Four Basic Tissue Types 2.0
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Epithelial tissue
form the basis of many of the body surfaces
→ so that one side of cell is in contact w/ the extorior and the other side in contact w/ the interior
Function: Absorption, Secretion, and protection against foreign substances
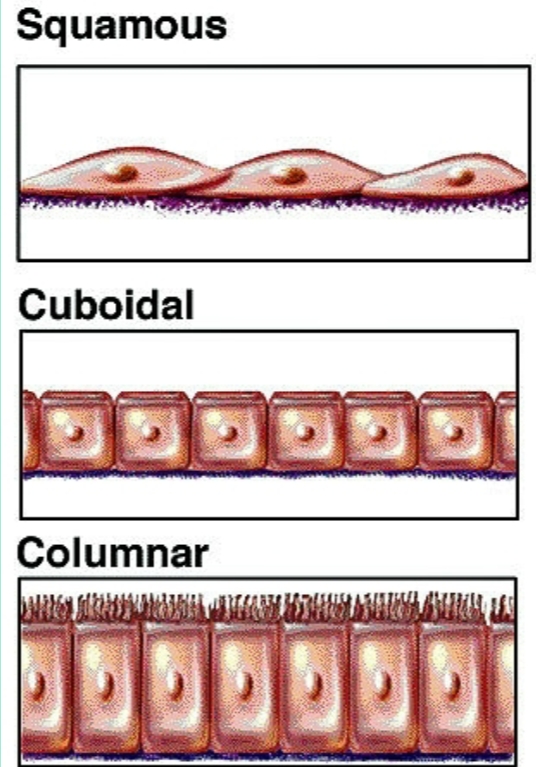
What shapes do the epithelial tissues have?
Squamous → flat/squashed
Cuboidal → like a cube
Columnar → like a column
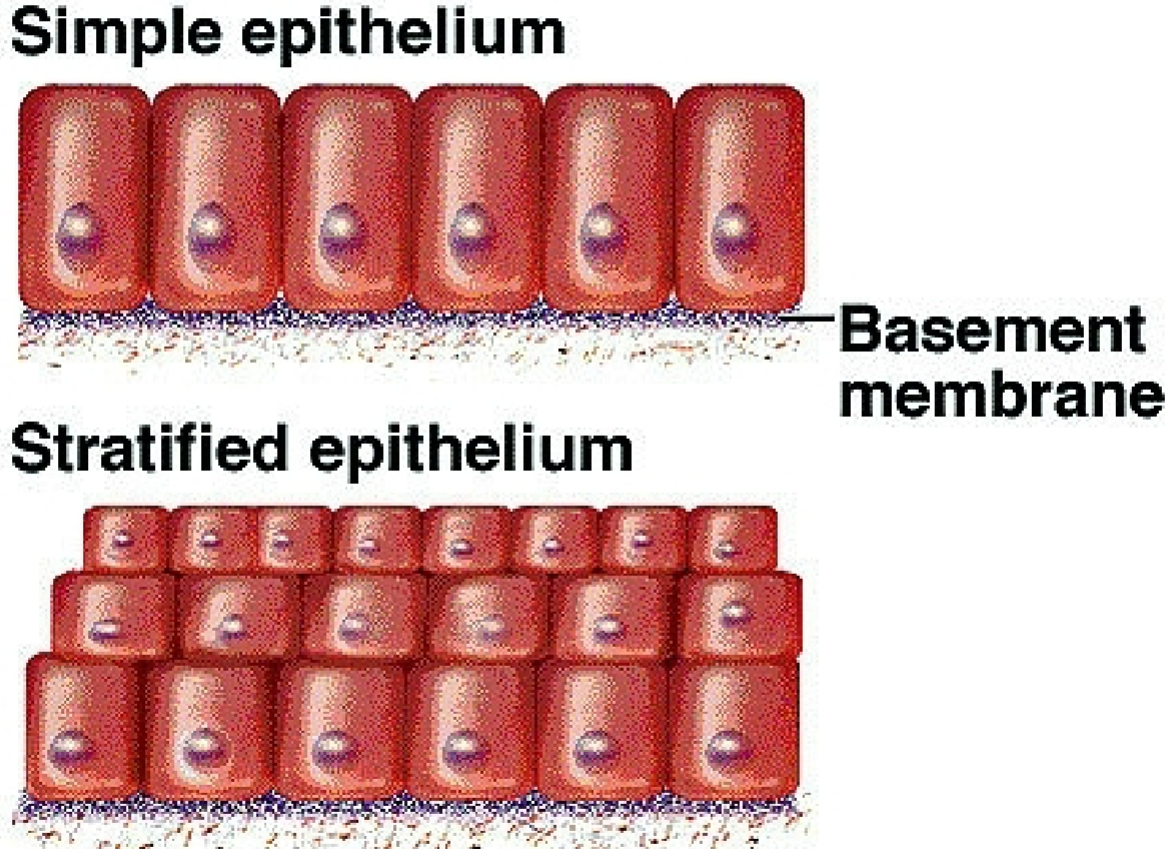
What layers do the epithelial tissues have?
Simple → one layer
Stratified → more than one layer
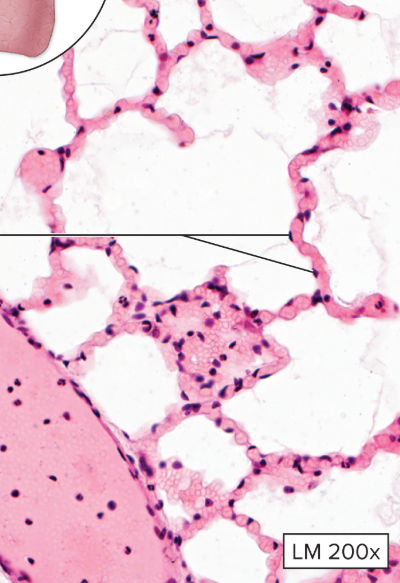
What type of epithelial tissue is this?
Simple Squamous Epithelium
single layer of thin, flat, irregularly shaped cells resembling floor tiles.
the single nucleus of each cell bulges at the center
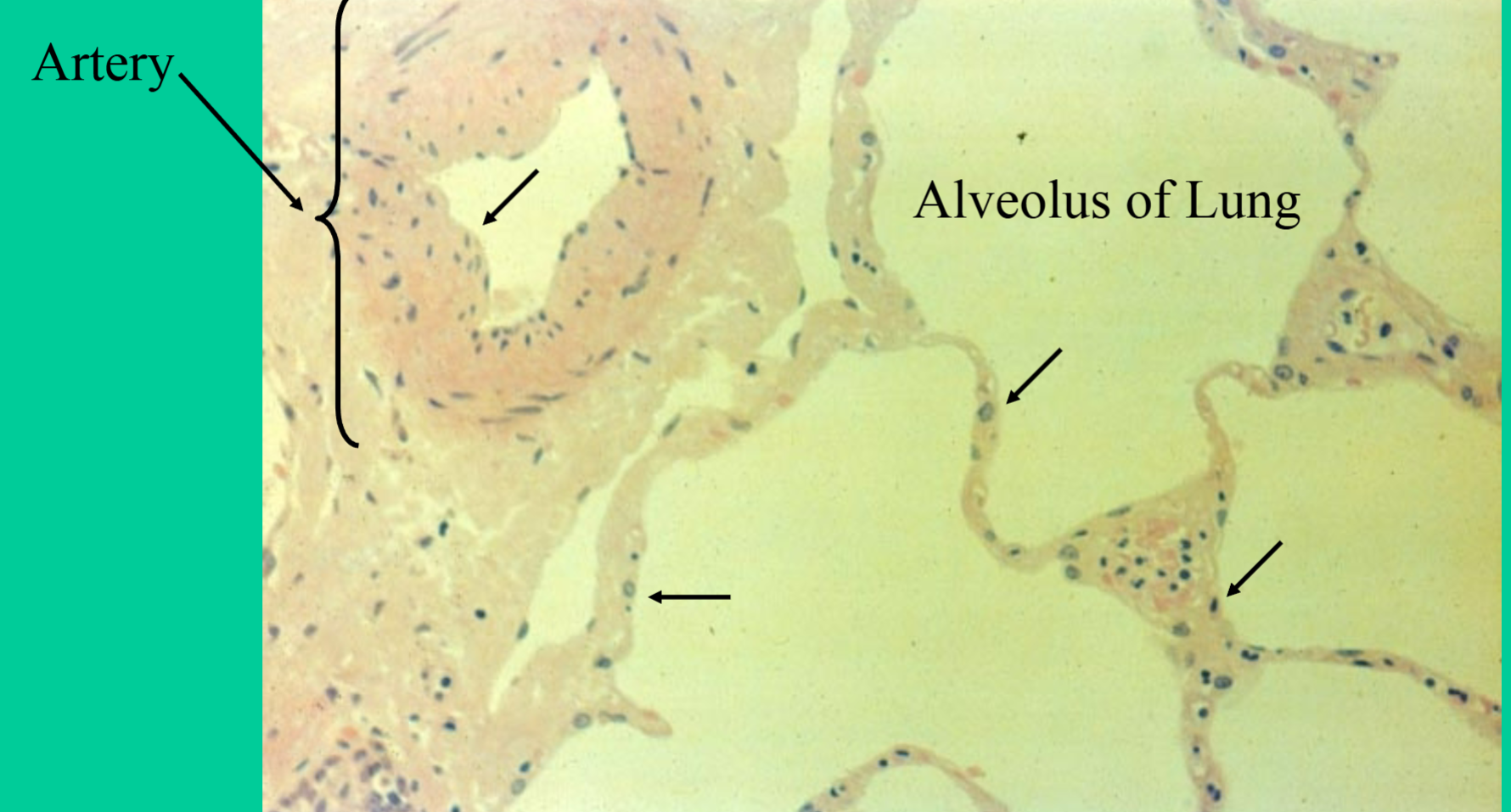
What is the function of the simple squamous epithelium tissue?
gas exchange
rapid diffusion, filtration, and some secretion in serous membranes
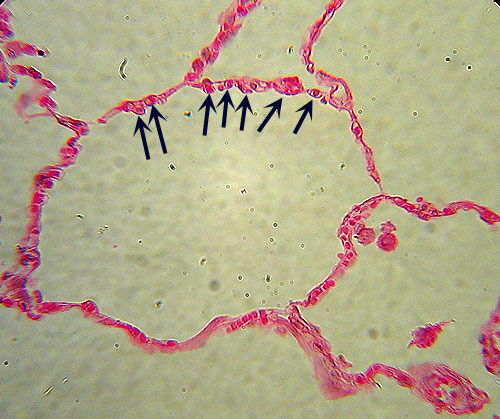
Where are simple squamous epithelial tissues found?
Alveoli → air sacs in the lungs
Endothelium → lining of the heart chambers and lumen of blood vessels
Mesothelium → serous membranes of body cavities
Amnion → sac-like membrane around the embryo
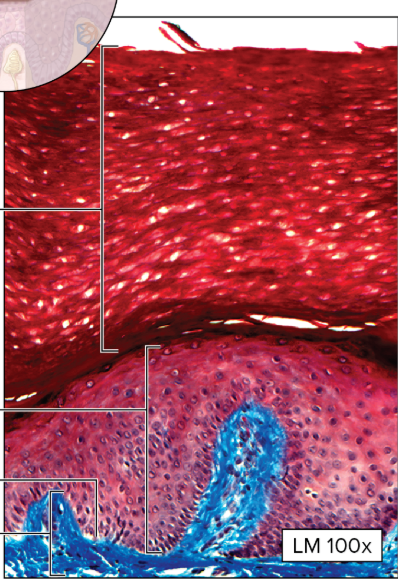
What type of epithelial tissue is this?
Stratified squamous
top layer of the skin
tough, anti-abrasive coverings, rapid mitosis
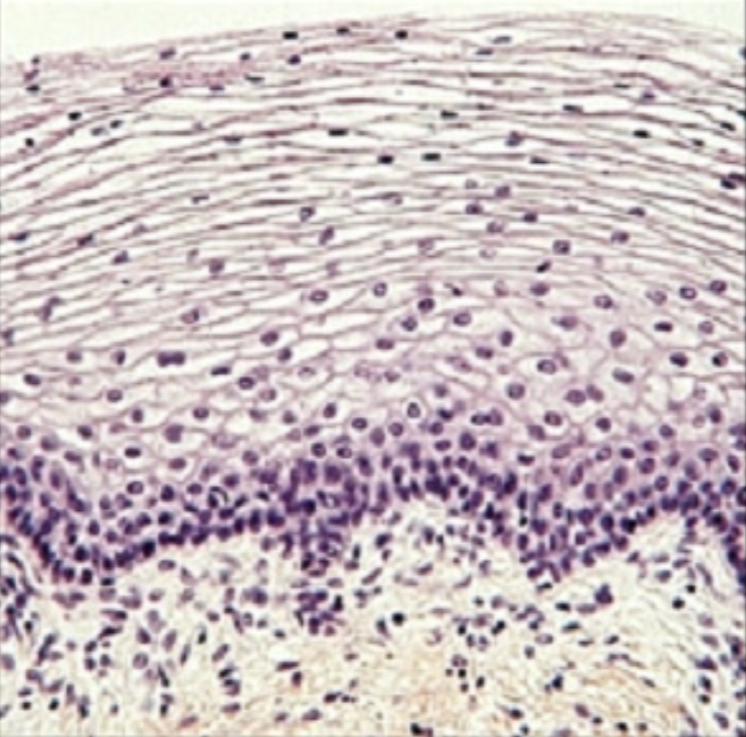
What is the function of the stratified squamous epithelium tissue?
Protection of underlying tissue
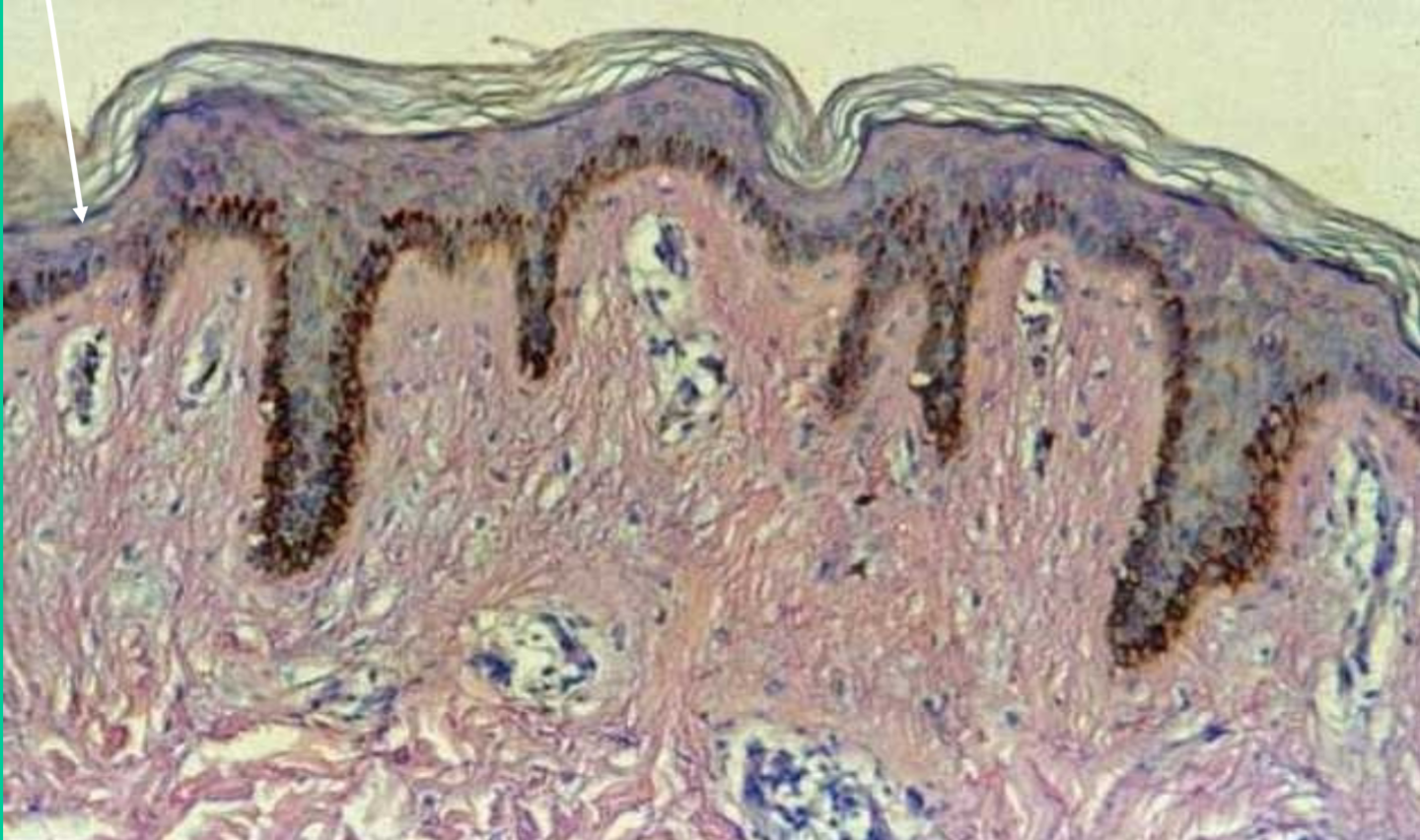
Where are stratified squamous epithelium tissues found?
Epidermis of the skin (top layer)!!!
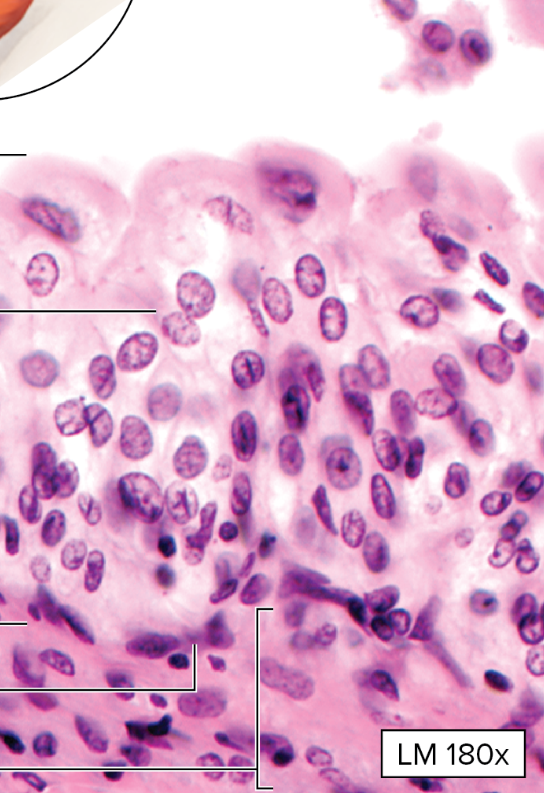
What type of epithelial tissue is this?
