Parasitology 6.08-6.14
1/207
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
208 Terms
What is the common name for phylum nematoda?
round worm
What is the common name for phylum platyhelminths?
flatworm
What is the common name for phylum Acanthocephala?
thorny-headed worms
What is the common name for class monogenea and what is it under?
under phylum platyhelmiths (flat worm)
Anchor worms
What is the common name for class trematoda and what is it under?
under phylum platyhelmiths (flat worm)
flukes
What is the common name for class cestoda and what is it under?
under phylum platyhelmiths (flat worm)
tapeworm

what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms)?
procercoid

what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms)?
plerocercoid

what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms)? where is it found and describe it.
cysticercoid
found in arthropodan IH
enclosed scolex, not inverted
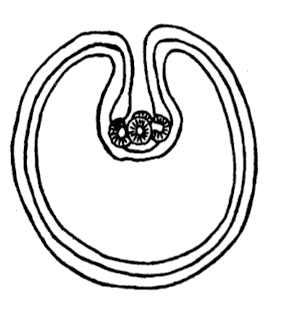
what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms)? where is it found and describe it.
cysticercus
found in vertebrate IH
single invaginated
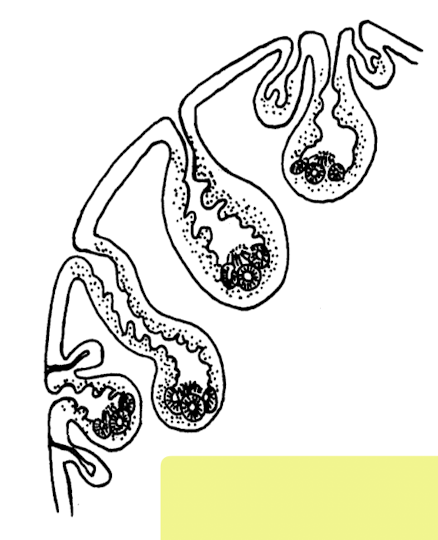
what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms)?
coenurus
found in vertebrate IH
multiple invaginated
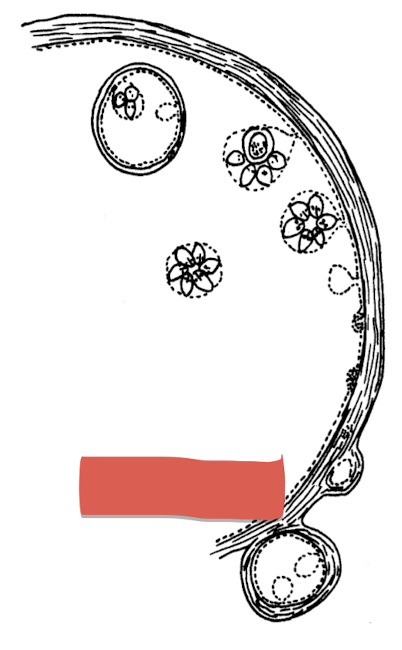
what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms)? where is it found
hydatid cyst
found in vertebrate IH
what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms)? what is the common name and how can you tell?
Taenia pisiformis adult
rabbit tapeworm
scolex with four suckers and a rostellum with two rows of hooks
rectangular segment
shiny white strobila
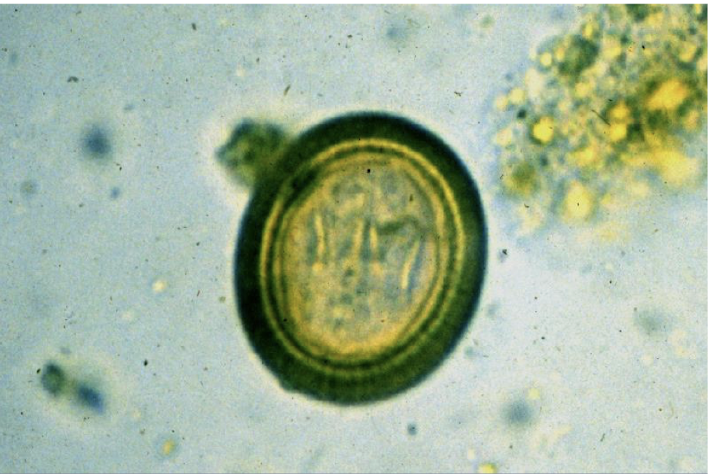
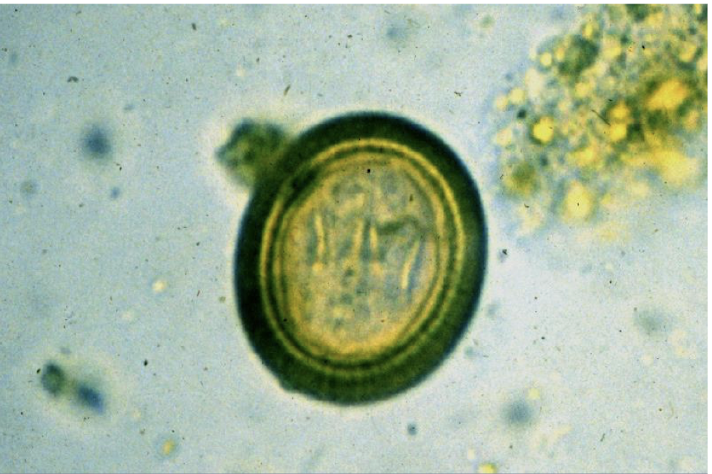
what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms)? what is the common name and how can you tell?
taeniid type egg
taenia pisiformis (rabbit tapeworm)
thick radially striated shell
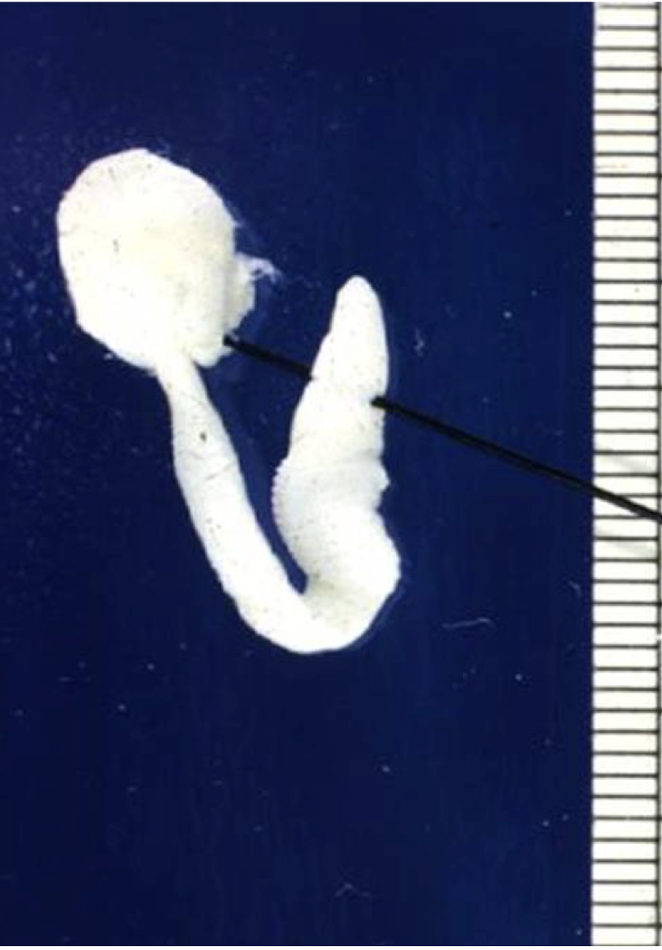
what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms)? what is the common name and how can you tell?
cycticercus pisiformis
cysticercus of Taenia pisiformis (rabbit tape worm) (larva)
fluid filled bladder with an invaginated scolex
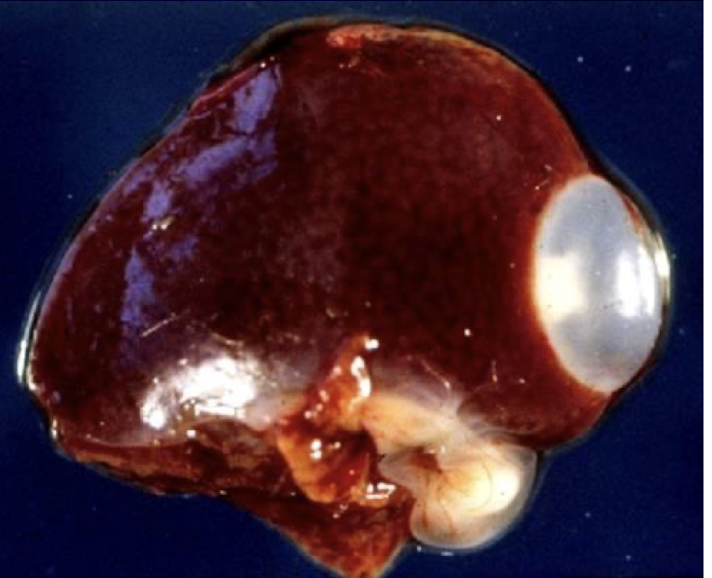
what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms)? what is the common name and how can you tell?
larva of rat tapeworm
strobilocercus of Taenia taeniaeformis
partially developed cysticercus with evaginated scolex and small strobila
What is this egg and species have this egg?
taeniid type egg
Taenia pisiformia
Taenia taeniformis
taenia spp.
