AP Human Geography Unit 1- Thinking Geographically
1/83
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Geography definition
Where people and activities are found across the Earth’s surface and the reasons they are found there.” Geo means “earth” and graphy means “write.”
Place definition
A point on Earth with a unique characteristic, every place has a different location on Earth. A place has special characteristics that make it memorable to people.
Region definition
A part of Earth that has defining characteristics, for example the Middle East, North America, Europe, etc.
Scale definition
Relationship between the part of Earth being studied and Earth as a whole. The scales can be as small as local all the way to global. Processes that affect humanity’s ability to live on earth can be global such as global warming. Or processes can be on a local scale such as the preservation of the natural environment of a place.
Space definition
The physical gap between two objects. Geographers notice that a lot of objects are distributed in a regular matter across space for discernable reasons.
Connection
The relationships between objects and people that are present despite the barrier of space/physical difference between them. Geographers study how these connections take place.
Map definition
Two-dimensional or flat-scale model of Earth or a part of it. The 2 key benefits of maps are that they are a reference tool (we reference it to find where places/objects are) and as a communications tool as maps are useful in depicting physical features or human activities on Earth. Maps are also useful in understanding why the physical features or human activities are distributed on Earth the way they are.
Cartography definition
The art of mapmaking, modern mapmakers are assisted by technology such as computers and satellites. The earliest, fully proved map was made in around 6200 BC.
Global Positioning System (GPS) definition
A technology using satellites that tracks your location on Earth, GPS is mostly used for navigation.
Mental map definition
A personal representation of a place on Earth that is based on what the person knows about the place and their impressions of it.
Geographic Information Systems definition
A system that stores, analyzes, and displays geographic information related to positions on the surface of the Earth. GIS consists of two types of data, vector and raster. Vector data consists of dots (ex. cities) and lines (ex. highways) while raster data consists of images such as landforms.
Geotagging definition
Identifying a piece of information by its latitude and longitude and storing it based on that. For example when we take a photo with our phone, Apple sometimes automatically adds the location of the photo taken.
Geographic Information Science (GIScience) definition:
Analysis of data about the Earth that was obtained through satellite and other electronic information technology
Remote sensing definition
obtaining information about the Earth's surface through a satellite or other long-distance method
Volunteered geographic information (VGI) definition
Creation and spreading of information by an individual voluntarily.
Citizen science definition
scientific research by amateur scientists.
Participatory GIS (PGIS) definition
Community based mapping, where a community works together to create and map geographic information.
Mashup definition
A map displaying information from more than one source.
Map scale definition
he relationship of a feature's size on a map to its actual size on Earth.
Written scale: A written scale describes the relationship between the map and Earth distance in words (ex. 1 cm = 10 km)
Graphic scale: A graphic scale usually consists of a bar line marked to show distance on Earth’s surface
On the scale of a small part of the Earth, many details can be included. On a big scale, details may have to be left out. But the data shown is data that would affect everyone.
Scale of analysis definition
The level at which you study geographic data, such as local, regional, or global. It determines how broad or specific your view is.
Projection definition
Interruption definition
Any part of the globe that has been split
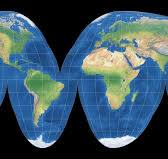
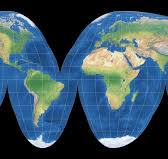
Goode-Homolosine map definition:
Pro: Preserves size Con: Weird shape, distorts shape near edges.
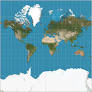
Mercator projection definition:
Pro: Preserves shape and direction Con: Distorts size
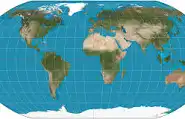
Robinson map projection definition:
Slight distortion of both size and shape.
Meridian/Longitude definition
Arc drawn between north and south poles. The location of each meridian is identified on Earths surface according to a numbering system called longitude.
Parallel definition
A parallel is a circle drawn around the globe parallel to the equator and at right angles to the meridians. The numbering system to indicate the location of a parallel is called latitude.