Simple Cuboidal
single layer of cells about as tall as they are wide; spherical, usually located in the nucleus
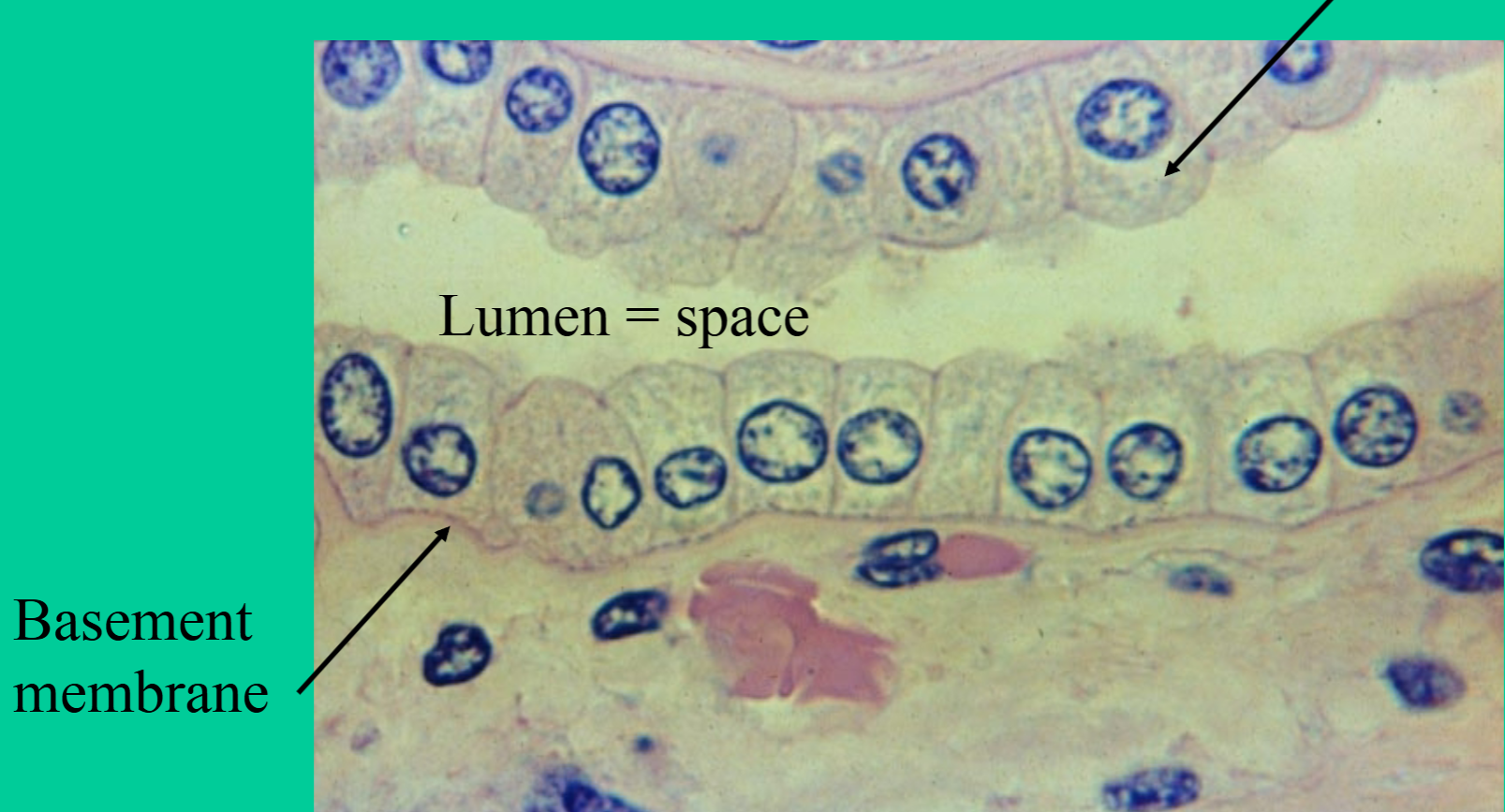
What is the function of the simple cuboidal epithelial tissue?
Absorption and Secretion
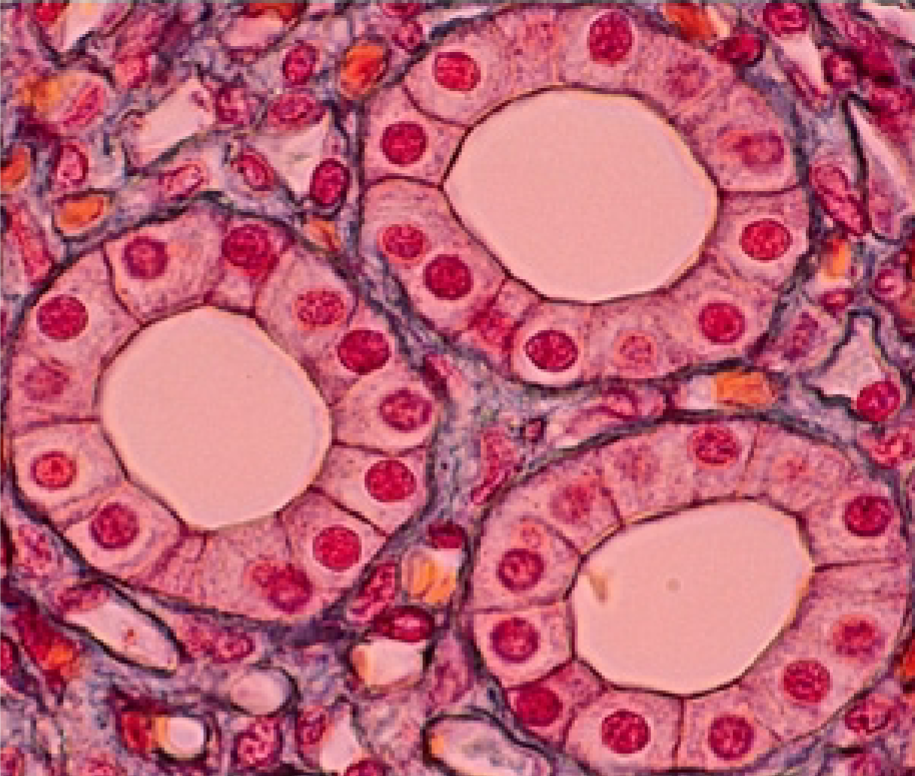
Where are simple cuboidal epithelial tissues found?
Kidney tubules,
thyroid glad follicles ,
ducts and secretory regions of most glands,
surface of ovary
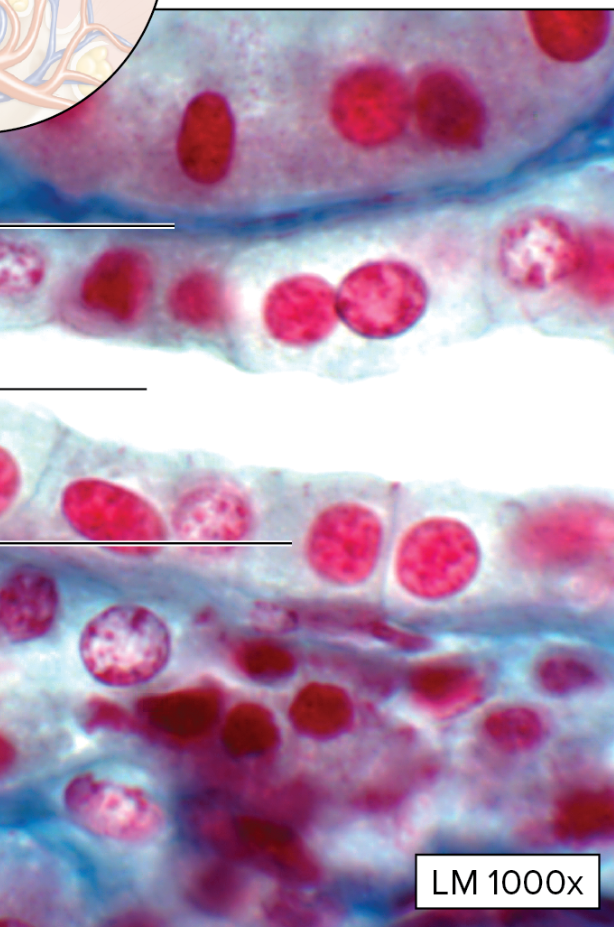
What type of epithelial tissue is this?
Transitional Epithelium
appearance varies, depending on whether the tissue is stretched or relaxed; shape of cells at apical surface changes; some cells may be binucleated (two nucleus)!!!!
change from cuboidal to squamous- line the urinary passage
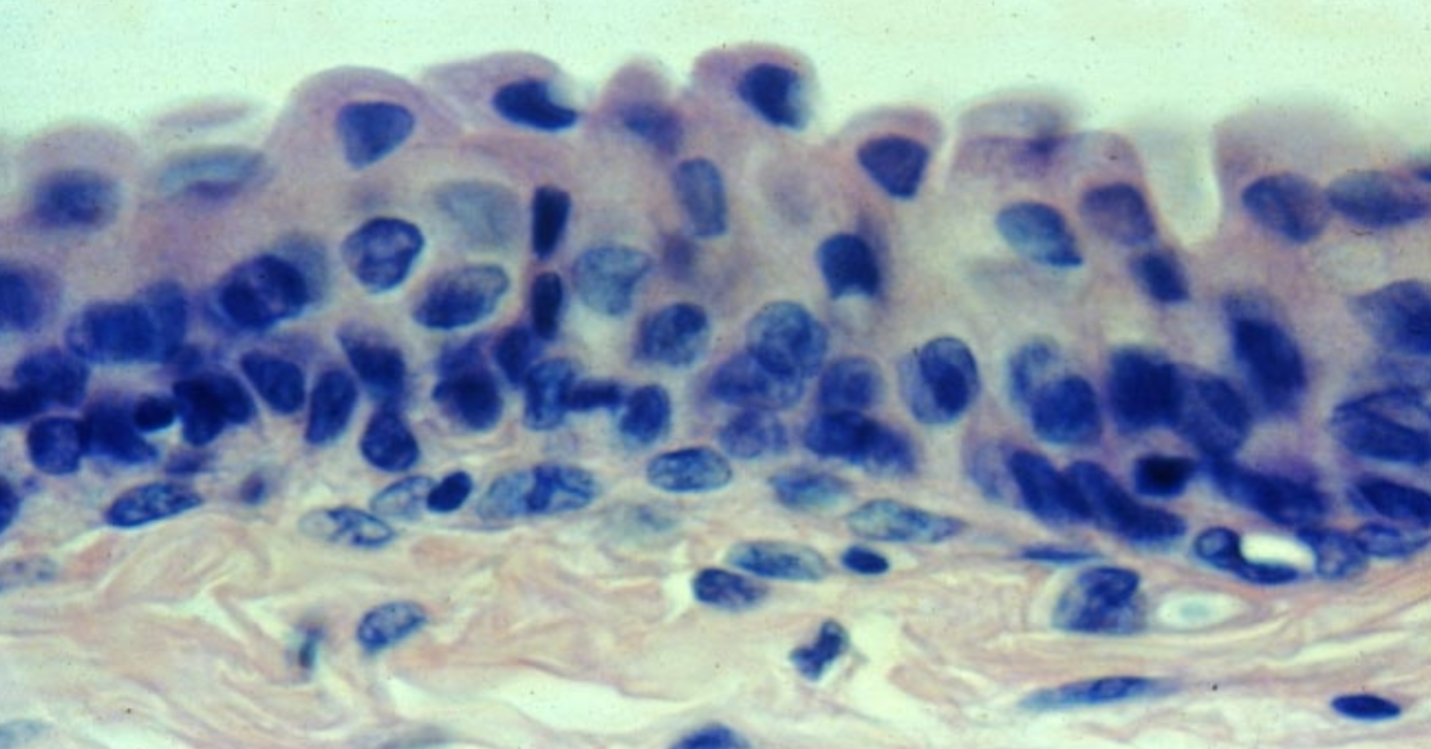
What is the function of the transitional epithelium tissue?
Distension and relaxation of to accommodate urine volume changes in bladder, uterus, and urethra
Where are transitional epithelium tissues located?
Lining of urinary bladder, uterus, and part of urethra
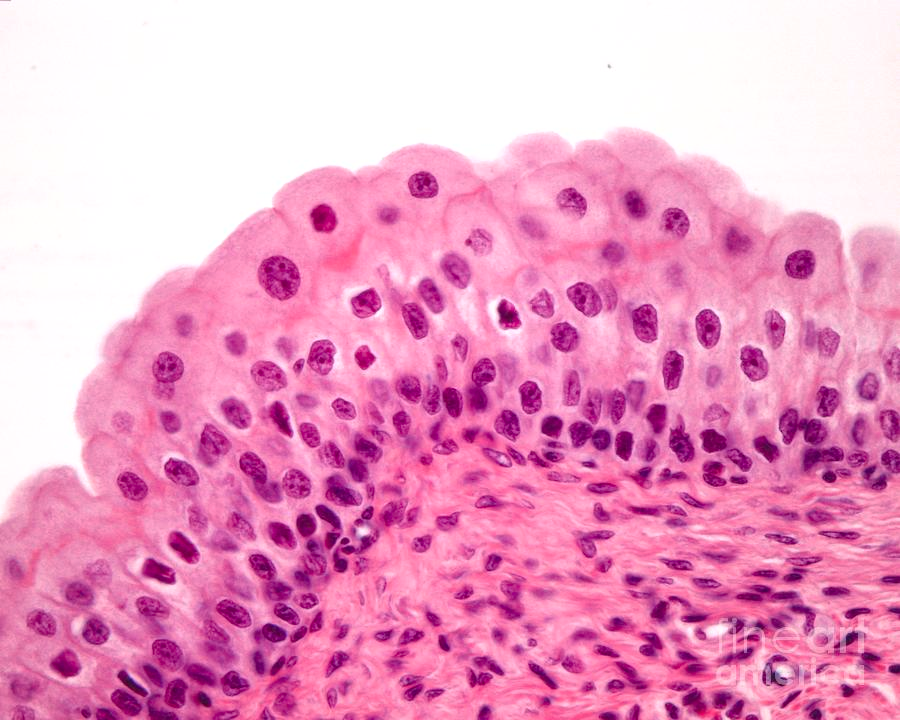
What is this type of epithelial tissue?
Nonciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium
single layer of tall, narrow cells
oval-shaped nucleus oriented lengthwise
may contain goblet cells
What is the function of the nonciliated simple columnar epithelium?
Absorption and secretion; secretion of mucin
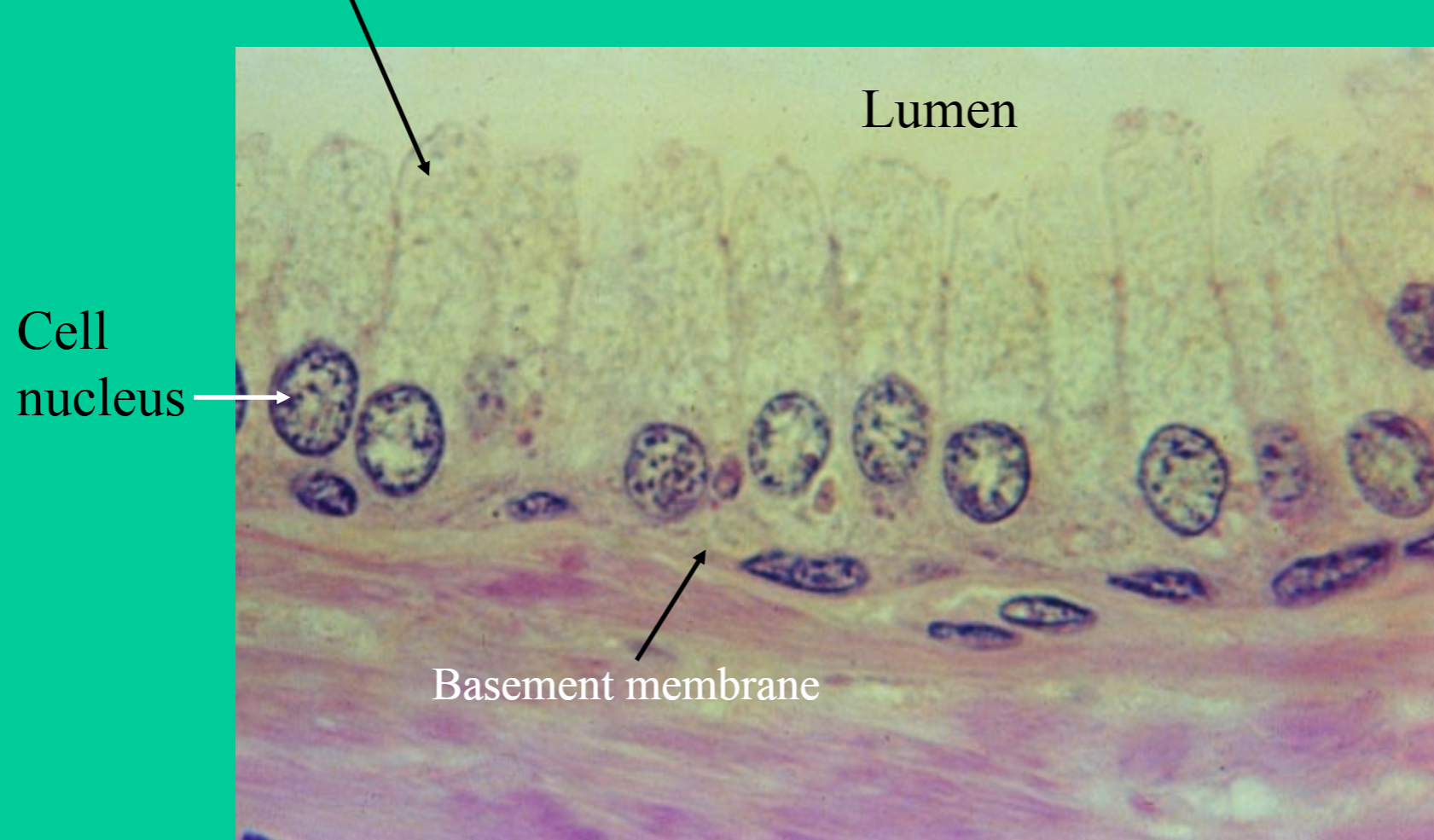
Where are nonciliated simple columnar epithelial tissues found?
