Lecture Nine: Posterior Segment
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
what does the posterior segment include?
Vitreous
Retina, Choroid, Scleral
Optic Nerve
posterior chamber?
Sulcus between the lens and ciliary body (behind the iris).
tests to look at the posterior segment?
- Menace response
- Dazzle reflex
- Pupillary light reflex (PLR)
- indirect ophthalmoscopy (28D or 2.2D lens) vs direct
- Electroretinogram (ERG) - flash, multifocal -- flash lights --> get waveform like ecg
- Imaging: Ultrasound, CT, MRI
- Neurologic exam
- Systemic workup
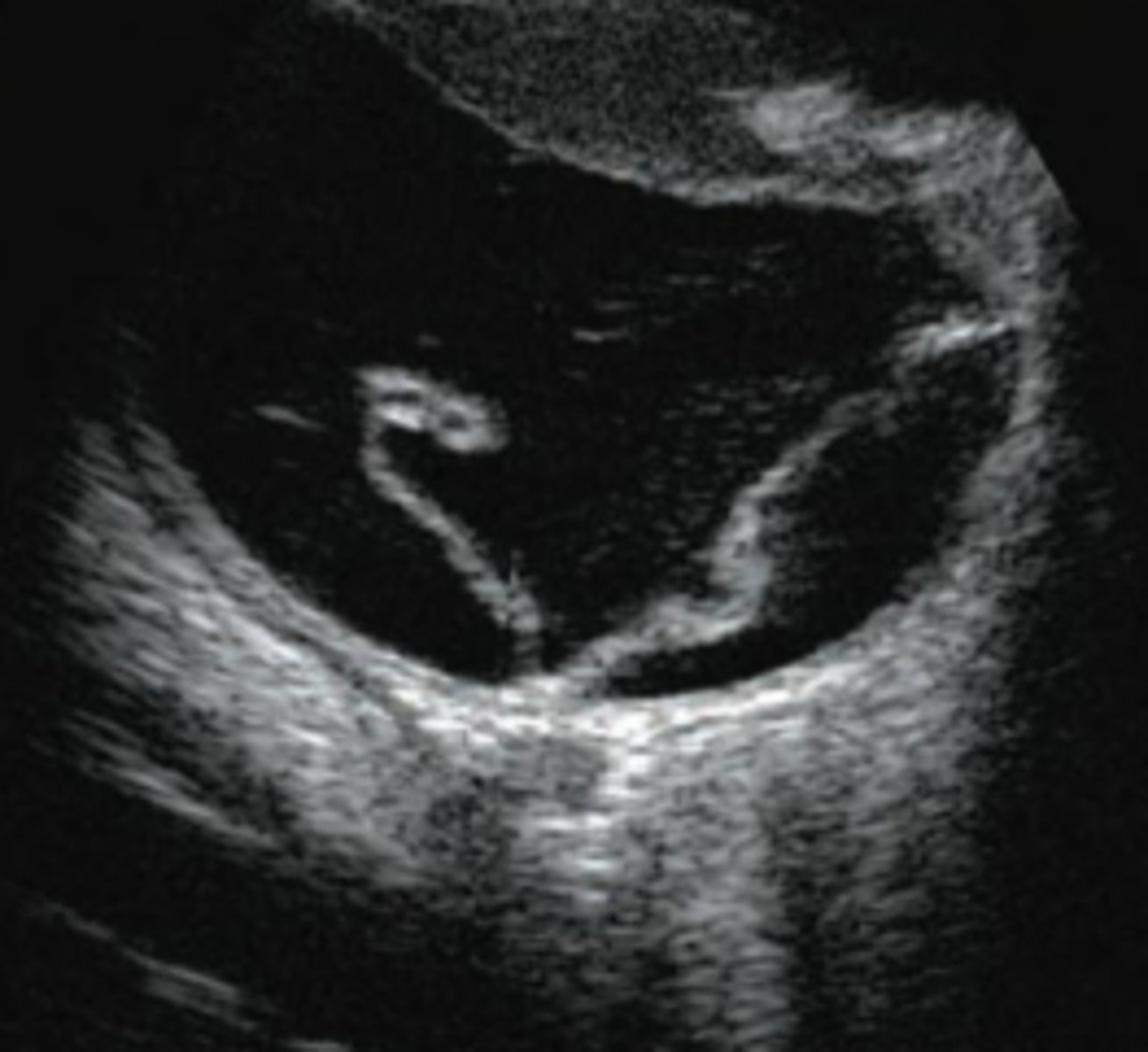
what is this?
retinal detachment
primary vitreous
Hyaloid vascular system
secondary vitreous
adult
tertiary vitreous
lens/zonules
vitreous makes up ? % of the eye's volume in domestic animals
75%
vitreous attached to?
optic nerve, ora ciliaris retinae, posterior lens
Persistent Hyaloid Artery?
