BIOLOGICAL BASES OF BEHAVIOUR
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
neuron
cell of nervous system specialized for sending and receiving neural messages
sensory neurons
carry messages from the sensory organs to spinal cord + brain
motor neurons
carry messages from brain + spinal cord to muscles and glands
interneurons
collect, integrate, + retrieve messages from various sources
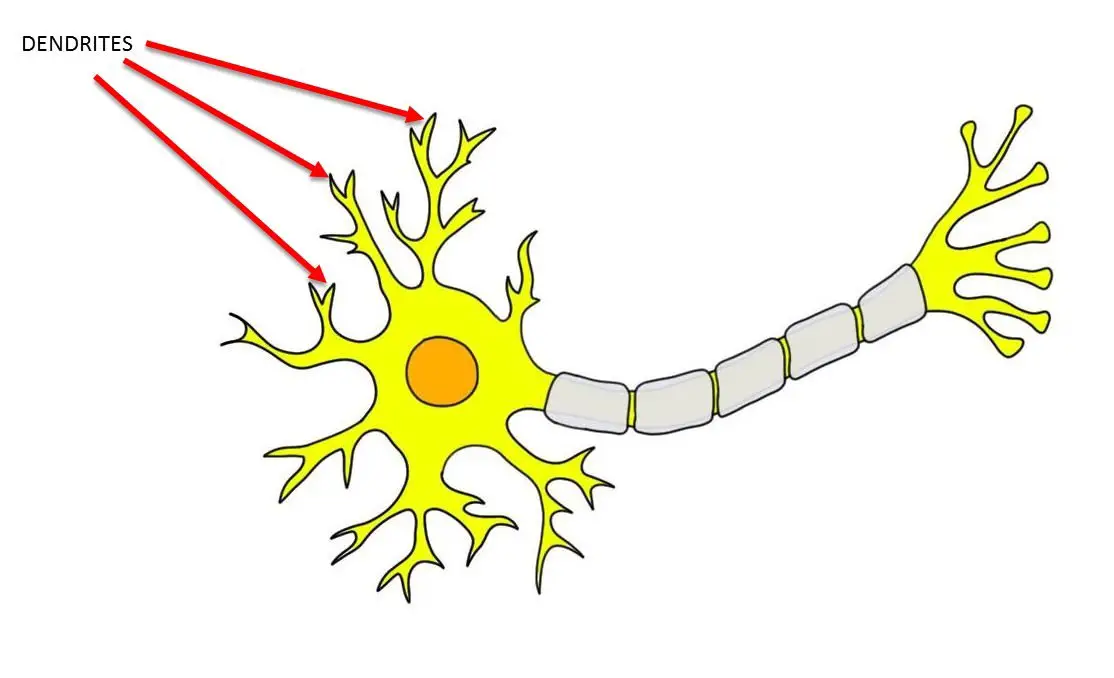
dendrites
receive chemical messages from other neurons
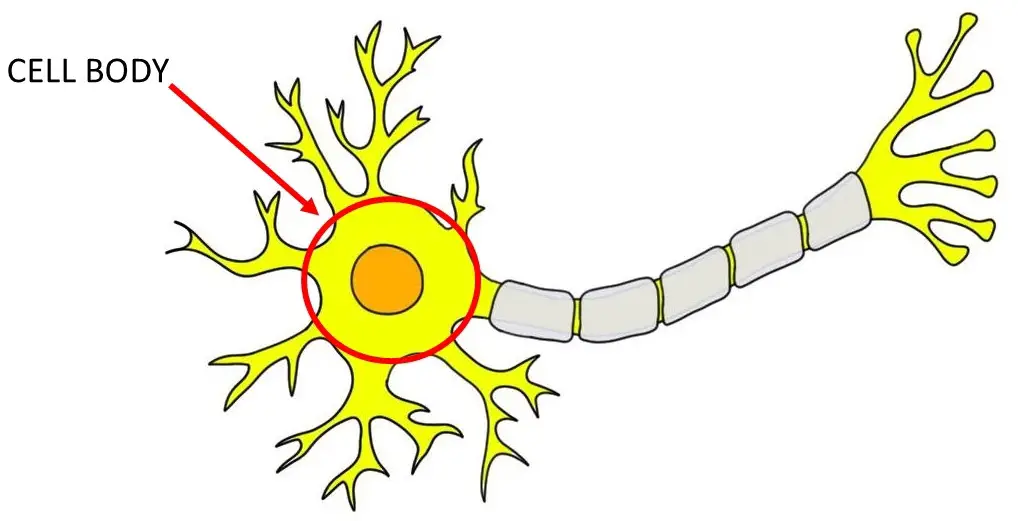
cell body/soma
collects neural impulses, contains nucleus, sustains cell functions
axon
transports electrical impulses to other neurons via the terminal branches
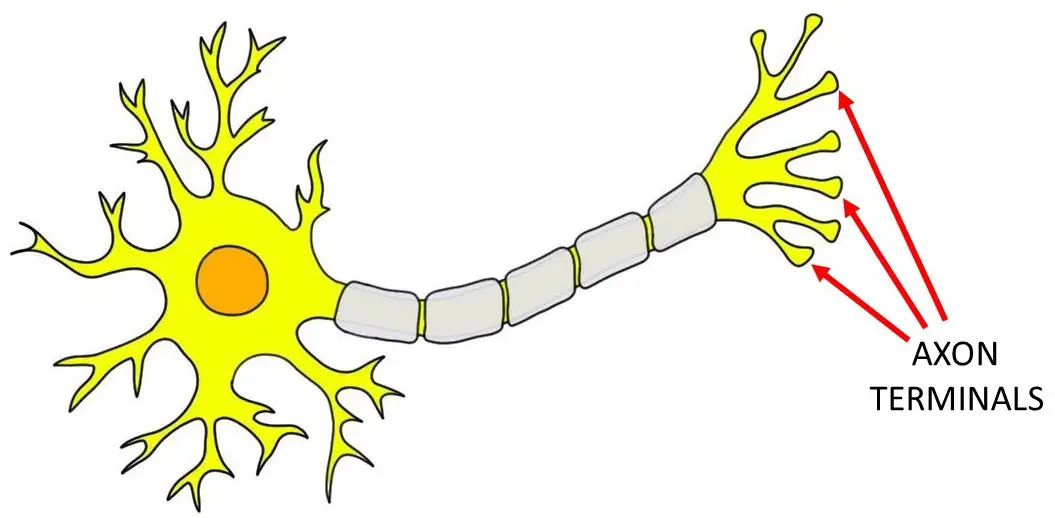
axon terminals
converts electrical signals into chemical messages
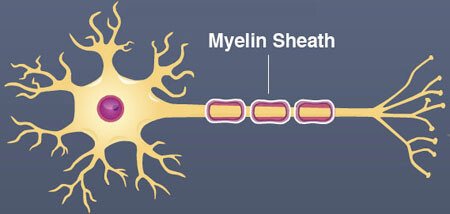
myelin sheath
fatty layer that insulates the axons + speeds up transmissions of electrical signals
glia
nervous system cells that perform variety of critical support functions (eg. provides structural support, clean up debris, nutrient supply)
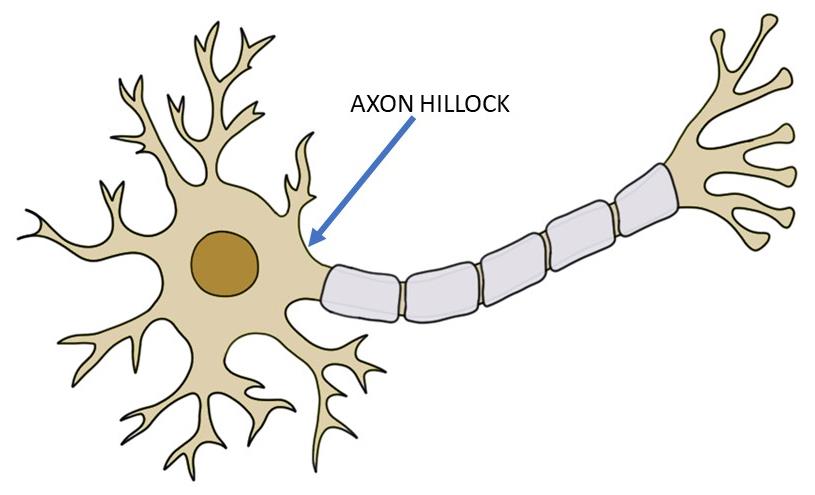
action potential
how neurons talk to each other via firing off electrical impulses (generated at junction between axon + cell body)
cell membrane
thin fatty skin enclosing the neuron (separation between intracellular fluid and extracellular fluid)
before an action potential
at rest, more negative ions are inside the cells relative to outside
resting potential
electrical charge across the membrane with more negative charge inside (-75 to -55 mV)
