ELECTENG 721: Radio Propagation
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What 2 design requirements must be satisfied when planning radio comms systems?
Provide adequate signal strength
Minimise interference to neighbouring systems
Why are radio waves transmitted in free-space
So that their wavefronts (surfaces of constant phase) are spherical and have radii of curvature which are continually increasing
What is an isotropic antenna
A theoretical antenna that radiates electromagnetic energy uniformly in all directions, meaning its power output is equal in all directions, like a perfect sphere.
What causes Free space attenuation
As the spherical wavefront propagates outwards, the energy per unit area of the wavefront decreases. Free-space attenuation arises due to this expansion of the wavefront and the resultant distribution of power over an increasingly larger area
What is the quantity Ptgt (W) also known as ?
Effective Isotropic Radiate Power
What is EIRP
Effective Isotropic Radiated Power, a measure of the power radiated by an antenna in a given direction compared to an isotropic antenna.
Define boresight
The direction along the axis of an antenna where it is most sensitive to incoming signals. It indicates the optimal angle for signal reception or transmission.
What is Pd and what are its units
The power density (with units W/m2) , representing the power per unit area received by an antenna.
What is P0 and what is its formula
The power received by a loss free antenna.
P0 = PdAe
What is Ae and what is its formula
Effective aperature of an antenna. It is a measure of how effectively an antenna can capture or transmit electromagnetic waves.
Ae = (gλ²)/4π,
where g is the gain and λ is the wavelength.
expressed in m2
What is the formula for rms field strength E at a point where the power density of a plane wave is Pd
E =sqrt(120π · Pd) (V/m)
What things can be designed using the basic free-space transmission formula
Satellite Links
Terrestrial Microwave links
UHF point to point links
What is the height gain effect and how can it be combatted?
The height gain effect occurs when the effective range of an antenna increases with height above the ground due to reduced obstructions. It can be combatted by using lower towers or antennas with higher directivity.
What is space diversity
A technique where signals are transmitted and received over multiple pathways or antennas in order to improve reliability and reduce the effects of fading.
What is the formula for the plane earth model
Pr (dBm) = 10 log10 (Ptgtgr) − 40 log10 (d) + 20 log10 (hthr)
What is the troposphere
The lower part of the atmosphere
What can cause variations in signal level with time for radiowaves?
Changes in temperature, pressure and humidity, rain
What is ducting and what is it caused by
Ducting is a phenomenon where radio waves are trapped and guided within a specific layer of the atmosphere allowing them to travel father than they normally would, beyond the typical line of sight range.
Caused by extended negative gradients
What is εr in practical atmospheric applications and what is it dependent on
εr > 1
Air pressure/temp
water vapour content
normaly εr decreases with height
What is subrefraction
an (unwanted) condition where radtio waves ebnd upwards away from the earths surface, more than they would under standard atmospheric conditions.
What can introduce diffraction loss
Irregular terrain features (obstacles such as hills and dense forests)
What Environmental factors act to increase path loss
Natural and constructed obstacles
vegetation
What are some environmental effects in urban areas
Shadowing
Fading
What is fading and what causes it
the loss of signal as seen by the radio receiver at its input. Cause by atmospheric conditions and path geometry
What are the 2 types of fading
Fading due to obstruction
Fading due to multipath interference
When does fading due to obstruction occur and what are the consequences
can occur when k changes in subrefractive conditions, and consequences include:
Increase in the effective height of obstacles
Earth blocking
When does Fading due to multipath interference occur
Fading due to multipath obstruction occurs when obstacles like buildings or trees block or reflect radio signals, causing multiple delayed signal paths to reach the receiver. These signals can interfere with each other—sometimes canceling out—leading to reduced signal strength or quality at certain locations.
Why is Fading due to multipath interference a big concern in mobile radio systems.
because it causes signal strength to vary rapidly with movement, leading to dropped calls and data errors. This unreliability must be managed to ensure consistent communication quality in mobile environments.
In Mobile Radio Propagation, What is the received signal comprised of in a multipath channel
a number of attenuated, phase shifted and delayed copies of the original transmission
What cause the significant variations in amplitude for the received signal in mobile radio propagation
Caused by phasor addition of the various multipath components which result in constructive and destructive interference.
