j) Adult & Foetal Haemoglobin
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
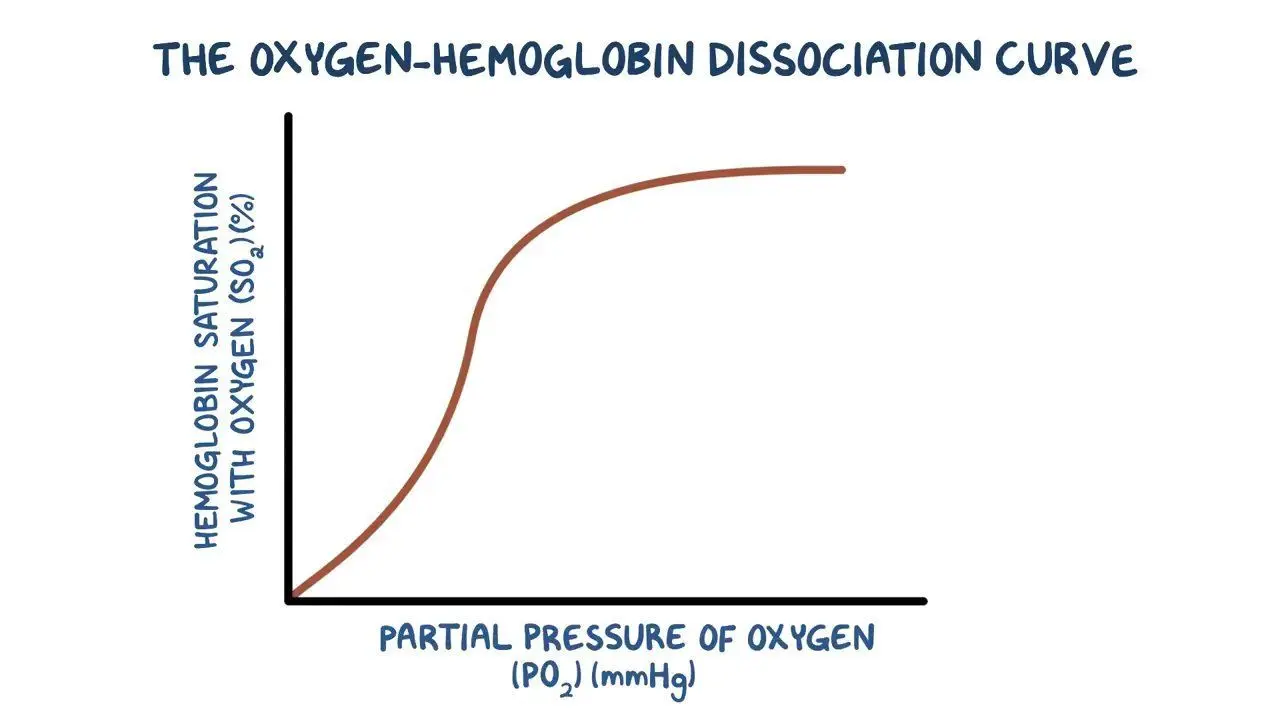
What does the Oxygen Dissociation curve show?
The rate at which oxygen associates and dissociated with haemoglobin at different partial pressures of oxygen (pO₂)
What is partial pressure of oxygen?
A measure of oxygen concentration
What does affinity for oxygen mean?
The ease with which haemoglobin binds and dissociates with oxygen
When haemoglobin has a high affinity...
it binds easily and dissociates slowly
When haemoglobin has a low affinity for oxygen...