Lining most of digestive tract
→ lining of stomach does NOT contain goblet cells
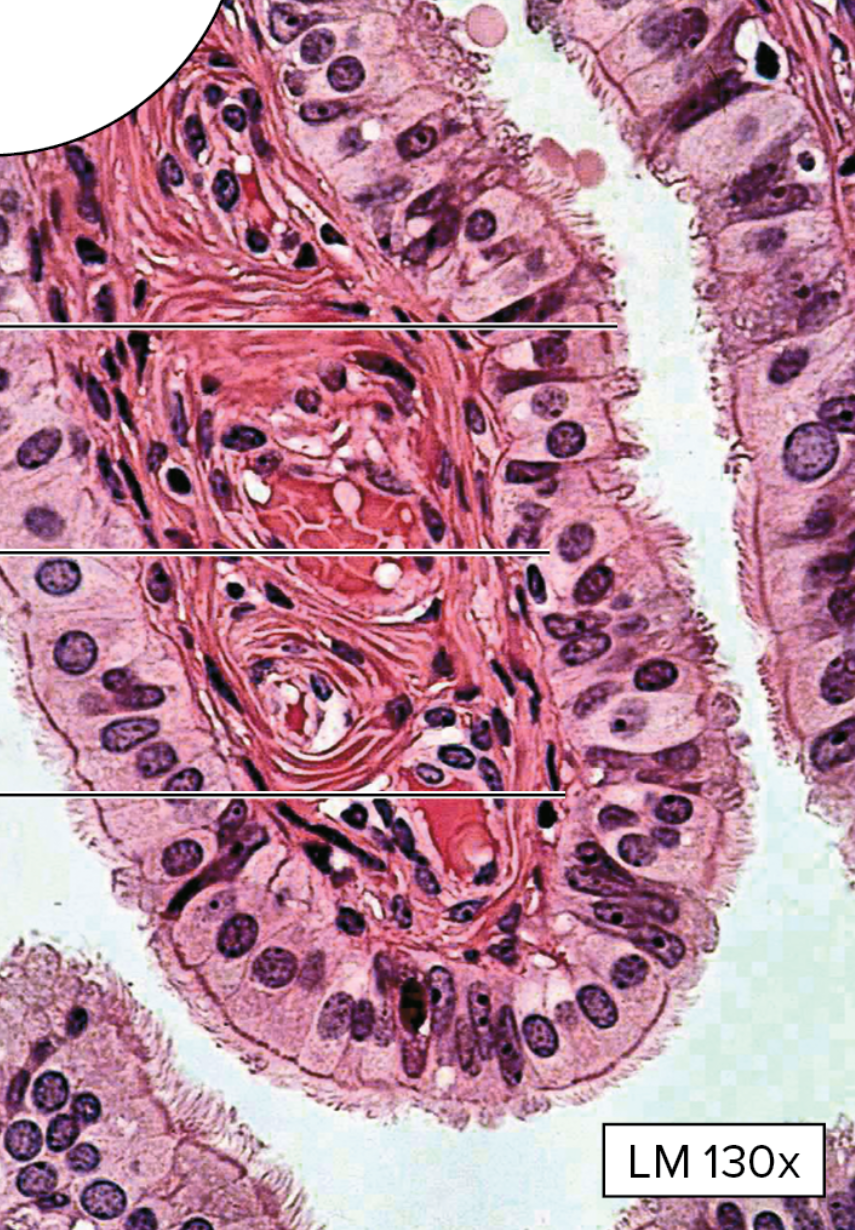
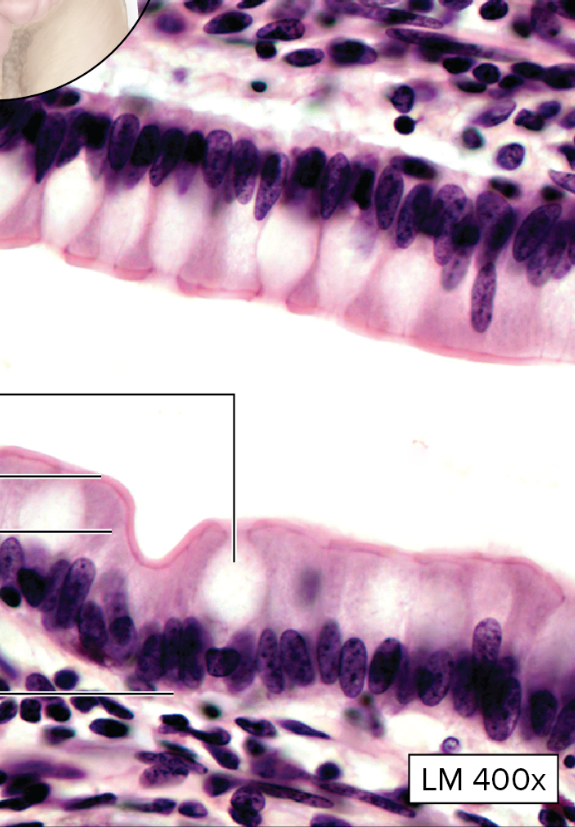
What type of epithelial tissue is this?
Cilliated Simple Columnar Epithelium
single layer of tall, narrow ciliated cells, oval chaped nucleus oriented lengthwise
globet cells may be present
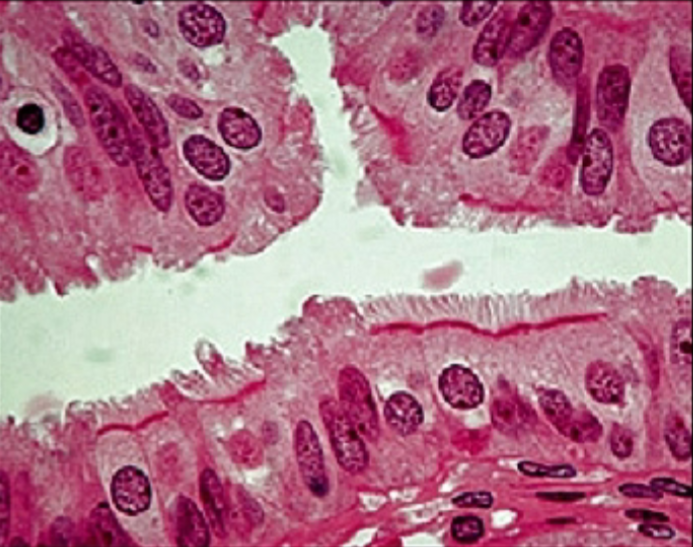
What is the function of the ciliated simple columnar epithelium?
secretion + movement of mucin along apical surface of epithelium by action of cilia
oocyte movement through uterine tube
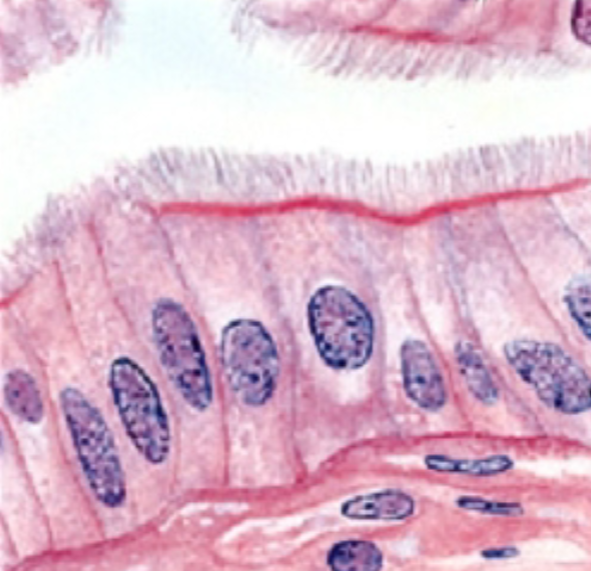
Where are ciliated simple columnar epithelial tissues found?
Lining of uterine tubes and large bronchioles of respiratory tract
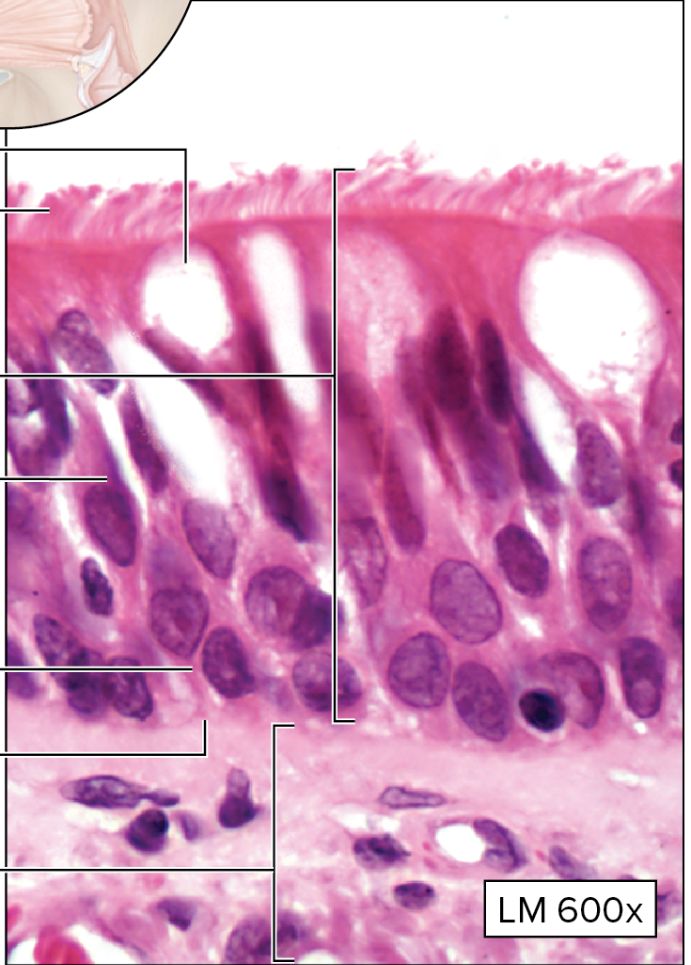
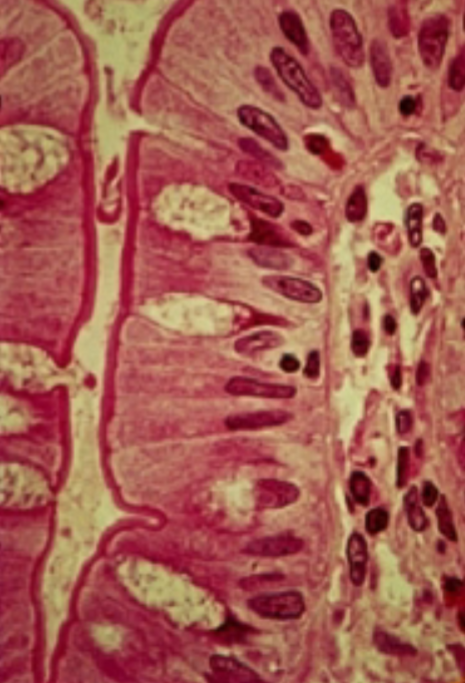
What type of epithelial tissue is this?
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
single layer of cells with different heights that appear multilayer
all cells connect at basement membrane
→ not all cells reach apical surface
Ciliated: has goblet cells and cilia
→ nonciliated does not
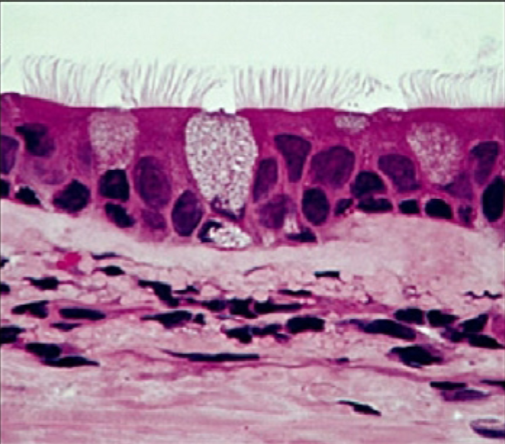
What is the function of the pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium?
Protection
Secretion + movement of mucin across surface by ciliary action
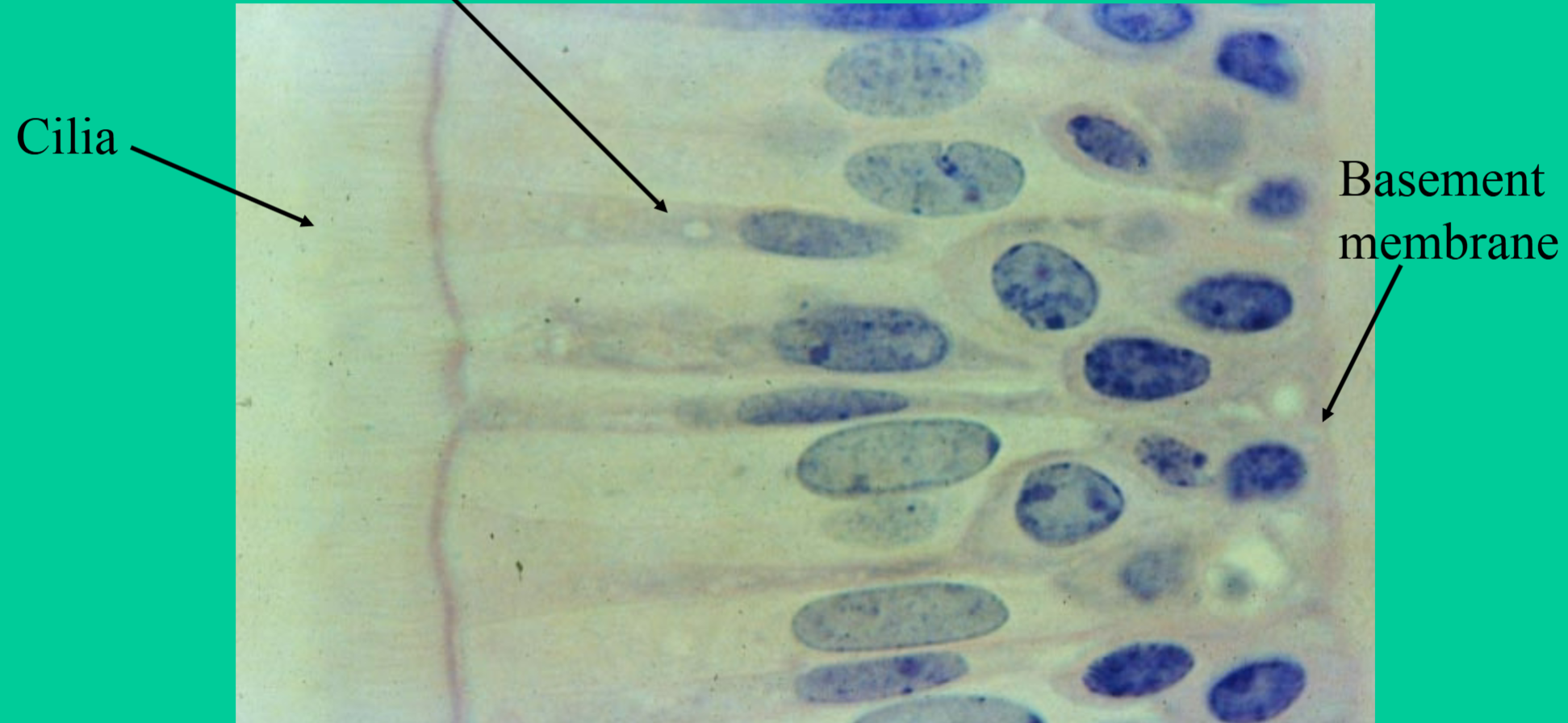
Where are pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium tissues found?
lining most of the respiratory tract
→ nasal cavity, part of pharynx, larynx, trachea, and bronchi
Noncilited form(rare): lines epididymis and part of male urethra
Connective tissue
living cells in a nonliving matrix
→ connective tissue proper
→ cartilage
→ bone
→ blood
bonding tissues together
provides support
provides nourishment
stores waste
repairs damaged tissues
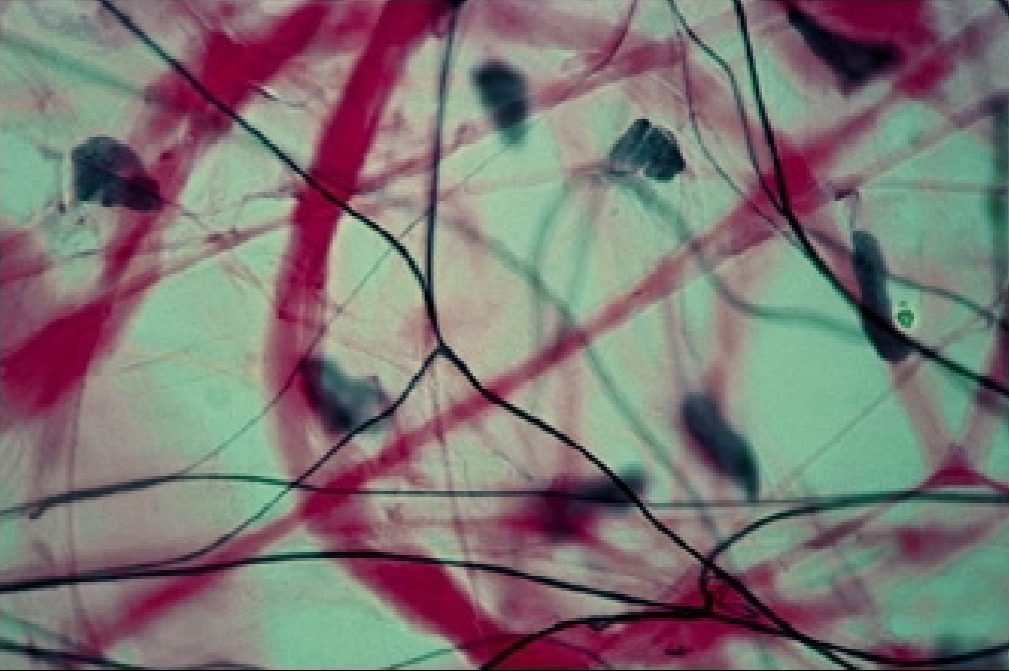
What type of connective tissue is this?
Loose connective tissue (Areolar)
Relatively fewer cells and fibers than in dense connective tissue
irregularly arranged fibroblasts and fibers
→ thin fibers = elastin
→ thick fibers = collagen
many blood vessels
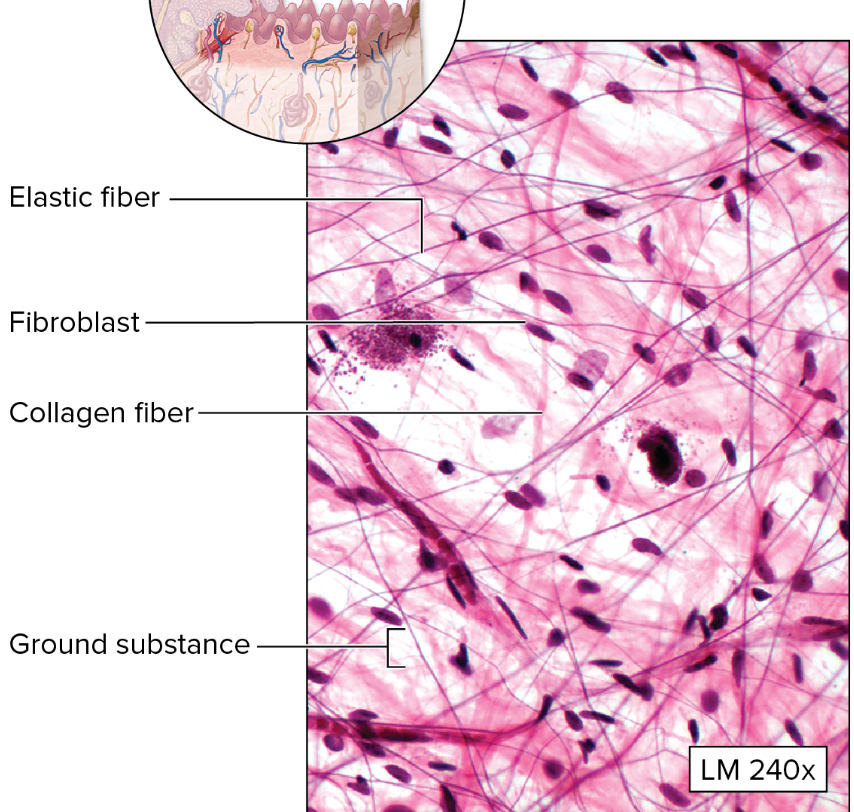
What is the function of loose (areolar) connective tissue?
surrounding + protecting tissues and organs
loosely binding epithelia to deeper tissues
providing nerve + blood vessel packing
Where is the loose (areolar) connective tissue found?