echinococcus granulosus
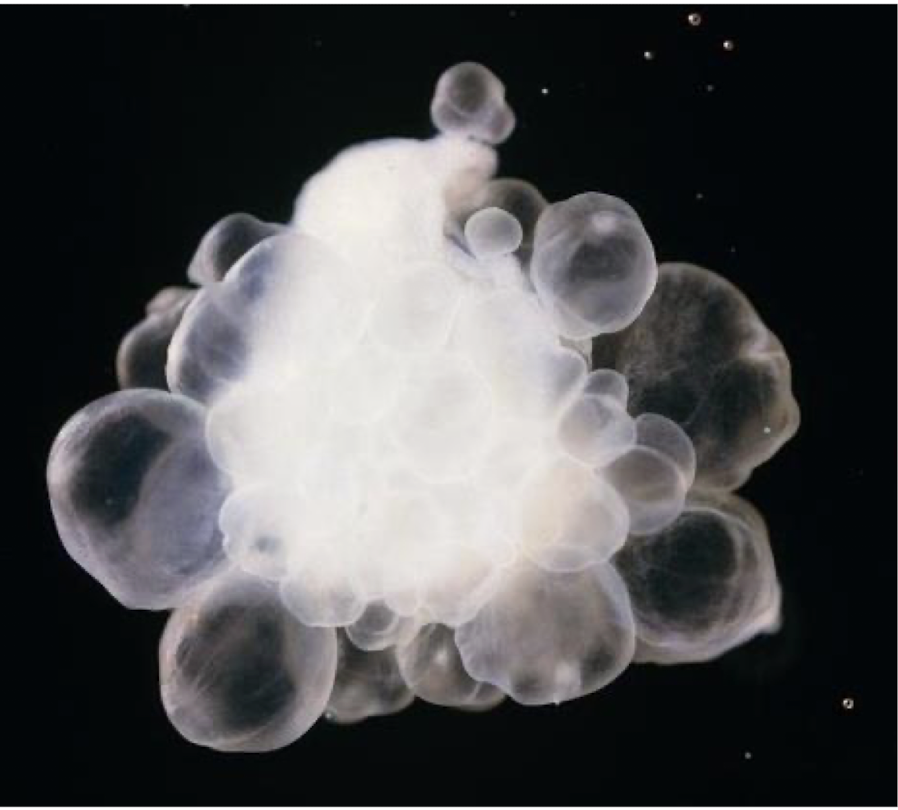
what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms) and what is the structure shown
Taenia crassiceps
budding cysticercus
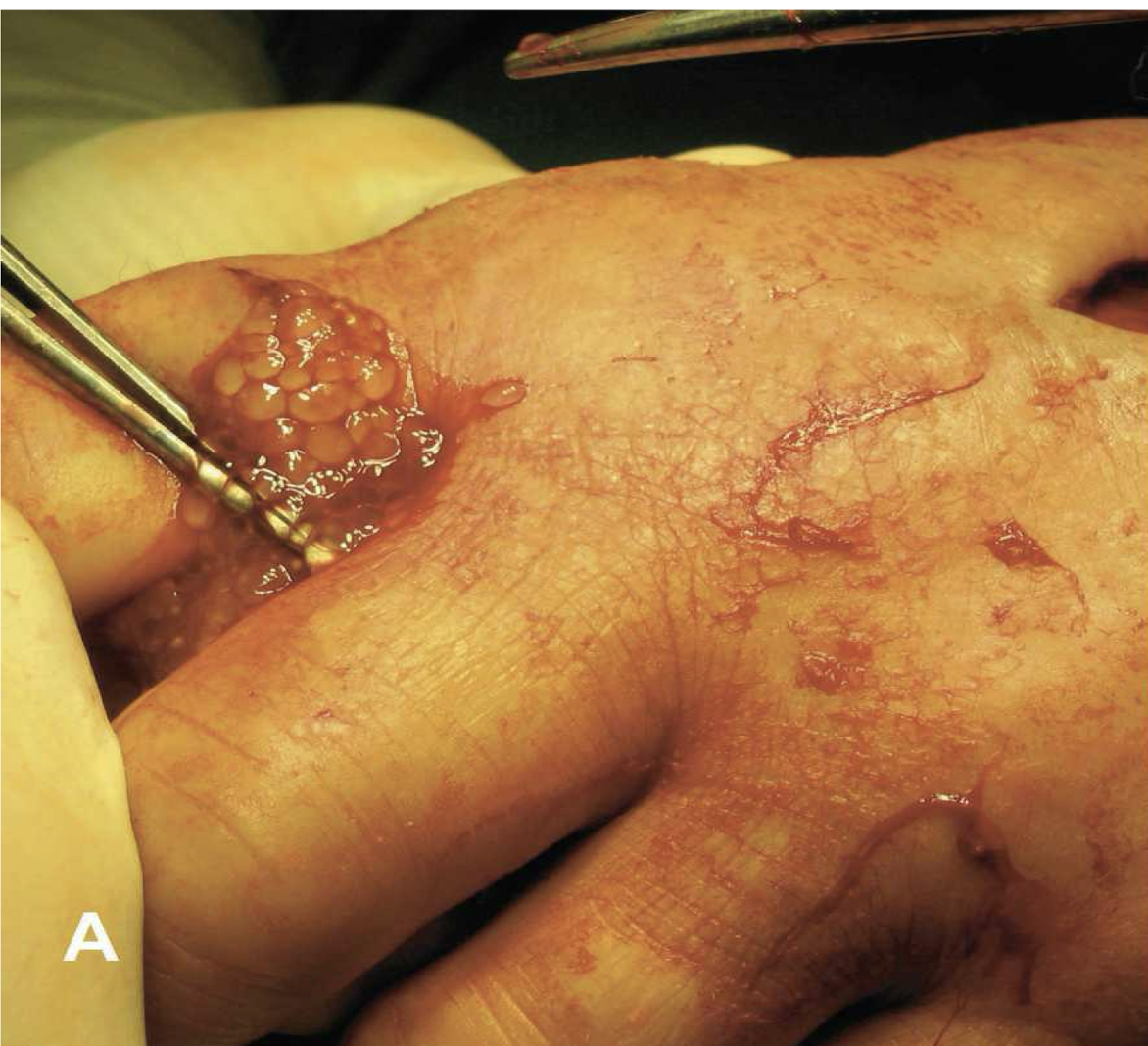
what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms)? what is the common name and how can you tell?
Taenia saginata adult
beef tapeworm
unarmed scolex with four suckers
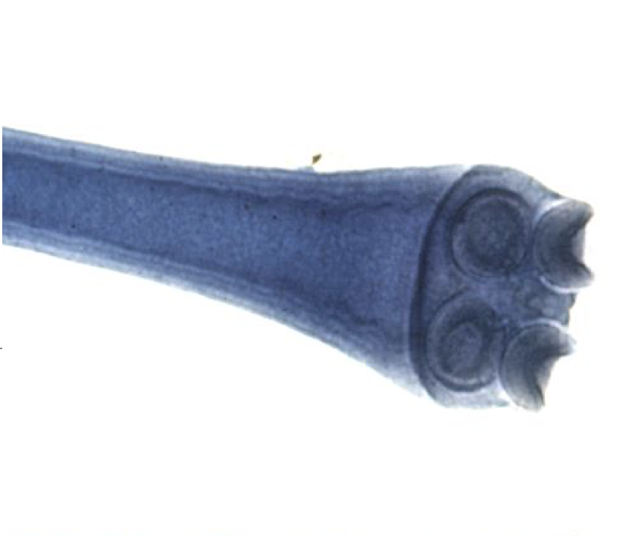
what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms)? how can you tell?
Echinococcus granulosus adult
3 or 4 sefments with the posterior segment greater than one half the length of the parasite
(scolex with four suckers and a rostellum with 2 rows of hooks)
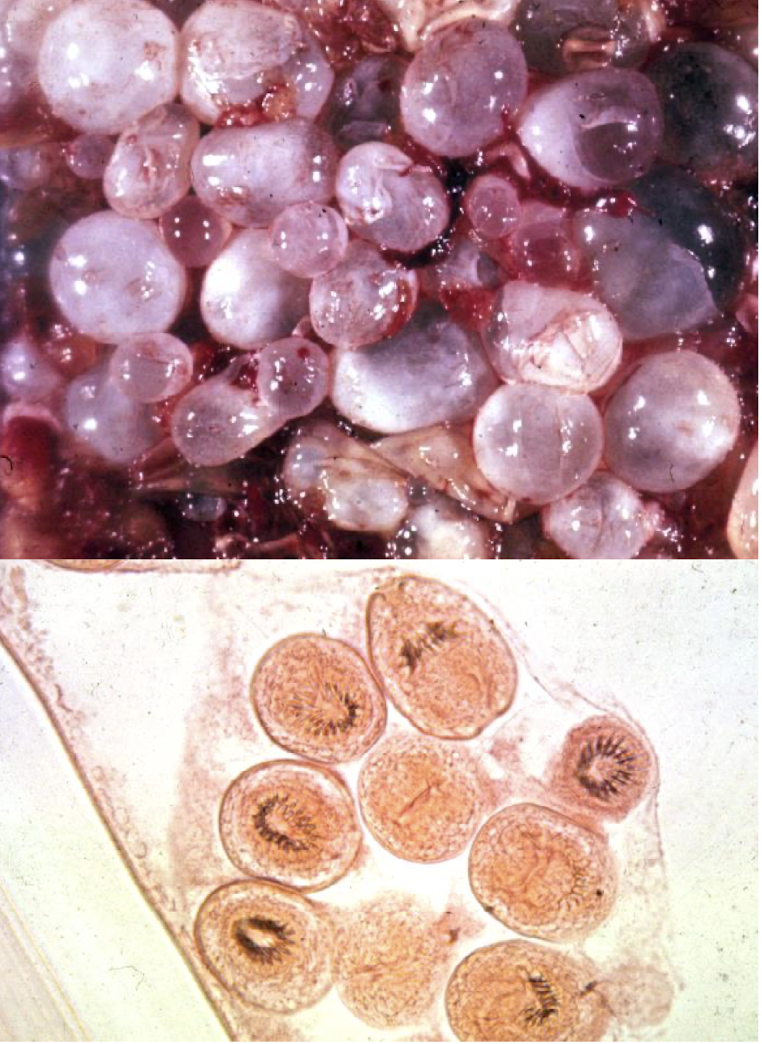
what is this structure in terms of cestodes (tapeworms) and what species is it?
Echinococcus granulosus larva
hydatid cyst
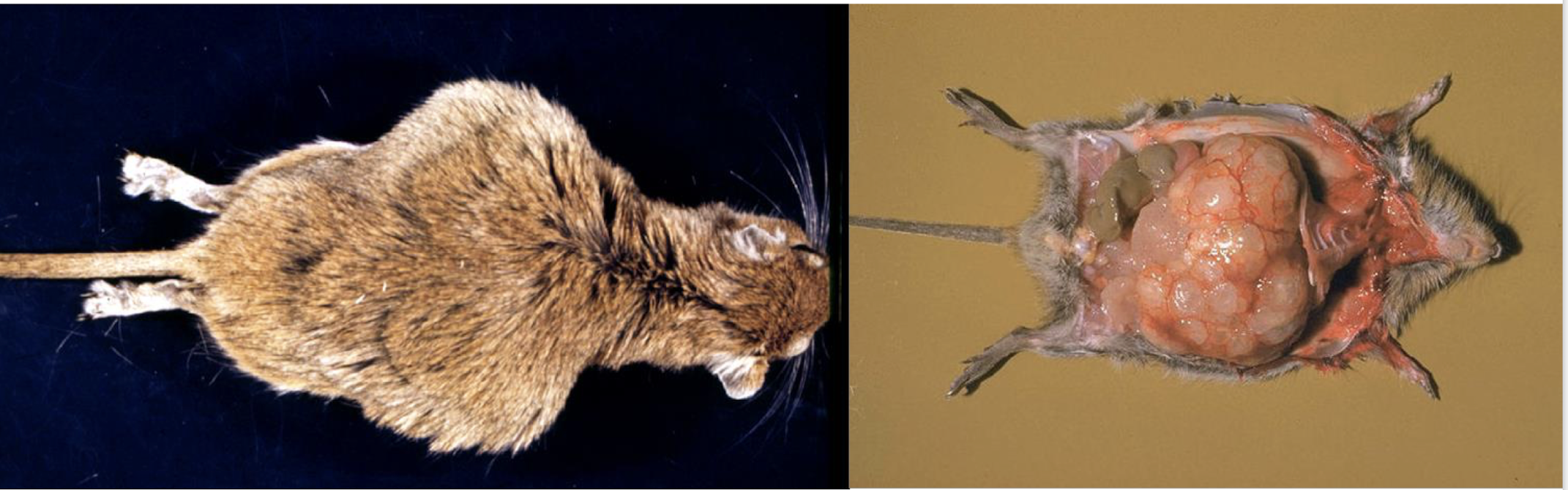
What caused this and how?
