Chapter 12- Firms in Perfectly Competitive Markets
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Name 3 characteristics of perfectly competative markets?
1) Many buyers and many firms (ie. sellers)
2) All firms in the market must sell identical products
3) There must be no barrier to new firms entering the market
What 2 things exist in a Perfectly Competitive Market?
Give an example of a perfectly competative market?
1) Firms are unable to control the price of the products they sell (Price taker)
2) Firms are unable to earn an economic profit in the long run
*Examplee: Agriculture Markets
What do we call A buyer or seller (ie. firm) that is unable to affect the market price?
Price Taker
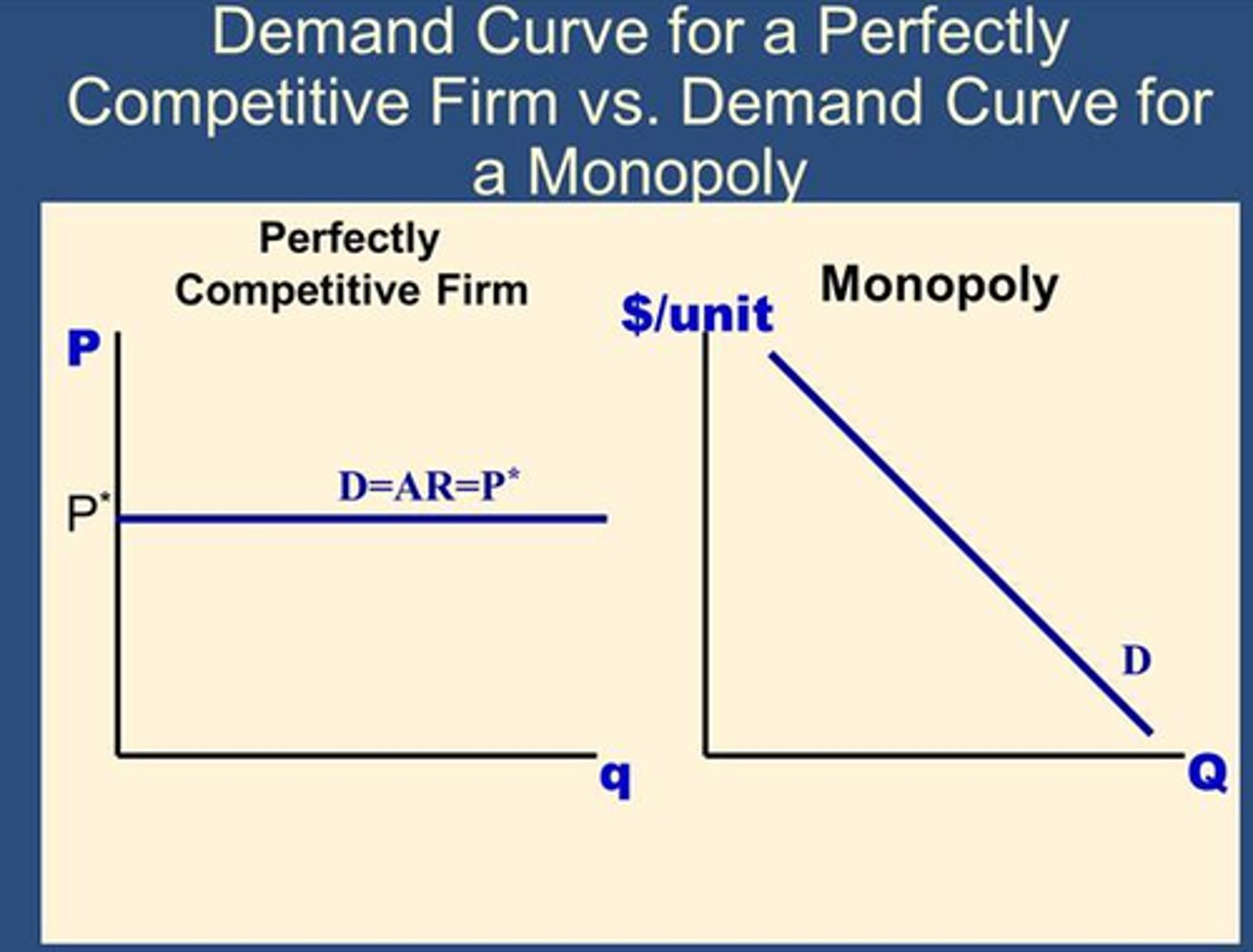
1) Draw a demand curve for firms products in a Perfectly Competitive Market. What is unique about it?
2) Why would a firm not sell below this price shown on this demand curve?
3) Why would it not sell above it?
1) See pic on left
Unique Characteristic of Demand Curve
a) Its Horizontal (making firms price takers)
b) The Demand Curve and the MR Curve and the AR Curve are all the same as each unit sold is sold at the same price
2) *B/c it can sell as much as it choose at market price
Market
3) Because it would sell nothing as consumers would buy from someone else
Marginal Revenue (MR)
a) Give the equation
b) In a perfectly competitive market the MR is equal to ________________
a) MR = ∆TR ÷ ∆Q
b) market price
Profit
- Give Equation?
