Bootcamp.com - Reproduction
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
all non-animals reproduce via _____
asexual reproduction
asexual reproduction means all offspring are _____ to the parent
genetically identical
what are some common examples of asexual reproduction?
binary fission; budding; regeneration; parthenogenesis
list the steps of binary fission:
DNA replication --> DNA migration to opposite cell poles --> septum formation --> septum splitting
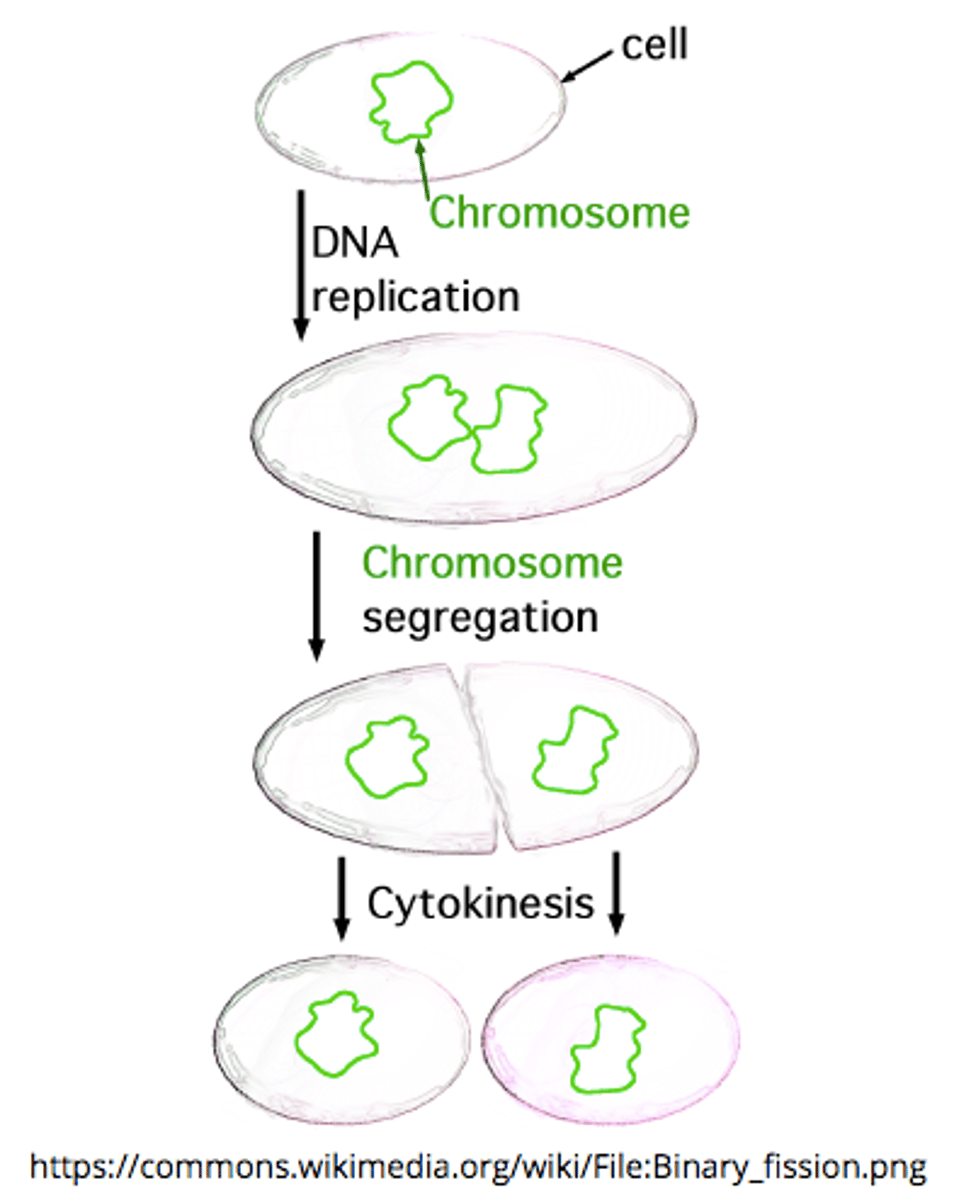
the _____ creates a dividing wall during binary fission
septum
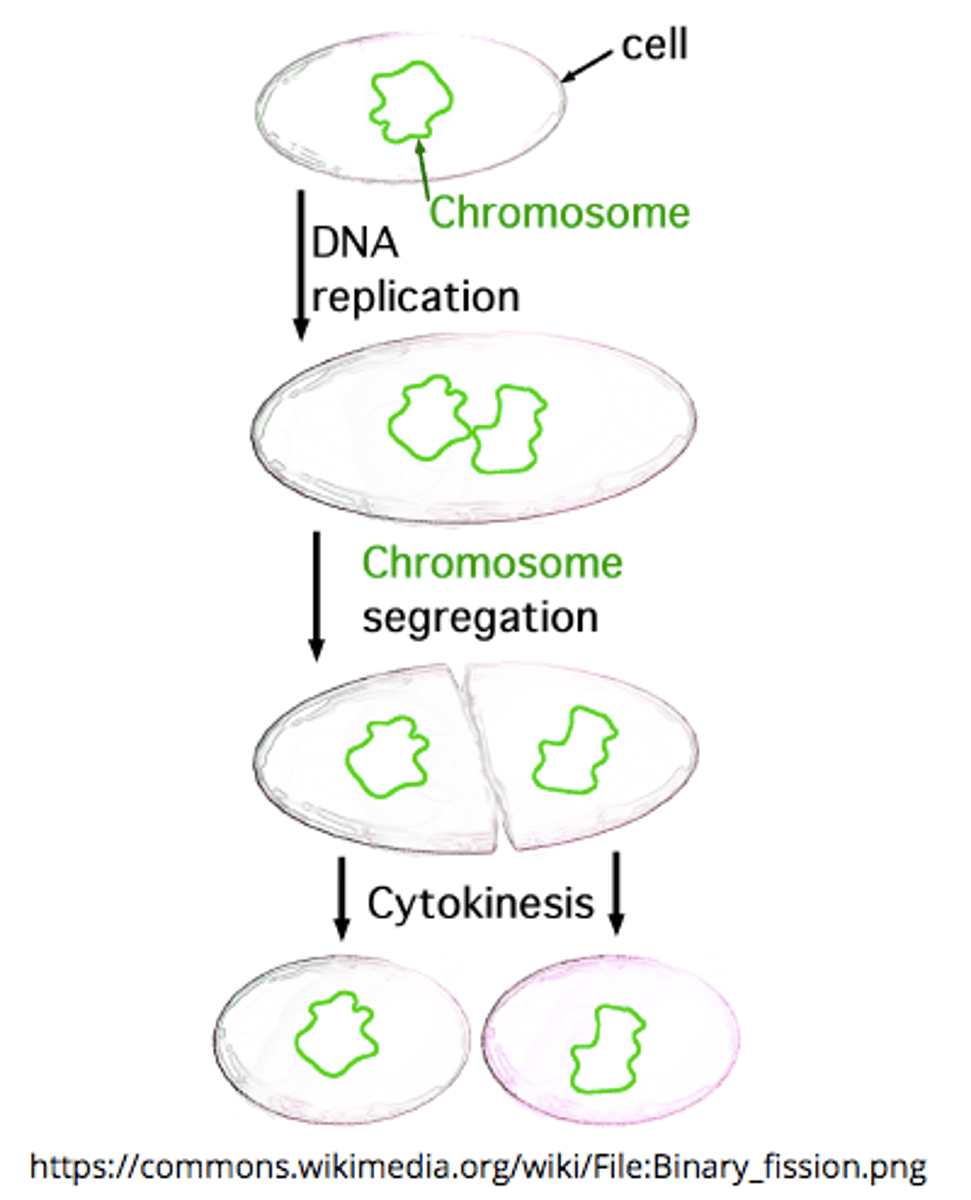
where does binary fission occur?
in prokaryotes and some organelles within eukaryotes (mitochondria and chloroplasts)
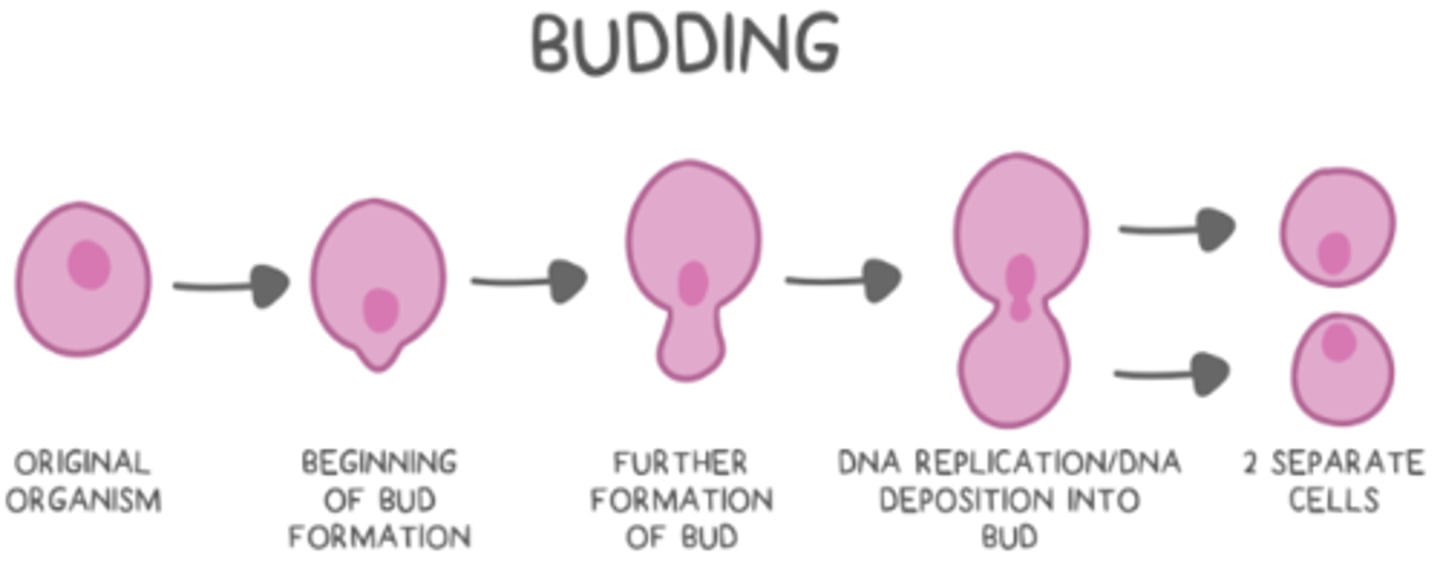
list the steps of budding:
outgrowth on original organism --> DNA replication --> replicated DNA deposition into the bud --> bud/organism separation
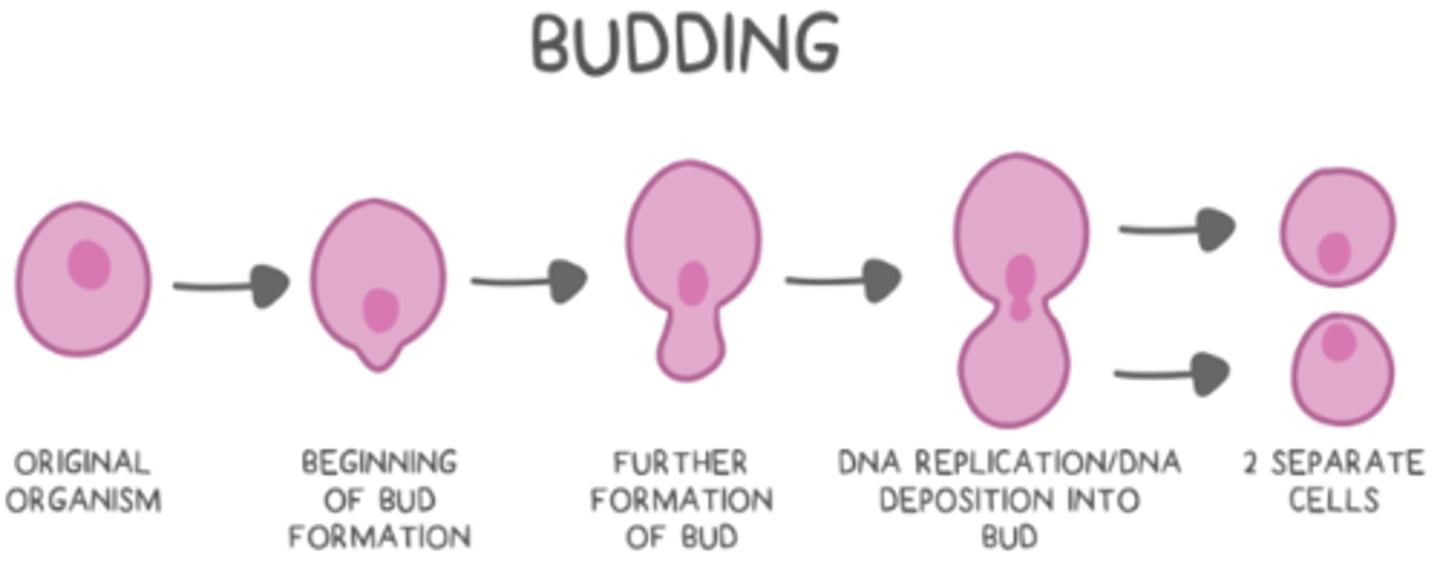
what is an example of a eukaryotic organism that uses budding?
yeast (fungus)
what is the result of regeneration (fragmentation)?
a part of an organism breaks off to create two new organisms that are half old and half new
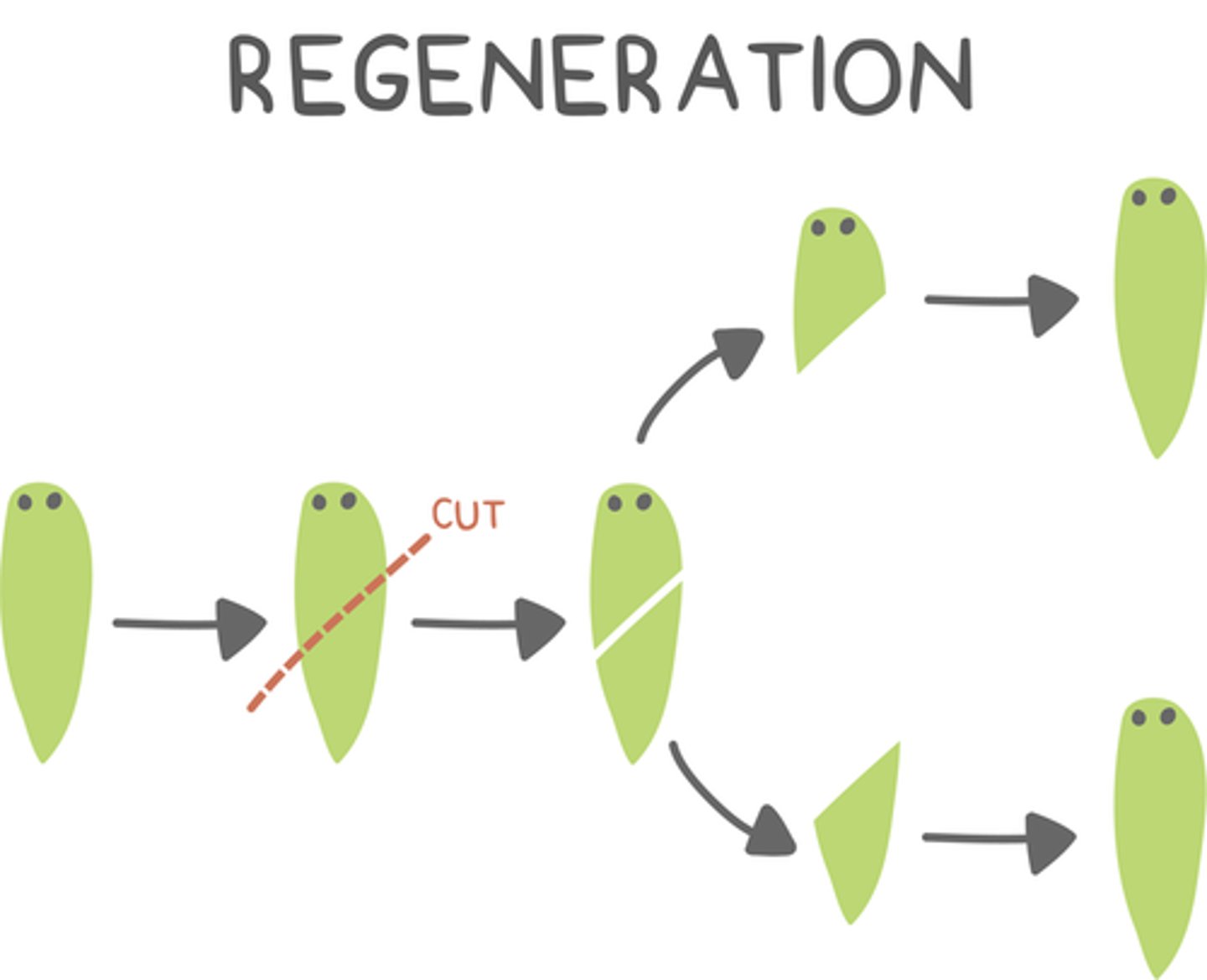
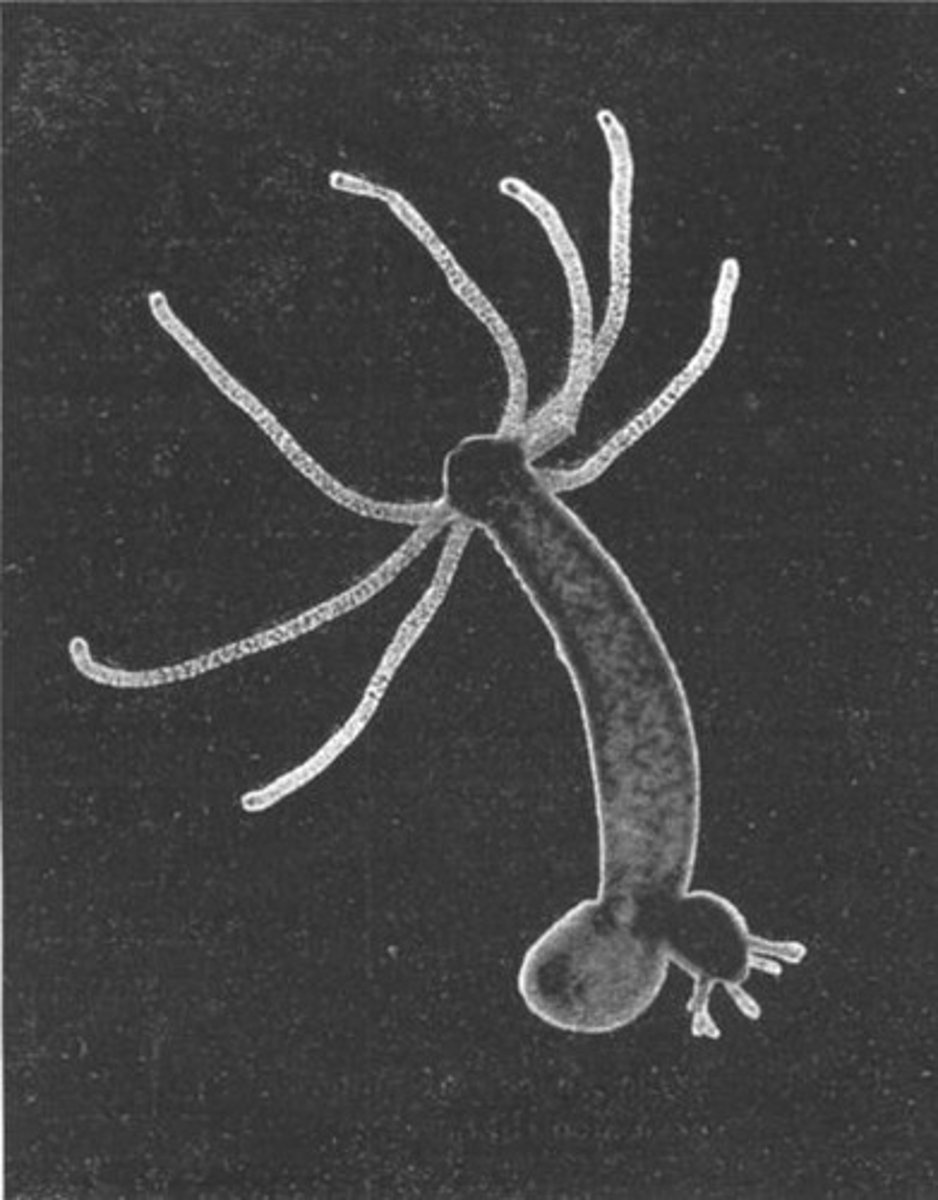
what are some examples of organisms that use regeneration (fragmentation)?
hydra and planaria flatworms
_____ occurs when an unfertilized egg develops into a viable organism
parthenogenesis
what is an example of a haplodiploid organism?
