Neurological System: Trauma, degeneration, and malacia/necrosis
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What does encephalo mean?
Brain
What does myelo mean?
Spinal cord
What does malacia mean?
Degeneration, necrosis, liquefaction
What does polio mean?
Grey matter
What does leuko mean?
White matter
What is polioencephgalomalacia?
Grey matter degeneration/necrosis of the brain
What is leukoencephalomalacia?
White matter degeneration/necrosis of the brain
What does thiamine deficiency cause?
Symmetrical hemorrhage and necrosis of inter and midbrain (polioencephalomalacia)
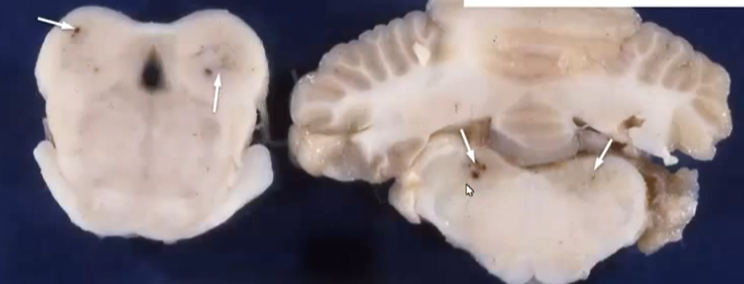
Thiamine deficiency
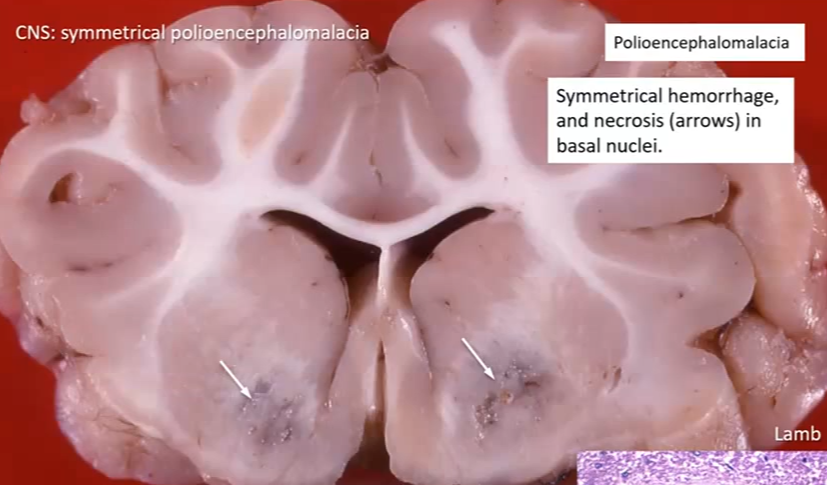
What is the pathogenesis of Clostridium perfringens?
Epsilon toxin causes vascular damage, perivascular edema, necrosis, and hemorrhage in gray matter nuclei symmetrically
What is a common cause of Nigropallidal encephalomalacia in horses?
