Common skin disorders and skin infections
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
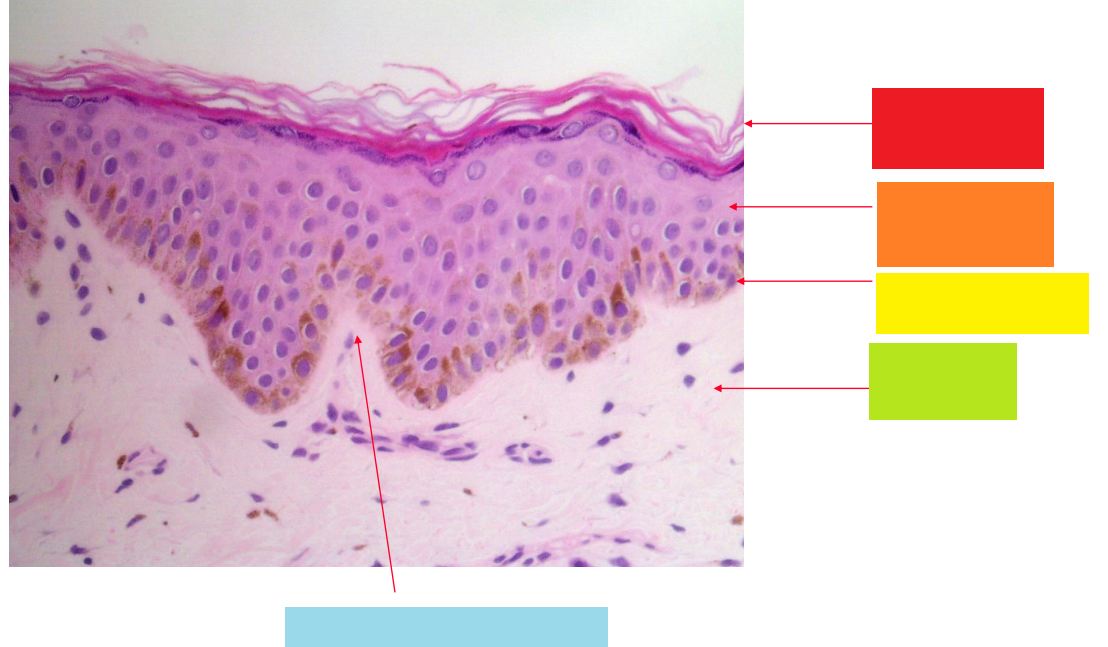
red
stratum corneum
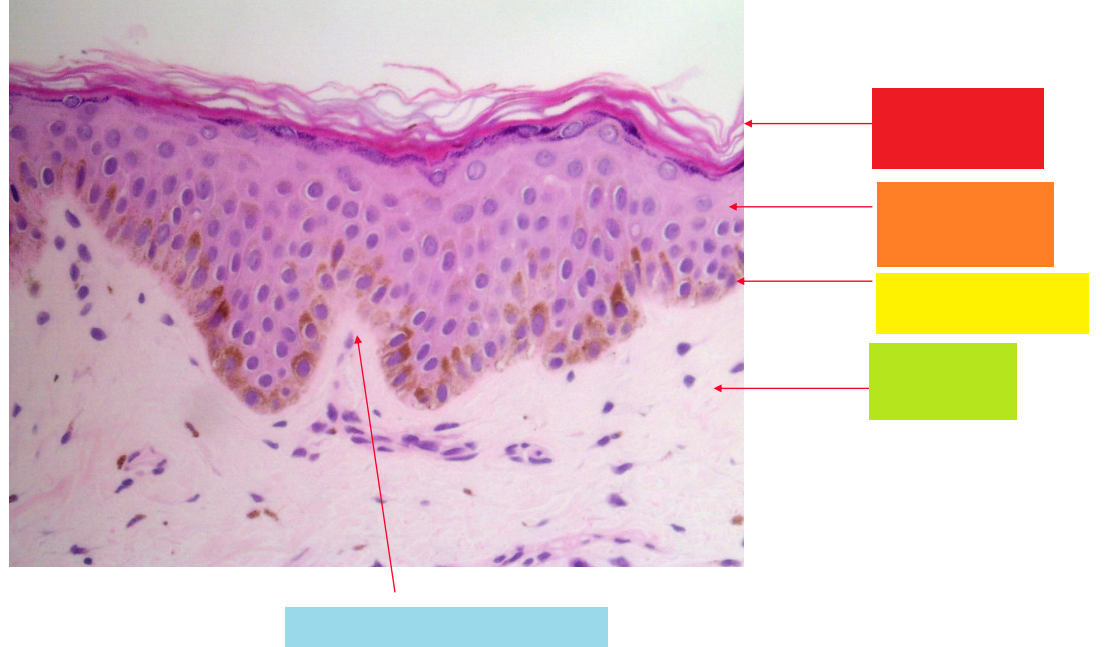
orange
stratum granulosum
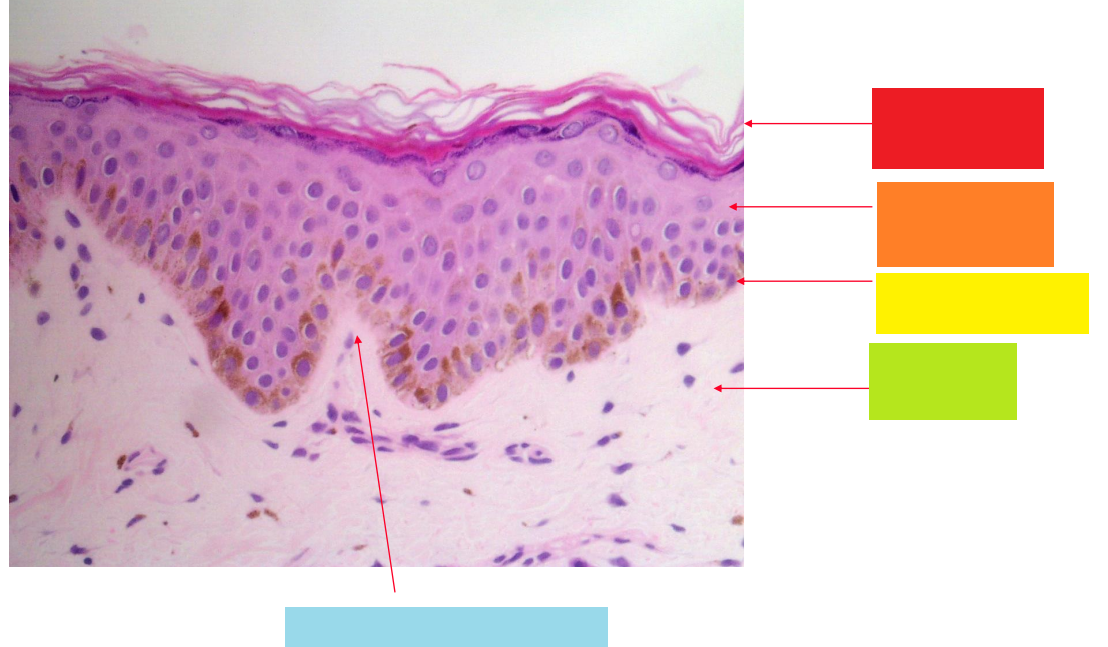
yellow
basal layer
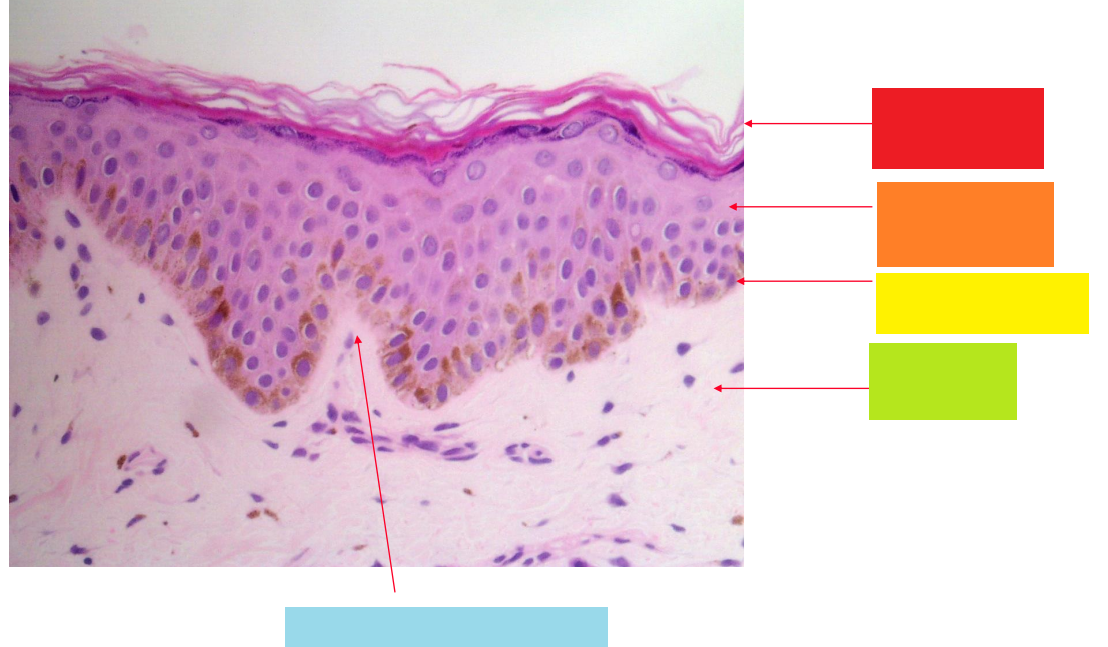
green
dermis
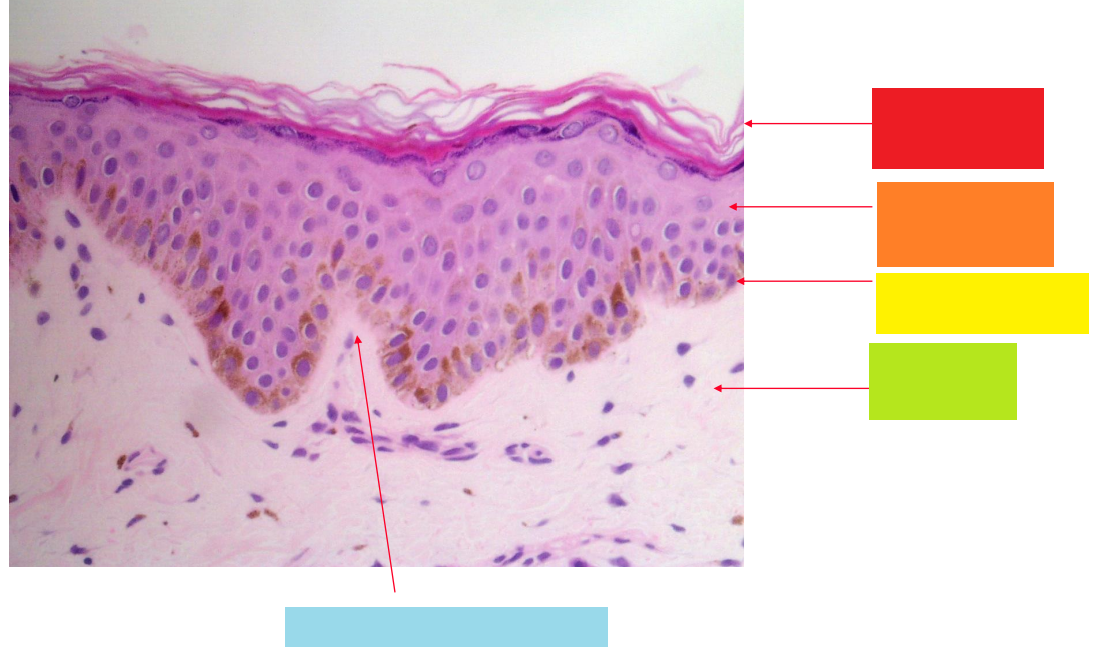
blue
dermal papilla
skin adnexae
hair, sebaceous/sweat glands
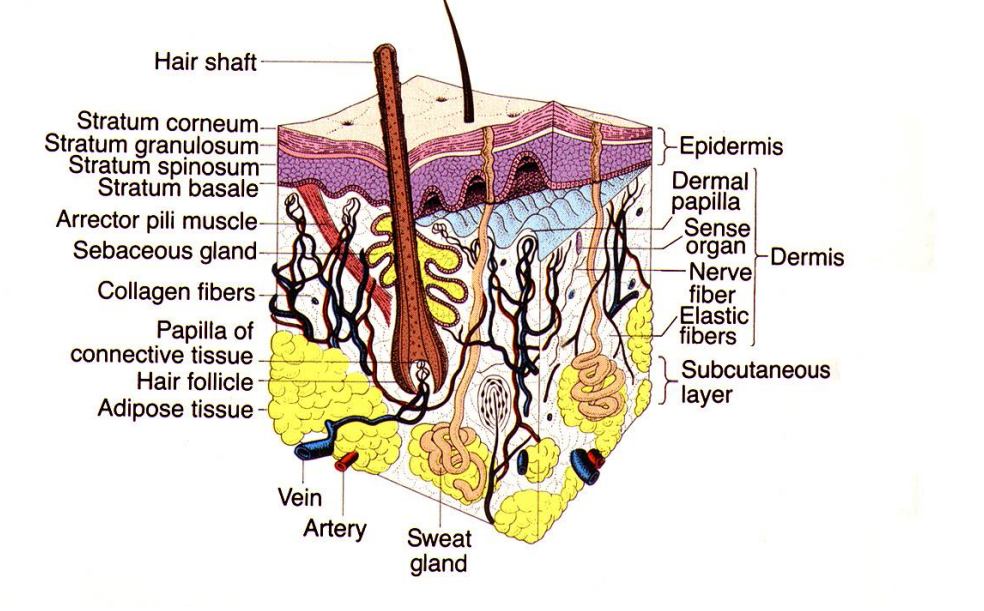
The skin is the largest organ in the body. In addition to skin adnexae (hair, sebaceous/sweat glands), there is a complex vascular network which allows the skin to shunt blood to the surface to dissipate heat or retain blood flow deeper in the dermis.
flexural sites - neck/groin →thin epidermis → be careful of treatments you use
thicker sites - palms and soles
Functions of the skin 6
Protection from the environment Chemical, thermal, physical, UV injury
Thermoregulation
Neuroreceptor → External stimuli - lips, genatalia, mouth
Antigen processing (Langerhans cells) → WHEN THIS GOES WRONG → contact sensitivity
Synthesis of vitamin D
Cosmetic
History taking in a patient with a skin disorder - what should you ask about? 8
Age, sex occupation
History of presenting complaint - symptoms/ initial site/ subsequent involvement
Relevant systems review
Current/past treatment
Past medical history
Family history
Drug history
Allergies
Examination - skin inspection
• should include careful complete skin inspection
‘Hidden sites’ e.g. scalp, nails, umbilicus, natal cleft
mucous membranes oral mucosa, eyes, nasopharynx ± genitalia
what factors should you consider when taking a skin inspection ?
