Prostate Gland & Seminal Vesicles - Chapter 19
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
What kind of gland are the Seminal Vesicles?
Accessory and paired glands
The Seminal Vesicles lie posterior to the _______________.
Urinary Bladder
The Seminal Vesicles lie superior to the _____________.
Prostate gland
The Seminal Vesicles lie medial to the ___________.
Right and left ureters
Each seminal vesicle angles ____________ towards the apex of the bladder.
Medially
What is the approximant size of the seminal vesicles?
5 cm in length, and less than 1 cm in diameter
What kind of structures are seminal vesicles?
Convoluted (coiled tubes), pouchlike structures
Where do the seminal vesicles drain into?
The distal portion of the ductus (vas) deferens
When the seminal vesicles join the ductus (vas) deferens, they form the
Ejaculatory ducts
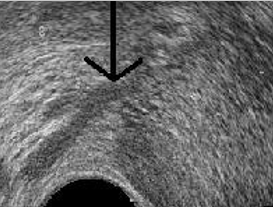
What structure is the black arrow pointing at?
Seminal Vesicle
What is semen?
Fluid that consists of sperm
The prostate gland and seminal vesicles secrete ___________?
Alkaline fluids that contribute to sperm viability
What is the function of the fluid that is produced by the prostate gland?
Neutralizes the acid environment of the vagina, uterus, and fallopian tubes, where neutralization of the ovum takes place
The alkaline fluids contribute between __________ of the volume of semen.
13 - 33 %
Semen can also be described as …
The secretion caused by the prostate and seminal vesicles, and other glands
What does the seminal vesicles secrete?
A viscous fluid rich in fructose
The viscous fluids contribute between __________ of the volume of semen.
60%
The prostate gland is what type of gland?
Accessory
What are the layers of the prostate gland?
Glandular parenchyma & Connective tissue
The prostate gland is anterior to the ___________.
Rectum
The prostate gland is inferior to the ___________.
Urinary bladder, ejaculatory duct, & seminal vesicles
The prostate gland is surrounds the ___________.
Prostatic urethra
Secretion aids in sperm in two ways…
Motility & Fertility
When we are scanning the prostate gland, what are we looking for?
The size of the gland
Prostatic ducts empty into the…
Prostatic urethra
What is the normal size of the prostate gland?
3.8 cm (length) x 3 cm (AP) x 4 cm (width)
What does hypertrophy mean?
Enlarged
Unlike most organs, the prostate sometimes ___________ with age.
Enlarges
What might an enlarged prostate cause?
Obstructed urine flow
Masks prostatic cancer (malignant tumors)
Benign changes
Infections
What is the shape of the prostate gland?
Cone with a central core, prostatic urethra
The tip of the cone, or apex is the ____________ of the prostate and provides an exit for the _________.
Inferior margin, urethra
The base of the prostate gland is the ___________.
Superior aspect, which is in contact with the urinary bladder
The prostate is perforated by ____________.
Two ejaculatory ducts
Where do the ejaculatory ducts enter and course?
Enter ~ prostate at its posterior margin
Course ~ obliquely and anterior
What is the verumontanum?
Area close to the center of the prostate
Where does the ejaculatory ducts join the prostatic urethra?
Near the verumontanum
What zones make up the glandular prostate?
Peripheral zone
Central zone
Transition zone
Periurethral glandular zone
What is the largest zone of the glandular prostate?
Peripheral zone (70%)
Where is the peripheral zone located?
An area lateral and posterior to the distal prostatic urethra
What percentage forms the central zone?
20% of the glandular prostate
Where is the central zone located?
On the superior edge bordering the bladder and seminal vesicles
What structure courses through the central zone?
Ejaculatory ducts
What percentage forms the transition zone?
5% of glandular prostate
Where is the transition zone located?
Two lobes situated on the lateral aspects of the proximal prostatic urethra superior to the verumontanum
What forms the periurethral glandular zone?
Tissue that lines the proximal prostatic urethra
What components make up the male pelvis?
Seminal vesicles
Prostate
Urethra/Penis
What is the prostate surrounded by?
Thin capsule consisting of dense fibrous tissue and smooth muscle
The thin capsule connects what?
Muscle layers of the prostatic urethra
What is the prostatic urethra divided by?
The verumontanum (area near the center of the prostate) into proximal and distal segments
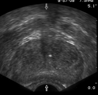
What is this structure?
Prostate Gland
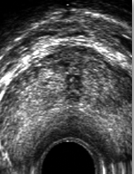
What is this structure?
Prostate Gland
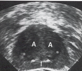
What is this structure?
Prostate Gland
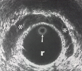
What is this structure?
Prostate Gland