What factors affect path loss
path length
frequency
antenna height
terrain
environment in vicinity of terminals
What is propagation loss on obstructed paths inluenced by
object size and shape
placement
frequency
number of obstacles
What are the 2 categories that terrestrial radio links are broken down into
Point to Point
Area Coverage: either Broadcasting or Mobile radio
What is the formula for the total system loss in a point to point system
As = A0 + AZ - (G1 + G2) + AF1 + AF2
A0 = basic free space transmission loss (dB)
Az = additional loss due to obstructions (dB)
AF = feeder losses (dB)
G =antenna gains (dB)
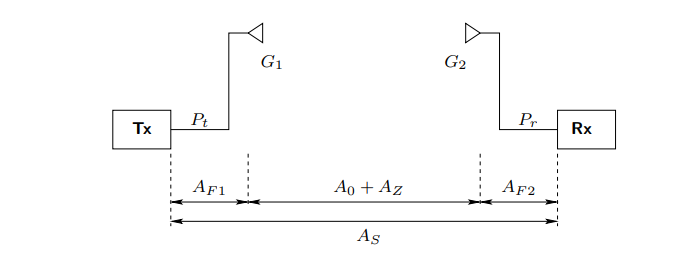
What is the formula for received power Pr and give its units
Pr = Pt -AS
basically just total power - total system loss
Units are dBm
What are the 2 alternative path profiles in any link budget calculations
Curved earth of radius ka and straight rays
Flat earth with rays of curvature kr
What are the possible ways that we can compensate for the diffraction loss in link budget design?
increasin antenna gain(s) or if this is not feasible then try relocating the link terminal(s)
What is the High-Low Technique
Uses high sites to cover areas with blocked or non-reflected paths, and low sites to handle reflected paths and improve coverage in obstructed or dense environments.
What is an example of area coverage systems
Mobile (cellular) radio systems
What is the β symbol used for in area coverage systems design
This is a clutter factor aka the excess loss. It is multiplied onto the rest of the Plane earth formula (Pr = Ptgtgr…)
What does the clutter factor depend on
Both frequency and levels of environmental clutter
What is the formula for thermal noise
Vn2 = 4kTBR
where
Vn2 = mean square value of the thermal noise voltage
k = Boltzmann’s constant = 1.38 × 10−23 J/K
T = absolute temperature (K) B = system noise bandwidth (Hz)
R = resistance (Ω)
What is thermal noise fundamentally caused by
caused by resistive components that are not at a temperature of absolute zero
What is the Noise Figure/ Noise Factor formula
NF = 10log10F
F can only have a max value of 1, so the noise figure of an ideal noiseless network is 0dB
units in (dB)
Receiver thermal noise formula
pA = FkTB
units in W
What is mds
minimum discernable signal or receiver noise floor is the signal with a power level equal to the noise level
How can we increase sensitivity
Cool receiver front end (Reduces T)
Reduce bandwidth
Redesign receiver to reduce NF
Why do we never design a system fo S/N =1
because the signal is barely distinguishable from noise, leading to unreliable communication with high error rates. For effective and robust performance, systems need a higher S/N to ensure clear signal detection and data integrity.
What is the required input signal level for a given S/N refered to as ?
system sensitivity
What is the mixer operation?
a three terminal deive (2 inputs, 1 output) that functions as an analogue multiplier. The 2 inputes are multiplied to produce the output.
What is gain compression`
As the input power increases, a point is reached when the output no longer increases in the same rate.
What is the dynamic range
The range between the minimum detectable signal (MDS) and the signal level where distortion matches the noise floor. It shows how well a receiver can handle both weak and strong signals without distortion.
What is the basic idea for a radar
illuminate a region with RF energy and observe the reflections to determine if something is there or estimate the distance (range).
What are some uses of radar
Tracking aircraft, people, weather, space objects, and mapping Earth's surface—even at night or through clouds.
How does radar detect targets?
Sends short pulses via directional antenna; reflected signals depend on target shape, material, and wavelength.
How is range calculated in radar?
The range of a target can be found from the time delay between when a pulse is transmitted and when it is received
Break down the steps on how a radar detects targets
Transmitter produces a short pulse, Directional antenna used to produce a focused incident wave.
Incident waves scatter from the target, scattering depends on the shape, material properties and wavelength.
Some of the scattered waves reach the radar antenna + receiver.
Time delay formula for a radar
T = 2R/C
Maximum unambiguous range formula
Ru = cTp /2
Ru = c /2fp
Range resolution formula
∆𝑅= 𝑅2 − 𝑅1 = 𝑐𝜏 / 2
What conditions must be met to detect a target using radar?
power of reflected signal > power of noise
How can SNR (radar) be increased
increase Pt and t , although a short t is preferred to improve ΔR
Multiple radar returns (assuming obeject does not move too much) can be integrated to increase SNR.