bees
_____ means that sex determination is based on whether the organism is haploid or diploid at that time
haplodiploid
bee offspring that arise from unfertilized eggs (parthenogenesis) are _____ (haploid/diploid) male drones
haploid
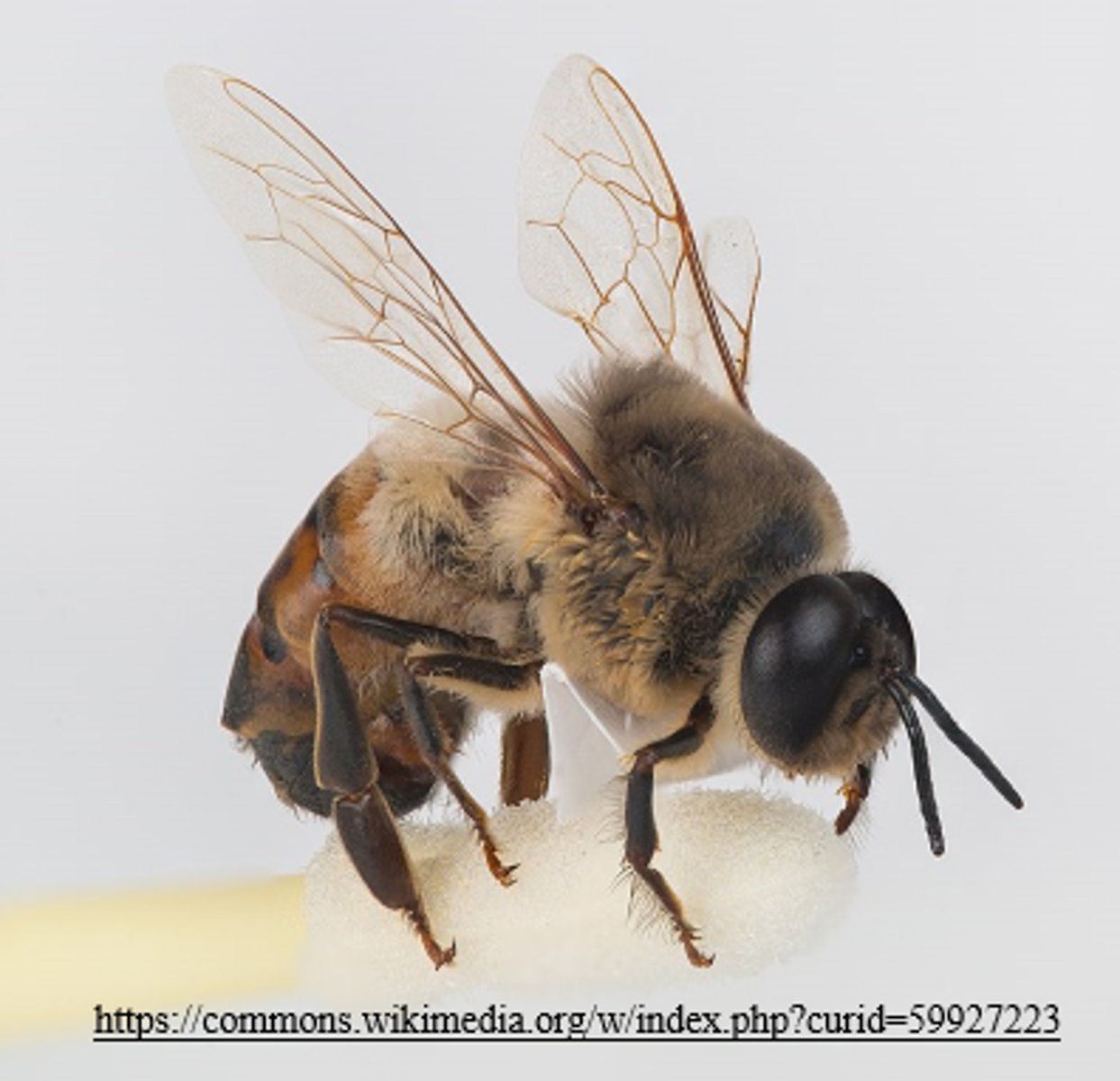

bee offspring that arise from fertilized eggs (sexual) are _____ (haploid/diploid) females
diploid
humans engage in sexual reproduction, meaning offspring are created when two _____ join
haploid gametes
_____ produce gametes
germ cells
germ cells produce gametes via ______
meiosis
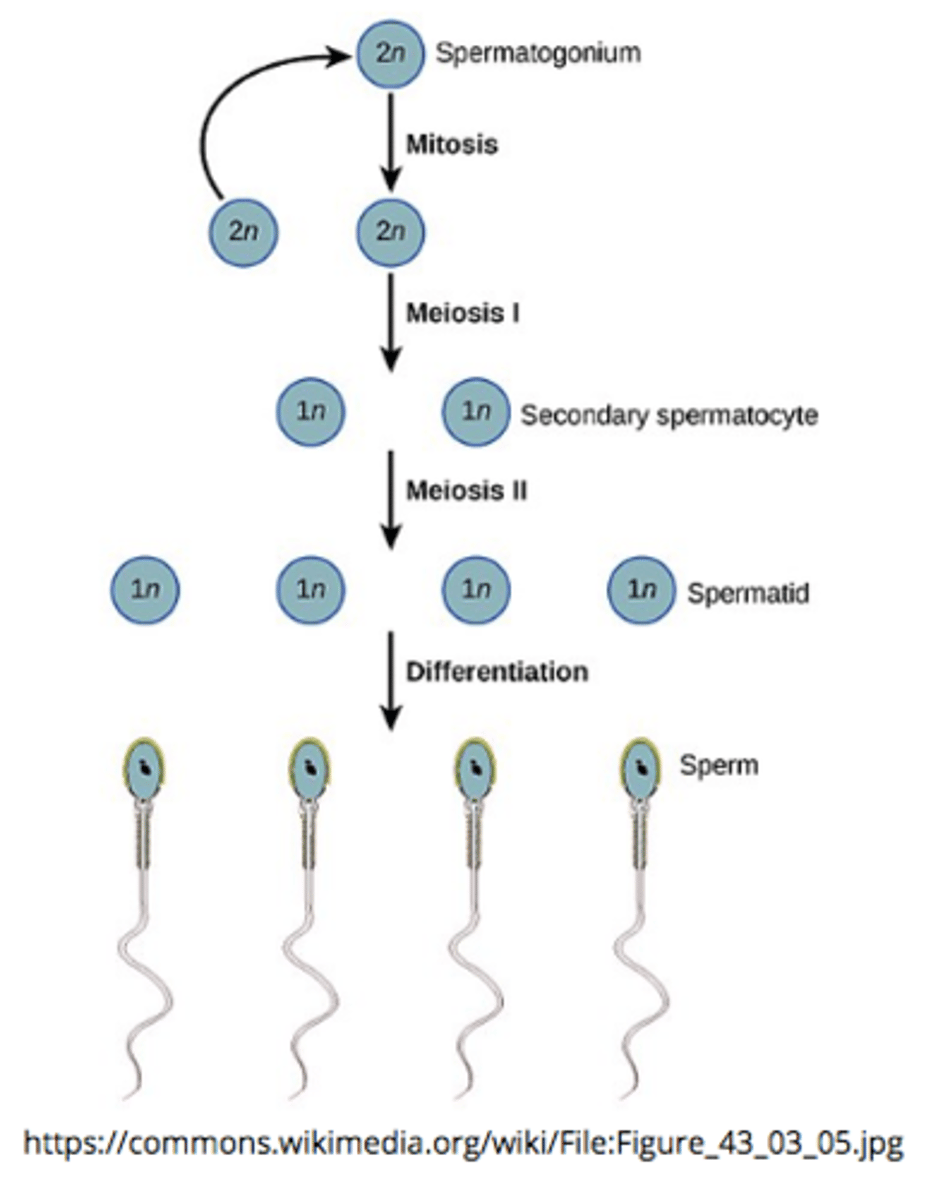
_____ are male germ cells
spermatogonia
_____ are female germ cells
oogonia
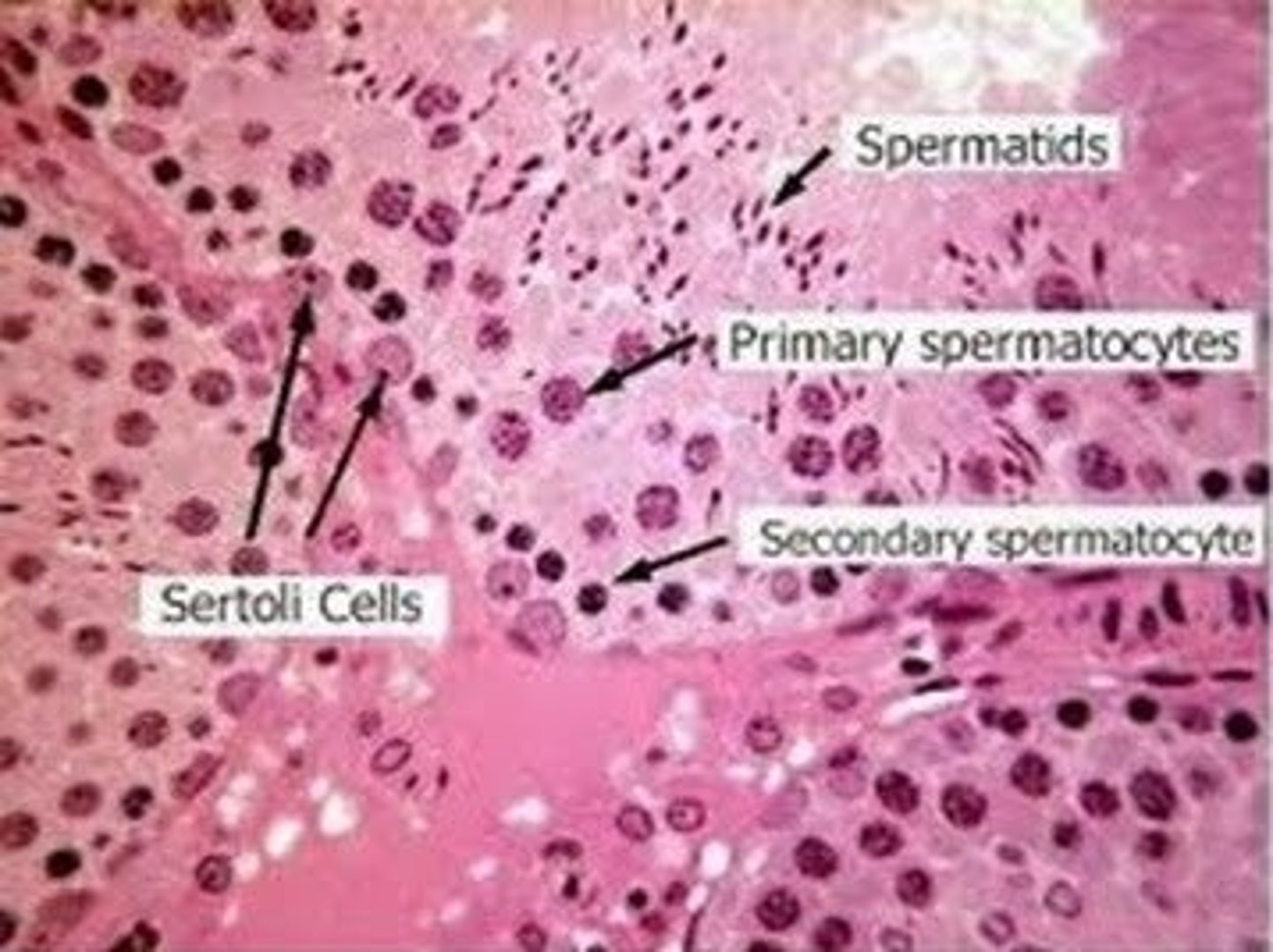
spermatogonium are replicated by _____ in the _____ of the testicle
mitosis; seminiferous tubules
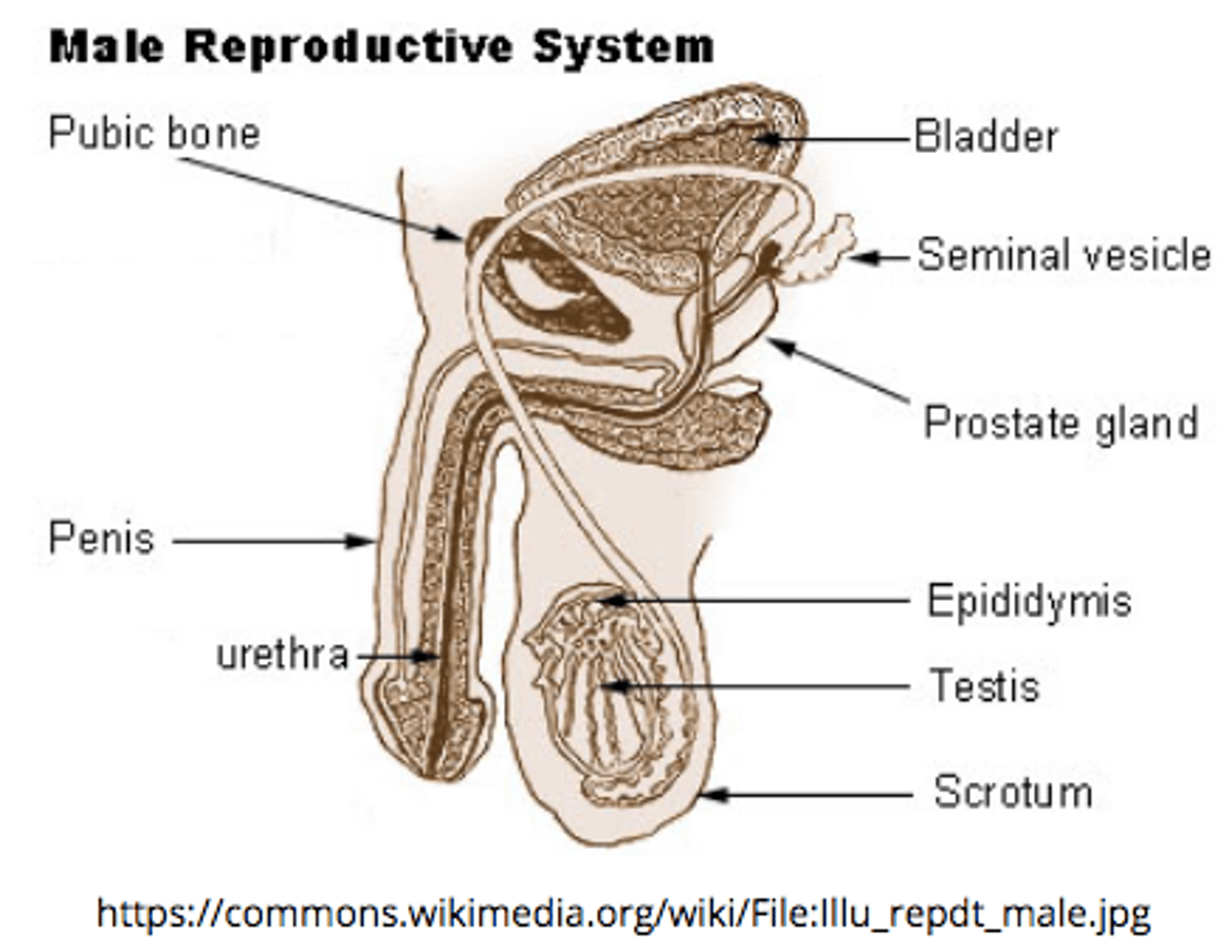
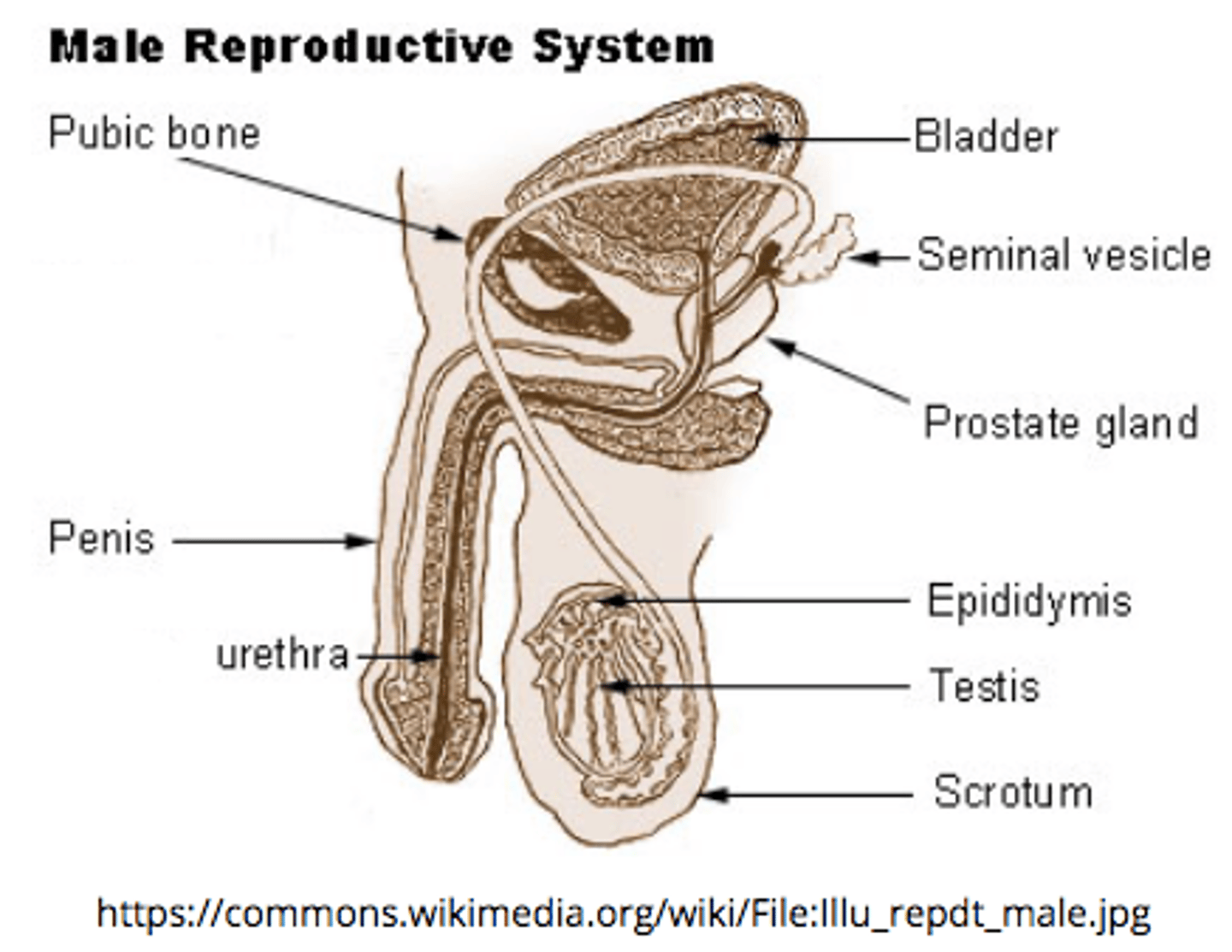
spermatogonium are the primordial (earliest) _____ cells
sperm
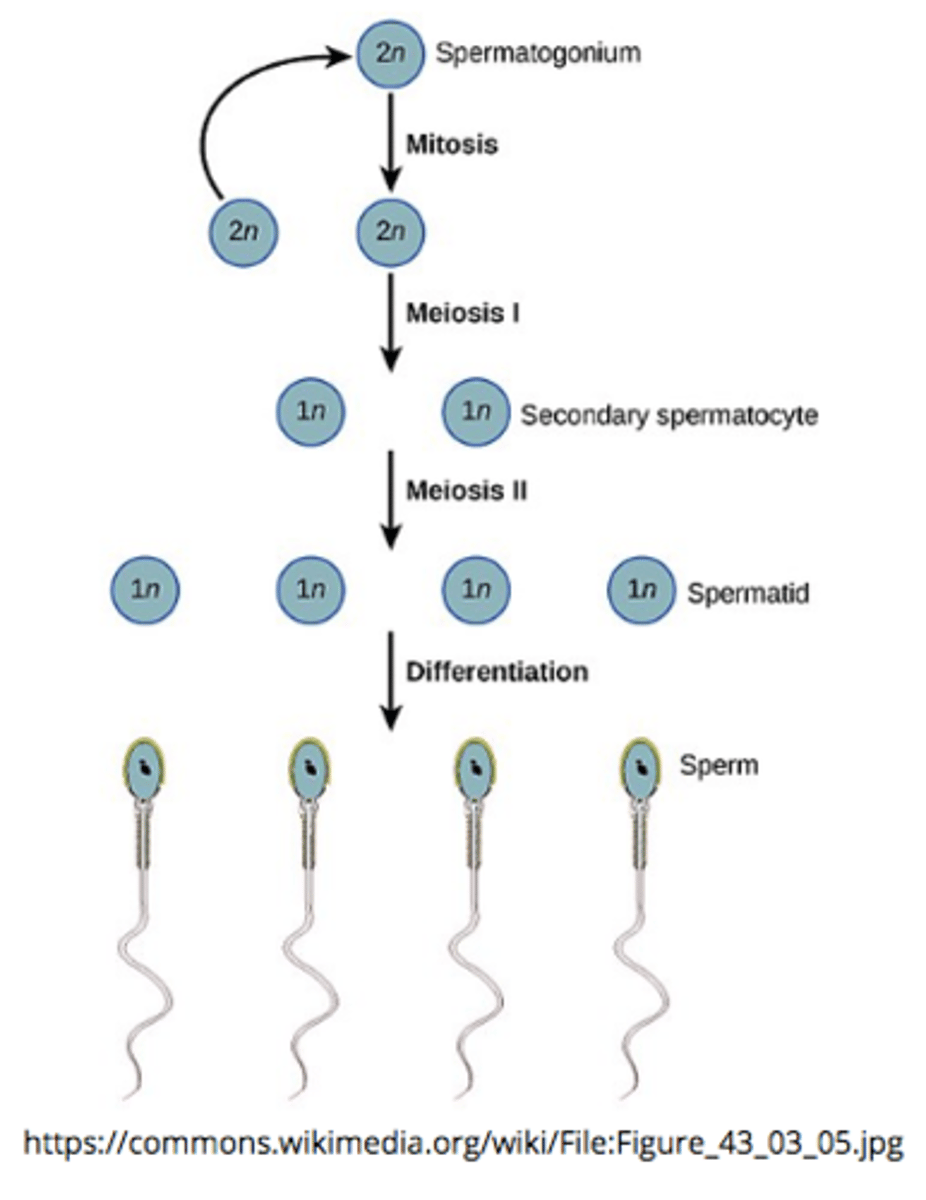
sperm production, known as _____, occurs in the _____ of the testes
spermatogenesis; seminiferous tubules
spermatogenesis is the process of converting 1 diploid spermatocyte into ____ haploid spermatids that differentiate into sperm via 2 _____ divisions
4; meiotic
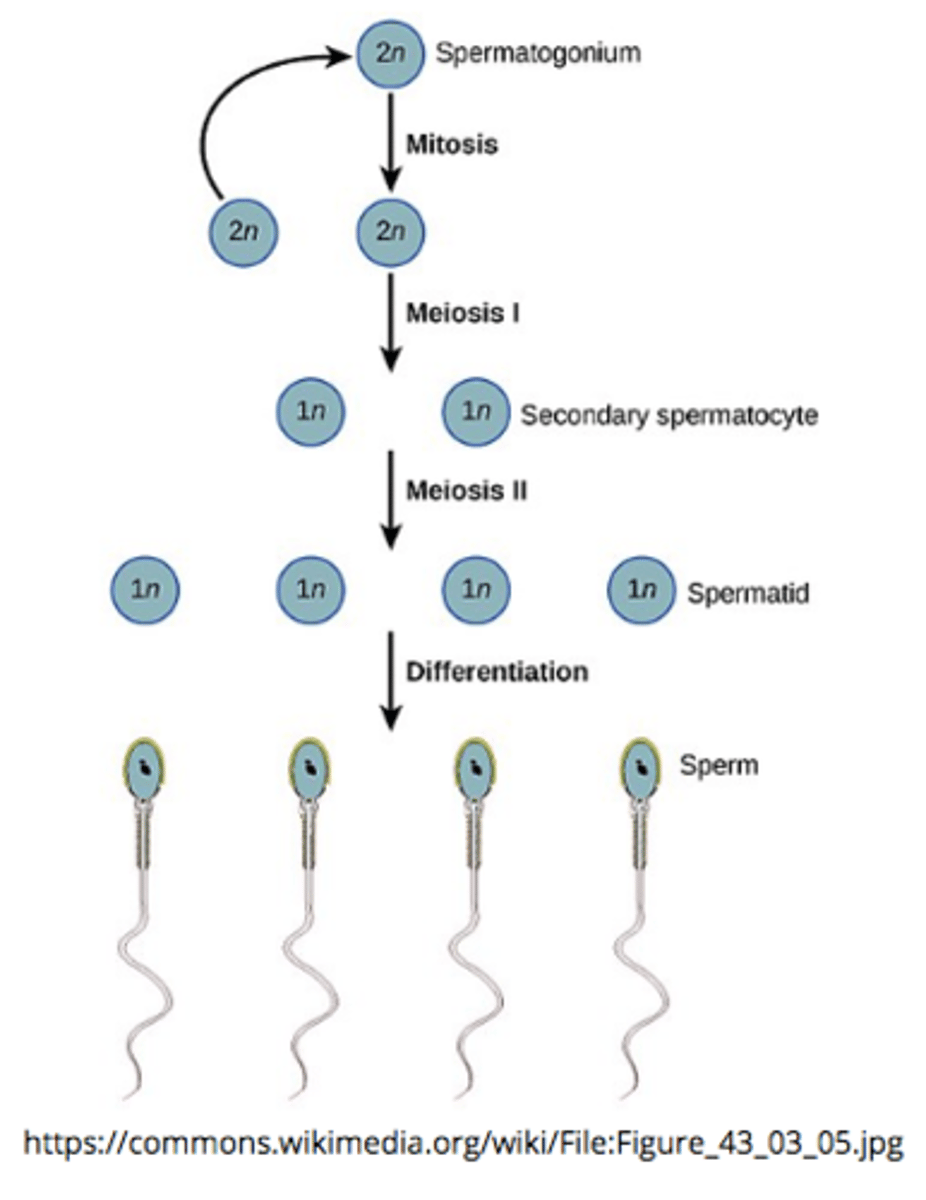
_____ is the final stage of spermatogenesis when immature haploid spermatids differentiate into mature, motile spermatozoa
spermiogenesis
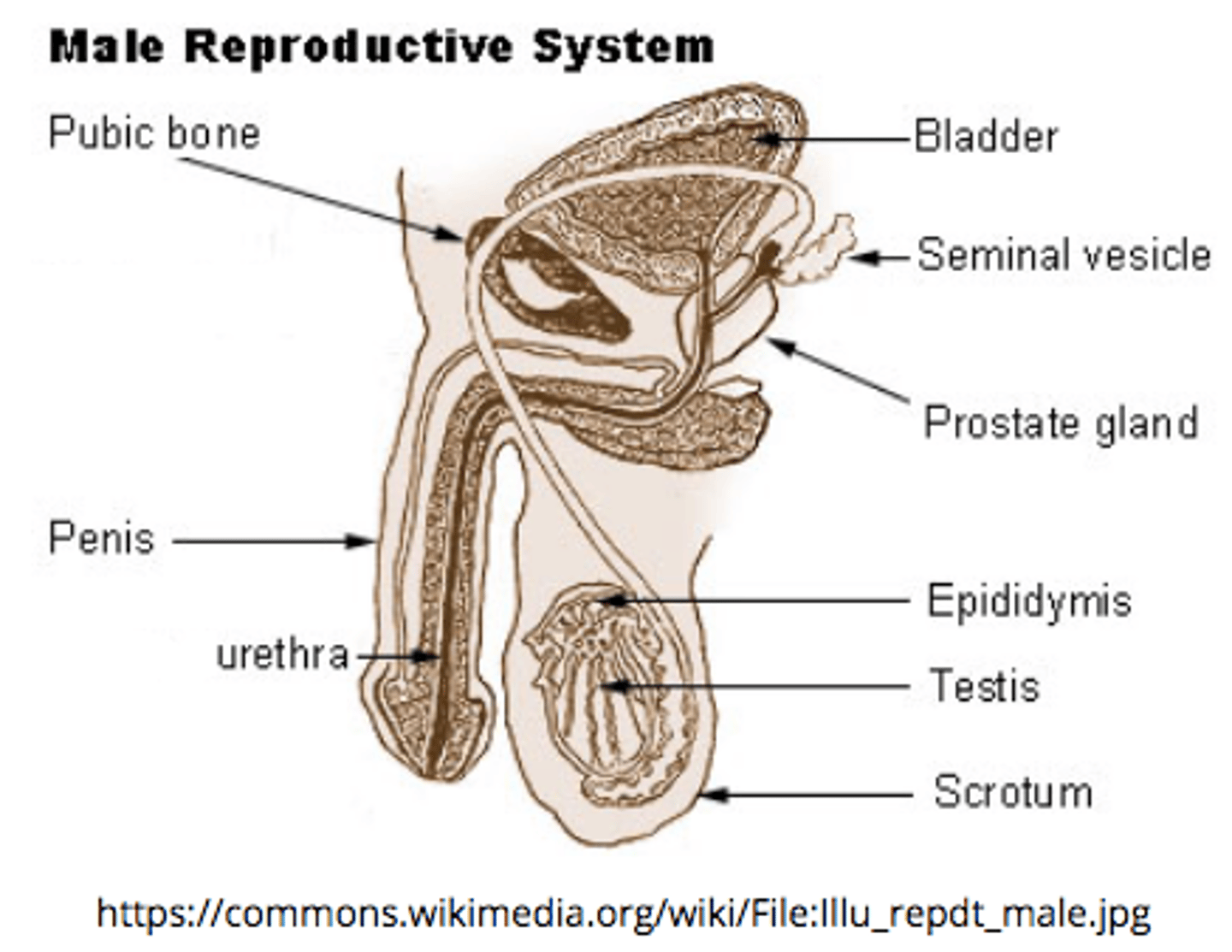
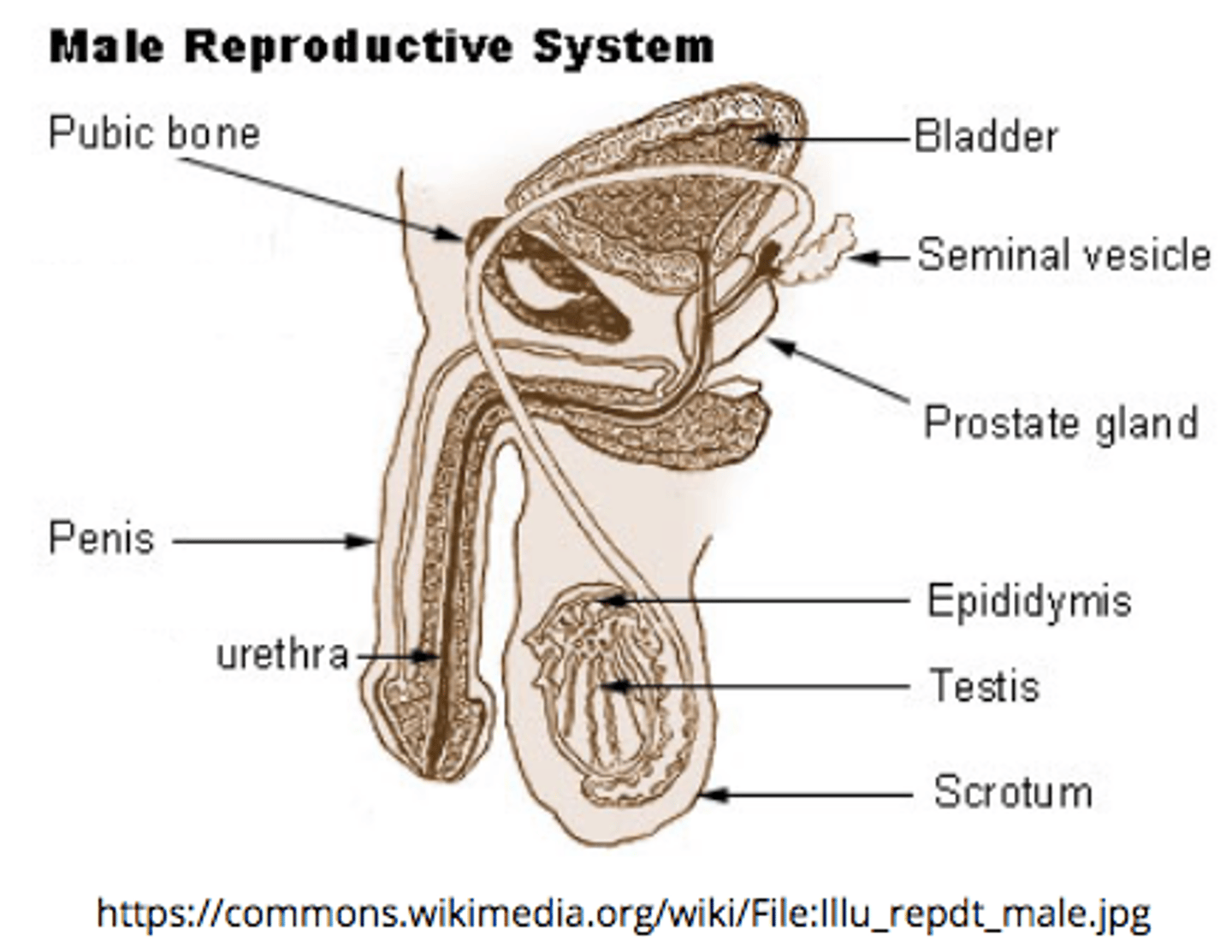