site: e.g. localised / generalised/ distribution skin and/or mucous membranes
morphology: e.g. mono / polymorphic, blister/ erosion/ scarring
background skin: normal/ erythema
palpable
cannot be touched - raised
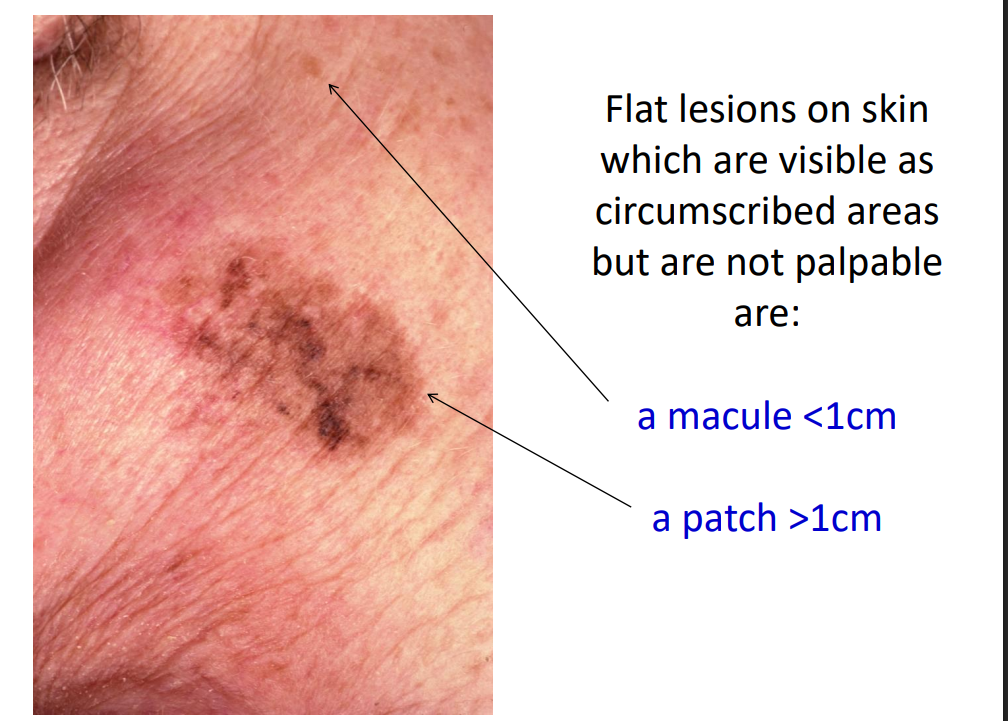
Flat lesions on skin which are visible as circumscribed areas but are not palpable are:
macule or patch
how do you distinguish a macule from a patch?
a macule <1cm a patch >1cm
a slightly raised flat topped lesion >1cm diameter
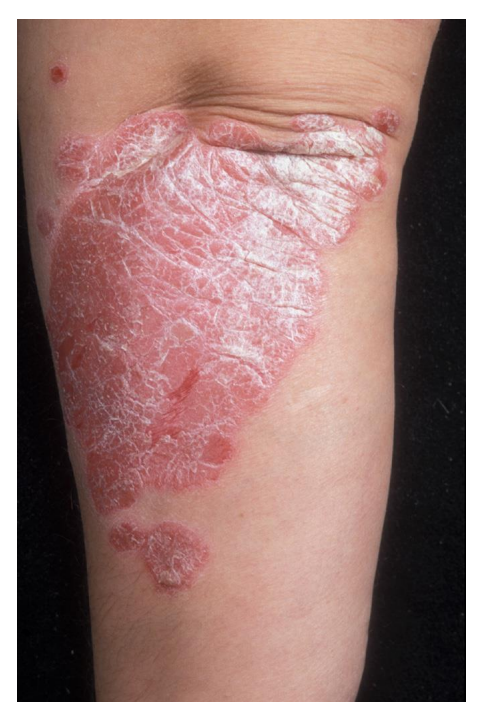
plaque
This patient has chronic plaque psoriasis
a circumscribed palpable elevation <1cm
a papule
These flat topped papules are lichen planus
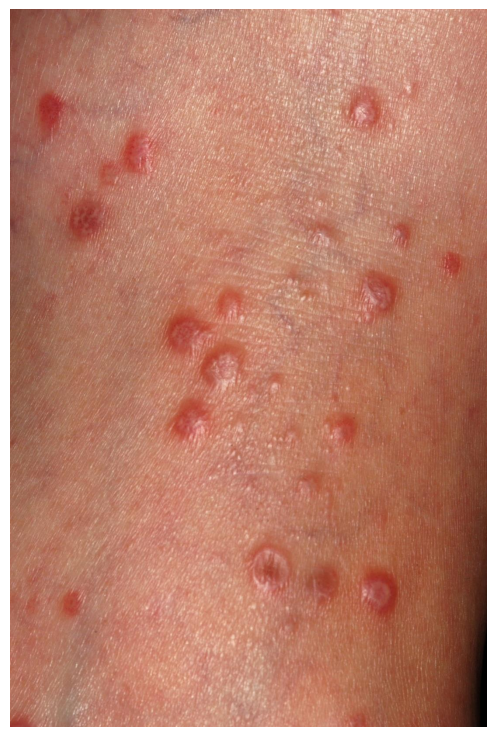
a palpable elevation >1cm
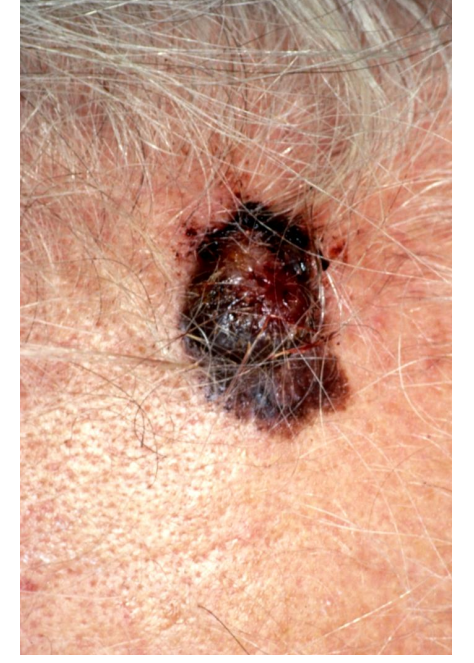
nodule
This patient has a nodular malignant melanoma on her forehead
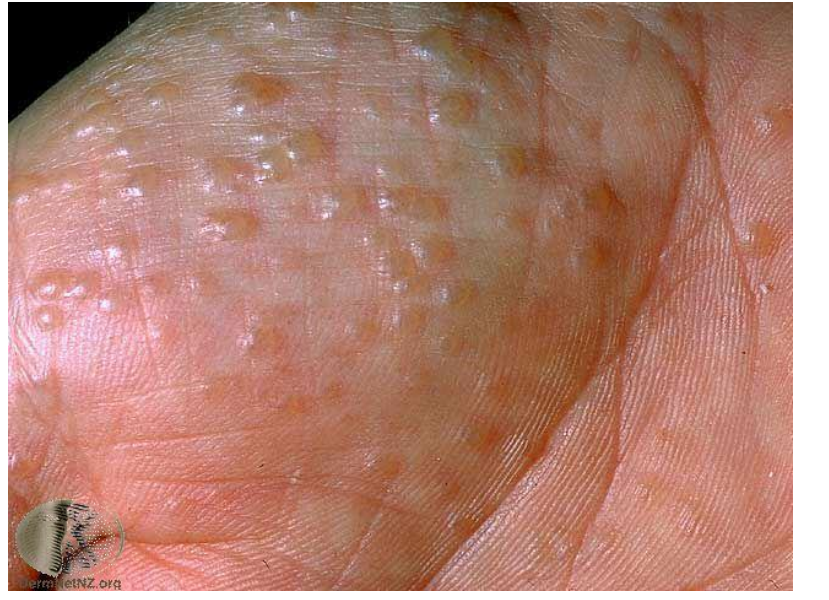
a blister <0.5cm diameter is known as a …
vesicle
This patient has pompholyx eczema on the thenar eminence (palm)
monomorphic lesions
a blister >0.5cm in diameter is known as a …
bulla
This patient has angina bullosa haemorrhagica
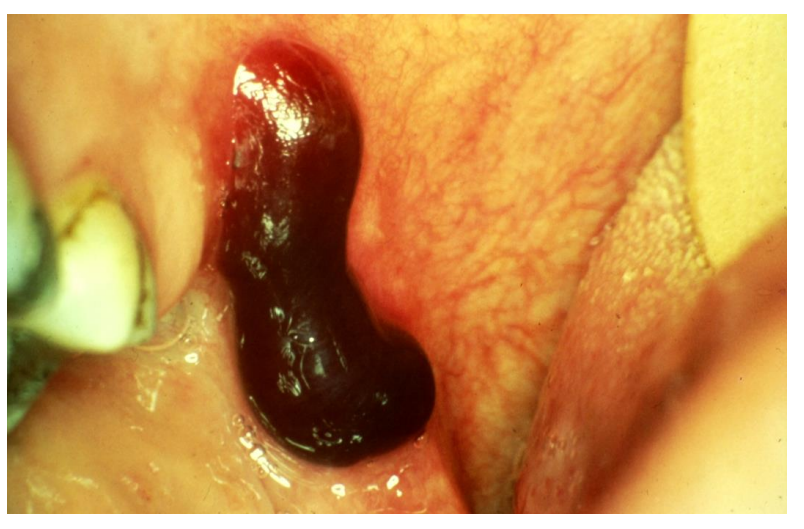
peeling of the stratum corneum /superficial epidermis
a scale
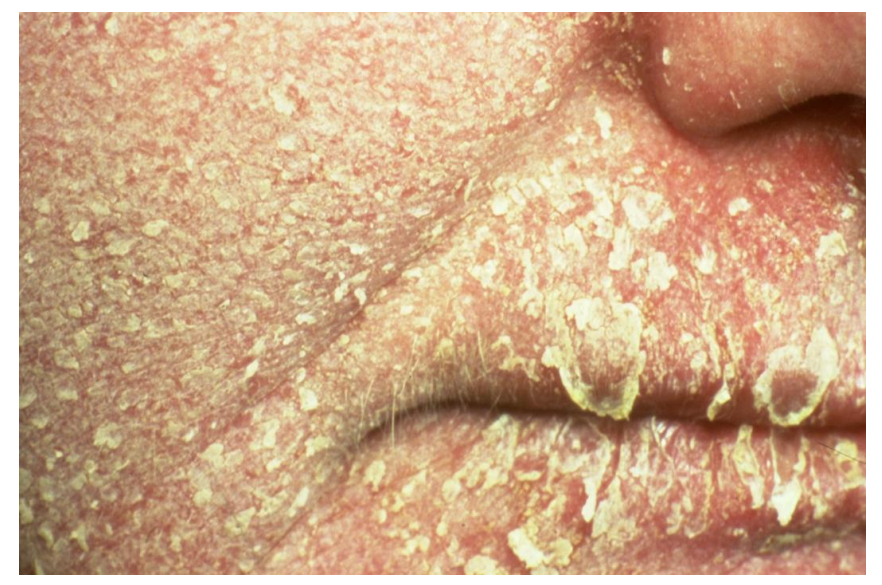
This patient has severe eczema