- What does Total Cost include?
a) Profit = Total Revenue (TR) - Total Cost (TC)
b) Both both explicit and implicit costs
- Explict Cost => a cost that involves spending money
- Implicit Cost => opportunity costs (no money outlay)
Economic Profit
total revenue minus total cost, including both explicit and implicit costs
Normal Profit
- Accounting profit (Rev - Expenses) when that is exactly equal to opportunity cost
Explain what happens under the following situations:
1) Economic Profit = $0
2) Economic Profit > $0
3) Economic Profit < $0
a) No firms/seller enter or leave the market
(note: Normal Profit = Oppor Cost)
b) Seller will enter the market which means the supply curve will shift left and prices will drop until Economic Profit =$0
(note: Normal Profit > Oppor Cost)
c) Seller will leave the market which means the supply curve will shift right and prices will RISE until Economic Profit =$0
(note: Normal Profit < Oppor Cost)
Average Revenue (AR)
a) Give equation
b) What is unique about AR in a perectly competative market
a) AR = TR ÷ Q
b) ALWAYS equal to market price so MR=AR=Market Price
How much does a firm produce to maximize profit?
-Firm's will keep producing until MR=MC
-Graphically: Profit maximizing output = the difference where the distance b/w TR and TC is the greatest
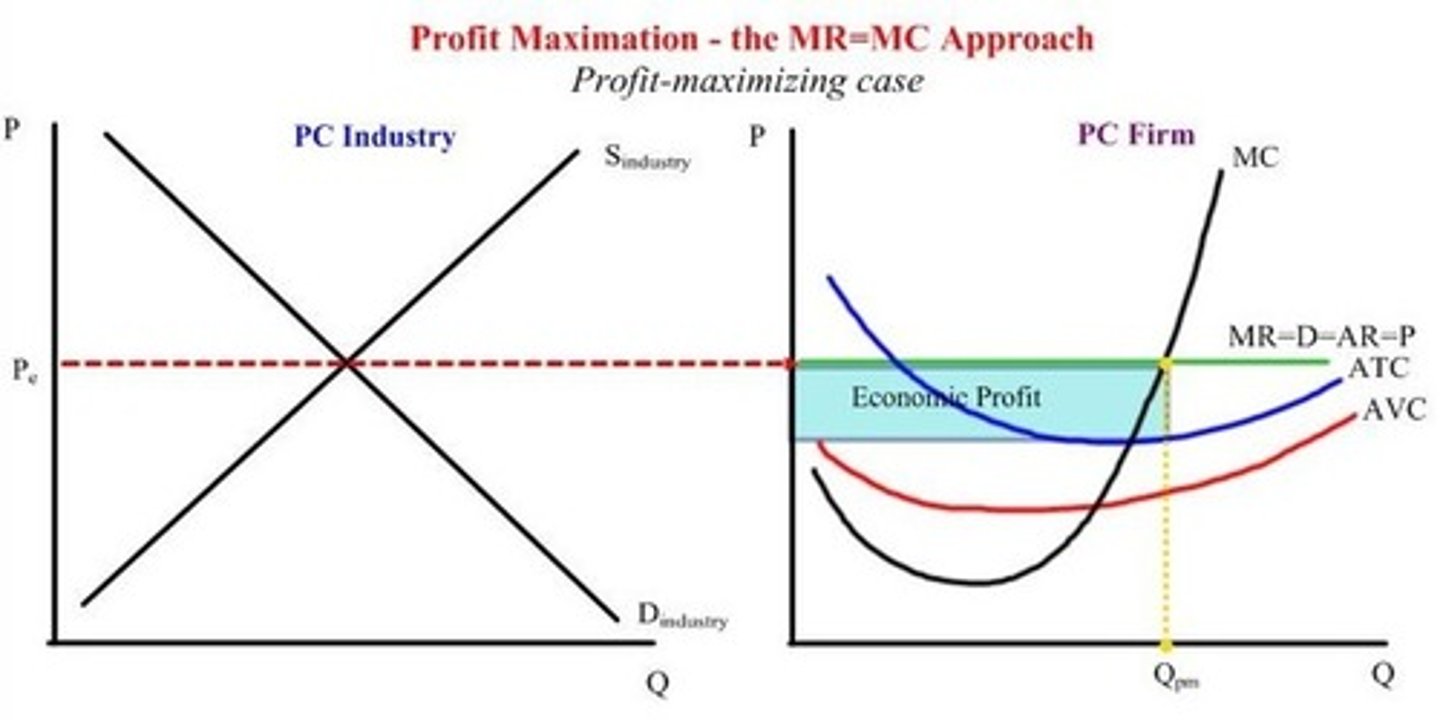
a) Draw a Graph that shows a firm producing an Economic Profit and is maximizing profit. Label the following:
- ATC
- AVC
- MC
- Economic Profit
- MR, D, AR, P (note: these are all the same so label them like "MR=D=AR=P"
- Q(optimal)
b) What is the relationship of P and ATV when there is there an Economic Profit?
c) What will happen to the Economic Profit in the LONG RUN?