Prime meridian definition
A special name given to the meridian at 0 degrees longitude.
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) definition
As Earth rotates daily, these 360 imaginary lines of longitude pass beneath the cascading sunshine. If we let every fifteenth degree of longitude represent one time zone, and divide the 360 degrees by 15, we get 24 time zones, or one for each hour of the day. GMT is the master reference time for all points on Earth by international agreement.
International Date Line definition
An imaginary line roughly along the 180 degrees meridian that marks where the date changes. You have to rewind 24 hours if you are moving eastward towards America or add 24 hours if you are moving towards Asia.
Location definition
The position that something is situated on the Earth’s surface
Toponym definition
Name given to a place on Earth.
Site definition
The physical character of a place. Important characteristics include, topography, climate, vegetation, etc.
Situation definition
location of a place relative to other places, this can help show the significant of the place.
Cultural Landscape definition
A region derives its unified character through the cultural landscape, which is a combination of cultural features such as language and religion, economic features such as industry and agriculture, and physical features such as climate and vegetation.
Formal region/uniform region definition
An area within where everyone shares in common one or more distinct characteristics. This shared characteristic could be a cultural value such as language, an economic activity such as a particular crop, or an environmental property such as the climate or elevation. The selected characteristic in a formal region is present throughout.
Functional region/nodal region definition
An area organized around a node or focal point. The characteristic that defines the region is strong at the center and slowly decreases in significance outward. The region is tied to the central point by transportation or communications systems or economic or functional associations.
Vernacular region/perceptual region
An area that people believe is a part of their cultural identity, it's basically the same as a formal region but the perceived shared characteristics might not be there.
Culture definition
body of beliefs, material traits, and social forms that together constitute the distinct tradition of a group of people. The word culture comes from the Latin word “Cultus.”
Spatial association definition
This occurs when the distribution of one characteristic is related to another characteristic. Spatial association is strong if two characteristics have very similar distribution and weak if not.
Globalization definition
A process that involves the entire planet and the result of the process is something that affects the whole globe.
Transnational corporation/multinational corporation definition
A corporation that sells products, operates factories, and does research in many countries and not just where it’s headquartered and where the main shareholders are located.
Distribution definition
The arrangement of a feature in a space, 3 main properties of distribution are density, concentration, and pattern.
Density definition
The frequency by which something occurs in space. The region that the feature is distributed across can be measured in any unit of area such as square km, square miles, hectares, acres, etc.
Concentration definition
The extent of a feature spread over space, if the objects in an area are close together, they are clustered; if they are relatively far apart, they are dispersed. Concentration is different from density, for example: in two pictures with the same area and equal density of houses. One picture will have more houses on the west side of the picture than the other, so that means that photo has a more clustered concentration.
Postructuralist geography definition
Studies how powerful group(s) in society dominate or seek to dominate the less powerful group(s), how the dominated groups occupy space, and confrontations that result from the domination. Geographers understand that space as the product of ideologies or value systems of ruling elites.
Humanistic geography definition
Branch of human geography that studies how individuals form different ideas about place and give those places symbolic meanings.
Behavioral geography definition
Studies the importance of understanding the psychological basis for individual human actions in space. Distinctive spatial patterns by gender, ethnicity, and sexual orientation are constructed by the attitudes and actions of cultural groups as well as the larger society. Basically it's studying how people decide where to live, work, etc. based on what they believe.
Spatial pattern definition
the location of places, people, and events, and the connections among places and landscapes. looks to answer the questions like “why or where?”
Uneven development definition
The gap in economic conditions between core financial areas (New York, Tokyo, etc.) and the outer area because of the globalization of the economy.
Hierarchical diffusion definition
Where an idea or trend spreads from the larger more influential places to smaller and less influential ones.
Assimilation definition
Process by which a group's cultural features change to resemble those of another group. The Cultural characteristics of one group may dominate the culture of the assimilated group.
