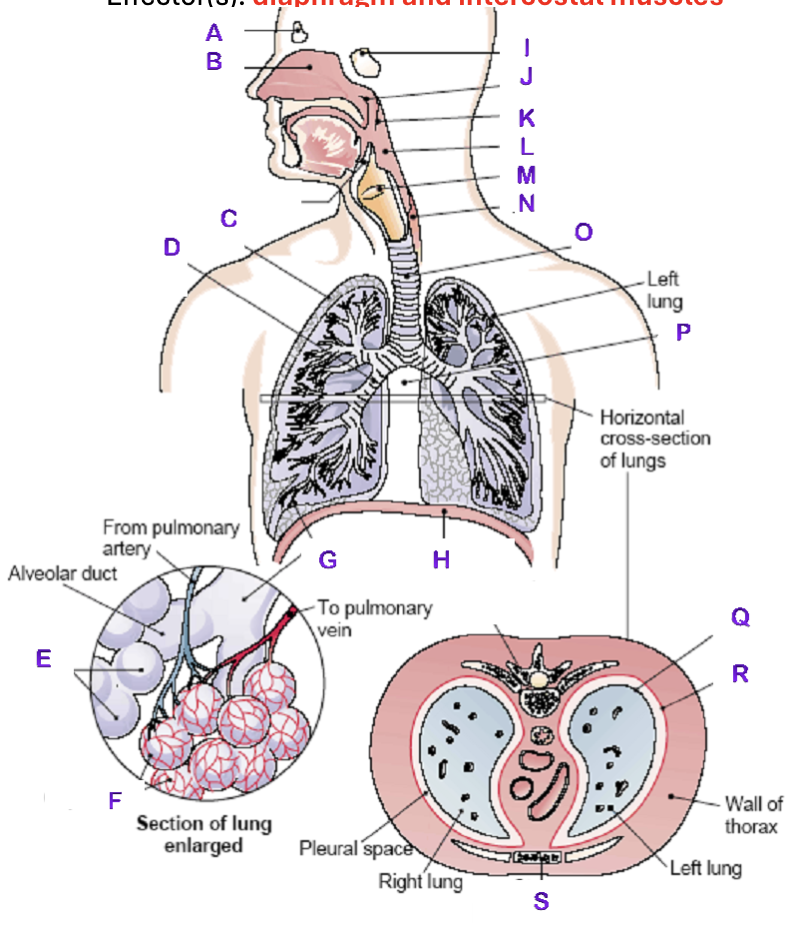
F?
Capillaries
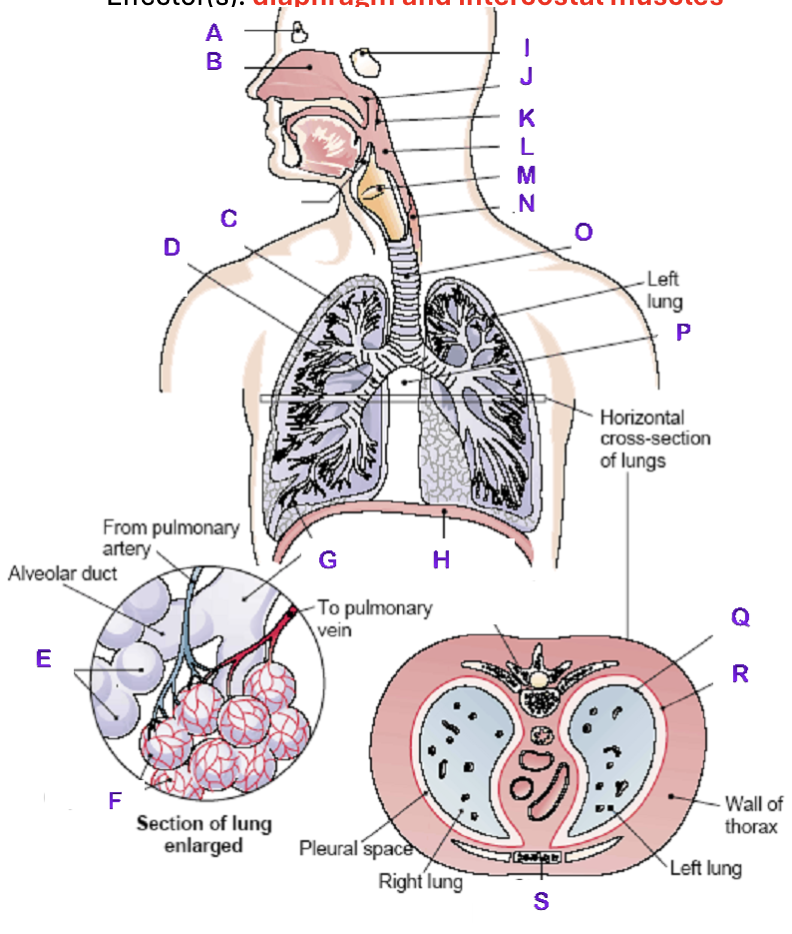
G?
Terminal Bronchiole
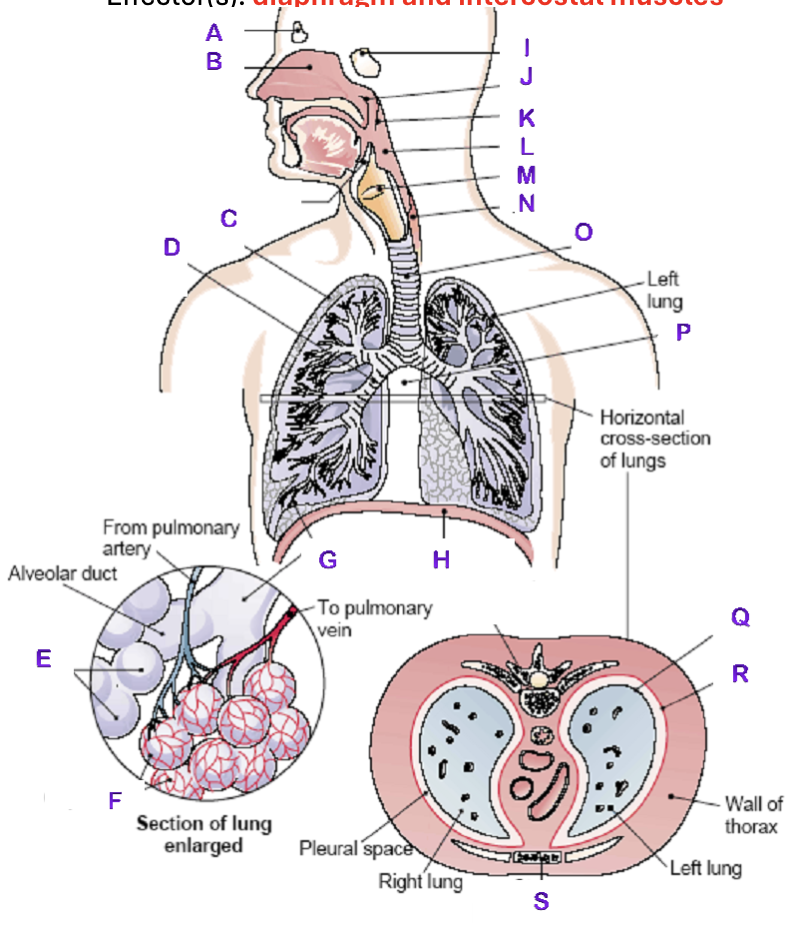
H?