a) See pic
b) P>ATV
c) Firms will enter market and shift the supply curve to the right lowering price until economic profit = $0
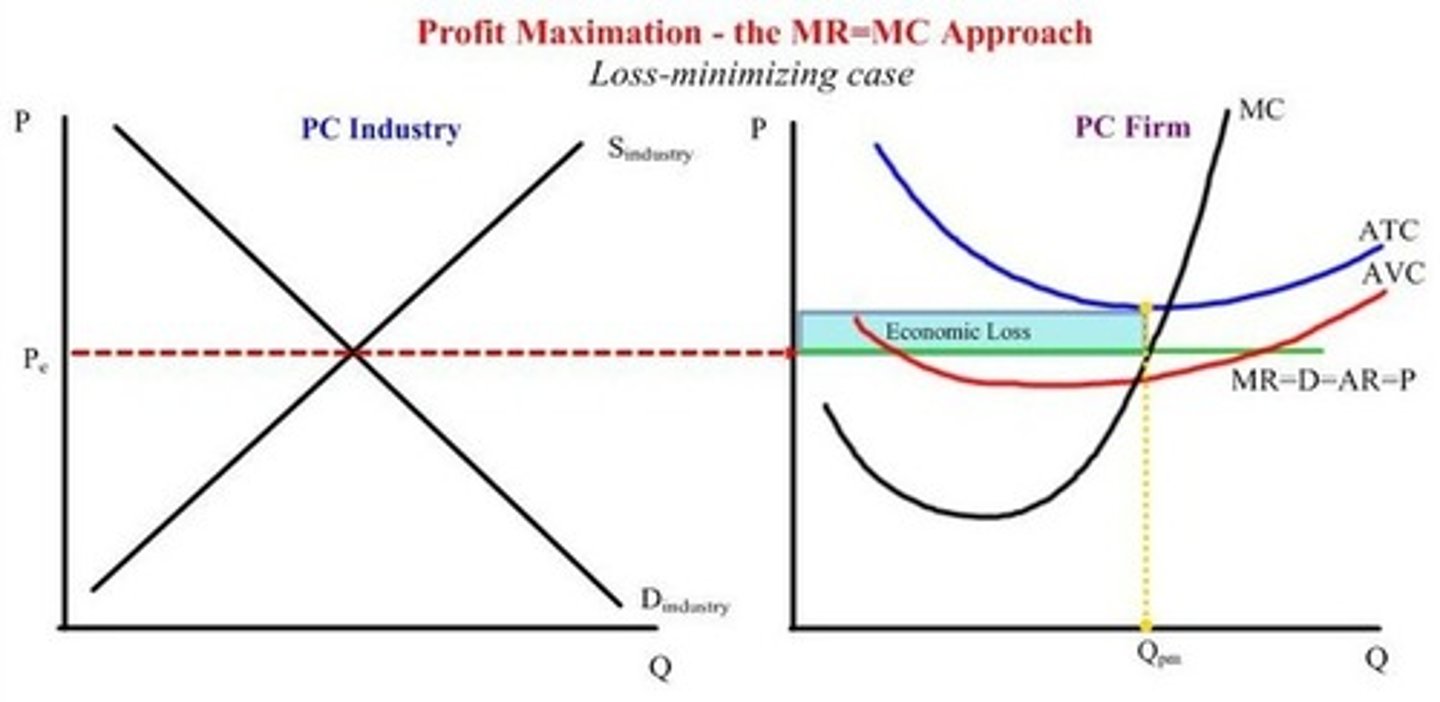
a) Draw a Graph that shows a firm producing an Economic LOSS but is making enough to cover AVC. Label the following:
- ATC
- AVC
- MC
- Economic Loss
- MR, D, AR, P (note: these are all the same so label them like "MR=D=AR=P"
- Q(optimal)
b) What is the relationship of P, ATC and ATV when there is there an Economic Loss but no shutdown?
b) What will happen to the Economic Loss in the LONG RUN?
a) See pic
b) ATV>P>AVC