Yellow star thistle causing necrosis of substantia nigra due to sesquiterpene lactones
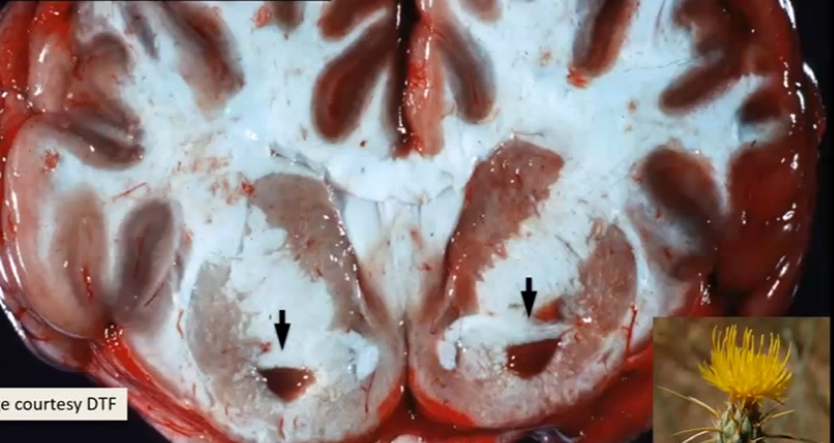
Nigropallidal encephalomalacia in horses
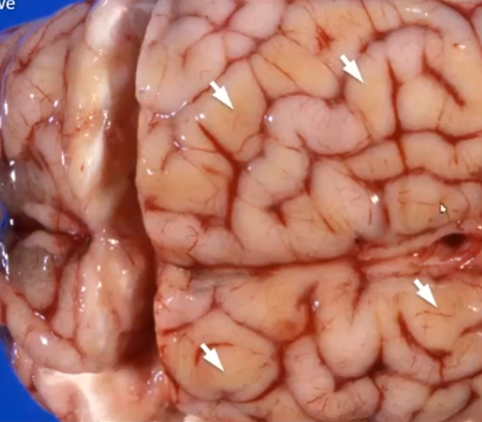
What does this yellow coloration mean?
Laminar cortical necrosis
What can cause thiamine deficiency in non carnivores?
High concentrate rations
Bacteria high in thiaminases
Ingestion of thiaminase containing plants
High sulfur diets
What can cause lesions similar to thiamine deficiency?
Lead poisoning
What is a good way to identify laminar cortical necrosis in the field?
UV light will create autofluorescence
What is the caused by thiamine deficiency in cattle?
Laminar cortical necrosis
What does salt toxicity (lack of water) cause in the brain?
Osmotic pressure in brain increases and when the animal drinks water again the influx causes edema in the brain. The edema causes laminar cortical necrosis
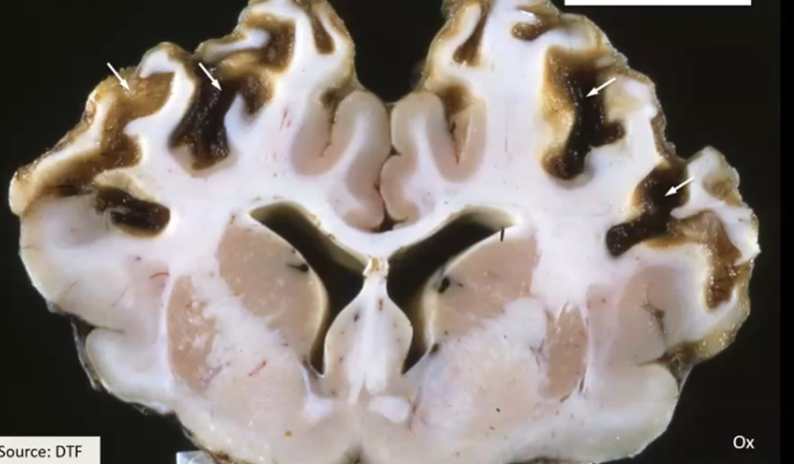
Chronic polioencephalomalacia
What happens during chronic polioencephalomalacia/
Glitter cells are activated and gray matter cavitation occurs
Water matter appears intact, but axons die
What is post-anesthetic hemorrhagic myelomalacia in horses?
Prolonged dorsal recumbency causes ischemic necrosis to cord, focal malacia of the cord, and paralysis
What causes encephalomalacia in chickens?
Vitamin E deficiency in affected chicks
What are the signs of vitamin E deficiency in chickens?
Ataxia, falling on back, frequent wing flapping, twisted heads
What lesions are associated with Vitamin E deficiency in chickens?
Encephalomalacia, edema, hemorrhage, necrosis of cerebellum
What does this white discoloration indicate?
Leukoencephalomalacia
What does Fusarium spp cause in horses?