• Rarely clinical problem, can cause cataract
• Mittendorf's dot, Bergmeister's papilla
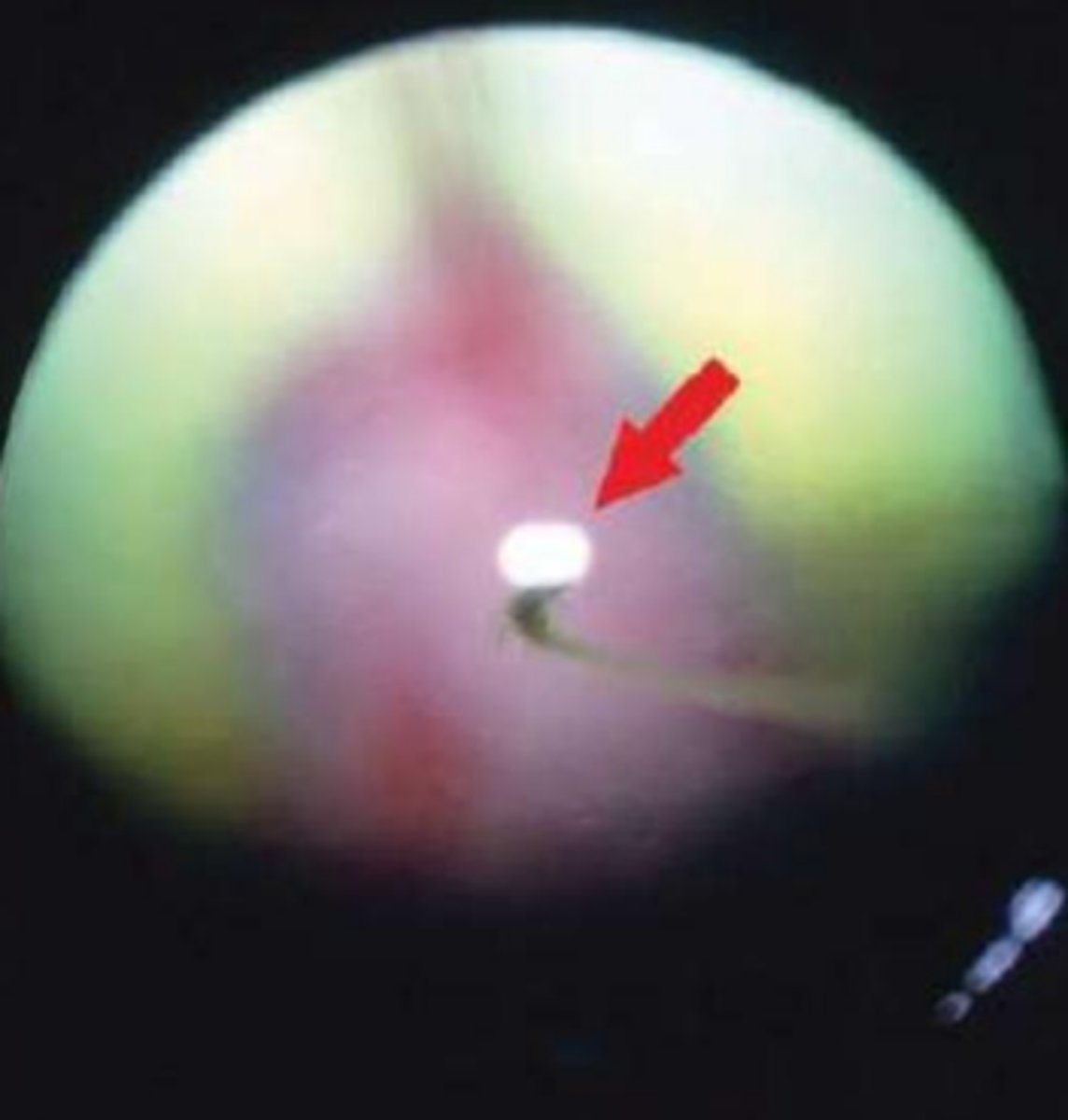
Persistent Hyperplastic Primary Vitreous?