Papillary layer of dermis
Subcutaneous layer under the skin
Surrounding the organs
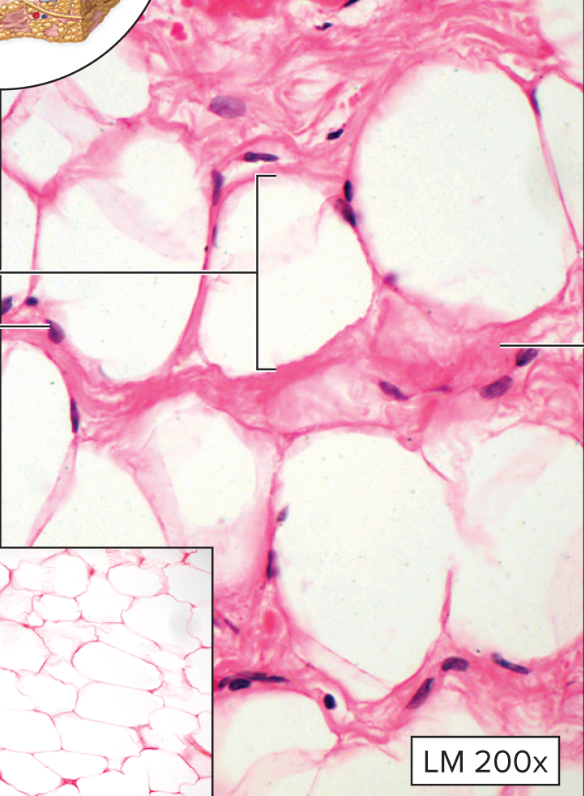
What type of connective tissue is this?
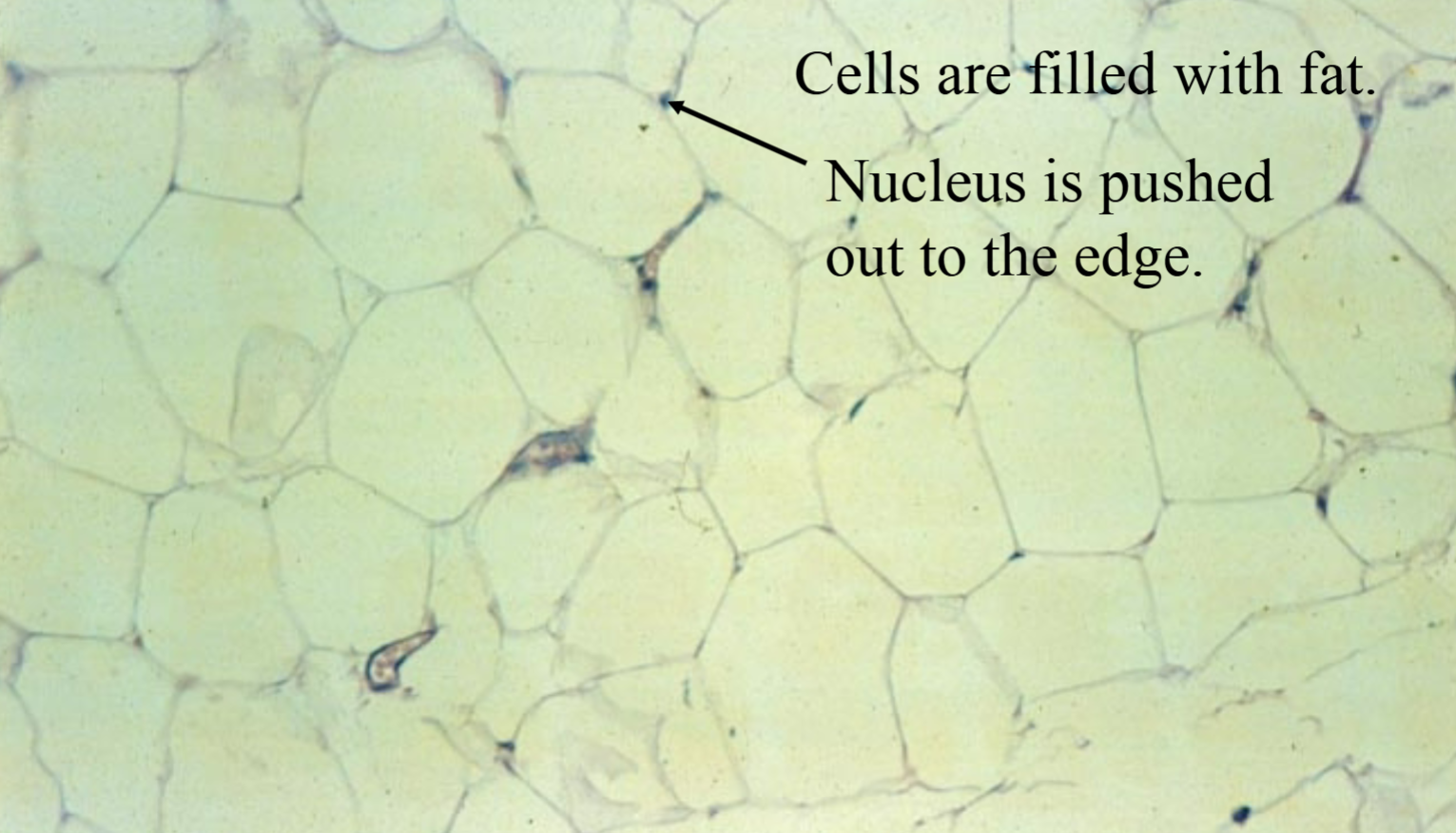
Adipose Connective Tissue
Closely packed adipocytes
→ “fat cells”
Nucleus is squeezed to one side by large fat droplet
What is the function of the adipose connective tissue?
Stores energy
→ protects
→ cushions
→ insulates
Where are adipose connective tissues found?
Subcutaneous layer
→ covering and surrounding most organs
What type of connective tissue is this?
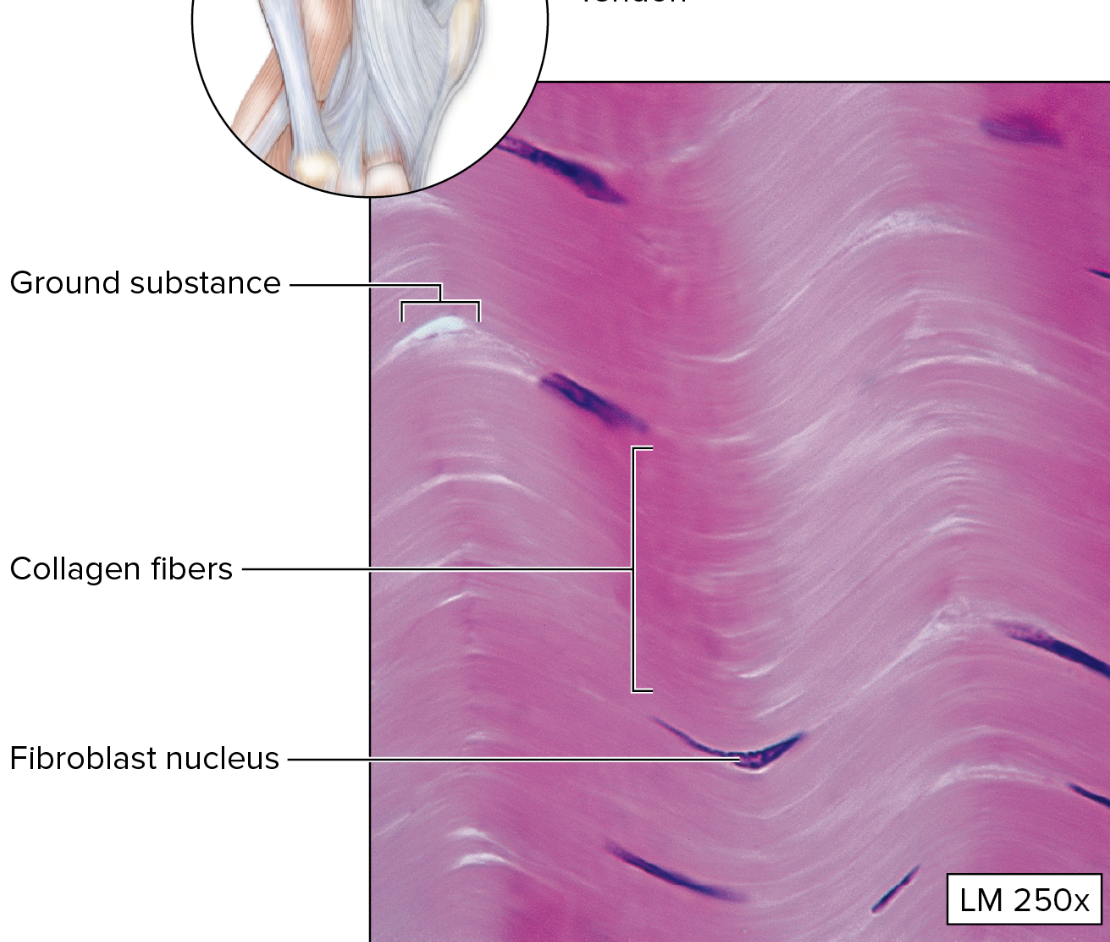
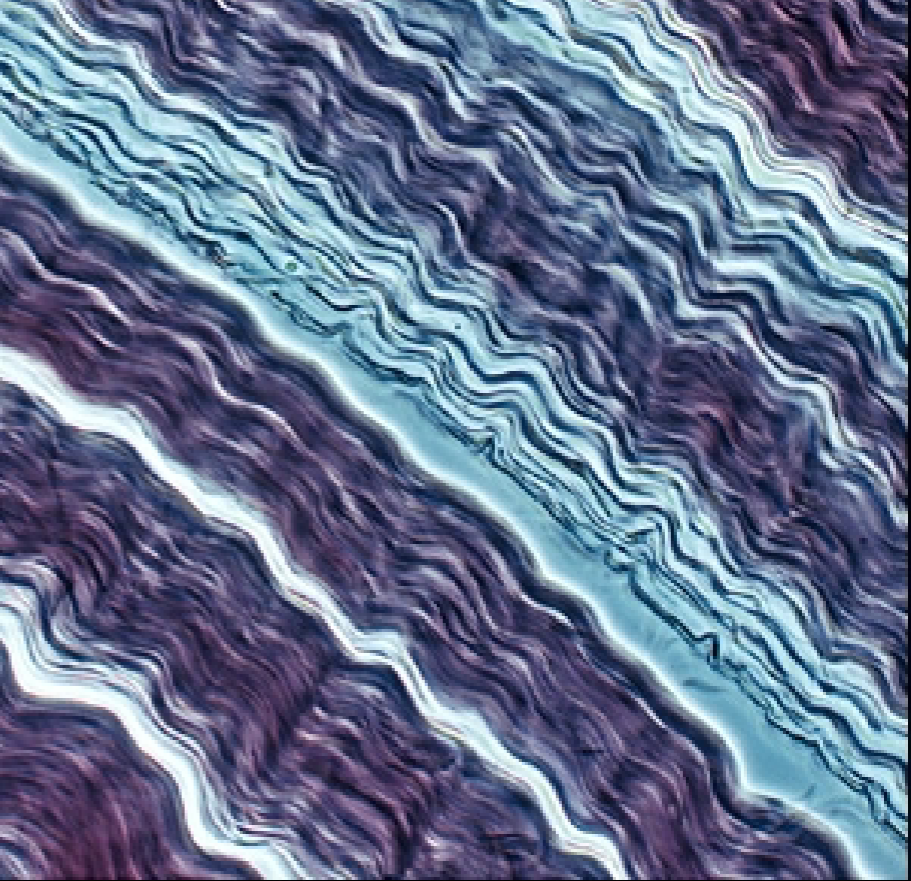
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
parallel collagen fibers (white fibrous tissue)
densely packed
fibroblast nuclei squeezed between layers of fibers
What is the function of the dense regular connective tissue?
Attaches muscles to bone + bone to bone
Resisting stress applied in one direction
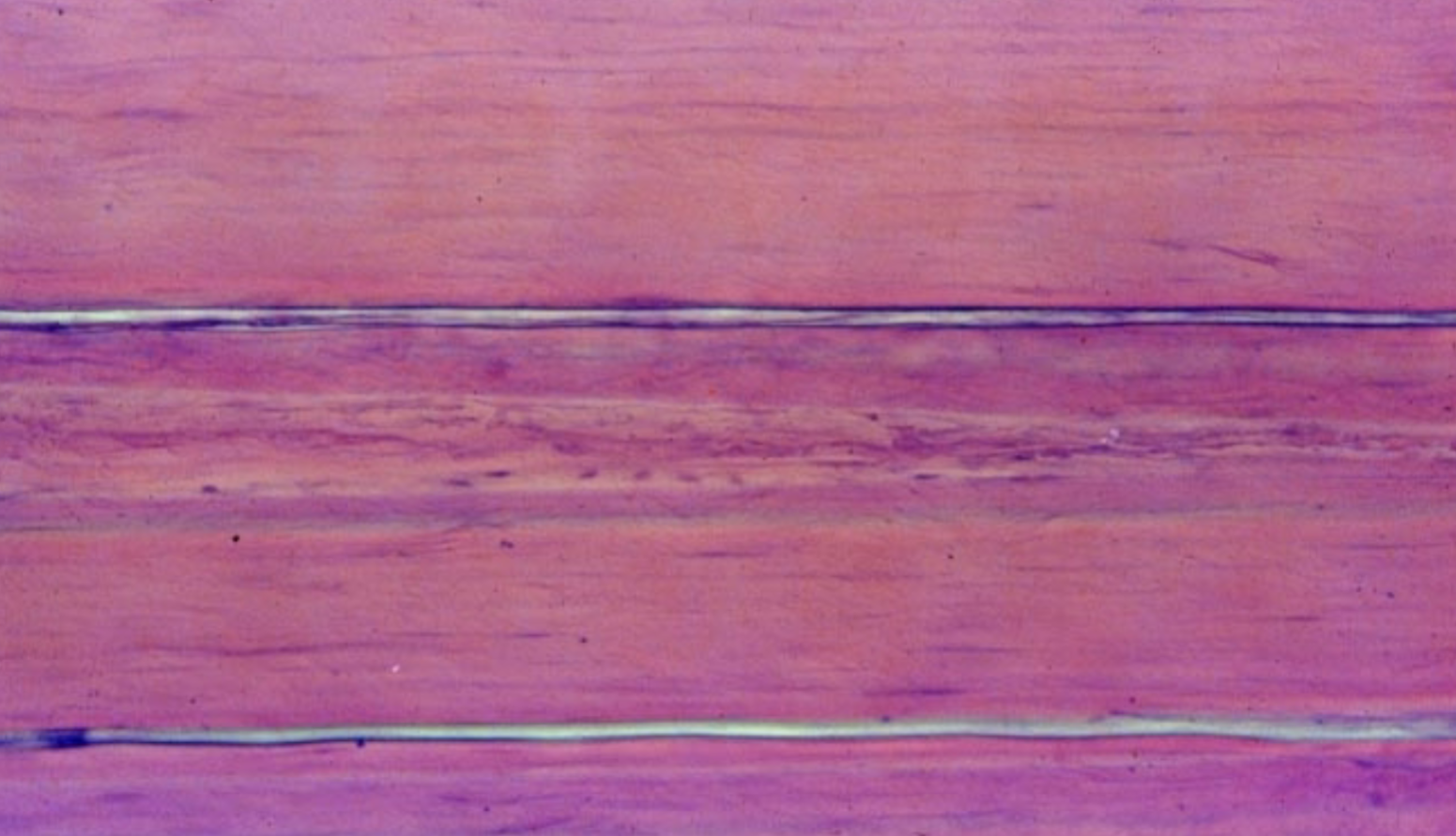

Where are dense regular connective tissues found?
Tendons, most ligaments
What type of connective tissue is this?