_____ are the male reproductive gland
testes
spermatogenesis ends with _____ (cell type)
spermatozoa (sperm)
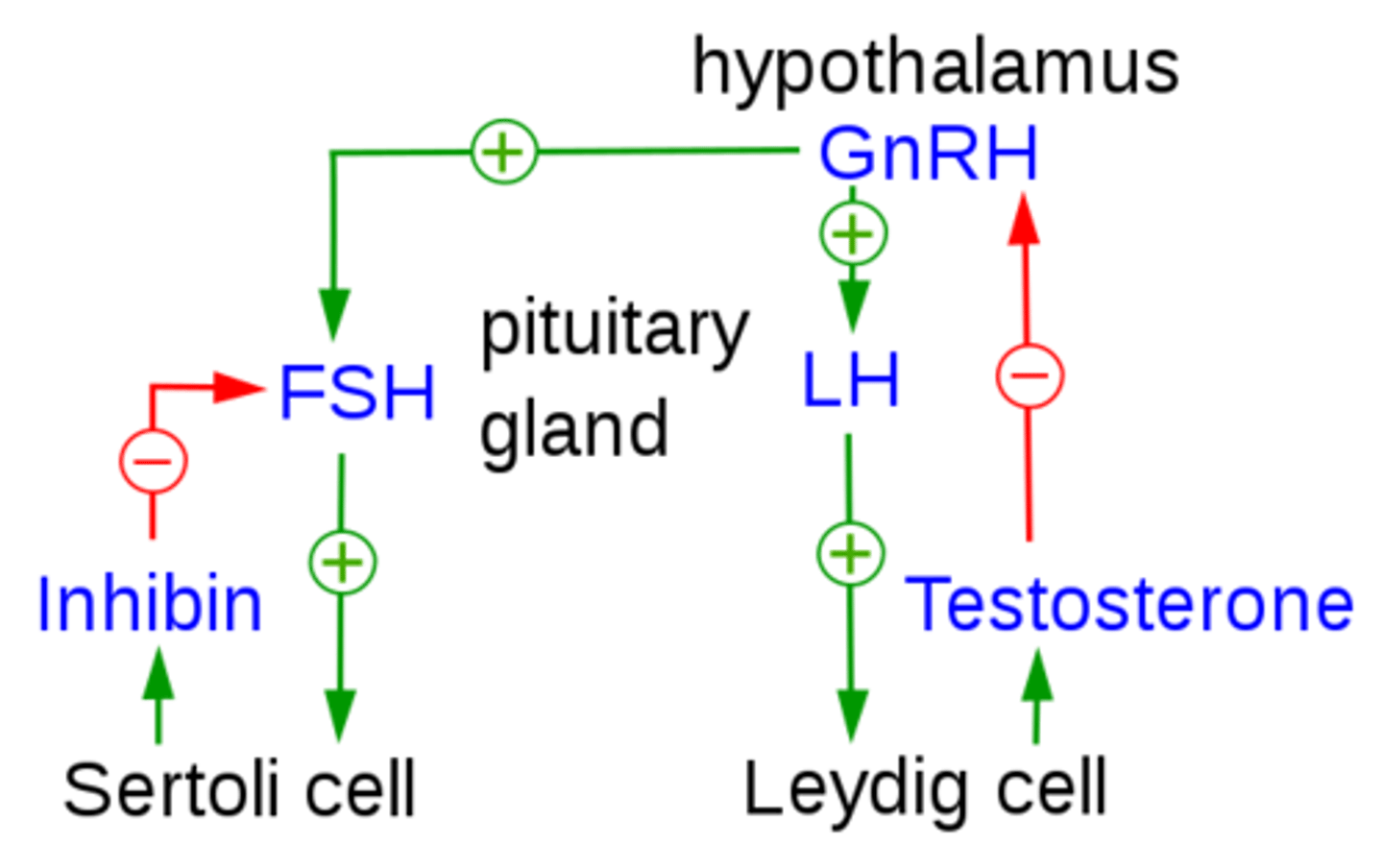
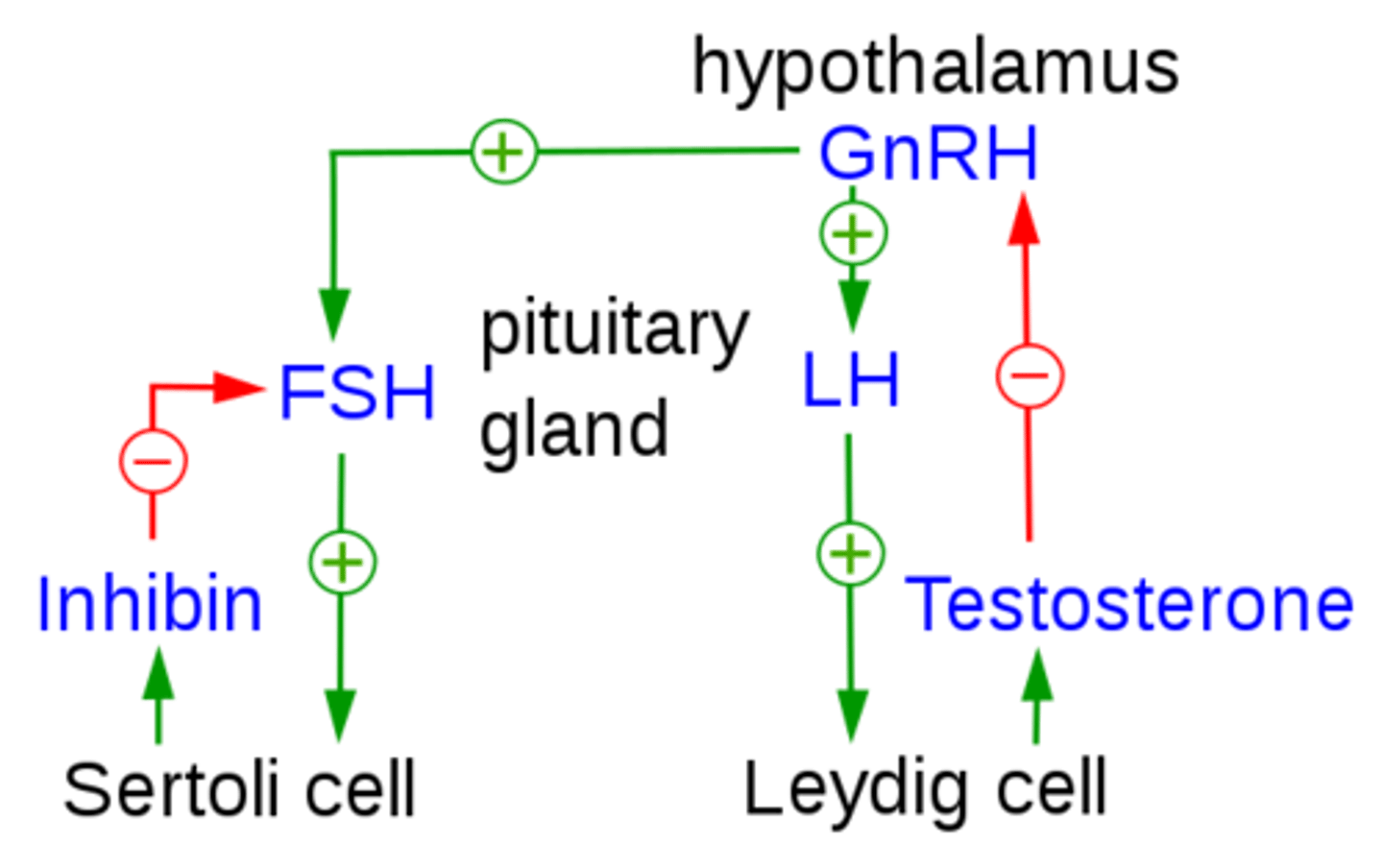
what is function of inhibin (from Sertoli cells), and how does it perform its function?
inhibits the further release of FSH (peptide hormone) by acting on the anterior pituitary
_____ surround and nourish sperm cells that are developing through spermatogenesis in the seminiferous tubules
Sertoli cells
what are the three main parts of a sperm cell?
head; midpiece; tail
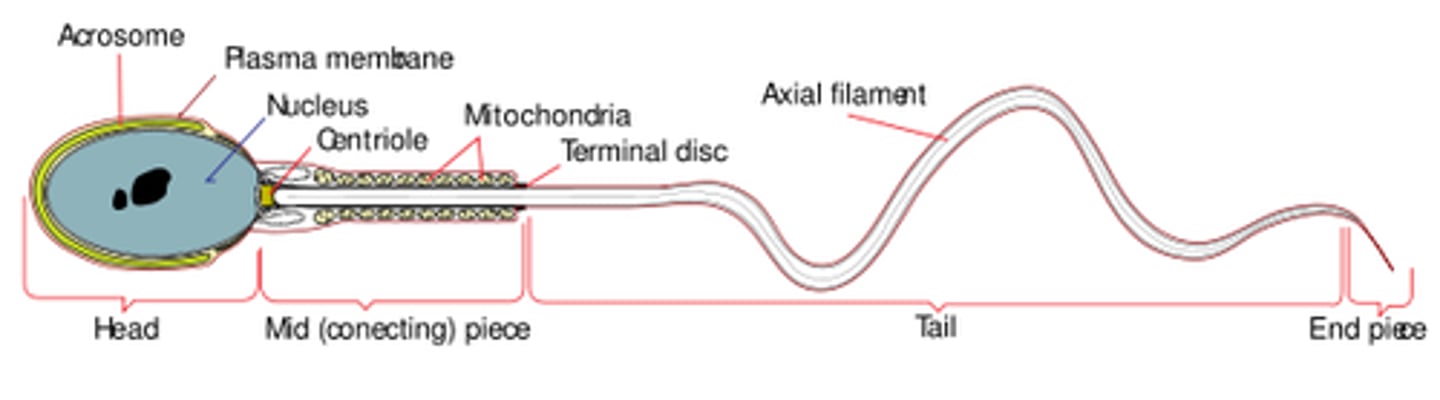
which portion of the sperm contains the nucleus?
head
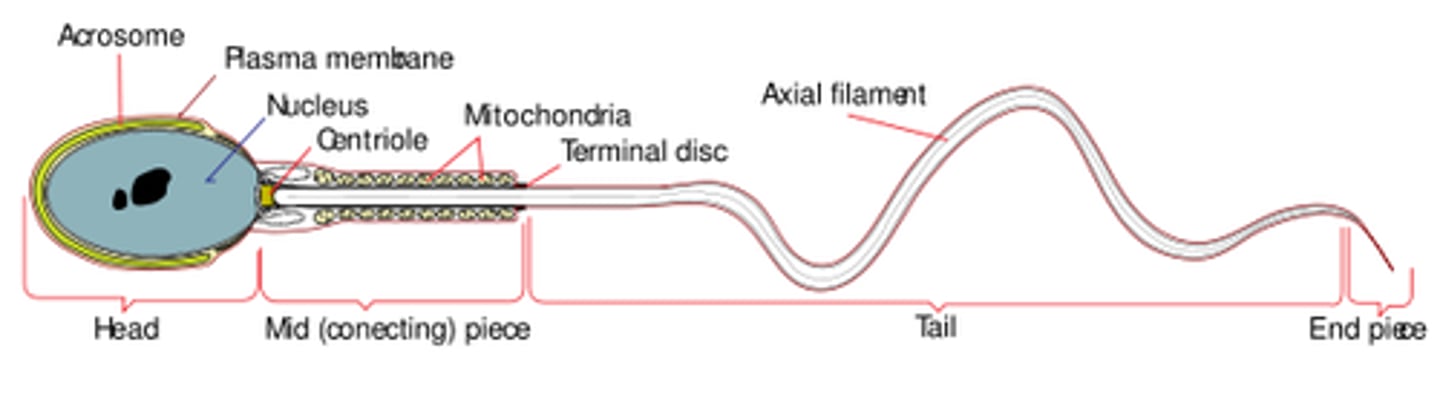
the _____ of sperm cell contains many mitochondria
midpiece
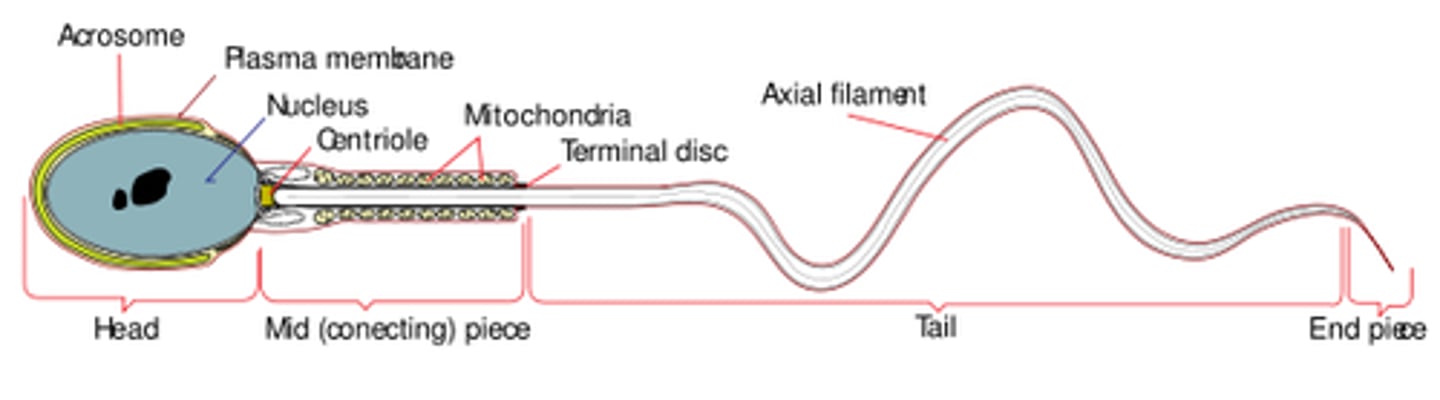
what is the function of the mitochondria in the sperm midpiece?
produce ATP to power flagellar motion in the sperm tail
the tail of a sperm cell is a _____, which moves in a whip-like motion in order to_____
flagellum; propel the sperm forward/provide mobility
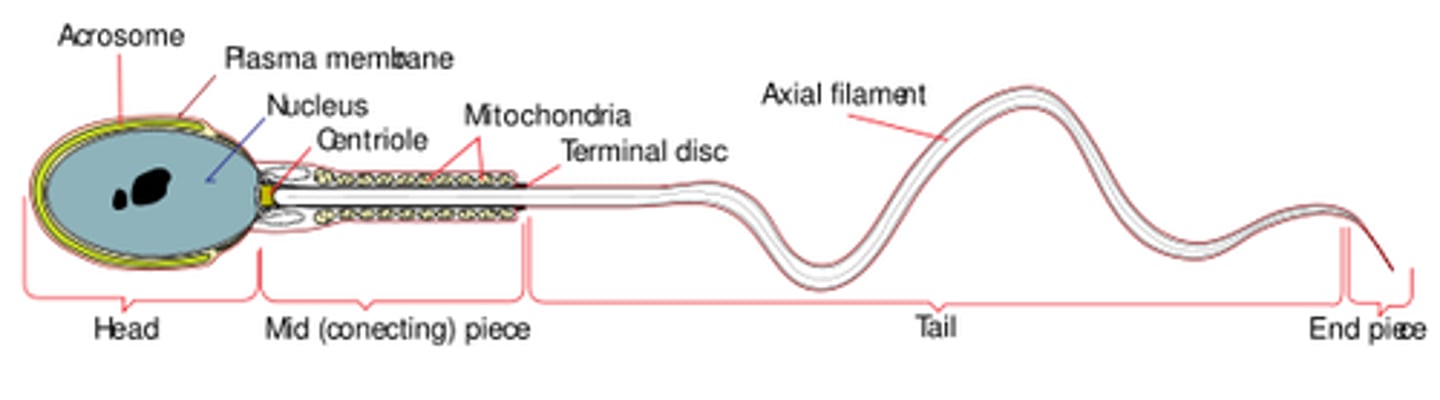
which protein building block makes up sperm cell's flagella?
microtubules
which hormone activates Sertoli cells?
FSH
do the sperm fully mature in the seminiferous tubules?
no; they mature in the epididymis
describe the structure and location of the epididymis:
a duct that sits around the testes
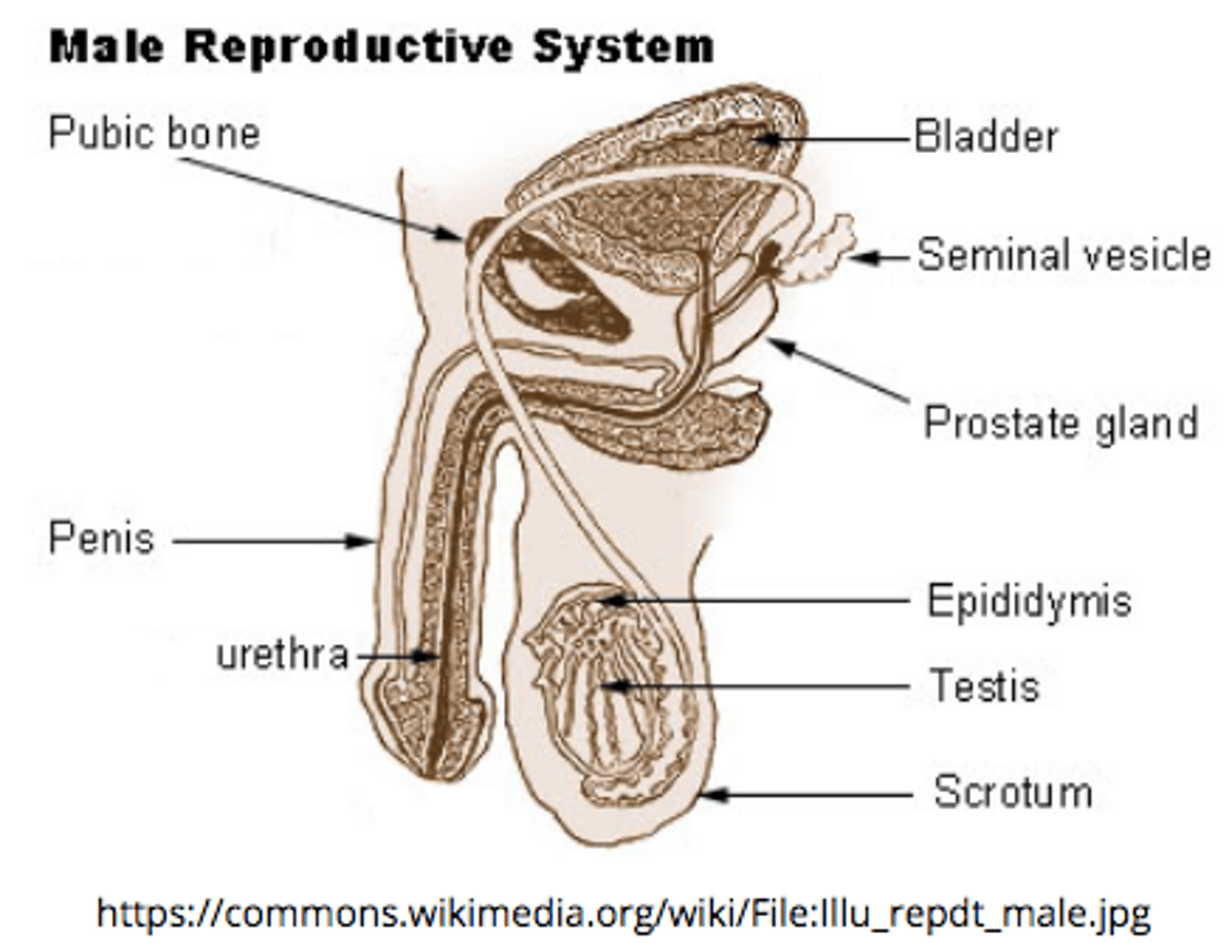
the _____ is the site of sperm storage before ejaculation (where sperm mature)