echinococcus multilocularis
massive replication (exogenous budding and metastasis)
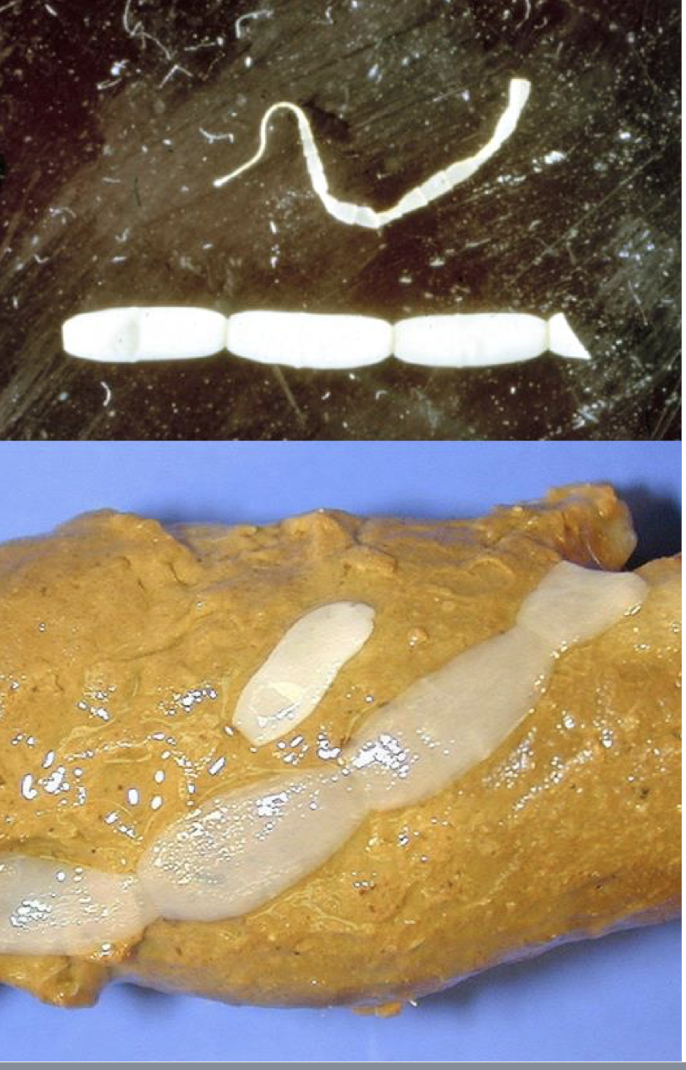
what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms)? what is the common name and how can you tell?
dipylidium caninum (flea tapeworm) adult
double pored tapeworm of dogs
fresh segments look like cucumber seeds
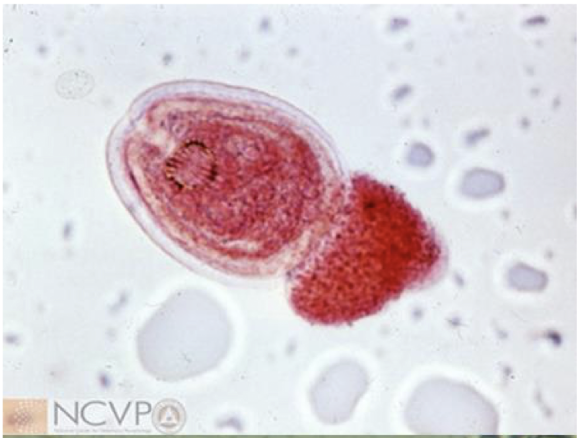
what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms)? what is the common name and how can you tell?
dipylidium caninum (flea tapeworm) larva
double pored tapeworm of dogs
cysticercoid encysted in hemoceol of insect IH
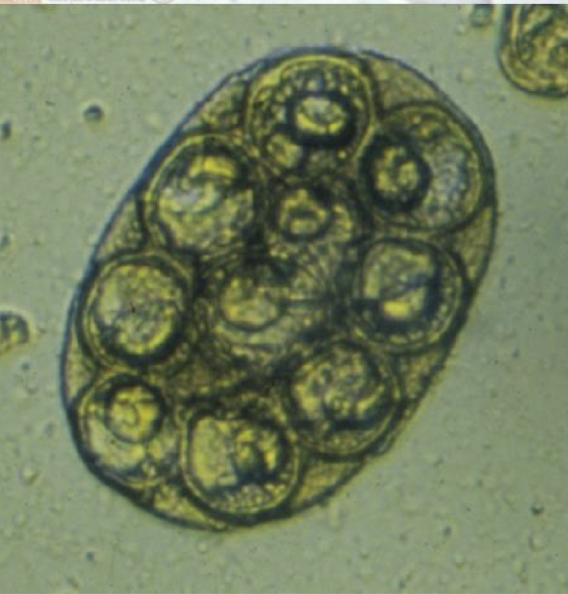
what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms)? what is the common name and how can you tell?
dipylidium caninum (flea tapeworm) egg
double pored tapeworm of dogs
eggs (oncosphere) in packets
each oncosphere in thick unstriated shell or embryophore
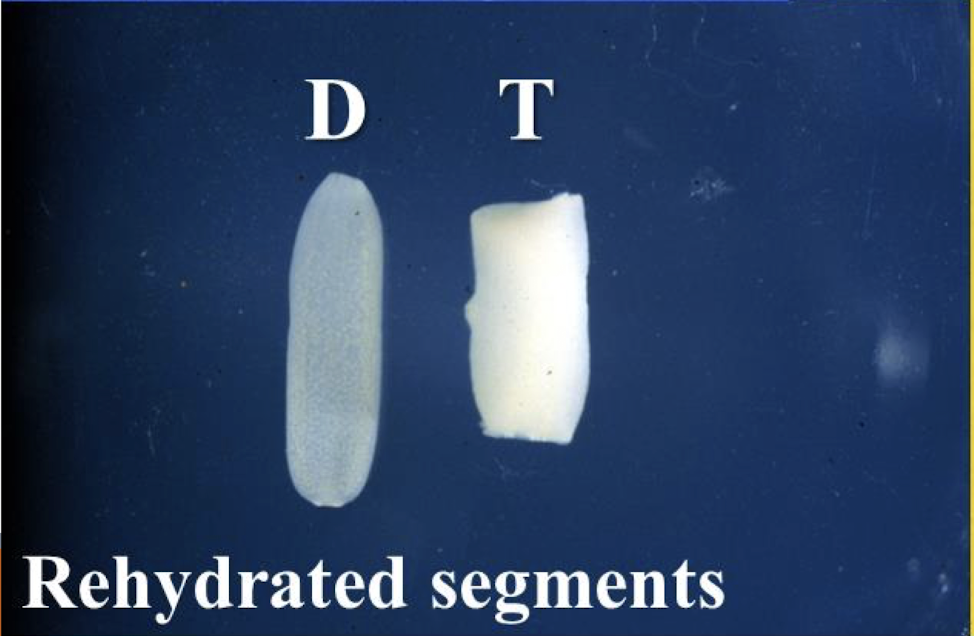
how do you know which segment belongs to which species?
trapezoidal is taenia spp.
cucumber seed is dipylidium caninum
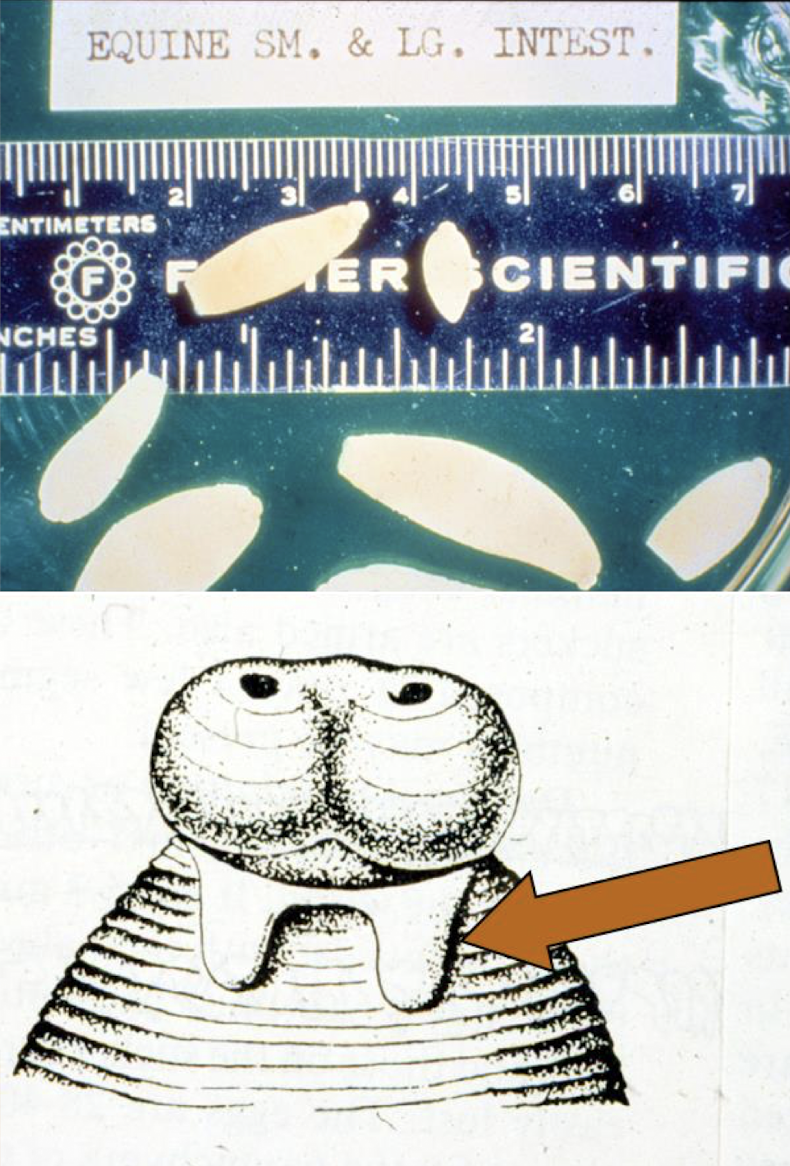
what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms)? what is the common name and how can you tell?