beginning depolarization
when a neuron is sufficiently stimulated by other neurons ions channels open at end of axon and positively charged sodium ions begin to enter
depolarization
when electrical charge across the membrane egins to reverse
voltage threshold
critical level to which a neuron’s membrane potential must be depolarized to initiate action potential
action potential
the moment when interior of cell is more positively charged than the outside
repolarization
after action potential, when sodium ions close but potassium ions remain open to allow flow out of the cell
refractory period
temporary dip between resting potential when the neuron struggles to refire
synaptic cleft
gap that separates neurons
communication across the synaptic cleft
electrical signals are converted to chemical signals via the sending of neurotransmitters (triggered by arrival of action potential)
neurotransmitters
chemical messengers sent between synapses
ways neurotransmitters are removed from the synapse
diffusion (drifting), degradation (broken down), reuptake (reabsorption into the presynaptic terminal)
excitation of neurotransmitters
receiving the neuron slightly depolarized (moving it closer towards voltage threshold + increasing likelihood of action potential)
inhibition of neurotransmitters
receiving the neuron slightly hyperpolarized (moving it further from voltage threshold + reducing likelihood of action potential)
types of neurotransmitters
GABA, acetylcholine, serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine
GABA
amino acid
most common inhibitory neurotransmitter
responsible for downregulation of stress, anxiety, fear
acetylcholine
triggers both excitatory and inhibitory signals
commonly found in neuromuscular junction
plays key role in autonomic nervous system + the brain circuits involved in learning + memory
norepinephrine
important for fight or flight
contributes to arousal (attention) + vigilance
serotonin
contributes to regulation of sleep, appetite, mood + aggression
dopamine
involved in movement, planning + Aspects of reword
most addictive drugs stimulate higher levels of activity in dopaminergic circuits
psychoactive drug
chemical substance that alters a person’s thoughts feelings, or behaviours by influencing activity of neurotransmitters
agonist
enhances action of a neurotransmitter
how agonists work
increase neurotransmitter release, blocks neurotransmitter uptake, or mimics neurotransmitter to activate its postsynaptic receptor
antagonist
inhibits action of a neurotransmitter
how antagonists work
block neurotransmitter release, destroys neurotransmitter in synapse, or mimics neurotransmitter to block its postsynaptic receptor
nerve
bundle of neurons
central nervous system
brain + spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
nerves connecting brain to the rest of the body
components of peripheral nervous system
somatic nervous system
autonomic nervous system
somatic nervous system
carries commands for voluntary movement from CNS to muscles
autonomic nervous system