Acculturation definition
Defines the process of changes in the culture of two groups after they meet. There might be changes in the cultures of both groups or just one, but the two groups still have two distinct cultures.
Syncretism definition
When the elements of two cultures combine into a new cultural characteristic. Two cultural groups combine to form a new culture.
Diffusion definition
Defines the process by which a characteristic/feature spreads across space to another over time. A feature always originates from a center and diffuses to other places from there.
Hearth definition
A place from which an innovation originates.
Relocation diffusion definition
Spread of an idea, innovation, etc. through physical movement of people from one place to another. This migration happens from the migration of people.
Expansion diffusion definition
Spread of a feature from once to another in an additive process. This expansion can happen from one of 3 processes: Hierarchical diffusion, contagious diffusion, and stimulus diffusion. This diffusion happens from the interaction between people.
Hierarchical diffusion definition
Spread of an idea from persons or nodes of authority or power to other persons or places. This can also be reverse meaning spread of an idea from persons or node with less power to other persons or places with more power.
Contagious diffusion definition
Rapid, widespread diffusion of a characteristic through the population. Examples: diseases spreading, music and memes spreading online.
Stimulus diffusion definition
Spread of an underlying principle even though a characteristic itself fails to diffuse. For example, features of Apple’s products have been adopted by competitors.
Network definition
Chain of communication that connects place, this is how interaction takes place.
Distance decay definition
As the distance between two parties increases, the less likely they are to interact. Contant starts diminishing as distance increases and eventually disappears.
Space-time comparison definition
Term used to describe the reduction in the time it takes for something to reach another place.
Resource definition
Material found in the environment that is useful to people and is economically and feasible to access, and socially acceptable to use.
Sustainability definition
Use of Earth’s resources in ways that makes sure that they are available in the future.
Renewable resource definition
Natural resource produced in nature more than it is used by humans.
Nonrenewable resource definition
Natural resource produced more slowly than it is used by humans.
Conservation definition
Sustainable use and management of Earth;s natural resources to meet human needs. Renewable resources such as trees and wildlife are conserved if they are consumed at a less rapid rate than they can be replaced. Nonrenewable resources such as coal are conserved if we use it responsibly so that they may be available for future generations.
Preservation definition
Maintenance of resources in their present condition, with as little human impact as possible.
Abiotic
System Is composed of non-living or inorganic matter.
Biotic
System is composed of living organisms.
Hydrosphere definition
All the water on and near Earth's surface
Water exits in liquid form in oceans, lakes, rivers, soil, rock, glaciers, in the atmosphere, etc. Over 97% of the world’s water is in the oceans.
Lithosphere definition
Earth’s crust and a portion of upper mantle directly below the crust.
Earth is made up of concentric spheres, the names of these spheres from deepest to outer are the core, mantle, and crust. Powerful forces in the Earth bend and break the crust to form mountain chains and shape the crust to form continents and ocean basins.
Geomorphology definition
The study of Earth’s landforms.
Ecosystem
Group of living organisms and the abiotic spheres with which they interact.
Ecology
Scientific study of ecosystems of ecology, ecologists study the interrelationships among living organisms and the interrelationships between living organisms and the 3 abiotic environments.
Cultural ecology definition
The geographic study of human-environment relationships, basically studying how different cultural groups modify the four spheres in different ways.
Environmental determinism
Belief that the physical environment caused social development, human geographers should apply laws from the natural sciences to understanding relationships between the physical environment and human actions. How societies developed was caused by the physical environment completely. The environment controls human actions and culture.
Possibilism definition
Physical environment may limit some human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to their environment. People can choose a course of action from many alternatives in the physical environment. Humans can adapt to and change their environment to shape their own future.
Polder definition
Piece of land that is created by draining water.
Dike definition
Barrier built to hold back water and flooding from land.
Not in textbook: Equal-area projection
Map projection that sacrifices shape for size
Not in textbook: Conformal projection
Map projection that preserves shape but distorts area and angles