epididymis
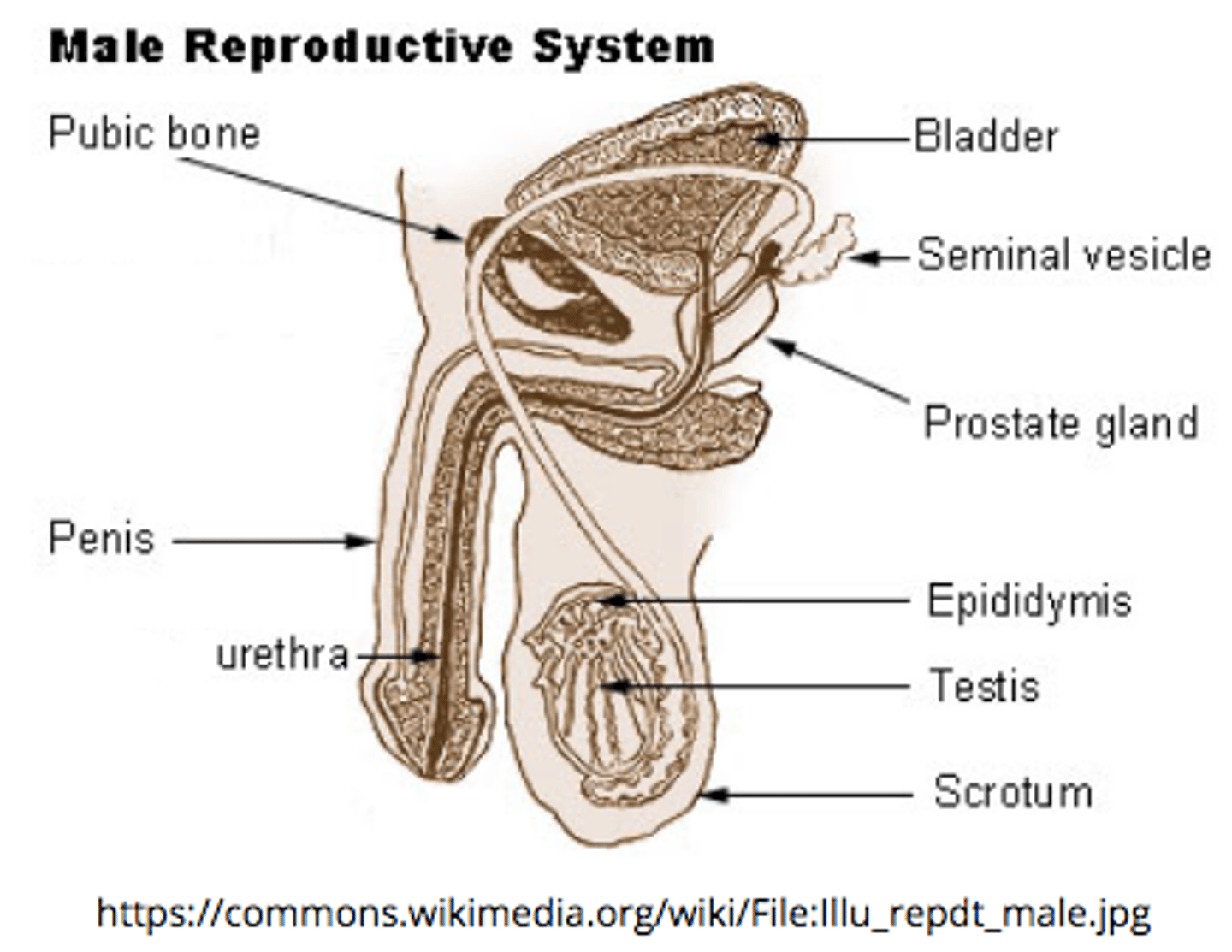
the _____ is a group of tubules that move sperm from the epididymis to ejaculatory ducts
vas deferens
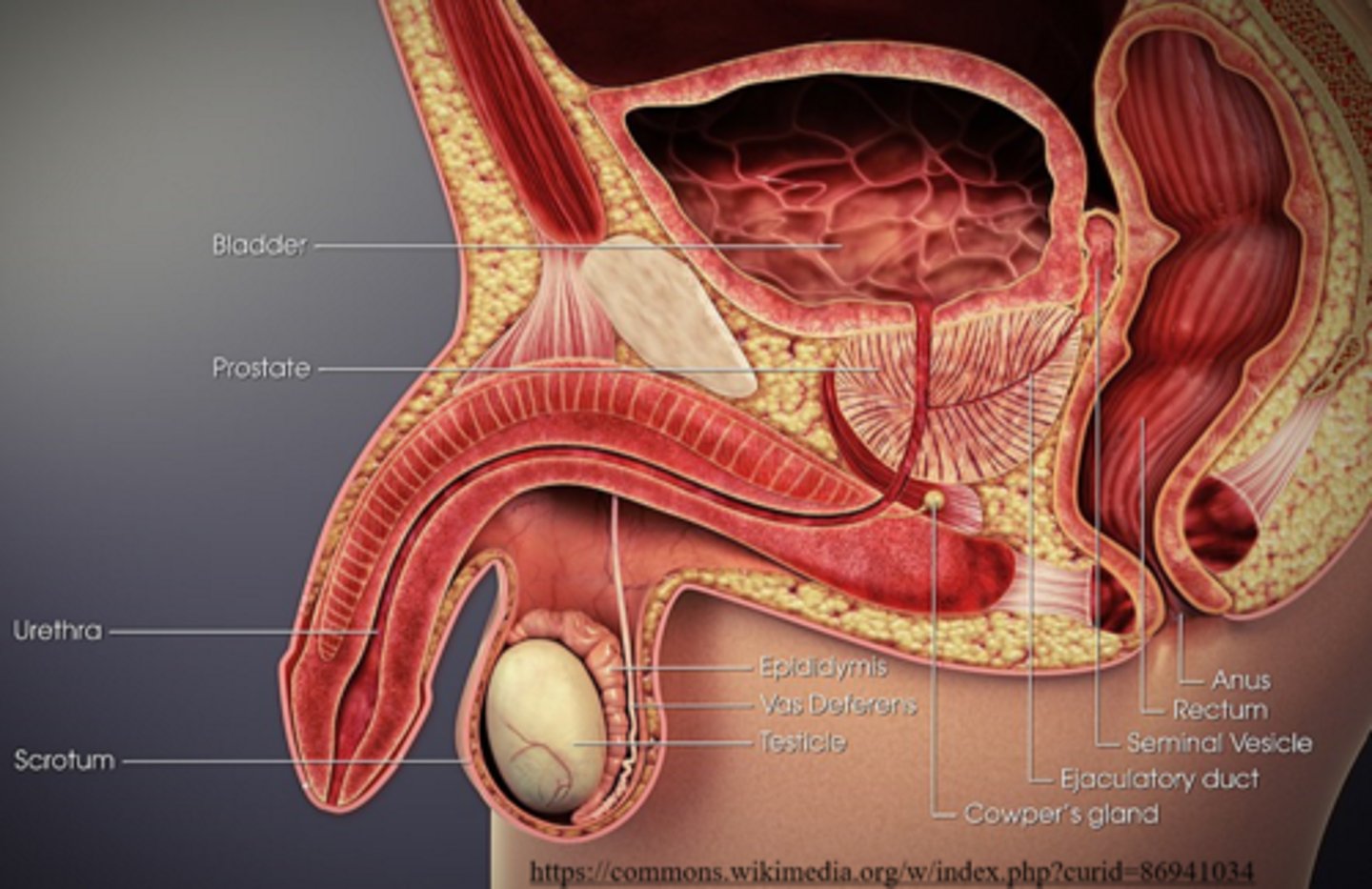
the _____ receives secretions from vas deferens and seminal vesicles
ejaculatory duct
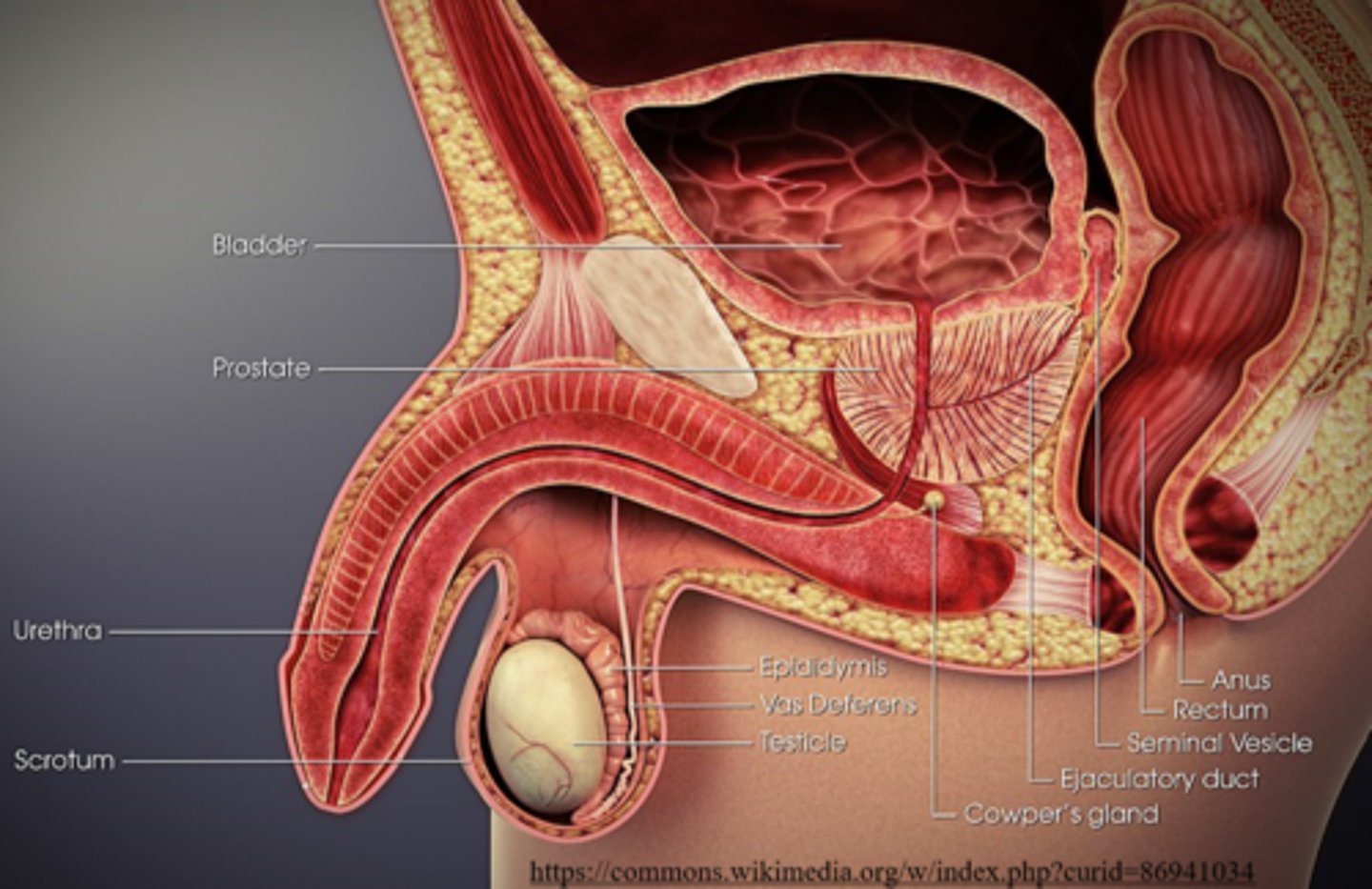
ejaculatory ducts propel the sperm into the _____, which leads to ejaculation of the sperm out of the penis as _____
urethra; semen
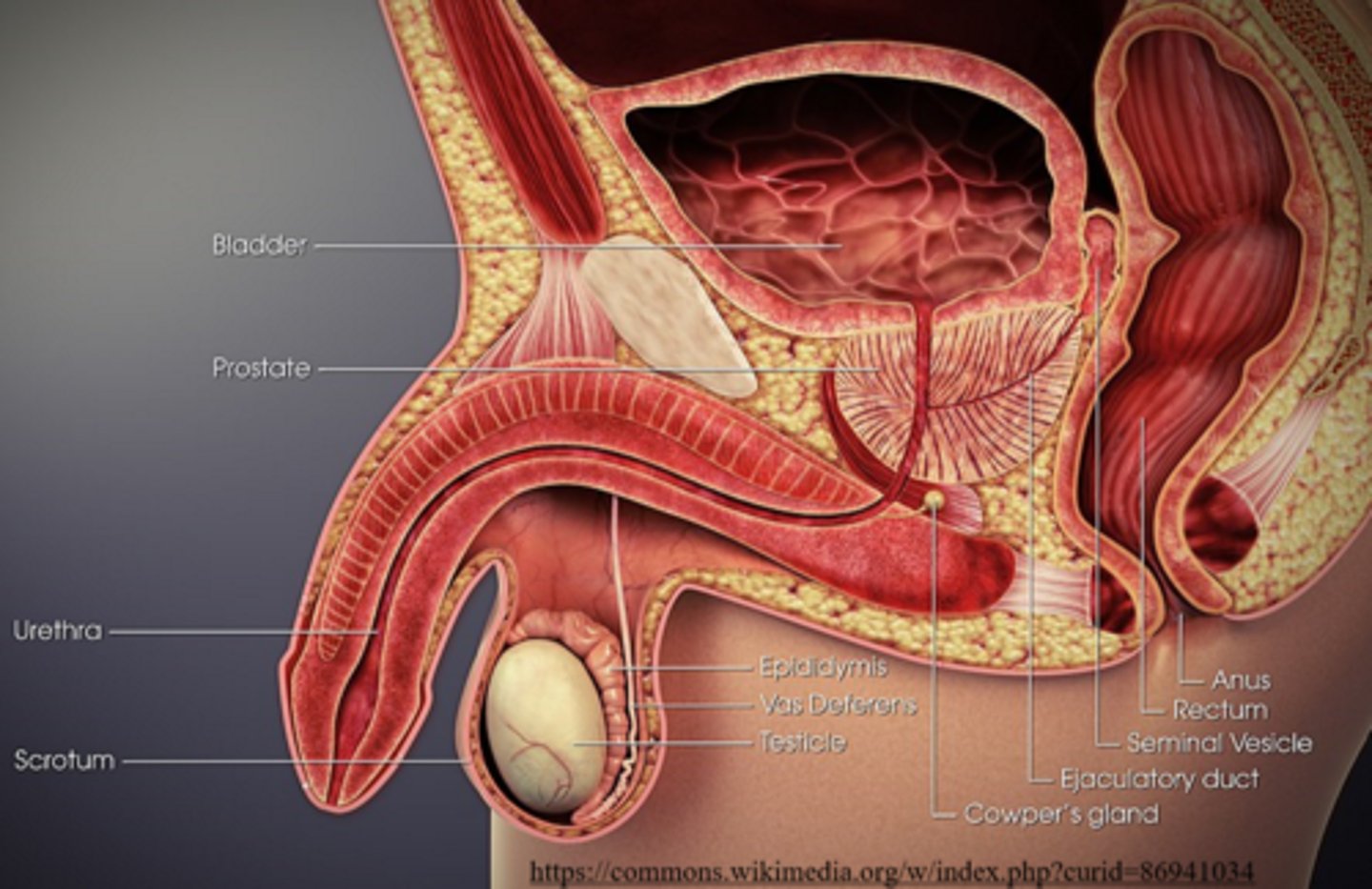
what is the pathway of sperm movement?
Seminiferous tubules --> Epididymis --> Vas deferens --> Ejaculatory duct --> Urethra --> Penis
Mnemonic: SEVEn UP
(n is nothing)
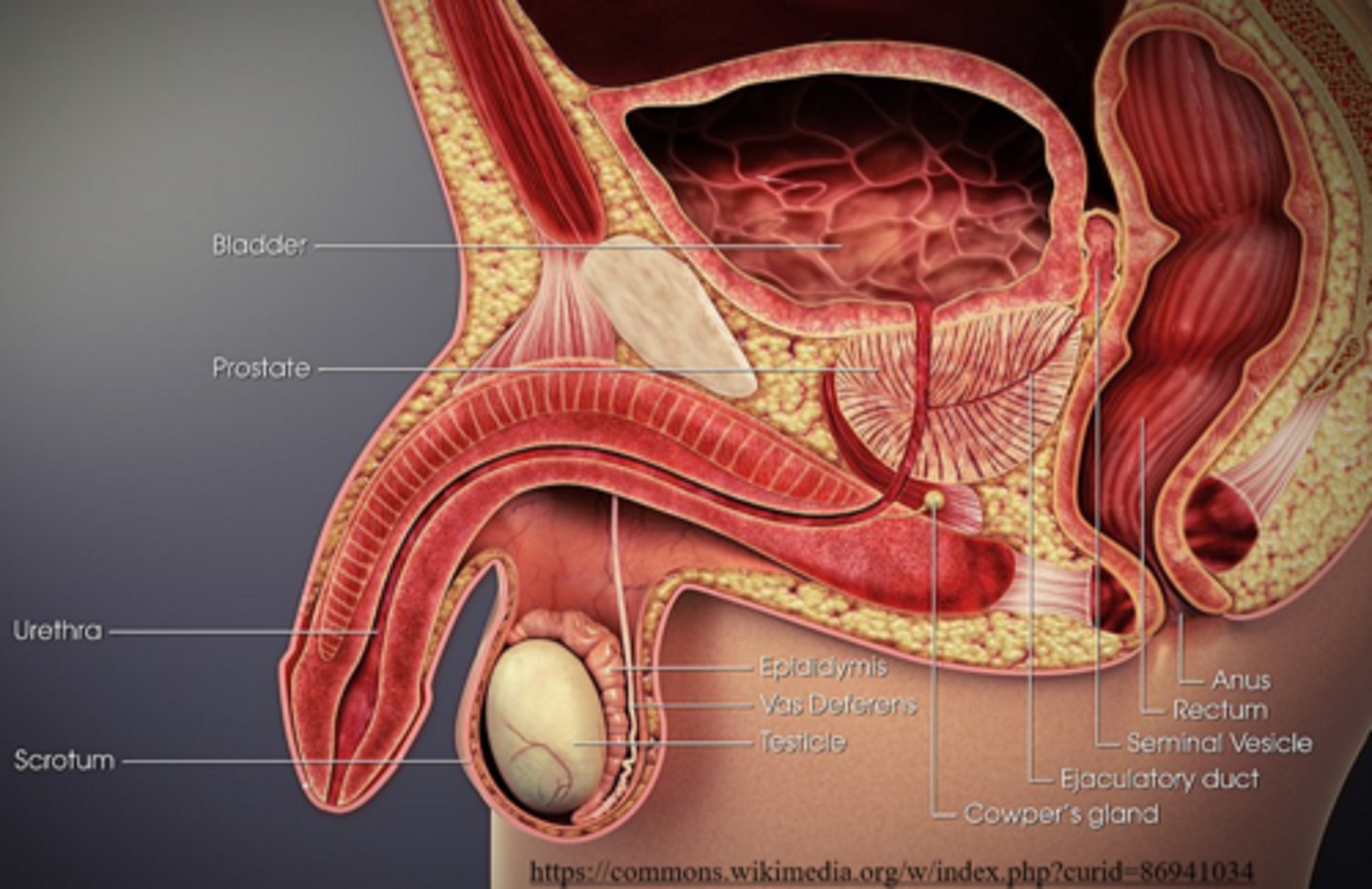
_____ is a combination of sperm and secretions from accessory glands
semen
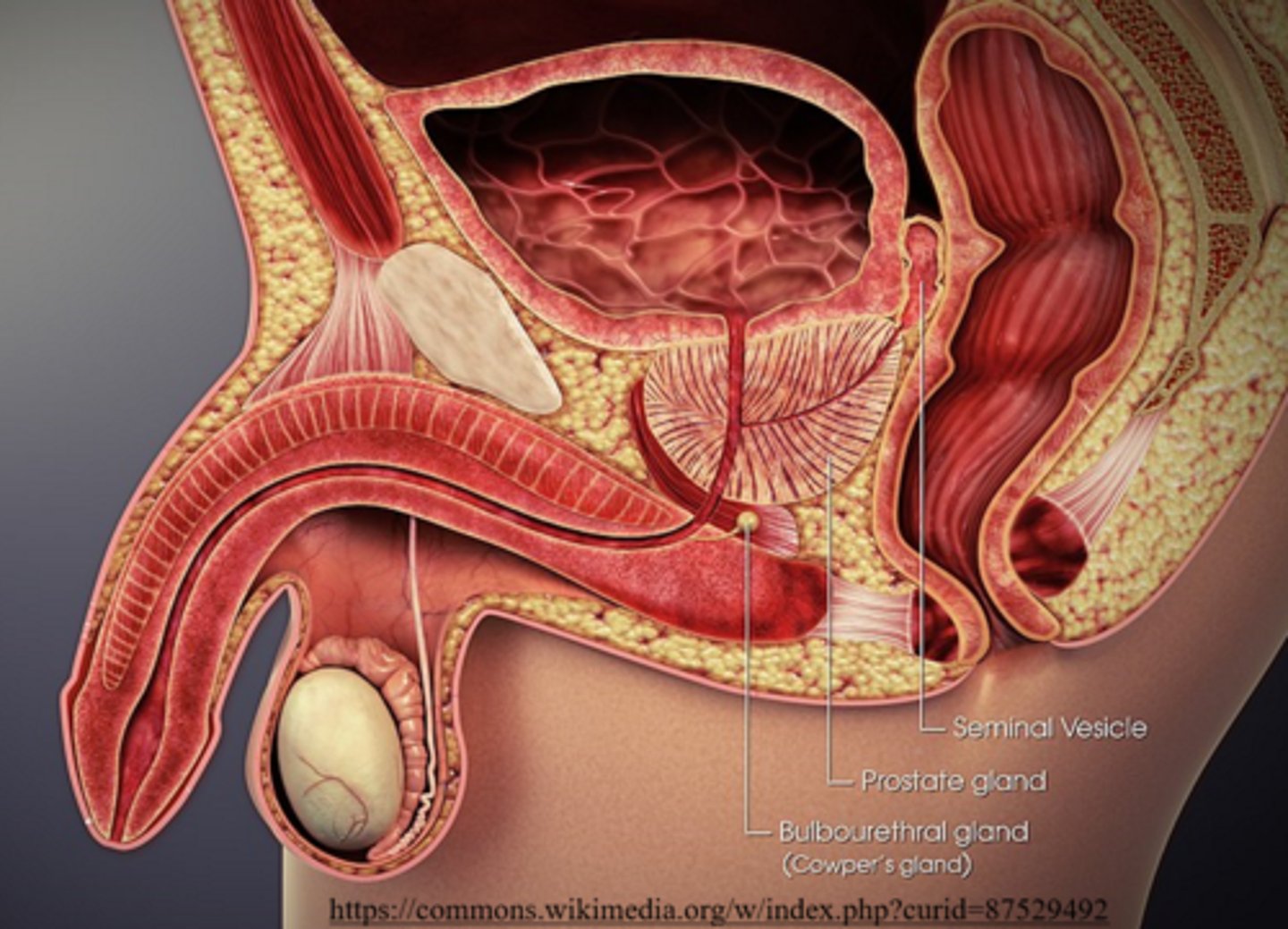
what are three accessory glands that contribute secretions to sperm?
seminal vesicles; prostate gland; bulbourethral glands
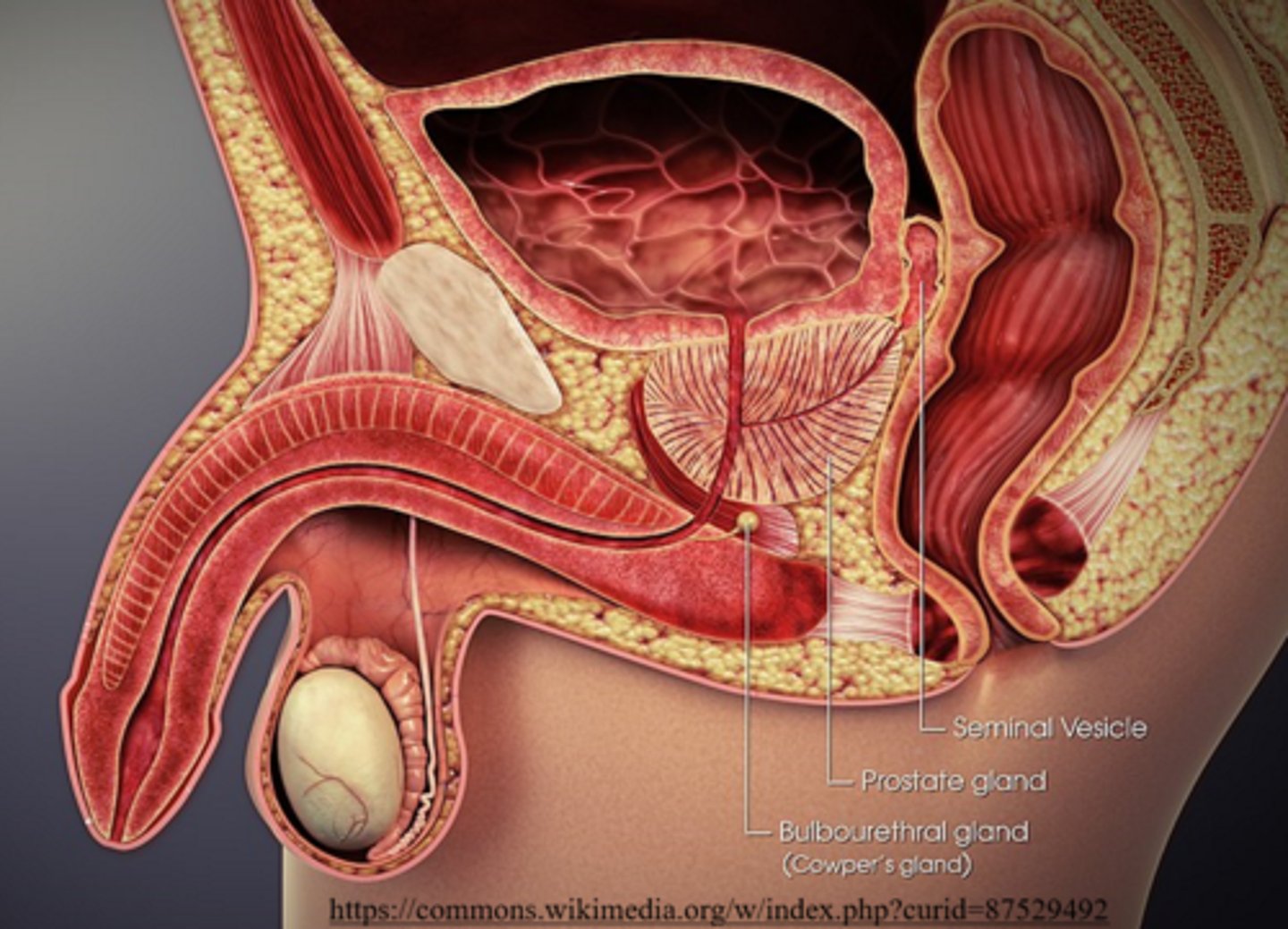
seminal vesicles produce secretions containing _____ sugars
fructose
fructose from the seminal vesicles acts to provide sperm with nutrients to produce _____ for motility
ATP
seminal vesicles secrete viscous mucus, which cleans/lubricates the _____
urethra
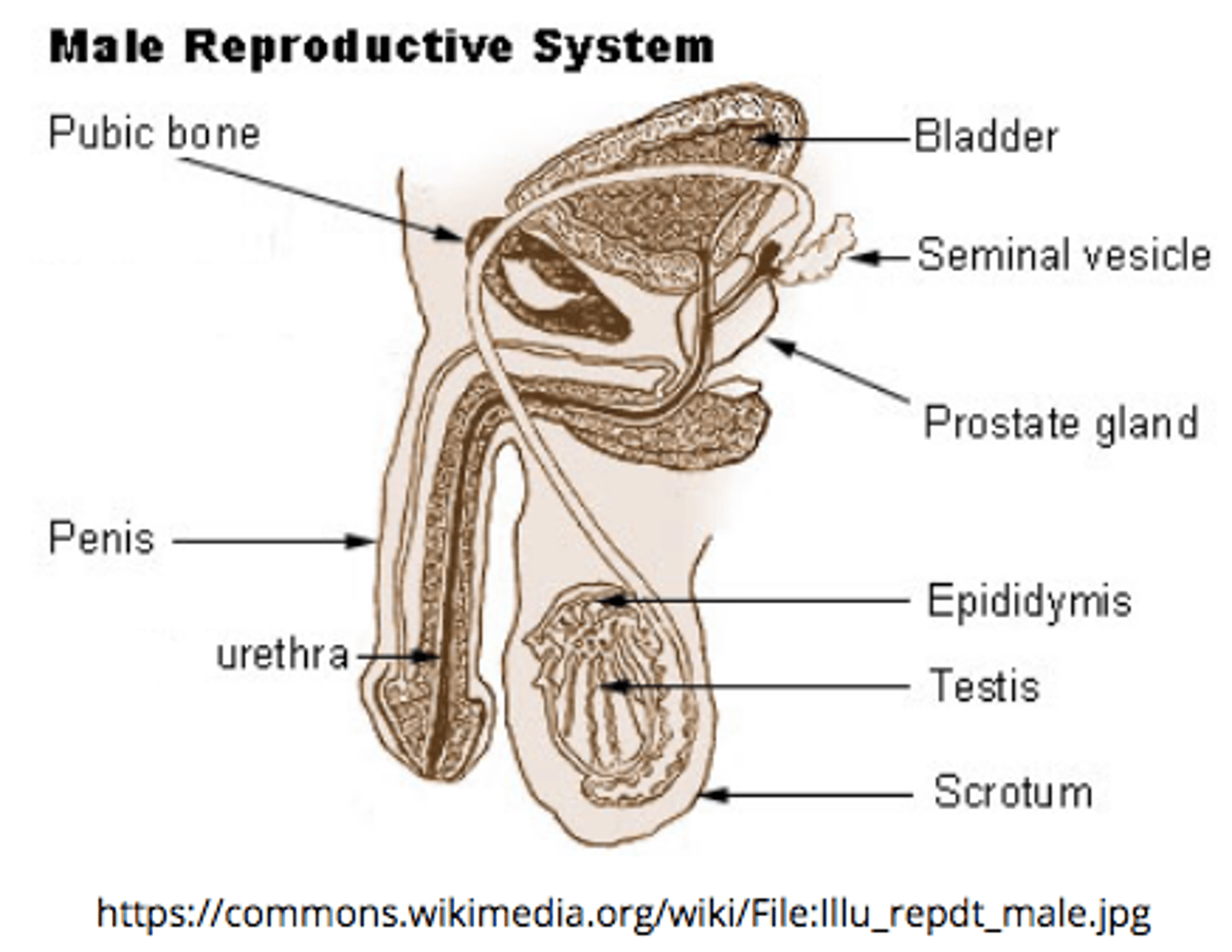
_____ secrete prostaglandins to stimulate contraction of the urethra
seminal vesicles
the _____ makes semen more alkaline
prostate gland
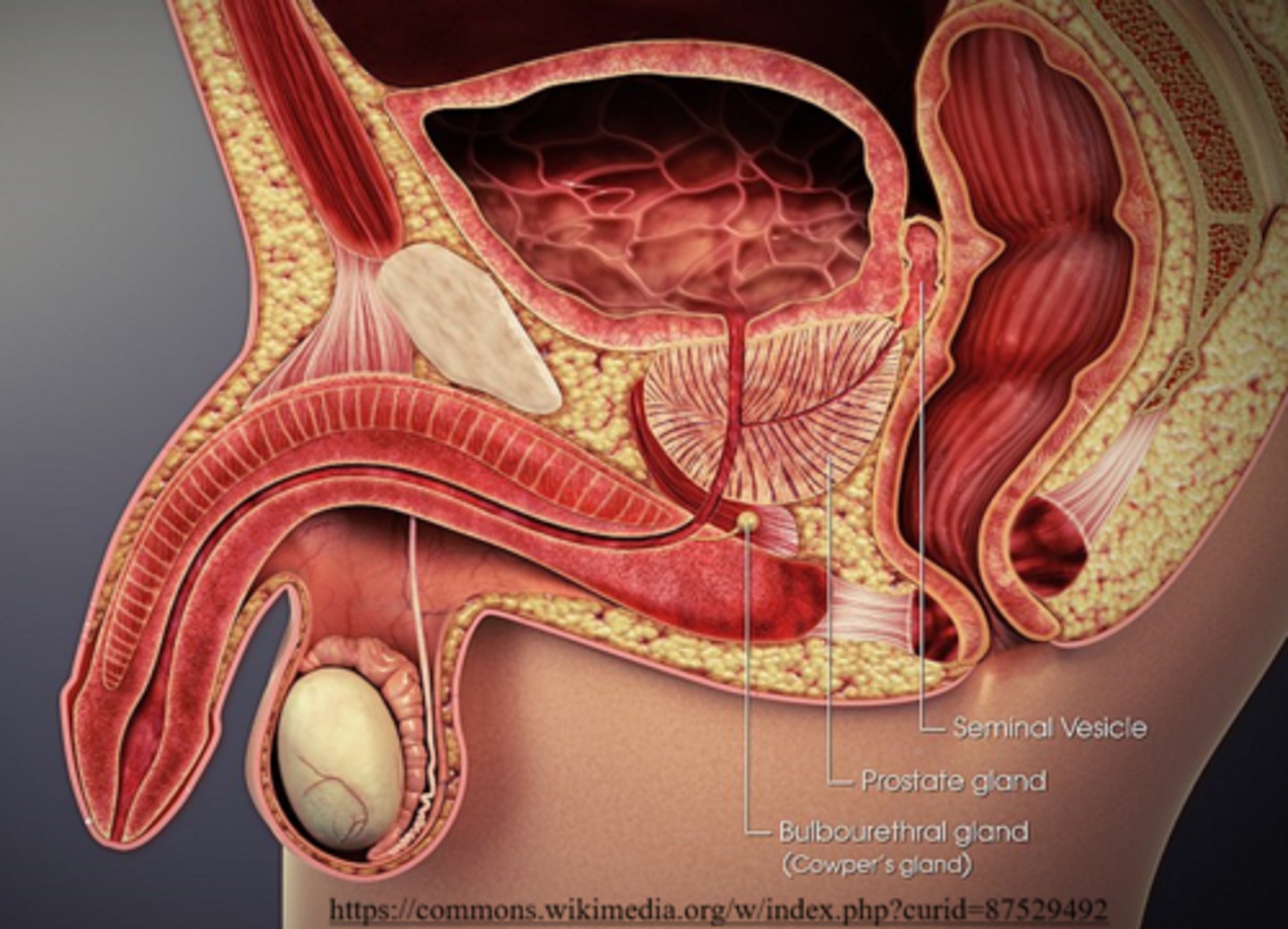
what is the purpose of the prostate gland making semen alkaline?