persistent fetal vasculature -- Normally regressed at 3wk (dogs), 8wks (cats)
white opacity in pupil -- Leukocoria
leave alone vs cataract surgery
dobermans and staff terriers
staged 1-6
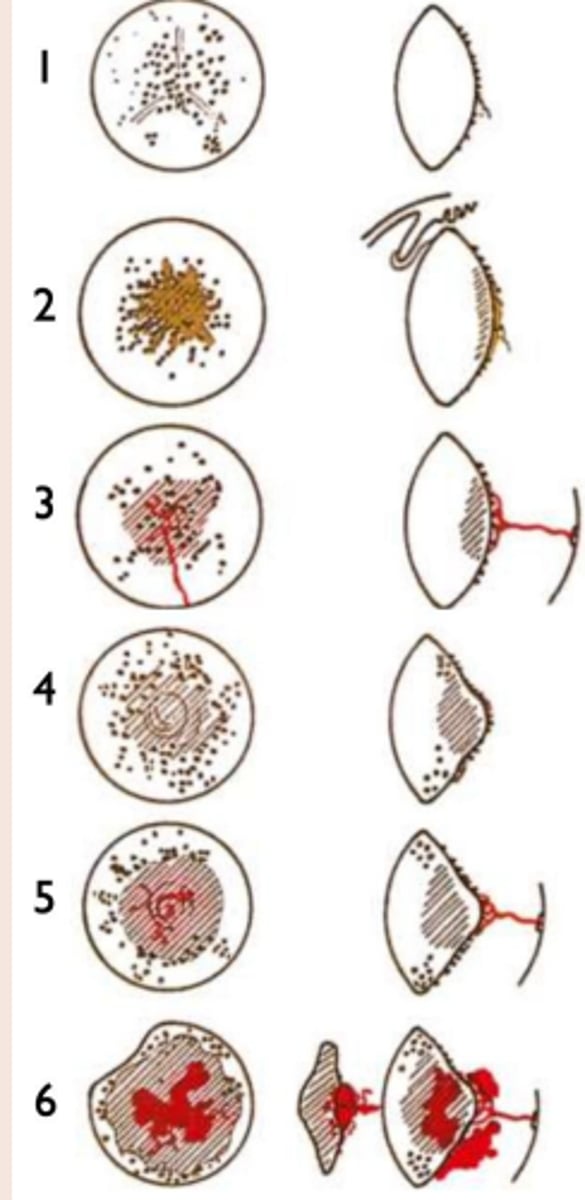
Asteroid Hyalosis?
aka floaters in vitreous
(Calcium/lipid complexes)
Vitreous Degeneration (Syneresis)?
Liquified, "sloshy" vitreous 🡪 predisposes to retinal detachment
other vitreous issues include ?
hemorrhage
inflammation
retina role?
Converts light into electrical signals for vision.