Diaphragm
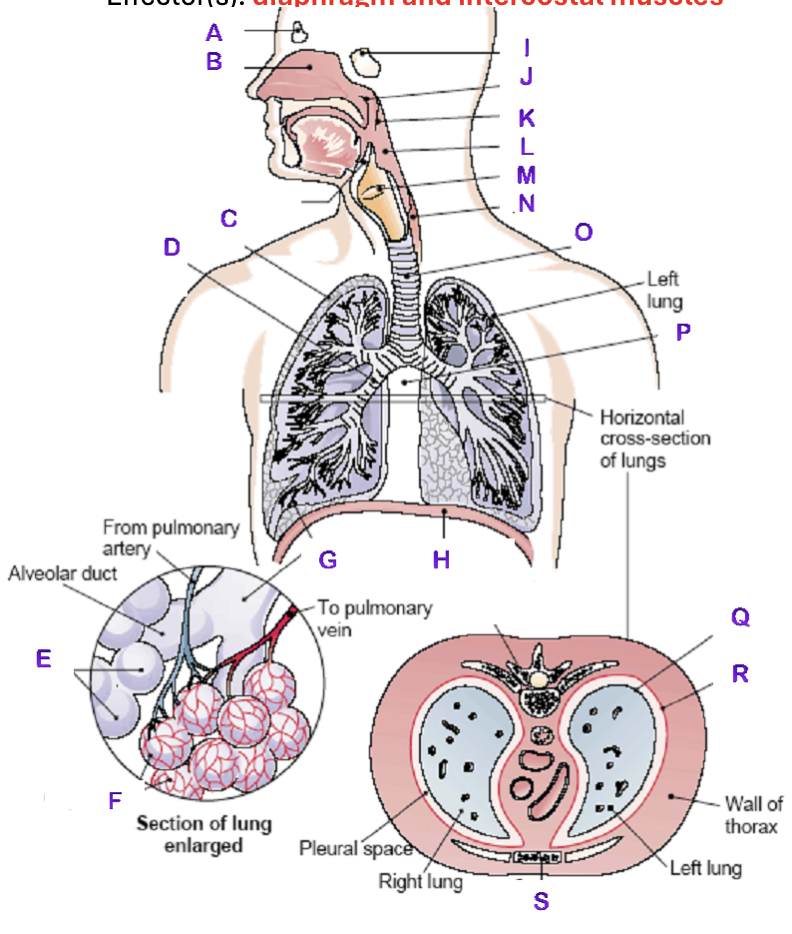
I?
Sphenoidal Sinus
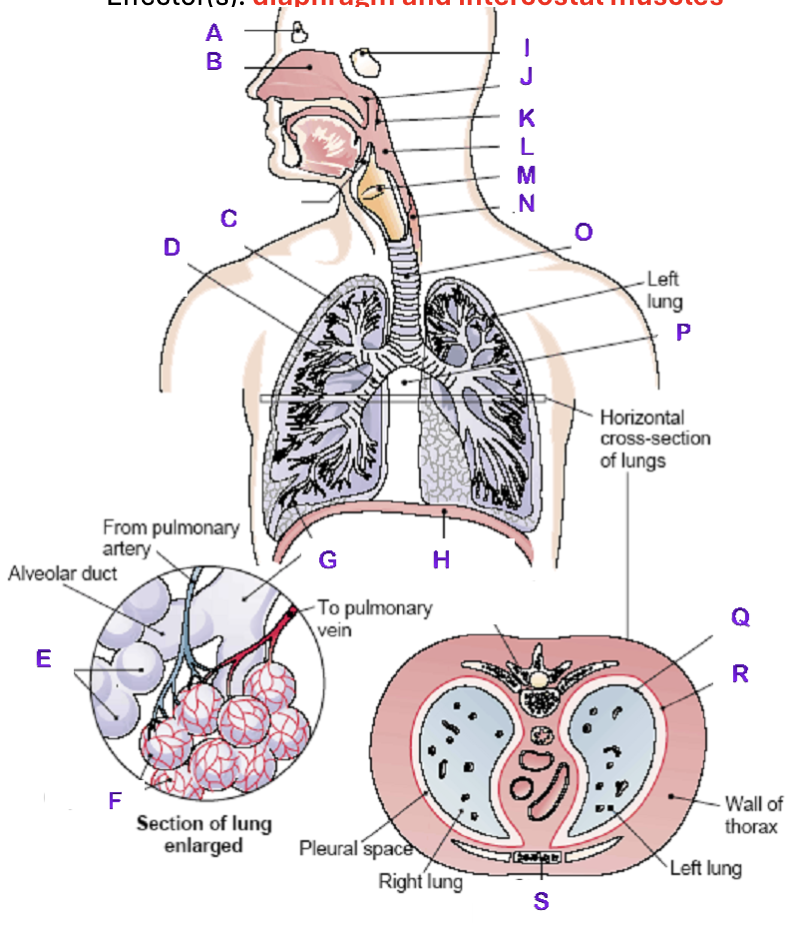
J?
