Flowering plant structure and tissues
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
What are the two systems of a flowering plant?
Root system (underground) , shoot system (above ground)
What is a node?
Where the leaf stem connects with the stem
What is an internode?
The distance between two nodes
What are the two types of roots/root systems?
Tap root. Fibrous roots
What is a tap root?
Main root going down the middle which may produce lateral roots
What is a fibrous root?
Grow from the base of the stem and branch
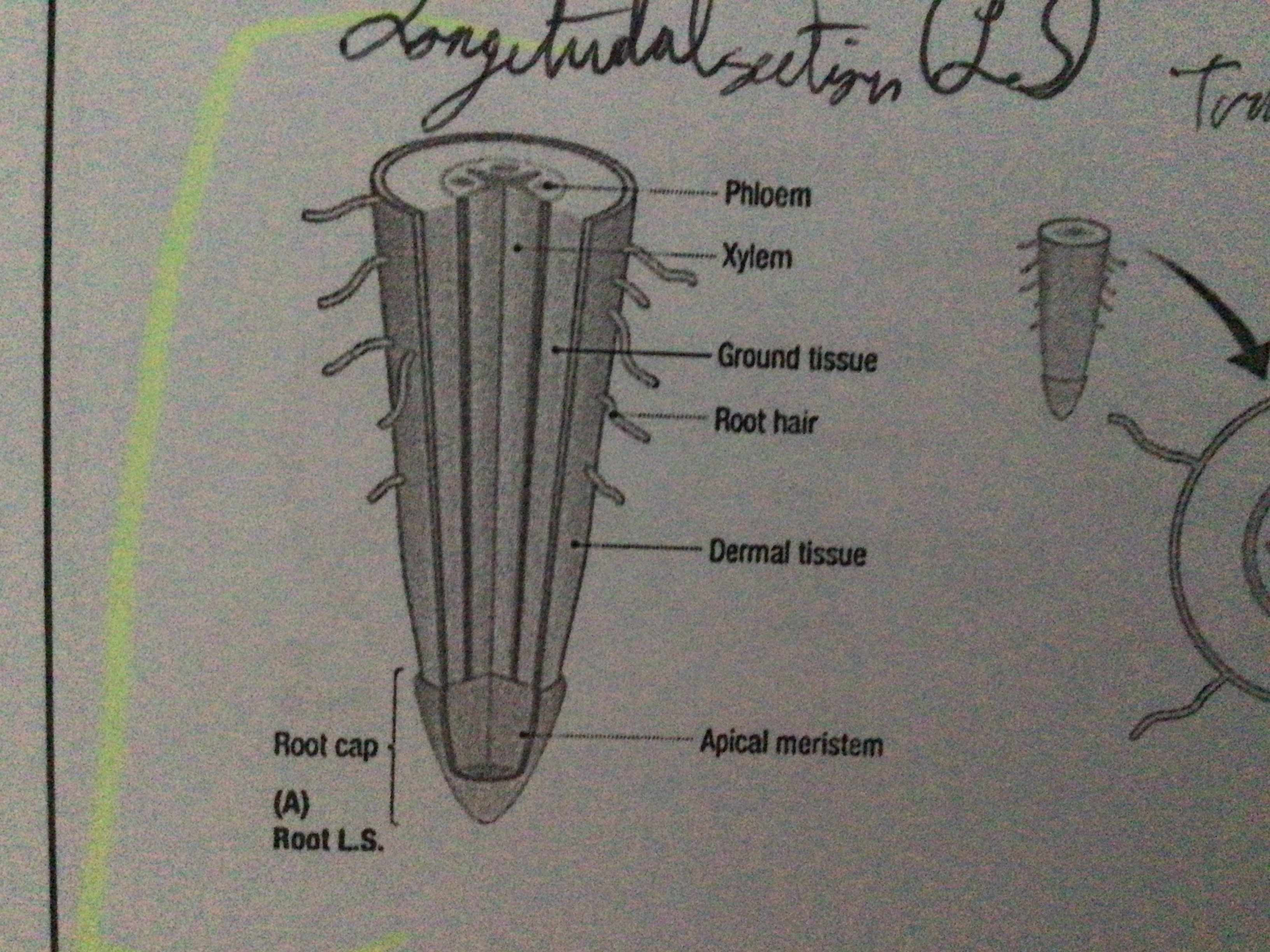
Root cap
Protects the tip of the root
Root hairs (function)
Fine hairs which absorb water and minerals. They increase the surface area for absorption
What are the three functions of the root?