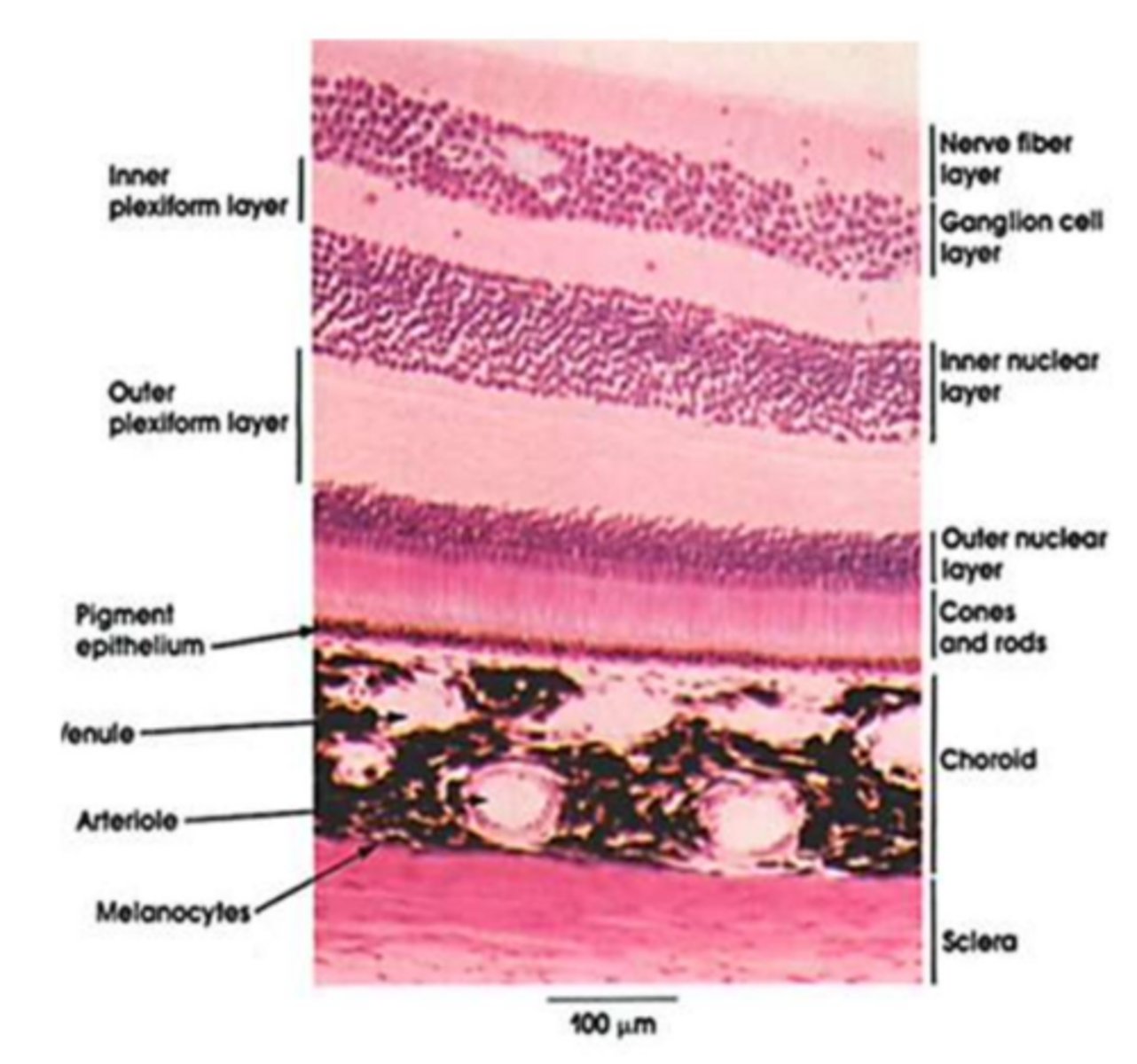
retina structure?
10 layers, including photoreceptors (rods & cones), ganglion cells, and retinal pigment epithelium (RPE).
choroid role?
Provides vascular supply to the retina
where is the tapetum?
choroid
retina layers (outside to in)?
Pigmented Epithelium
Photoreceptors (Rods/Cones)
External Limiting Membrane
Outer Nuclear Layer
Outer Plexiform Layer
Inner Nuclear Layer
Inner Plexiform Layer
Ganglion Cell Layer
Nerve Fiber Layer (optic nerve)
Internal Limiting Membrane