Nasopharynx
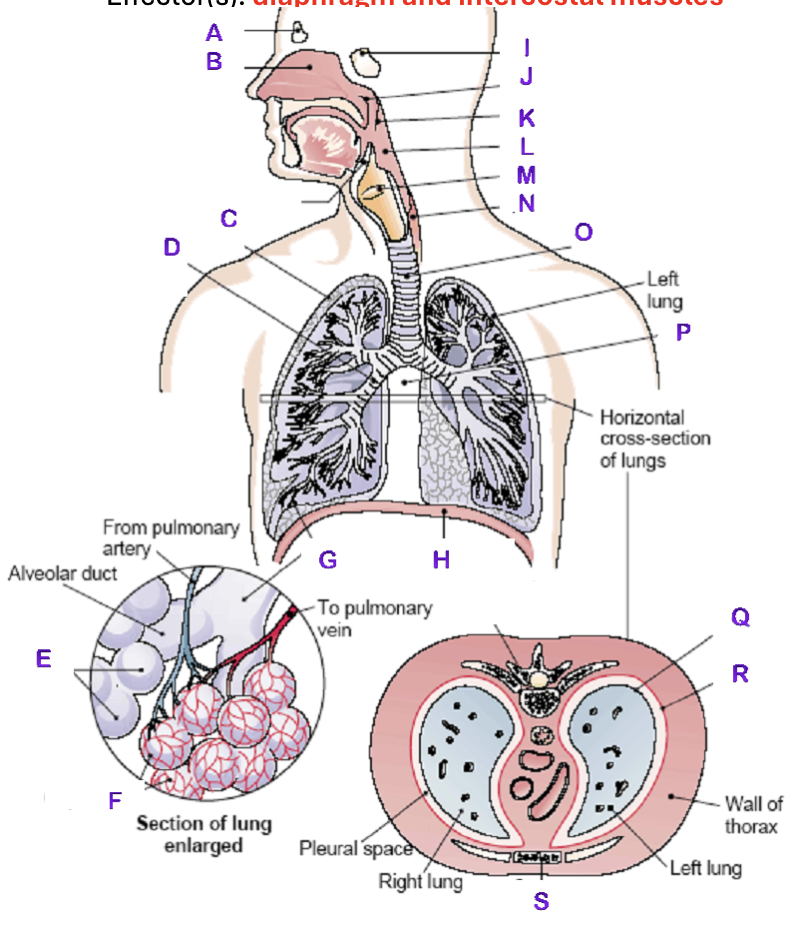
K?
Uvula
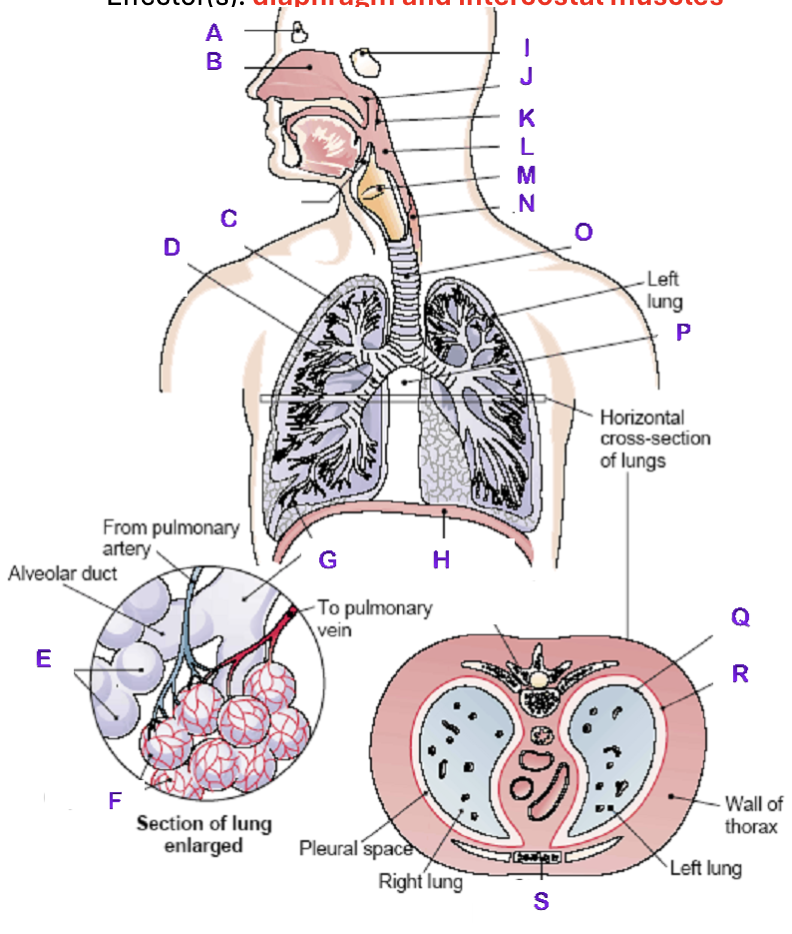
L?
Laryngopharynx
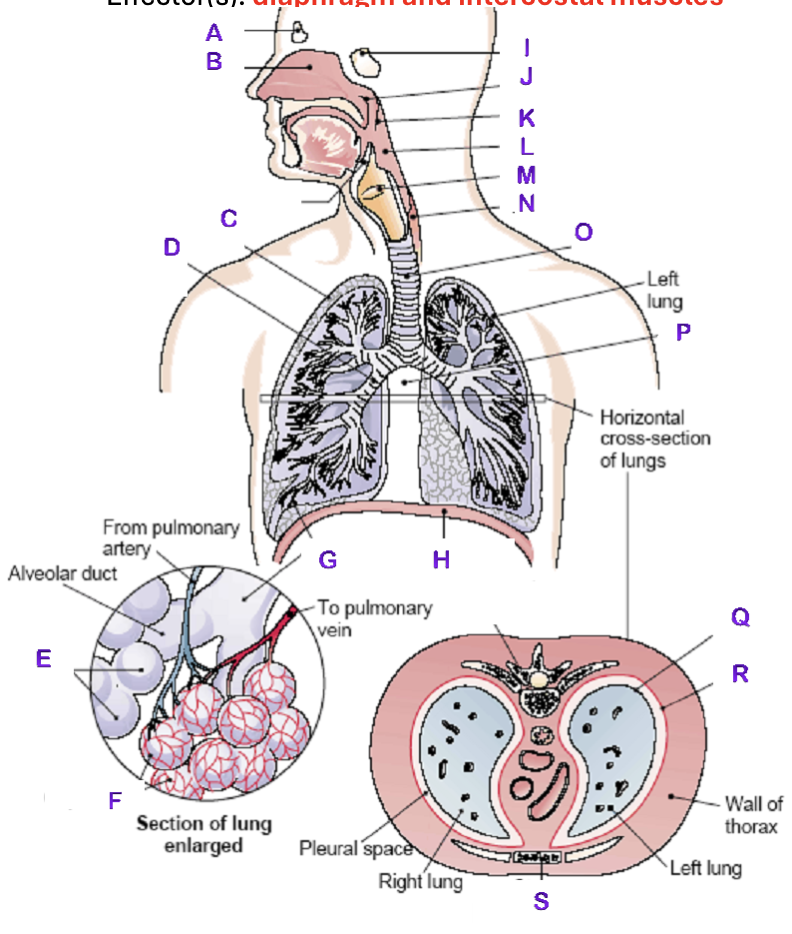
M?
Epiglottis

N?