b) Firms will leave the market (they can make more elsewhere) and this shift the supply curve to the left increasing price until economic profit = $0
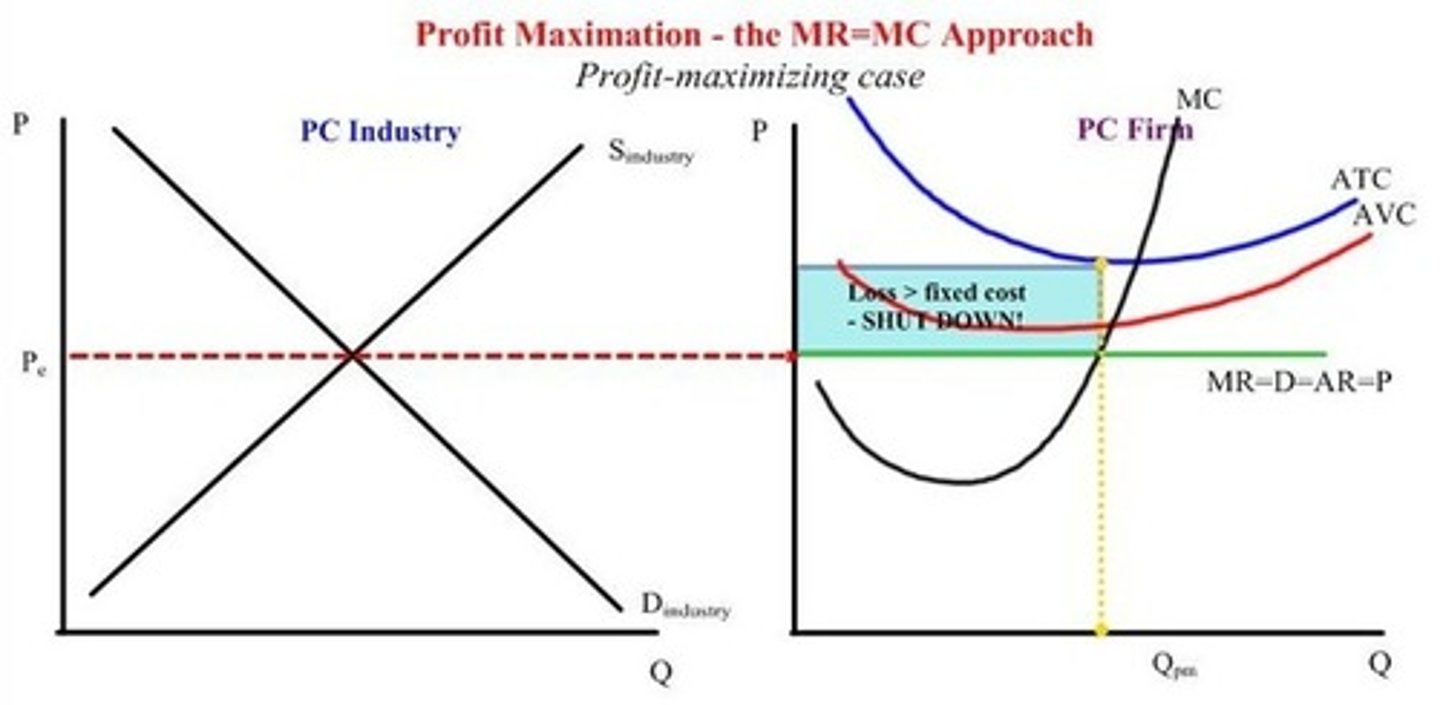
a) Draw a Graph that shows a firm producing an Economic LOSS and all the costs are above the equilibrium price line, meaning that the company will just lose money by producing any goods.
- ATC
- AVC
- MC
- Economic Loss
- MR, D, AR, P (note: these are all the same so label them like "MR=D=AR=P"
- Q(optimal)
b) What should the company do in this case?
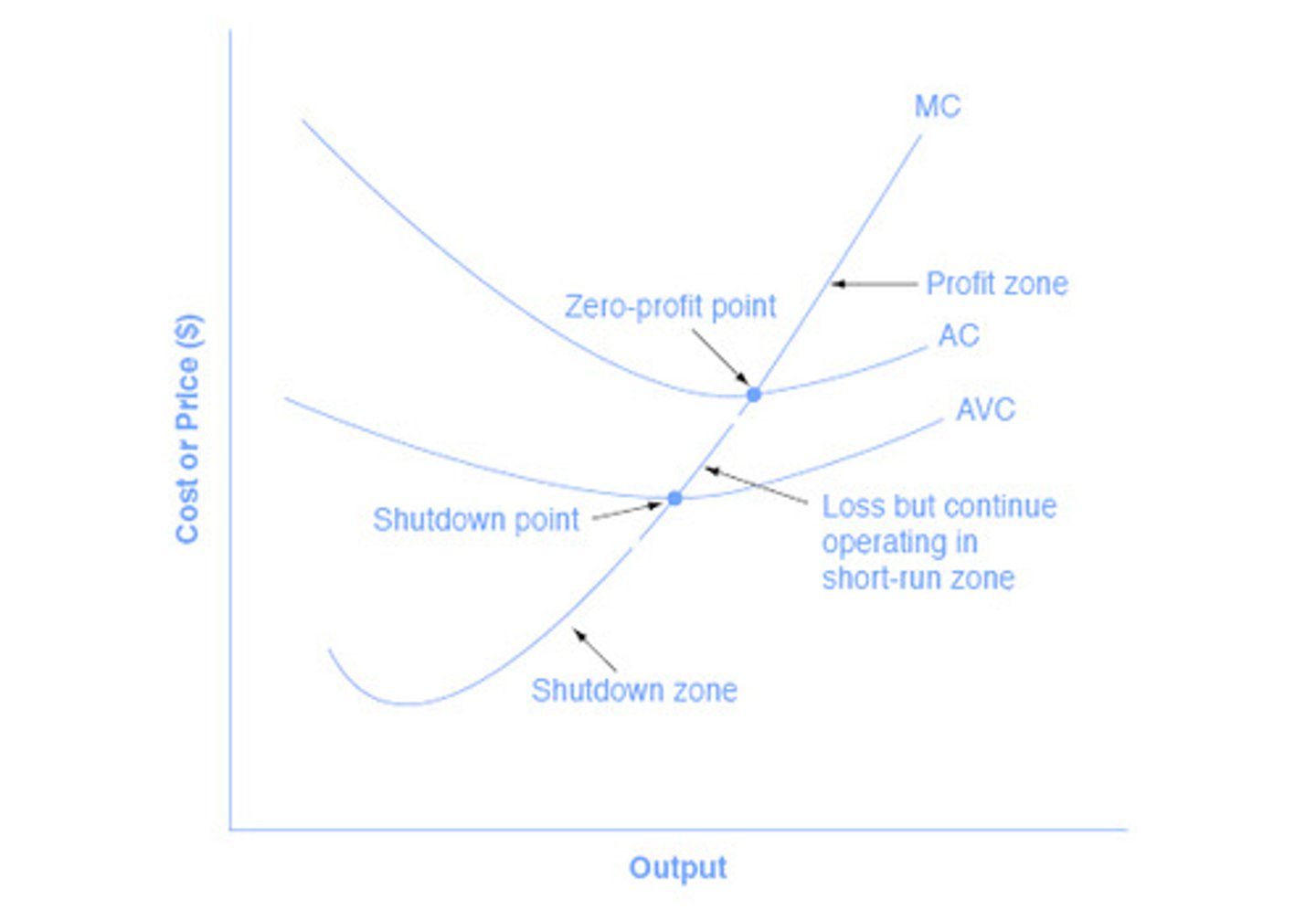
c) What is the rule for when a company should shut down in terms of P and AVC
a) See pic
b) Shut down the plant. The more they produce the more they lose.