Moldy corn poisoning and leukoencephalomalacia due to Fumonisin B1 toxin
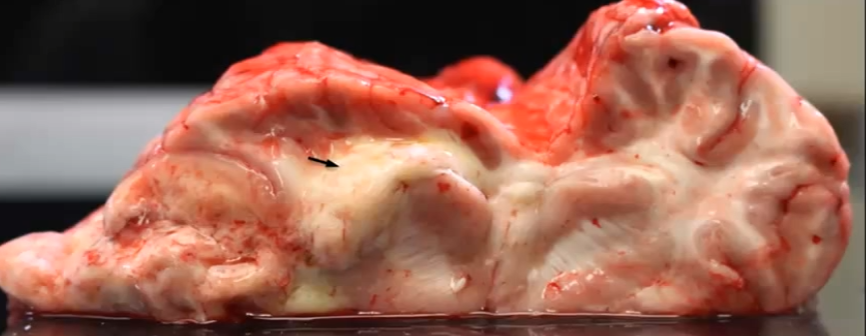
Moldy corn poisoning from Fusarium spp. (Equine leukoencephalomalacia
What is the distribution of Leukoencephalomalacia compared to polioencephalomalacia?
Leukoencephalomalacia is usually asymmetric and polioencephalomalacia is symmetrical
What are some causes of hepatic encephalopathy?
Portosystemic shunts
Hepatotoxicants
Severe hepatic fibrosis
Equine serum hepatitis
What is the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy?
Liver dysfunction causes impaired ammonia detoxification
Elevated serum ammonia
Induction of Alzheimer type II astrocytes
Vacuolation of white matter
Neurologic impairment
What are the gross lesions of hepatic encephalopathy?
None
What is the pathogenesis of Acquired Lysosomal Storage Disease due to Locoweed toxicosis?
Locoweed ingestion
Swainsonine toxicosis
Inhibition of alpha-mannosidase
Excess intracytoplasm alpha-mannosidosis
Accumulation in lysosomes
Neurologic dysfunction
What does locoweed toxicosis cause?
Acquired lysosomal storage disease
What are the gross lesions of locoweed toxicosis?
None
What is the most common lysosomal storage disease in domestic animals?
Globoid cell leukodystrophy
If you suspect neurologic disease in a large animal how should you not euthanize?
Captive bolt euthanasia or firearms
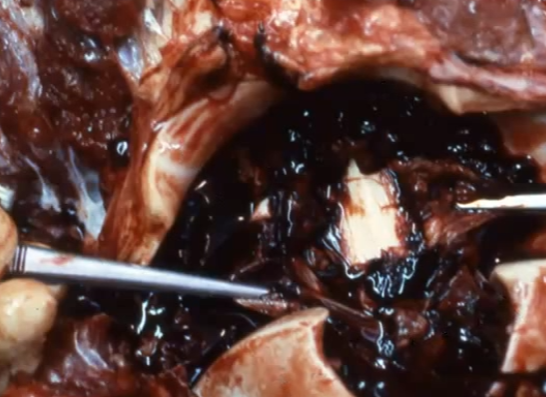
Intracranial and subdural hemorrhage due to a high velocity projectile being used for euthanasia
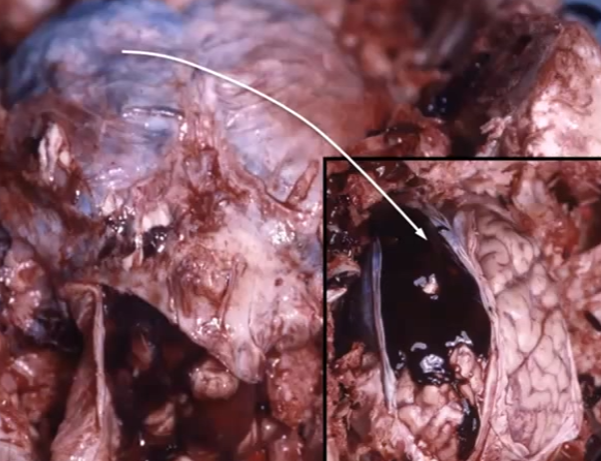
Subdural hematoma due to a high velocity projectile

What type of CNS injury is this?