Anchor the plant. Absorb water and minerals from the soil. Store food in certain plants, e.g. carrots
What are the three functions of the stem?
Transport water and minerals from the roots to the leaves and flowers. Transport goods made in leaves around the plant. Support the parts of the plant, e.g. flowers, leaves
What is a bud?
An underdeveloped shoot
What are apical buds?
Buds that lie at the tip of the stem. Grow upwards
What type of tissue do apical buds have?
Meristematic tissue
What are lateral buds?
Side of the stem, give rise to side shoots and branches
What is the axil of a leaf?
Angle between leaf and stem
What are leaves attached to the stem with?
Petiole (leaf stalk)
Sessile meaning
When the leaf is directly attached to the stem
Function of the veins on a leaf
Support. Allow nutrients (food, water, minerals) to be transported.
What are the two patterns that a leaf's vein can be arranged in?
Netted. Parallel
What are the four functions of the leaf?
Make food (photosynthesis). Gaseous exchange (stomata). Allow transpiration. Store food in plants like cabbage and lettuce
Where are stomata located?
underside of the leaf
Function of the flower
Reproduction
What happens to buds after a flower is formed?
They don't grow anymore
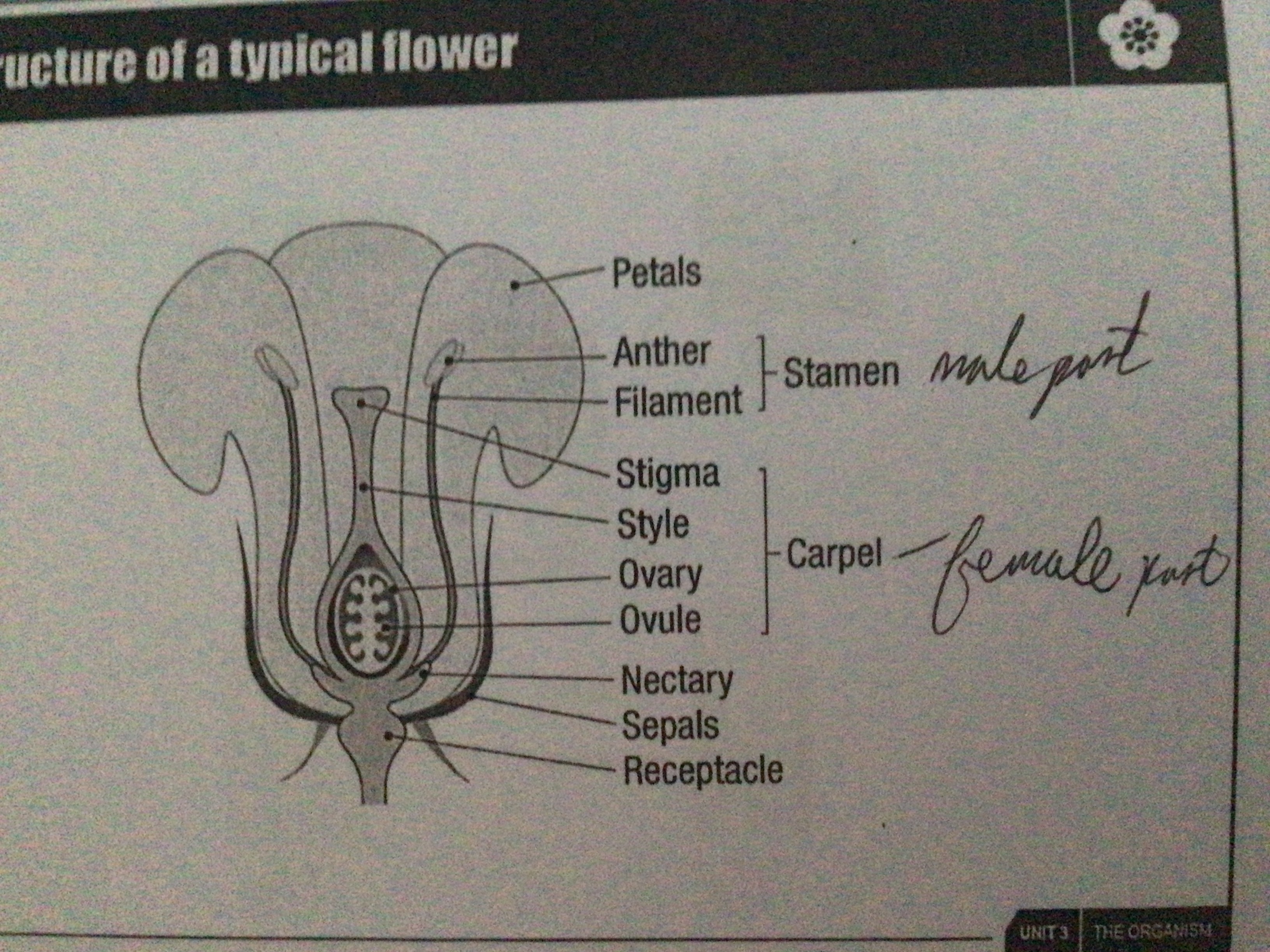
What does a flower consist of?
Groups of modified leaves arranged in whorls e.g. petals, stamen, carpel
Meristem (definition)
The region of active cell division in a plant