c) Price will be below AVC
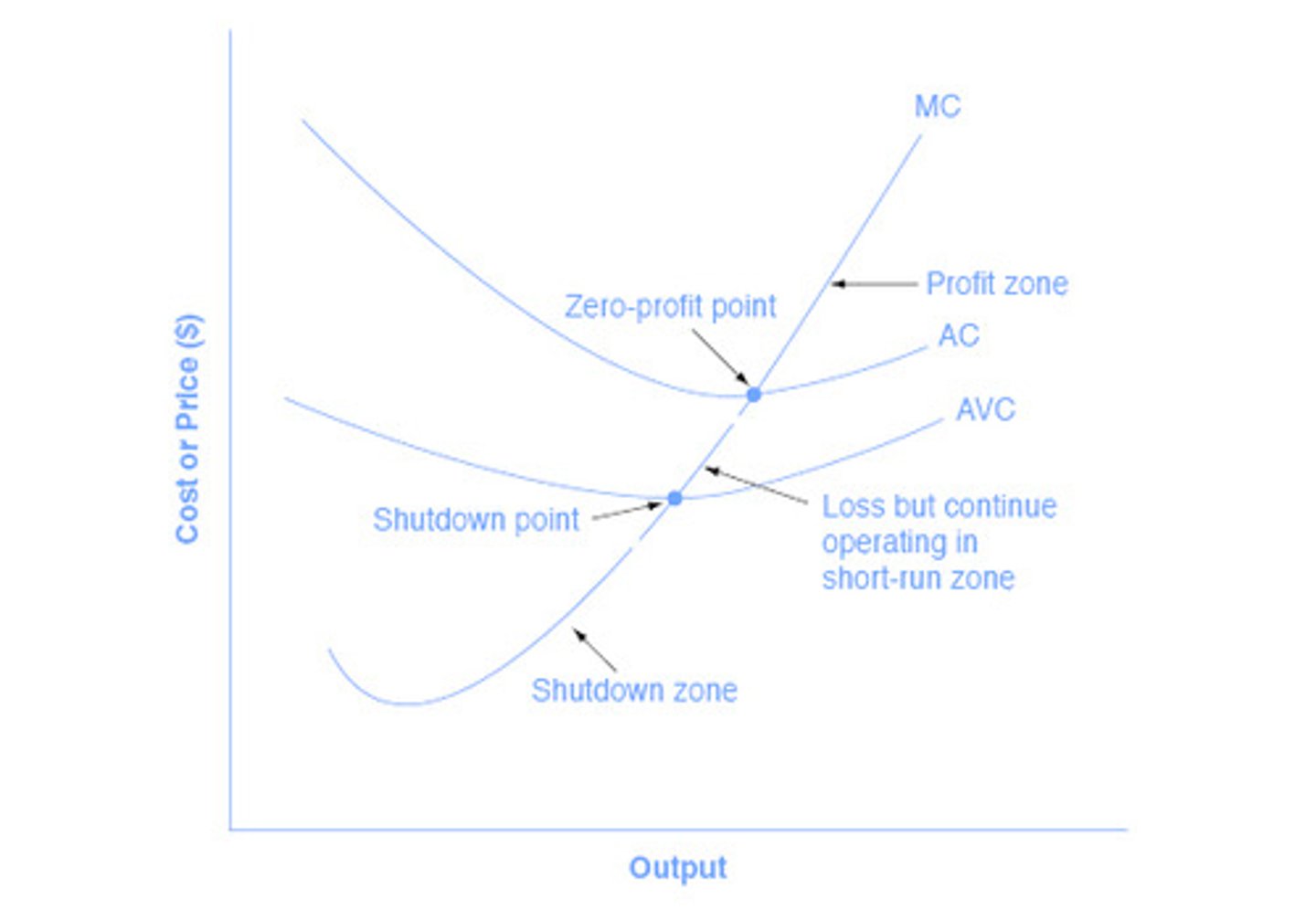
Average Cost or ATC
- What is the equation
- What two components are in the ATC or AC
- The total cost divided by the number of units
TC/units
- Variable Cost (ie. AVC) and Fixed Cost