so sperm can survive the acidity of the female reproductive tract
bulbourethral glands are similar to seminal vesicles because they also secrete _____
viscous mucus
(bulbourethral glands are also called Cowper's glands)
what does follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) do in males?
stimulates sperm to develop in the seminiferous tubules
(FSH comes from the anterior pituitary)
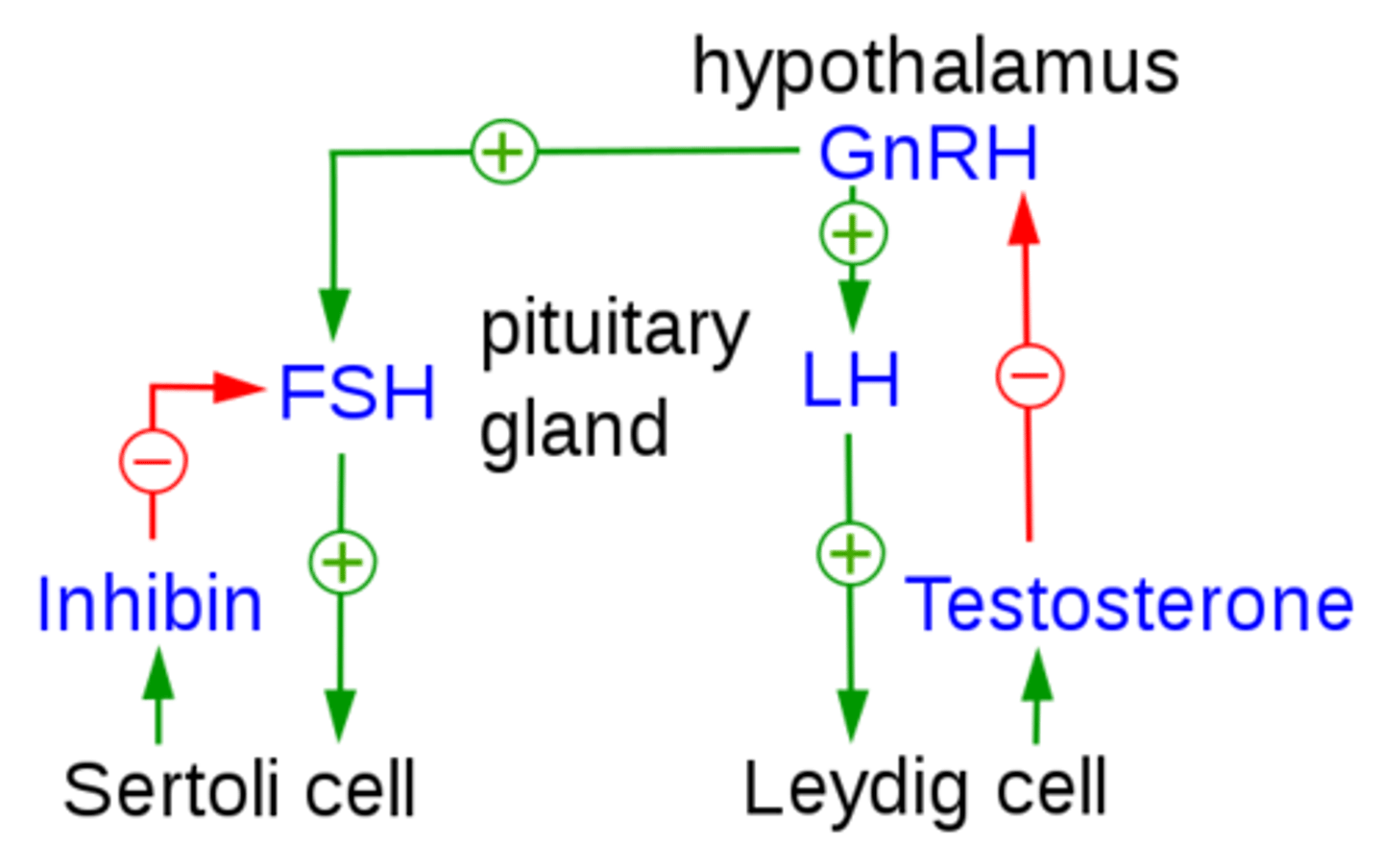
what does luteinizing hormone (LH) do in males?
stimulates the Leydig cells of the testes to produce testosterone
(LH comes from the anterior pituitary)
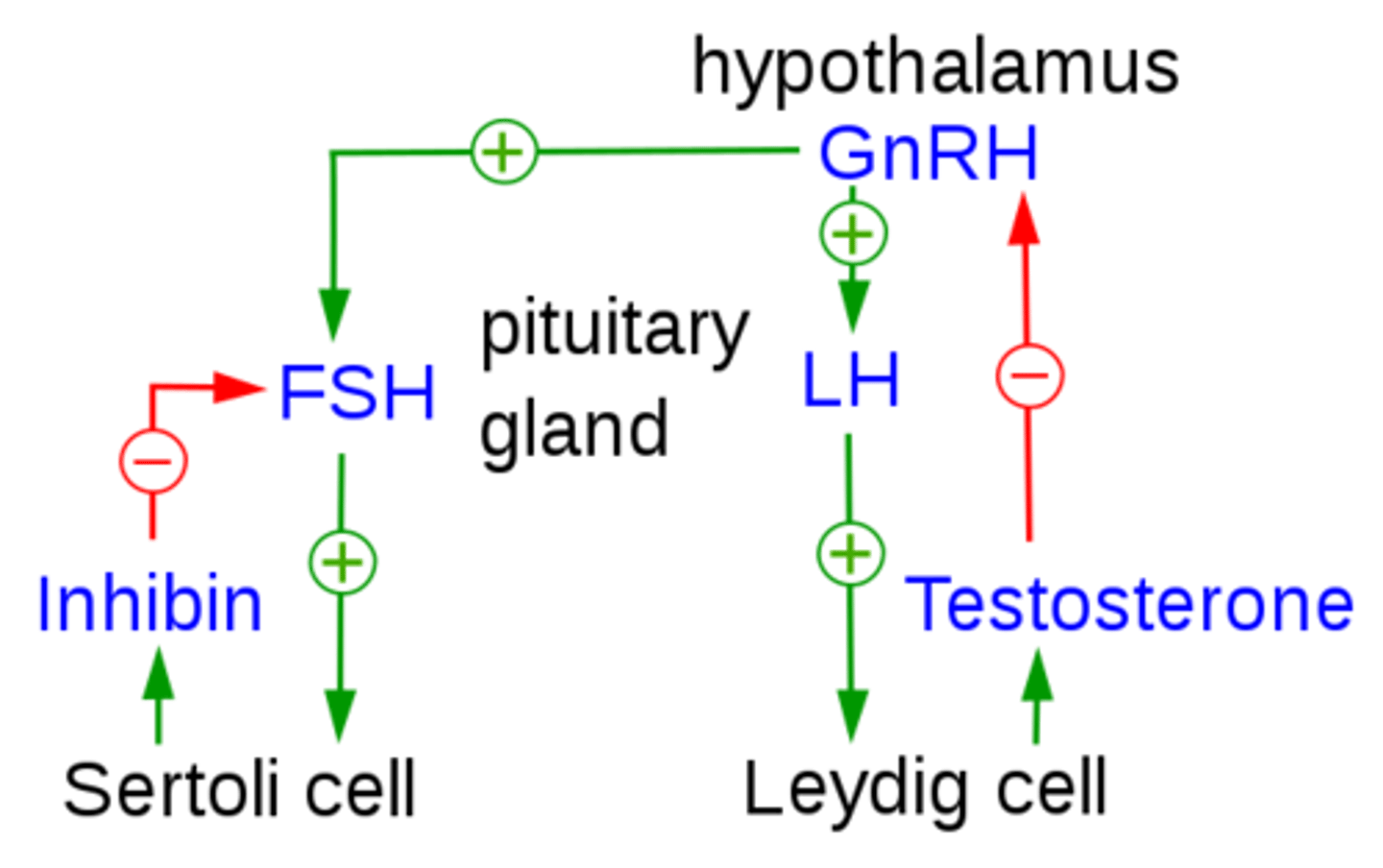
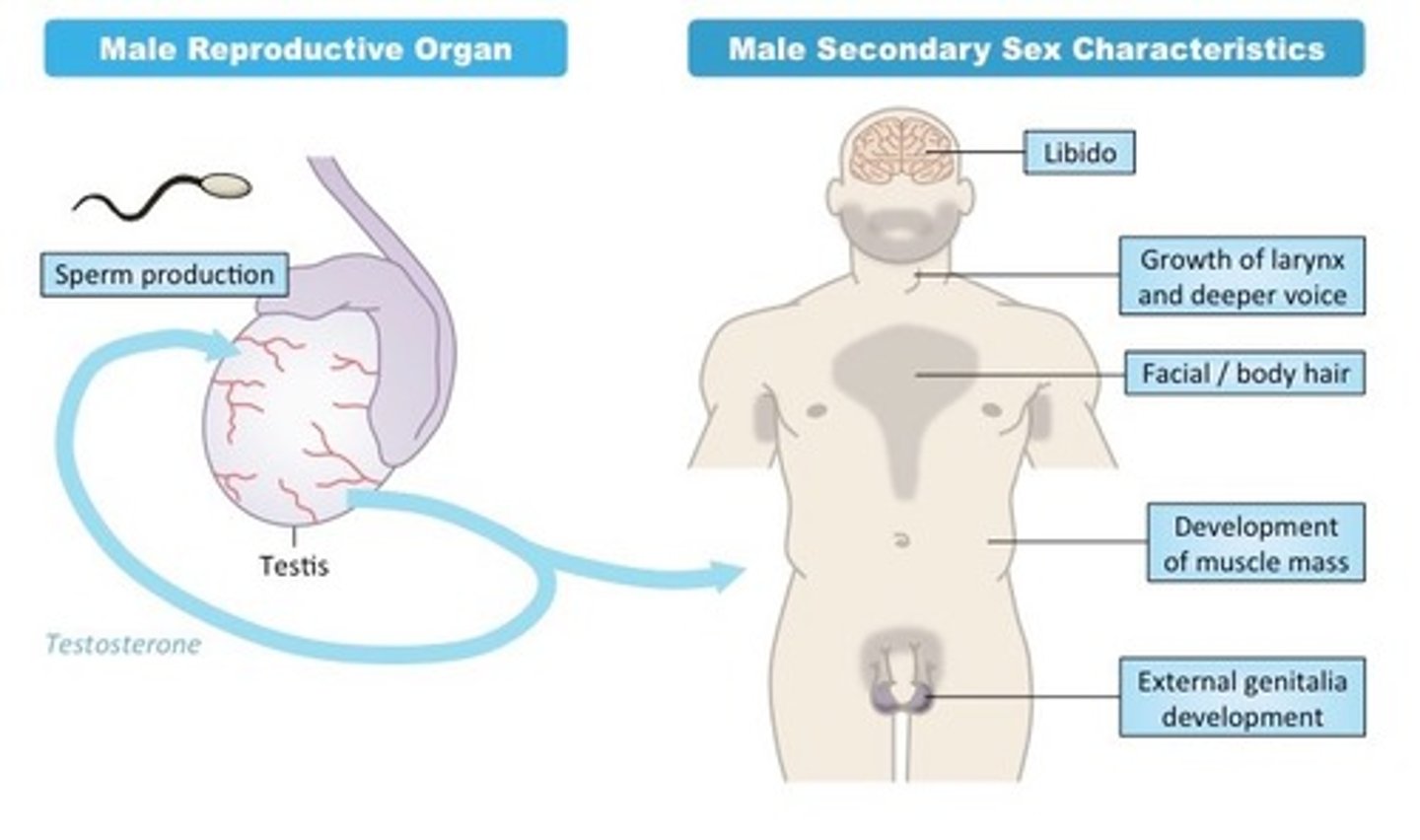
testosterone functions in spermatogenesis to ________
mature the sperm
_____ is responsible for contributing to male secondary sex characteristics
testosterone
the vagina acts as the opening between the _____ and _____
uterus; external environment
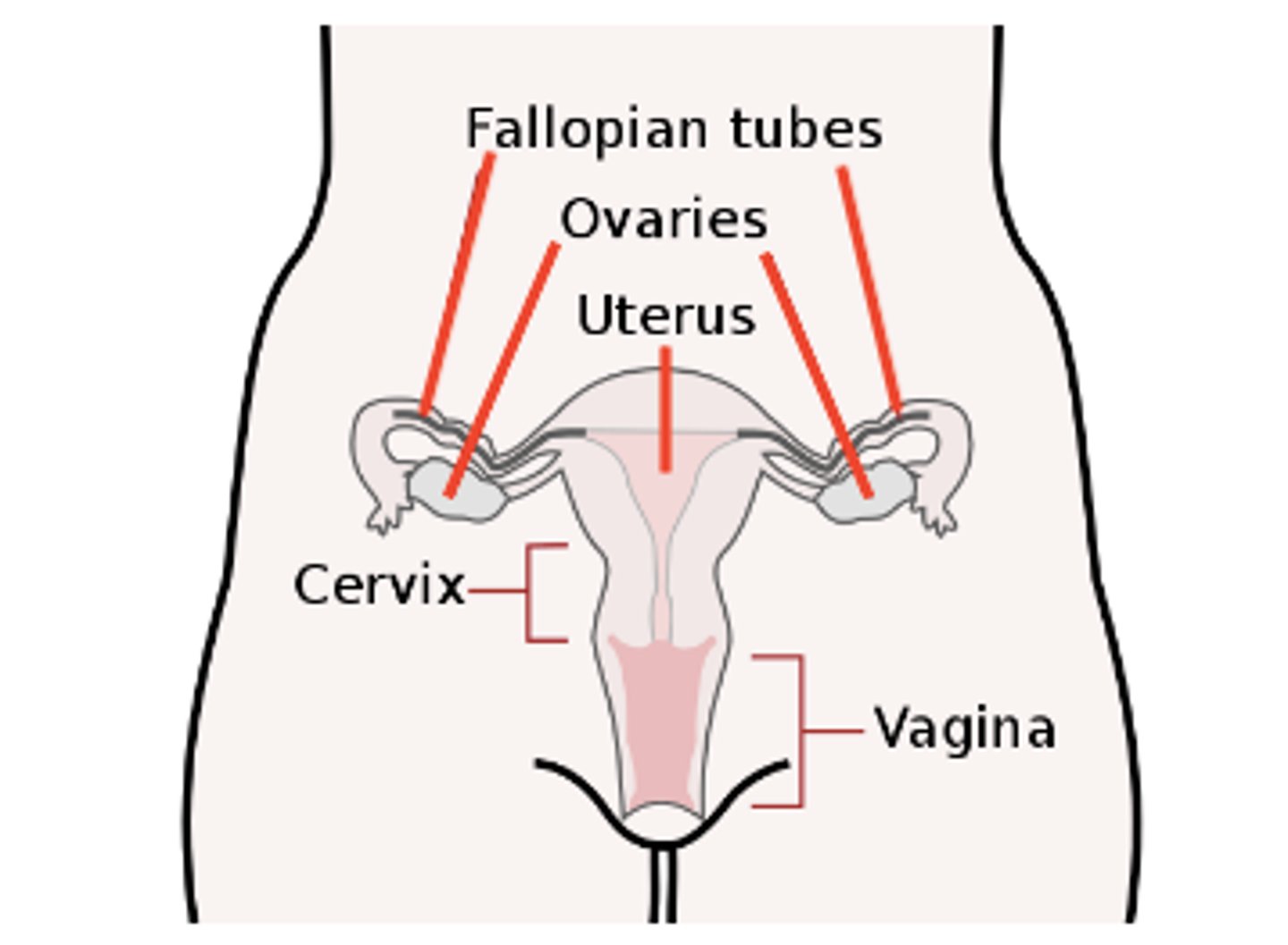
the ovaries are responsible for the production of _____
ovums (eggs)
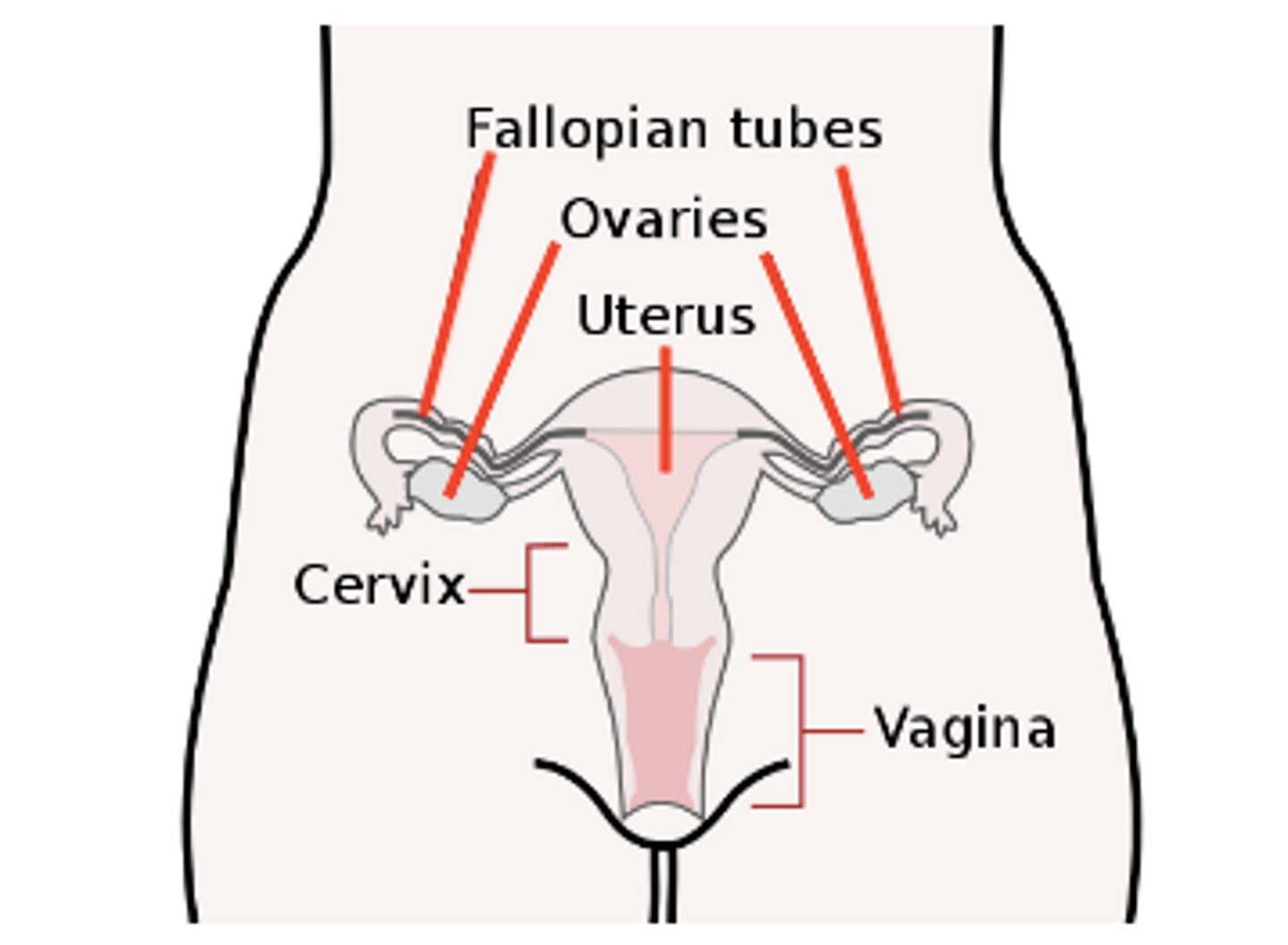
ovums (eggs) travel through the _____ after they are released from an ovary
oviduct (fallopian tube)
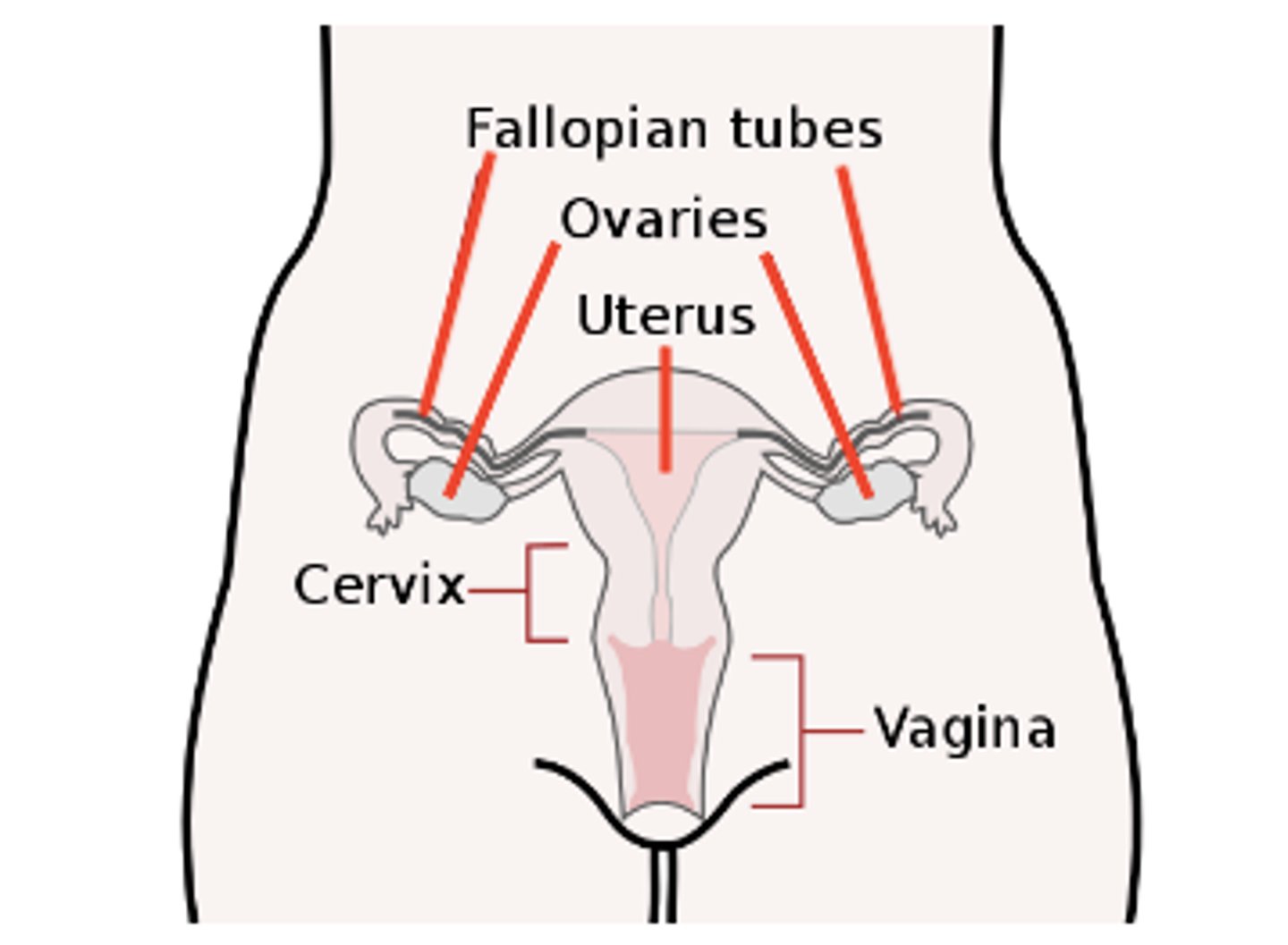
oviducts (fallopian tubes) connect the ovaries and the _____
uterus
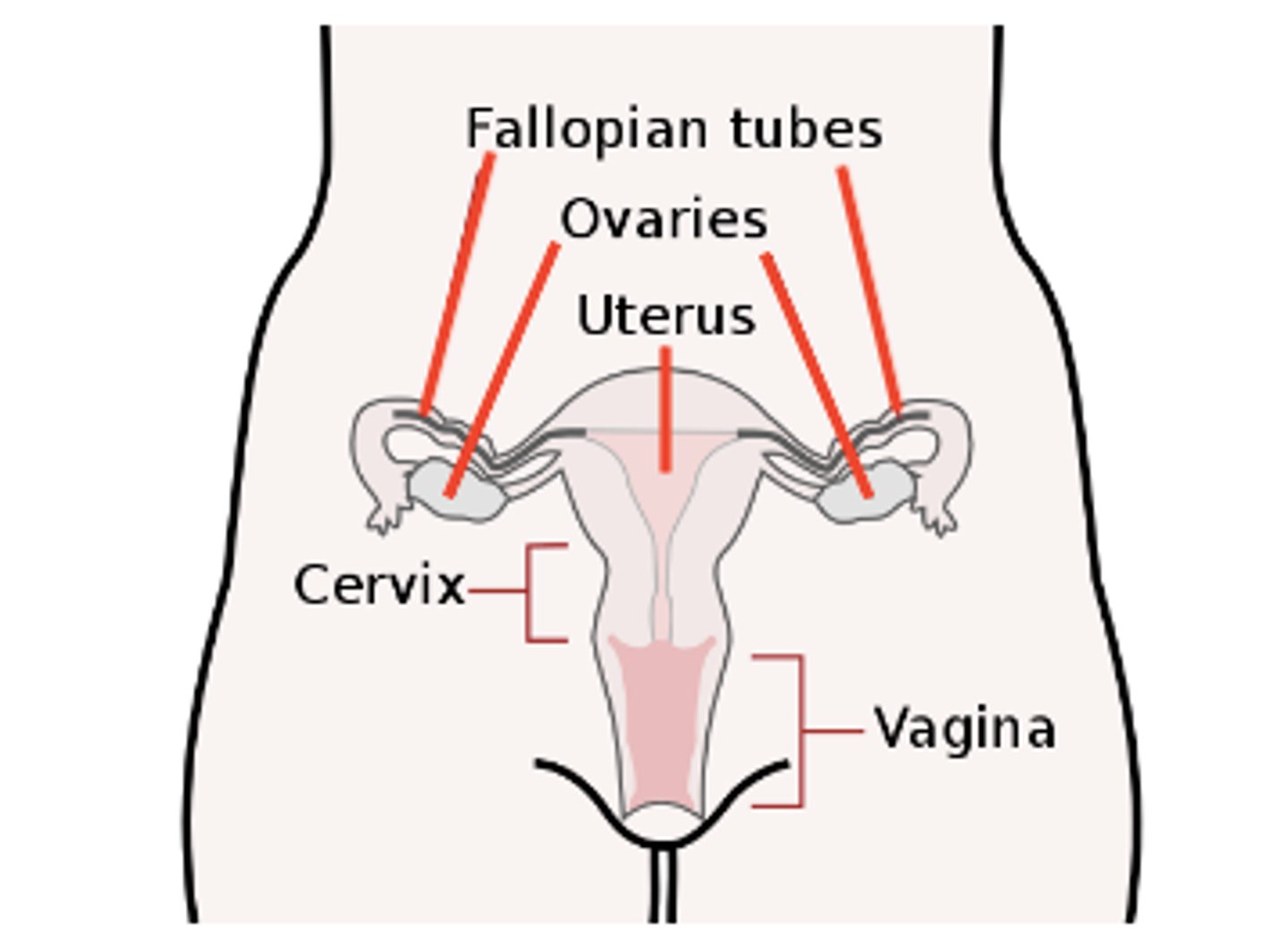
the uterus is a muscular organ ideal for _____