it binds slowly and dissociates easily
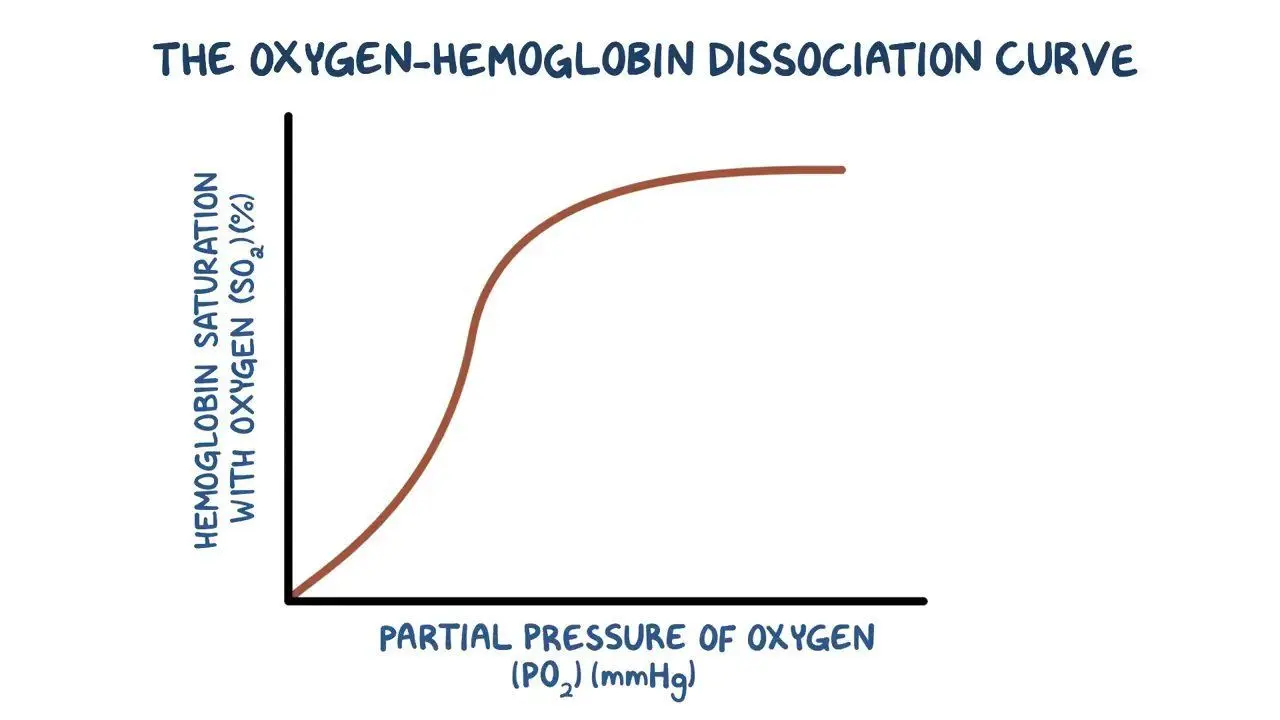
Why does the oxygen dissociation curve level off at the end?
As the haemoglobin molecule approaches saturation it takes longer for the 4th oxygen molecule to bind due to the shortage of remaining binding sites.
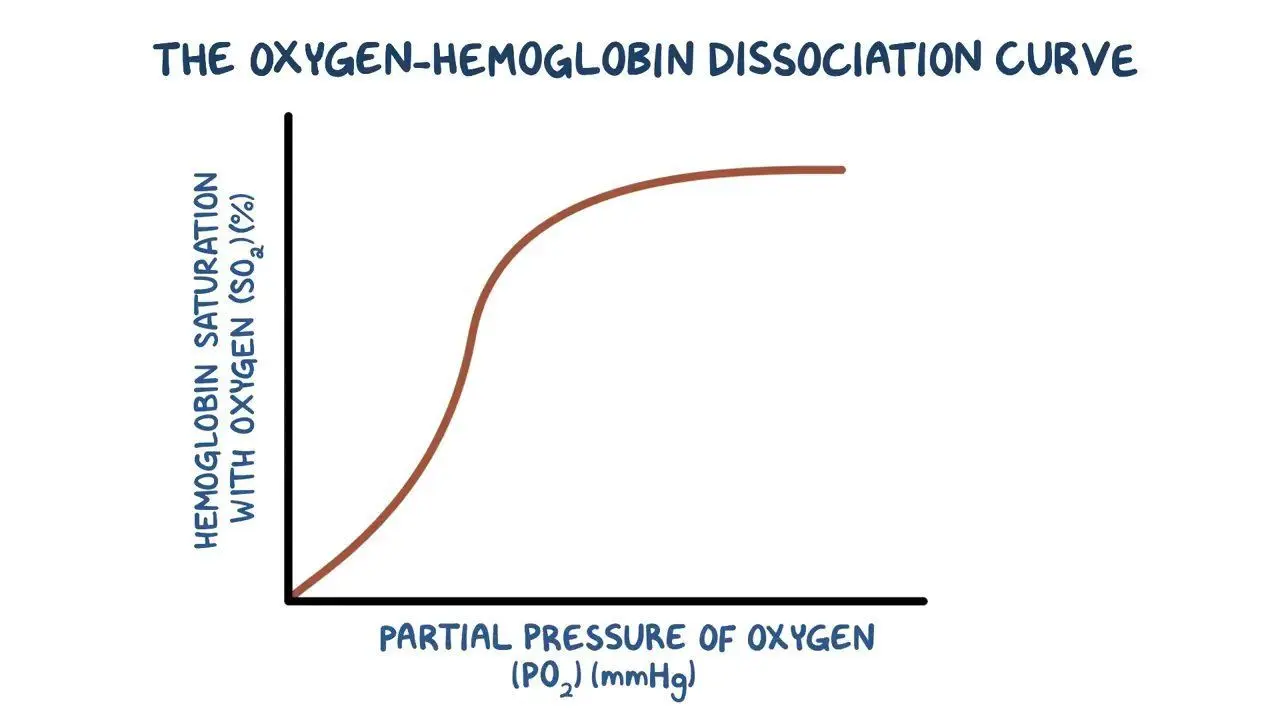
At low partial pressures of oxygen...