anoplocephala perfoliata adult
creamy white, wedge shaped
scolex has lappets (bib like structure)
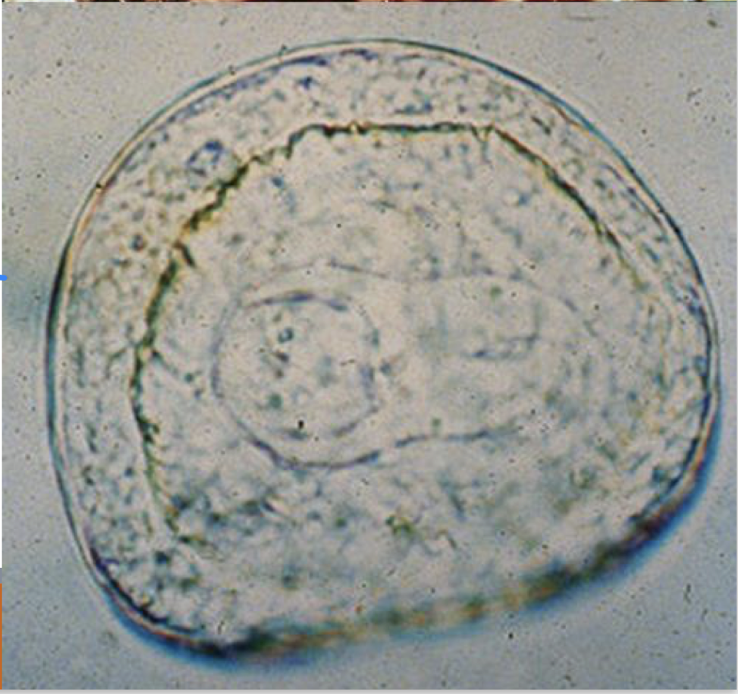
what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms)? how can you tell?
anoplocephala perfoliata egg
chocolate covered cherry shaped
thick shelled
a spair of pring like processes (pyriform apparatus)
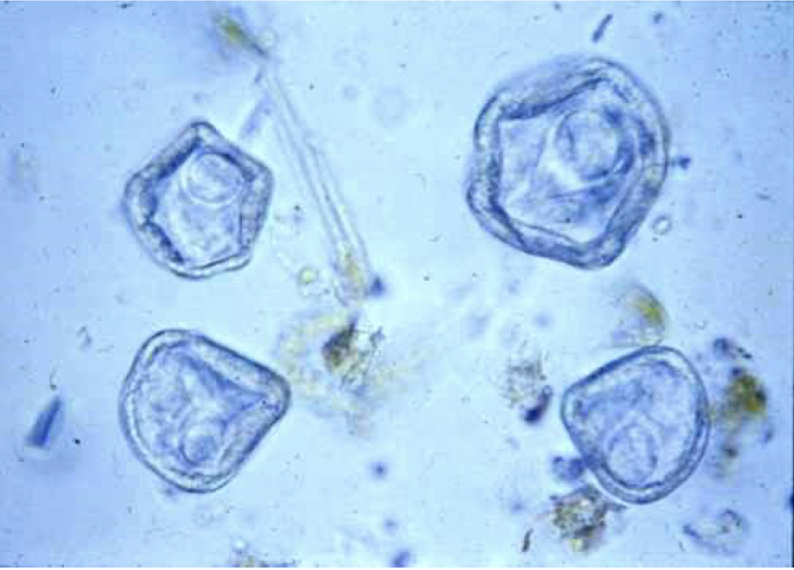
what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms)? how can you tell?
moniezia spp. eggs
triangular to square
thick shelled
pyriform apparatus
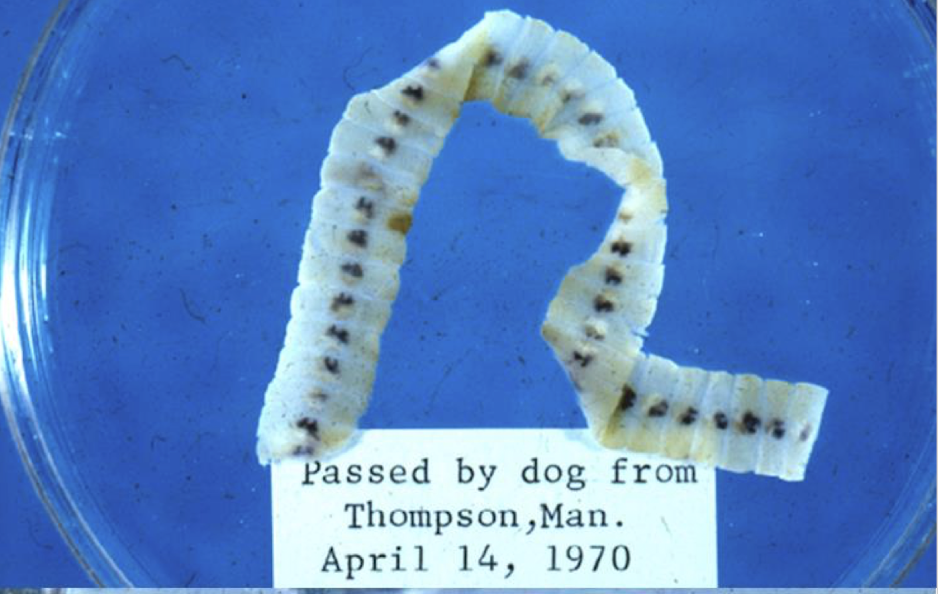
what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms)? what is the common name and how can you tell?
Diphyllobothrium latum adult
scolex has a pair of bothria (groove)
large strobila
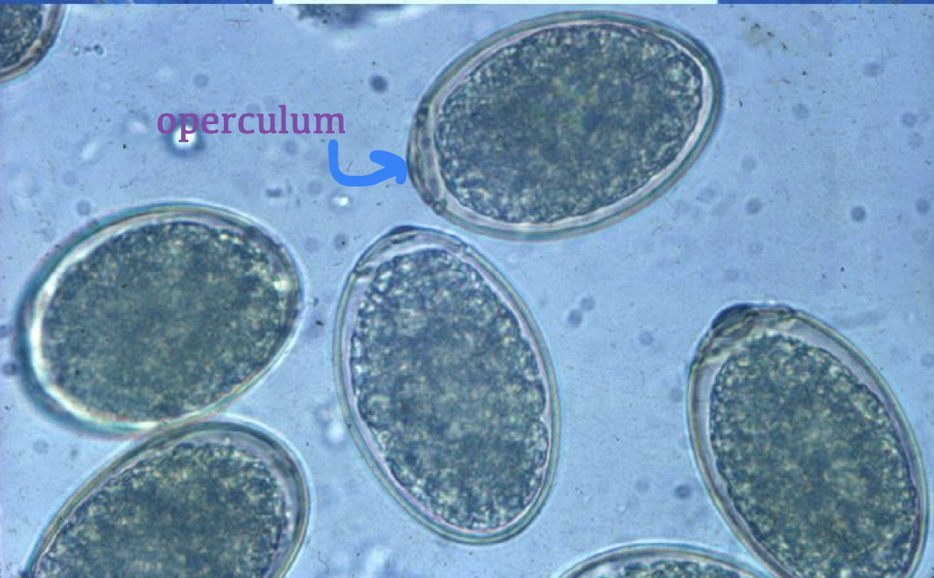
what is this in terms of cestodes (tapeworms)? how can you tell?
Diphyllobothrium latum eggs
operculate, light brown egg
ciliated hexacanth embryo called a coracidium
Describe major characteristics of cyclophyllidean cestode egg
spherical or oval
30-50 um
thick, usually striated outer shell
shell surrounding hexacanth embryo
no operculum
ingestion is the mode of transmission
How do humans become infected with Taenia crassiceps? and what is the medical importance?
ingestion of tapeworm egg from dog feces
cysticercus can occur in the eye and cause blindness
Describe the zoonotic and human medical importance of Taenia saginata and the means through which humans become infected?
normal human parasite
infection through eating uncooked beef containing cysticercus
Is Echinococcus granulosus zoonotic?
Yes
Describe the zoonotic and human medical importance of echinococcus granulosus and the means through which humans become infected
people can have hydatidosis after ingestion of an egg passed in the feces of the dog
expanding hydatid is a space occupying lesion causing pressure necrosis
rupture of hydatid can cause anaphylactic shock and death
Describe the zoonotic and human medical importance of echinococcus multilocularis and the means through which humans become infected
people can have alveolar hydatidosis after ingesting and egg passed in the feces of the dog.
expanding and invasive alveolar hydatid.
metastases act as a space occupying lesion which causes pressure necrosis of surrounding tissue
general fatal in spite of treatment
Whats the DH and IH of Dipylidium caninum?
DH: Dogs, cats, rarely humans
IH: primarily fleas, also biting lice
Describe the zoonotic and human medical importance of Diphyllobothrium latum and the means through which humans become infected
1st IH is copepod (procercoid) → 2nd IH is fish (pleurocercoid) → DH is fish eating mammals including humans
competition between parasite and host for Vitamin B12, cause anemia in host
which species have taeniid type eggs?
Taenia spp. and Echinococcus granulosus
Which of the species with taeniid type eggs are zoonotic?
Taenia solium
Taenia saginata
Echinococcus granulosus
what is the clinical implication for the dog if we find a taeniid type of eggs in the dog feces?
indicate an active tapeworm infection
dog is a definitive host
what is the clinical implication for the human if we find a taeniid type of eggs in the dog feces?
need to differenciate between Taenia spp. (low zoonotic risk) vs Echinococcus spp. (high zoonotic risk)
What’s the life cycle of Taenia pisiformis (rabbit tapeworm)?
predator-prey life cycle
eggs released from segments are ingested by the IH (rabbit)
hexacanth larva hatches and migrates to the peritoneal cavity or liver to mature to a cysticercus
when a dog eats the rabbit, the scolex in the cysticercus evaginates, attaches to the gut and begins to form strobila
PPP 6-8 weeks
How do you control and treat Taenia pisiformis (rabbit tapeworm)?
specific cestodicides - praziquantel (Droncit), nitroscanate (Lopatol), epsiprantel (Cestex)
prevent hunting to block transmission
What’s the life cycle of Taenia taeniaeformis (rat tapeworm)?
typical predator-prey life cycle
eggs released from segments are ingested by the IH (rat)
hexacanth larva hatches and migrates to the peritoneal cavity or liver to mature to a cysticercus
when a cat eats the rat, the scolex in the cysticercus evaginates, attaches to the gut and begins to form strobila
PPP 6 weeks
How do you control and treat Taenia taeniaeformis (rat tapeworm)?
specific cestodicides - praziquantel (Droncit), nitroscanate (Lopatol), epsiprantel (Cestex)
prevent hunting to block transmission
What’s the life cycle of Taenia saginata (beef tapeworm)?
eggs released from segments are ingested by the IH (cattle)
hexacanth larva develops and penetrate small intestine to skeletal and cardiac muscle
second stage larva (cysticercus) are infective in 10-12 weeks and remain viable for 9 - 24 month.