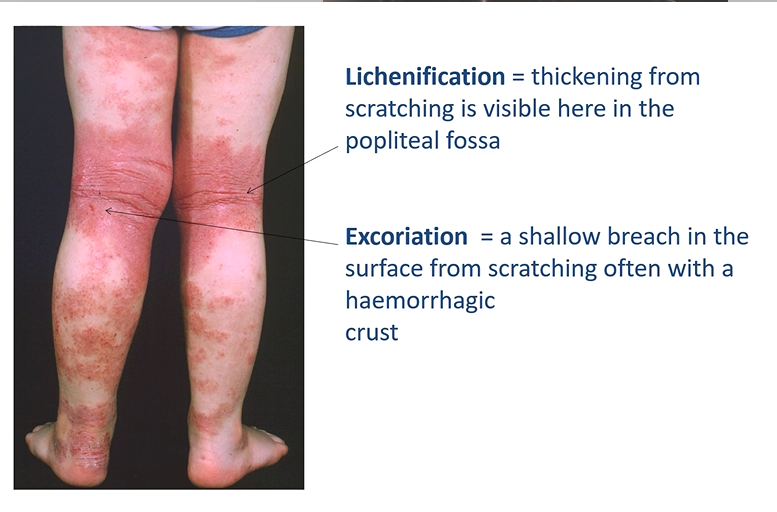
lichenification vs excoriation
Lichenification = thickening from scratching is visible here in the popliteal fossa
Excoriation = a shallow breach in the surface from scratching often with a haemorrhagic crust
This patient has severe atopic eczema.
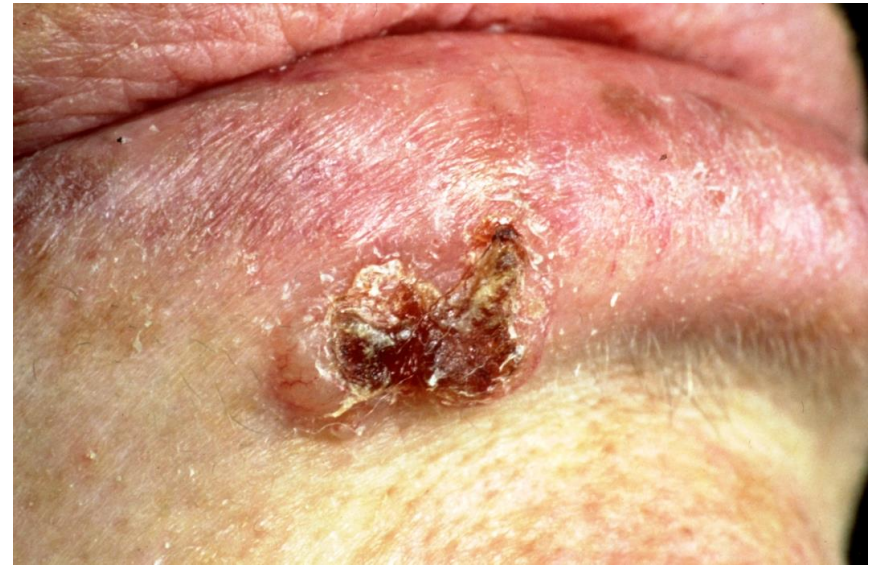
full thickness loss of epidermis
ulcer
This patient has an ulcerated nodular basal cell carcinoma
raised margin, looks see through (opalescent)
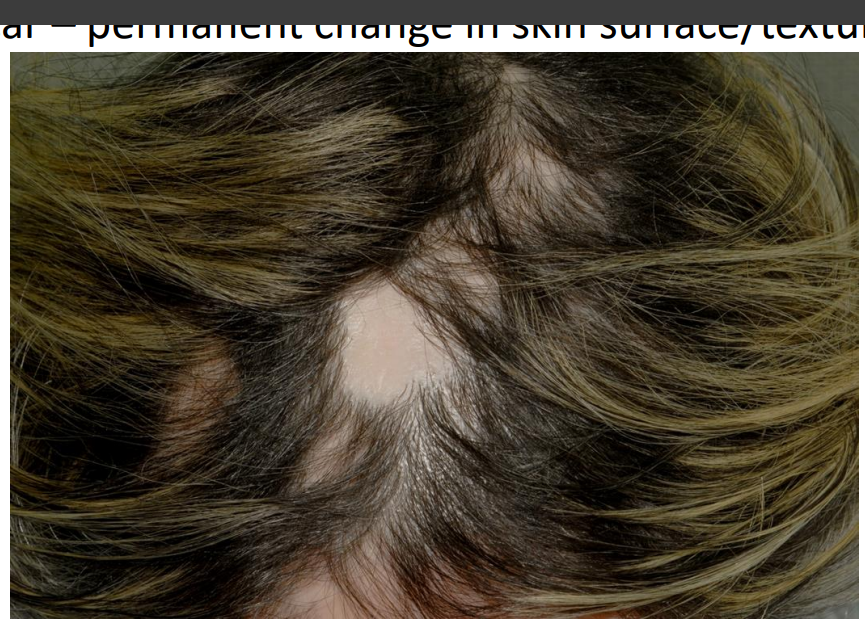
permanent change in skin surface/texture
scar
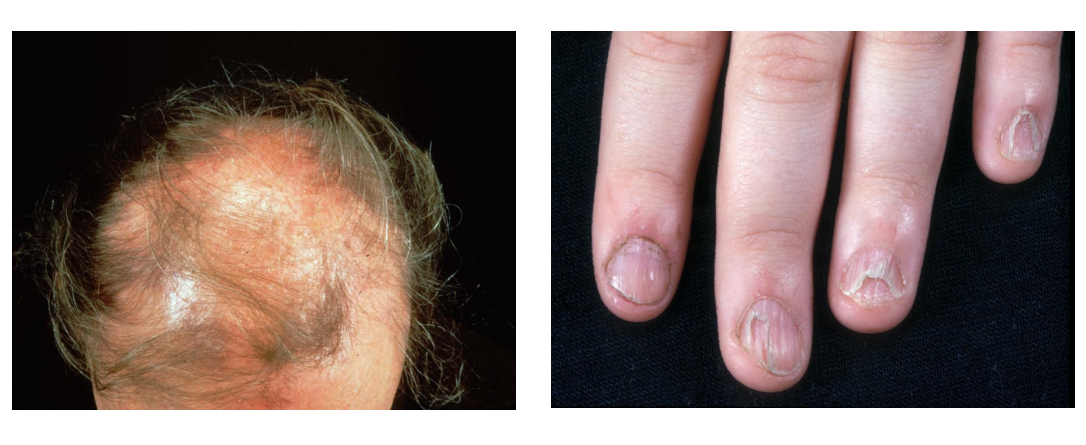
This patient has lichen planus in the scalp (lichen planopilaris showing patchy hair loss so called ‘footprints in the snow’)
In order to clarify or confirm a diagnosis the following tests may be needed: 4 investigations
Skin swabs/scrapings → Bacteriology, virology, mycology
Skin biopsy → Histology, Culture, Immunofluorescence
Patch tests → Undertaken if a contact allergy is suspected
Photo-tests → to investigate a possible sensitivity to UV
If a patient is unwell and either infected or in need of systemic therapy, the following blood investigations may be required - investigations 4
Haematology: FBC, ESR
Biochemistry: U+E, LFT, glucose, CRP
Immunology: ANA, DNA (