....oxygen binds slowly to the haemoglobin.
This means that haemoglobin cannot pick up oxygen and become saturated as blood passes through the body's oxygen depleted tissues.
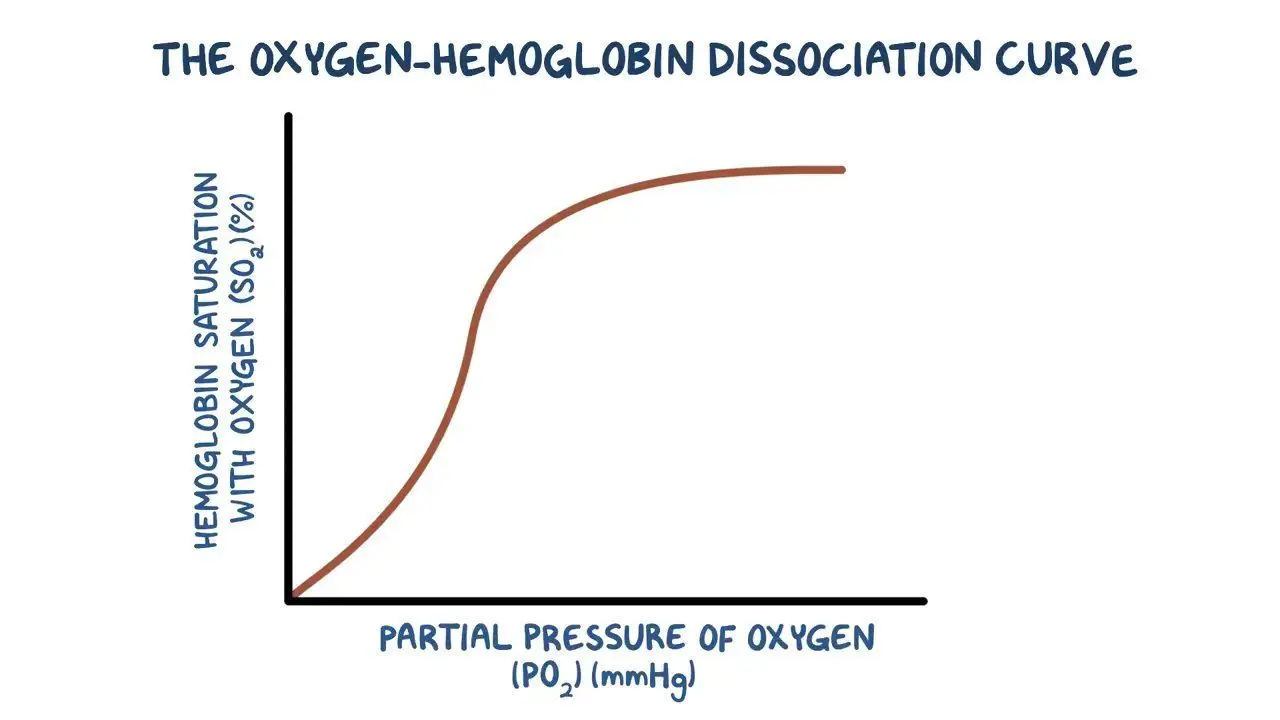
What is the saturation percentage when haemoglobin has low affinity for oxygen at low partial pressure of oxygen?
