Antibodies and B cells
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
PRRs
general binding when something is wrong, binds PAMPs and DAMPs, same receptors found in most humans, used for innate immunity, many cells produce but immune cells produce the most
AgRs
allow for a very specific response to be generated, bind epitopes, creates immune memory, different between humans, used in adaptive immunity, made randomly in advance of any infection
secondary lymphoid tissue
where T and B cells go after formation
clonal selection and expansion
factors of the adaptive immune system that allow the response to be specific and effective
surface bound (BCR) and secreted (Abs)
two types of antibodies
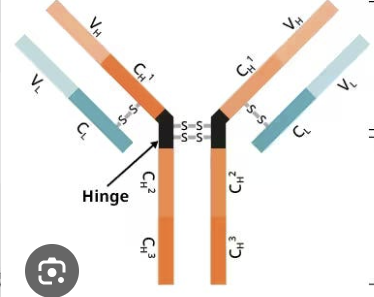
variable
this part of the antibody binds the antigen, greatly differs from one antibody to the next
constant
this part of the antibody is responsible for effector functions, does not differ from one antibody to the next
heavy chain, IgM, IgG, IgA, IgD, IgE
orange (name and types)
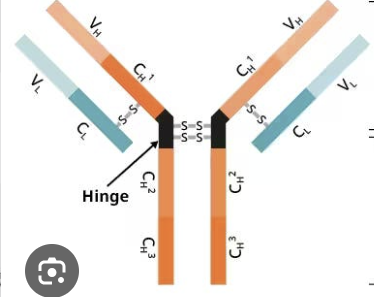
light chain, kappa, lambda
blue (name and types)
IgA dimer, IgM pentamer
two classes of antibodies that can glutonate using J chains
all types of biomolecules (proteins, carbs, lipids, nucleic acids)
antibodies can bind epitopes from
Igalpha and IgBeta
BCR requires these signaling protiens and a membrane-bound antibody to allow signaling for robust proliferation (secretion of the same class of antibody with the same antigen specificity)
one unique
each b cell has ____ BCR(s) that recognize(s) an antigen epitope EXCEPT during development
alternative splicing and recombination before transcription
how we get diversity from only 25k genes
D
segment spliced in the variable region for the heavy chain (in front of the constant region)
VJ
segment spliced in the variable region for the light chain (in front of the constant region)
TdT (deoxynucleotidyl transferase)
cut off loop in Ig gene arrangement, add random nucleotides to the gene (DNA) to increase diversity in antigen specificity (variable region)
RAG 1 and 2
create loop between genes during somatic recombination of DNA
IgM and IgD
Ig gene arrangements that are expressed together on one B cell, since no switch region exists between them, difference between them determined by RNA splicing (NOT DNA)
RNA splicing
determines IgM/IgD (constant region)(determined by polyadenylation), and if membrane-bound or secreted (include hydrophobic region or not)
DNA splicing
determines variable region (VDJ) (same within the same B cell)
B cell activation
not made in response to pathogen, select specific cell that proliferates creating an army of cells that can respond
internalize pathogens and present to T cells and secrete antibodies that flag pathogens for destruction
B cell immunity
T-independent type 2 antigens (TI-2)
have repeating epitopes, allowing cross-linkage of several BCRs to stimulate activation, low affinity but made quickly, can cross link multiple receptors
T-independent type 1 antigens/mitogens
bind PRRs (similar to TLRs) in addition to the BCR to stimulate activation, will bind to any biomolecule class, low affinity and antigen specific, produces IgM that can then switch
T-dependent antigen (TD)
activation signals provided by T cells, has to have a protein antigen, antigen-specific and high affinity, require Th cells, class other than IgM
linked recognition
T and B cells activated by the same antigen but different epitopes
formation of germinal centers
TD B cells interacting with CD4 T cells (Tfh) in 2ndary lymphoid tissue= activation of B cells and
antigen binding, costimulation from CD40/CD40L, cytokines
signals required for activation of B cells
germinal centers
cluster of proliferating b cells that interact with follicular dendritic cells and T cells that produce high affinity antibodies such as IgG or IgA
somatic hypermutation
mutations in the VJ and VDJ regions of the light and heavy chains of B cell clones that change their affinity for the antibody (NOT change their specificity), can’t bind= die by apoptosis
follicular dendritic cells
hold antigen on their “dendrites” to allow B cell clones to compete for binding, selecting for the cells with the best BCRs (affinity maturation), selected cells allowed to class switch and proliferate
class switching
change in the heavy chain constant region of a BCR, requires CD40+CD40 L, turning on AID (transcription factor that changes location of loop)
IFN gamma
cytokine secreted by CD4 T cell that leads to class switching to IgG
IL-4
cytokine secreted by CD4 T cell that leads to class switching to IgE
TGF-beta
cytokine secreted by CD4 T cell that leads to class switching to IgA
FC receptors
receptors found on many cell types bind to stick portion of antibody, allows the antibody to regulate that cell’s functions
secretory IgA
plasma mainly secretes IgA, must be turned into a dimer to cross cells
IgG
most useful/versatile antibody due to its monomeric structure and available Fc region to bind FC gamma Rs, 4 types, crosses the placenta, opsonization
IgM
first antibody produced in response to an antigen, first produced in a developing child, classical complement activation, membrane bound
IgD
membrane bound, no effector function known
IgA
predominant secretion antibody, first line of defense vs microorganisms
IgE
defense vs parasites, associated with allergic reactions, found mainly in tissues