Crushing injury
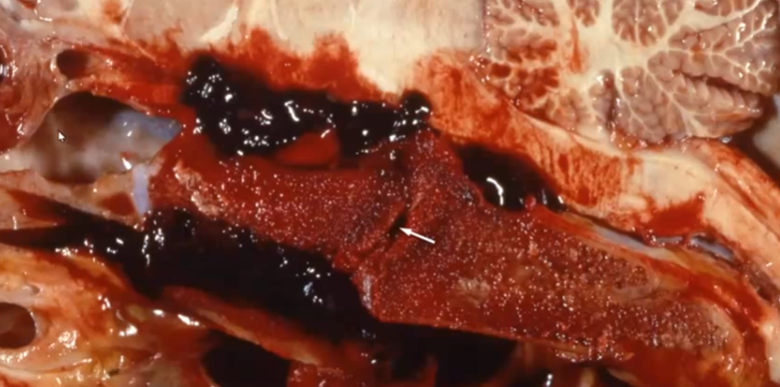
Basisphenoid fracture (CNS traumatic injury)
What are basisphenoid fractures more likely?
Foals that are being halter broken and they flip backwards trying to resist (blunt force on top of the skull)
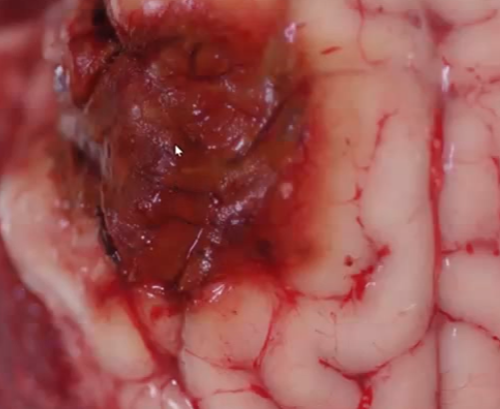
Thermal injury due to dehorning
What is a coup-countrecoup injury?
One lesion on the area of trauma
Other lesions on the opposite side of the trauma
What lesions are on the coup side of a coup-countrecoup injury?
SQ hemorrhage
Skull fracture
Subdural hemorrhage
Brain contusion
What are the lesions on the countrecoup injury?
No SQ hemorrhage or skull fracture
Subdural hemorrhage
Brain contusions
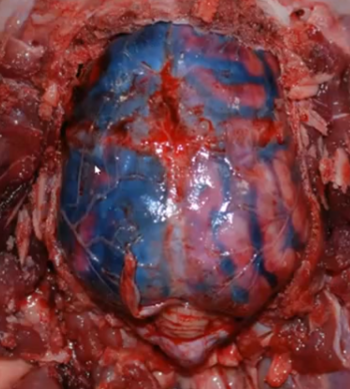
Subdural hematoma
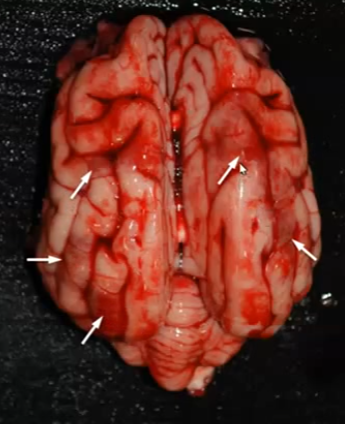
Cerebral hemorrhages
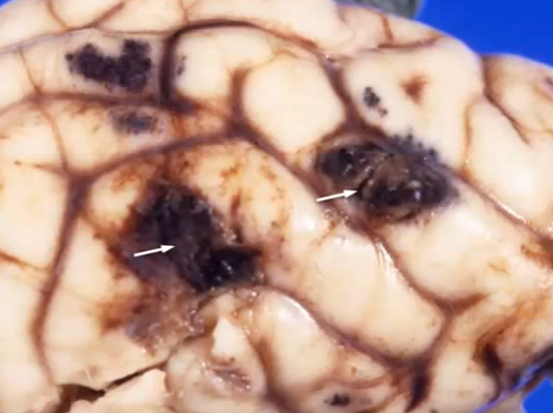
Brain laceration from multiple pellets

Spinal cord hemorrhage (contusions)
What are some causes of spinal cord hemorrhage
Horse racing injury
Lightening strike
High velocity projectile
What can cause cervical stenotic myelopathy?