People ingest uncooked meat and gets infected.
cysticercus evaginates and attaches to the small intestine and begin to from strobila
PPP 3.5 months
How do you control Taenia saginata (beef tapeworm)?
full cook the meat before eating
describe the life cycle of Taenia crassiceps
predator-prey cycle (foxes and groundhogs)
zoonotic threat if dog becomes infected through hunting
what is the control of Taenia crassiceps?
specific cestodicides - praziquantel (Droncit), nitroscanate (Lopatol), epsiprantel (Cestex)
precent hunting to block transmission
describe the life cycle of Echinococcus granulosus
predator and prey cycle
Sylvatic moose and wolf
adult infect the small intesine of the wolf
immature stages found in the liver and other organs of the moose
PPP: 6 weeks
What is the control and treatment of Echinococcus granulosus for both dog and human
Dog
praziquantel
human
cyst usually identified radiographically and commonly misdiagnosed as tumour
surgical intervention + anhelmintics
describe the life cycle of Echinococcus multilocularis
predator prey cycle
sylvatic fox and rodent
adult infect the small intestine of the fox
immature stages found in the liver and other organs of the rodent
PPP: 6 weeks
What is the control and treatment of Echinococcus multilocularis for both dog and human
Dog
praziquantel (Droncit)
human
cyst usually identified radiographically and commonly misdiagnosed as tumour
surgical removal of alverolar hydatid cyst is difficult and can be unsuccessful (fatal disease)
Describe the life cycle of Dipylidium caninum (flea tapeworm)
eggs usually passed within segments (MOTILE)
liberated eggs are ingested by flea larvae
hexacanth embryo hatches from embryophore and penetrates into body cavity of flea
cysticercoid matures there (survive metamorphosis)
When adult flea is ingested, scolex attaches to gut and strobilla matures
PPP: 2-3 weeks
How to control and treat Dipylidium caninum?
cestocides - e.g. praziquantel (droncit), epsiprantel (Cestex)
flea control to reduce transmission
Describe the life cycle of Anoplocephala perfoliata
eggs released from segments are ingested by the IH (oribatid mite)
hatches and the hexacanth larva develops into second stage larva (cysticercois)
equid ingest infected mite, scolex from immature tape worm attach to mucosa of the intestine and forms strobila
PPP: 6 weeks
Describe control and treatment of Anoplocephala perfoliata
strongid P or strongid T
describe the life cycle of moniezia spp.
eggs (feces) → oribatid mite → ruminant
PPP: 6 weeks
what is the treatment of moniezia spp.
albendazole
Describe the life cycle of Diphyllobothrium latum
1st IH copepod (procercoid) → 2nd IH fish (pleurocercoid) → DH fish eating mammals
What is the treatment of Diphyllobothrium latum
No cestodicides have label claim but can try praziquantel
what is the common name for Nematoda?
roundworms
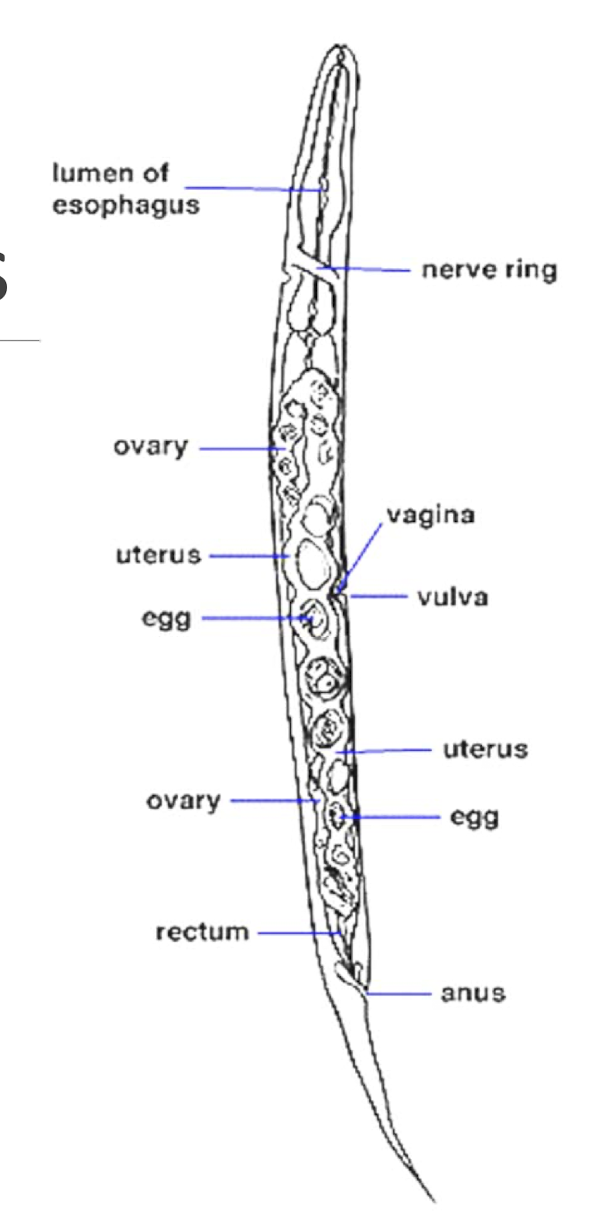
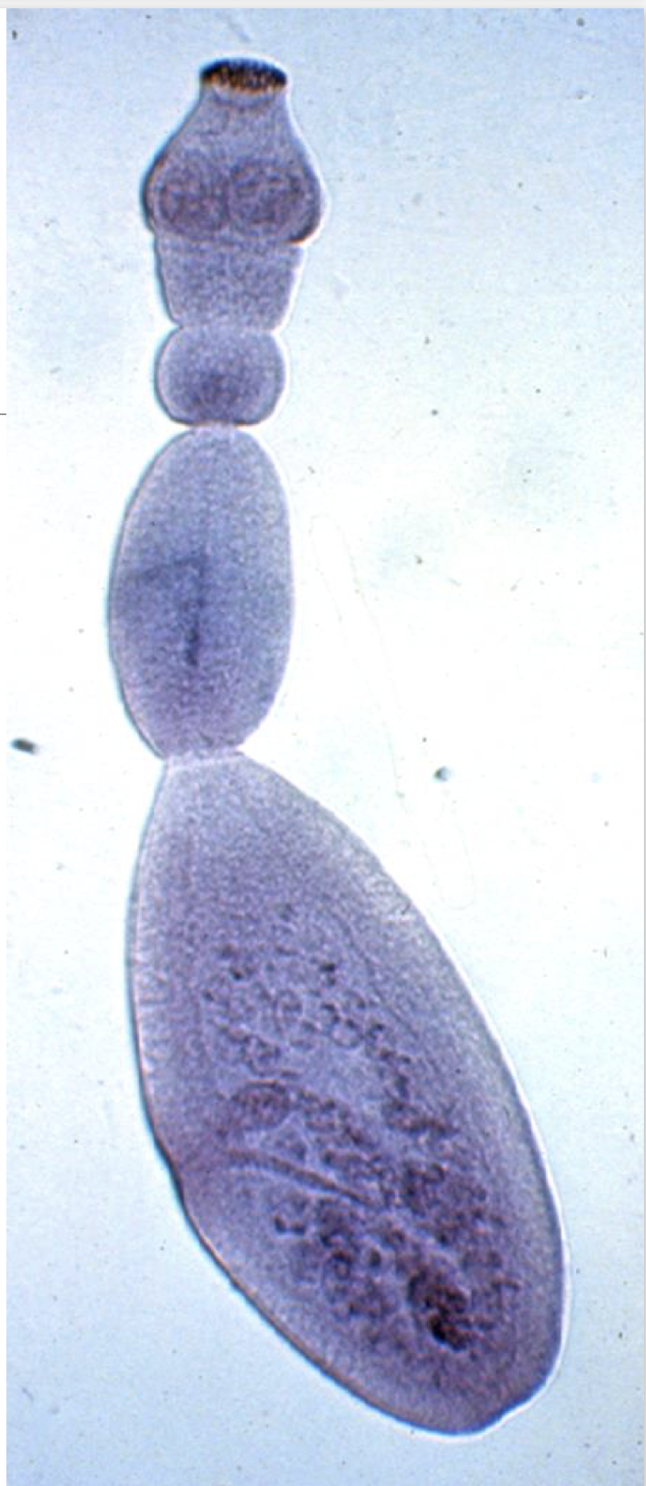
What is this
female nematodas (roundworms)
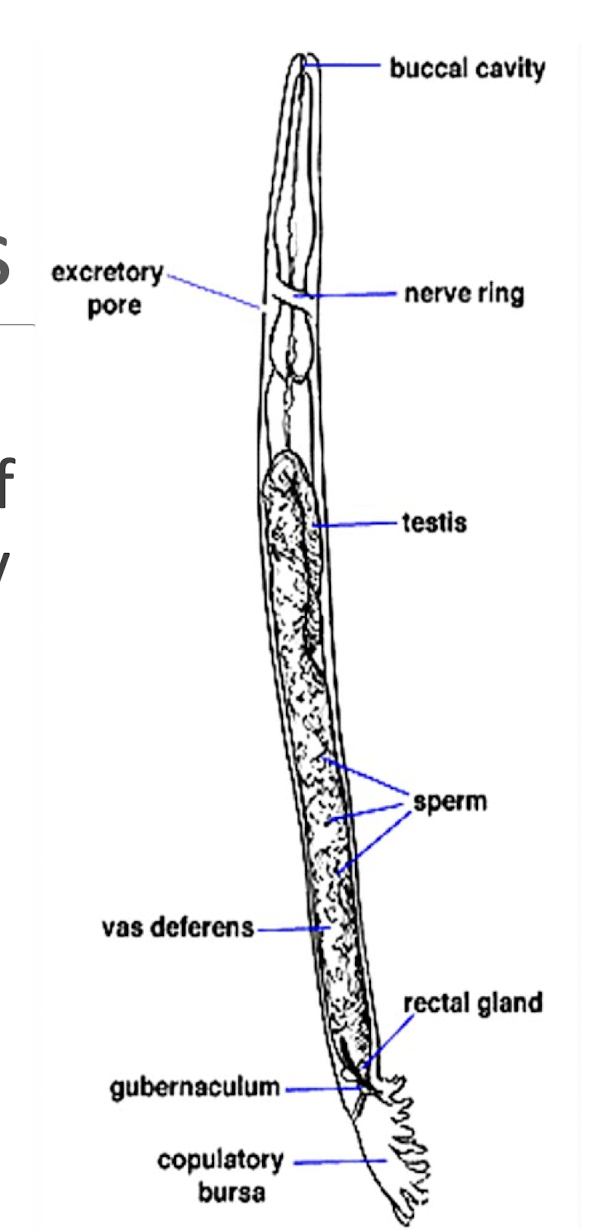
What is this?