lupus), organ specific antibodies (thyroid/liver)Virology: herpes simplex serology
management - general measures
assess need for admission : e.g. fluid balance, thermoregulation nutrition, infection control
management - topical
infection - antibacterial agents, candida corticosteroids creams, mouthwash
management - systemic
prednisolone +/- steroid sparing agents antibiotics
management - referrals
Ophthalmology, Dermatology, ENT

what is Eczema?
This is a pruritic inflammatory condition associated with dryness and erythema of skin. Scratching results in excoriation and lichenification
is aka dermatitis
image - flexural eczema
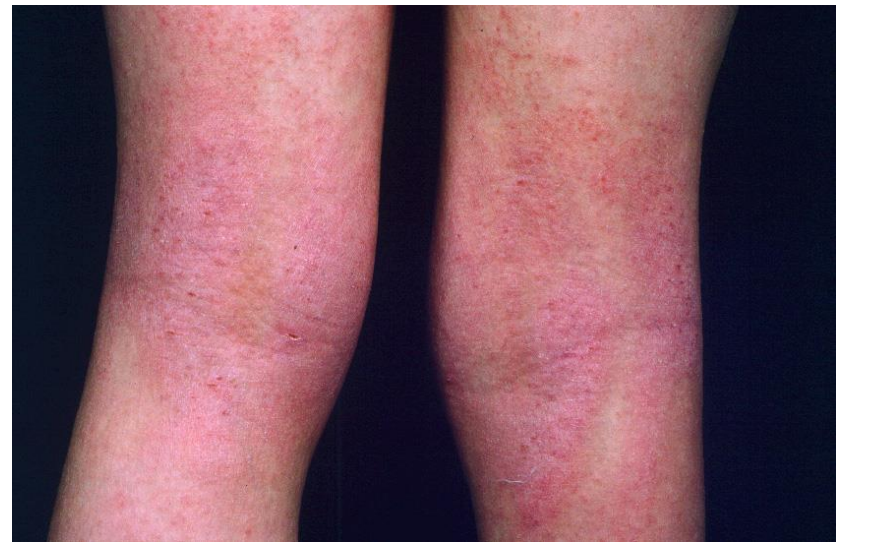
eczema scratching results in…
excoriation and lichenification
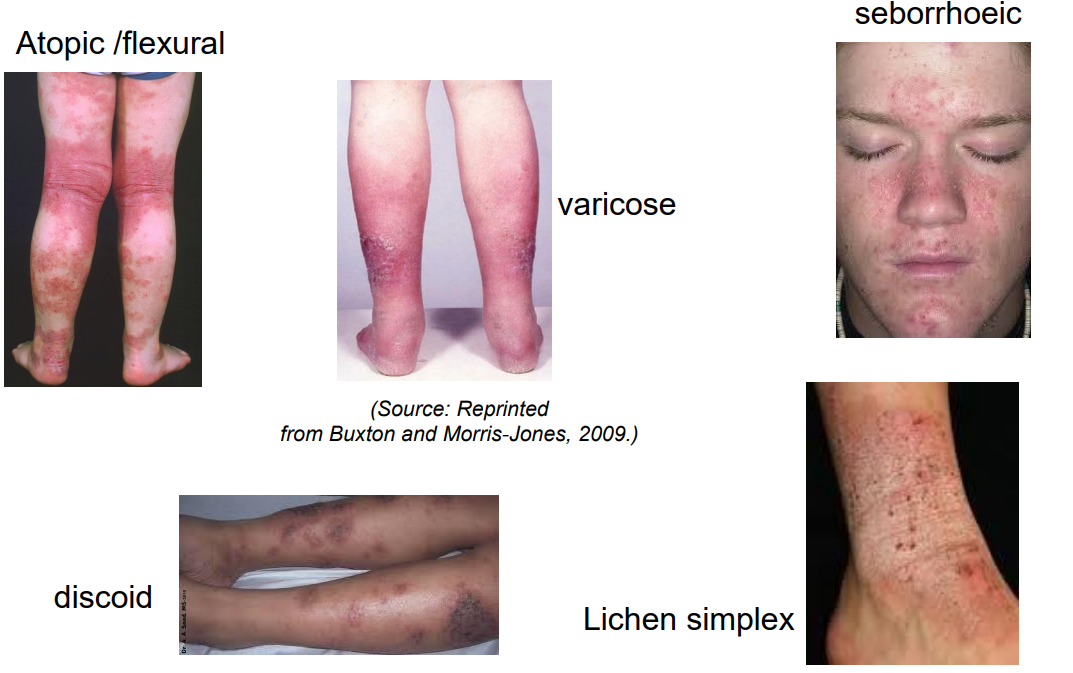
There are several sub-types of eczema: list them
Atopic /flexural - young
varicose - old, venous incompetence
seborrhoeic - centre of face and the scalp , anogenital skin
discoid - coin shaped
Lichen simplex
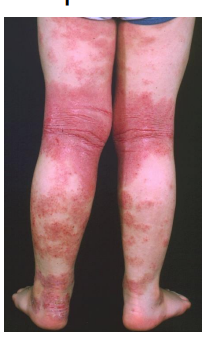
what type of eczema is this?
Atopic /flexural
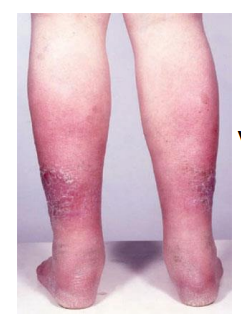
what type of eczema is this?
varicose
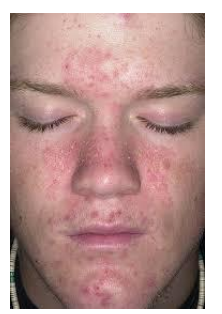
what type of eczema is this?
seborrhoeic
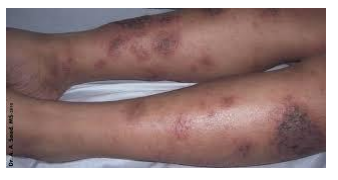
what type of eczema is this?