Narrowing of the vertebral canal or overextension of vertebral joints leads to compression of the spinal cord
What are the lesiosn of cervical stenotic myelopathy?
Compressive injury causing Wallerian degeneration, ataxia, paresis
What are the 2 syndromes of cervical stenotic myelopathy?
Cervical static stenosis
Cervical vertebral instability
What does cervical vertebra flexion cause?
Dynamic compression of the spinal cord in the canal
What animals typically get equine wobblers syndrome?
Younger
What is equine wobblers syndrome?
Flexion of cervical vertebra causing dynamic compression of the spinal cord
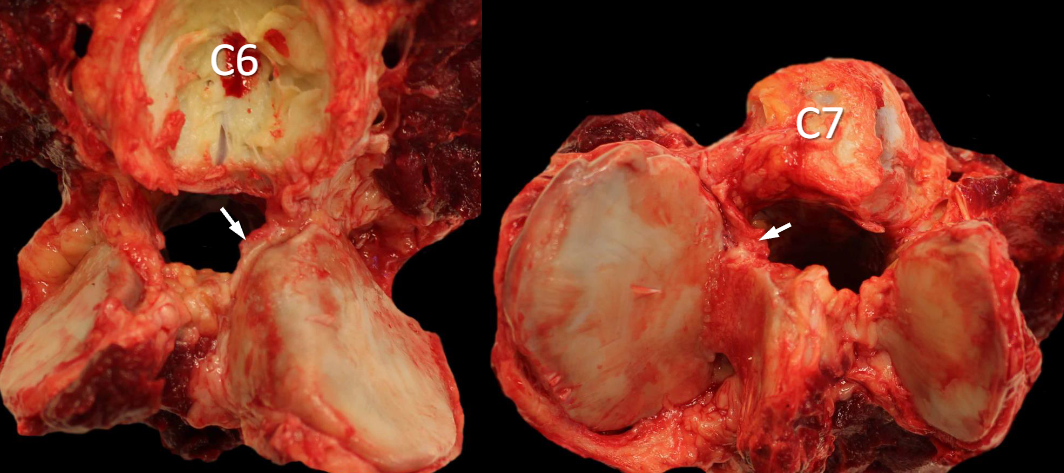
Equine Wobblers Syndrome
Articular facets are asymmetrical causing stenosis, progressive spinal cord compression, and Wallerian degeneration
What is the hallmark of Wallerian degeneration?
Macrophages infiltrating and phagocytizing axonal debris and degenerative myelin
What is the pathogenesis of intervertebral disk extrusion?
Sudden compression
Extrusion of IVD into spinal canal
Spinal cord compression
Neurologic deficits
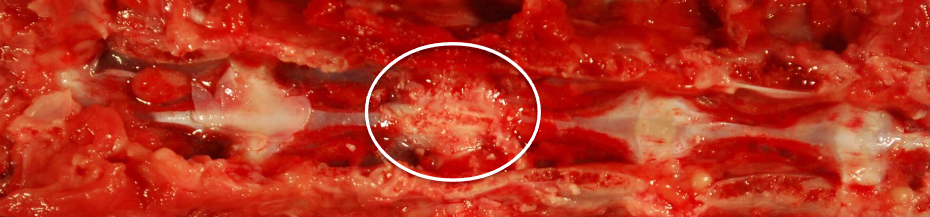
IVD
What is a Hansen type I IVD?