Where are apical meristems found?
Tip of shoot and root. Buds. Vascular buds of some stems
Draw a diagram of a plant's flower
...
Dermal tissue (function)
Protection
Dermal tissue (location)
Surface of the plant
Ground tissue (location)
between dermal and vascular tissue
Ground tissue (function)
Photosynthesis in the leaf. Support
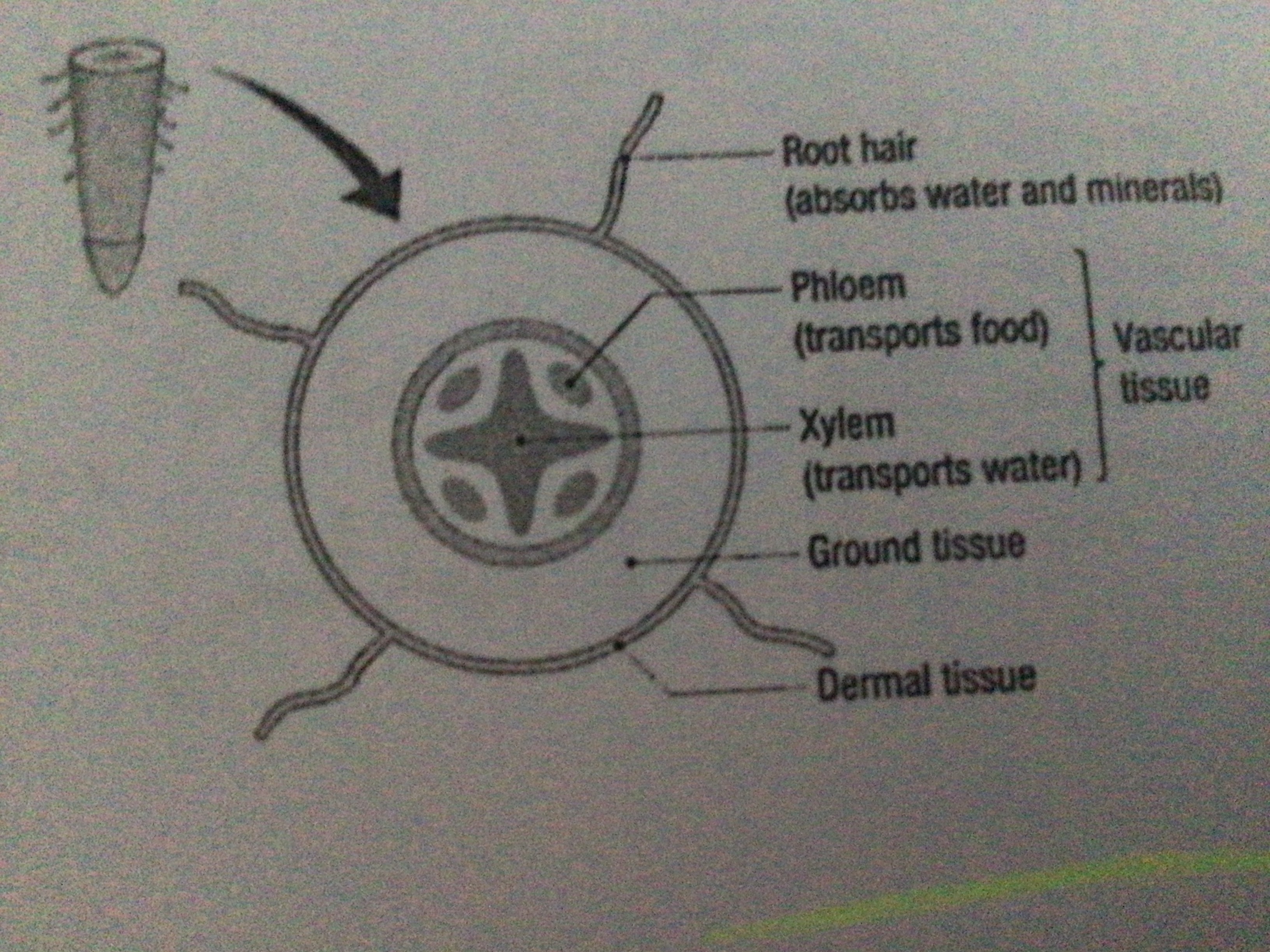
Vascular tissue (location)
Veins of leaves, vascular bundles of stems
Vascular tissue (function)
transport materials around the plant
Draw the longitudinal section of a root
...
Draw the Transverse section of a root
...
Air spaces in leaf (function)
Loosely packed to each other to allow rapid diffusion of gases in and out
What is the name of the ground tissue in the leaf?
