[26] Organic Chemistry
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
what are organic compounds?
All carbon-containing compounds (except CO, CO₂, and carbonates) are organic compounds.
Hydrocarbon
A compound containing only hydrogen and carbon atoms.
Alkane
A saturated hydrocarbon with only single C–C bonds.
Homologous Series
A group of compounds with similar chemical properties, the same general formula, and each member differs by a CH₂ group.
General Formula of Alkanes
CₙH₂ₙ₊₂
Isomers
Compounds with the same molecular formula but different displayed formulae.
Effect of Isomer Shape
Fewer surface contact points → weaker intermolecular forces; more surface points → stronger intermolecular forces.
Crude Oil
A mixture of hydrocarbons of different chain lengths.
Fractional Distillation of Crude Oil
Separates hydrocarbons by boiling point. Small molecules (top) have low boiling points; large molecules (bottom) have high boiling points.
order of fractional distillation of crude oil from lowest bp to highest bp
refinery gases
gasoline
kerosene
diesel
fuel oil
bitumen
Trends in Fractional Distillation (small to large molecules)
Boiling point increases; viscosity increases; flammability decreases; flame gets smokier; colour gets darker.
Small Alkanes
Low boiling points, runny, easy to ignite, burn with a clean flame.
Large Alkanes
High boiling points, viscous, hard to ignite, burn with a smoky flame.
Cracking
Long-chain alkanes are broken into shorter alkanes and alkenes by heating. It is a thermal decomposition reaction.
Purpose of Cracking
To produce more short-chain hydrocarbons (like petrol) that are in higher demand.
Alkenes
A homologous series of hydrocarbons with at least one double C=C bond (unsaturated).
Difference Between Alkanes and Alkenes
Alkanes have single bonds (saturated); alkenes have double bonds (unsaturated).
General Formula of Alkenes
CₙH₂ₙ
Test for Alkenes
Add bromine water — it changes from orange to colourless.
Test for Alkanes what is this called
Add bromine water — no colour change unless UV light is present which will be a substitution reaction
complete combustion for hydrocarbons
hydrocarbon + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water.
Incomplete Combustion equation
hydrocarbon + oxygen → carbon monoxide + water / carbon + water
Signs of Incomplete Combustion
Yellow, smoky flame and formation of soot or CO.
Methane formula
CH₄
Definition of Saturated
A molecule with only single carbon-carbon bonds
Definition of Unsaturated
A molecule that contains at least one double carbon bond.
what is a suitable catalyst for cracking
aluminium oxide
what is a suitable temp for cracking
600-700 degrees
what type of reaction is cracking
thermal decomposition
what happens in an addition reaction in an alkene
double carbon bond turns into a single carbon bond
what does the addition reaction of a hydrogen with an alkene require?
150 degrees and a nickel catalyst
what does the structural formulae of ethene after addition reaction with water

how are alkenes made
by cracking
what is a monomer
alkene molecules
disadvantage of addition polymers
do not biodegrade
features of alcohols
burn well with oxygen and in the lab, alcohols can be oxidised slowly by mild oxidising agents to form carboxylic acids
what is it called when you leave alcohols in the open air
microbial oxidation
what is an example of an oxidizing agent that can be used to make carboxylic acids (reflux) and what is the colour change
acidified potassium dichromate it stars as orange and turns green
2 ways to make ethanol
fermentation and hydration of ethene
conditions for making ethanol with hydration of ethene method
300 degrees celcius, 60-70 atmospheres pressure and phosphoric acid catalyst
what is the process of the hydration of ethene
passing steam and ethene over a heated phosphoric acid catalyst
process of fermentation to make ethanol
raw materials are mixed with water and yeast at just above room temp which contains enzymes
the sugars in the raw materials react with the enzymes to form ethanol and carbon dioxide, the carbon dioxide is allowed to escape but air is prevented from entering the reaction vessel to stop oxidation of ethanol to ethanoic acid
when the reaction is over the ethanol is separated from the reaction mixture by fractional distillation
conditions needed for fermentation to make ethanol
30-40 degrees celcius, presence of water, sugar as glucose, absence of oxygen for anaerobic respiration to avoid anaerobic respiration where ethanol is oxidised to become ethanoic acid
pros and cons of hydration of ethene to make ethanol
is continuous and fast, the process gets you pure ethene but it uses fossil fuels which is a finite source
pros and cons of fermentation to make ethanol
does not use fossil fuels it uses crops that can be used again but the ethanol made is not pure so we have do distilled it so it has many steps and fermentation is a slow process and not continuous
features of carboxylic acids
weak acid so they do not dissociate fully in water meaning they only partially donate protons
react with alcohols to form esters
carboxylic acid + metal → ?