tapetum role?
Reflective to aid in dim light
Develops post-natally
Variable color between breed, coat color, species, etc.
Choriocapillaris?
Capillaries from choroid feeding posterior retina
Accumulation of ganglion cell axons leaving the eye within a fragile lamina cribrosa?
optic nerve
axonal flow goes from ? to ? for nutrients
CNS to eye
optic nerve & axon flow damaged during?
glaucoma
optic nerve shape in dog
triangle
optic nerve shape in cat
round
optic nerve shape in horse
ovoid
optic nerve shape in bird
cant see -- behind pecten
? effects the shape
myelination
puppy vs adult tapetum
blue vs yellow/green
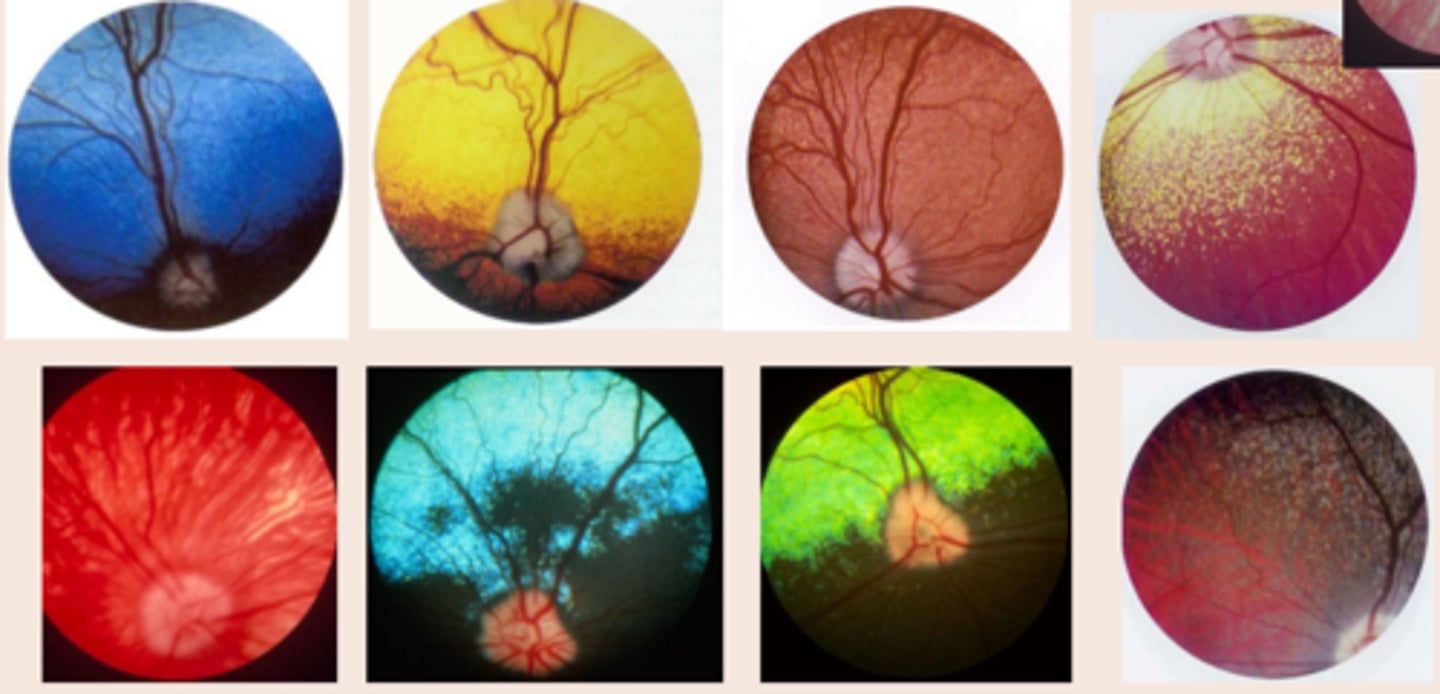
do all dogs have pigment in the RPE?
no
Holangiotic retina vascular pattern?
in who?
whole retina
dog, cat, sheep, pig, human
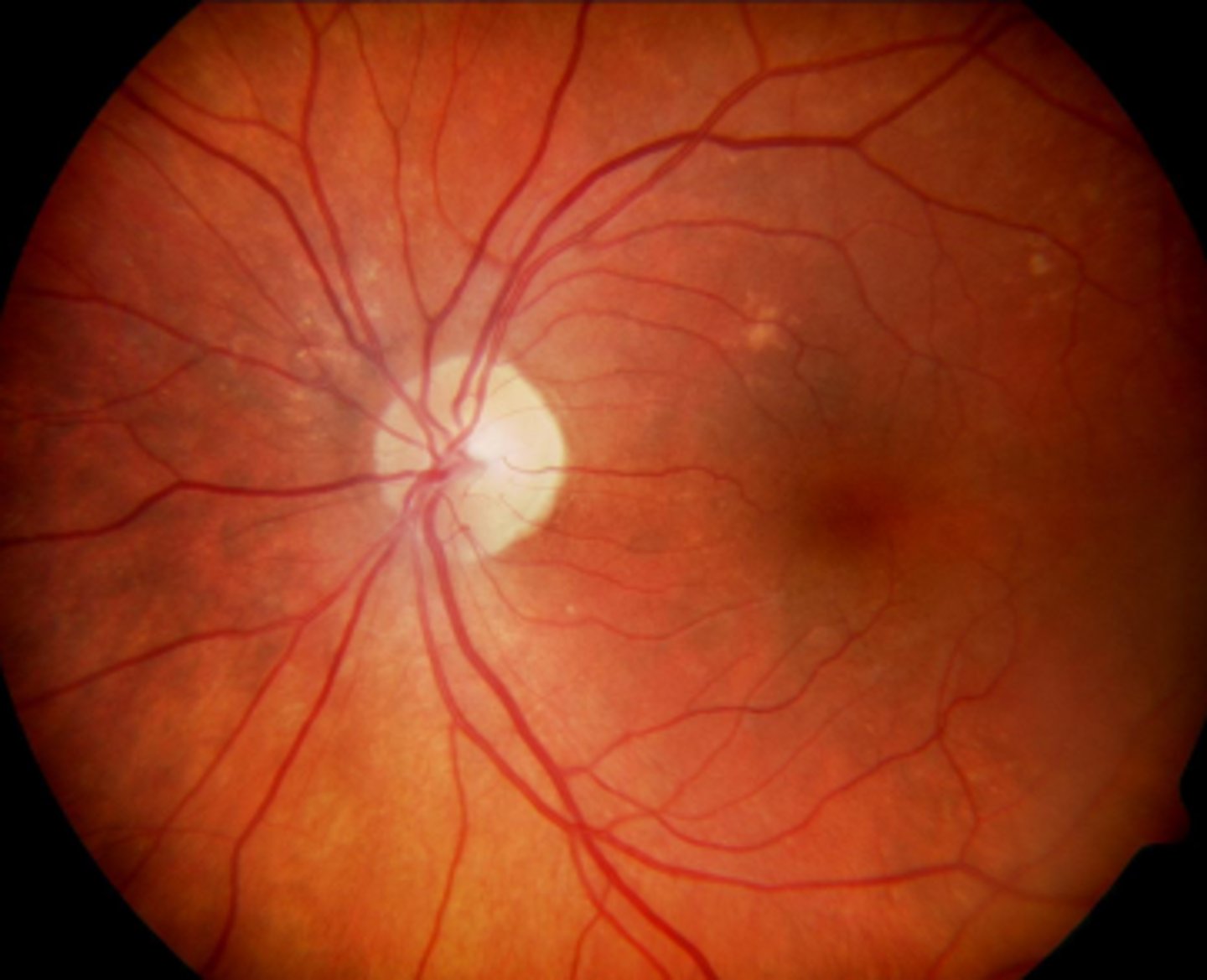
Paurangiotic retina vascular pattern?
in who?
only extend out a little bit
horses, guinea pigs, Elephants
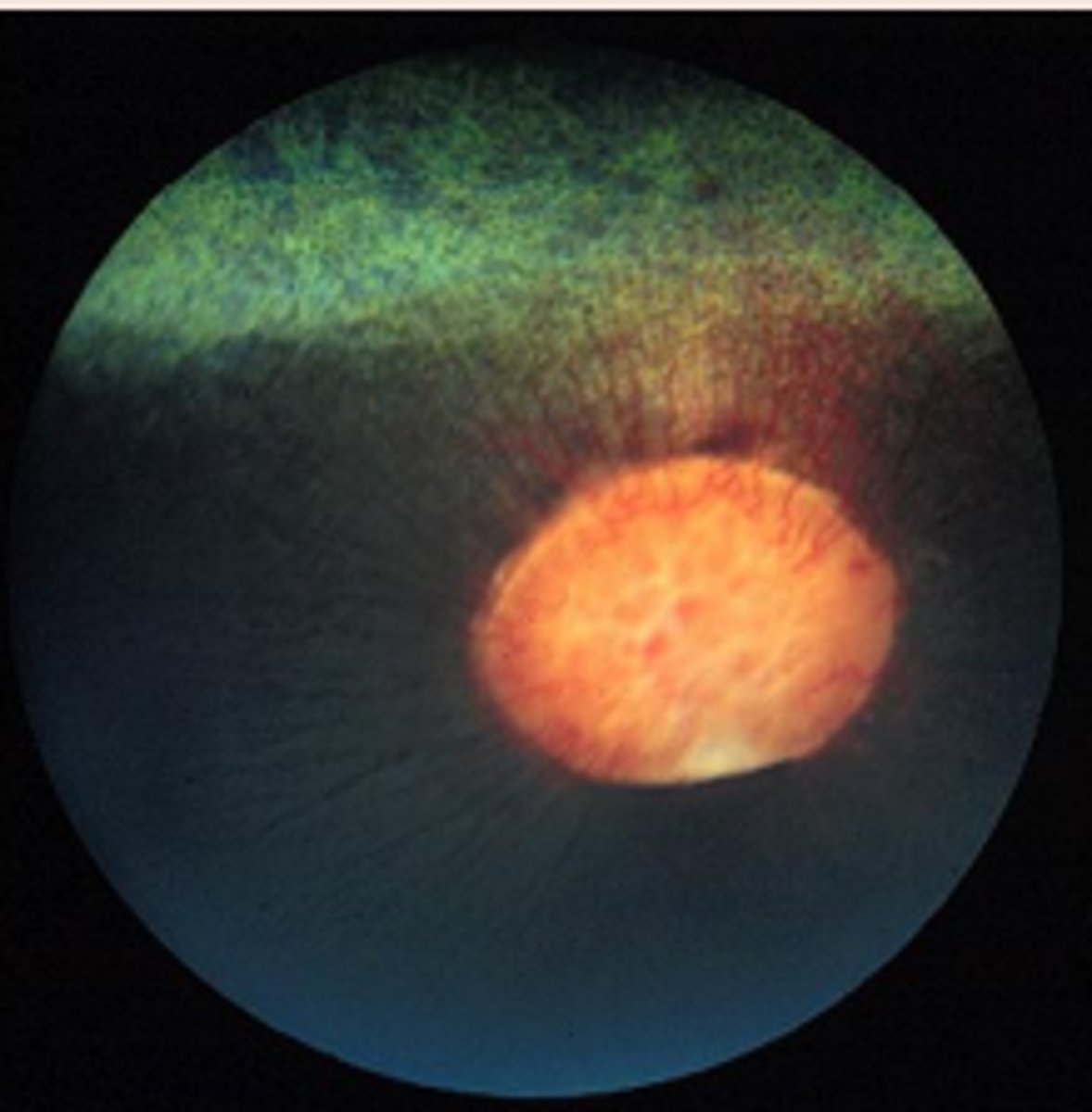
Merangiotic retina vascular pattern?
