biotech I
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
EFB
european federation of biotechnology
the technique to alter the chemistry of genetic material to introduce these into host organism and thus change the phenotype of the host organism
genetic engineering
chromosome has a specific DNA sequence called ____ which is responsible for initiation of replication
origin of replication
1st recombinant is formed by the native plasmid of _____
salmonella typhimurium
scientist who performed 1st genetic engineering
stanley cohen, herbert boyer
in which year 1st genetic engineering was done
1973
the linking of DNA with antibiotic resistance gene with the plasmid vector became possible because of
DNA ligase
bacterium closely related to salmonella
E.coli
enzyme responsible for restricting the growth of bacteriophage in E.coli
restriction endonuclease
1st restriction endonuclease
Hind II
Hind II has recognition site of __ bp
6
about more than___ restriction enzyme are discovered
900
the restriction enzymes isolated from over ____ strains of bacteria
230
in EcoRI, R represents
name of strain
in EcoRI, I represents
order of isolation
Restriction endonuclease breaks the two strands of double helix at point
sugar phosphate backbone
the restriction endonuclease recognise a specific
Palindromic nucleotide sequence
fragments of DNA formed by restriction endonuclease is separated by
gel electrophoresis
the most commonly used matrix in gel electrophoresis is
agarose
the separated DNA fragments can be visualised after staining it with
ethidium bromide in UV light
the process of cutting of desired DNA fragment from agarose is called
elution
______ have a very high copy number of their genome
bacteriophage
sequence from where replication starts and any piece of DNA is linked to this sequence can be made to replicate within the host cells
origin of replication
helps in identifying and eliminating non transformants and selectively permit growth of transformants
selectable marker
which organism naturally doesn’t have antibiotic resistance genes
E.coli
non recombinant DNA in presence of chromogenic substrate
blue
recombinant DNA in presence of chromogenic substrate
white
which pathogen can deliver a piece of DNA to several dicot plants and transform it into tumour cell
agrobacterium tumefaciens
DNA is a
hydrophilic molecule
transfer of rDNA in animals
micro-injection
transfer of rDNA in plants
gene gun
in which method cells are bombarded with high velocity of microparticles of gold and tungsten coated with DNA in a method known as
gene gun
enzyme to digest bacterial cell wall
lysozyme
enzyme to digest fungal cell wall
chitinase
enzyme to digest plant cell wall
cellulase
the DNA that is precipitated out after adding chilled ethanol is removed by
spooling
PCR full form
polymerase chain reaction
It involves heating the DNA to around 94-98 degrees Celsius. This high temperature causes the double-stranded DNA to "denature" or separate into two single strands, making them accessible for primer binding
denaturation
It involves cooling the reaction mixture to around 50-65 degrees Celsius. During this phase, short DNA primers bind to their complementary sequences on the single-stranded DNA templates
annealing
the temperature is raised to about 72 degrees Celsius. Here, a heat-stable enzyme adds nucleotides to the primed DNA strand, synthesizing a new strand complementary to the template. It extends from the primers, effectively duplicating the DNA
extension
the enzyme used in the process of extension
taq polymerase
enzyme taq polymerase is obtained from
thermus aquaticus
to express a gene from a different species, often for research or biotechnological purposes is called
heterologous host
_____ type of culture method produces large biomass of desired product
Continuous culture system
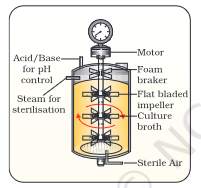
which type of stirrer is this
simple stirrer tank
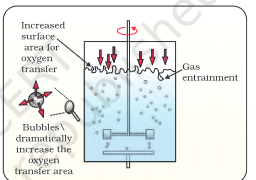
which type of stirrer is this
sparged tank bioreactor
which type of tank has usually cylindrical base or curved base to facilitate the mixing
simple stirred tank
which tank facilitates even mixing and oxygen availability throughout the reactor
simple stirrer tank
which type of tank has agitator system, oxygen delivery system, and foam control system, temperature control and pH control system
sparged tank bioreactor
which type of tank has sampling ports
sparged tank bioreactor
downstream processing include
separation and filtration