Esophagus
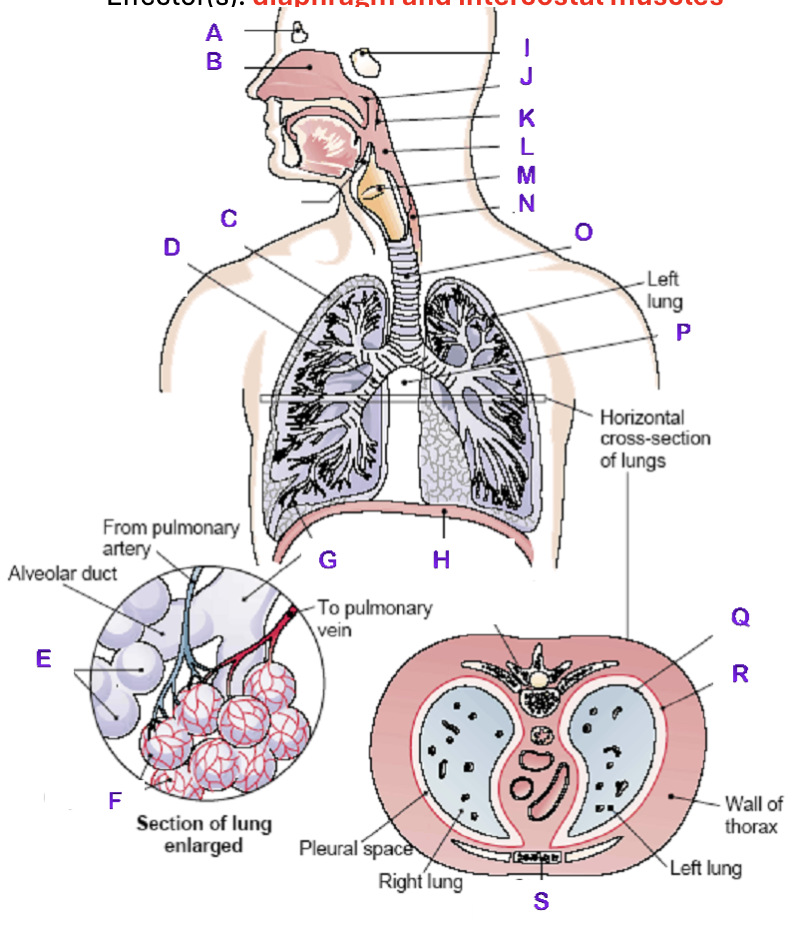
O?
Trachea
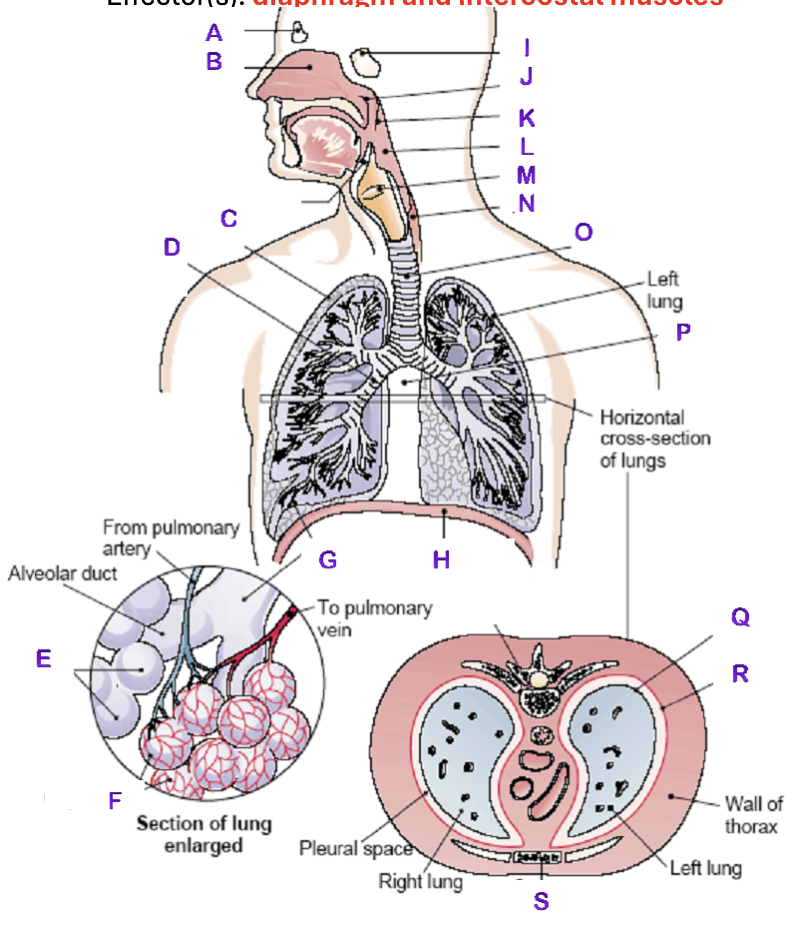
P?
Mediastinum (heart)
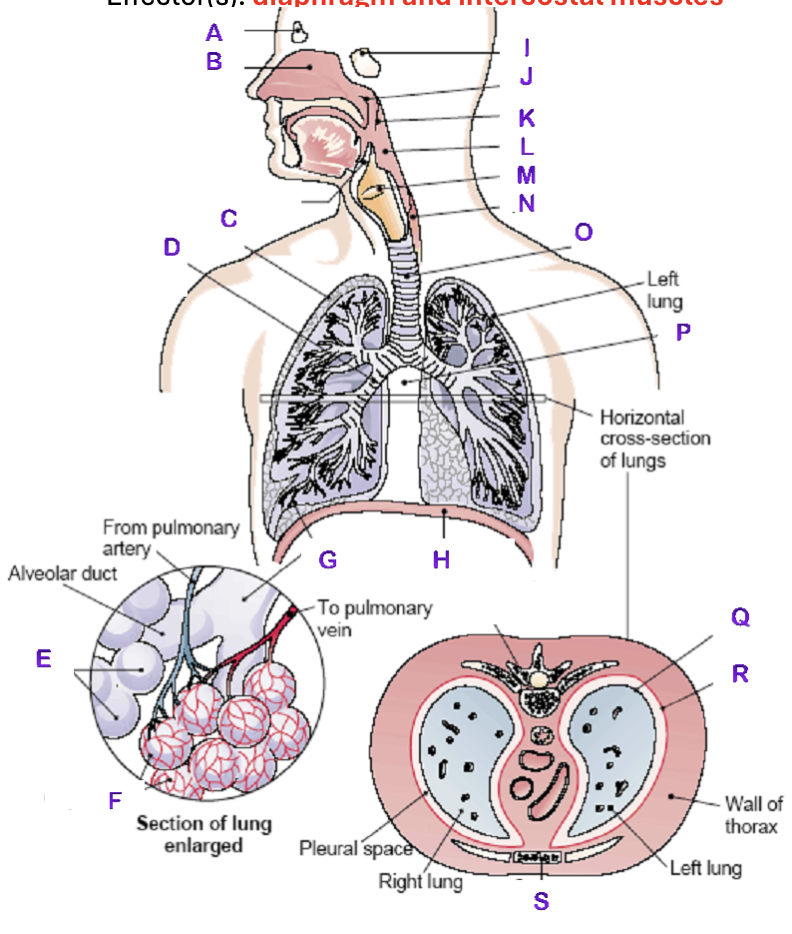
Q?