embryo implantation
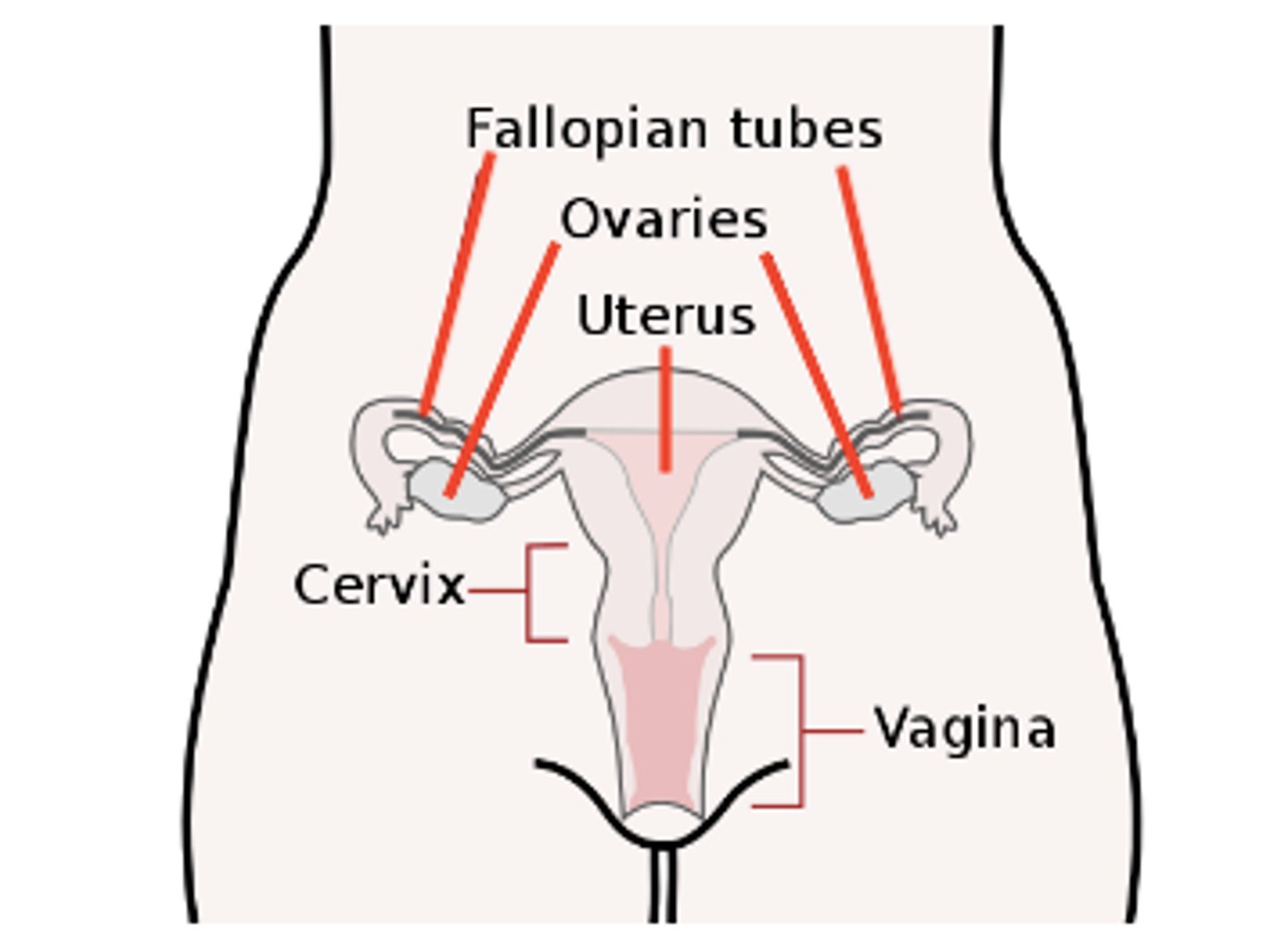
what are the three layers of the uterus?
perimetrium (outer layer); myometrium (smooth muscle, middle layer); endometrium (inner epithelial layer, lined by mucous membranes)
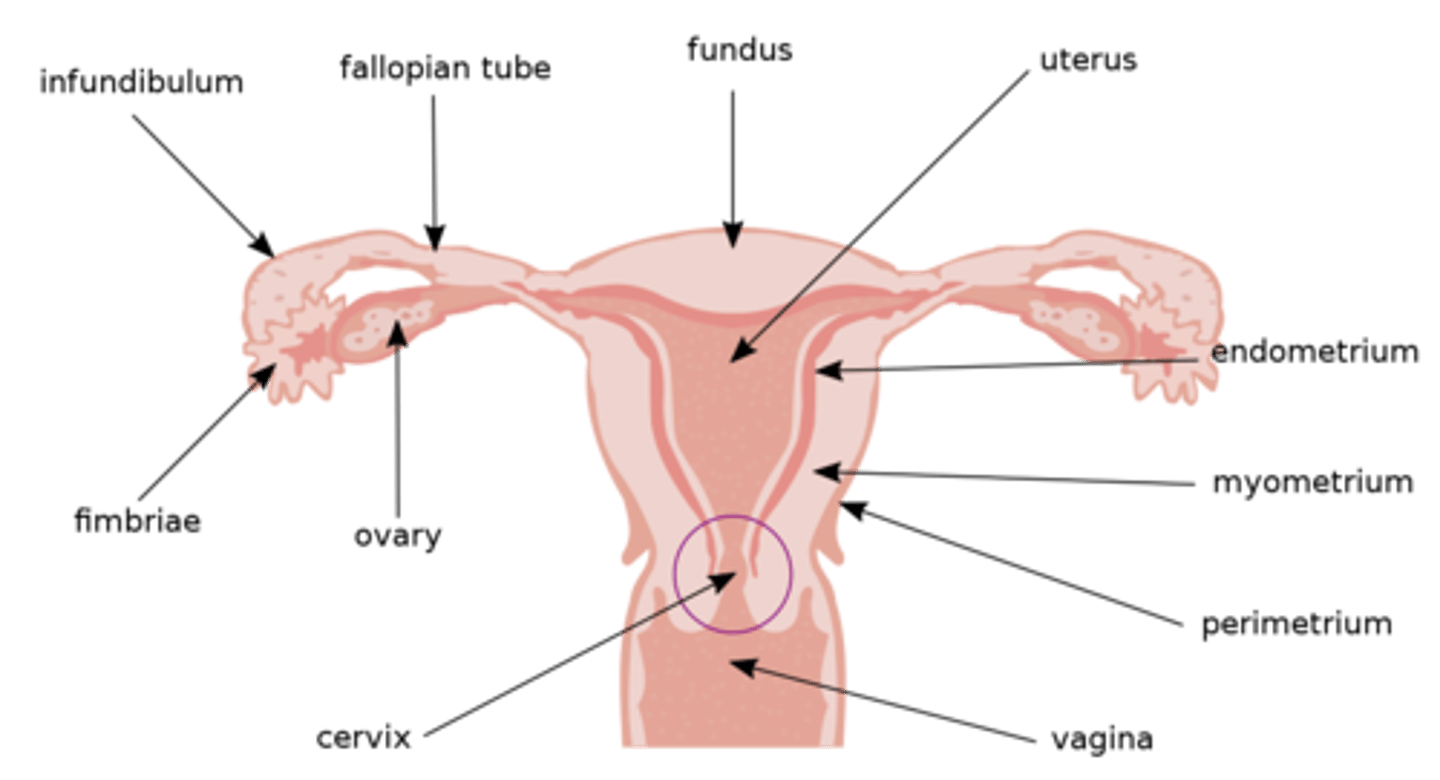
where do sperm first enter a female body?
the vagina
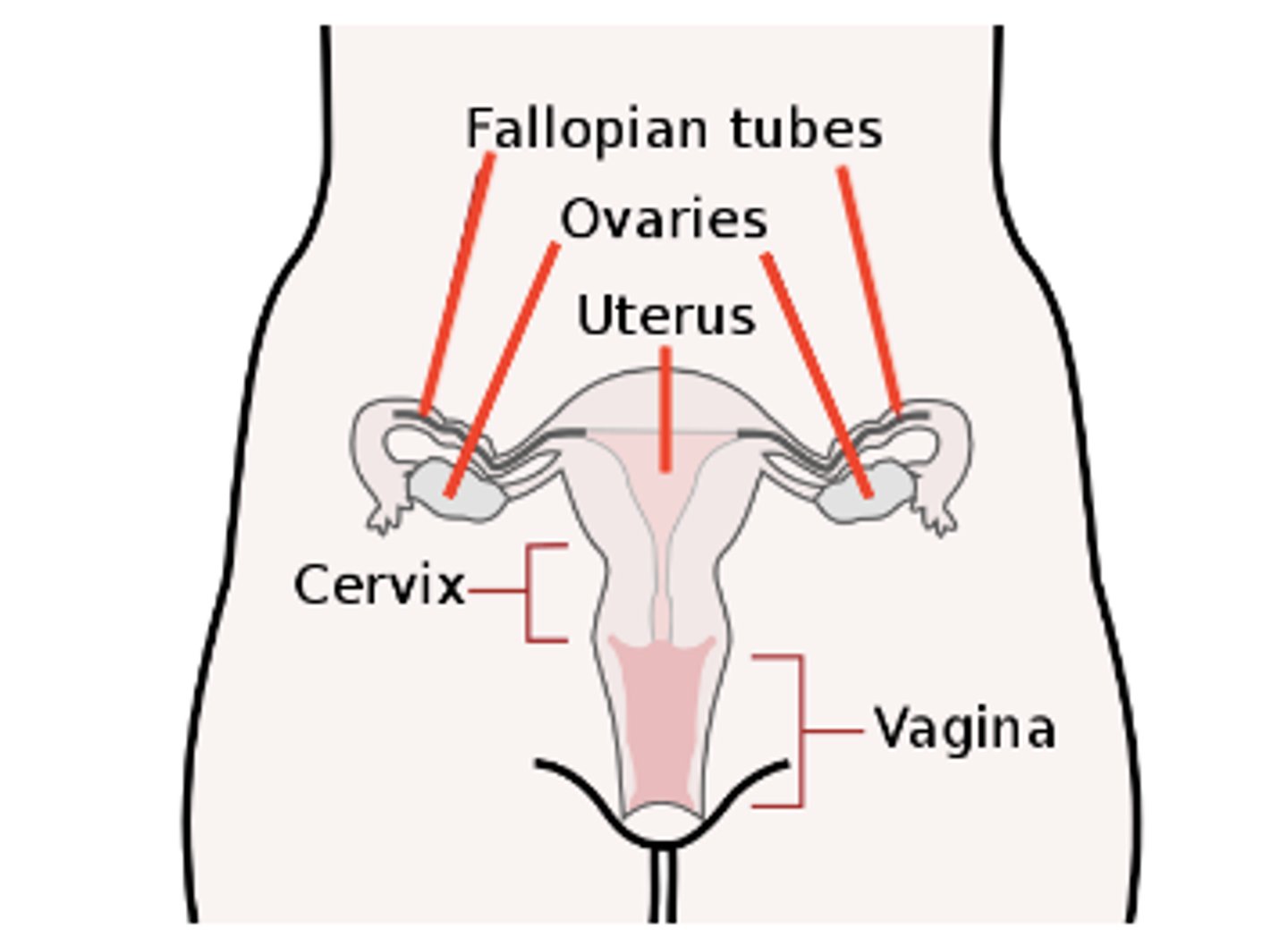
where does parturition (giving birth) occur?
the vagina
oogonia differentiate to produce _____
primary oocytes
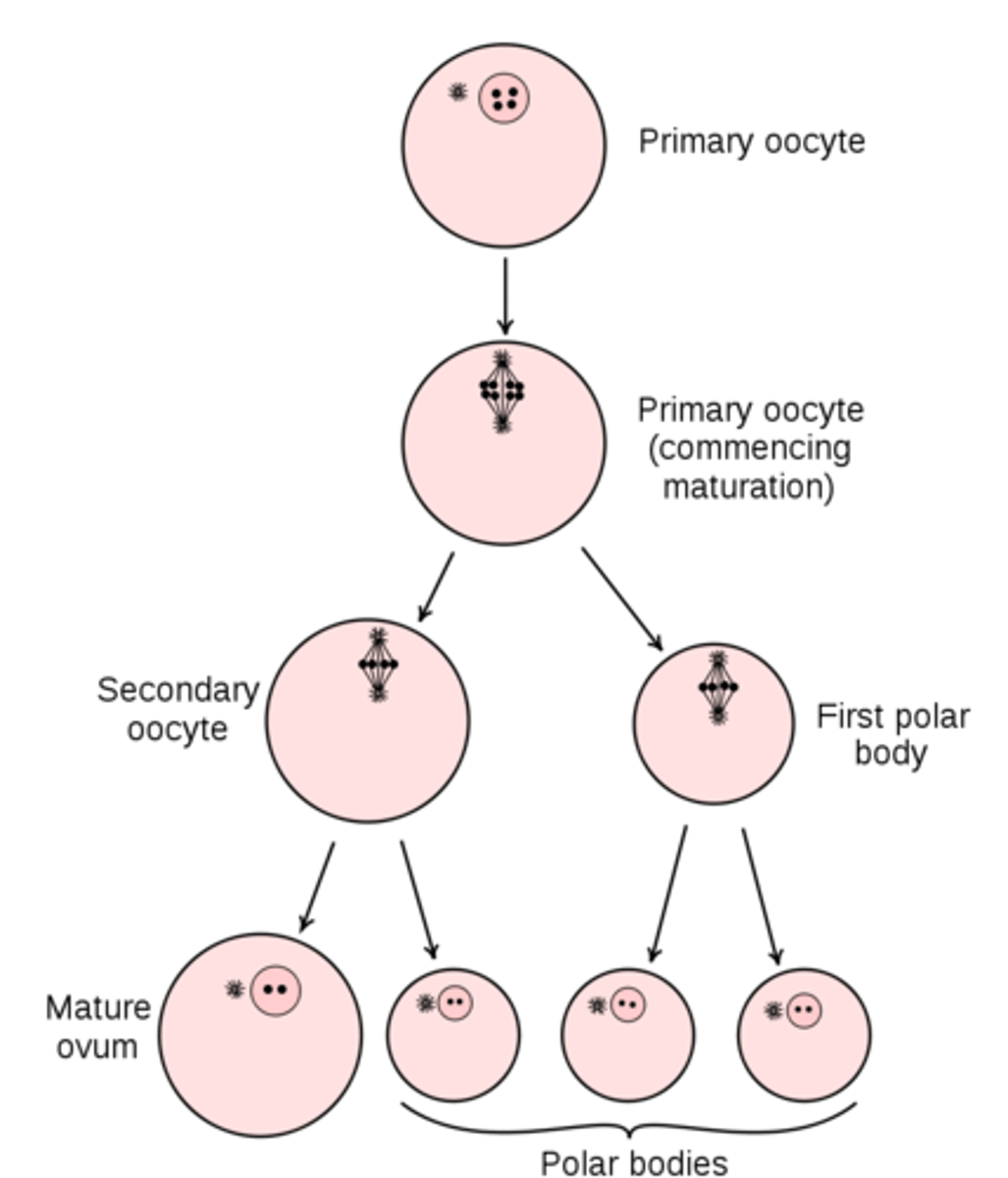
_____ begin meiosis I in oogenesis, but they will not complete meiosis I until puberty
primary oocytes
primary oocytes begin _____ in oogenesis, but they will not complete it until _____
meiosis I; puberty
when a female hits puberty, one of her _____ (arrested at meiosis I) will go through ovulation each _____
primary oocytes; month
ovulation occurs when a primary oocyte completes meiosis I to create which two things?
a large secondary oocyte and a small polar body
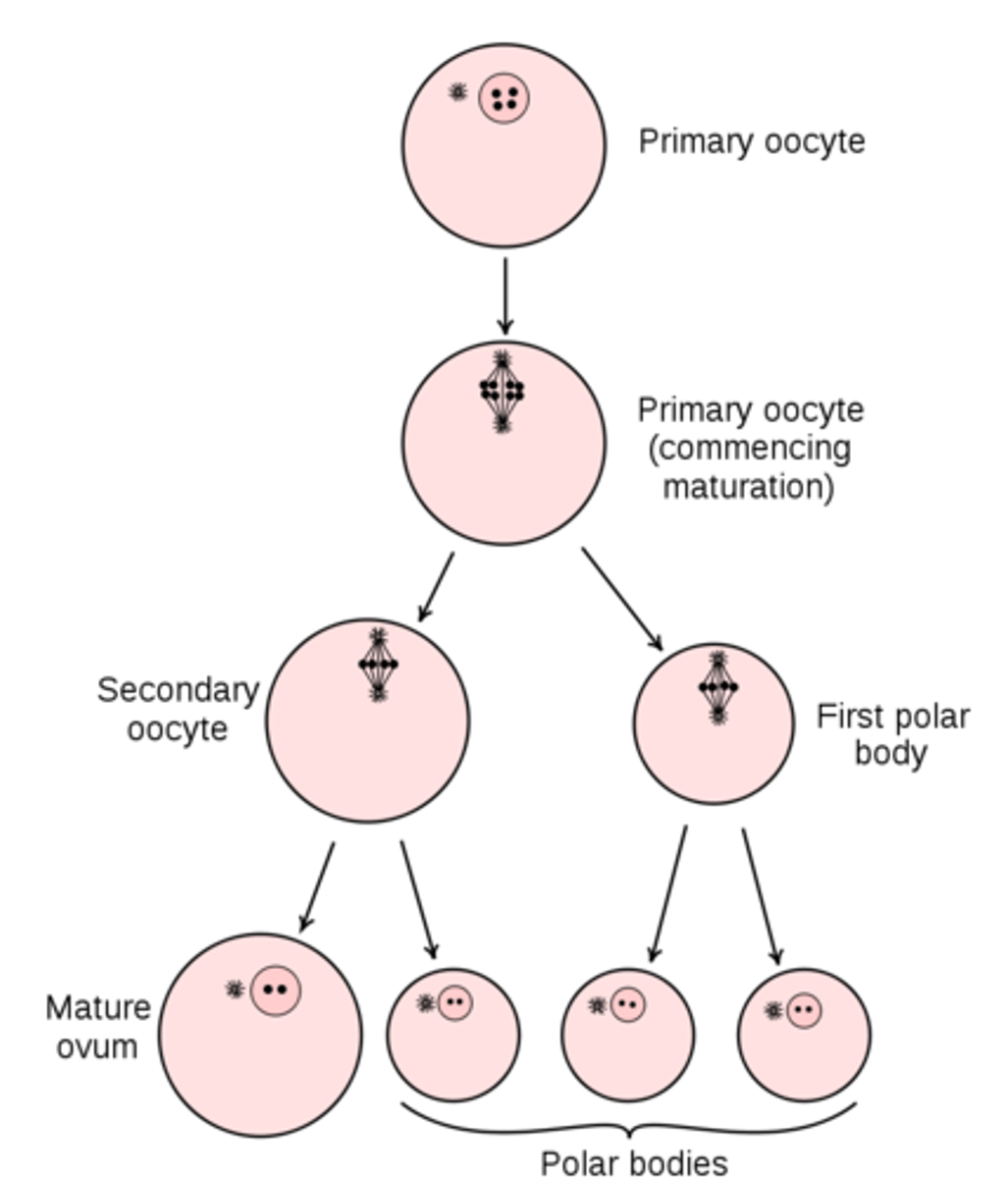
the secondary oocyte produced by ovulation will arrest at _____
metaphase II
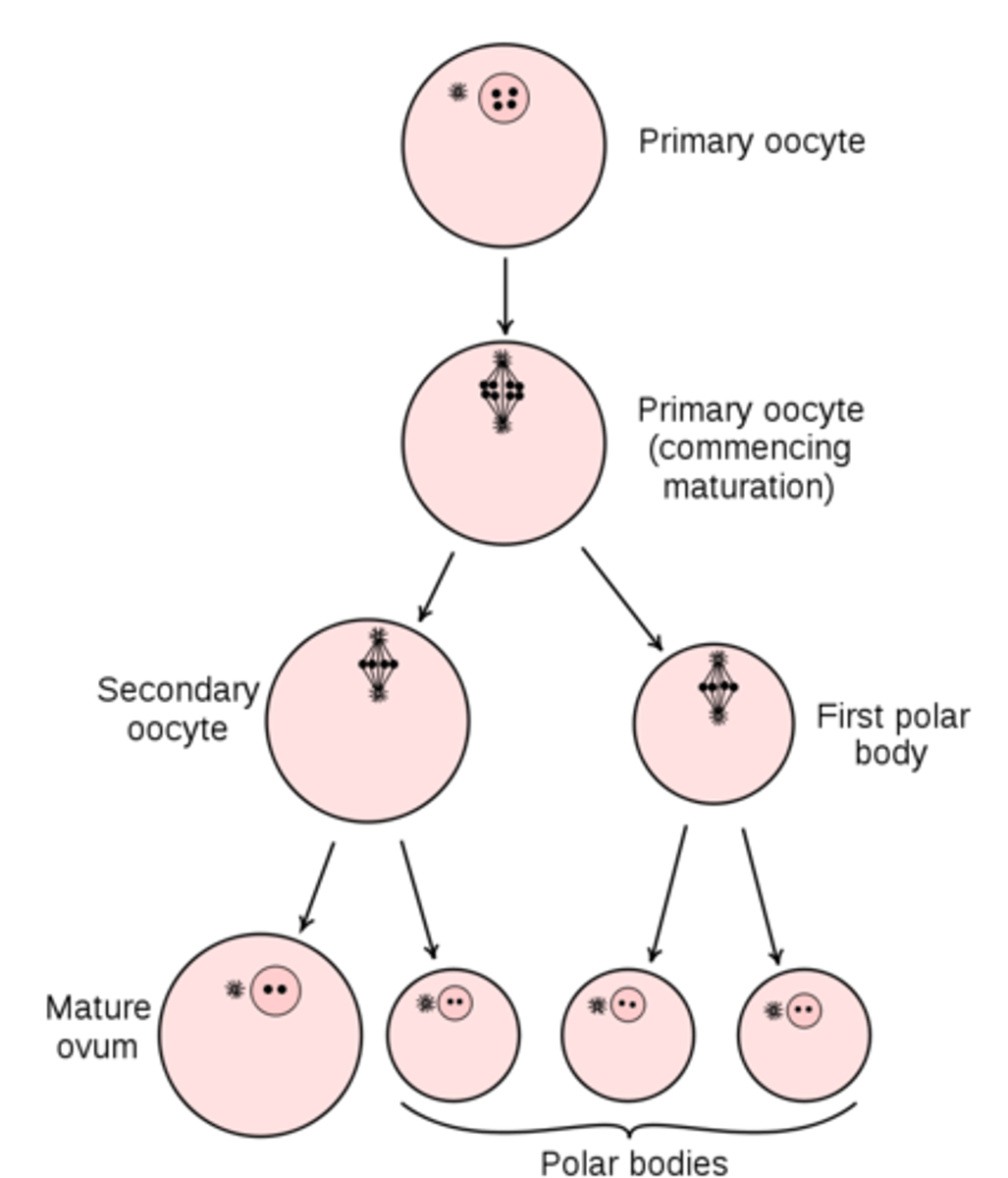
secondary oocytes only complete meiosis II if _____ occurs
fertilization
at the end of meiosis II in oogenesis, 2-3 ___ and 1 ___ are produced
polar bodies; oocyte
can polar bodies contribute to a viable offspring?