male nematodes (roundworms)
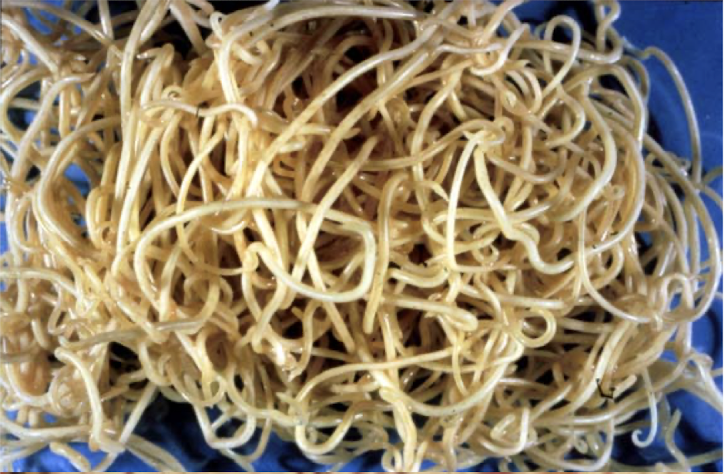

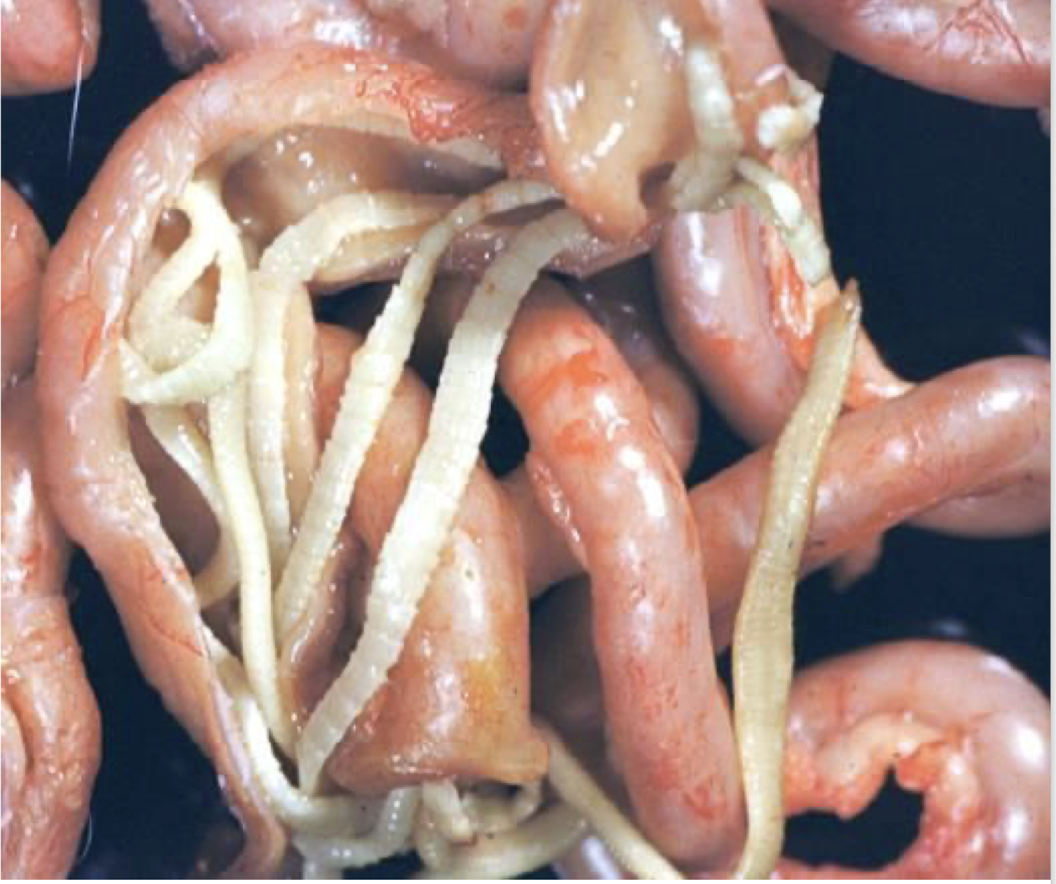
What is this and why?
adult Toxocara canis
Large and white
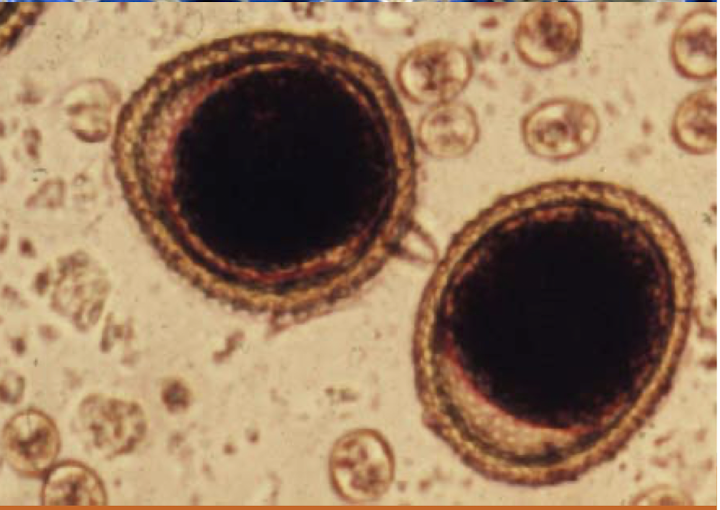
What is this and why?
Toxocara canis egg
thick shelled
pitted egg containing a single larva
dark brown
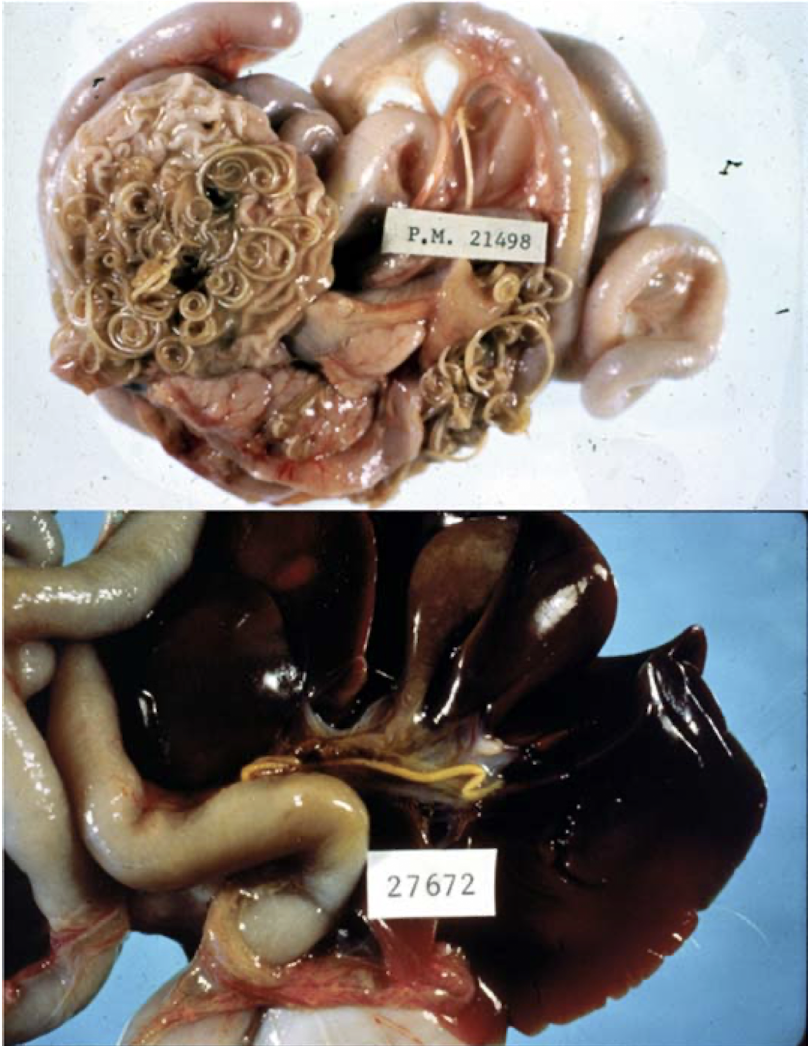
this is from a dog with painful stomach, worms are foudn at bile ducts, what species can this be?
Toxocara canis
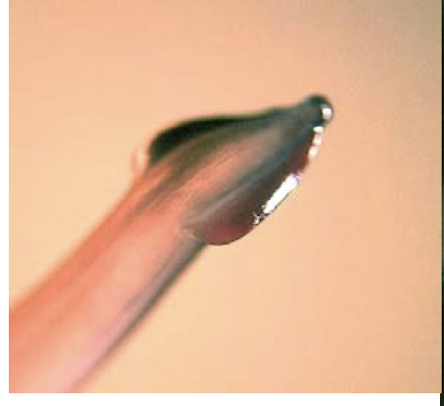

What is this and why?
toxocara cati
cervical alae (arrow head)

What is this and why?
toxocara cati
cervical alae (arrow head)
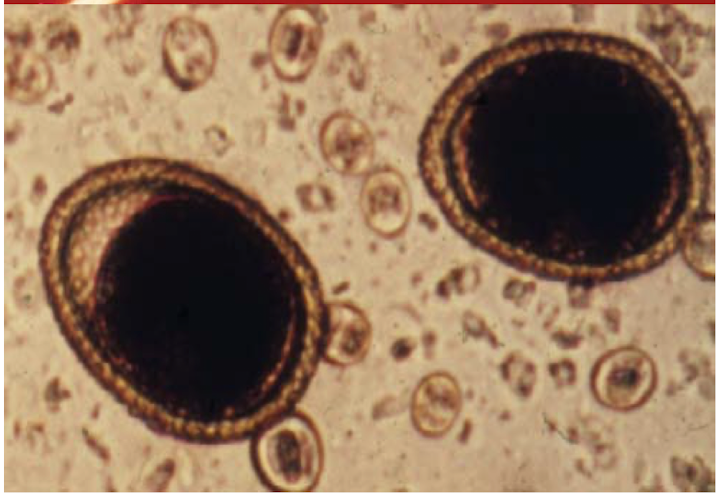
What is this and why?