Visceral Pleura
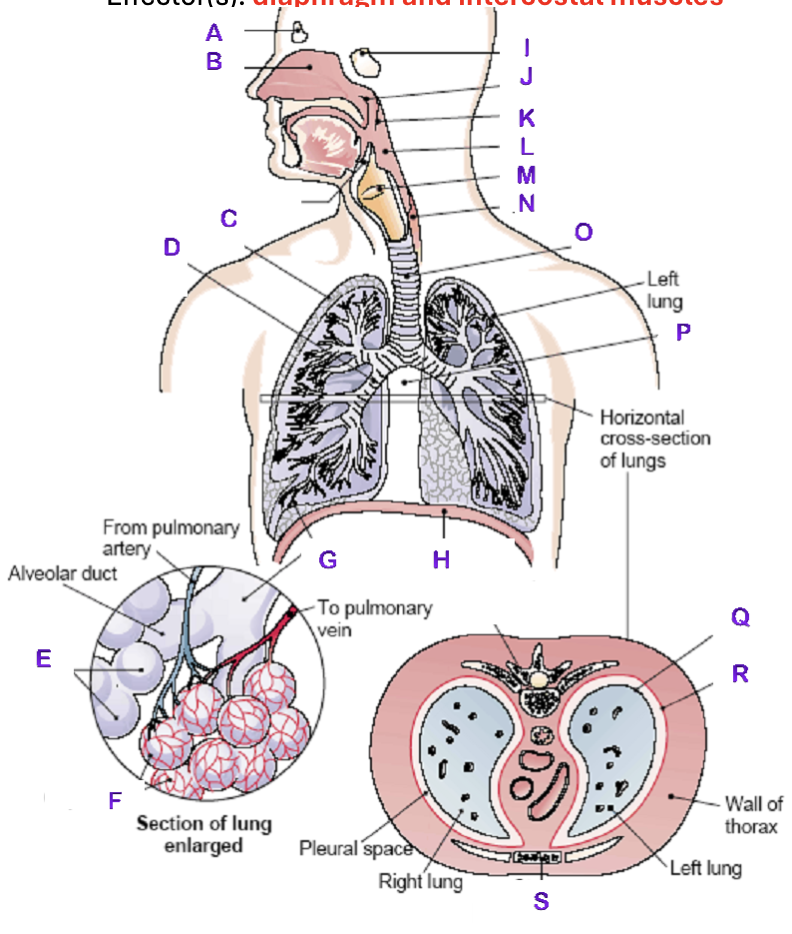
R?
Parietal Pleura
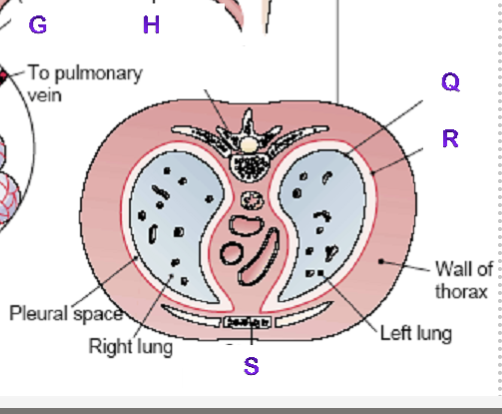
S?
Sternum
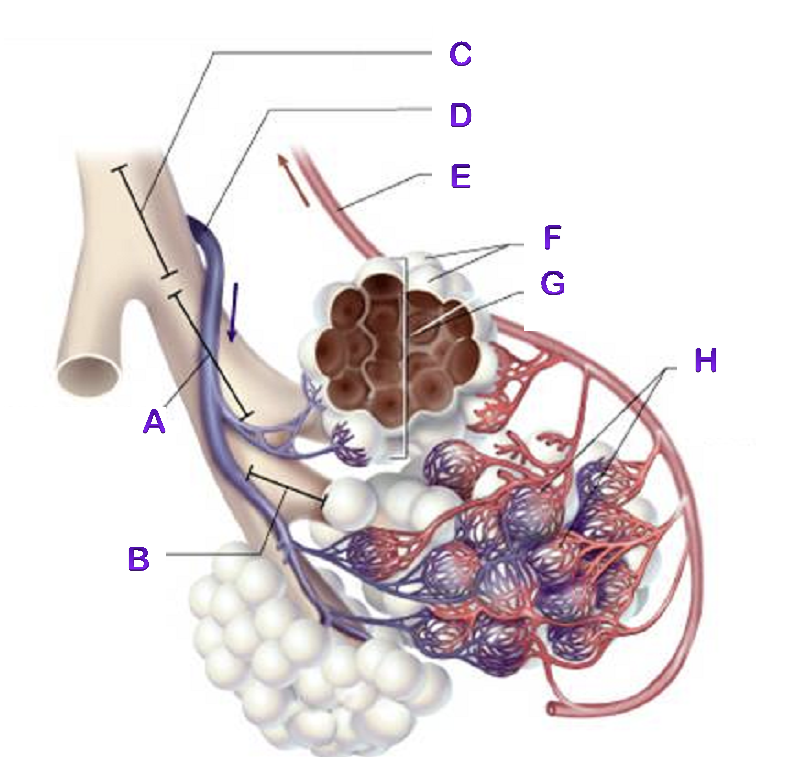
A?