no, only the secondary oocyte can
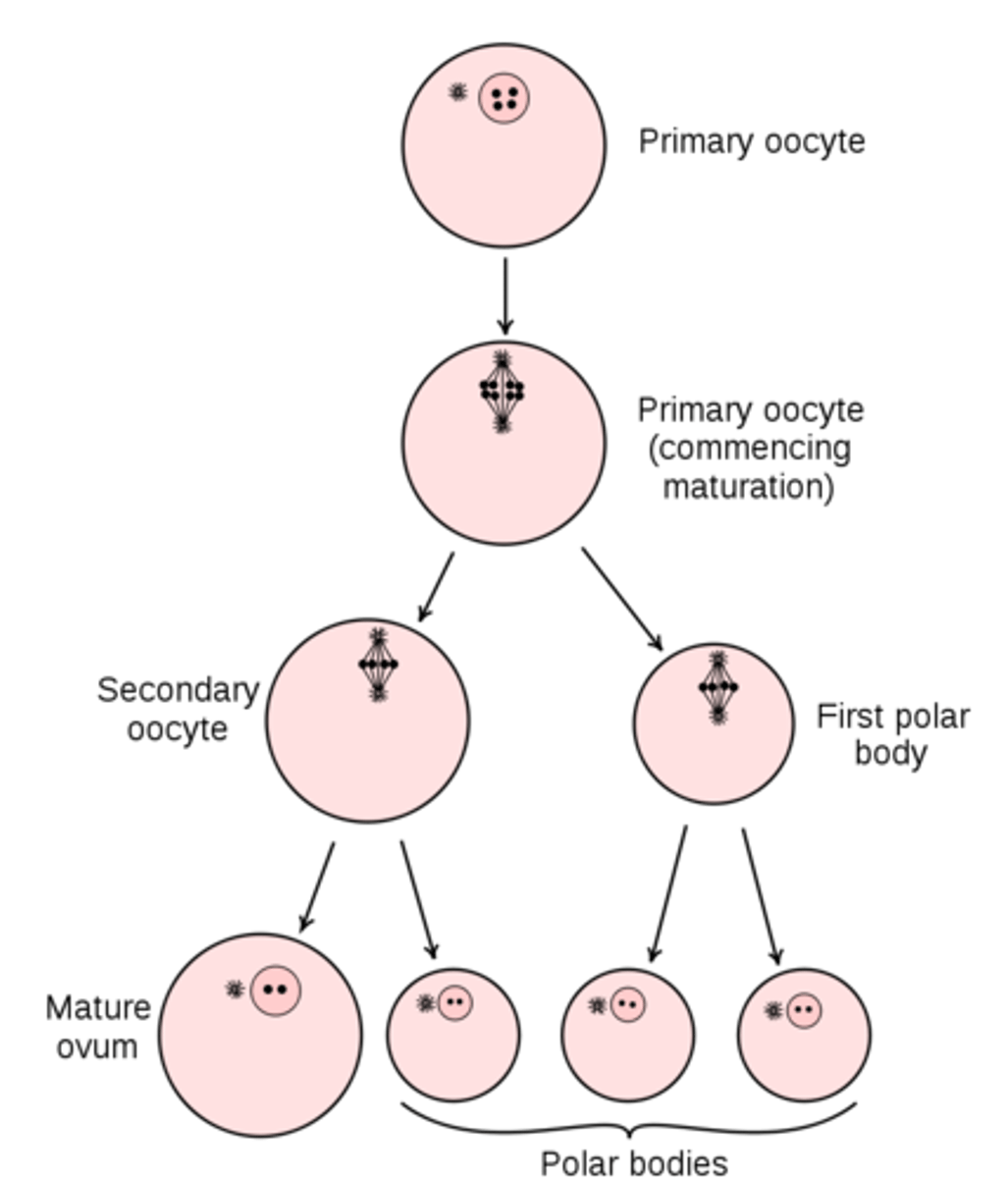
what contains majority of cytoplasm, mitochondria, and nutrients for the fetus?
oocyte
what does follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) do in females?
follicle development in the ovary & production of estrogen and progesterone
(FSH is secreted from the anterior pituitary)
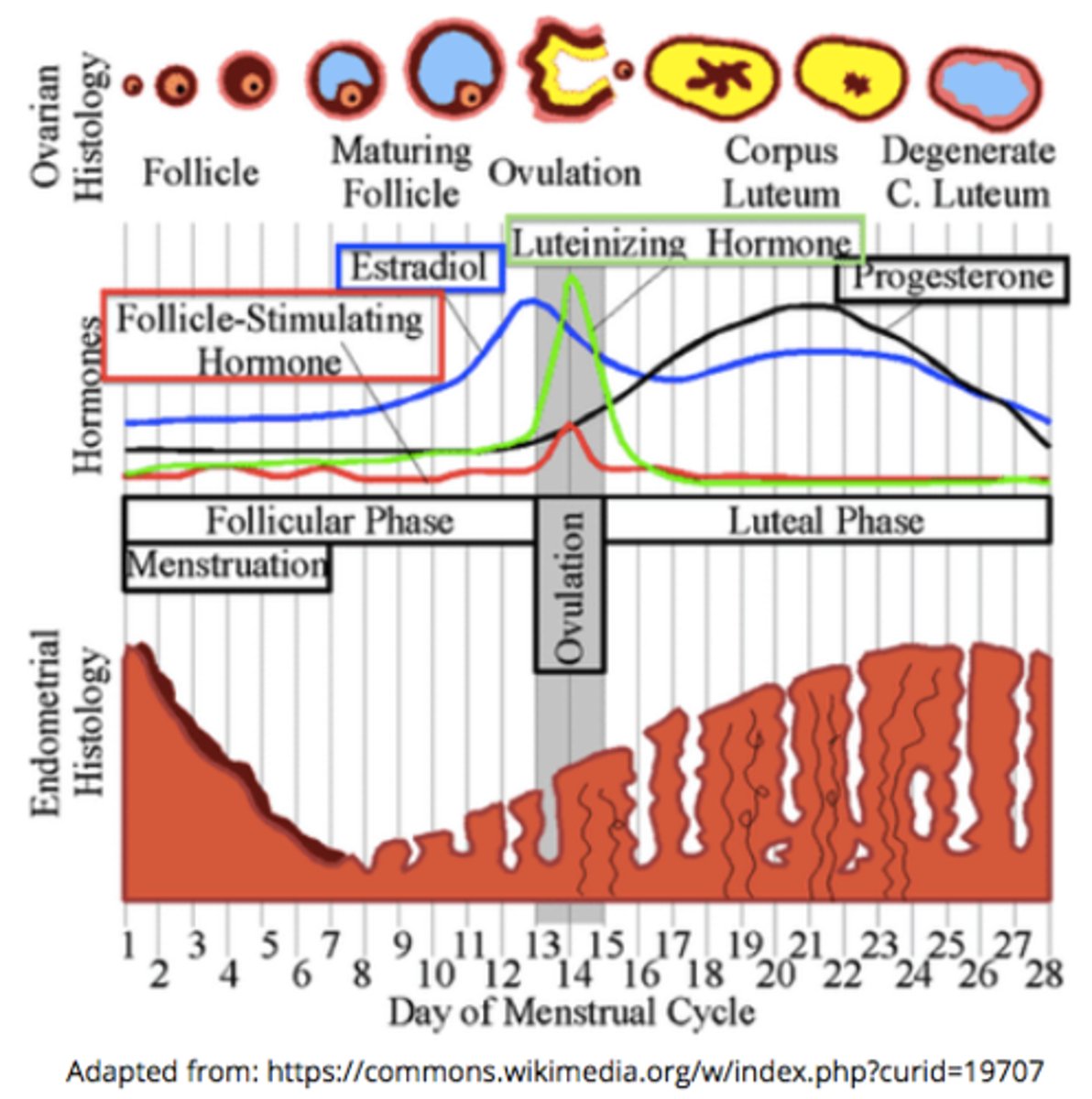
____ are fluid filled sacs on the ovaries that contain an immature egg that is arrested at meiosis I
follicles
what is the temporary endocrine structure formed by the dominant follicle after the egg ovulates?
corpus luteum
what does luteinizing hormone (LH) do in females?
stimulates ovulation of the egg; formation of corpus luteum, which produces estrogen & progesterone
(LH is secreted from the anterior pituitary)
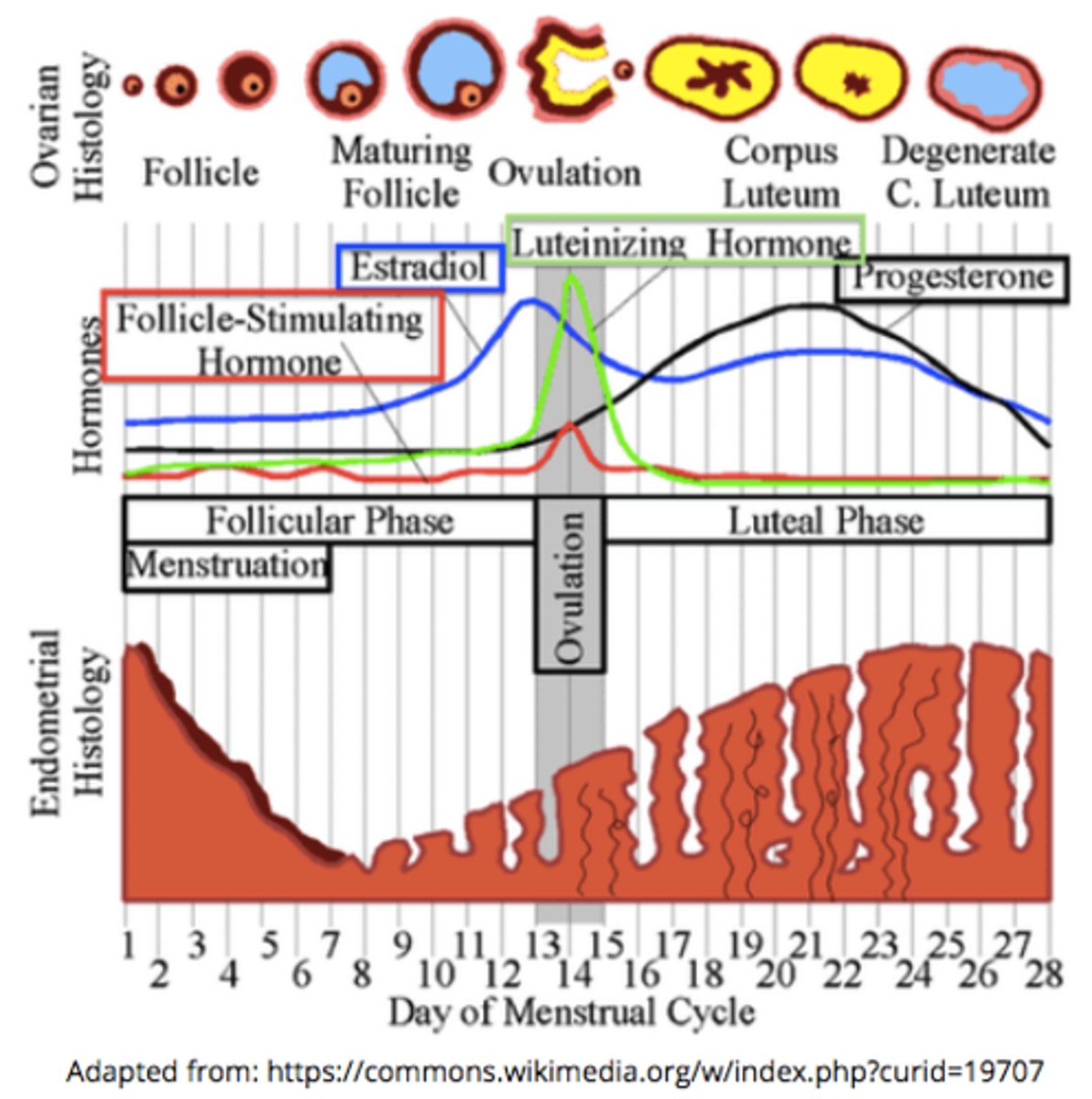
_____ and _____ are the female sex hormones
estrogen; progesterone
female sex hormones contribute to the _____ and _____
menstrual cycle; reproduction
female sex hormones cause development of _____
secondary sex characteristics
birth control pills release synthetic estrogen and progesterone, which inhibits ___ production during the menstrual cycle through ___ feedback
GnRH; negative
the hypothalamus produces _____, a tropic peptide hormone that acts on the anterior pituitary
gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH)
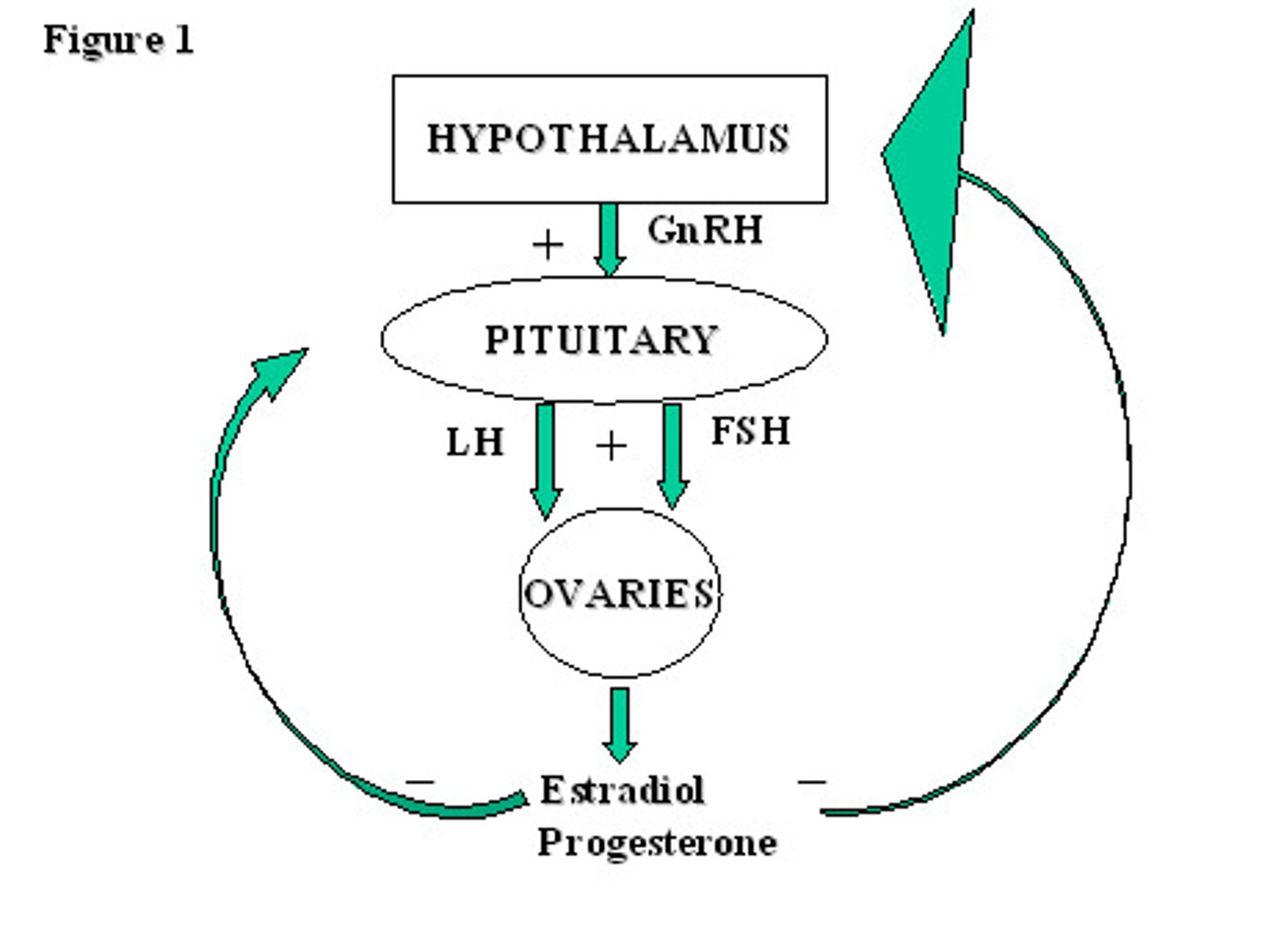
GnRH causes the release of _____ (peptide hormones) from the anterior pituitary gland
FSH & LH
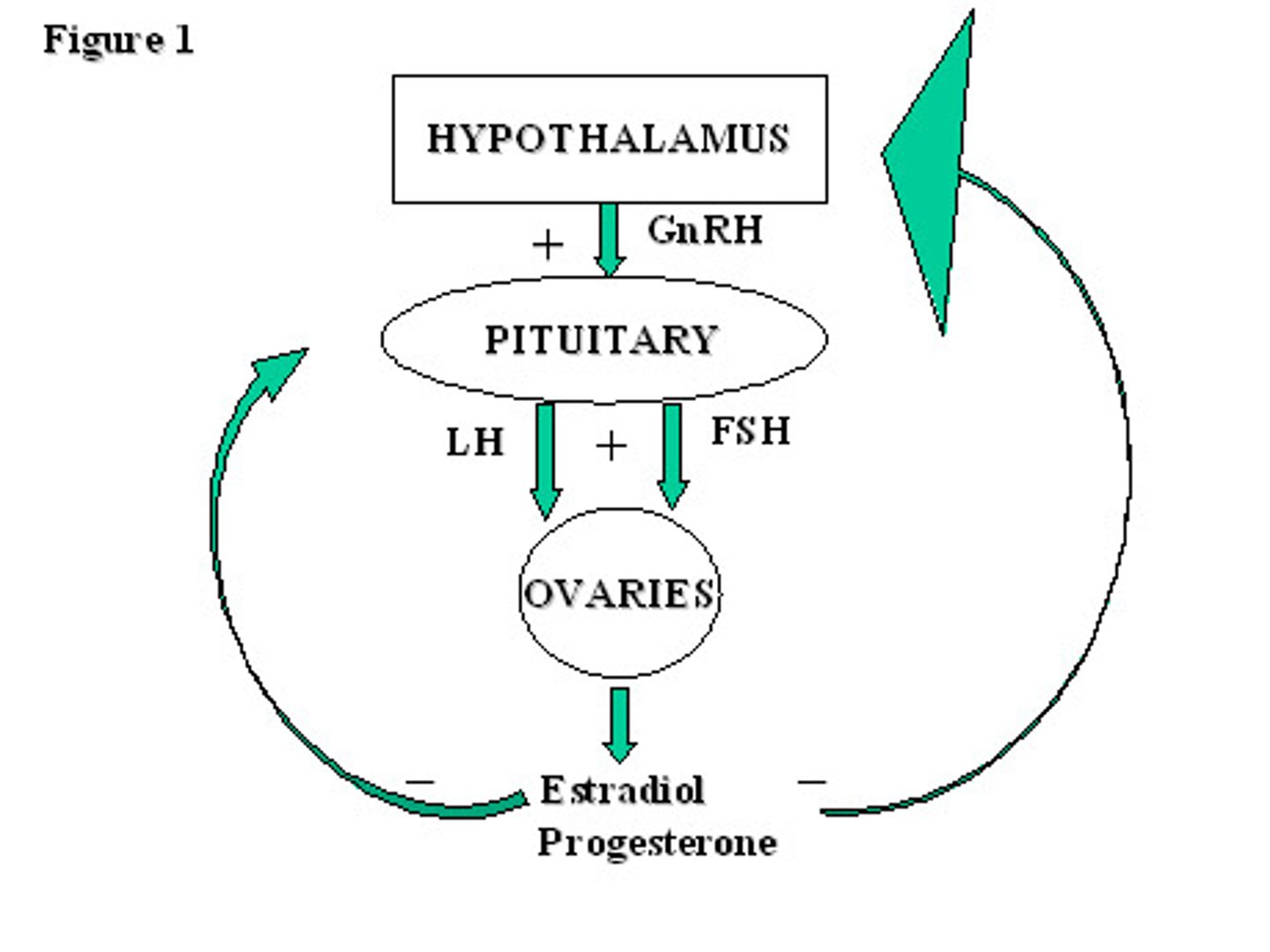
in the menstrual cycle, FSH binds to the _____ to cause follicular development
ovaries
during the follicular phase, the developing follicules release ____, causing the endometrium to thicken & causing a rapid ___ spike that leads to ovulation
estrogen; LH
increasing estrogen levels during the follicular phase stimulates a rapid spike in _____
LH (FSH to a lesser extent)
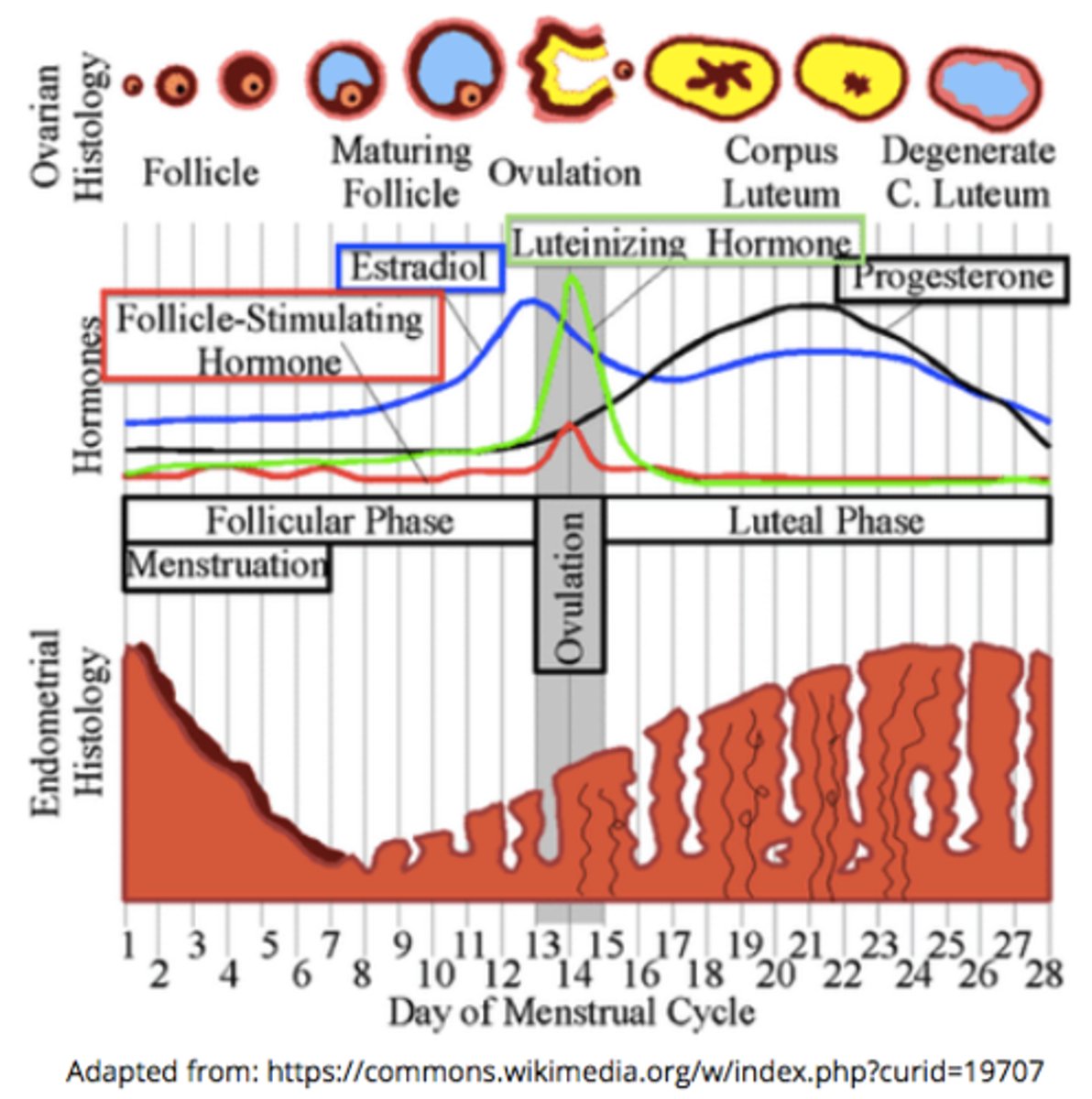
the spike in LH around day 15 of the menstrual cycle triggers _____
ovulation (release of the secondary oocyte from the Graafian follicle)
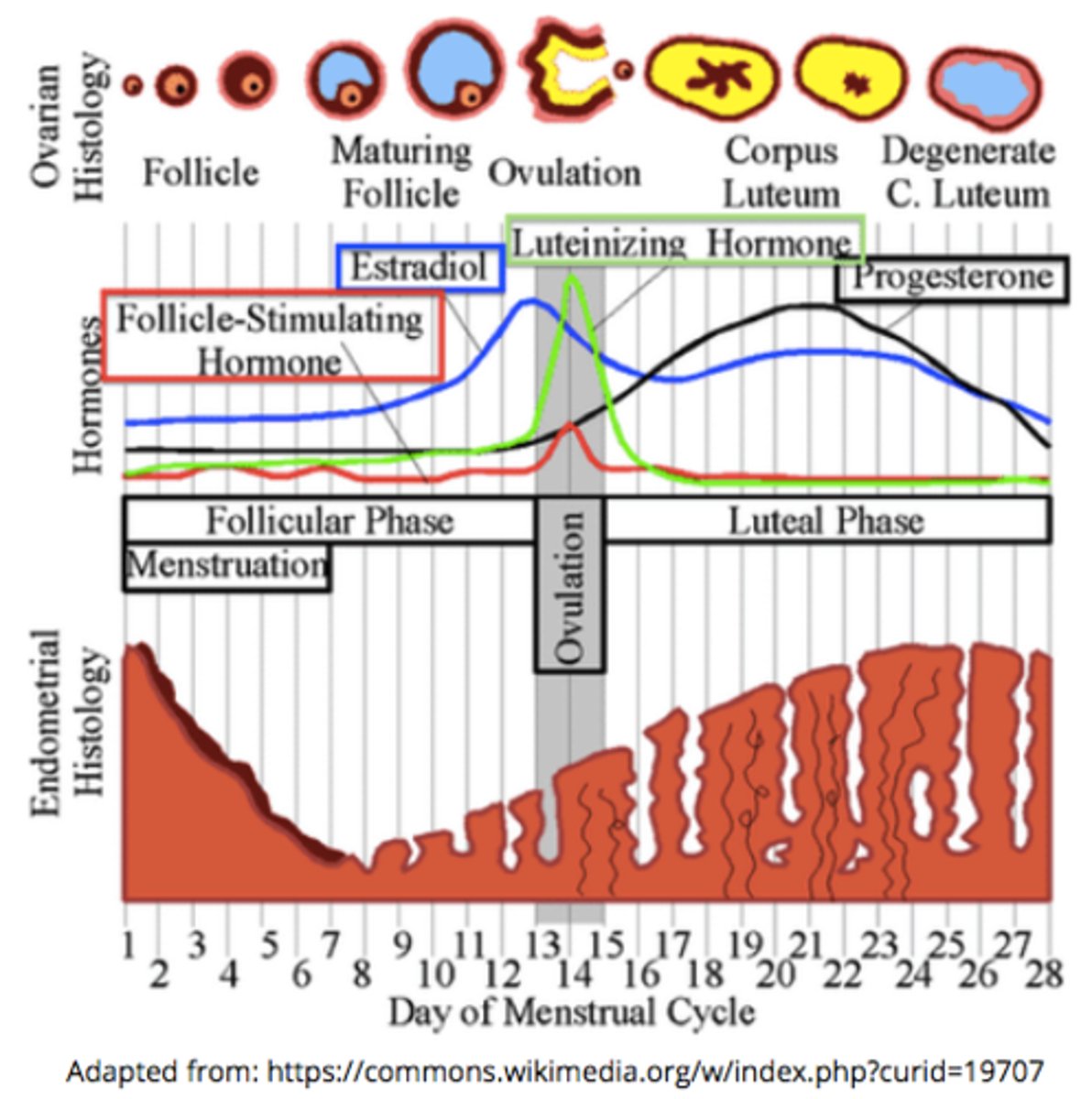
the _____ is where the secondary oocyte will release from during ovulation
Graafian follicle
what tissue becomes thicker and more vascularized during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle (thanks to estrogen)?