eggs of toxocara cati
thick shell
outter shell finely pitted
dark brown
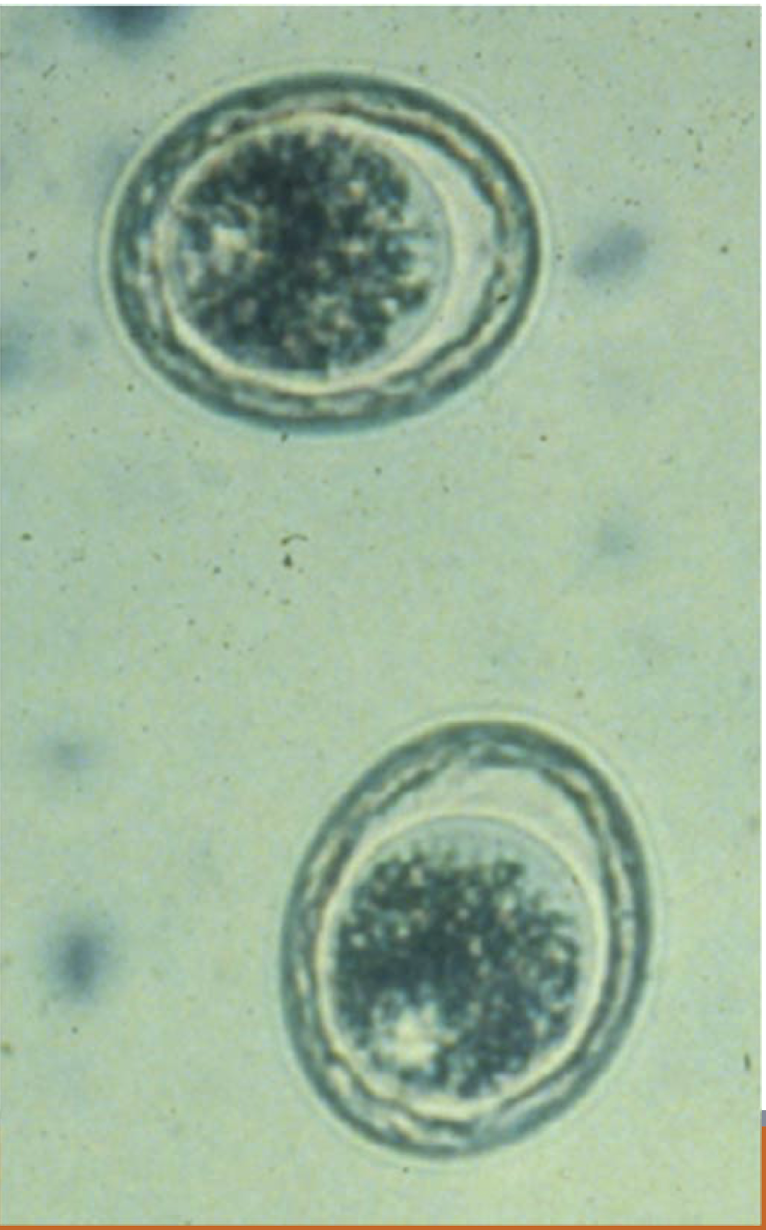
What is this and why?
toxascaris leonina
oval and light coloured
smooth thick outer shell
ruffled appearance of inner shell
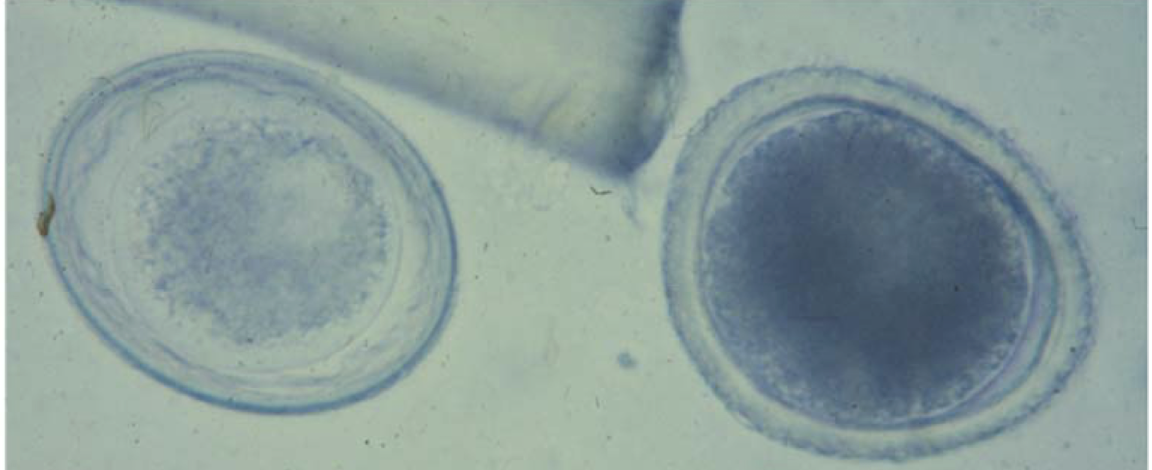
whats shown in the image?
Left: toxascaris spp. egg
right: Toxocara spp. egg
what does it mean if a species name has “ascaris” in it?
there is no vertical transmisison
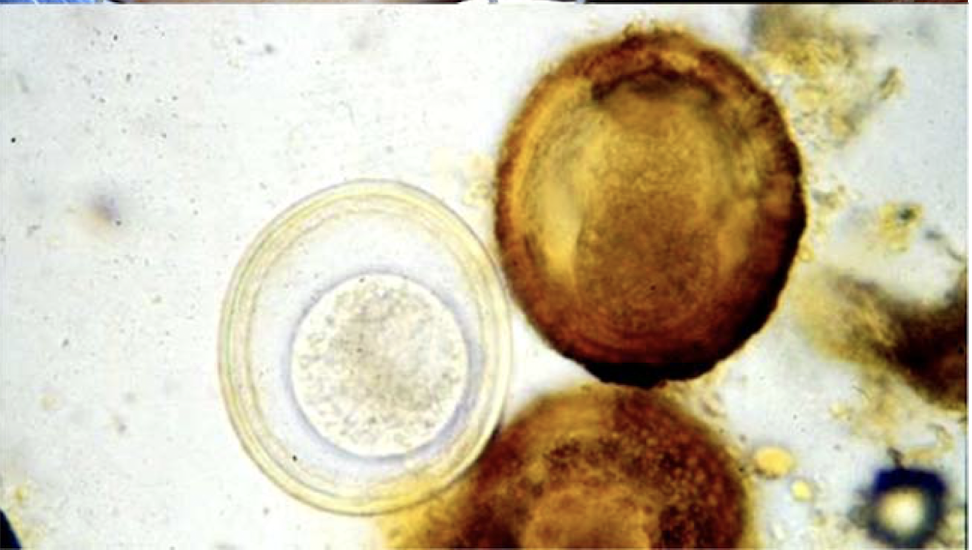
What is this and why?
parascaris equorum
dark egg
thick finely pitted outer protein shell
if the protein layer is lost during flotation procedure, the egg is smooth, colourles, middle layered shell exposed
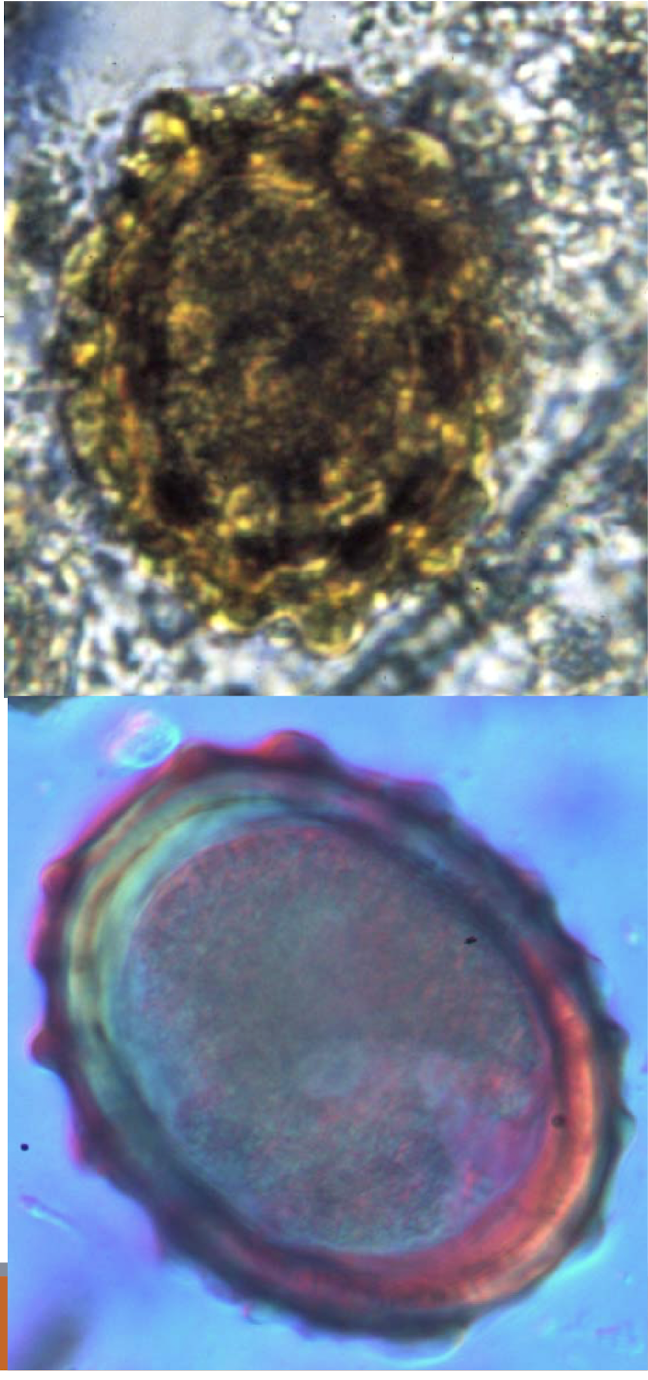
What is this and why?
ascarid suum
ovoid and yellow
thick shelled
irregularly mamillated outer shell
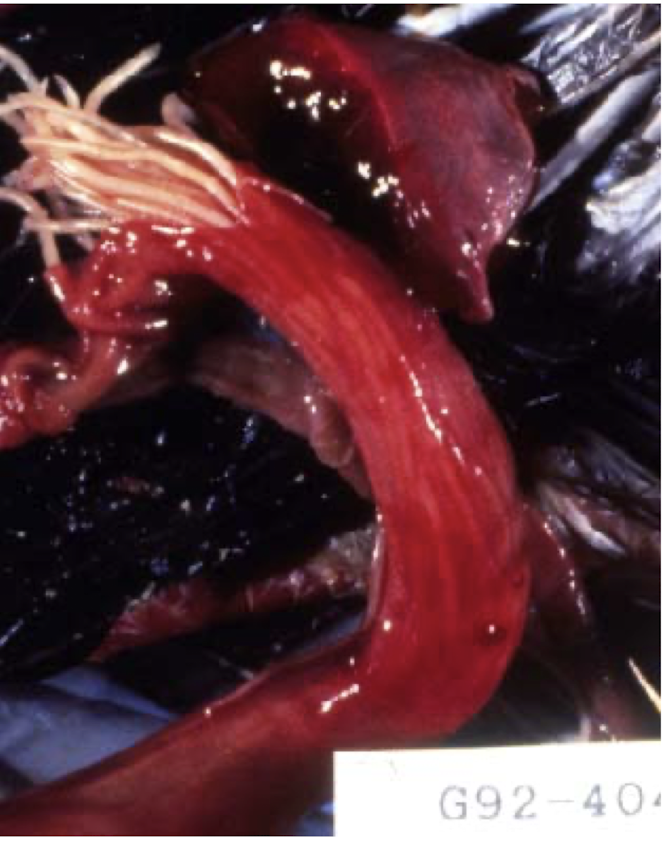
Which species would this be if this was found in the intesine of chickens, pigeons and turkeys?