Palisade mesophyll cells
Draw diagram of a leaf
...
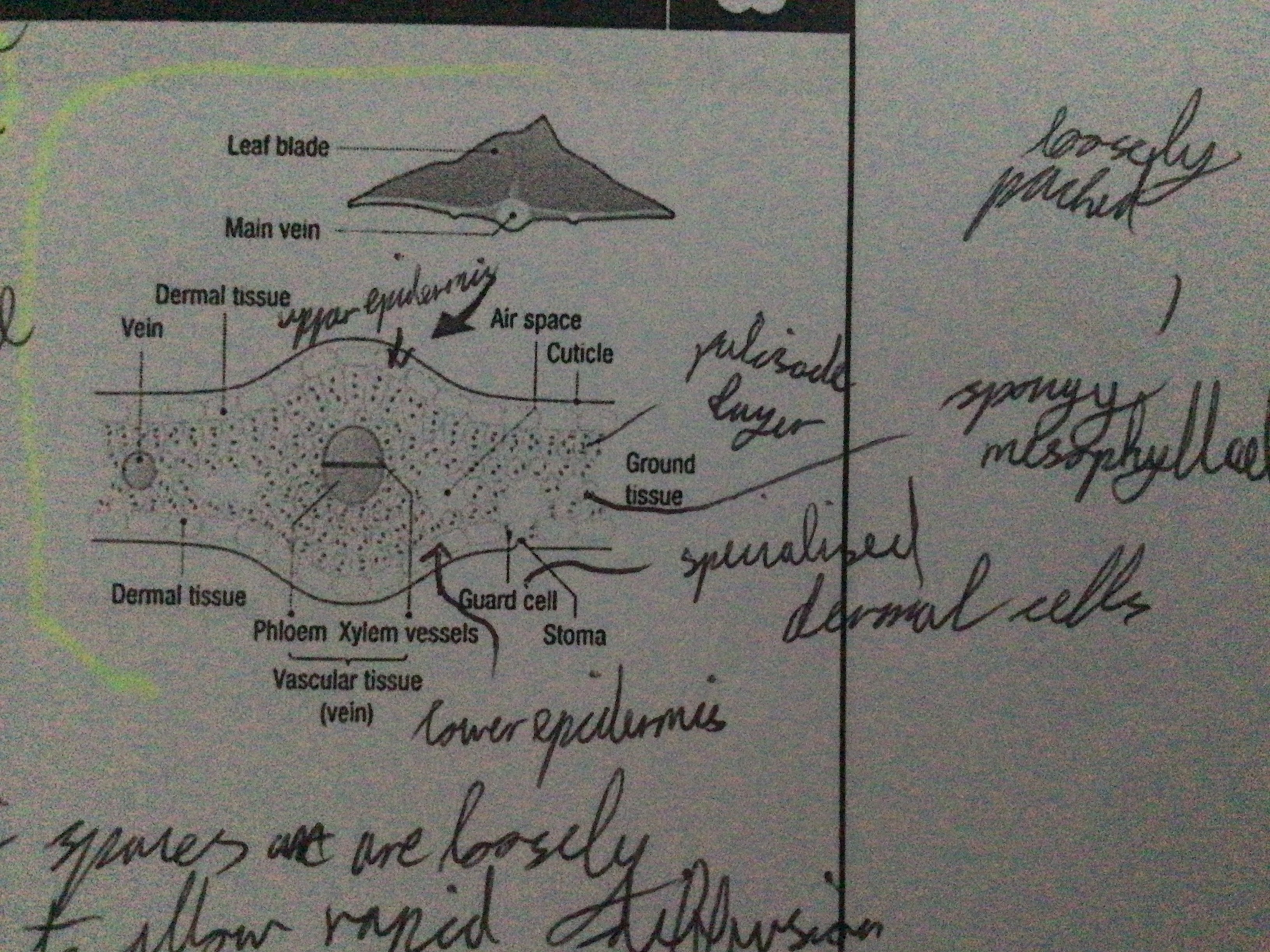
Where is the vascular tissue located in flowering plants?
Veins of leaves. Vascular bundles. Core of root
What are the two types of vascular tissue?
Xylem. Phloem
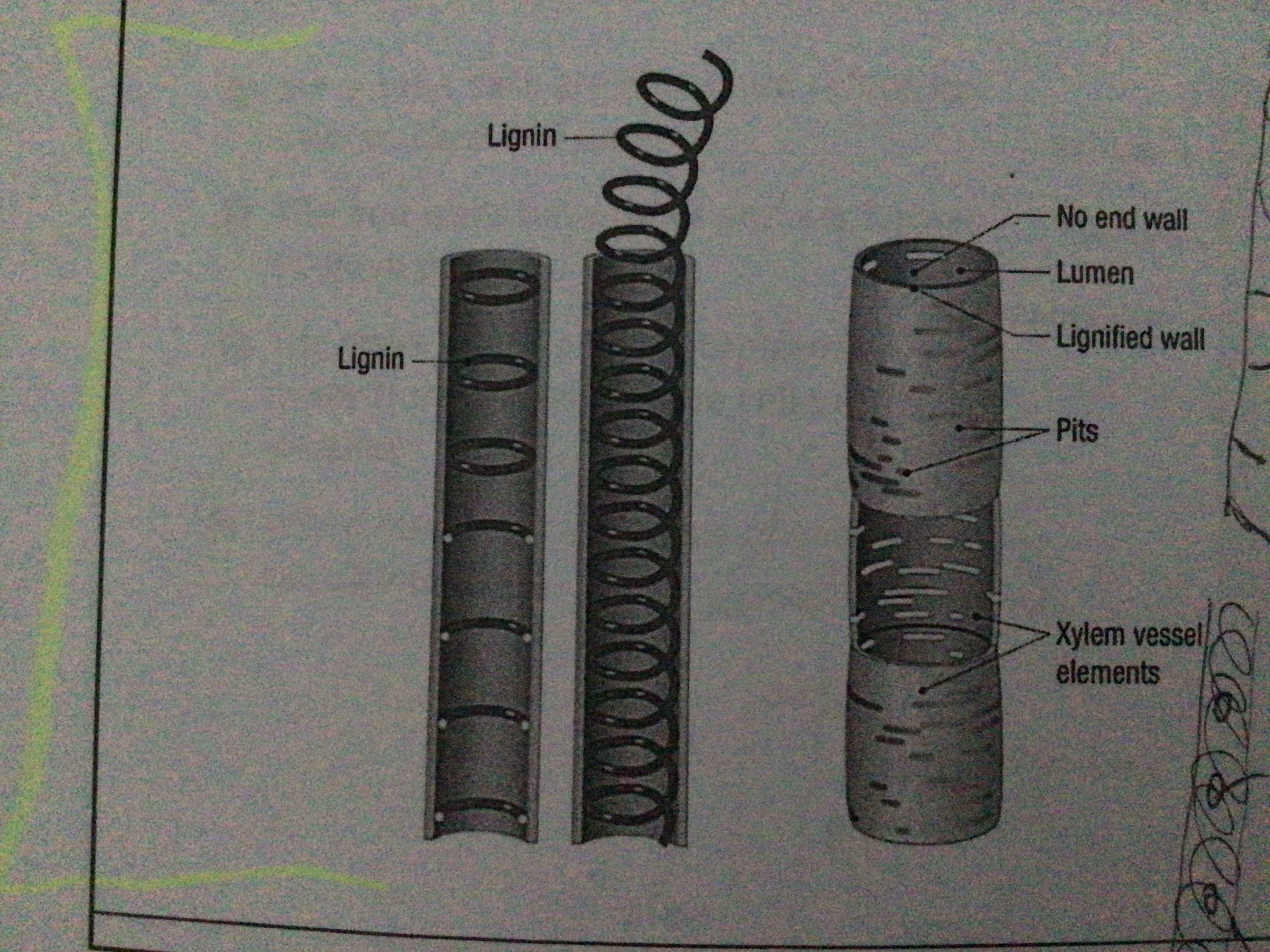
Xylem (function)
Transport water and minerals up the plant. Provide support
What are the two types of cells in xylem tissue?
Tracheids. Vessels
Features of xylem tracheids
Long narrow cells, pits in walls, dead and hollow, end walls with gaps, walls have lignin
Draw a xylem tracheid
...
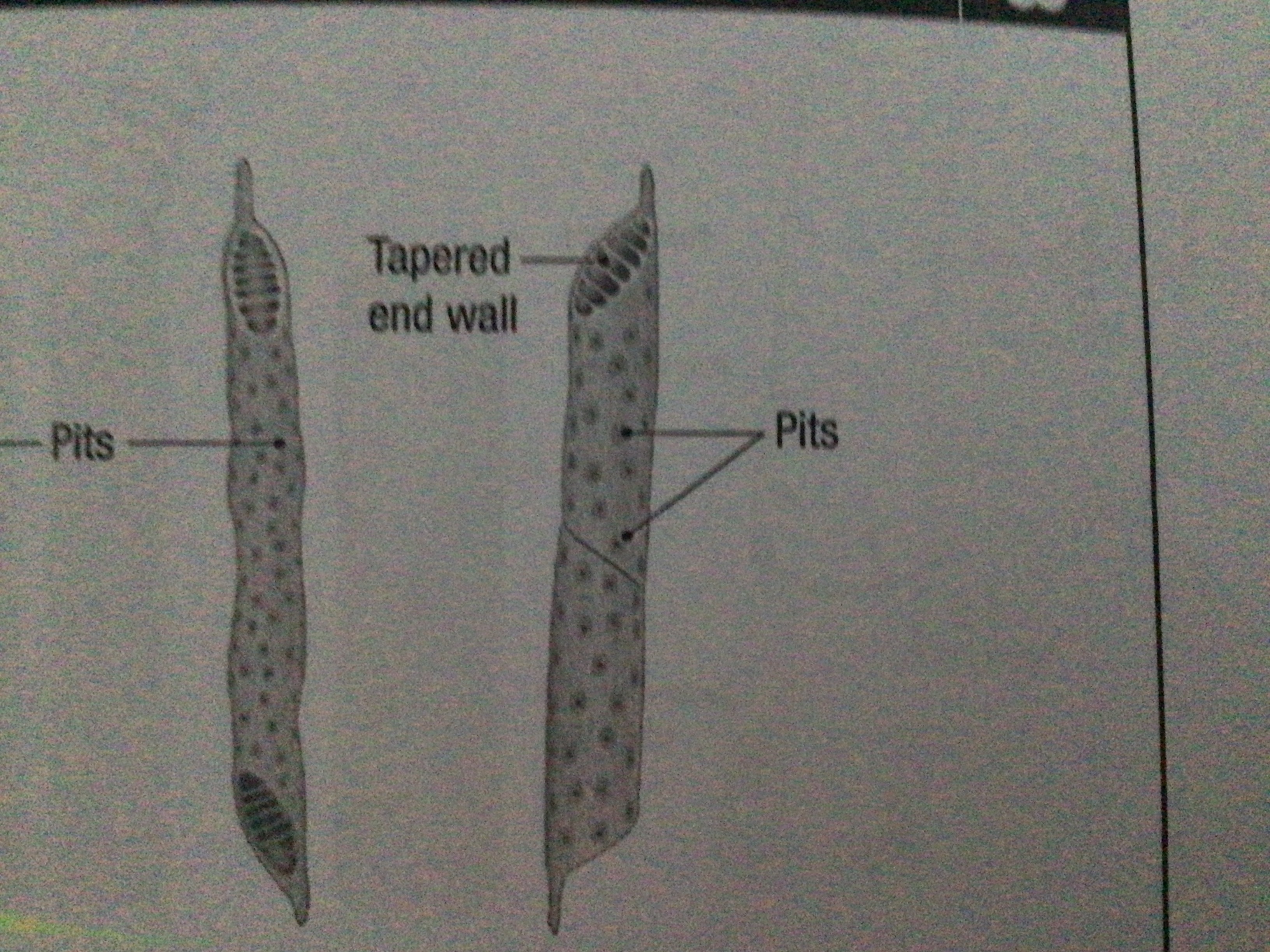
Features of xylem vessels
Hollow, dead cells. Contain lignin. No end walls. Form a continuous pipe. Wider than tracheids