Low
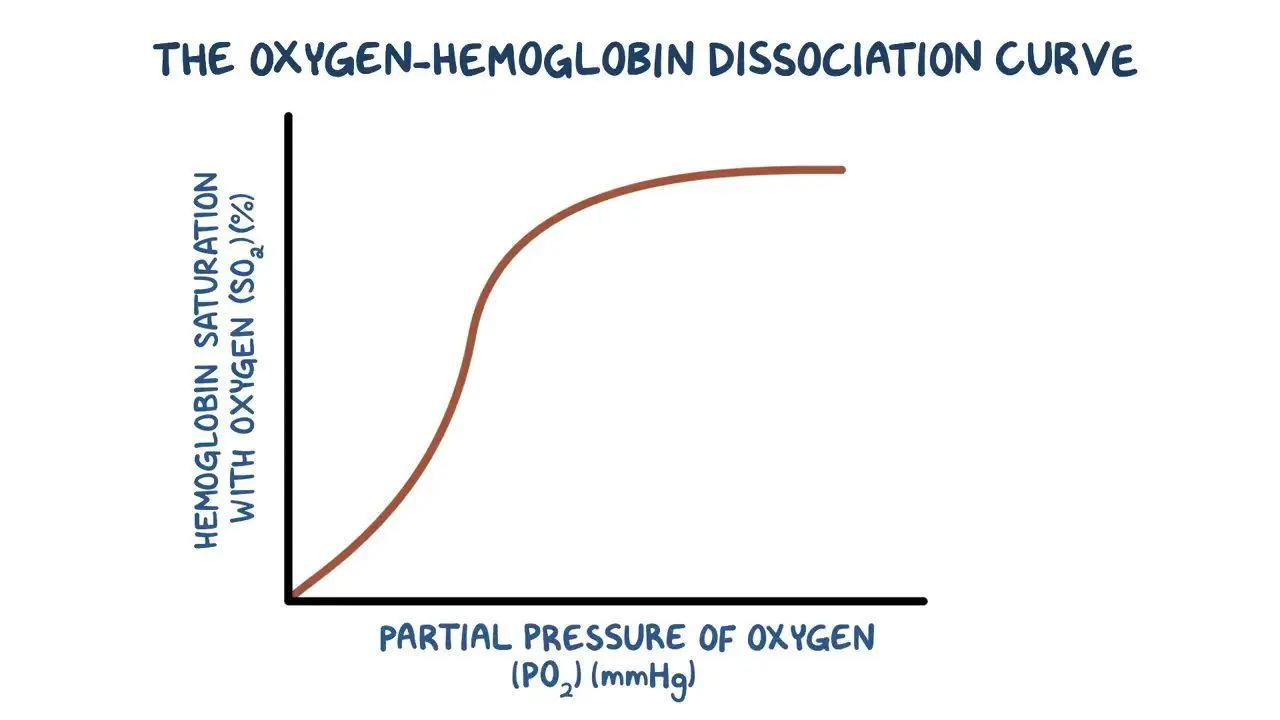
At medium partial pressure of oxygen...
Oxygen binds more easily to haemoglobin and saturation increases quickly; at this point on the graph a small increase in pO2 causes a large increase in haemoglobin saturation
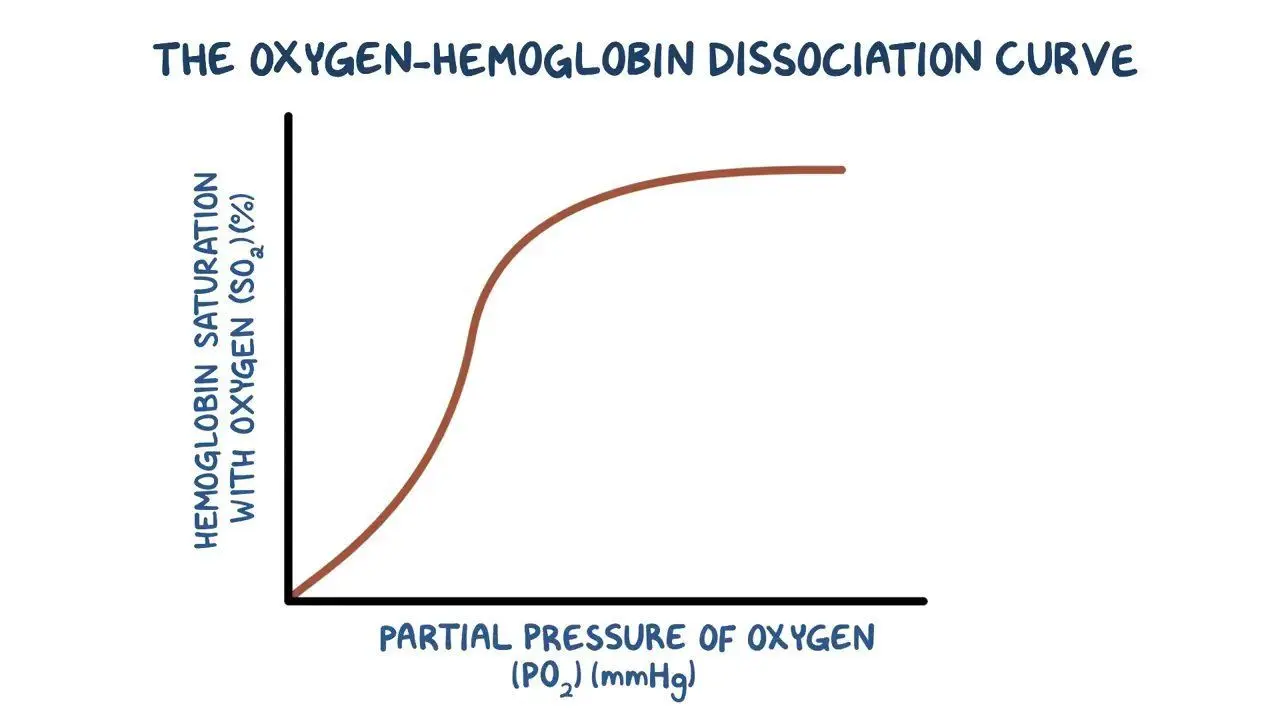
At high partial pressure of oxygen...
Oxygen binds easily to haemoglobin; this means that haemoglobin can pick up oxygen and become saturated as blood passes through the lungs