Ascaris galli
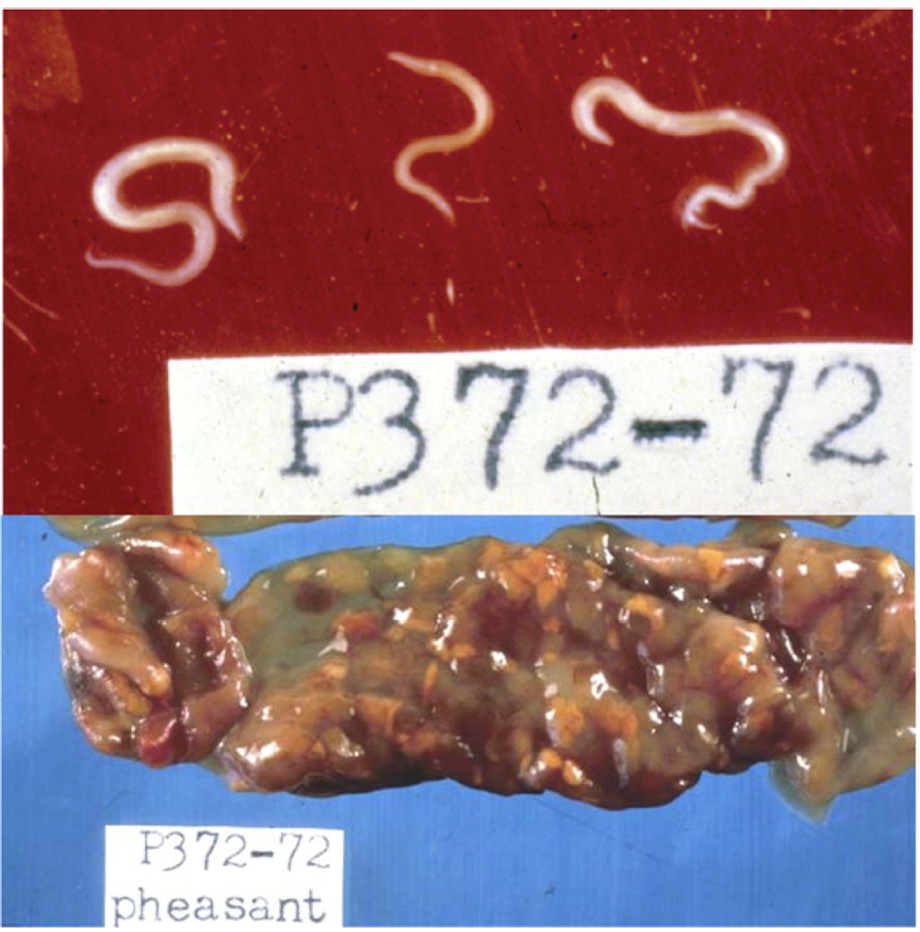
cecal leision caused by mucosal migration of the larvae, what could this be?
Heterakis gallinarum
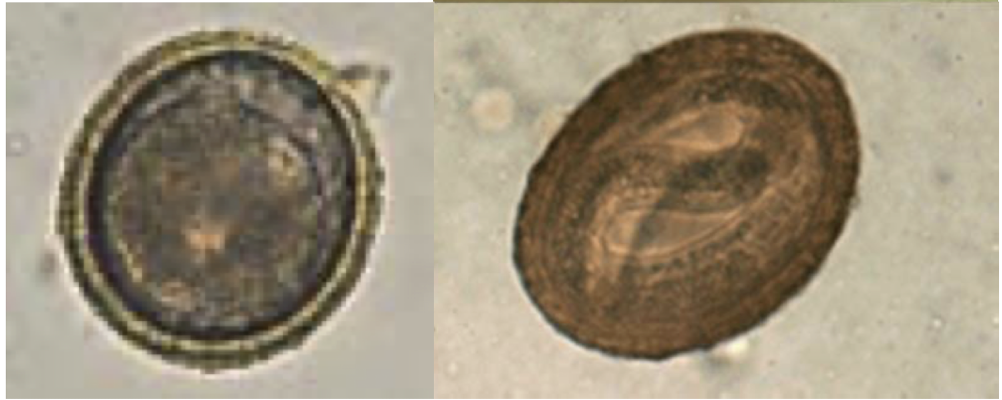
what is this and why?
Baylisacaris procyonis
dark or amber
embryo more or less completely fill the shell
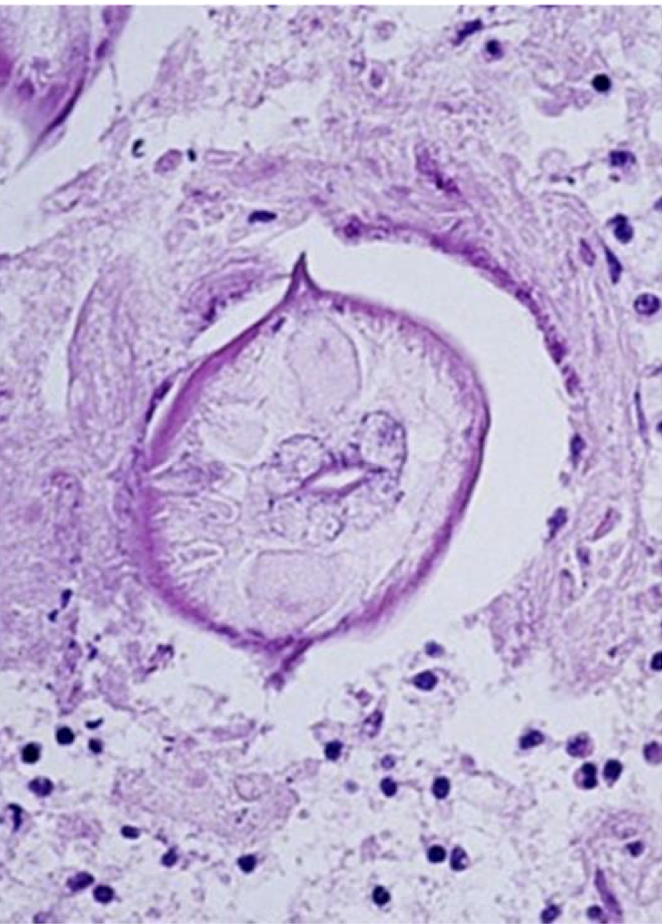
If this larva migrate in the brain and cause neurological issue, what could this be?
Baylisascarid procyonis larva
What is the biological characteristics of Ascarid eggs?
highly resistant to environmental eggs
eggs mature to contain L3 in the environment before becoming infective
eggs remain infectious for extended periods
what is the morphological characteristics of Ascarid eggs?
Shape | Round to oval |
Size | Varies by species (typically 60–90 µm in diameter) |
Shell | Thick, multi-layered shell |
Outer Surface | Often rough or pitted (Toxocara spp.) or smooth (Parascaris spp.) |
Color | Yellow-brown |
Contents | Single-celled zygote |
How do humans get infected with Ascarids
usually fecal oral infection
Describe the zoonotic and human medical importance of ascarid nematodes
humans can become paratenic host with larva migrating through the body
ascarid larval migration can give rise to the syndromes of visceral larva migrans (VLM) and ocular larva migrans (OLM)
species particular important: toxocara canis of dogs and Baylisascaris sp. in racoon
in which species that vertical transmission is esp important when it comes to Ascarid infection.
Toxocara canis
Toxocara cati
what types of vertical transmission does toxocara canis use?
pups are primarily infected in utero by transplacental transmission
some larval can be transmitted through transmammary transimission
what types of vertical transmission does toxocara cati use?
young kittens are infected primarily by transmammary passage of larva
Describe the role of vertical transmission in the epidemiology of ascarid infections in small animals
High Prevalence in Neonates
almost 100% of puppies from infected mother with toxocara canis are infected.
high environmental contamination
infected neonate shed within a few weeks
eggs are environmentally resistant
increased risk of zoonotic transmission
early infection of puppies and kittens shed a large number of eggs
difficult to eradicate in breeding population
Describe a general ascarid lifecycle
direct life cycle
prolific (as many as 200k eggs per female)
eggs mature to contain L3’s in the environment before becoming infective - oral infection usually
L3 penetrate small intestine and undergo migration
many alternate routes with hypobiosis as well as transmammary and/or transplacental transmission
larvae eventually reach the small intestine and rapidly mature to adults and begin to produce eggs
PPP variable but usually long if the larvae undergo significant migration
paratenic hosts may be involved
eggs remain infectious for extended period
How does toxocara canis’s life cycle vary from the general ascarid life cycle?
life cycle in pups
less than 3 months (tracheal migration with PPP of 4-5 weeks)
3-6 months (increasing somatic migration)
6 months or older (only somatic migration)
most pups infected in utero by transplacental migration of larvae from bitch to fetus
how does the transplacental and transmammary transmission work for Toxocara canis?
some (not all) arrested (hypobiotics) larvae are mobilized by pregnancy
enter liver and lung of fetus and wait for birth of pup
finish (do not undergo complete) tracheal migration and form adults - PPP shortened to 3 weeks
some larvae may enter milk and infect pups by transmammary route (rarely)
how does other routes of transmission work for Toxocara canis?
bitch may get infected by ingesting larvae in feces of pups
ingestion of paratenic hosts containing larvae may give rise to short-lived patent infections in adult dogs (no migration)
How does taxocara cati’s life cycle vary from the general ascarid life cycle?
L3 undergo tracheal migration in kittens
L3 undergo somatic migration in older feline
transmammary infection is most important
paratenic hosts may give rise to short lived infections in older cats with oppotunity to hunt
How does toxascaris leonina’s life cycle vary from the general ascarid life cycle?
eggs release L3 in intestine and they undergo a mucosal migration (NO tracheal migration)
How does parascaris equorum’s life cycle vary from the general ascarid life cycle?
direct life cycle with tracheal migration through liver and lungs
How does Ascaris suum’s life cycle vary from the general ascarid life cycle?
direct life cycle with tracheal migration through liver and lungs
How does Ascaridia galli’s life cycle vary from the general ascarid life cycle?
L3 enter mucosal and undergo mucosal migration
How does Heterakis gallinarum’s life cycle vary from the general ascarid life cycle?
larva migrate to CECA and enter mucosa
larval moves to lumen again after 3 molts to become adults (mucosal migration)
How does Baylisascaris procyonis’s life cycle vary from the general ascarid life cycle?
visceral larval migrans in paratenic host