What are the features of xylem vessels that make them suitable for conducting/carrying?
Lack end walls, hollow and dead, continuous tube
Draw a xylem vessel
...
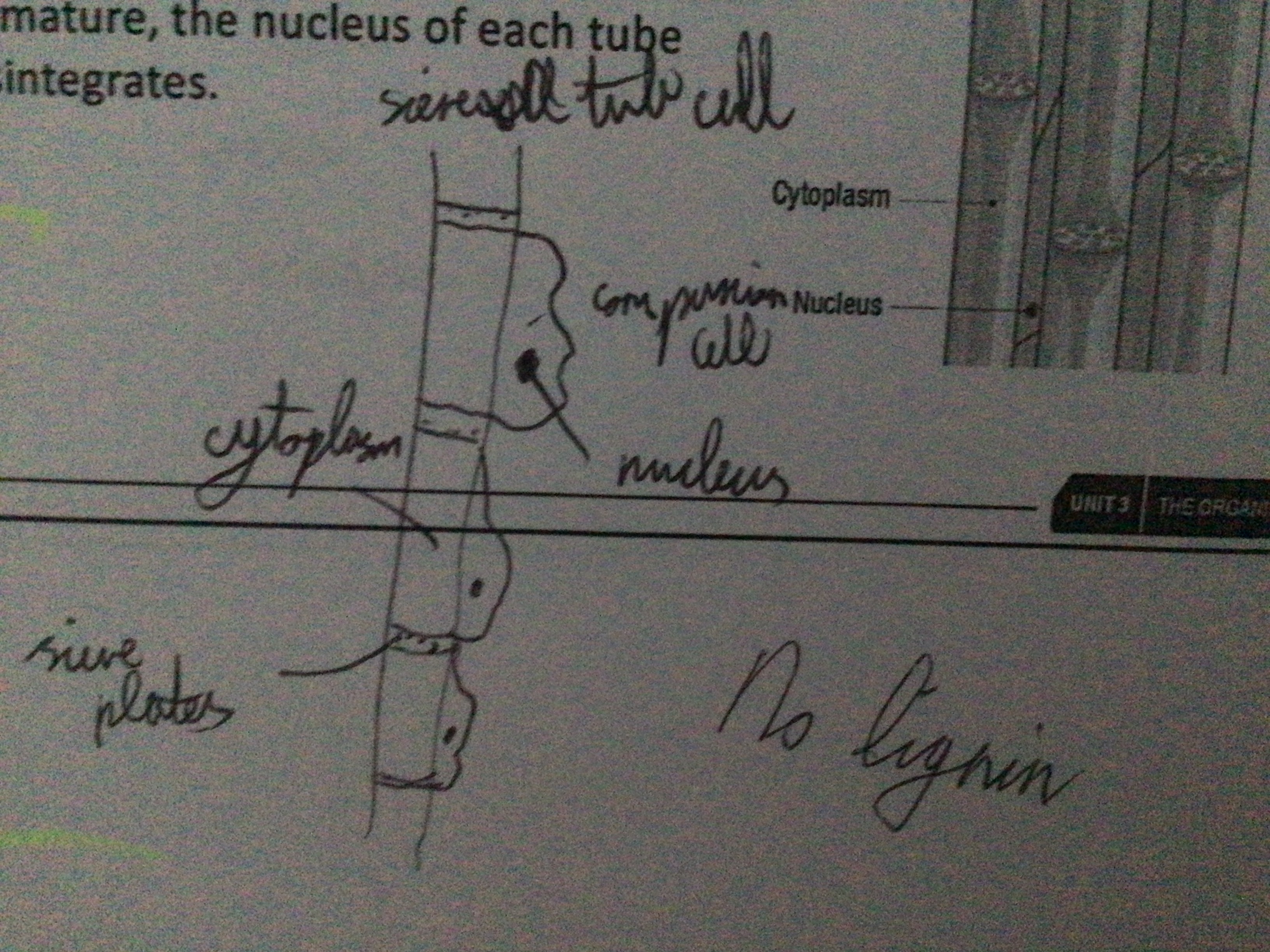
Phloem (functions)
Transport sugars up and down the plant. Transport plant growth regulators.
Translocation
Movement of food in the phloem
What are the two types of cells in phloem tissue?
Sieve tube cells. Companion cells
Sieve tubes features
Have end walls with gaps (cell plates). No nucleus.
Draw a sieve tube
...
Differences between Xylem and Phloem (Xylem)
Dead at maturity, lignified, transports water and minerals, provides support
Differences between Xylem and Phloem (Phloem)