Does foetal haemoglobin have a higher or lower affinity for oxygen than adult haemoglobin?
Higher
(foetal ends in l so moves to the left)
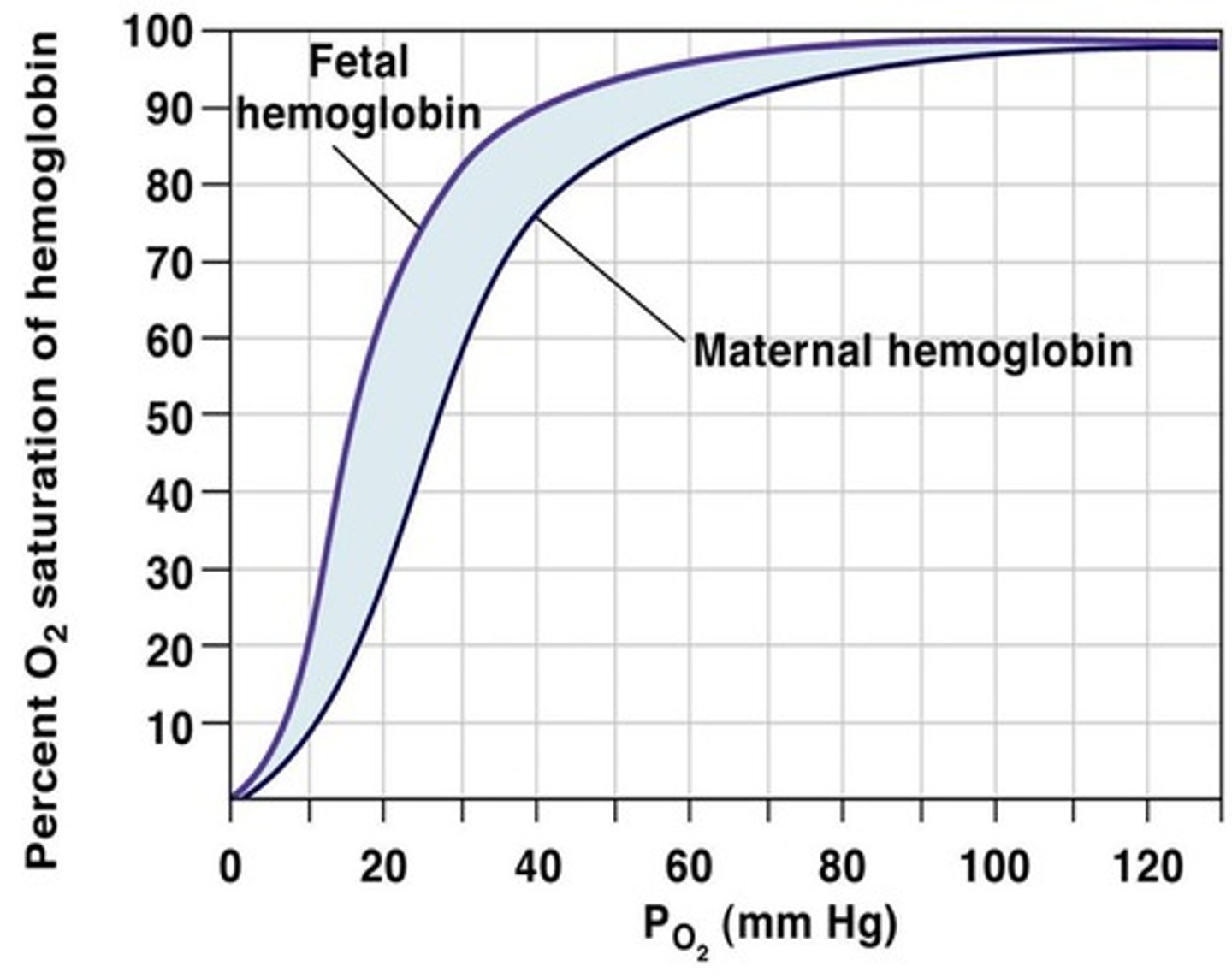
What does foetal haemoglobin look like on a dissociation curve? What does this mean?
It shifts to the left of that of adult haemoglobin
(foetal ends in l so moves to the left)