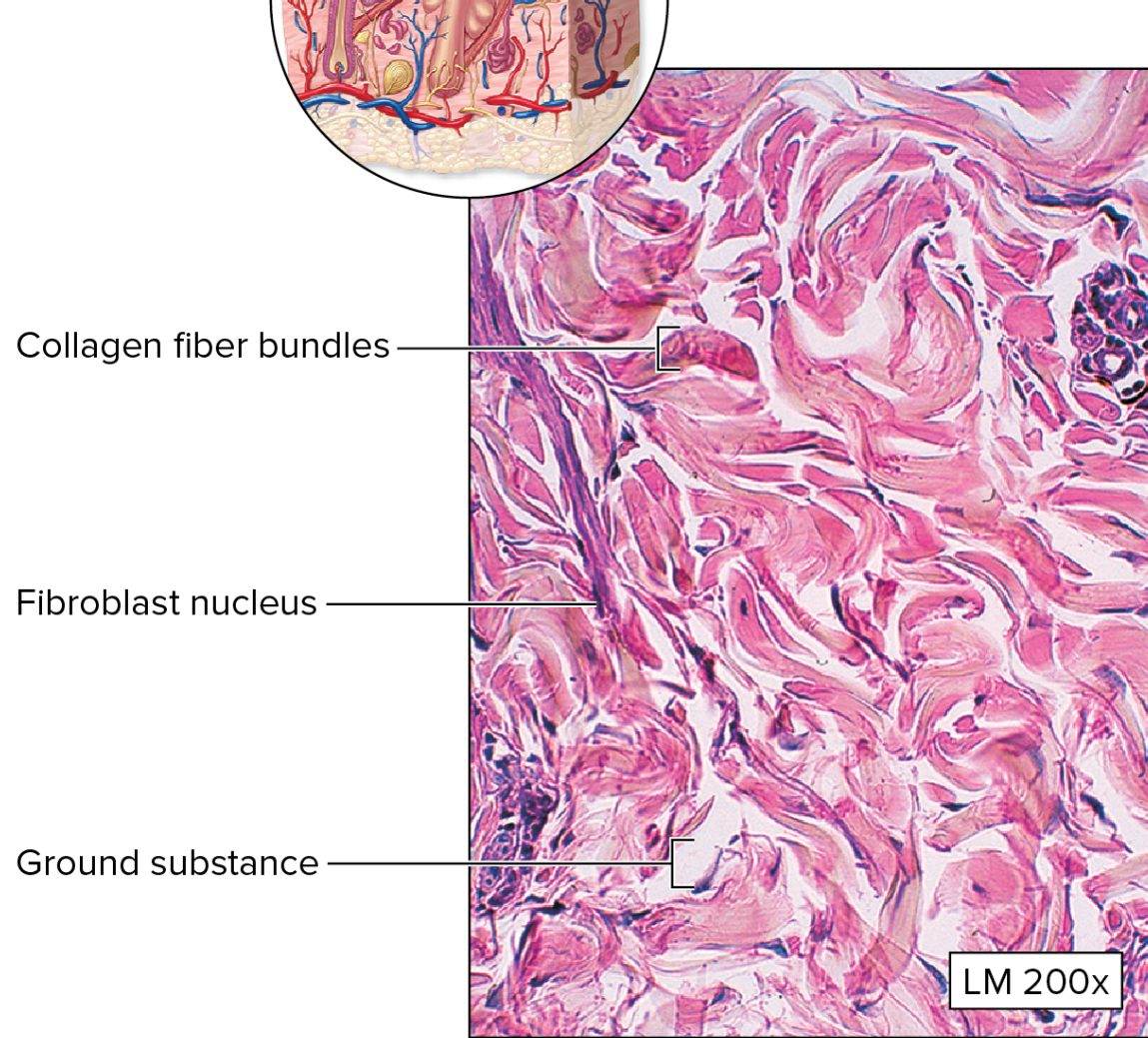
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
predominantly collagen fibers
randomly arranged + clumped together
more ground substance than in dense regular connective tissue
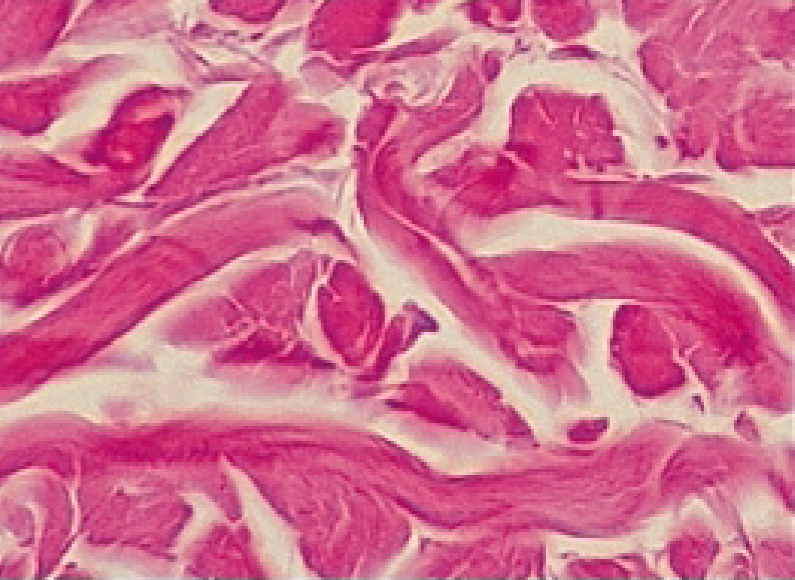
What is the function of the dense irregular connective tissue?
Withstands stresses applied in all directions; durable
Where are dense, irregular connective tissues found?
Dermis
periosteum covering bone
Perichondrium covering cartilage
Organ capsules
Connective Tissue: Cartilage
Chondrocytes in a matrix of a thick gel
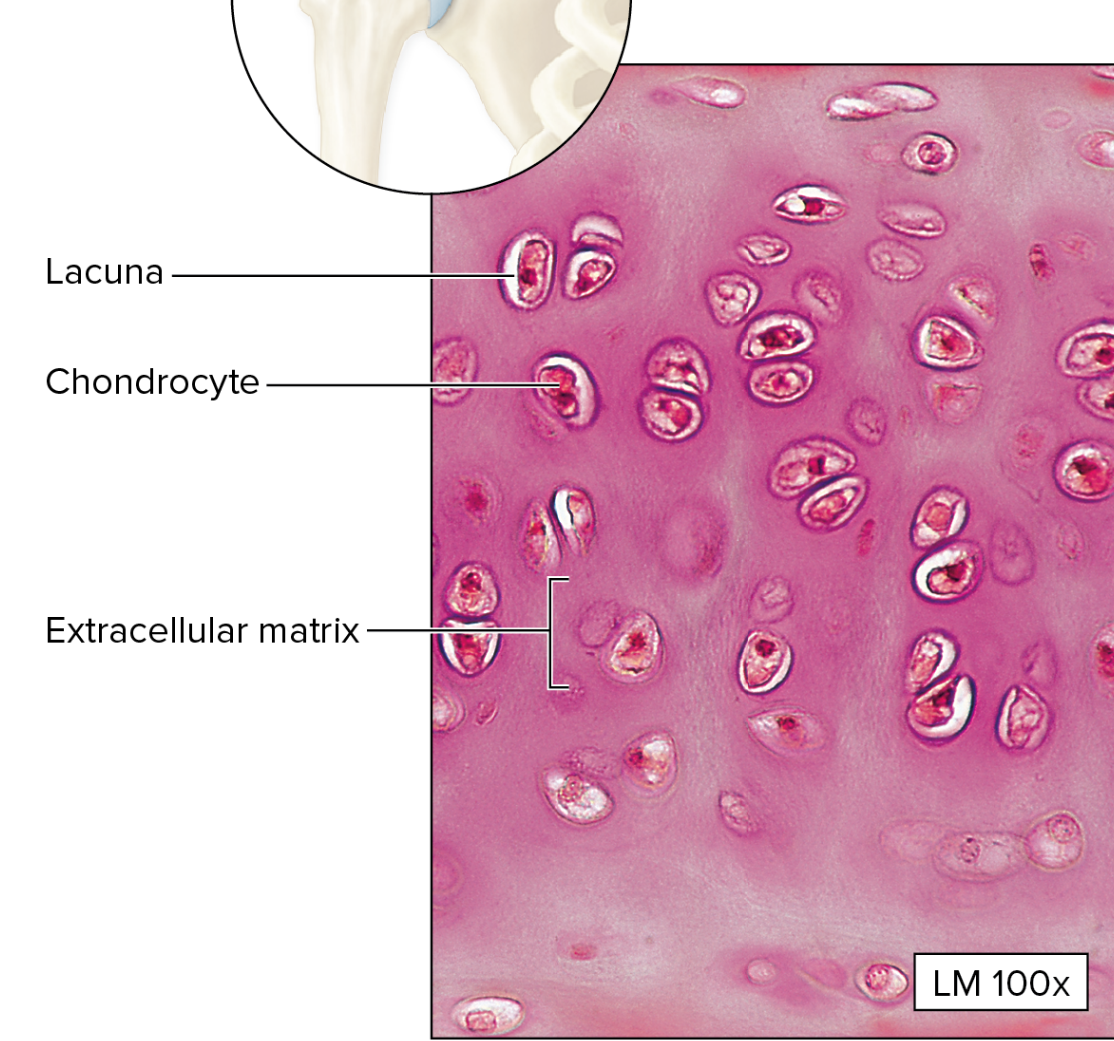
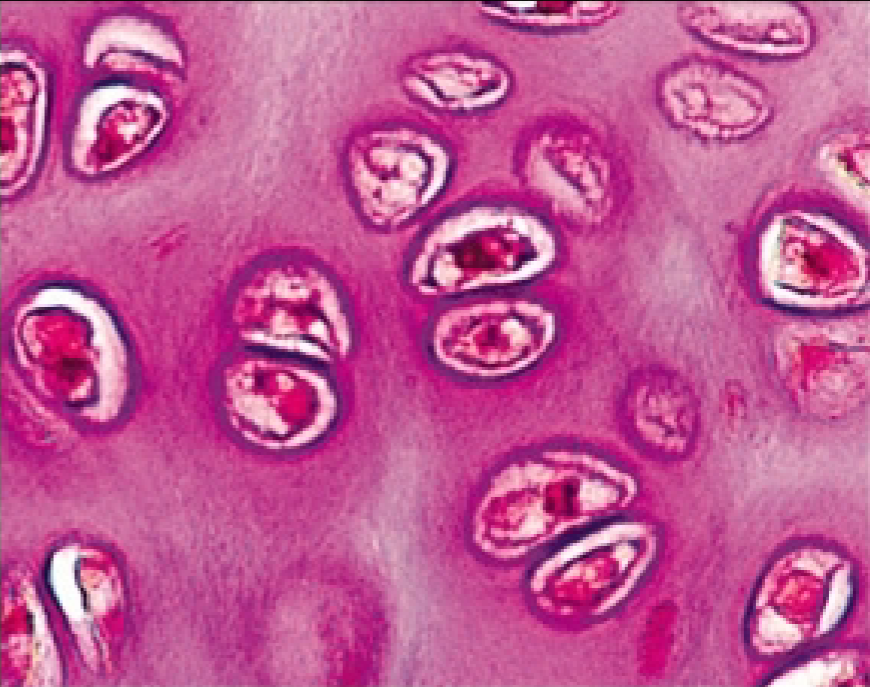
What type of Cartilage Connective Tissue is this?
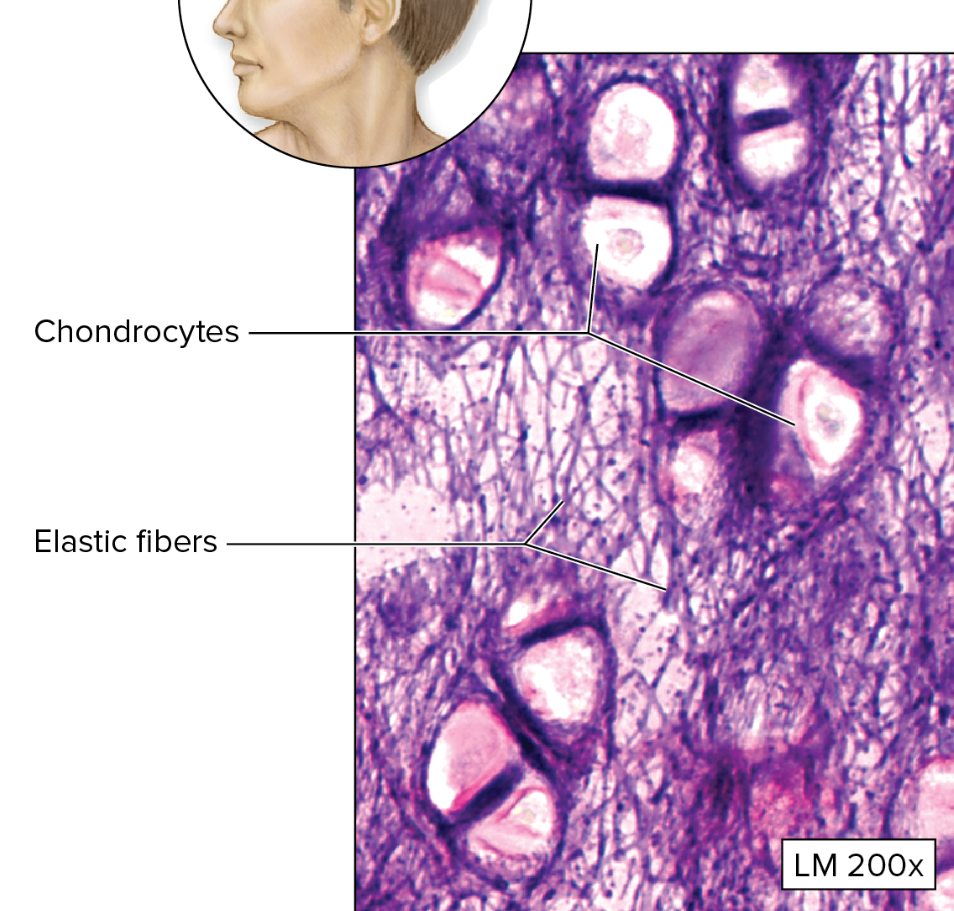
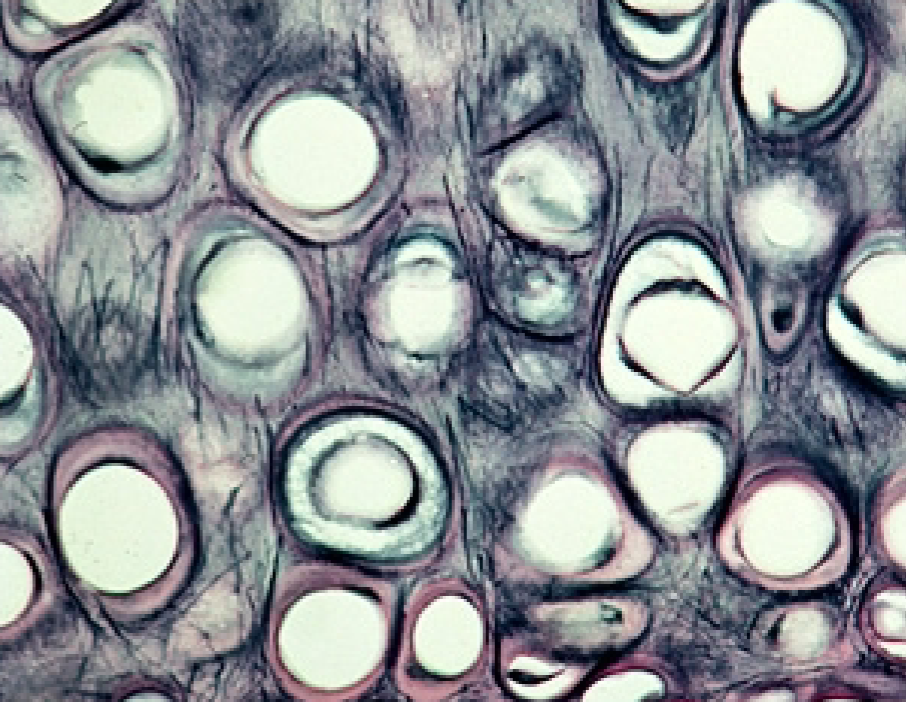
Hyaline Cartilage
clear matrix
lacunae house chondrocytes
covered by perichondrium
What is the function of the Hyaline Cartilage (Connective Tissue)?
smooth surfaces for movement of joints
model for bone growth
supporting soft tissue
Where is the Hyaline Cartilage (Connective Tissue) found?
covering the articular ends of long bones
most of fetal skeleton
costal cartilage
most of the larynx, trachea and nose
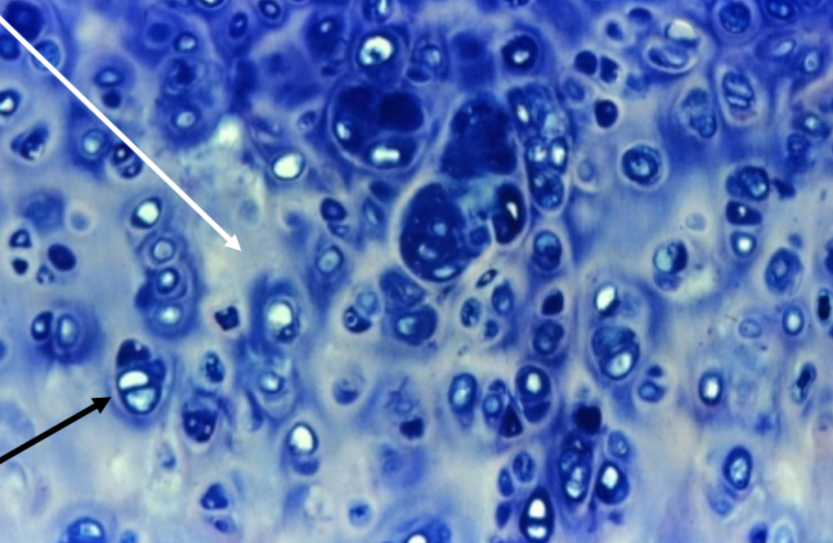
What type of Cartilage Connective Tissue is this?
Elastic Cartilage
matrix with thin (elastic) fibers → wiggle + stretch!
What is the function of the Elastic Cartilage (connective tissue)?
maintains structure + shape while being flexible
Where are the Elastic Cartilages (connective tissue) found?
External ear
Epiglottis of larynx
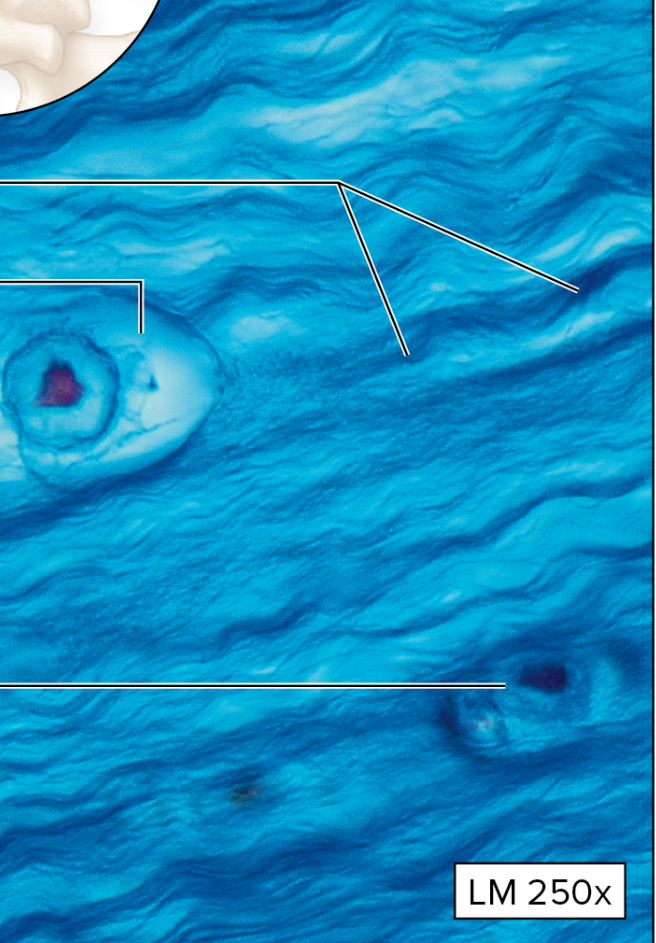
What type of Cartilage Connective tissue is this?