Living, not lignified, transport sucrose and auxins (plant growth hormones)
Cotyledon (definition)
Embryonic seed leaf
Cotyledon (function)
Provides nutrients for the developing embryo plants
Monocotyledons (definition)
Have one seed leaf
Dicotyledons (definition)
Have two seed leaves
Differences between Monocots and Dicots (Monocots)
Vascular bundles are scattered. Parallel leaf veination. Petals in multiples of three. Herbaceous.
Differences between Monocots and Dicots (Dicots)
Vascular bundles in ring pattern. Netted leaf veination. Petals in multiples of 4 or 5. Woody or herbaceous
examples of monocots
Grass, onions
Examples of Dicots
Roses, dandelions
Function of apical bud
Will produce the following year's growth
When does a leaf scar occur?
Occurs when a leaf falls off
When does a scale scar occur and how to examine a year's growth?
Marks the location of previous apical buds. Difference between 2 scale scars indicates one year's growth
What is a herbaceous plant?
Doesn't contain wood
What is a woody plant?
contains wood
Lenticels (function)
Gas exchange
Difference between lenticels and stomata
Lenticels found on woody stems. Stomata found on leaves
Name the four root zones
Differentiation, elongation, meristematic, protection
Differentiation zone
Contains three types of tissue (dermal, ground, vascular)
Elongation Zone
Cells increase in size/stretch. Plant growth hormones and active
Meristematic Zone
New cells of mitosis, rapid growth
Protection Zone
Root cap protects root