What does the firm do if:
If price < AVC
firm shuts down and incurs a loss equal to TFC
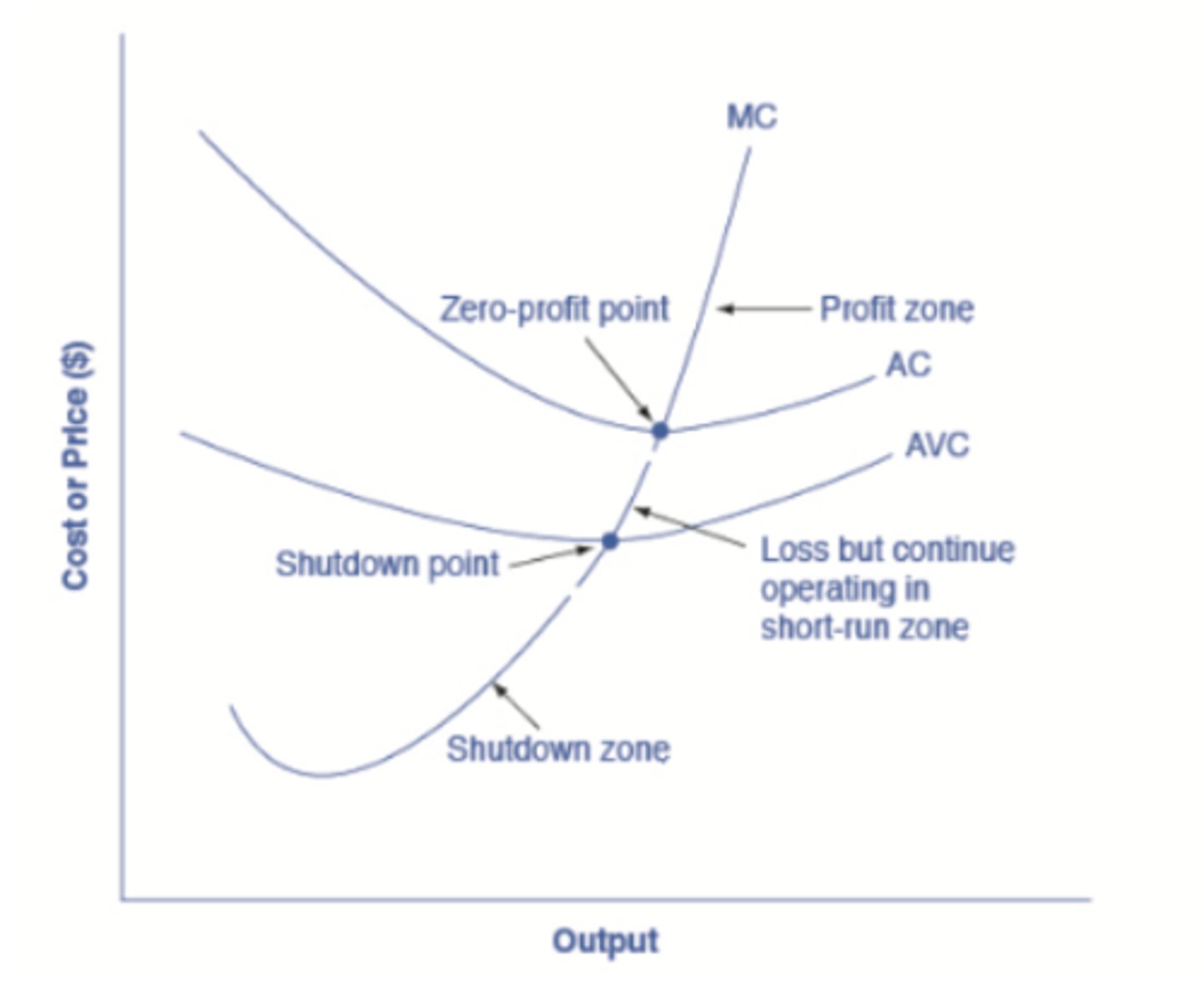
If price > AVC but < ATC
firm keeps producing in order to minimize losses (loss will be less than TFC). In this case it will be an economic loss.