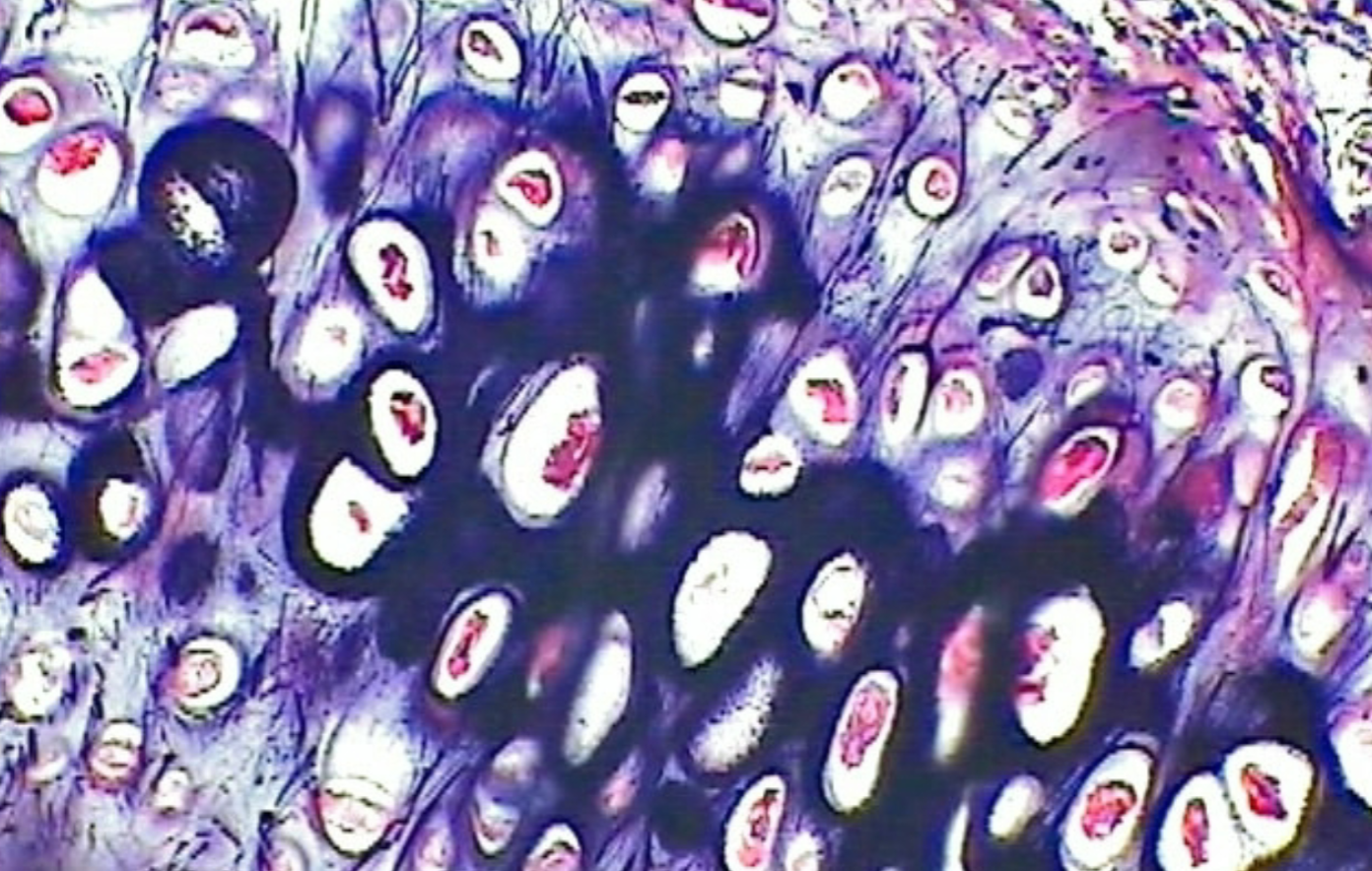
Fibrocartilage
matrix with thick (collagen) fibers
easy to see
no perichondrium
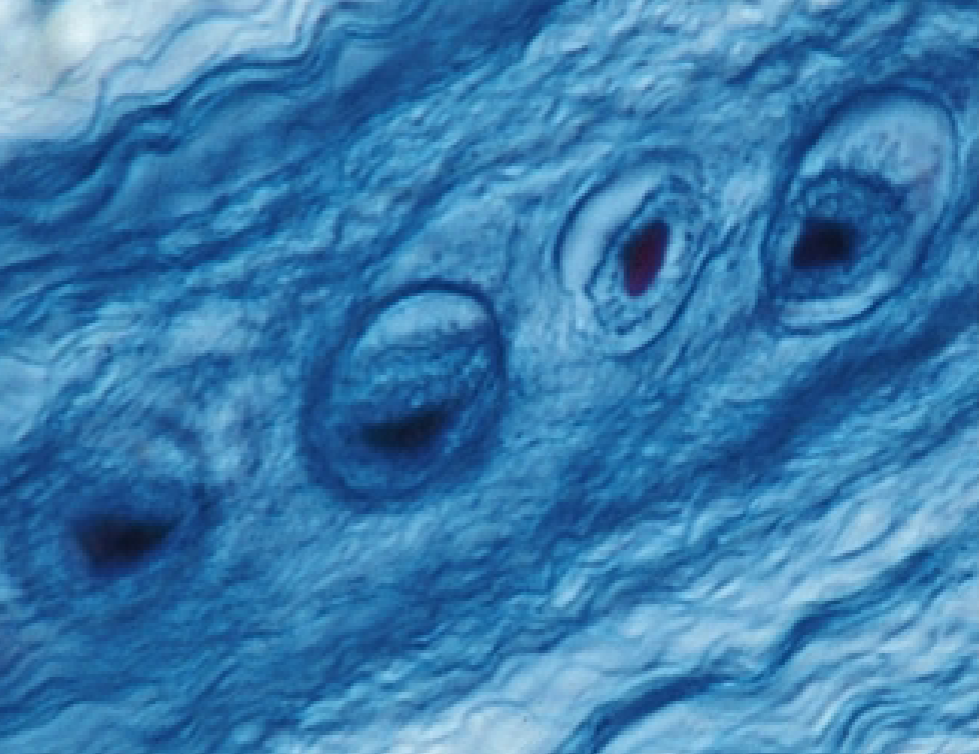
What is the function of the Fibrocartilage? (connective tissue)
resisting compression
absorbing shock in some joints
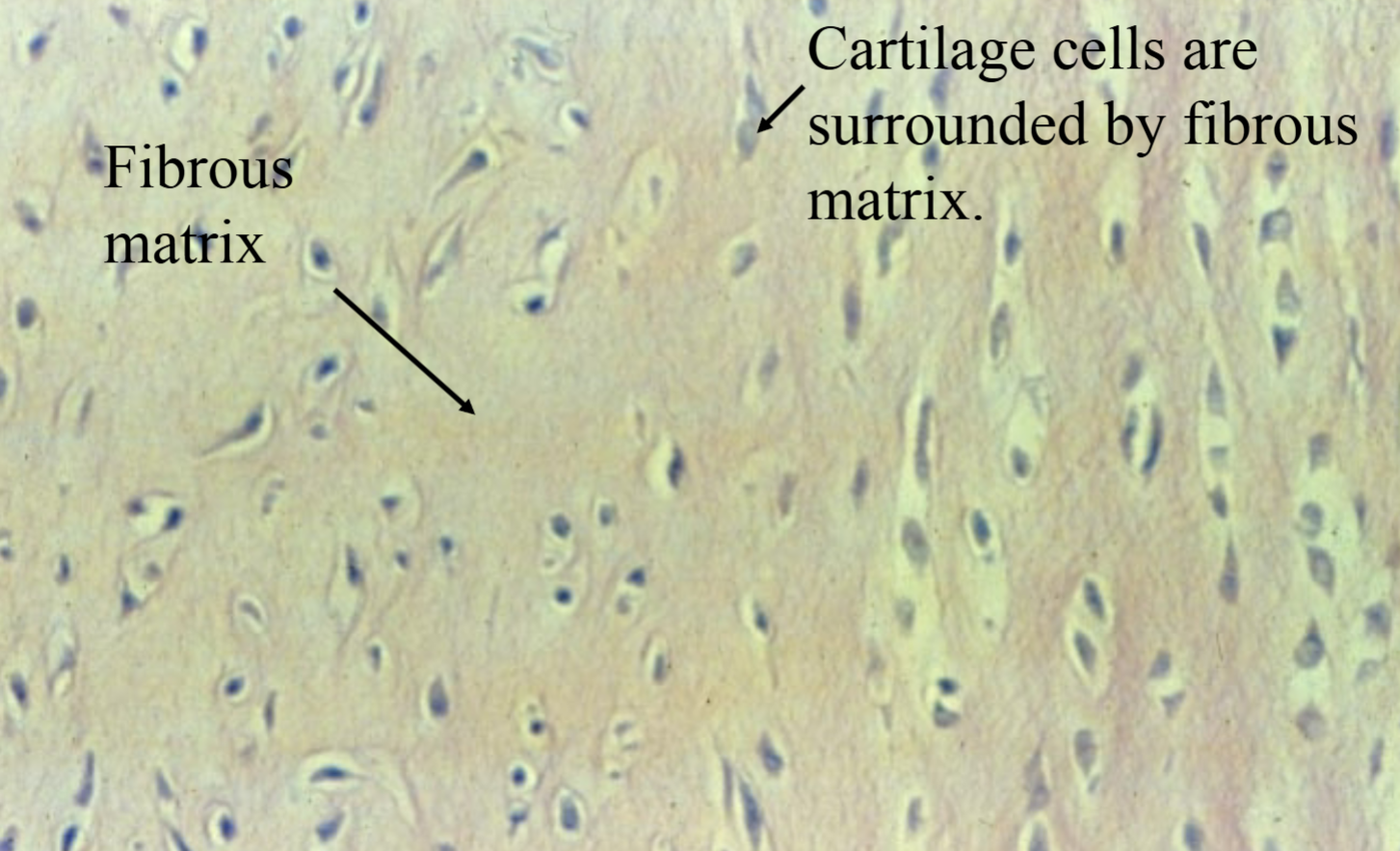
Where is fibrocartilage found? (connective tissue)
intervertebral discs
Pubic symphysis
Menisci of knee joints
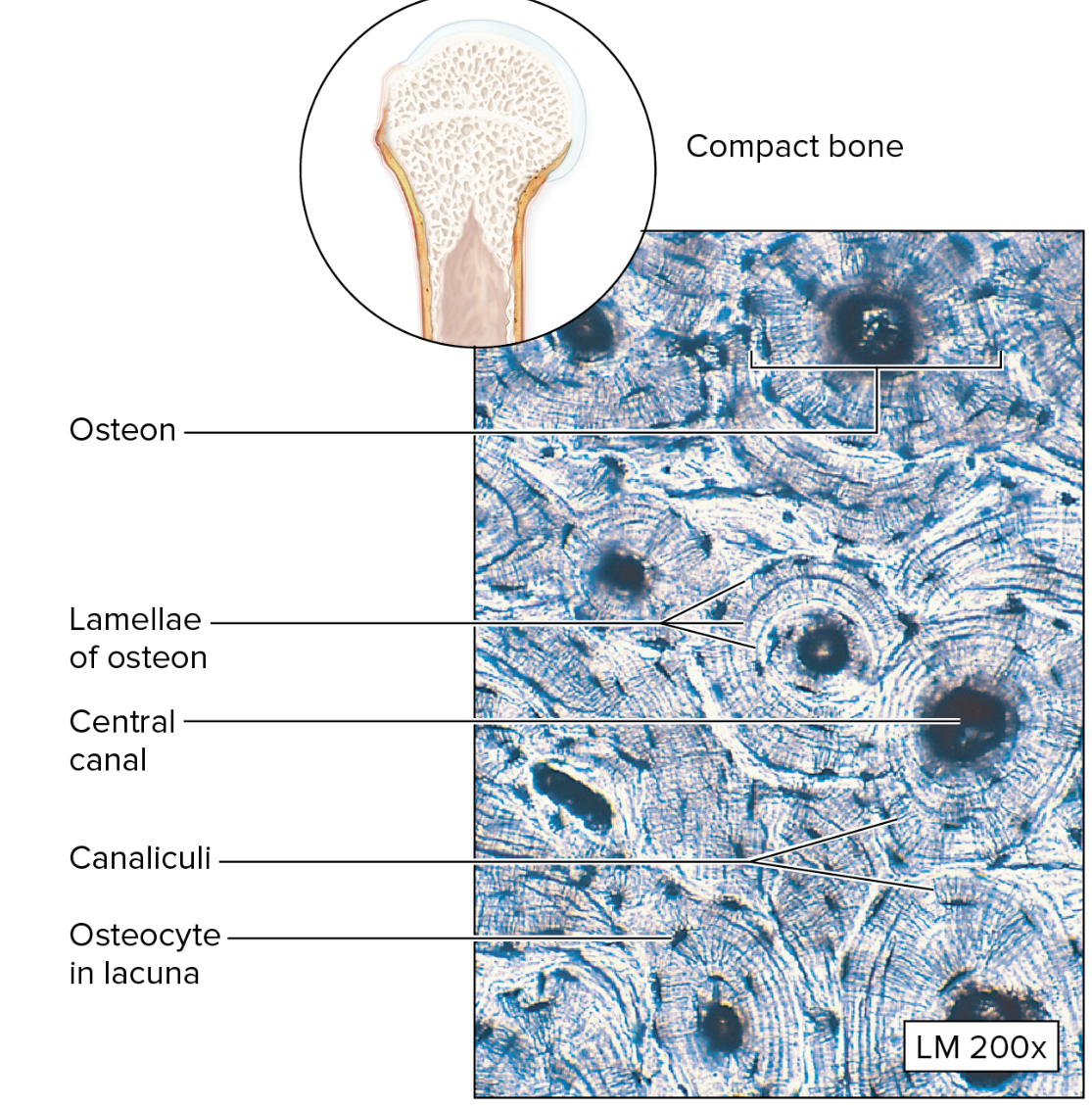
Connective Tissue: Bone
Osteocytes embedded in a solid mineral matrix
Compact Bone: calcified matrix arranged in osteons
Spongy bone: lacks the organization of a compact bone; contains macroscopic spaces ; arranged in mesh pattern
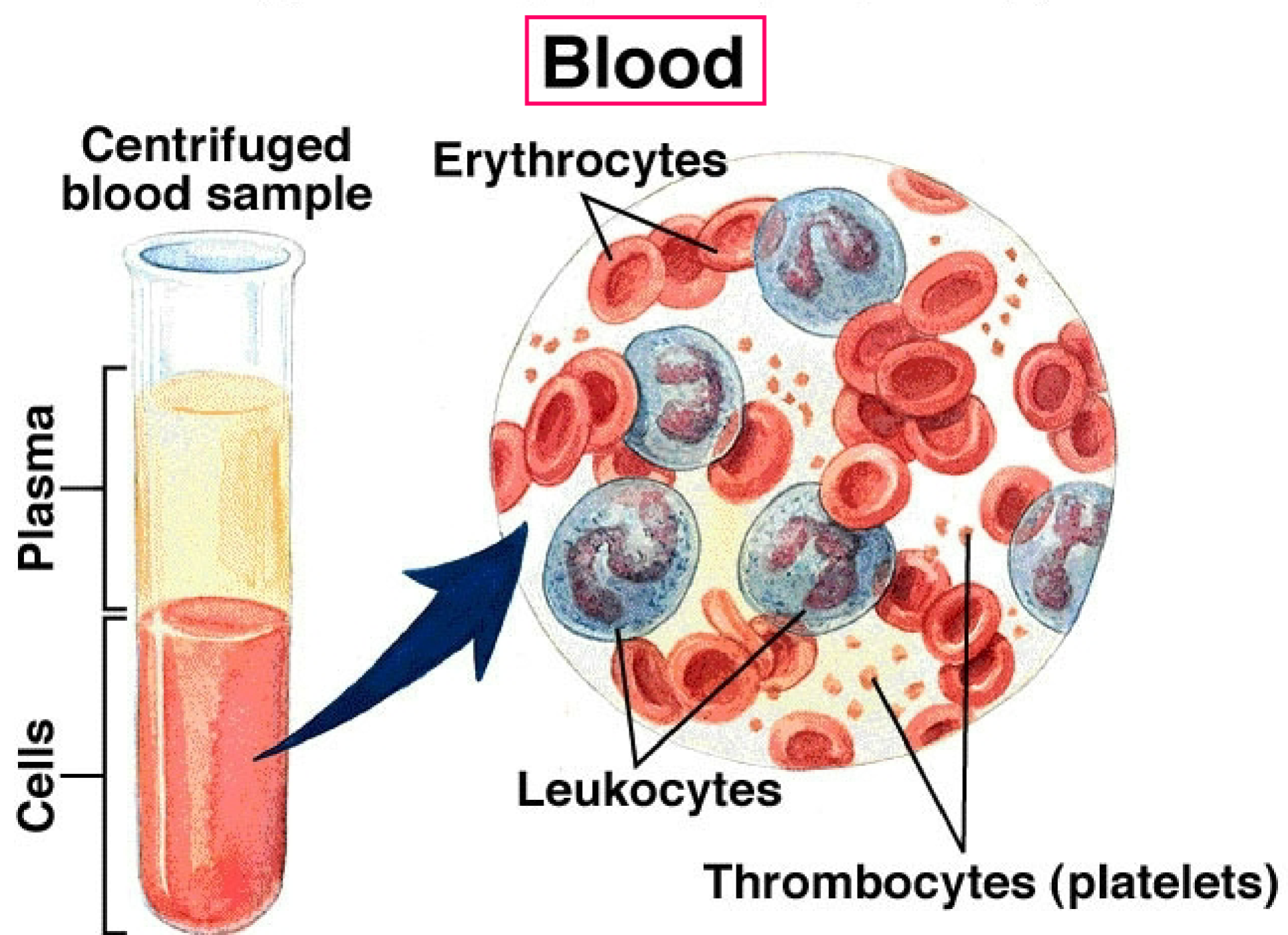
Connective Tissue: Blood
liquid matrix with formed elements
erythrocytes (red blood cells)
leukocytes (white blood cells)
thrombocytes (plateles)
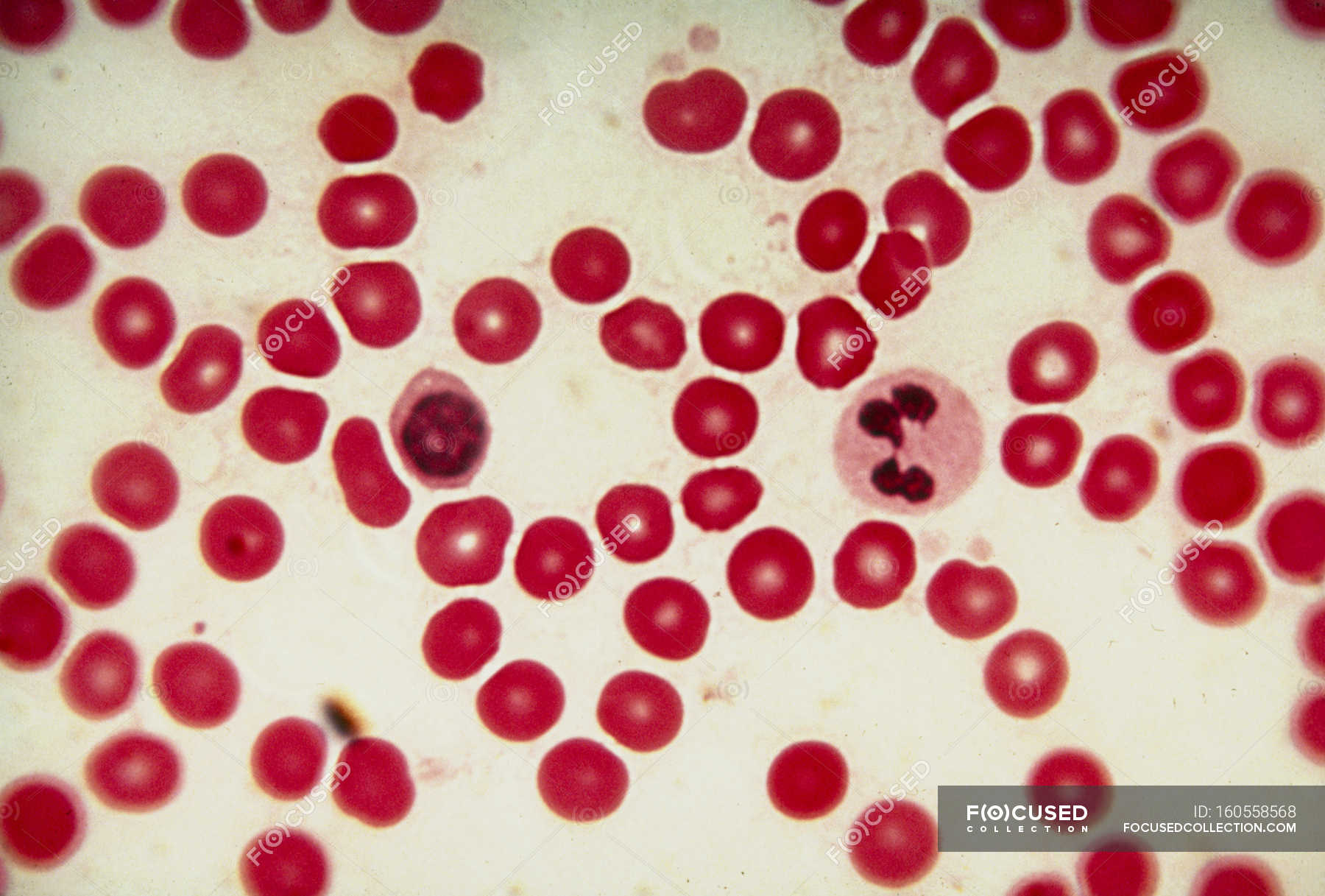
What is the function of Erythrocytes?