carboxylic acid + carbonates→ ?
carboxylic acid + alkalis → ?
salt+ hydrogen
salt + water + carbon dioxide
salt + water (neutralization)
what are salts formed by ethanoic acid called
ethanoates
functional group of carboxylic acids
COOH
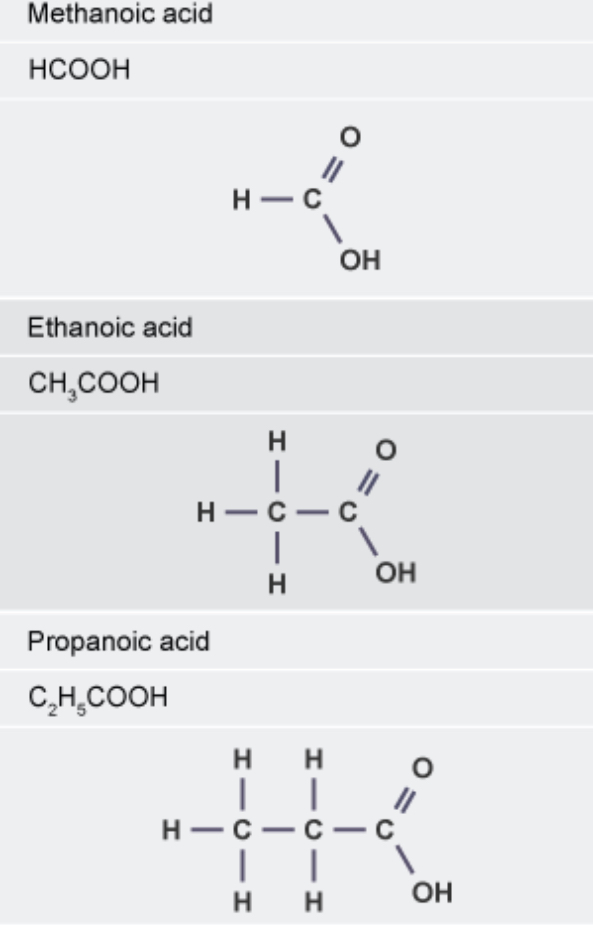
molecular formula for propanoic acid ethanoic acid and methanooc acid
propanoic acid → CH₃CH₂COOH
ethanoic acid → CH₃COOH
methanoic acid→ HCOOH
displayed formula of methanoic ethanoic and propanoic acid
What is addition polymerisation?
A reaction where alkene monomers join to make a polymer without producing any by-products.
Why are addition polymers non-reactive?
Because they contain strong C–C single bonds and no reactive double bond.
Why are addition polymers a disposal problem?
They are non-biodegradable and persist for hundreds of years.
Name two problems caused by incineration of addition polymers.
1) Releases toxic gases, 2) Contributes to air pollution.
What is condensation polymerisation?
A reaction where monomers with two functional groups join, forming a polymer and a small molecule usually water
What two types of molecules form polyesters?
A diol and a dicarboxylic acid.
What functional group is formed in polyesters?
Ester links (–COO–)
Are condensation polymers biodegradable?
Some are, because ester links can be broken down easily
uses of alkenes
Alkenes are used to make plastics because their carbon–carbon double bond is reactive, allowing them to undergo polymerization and form long, strong polymer chains.
uses of short chain alkanes
used as petrol because they have lower boiling points, highly flammable and release alot of energy when burnt