Bronchiole
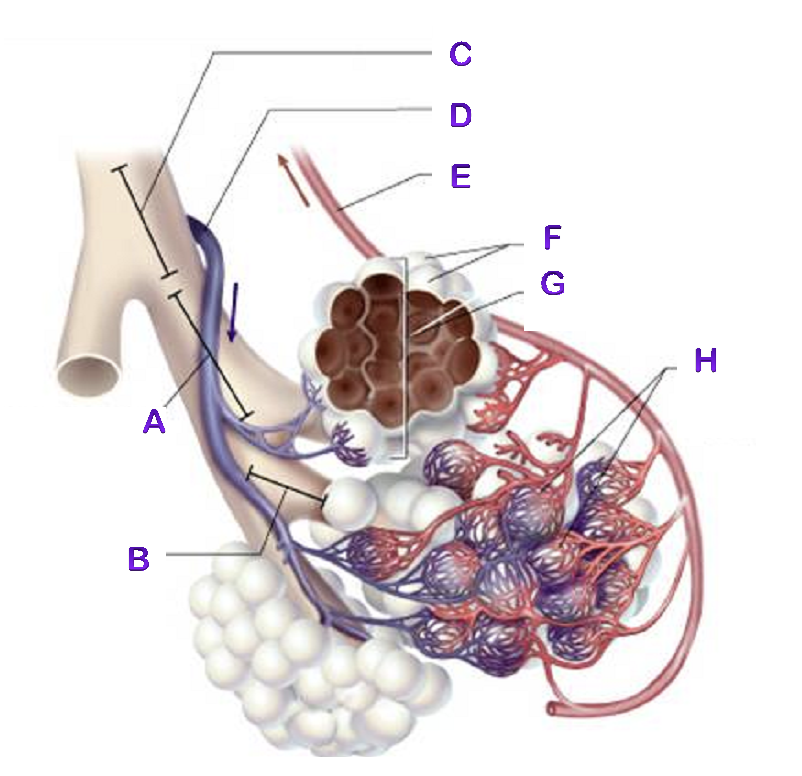
B?
Terminal Bronchiole
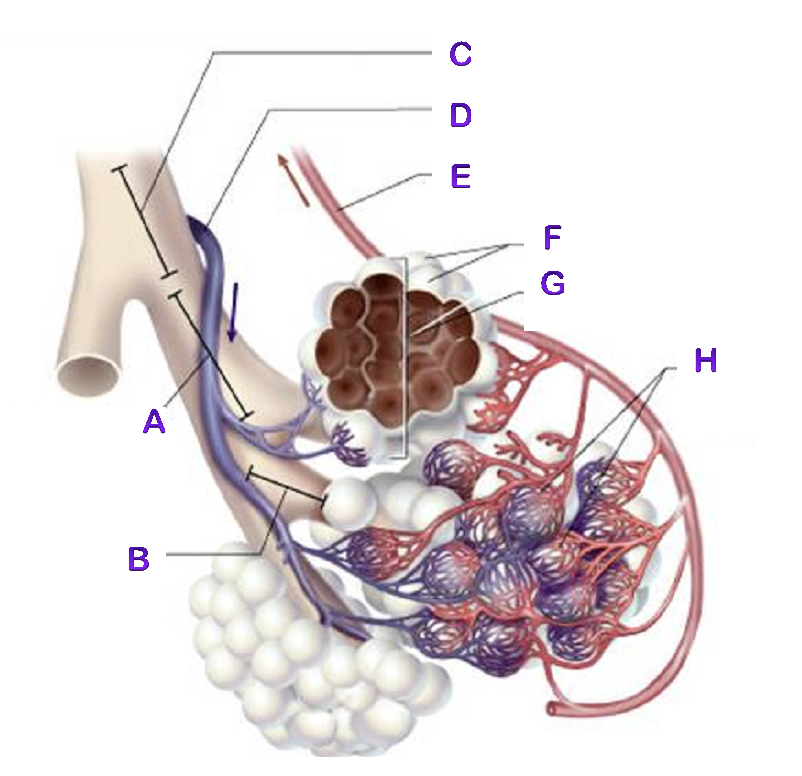
C?
Terminal Bronchiole
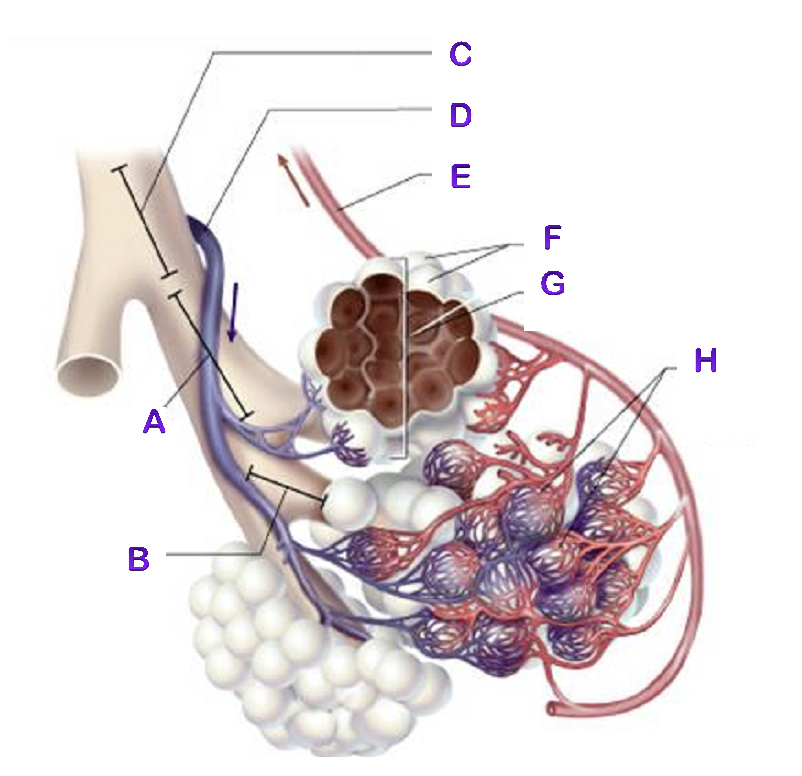
D?
Pulmonary Artery
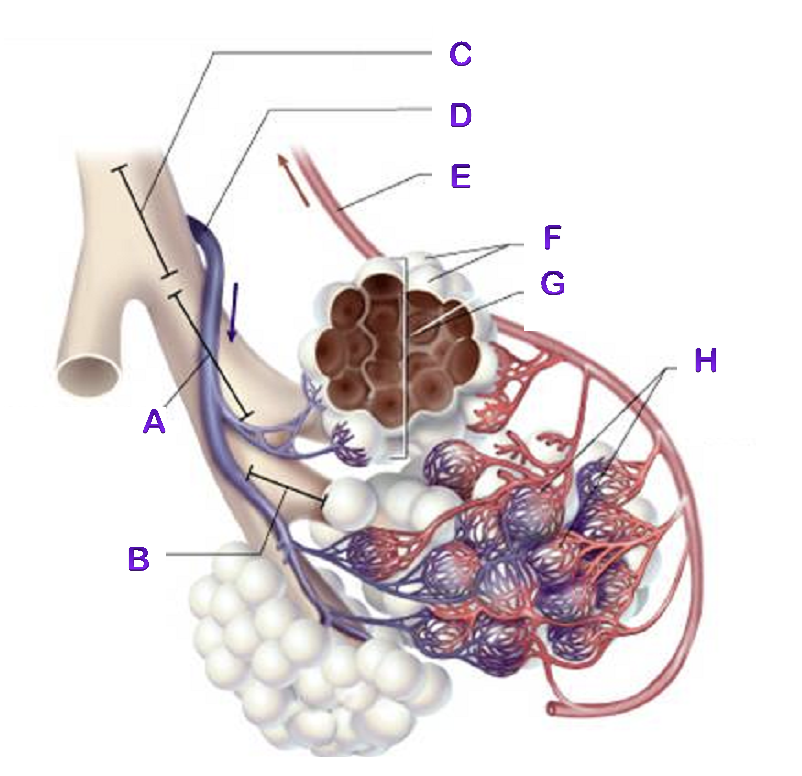
E?