Rapid
Disk material is extruded
Spinal cord compression causes hemorrhage and necrosis
What dogs are more likely to get Hansen Type 1 IVD?
Dachshunds and other small breeds
What is Hansen type II IVD?
Slow
Bulges, does not have extruded disk material
Gradual weakness
What is the lesion from Hansen type II IVD analogous to?
Wobblers
What is the most severe consequence of Hansen type 1 injury?
Progressive hemorrhagic myelomalacia (ascending-descending)
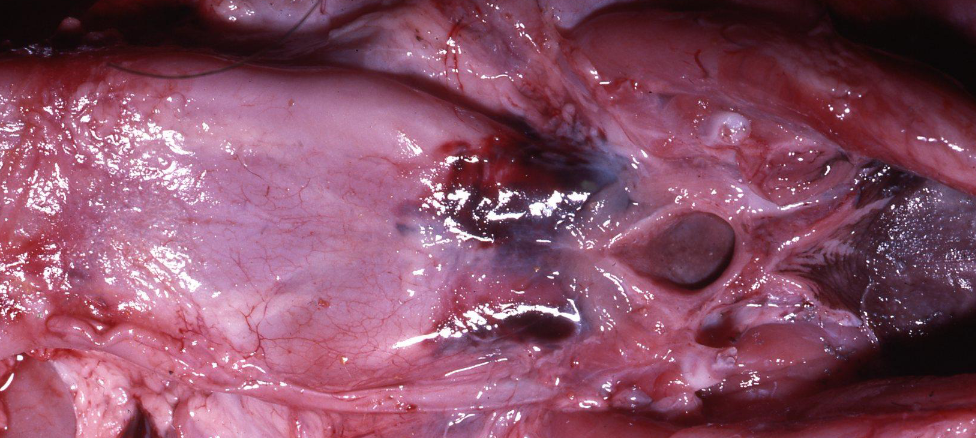
Atlanto-occiptal luxation
What animals are more like to get atlanto-occipital luxation?
Calves, small ruminants, pigs in dystocia
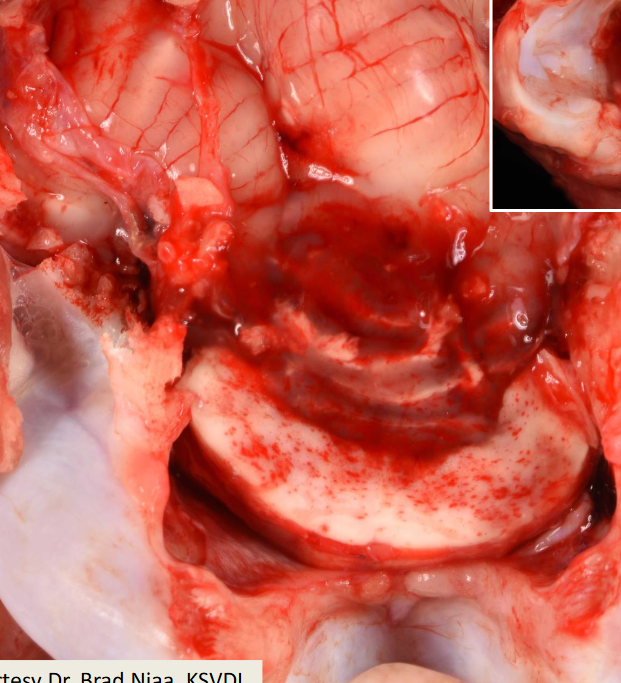
Cause of this traumatic injury?
Mistake while trying to collect CSF