SEE "Loss but continue to operate in short run zone" on pic
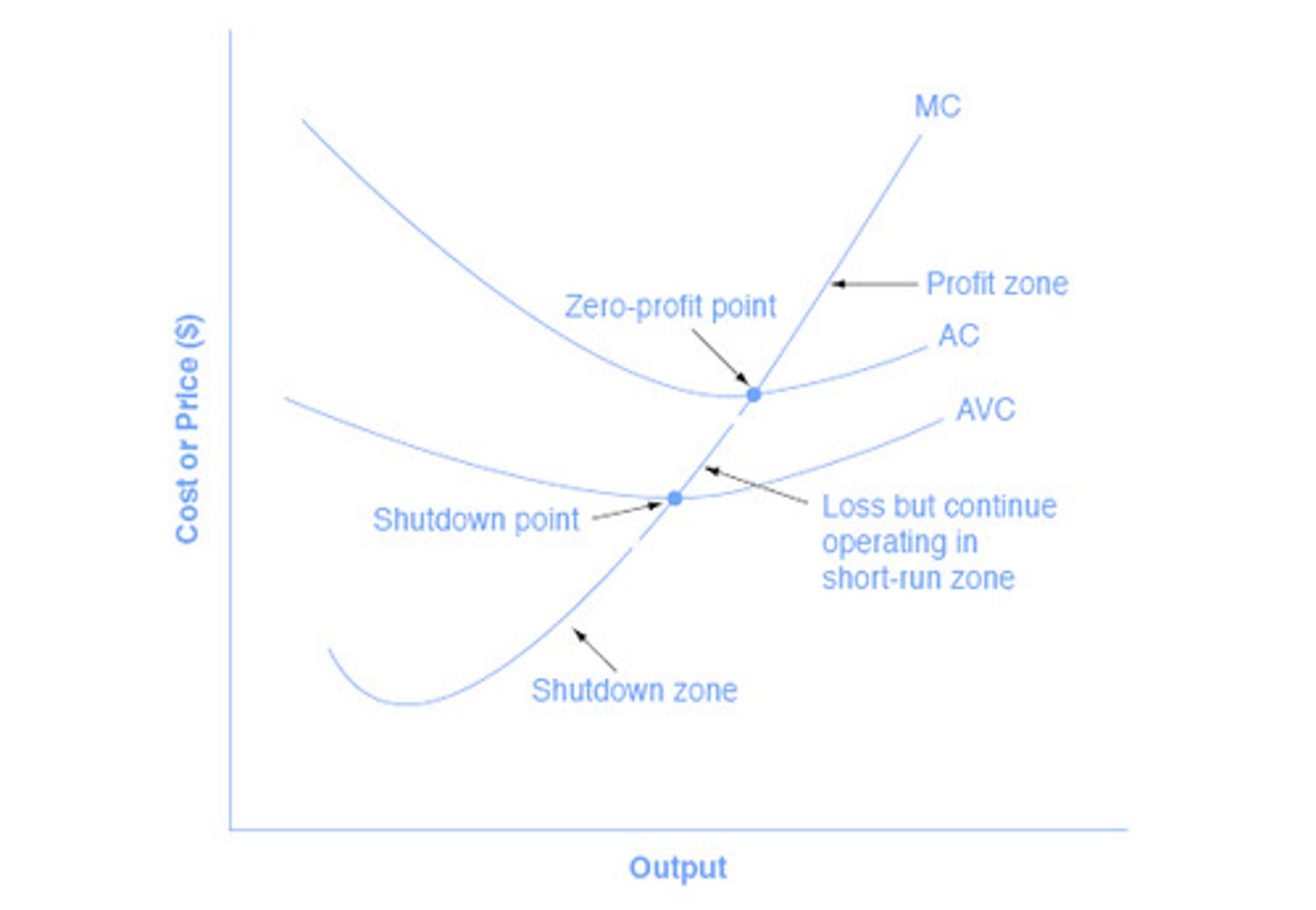
If Price is > ATC
firm will keep producing and in this case will have an economic profit (See Profit Zone)
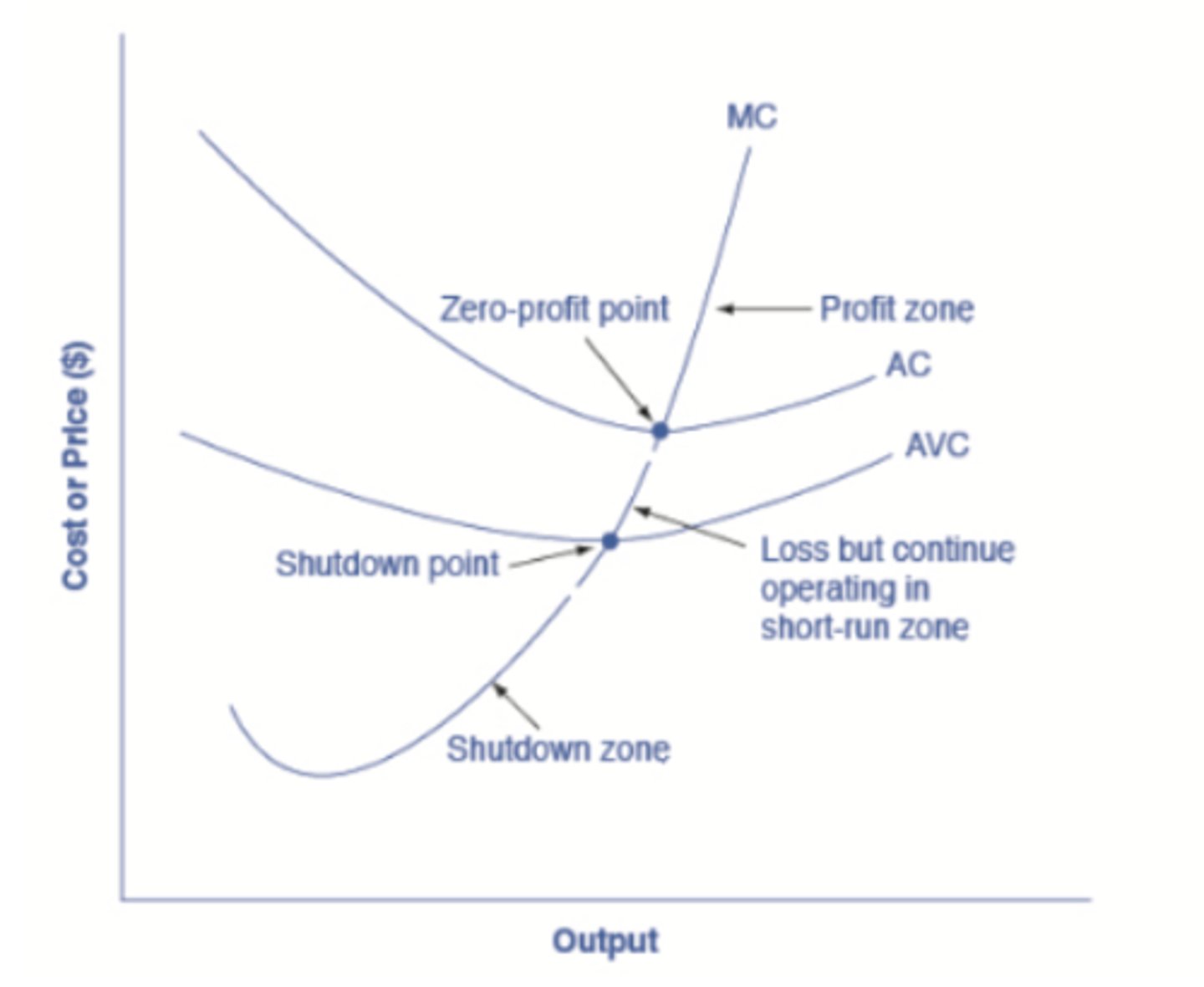
If Price = ATCmin
This is the Break Even Point (see ZERO PROFIT POINT)
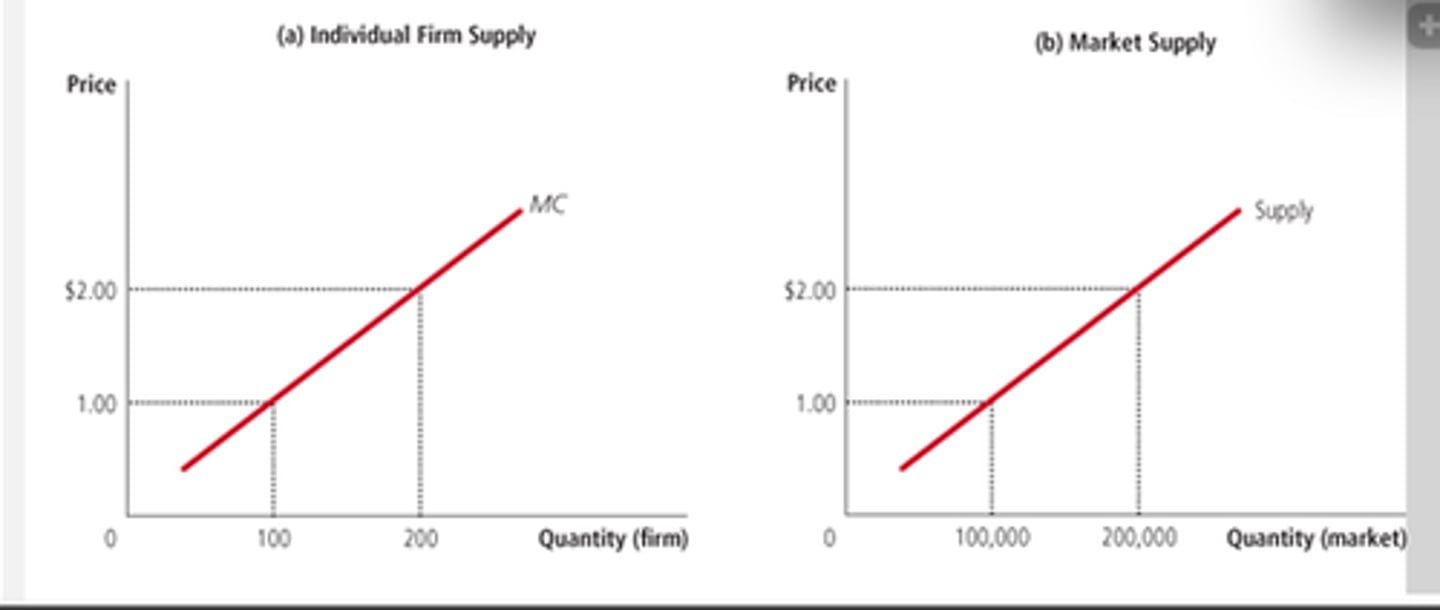
The short run market supply is equal to _____________________________.
Sum the quantities supplied by all the firms at each price (see pic)
Long-run equilibrium
- What does this mean
the process of entry or exit is complete - remaining firms earn zero economic profit
When ℼ = Economic Profit discuss whether under each scenario if firms enter or exit the indusctry
A) ℼ < 0
B) ℼ > 0
C) ℼ = 0
A) ℼ < 0 => some firms exit the industry
B) ℼ > 0 => some new firms enter the industry
C) ℼ = 0 => there is no entry or exit
When an industry is in Long term equilibrium what 4 things exist?
See Zero Profit POINT on graph
1) P = minATC (ie AC)
2) P = point where MR = MC
3) there is $0 econ profit
4) No entry or exit in industry