Pulmonary Vein
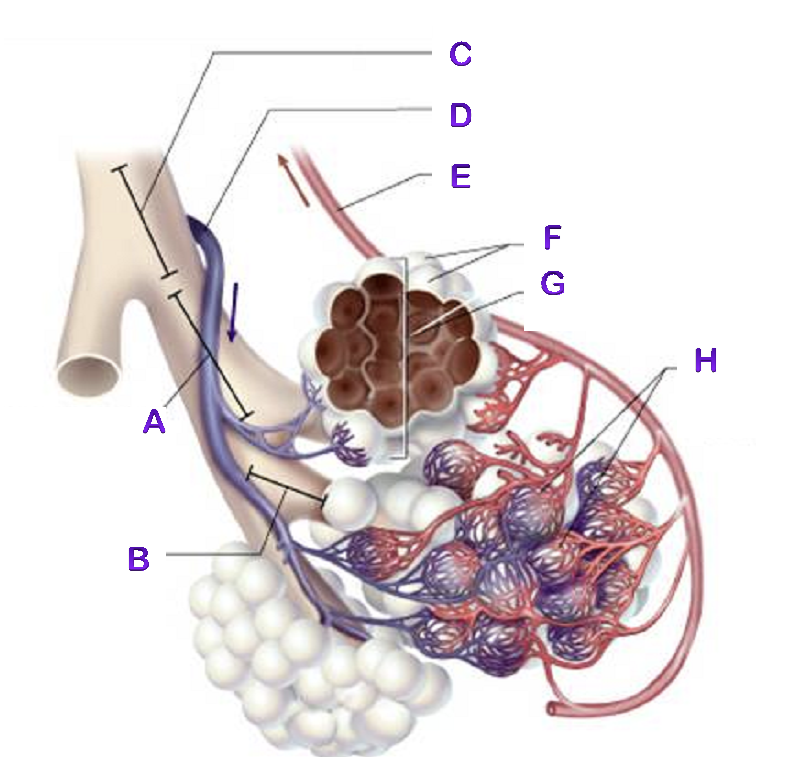
F?
Alveoli
G?
Alveioli Sac
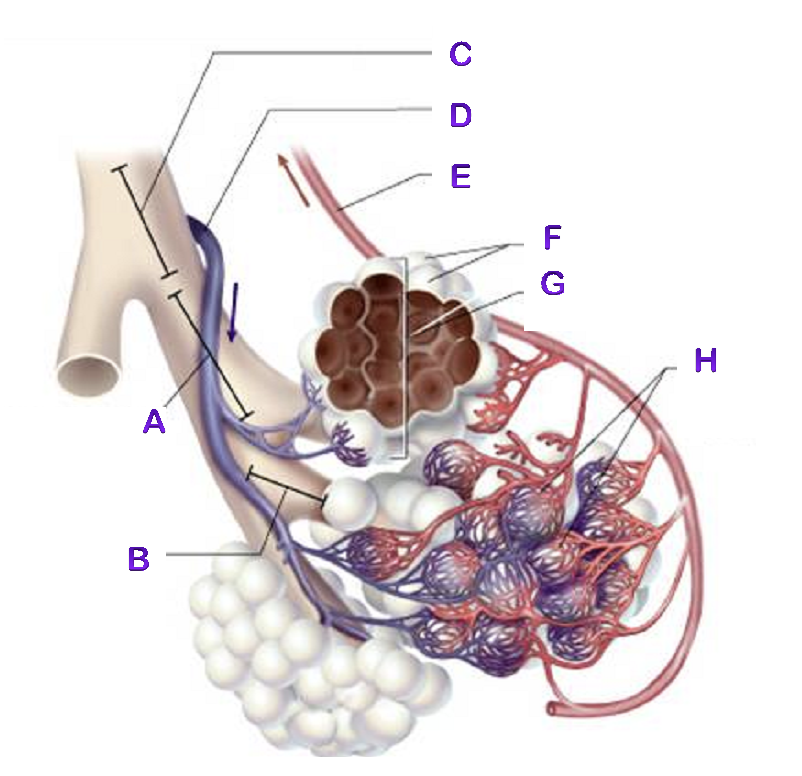
H?
Capillaries
1a. The ___ contracts, pulling the ribs up
Intercostal Muscles
1b. After the intercostal muscles contract and ribs are pulled up, the ___ contracts and moves down, pulling air into the body through the mouth/pharynx
diaphragm
2a. Air passes through the
Nasopharynx or oral pharynx
2b. After air passes through the nasopharynx or oral pharynx, air passes through the _____ which prevents food from entering the trachea
Epiglottis
4a. Air moves down the ___ which branches off into the right and left bronchi
Trachea
5a. Right and left bronchi continue to branch, much like an upside down tree, into smaller limbs called
bronchioles
6a. The bronchioles end in tiny air sacs called ___ where gas exchange will occur
Alveoli
7a. Alveoli have extremely thin membranes surrounded by ___ from the cardiovascular system
Pulmonary capillaries
An adult has approximately how many avleoli?
300 million
8a. Oxygen that has been pulled through the alveoli diffuse through the alveoli membrane and into the ___ to be circulated throughout the body for cellular respiration
capillaries
9a. Carbon dioxide that has been created by the body through cellular respiration is brought by the ___ to the alveoli and diffuses into the alveoli
10a. The ___ relaxes, moving up and causing the air to be exhaled
Diaphragm
Moves down, and pulls air into the body through mouth and nostrils on inhale
Diaphragm contracts
Moves, and causes air to move OUT of the nose and mouth on exhale.
Diaphragm relaxes
Gas exchange between the lungs and the blood capillaries occur at the ____.
Alveoli
Contracts, moves down, and pulls air into the body through mouth and nostrils
Diaphragm on inhale
Contract, pull the ribs up and pull air into the body .
Intercostal muscles on inhale
Relaxes, moves up, and causes air to move OUT of the nose and mouth.
Diaphragm on exhale
Relax, let the ribs relax, and allow air to exit the system.