At any given partial pressure of oxygen, foetal haemoglobin has a higher percentage saturation than adult haemoglobin
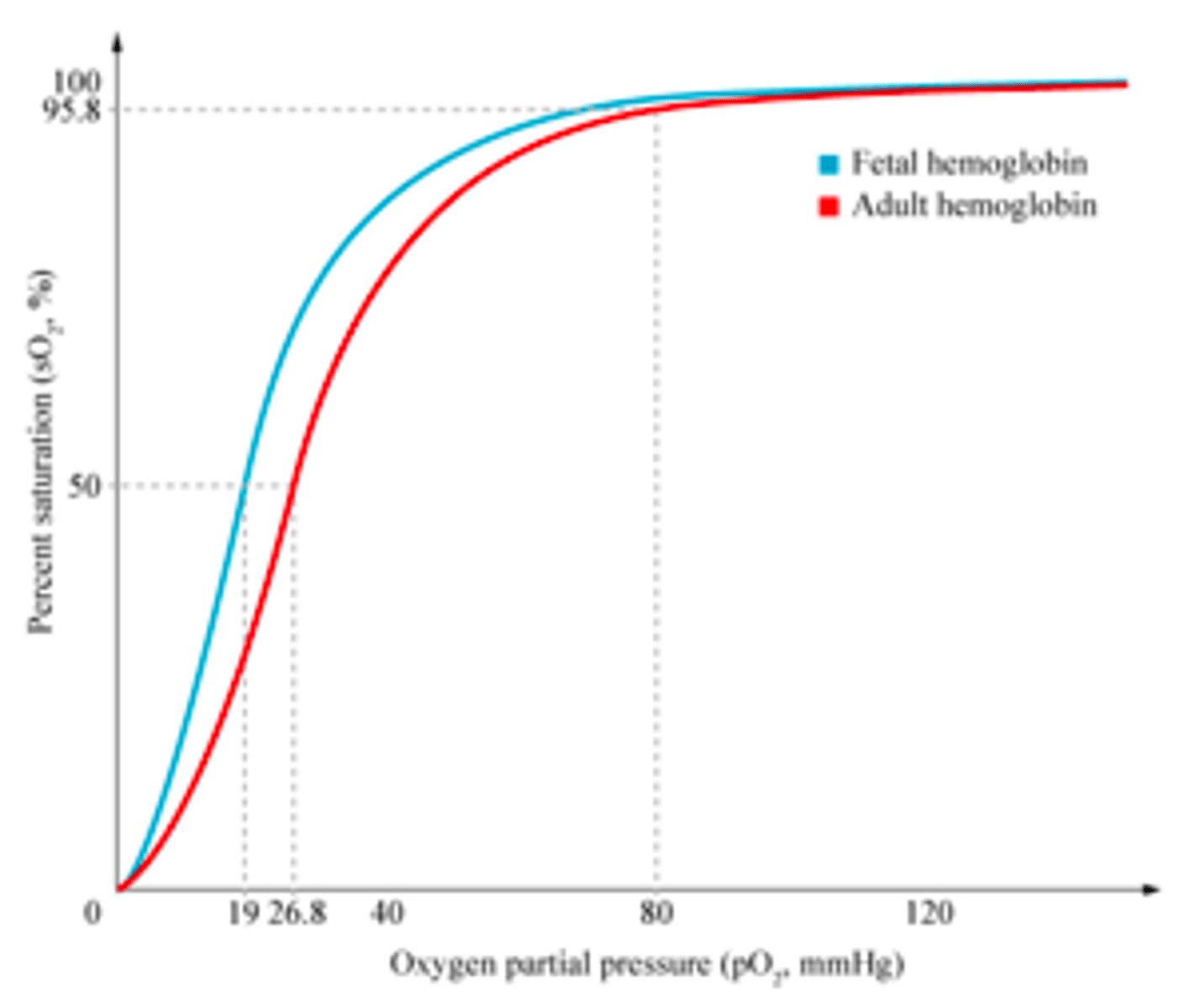
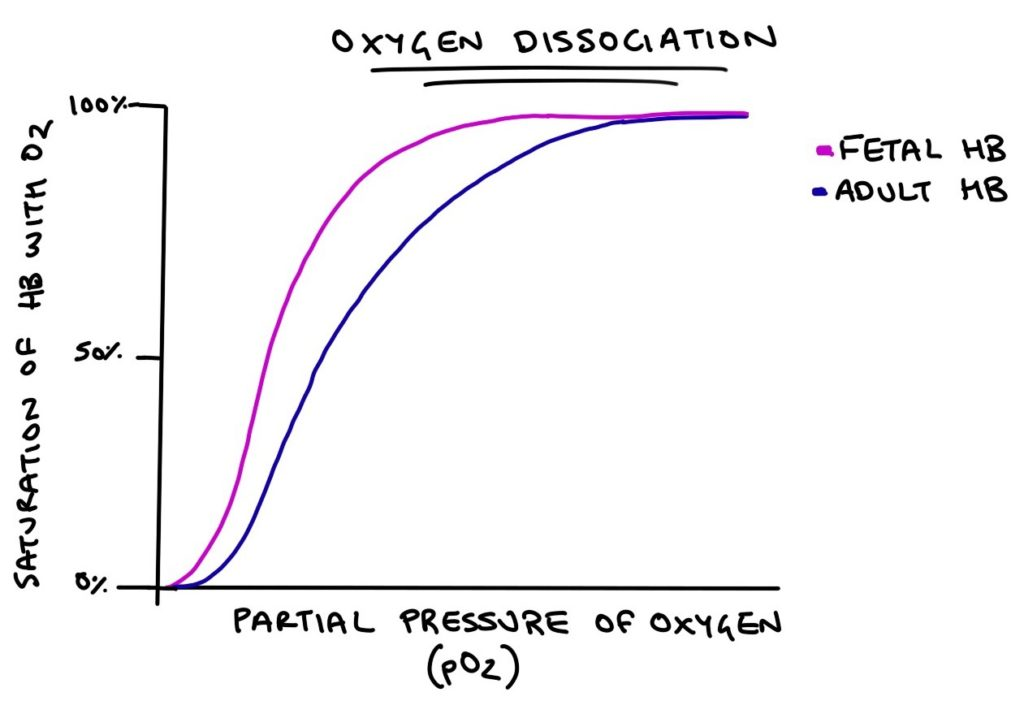
Why is it important that foetal haemoglobin has a higher affinity?
It allows a foetus to obtain oxygen from its mother's blood at the placenta.
Foetal haemoglobin can bind to oxygen at low pO₂
At this low pO₂, the mother's haemoglobin is dissociating with oxygen
Foetal Haemoglobin
Foetal haemoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen than adult haemoglobin.
Foetal haemoglobin takes up oxygen in lower partial pressure of oxygen.
Placenta has low partial pressure of oxygen.
At low partial pressure of oxygen in the placenta, the adult oxyhaemoglobin will dissociate.
Why do babies after birth begin to produce adult haemoglobin?
For the easy release of oxygen in the respiring tissues of a more metabolically active individual