transport oxygen and some carbon dioxide
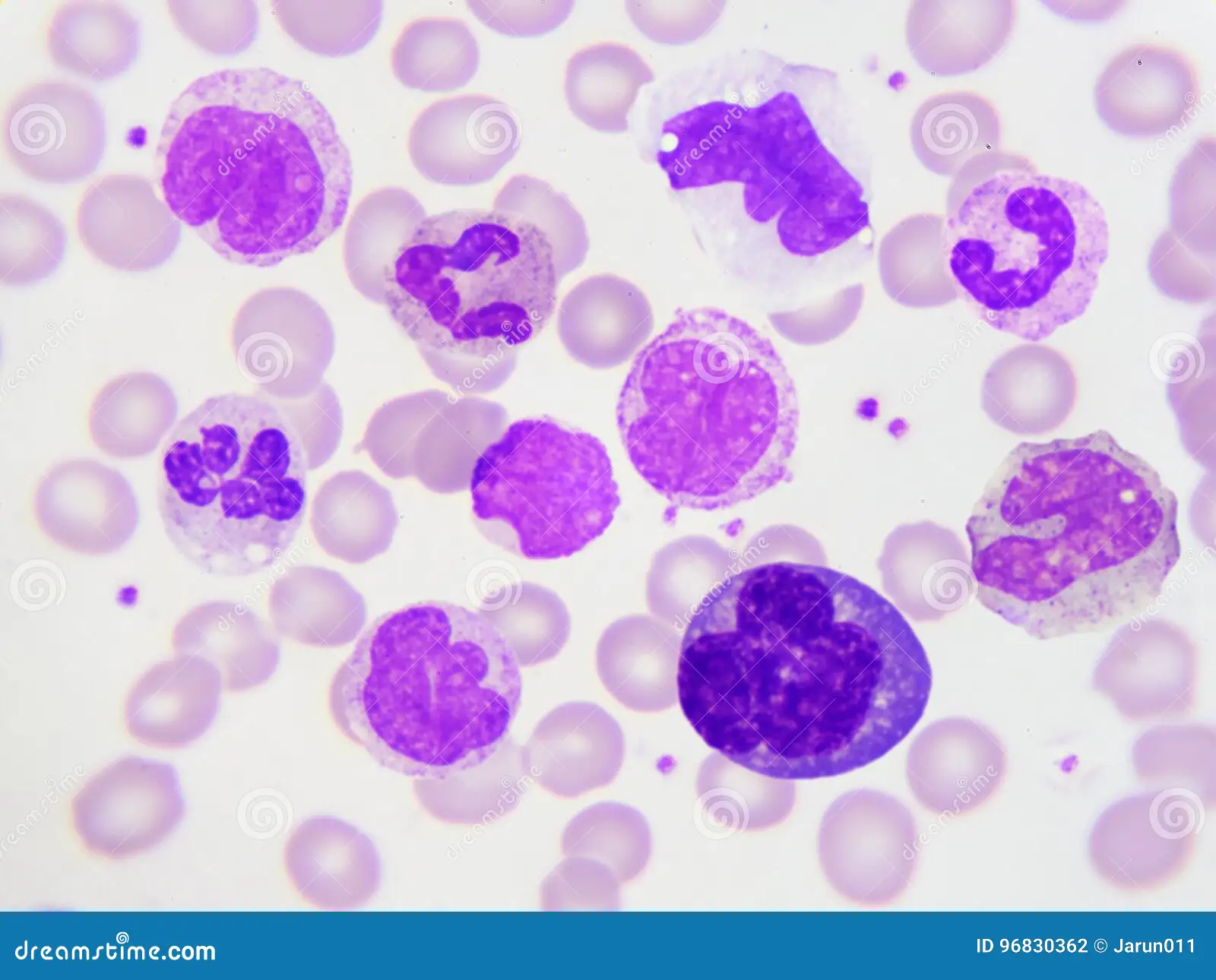
What is the function of Leukocytes?
Initiate + control immune response
What is the function of plasma?
contains clot elements to stop blood loss
transporting nutrients, wastes, + hormones throughout the body
Muscle Tissue
Contractile Tissue
Skeletal (striated+voluntary)
Cardiac (striated+involuntary)
Smooth (nonstriated+involuntary)
Cylindrical cells with an evident nuclei
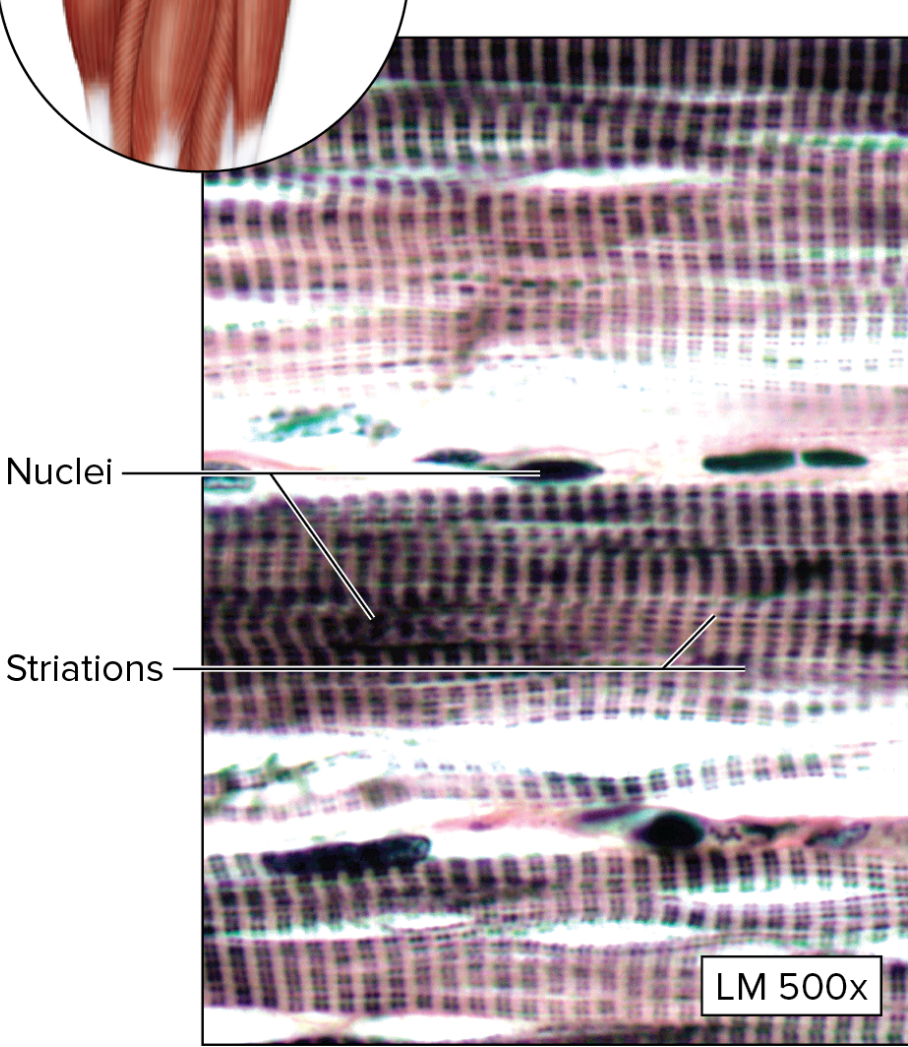
What type of muscular tissue is this?
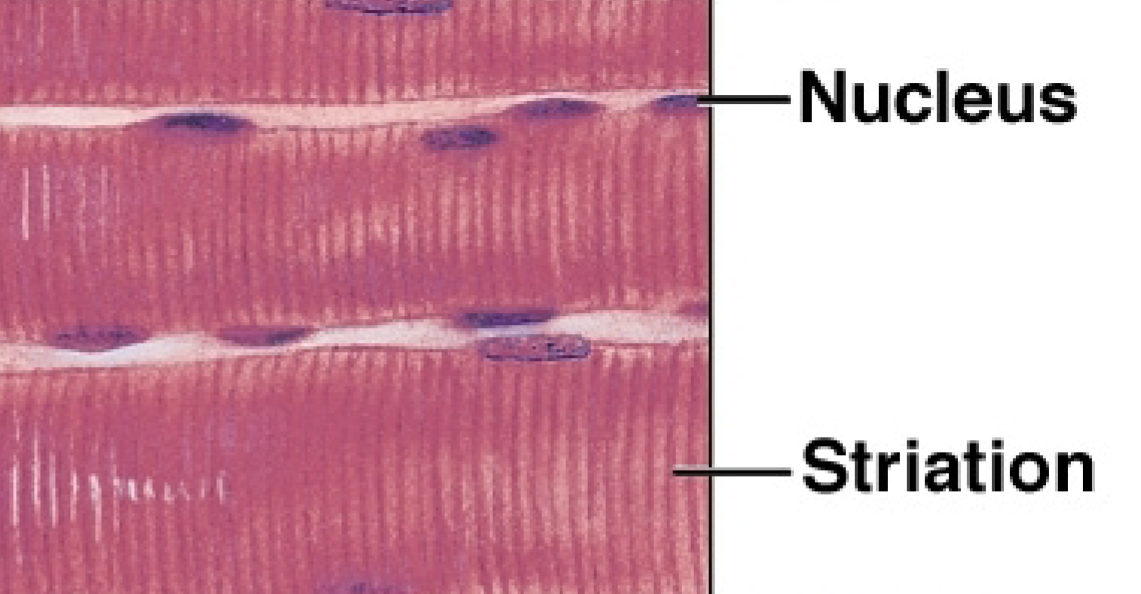
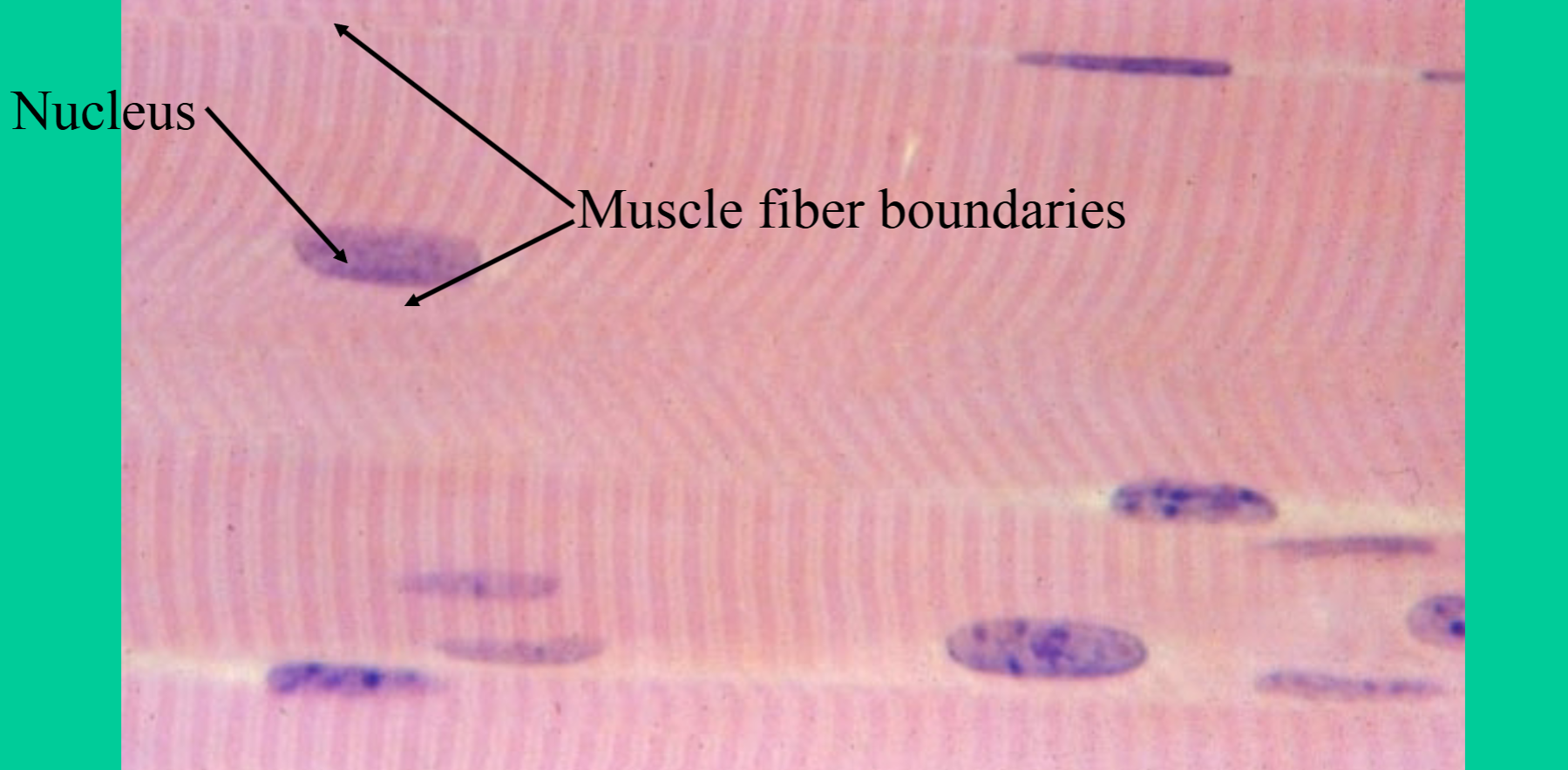
Skeletal Muscle
Fibers are long, cylindrical, striated, parallel, + unbranched
striated cells have multiple peripheral nuclei
What is the function of the skeletal muscular tissue?
moves the skeleton
→ voluntary body movements, locomotion, + heat production
Where are skeletal muscle tissues found?
attaches to bones (sometimes the skin) → facial muscles
sphincters= lips, urethra, + anus
What type of muscular tissue is this?
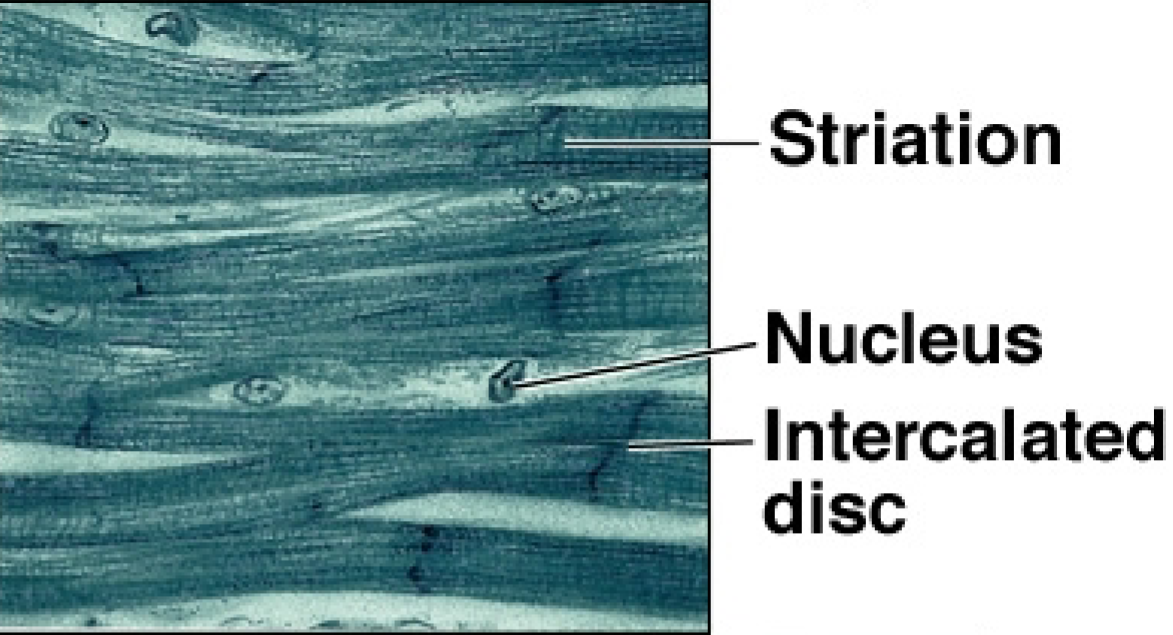
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
small, striated cells with branches and intercalated discs
one or two nuclei
What is the function of a cardiac muscle tissue?