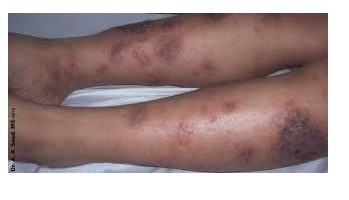
what type of eczema is this?
lichen simplex
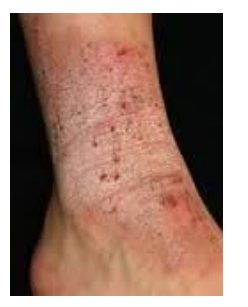
Dermatitis may also be secondary to contact with a substance 2
Irritant contact e.g.. over hand washing - can affect anyone
Allergic contact dermatitis - only found in patients who have a hypersensitivity to a specific allergen
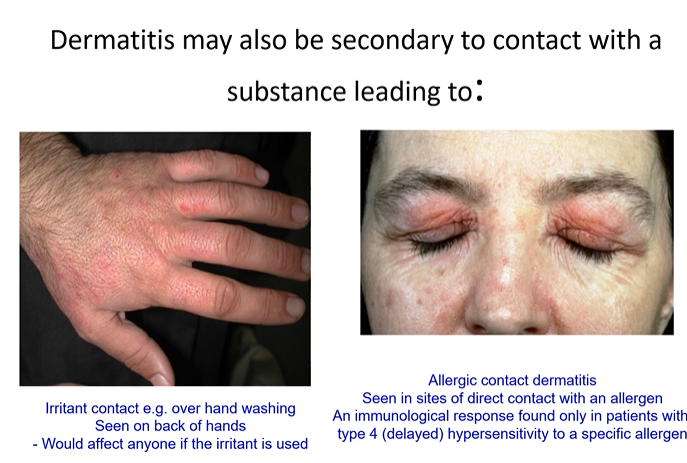
Eczema may be secondarily infected with: 2
Staphylococcus aureus (impetiginised eczema) yellow crust and weeping (not impetigo)
Herpes simplex (eczema herpeticum) Monomorphic lesions - eye can be permanently affected - ophthalmologist needs to be involved
eczema - Management
Avoid soap, shower gel and contact with irritants such as domestic cleaning agents
Advise use of:
Emollients e.g. soap substitutes, moisturisers
Topical steroids
Oral antibiotics
Antihistamines (sedative)
Wet wraps
Acyclovir if suspect herpes simplex (eczema herpeticum)
Psoriasis – clinical features
2% prevalence.
Strong family history
Symmetrical well-defined red plaques with thick silvery scale
Elbows and knees common sites
Lasts for many years - increases in severity
Psoriasis – types
Psoriasis vulgaris - common
Guttate - tear drops → follows a throat infection
Erythrodermic - red in widespread distribution
Pustular - needs to be hospitalised
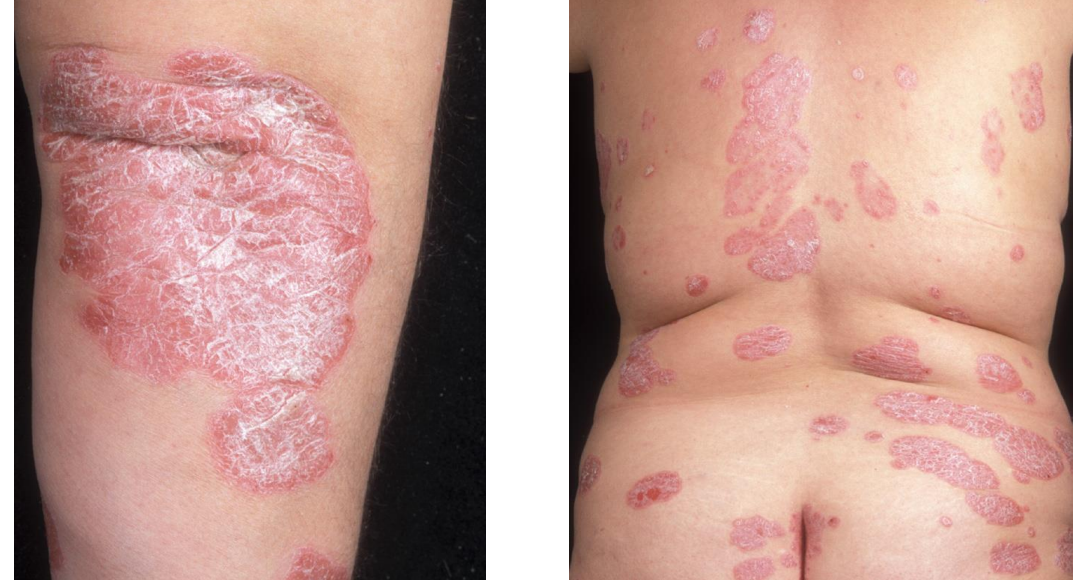
Psoriasis vulgaris = chronic plaque psoriasis
Well-defined salmon pink plaques with silvery scale
psoriasis - scalp and nails
The scalp and hairline are frequently affected
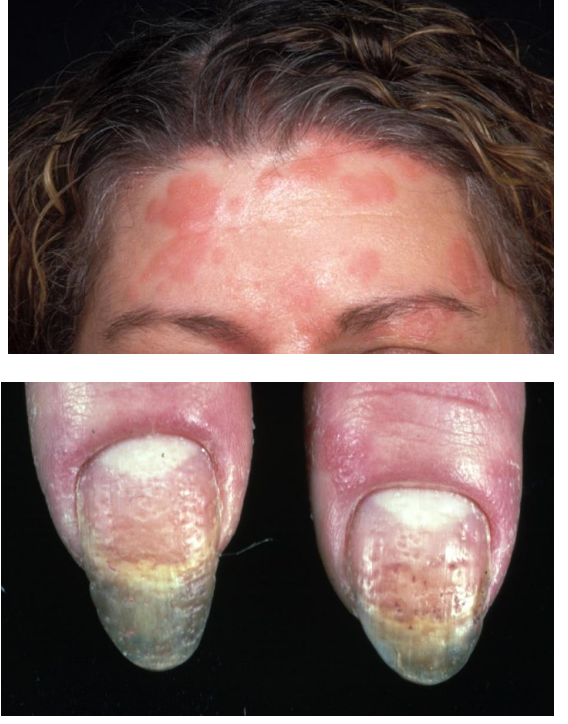
Nail pitting and subungual hyperkeratosis is sometimes present → due to plaques under the nails
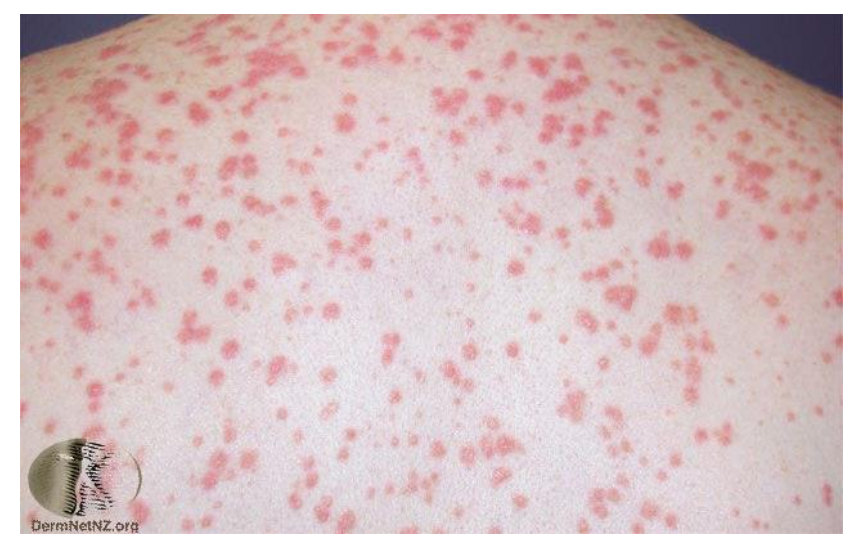
guttate psoriasis