Intercostal muscles on exhale
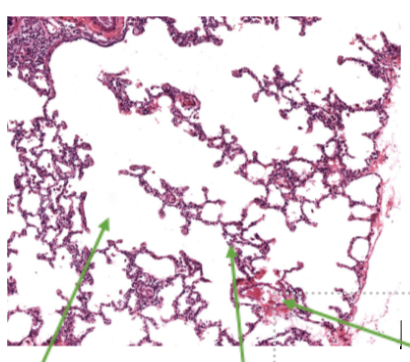
Green 1
Alveoli
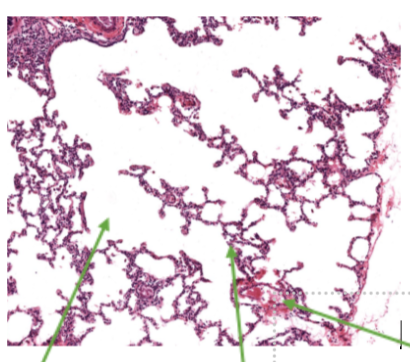
Green 2
Lung Cells
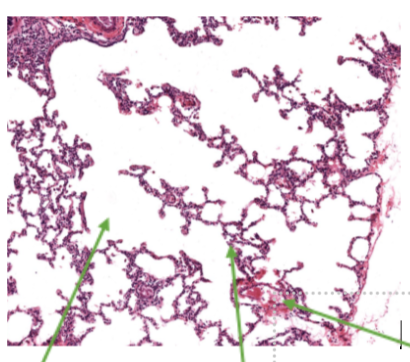
Green 3
Capillaries
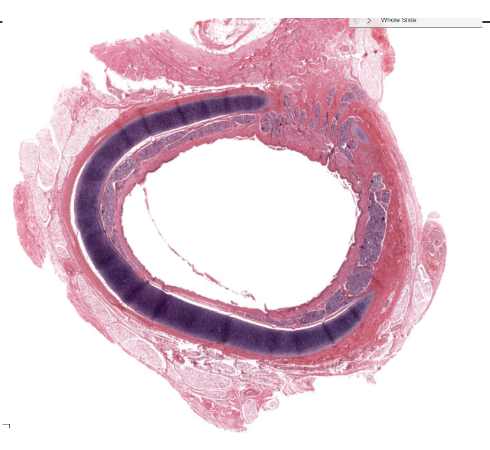
What is this?
Trachea
What makes up the rings of the trachea?
Hyaline cartilage
Progressive disease that makes it more difficult to breath; includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis
Cough, infections, dyspnea, wheezing, fatigue
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder (COPD)
Alveoli become weak and lose ability to stretch
Dyspnea (shortness of breath or trouble breathing), chest pain, cough, wheezing
Emphysema
Bacterial infection by Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Cough with blood or mucus, fatigue, fever, chills, night sweat, weight loss
Tuberculosis
Thickening and inflammation of the bronchi
Cough, mucus, fatigue, chills, fever, chest pain
Chronic Bronchitis
Inflammation and fluid in the lungs
Cough, muscle ache, nausea, vomiting, dyspnea, chills, fever
Pneumonia
Mass of uncontrolled cell growth in the lungs
Recurrent cough, chest pain, dyspnea, wheezing, headache, weight loss
Lung Cancer
Recessive genetic disease that causes mucus to build up in the lungs
Salty skin, infections, weight loss, cough, bowel abnormalities
Cystic Fibrosis
Inflammation of the bronchial tubes
Cough, dyspnea, chest pain, wheezing
Asthma
What happens to oxygen partial pressure in the blood during exercise?
It decreases because oxygen is used by muscles to make ATP, lowering blood oxygen levels.
How does exercise affect oxygen diffusion between alveoli and blood?
It increases due to greater oxygen demand, causing deeper breathing and a steeper diffusion gradient.
How does pneumonia affect gas exchange?
It thickens the barrier between alveoli and capillaries, reducing gas diffusion and oxygen intake.
How does severe asthma affect gas exchange?
It decreases oxygen diffusion due to airway inflammation, leading to lower oxygen in blood and reduced tissue oxygenation.
What is the partial pressure of oxygen (PO₂) in inspired air?
160 mmHg
What is the partial pressure of oxygen (PO₂) in expired air?
120 mmHg
How do gases move according to partial pressure gradients?
From areas of higher partial pressure to areas of lower partial pressure.
What is the relationship between barrier thickness and diffusion?
The thicker the barrier, the more resistance to diffusion; the thinner the barrier, the easier diffusion occurs.
What happens at the tissues during gas exchange?
Oxygen moves from capillaries to cells, and carbon dioxide moves from cells to capillaries.
What happens at the alveoli during gas exchange?
Oxygen moves into the blood, and carbon dioxide moves out of the blood into the alveoli.
Describe the structure and function of bronchi.
Bronchi are the main passageways that branch from the trachea into each lung to allow air to make its way to the alveoli for gas exchange
Explain the role of the alveoli.
Alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs
What is the significance of the diaphragm in the breathing cycle?
Diaphragm contracts to allow air into the lungs during inhalation and relaxes to help push air out of the lungs during exhalation.
What is diffusion in the context of gas exchange?
Diffusion allows oxygen to travel from the alveoli to the blood capillaries via a concentration gradient, and allows carbon dioxide to move from the blood into the alveoli due to a concentration gradient
Explain how gas exchange occurs in the alveoli.
Gas exchange occurs in the alveoli when oxygen from inhaled air diffuses into the blood, and carbon dioxide from the blood diffuses into the alveoli to be exhaled.
What is asthma? Describe its main characteristics and how to manage the disease.
Asthma is a chronic condition that causes the airways (bronchi and bronchioles) to become inflamed, making breathing difficult. It is characterized by wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. Asthma can be managed effectively with inhalers and avoiding triggers or allergens.
How can you identify a person experiencing respiratory distress?
Indicators of respiratory distress may include rapid/shallow breathing, use of accessory muscles for breathing (exaggerated muscle movement), cyanosis (bluish color of the lips or face), nostrils flaring, leaning over or standing with hands on knees.
Above or below the normal respiratory rate of 12-24 breaths per minute.
Respiratory Rate Distress Sign
More than 24 breaths per minute
Tachypnea
Less than 12 breaths per minute
Bradypnea
The cessation of breathing completely into the lungs
Apnea
Breathing is too fast and shallow to bring oxygen
Hyperventilation
Breathing is too slow and shallow to get enough oxygen to meet the needs of the body
Hypoventilation
Paleness or cyanosis (blue tint) of the skin may indicate a
Lack of perfusion (oxygen circulation)
Excessive sweating /Panic because of difficulty breathing
Diaphoresis