in who?
long meridian plains
rabbits
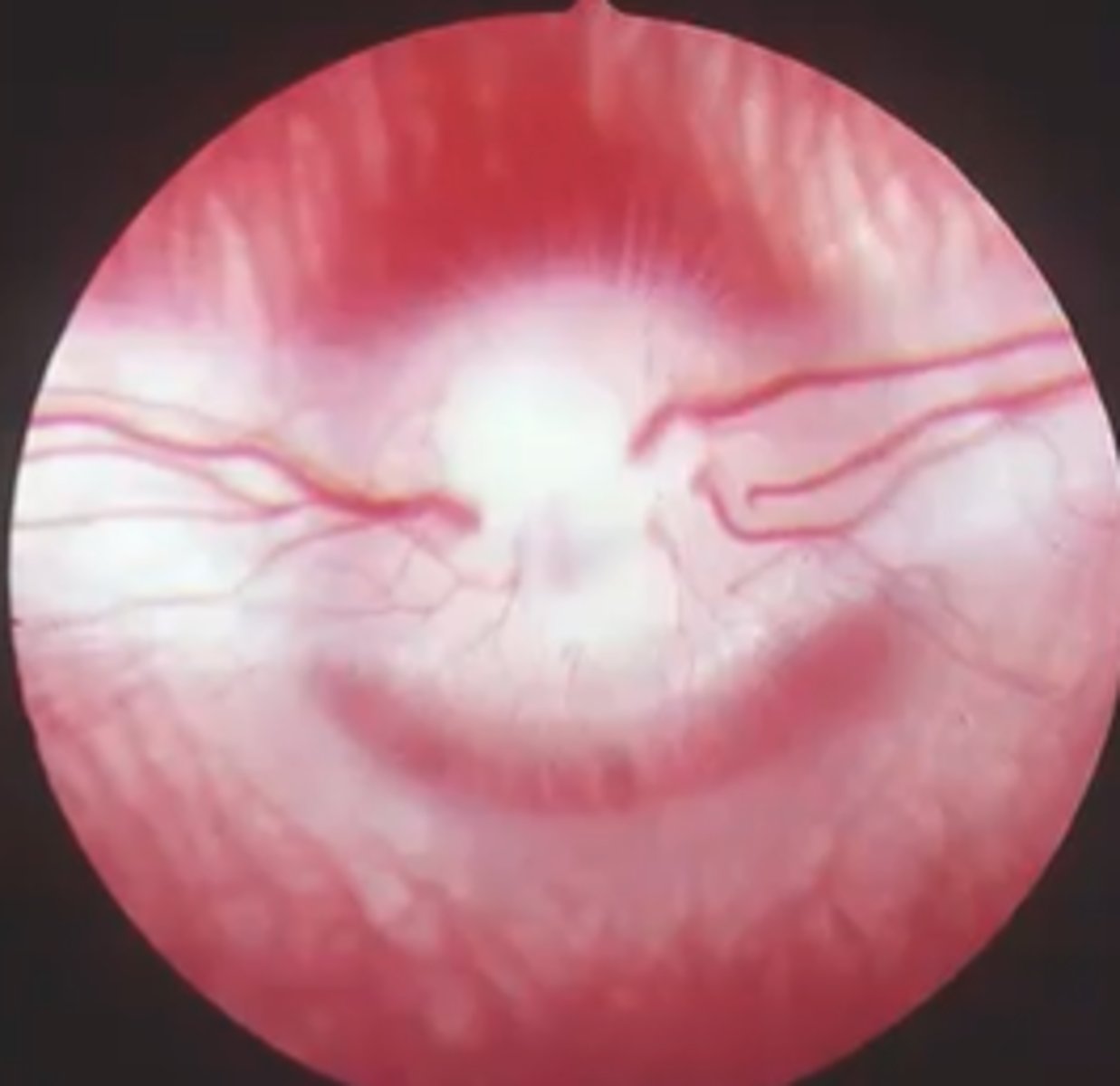
Anangiotic retina vascular pattern?
in who?
thinner retina (other than bat is thick)
birds, reptiles, bats
what does it mean when the tapetum is REALLY shiny from afar?
retinal thinning / atrophy

dull tapetum?
something in the way (retinal edema, other
causes of tapetum hemorrhage?