Involuntary Contraction + relaxation pump in heart
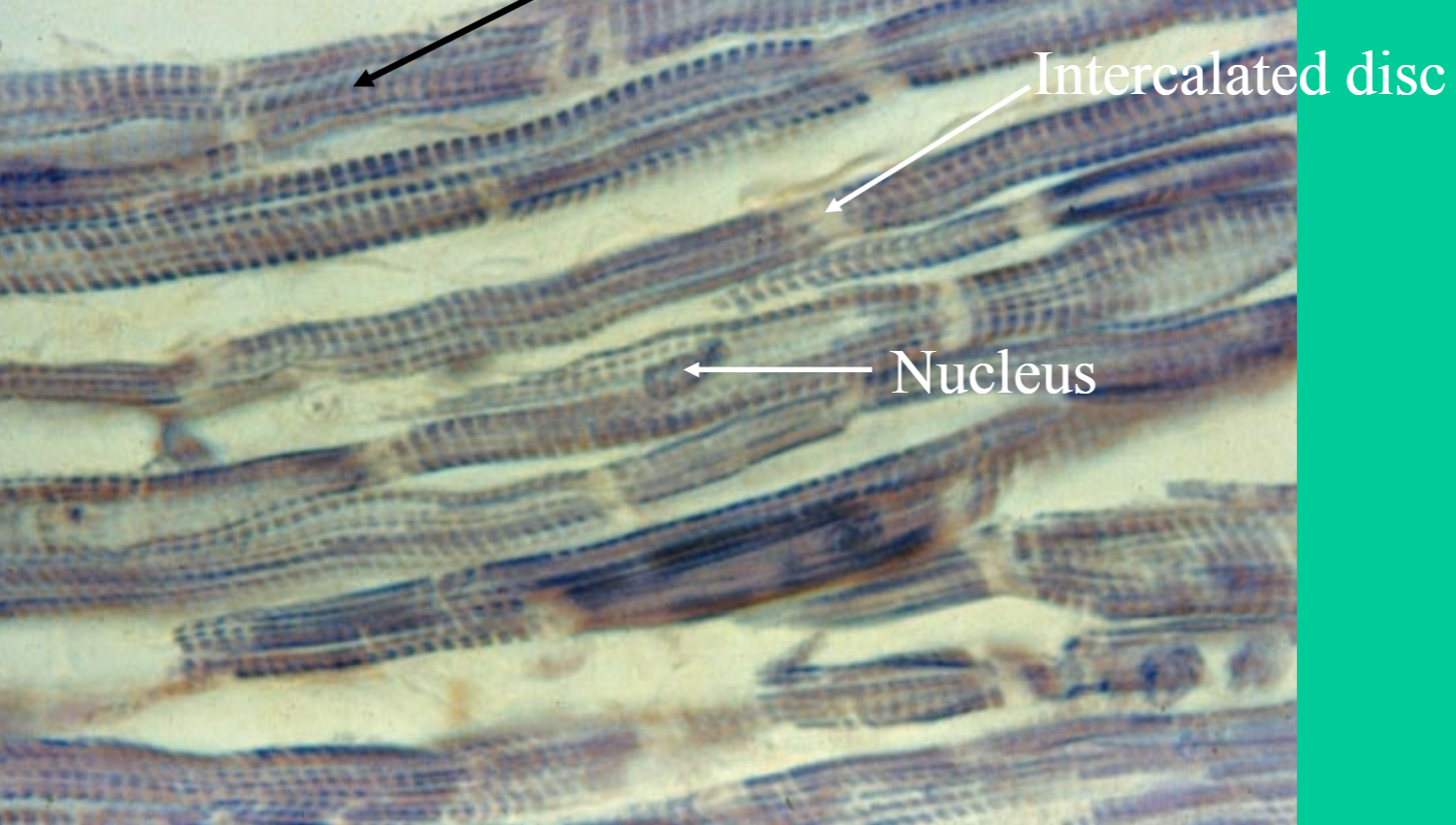
Where is the cardiac muscular tissue found?
Heart wall (myocardium)
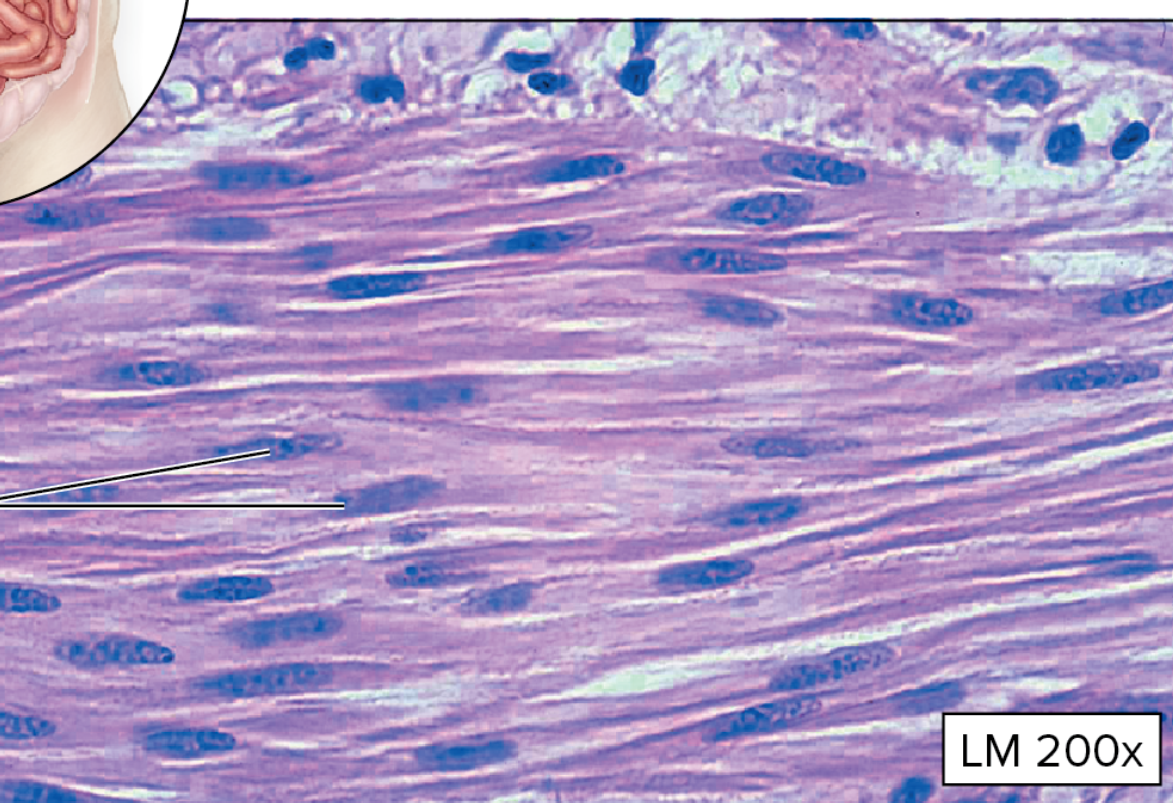
What type of muscular tissue is this?
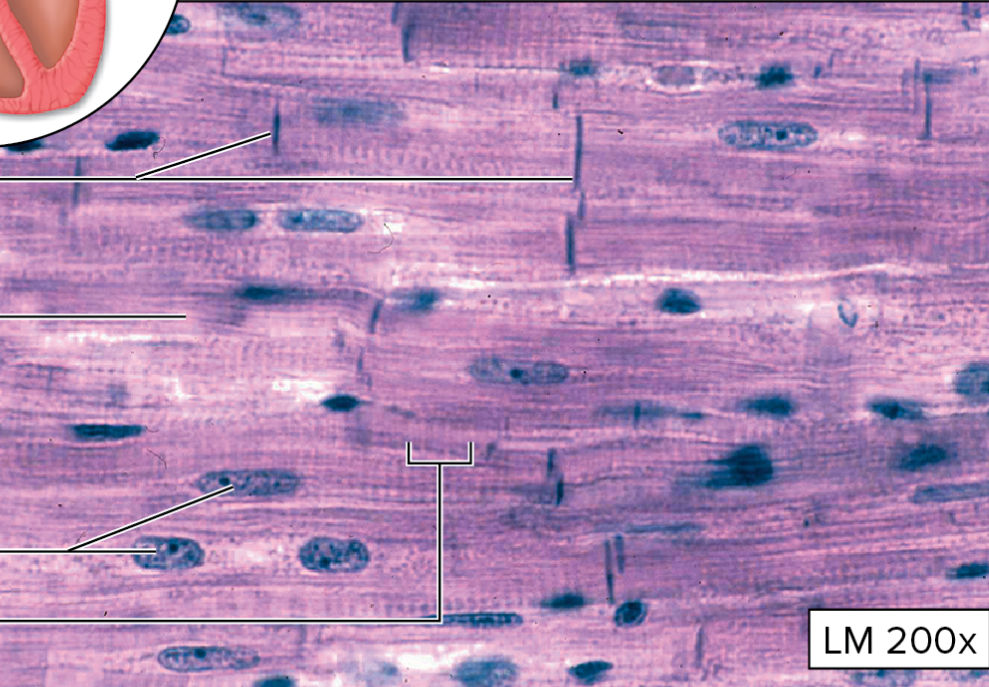
Smooth Muscle tissue
small, nonstriated cells with tapering ends
one nucleus
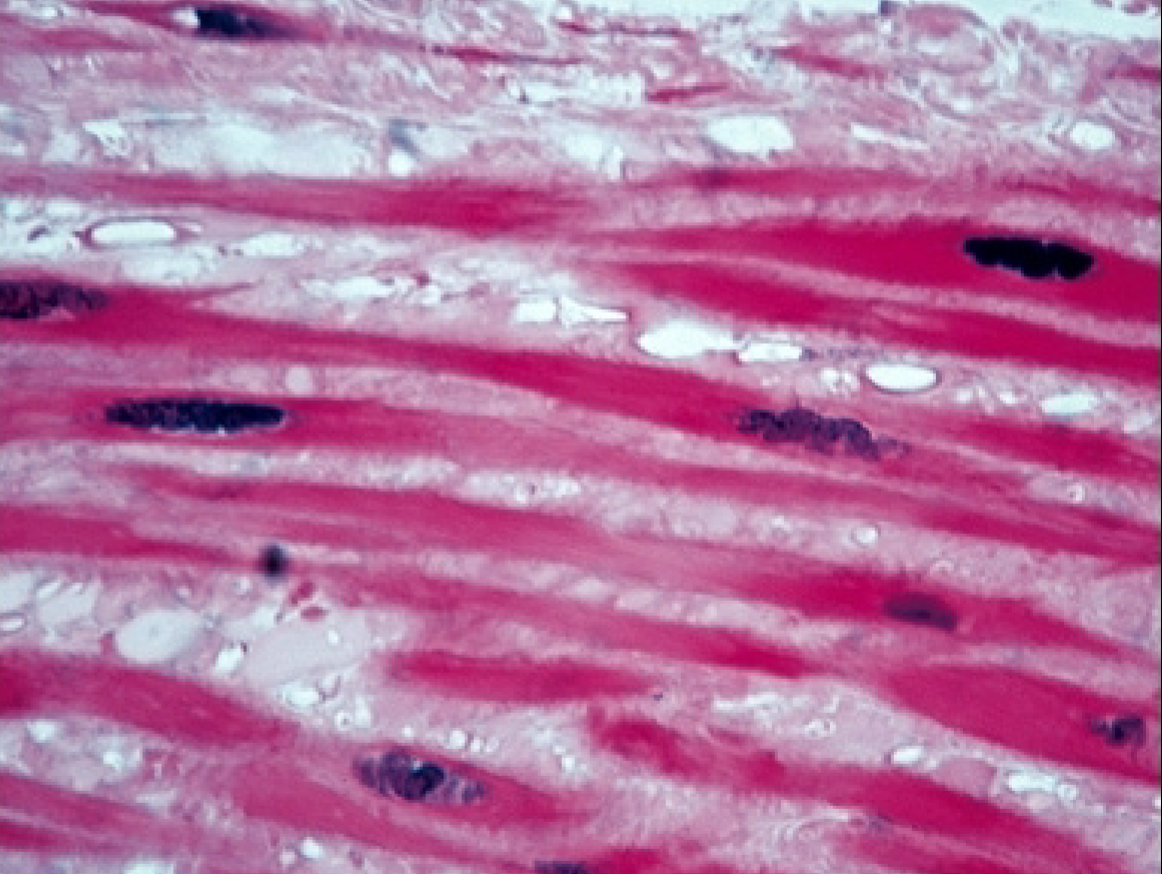
What is the function of the smooth muscle tissue?
involuntary movements + motion
moves materials through internal organs
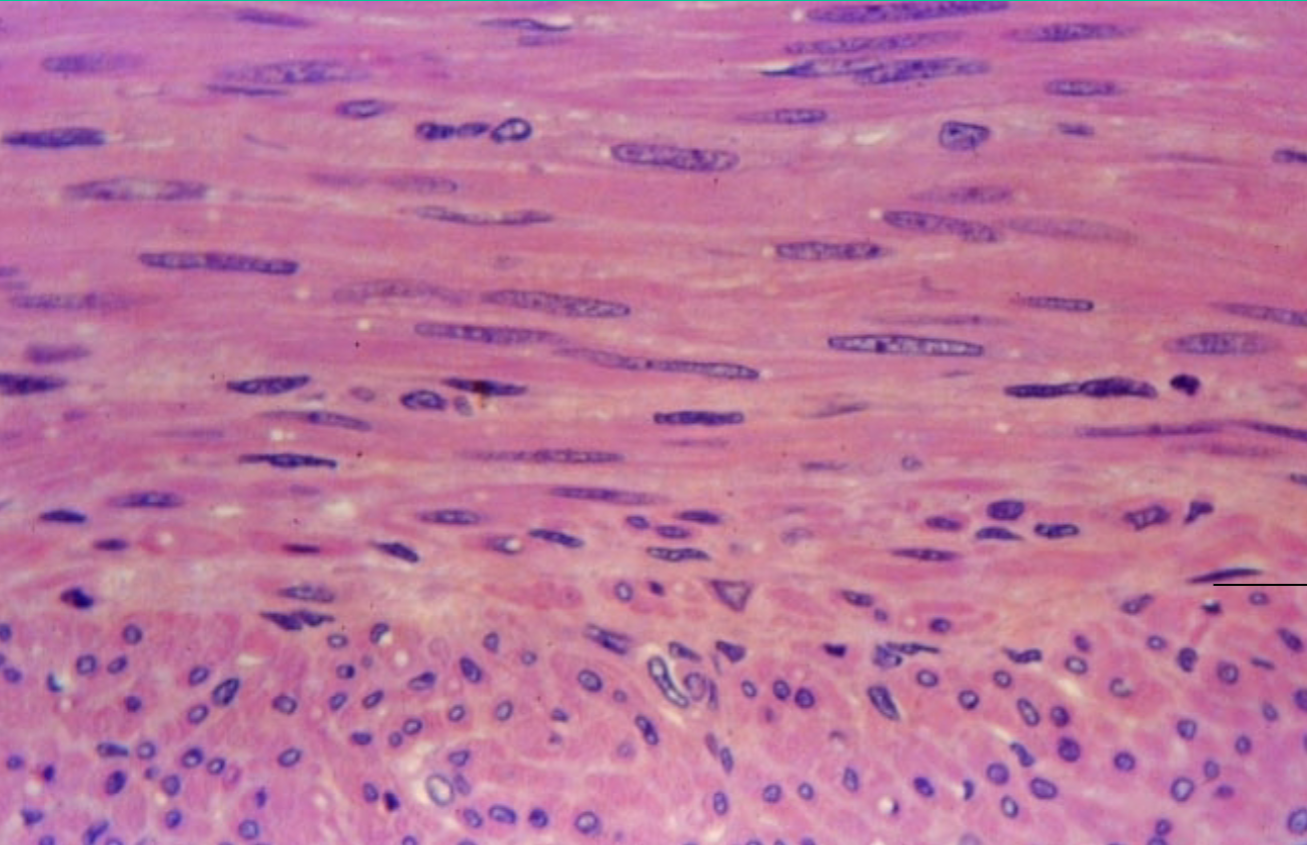
Where is the smooth muscle tissue found?
walls of hollow internal organs
→ vessels, airways, stomach, bladder, uterus
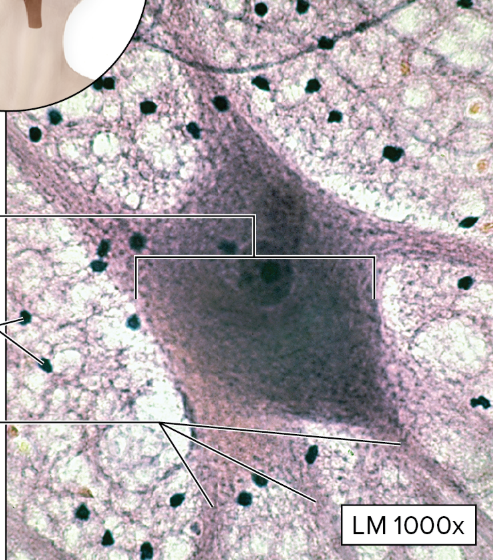
Nervous Tissue
contains neurons with rounded or stellate cell bodies + an axon and dendrites extending from the cell body
Neuroglia (glial cells) lack extensive fibrous processes
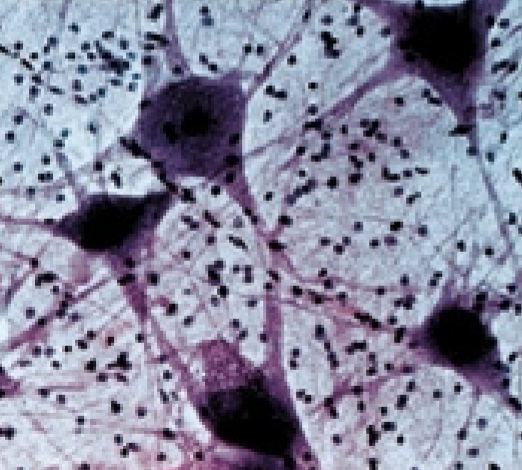
Nervous Tissue: What is the function of the Neurons?
responsible for control
information processing, storage, and retrieval, internal communication
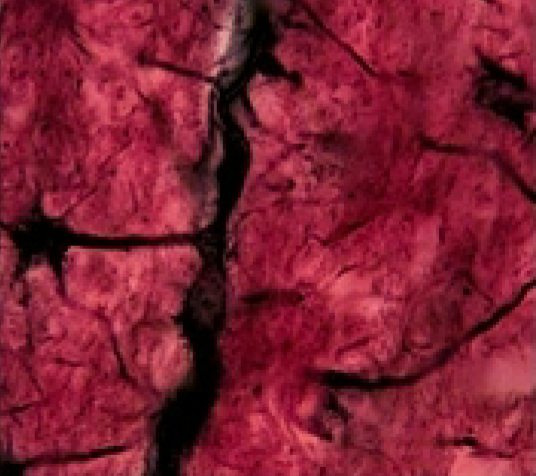
Nervous Tissue: What is the function of the Neuroglia (glial cells)
supporting and connecting neurons