raindrop size lesions often follows a streptococcal throat infection
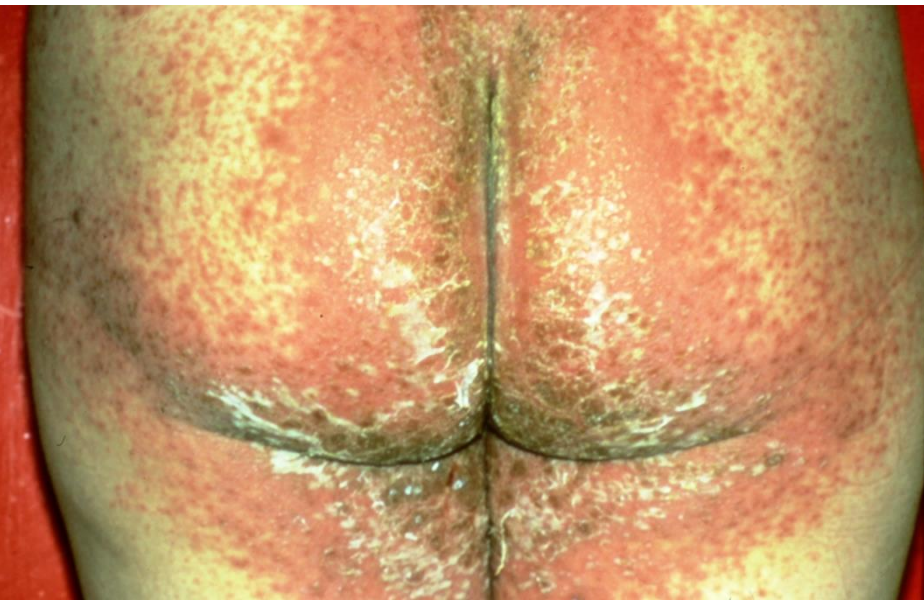
Generalised pustular psoriasis (a severe but uncommon variant) - flexural regions
Psoriasis - treatment
Emollients/ bath oils
Vitamin D analogues – e.g. calcipotriol
Tar preparations
Topical steroids
Dithranol
UVB, PUVA
Systemic – acitretin, methotrexate, cyclosporin, biologics
Lichen planus
Unknown aetiology - perhaps autoimmune
1-2% population
Onset 30-60yrs
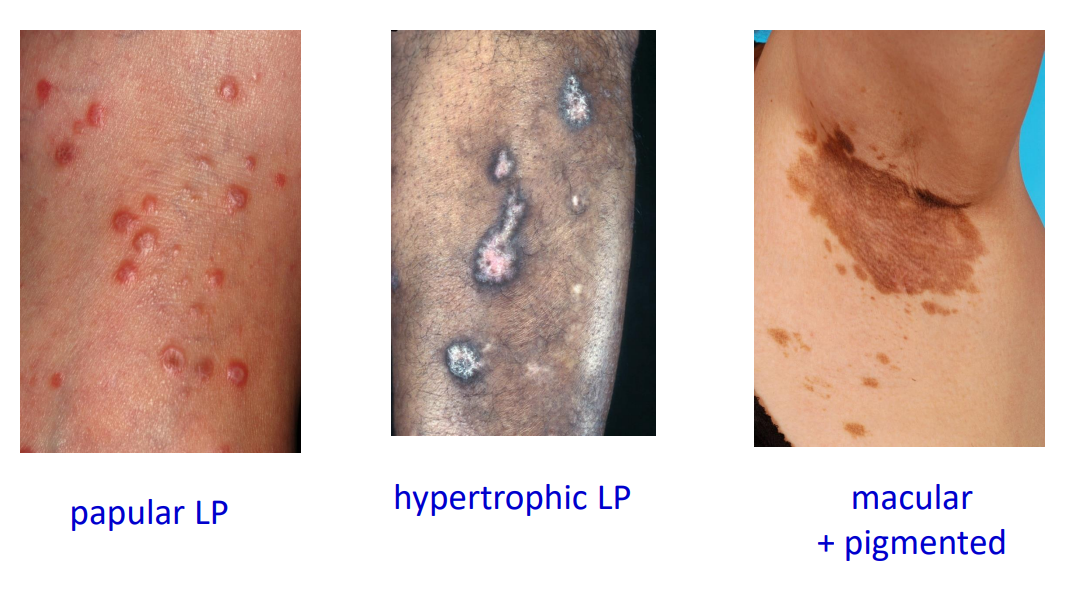
Flat-topped violaceous papules on skin
Predilection for flexor surfaces and lower back
Lichen planus Clinical variants
Hypertrophic →thick plaques
annular → ring
plantar → flat tops
Oral – several sub-types
Lip
genital
scalp – lichen planopilaris
most common around flexture surfaces
a range of presentations
Lichen planus results in scarring in some sites
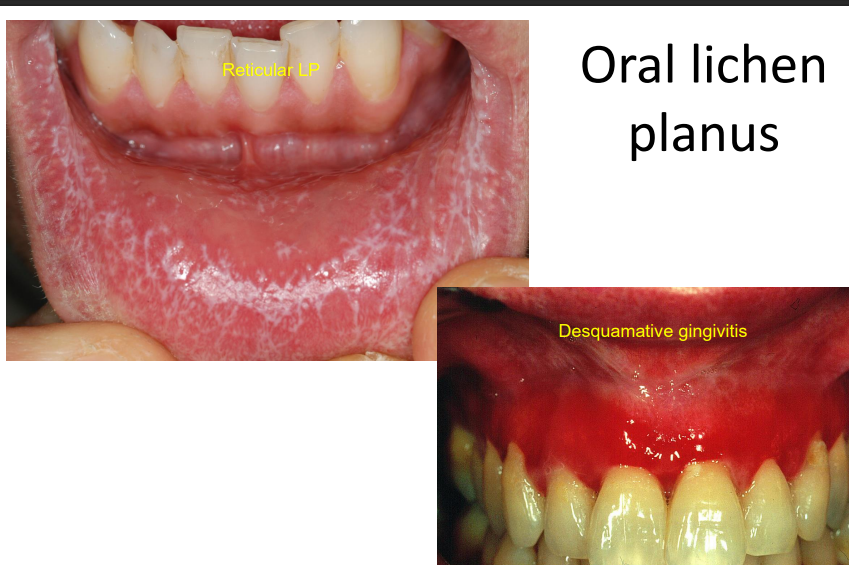
Oral lichen planus
Desquamative gingivitis may be caused by LP
Lichen planus - treatment - topical
emollients
topical steroids (check candida count orally - can be a secondary infection)
Lichen planus - treatment -systemic
Prednisolone
azathioprine/ mycophenolate
methotrexate
(immunosuppressants)
Pruritus
itching
causes of Pruritus 9
Xerosis → dry skin
Dietary → iron deficiency anaemia
Endocrine → thyroid disorders, diabetes mellitus
Inflammatory → eczema, urticaria
Autoimmune → lichen planus, dermatitis herpetiformis
Infective → chicken pox
Infestation → scabies
Parasitic →cutaneous larva migrans
Neoplastic → cutaneous T cell lymphoma, myeloproliferative, lymphoma
Viral infections: varicella
chicken pox (polymorphic)and shingles
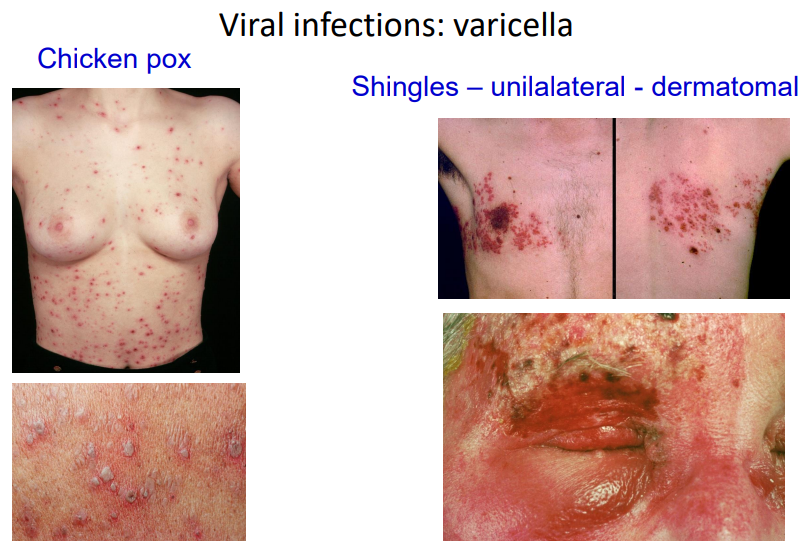
how can you describe shingles?