the endometrium (inner lining of the uterus)
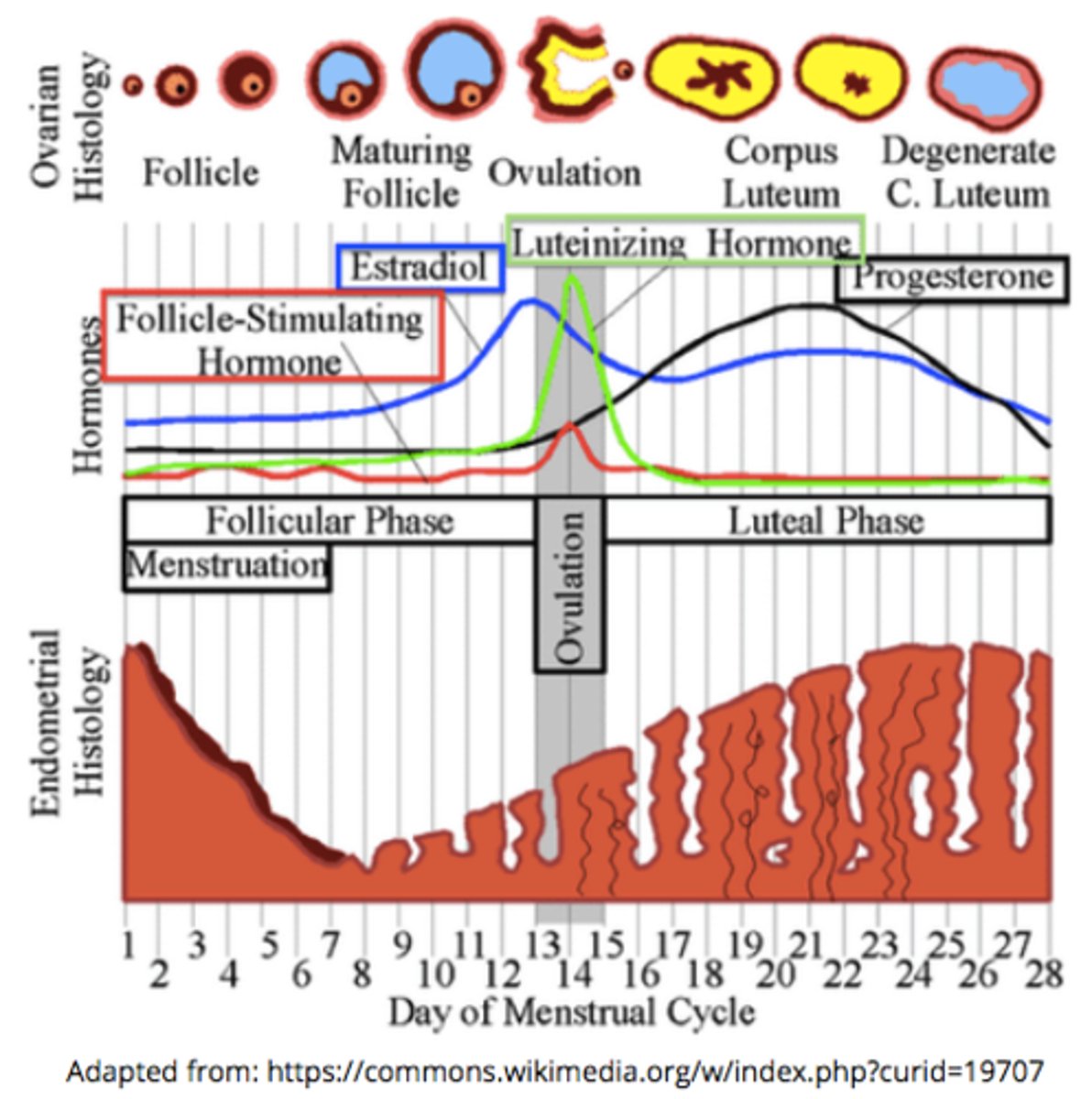
____ on oviduct catches the egg, and ____ act to sweep ovulated secondary oocytes into the oviduct
fimbriae; cilia
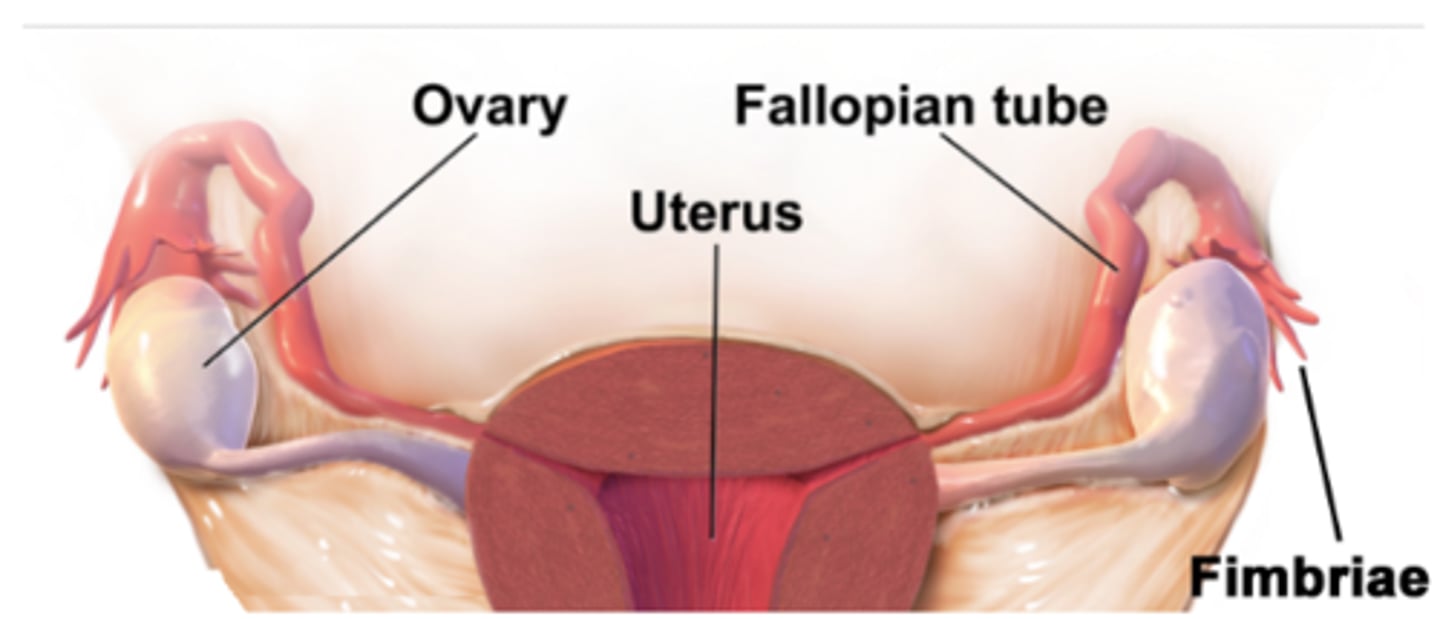
the corpus luteum produces _____ & some _____
progesterone; estrogen
the uterine lining thickens and prepares for ____ due to the production of progesterone & estrogen by the corpus luteum
implantation
which peptide hormones maintain the corpus luteum?
FSH and LH from the anterior pituitary
increased progesterone & estrogen during the luteal phase causes negative feedback to the hypothalamus/pituitary - what happens as a result of this negative feedback?
FSH & LH release decreases from the anterior pituitary, so the corpus luteum begins to degenerate
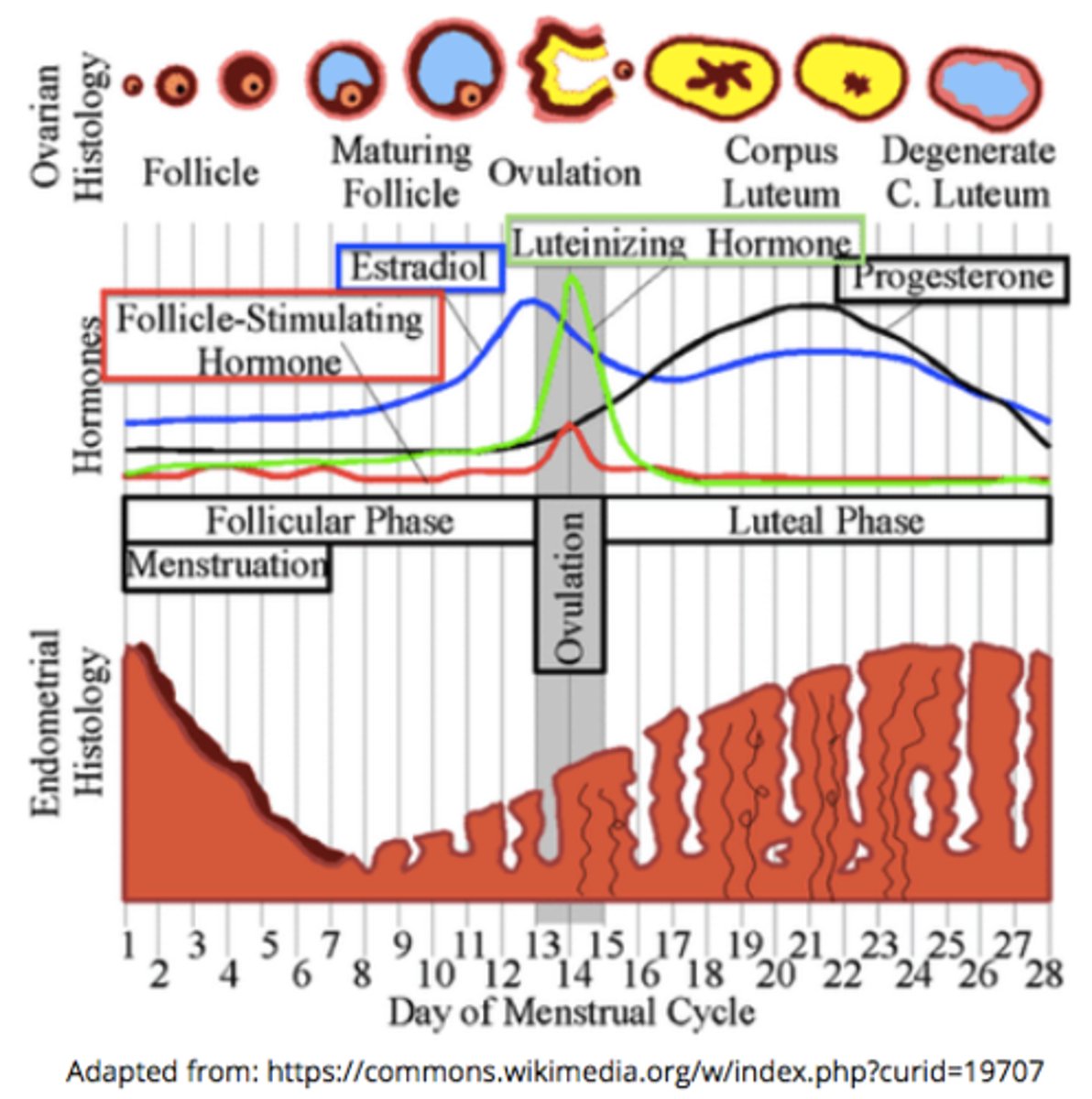
what happens if implantation does not occur?
the corpus luteum degenerates --> progesterone & estrogen decrease --> the endometrial lining sloughs off (menses)
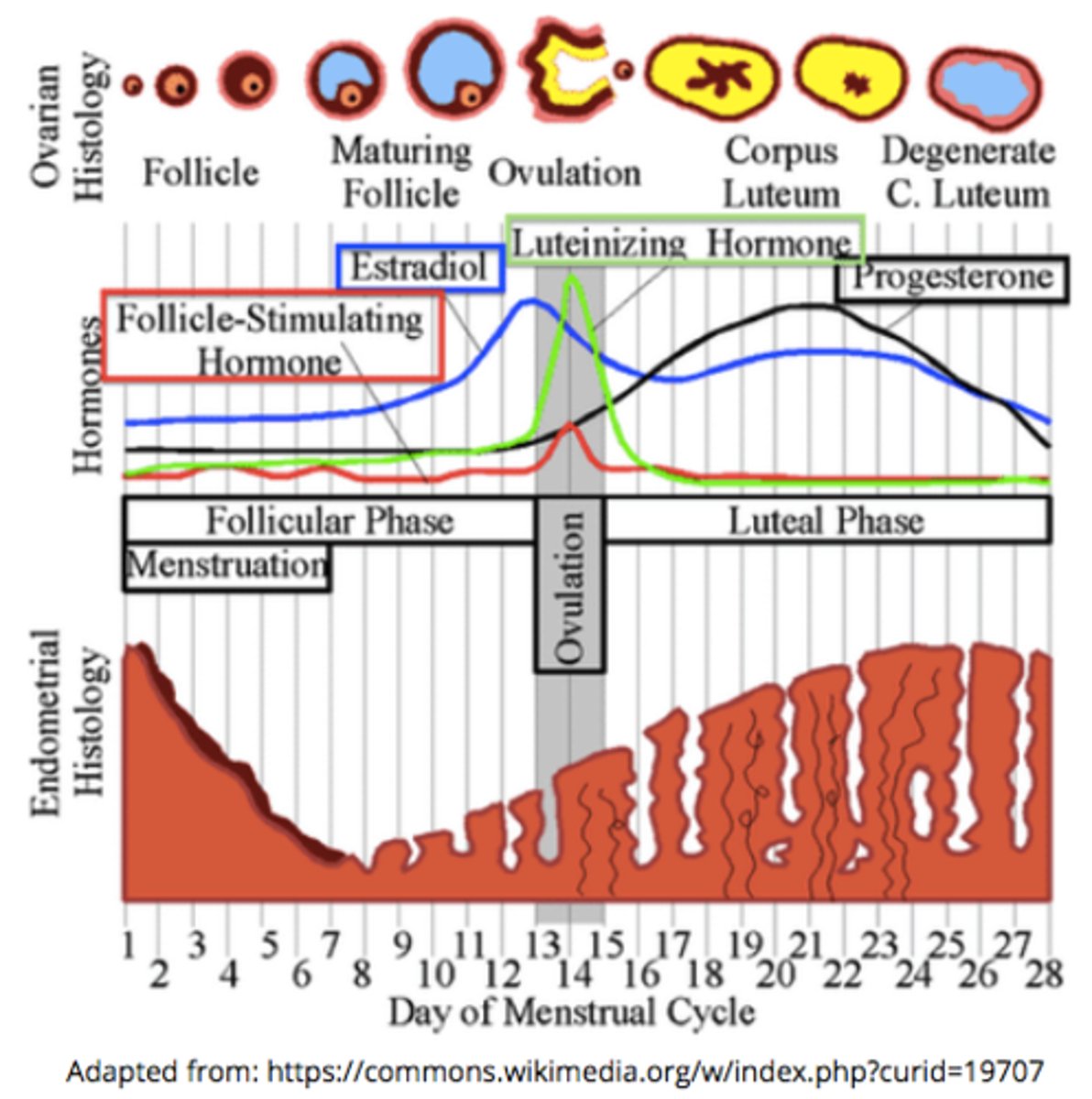
_____ is when the endometrial lining sloughs off
menses/menstruation
(beginning of the follicular phase)
what begins the next menstrual cycle?
a decrease in the amount of estrogen and progesterone from the previous cycle
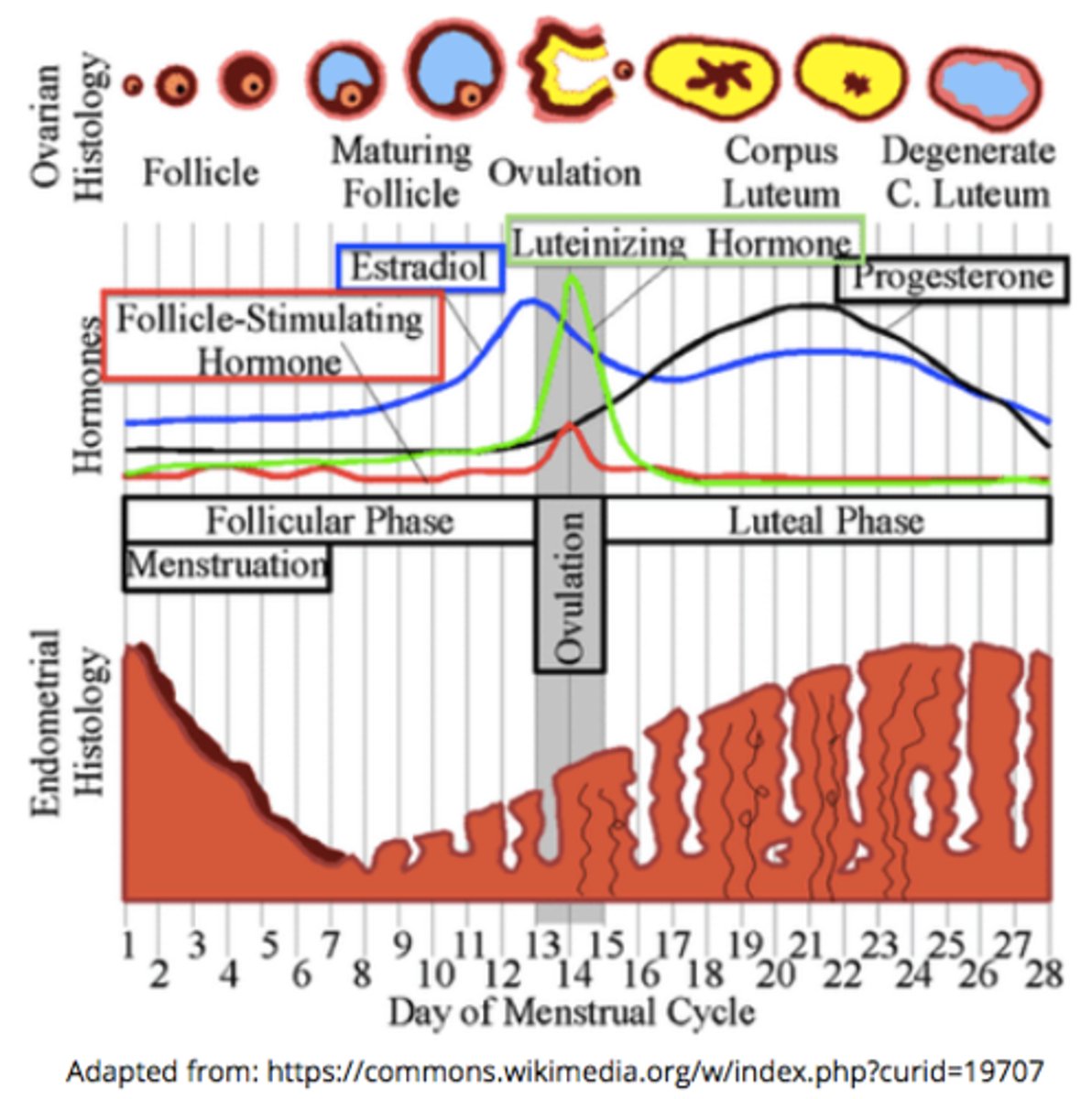
how does a decrease in estrogen and progesterone allow the next menstrual cycle to start?
the endometrial lining can no longer be maintained, and the hypothalamic/pituitary inhibition is lost
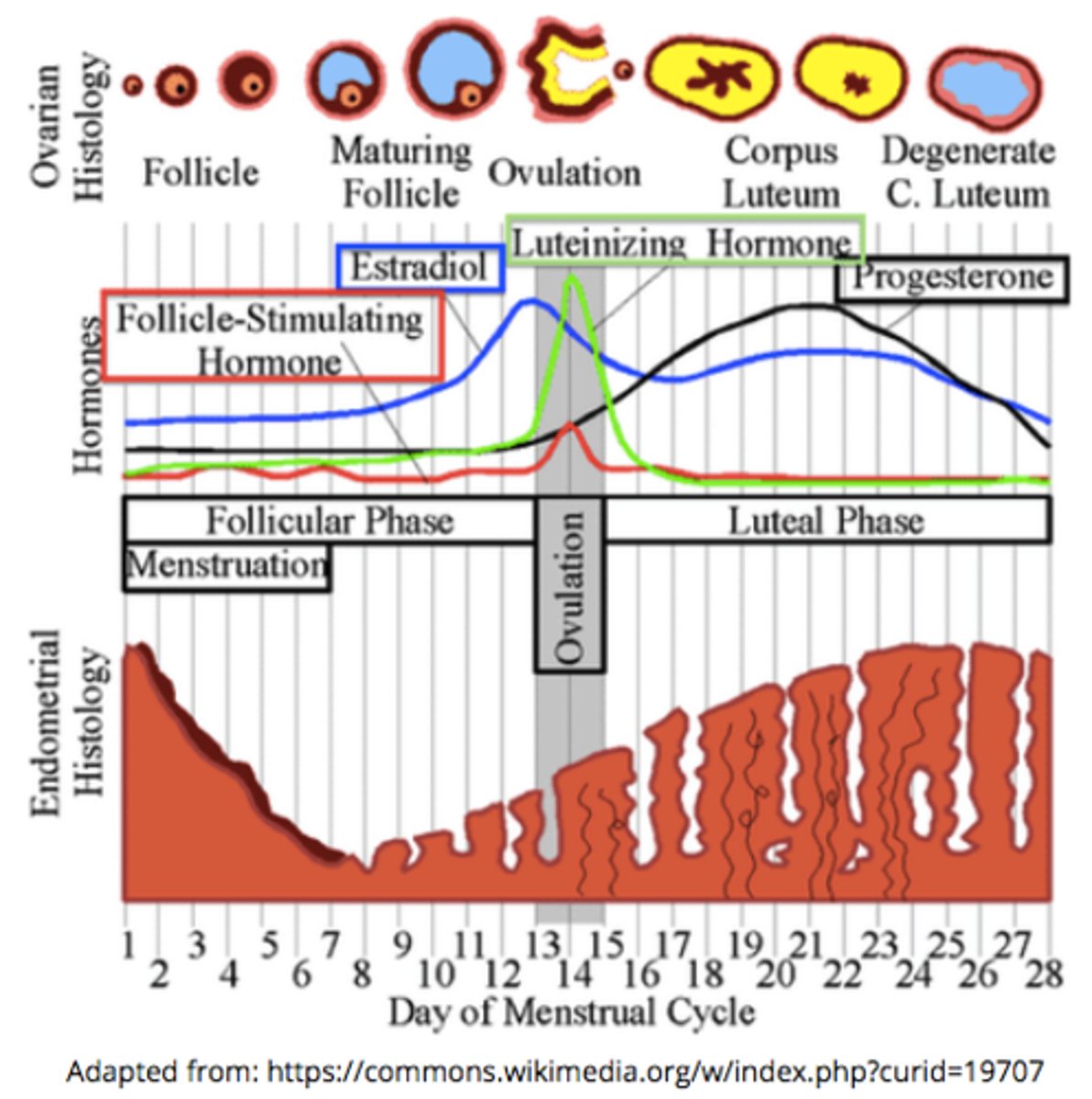
what happens if implantation does occur?
menstruation prevention due to HCG release