Hypertension, thrombocytopenia, coagulopathy, hyperviscosity, DIC, etc.
developmental Disorders of the Posterior Segment?
PHPV
Retinal Detachment
Retinal Dysplasia
Collie Eye Anomaly
Merle Ocular Dysgenesis
PHPV
Persistent Hyperplastic Primary Vitreous
Focal or generalized jumbling of retina in rosettes +/- folds, focal detachments?
retinal dysplasia
non-inherited forms of retinal dysplasia?
• Panleukopenia/FeLV in cats
• Adenovirus/Herpes in dogs
• BVD in cows
retinal dysplasia may be associated with?
oculoskeletal dysplasia in labs
what am i describing?
- Congenital, bilateral, asymmetric anomaly of choroid, optic nerve, sclera
- Choroidal hypoplasia, posterior pole colobomas, retinal detachment, tortuous vessels, hyphema, variable vision loss
Collie Eye Anomaly (CEA)
what percent of collies get Collie Eye Anomaly
85% !!!
what am i describing?
- failure of RPE development 🡪 failure of nearby retina, choroid, sclera to differentiate
- merling gene defect
- Homozygous = mostly white, multiple ocular defects
- Heterozygous = mild
Merle Ocular Dysgenesis
acquired posterior segment diseases include?
• Degeneration
• Inflammatory
• Detachment
• Neoplasia
• Generalized OMSD
what am i describing?
- Photoreceptor loss
- slow onset
inherited PRA (Progressive Retinal Atrophy)
inherited PRA (Progressive Retinal Atrophy) tx?
none
inherited PRA (Progressive Retinal Atrophy) in persians
recessive, early onset, rapid progression
inherited PRA (Progressive Retinal Atrophy) in abyssinians
early has rapid progression, can have gradual form
taurine deficiency causes ? due to ?
"Feline Central Retinal Degeneration"
+ heart disease
- Irreversible lesions, begin in area centralis 🡪 progress to entire retina if deficiency not corrected
home made diets
Enrofloxacin (Fluoroquinolone Associated Retinal Toxicity) causes what?
acute irreversible toxicity
destroys retina / blind
If must use enrofloxacin, only
5mg/kg/day
SARDs?
sudden acquired retinal degeneration
sards symptoms and signalment?
Acutely blind
Middle-aged +/- fat, female, Cushings common
NORMAL Fundus exam for quite some time
FLAT ERG
dark spots (hypo-reflective) in the eye may indicate
active inflammatory signs
Sharp borders + Hyperreflectivity =
inactive inflammation
acquired inflammatory dogs?
Distemper, Rikettsia, Fungi
acquired inflammatory cats?
FIV, FeLV, FIP, Toxo, Fungis (Crypto, Histo)
Uveodermatologic Syndrome?
• Attach on melanocytes
• Skin, uveal issues
• Great risk for secondary glaucoma
Uveodermatologic Syndrome tx?
steroids
Expect some damage to vision/blindness even if not detectable (focal)
underlying problem
causes of retinal detachment?
Hypertension, Exudative, Serous, Neoplasia, Congenital, Vitreous Traction
Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment?
hole/tear in retina
retinal detachment tx?
promptness critical!! -- Retina needs choroid for oxygen, degeneration can be fast (1mo)
1. Medical – treat underlying condition
2. Surgical (a must of there is a tear) – Retinopexy vs. intravitreal surgery
optic nerve coloboma?
portion of the optic nerve or surrounding structures (such as the retina or choroid) is missing or underdeveloped
optic nerve Micropapilla
vision
underdeveloped or abnormally small optic disc (the point where the optic nerve enters the eye)
optic nerve Hypoplasia/Aplasia
no vision
optic nerve Papilledema
vision
swelling of the optic nerve head (optic disc) due to increased intracranial pressure
Optic Neuritis
(no vision) - guarded prognosis (50%)
- Acute blindness, mydriasis, absent PLRs, swollen/red ON (may not see if retrobulbar portion of ON...