unilateral and dermatomal
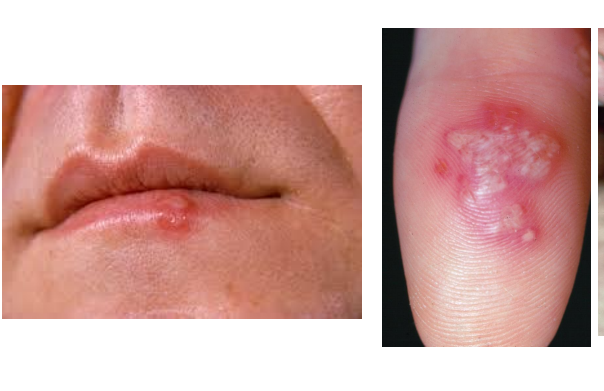
Herpes simplex
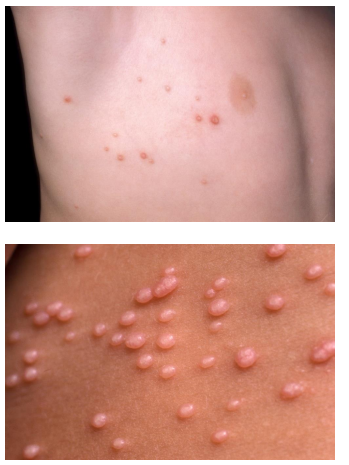
Molluscum contagiosum (pox virus)
umbilication
small, central depression on papules
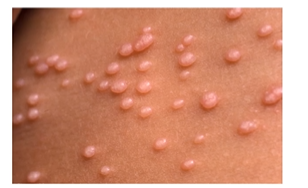
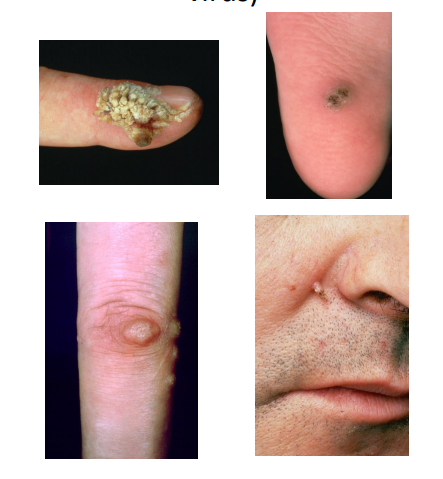
Warts (human papilloma virus)
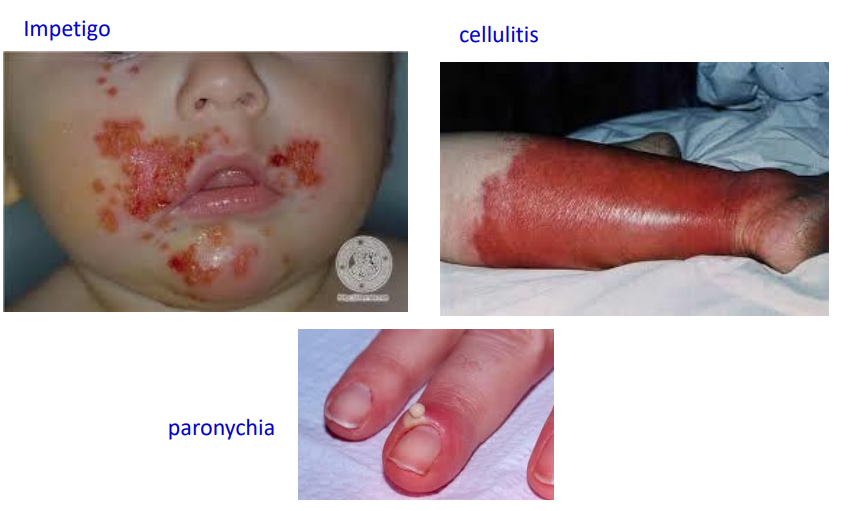
Bacterial infections Staphylococcus aureus/ streptococcal infections 3
Impetigo
cellulitis
paronychia
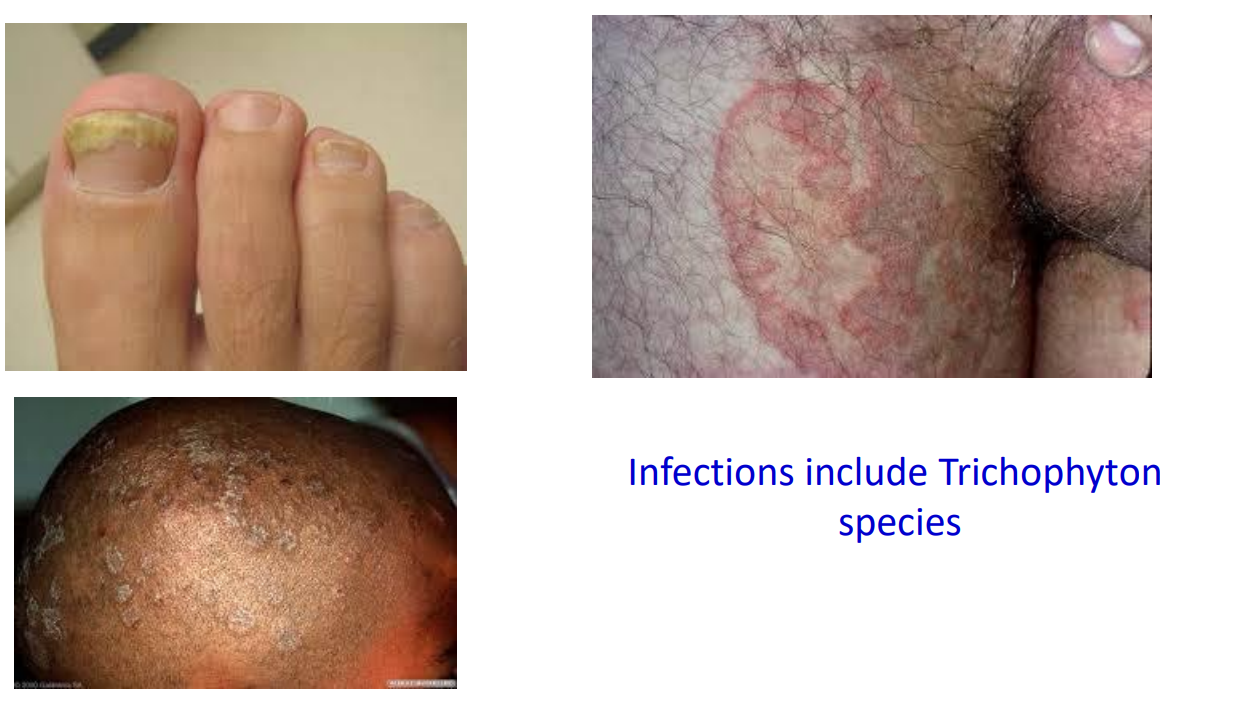
Fungal infections
Infections include Trichophyton species