carries involuntary commands to organs, blood vessels + glands
components of autonomic nervous system
sympathetic branch
parasympathetic branch
sympathetic nervous system
prepares body for situations requiring energy (fight or flight)
parasympathetic nervous system
controls glands + organs during calm periods, returning body to resting state (rest + digest)
endocrine system
network of glands (hormone-sending organs) that work with central and autonomic nervous system
hormone
blood-borne chemical messengers
adrenal hormones
hormones released by adrenal glands (on top of kidneys) during stressful events
boost energy, increase heart rate + blood pressure
ex. cortisol + adrenaline
pituitary gland
master gland that directs other glands (regulates hunger, sexual arousal, growth + sleep)
oxytocin
hormone released into bloodstream by pituitary gland (plays role in social bonding as those with higher levels are more trusting of others and show an improved ability to accurately perceive the emotions of people to whom they feel similar)
spinal cord
initiates spinal reflexes (aka responses to stimuli without involvement of the brain)
brainstem
lowest region of the brain that sits on top of the spinal cord
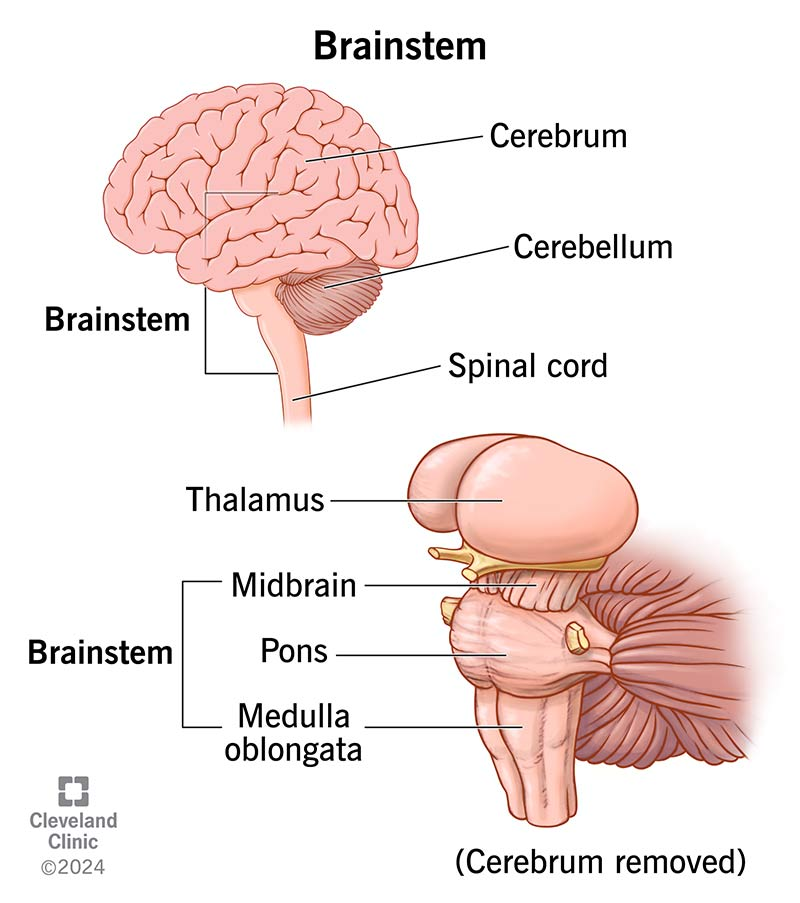
midbrain
controls salient stimuli (tegmentum), movement (substantia nigra), motivation + rewards (ventral tegmental area), downregulation of pain (periaqueductal grey)
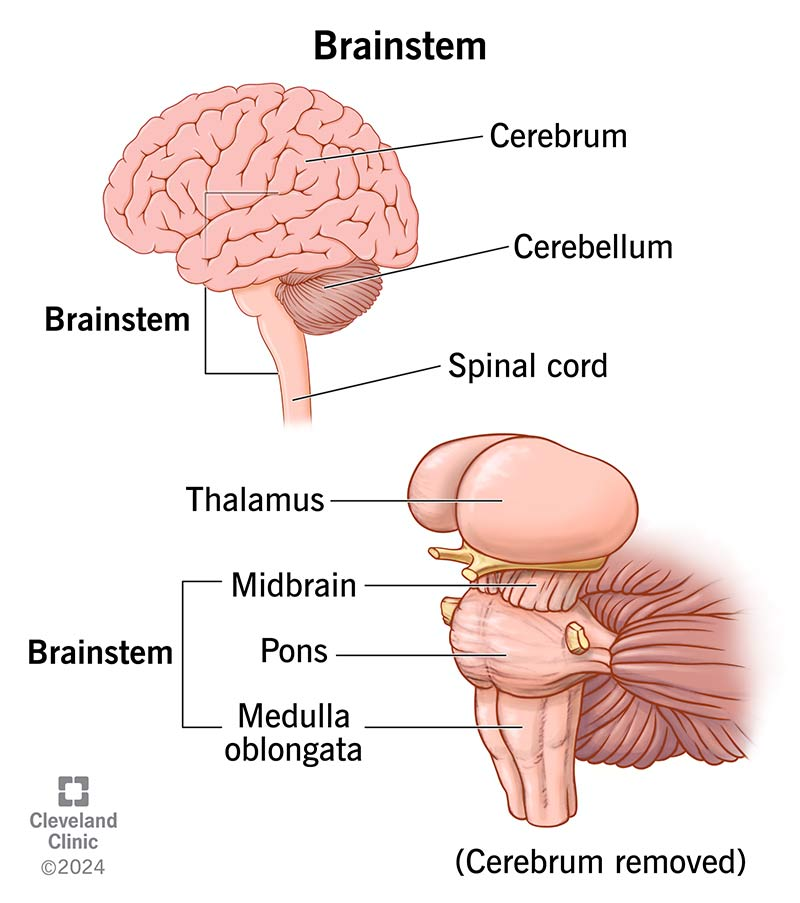
medulla
controls heart rate, blood pressure, reflexes like coughing + swallowing
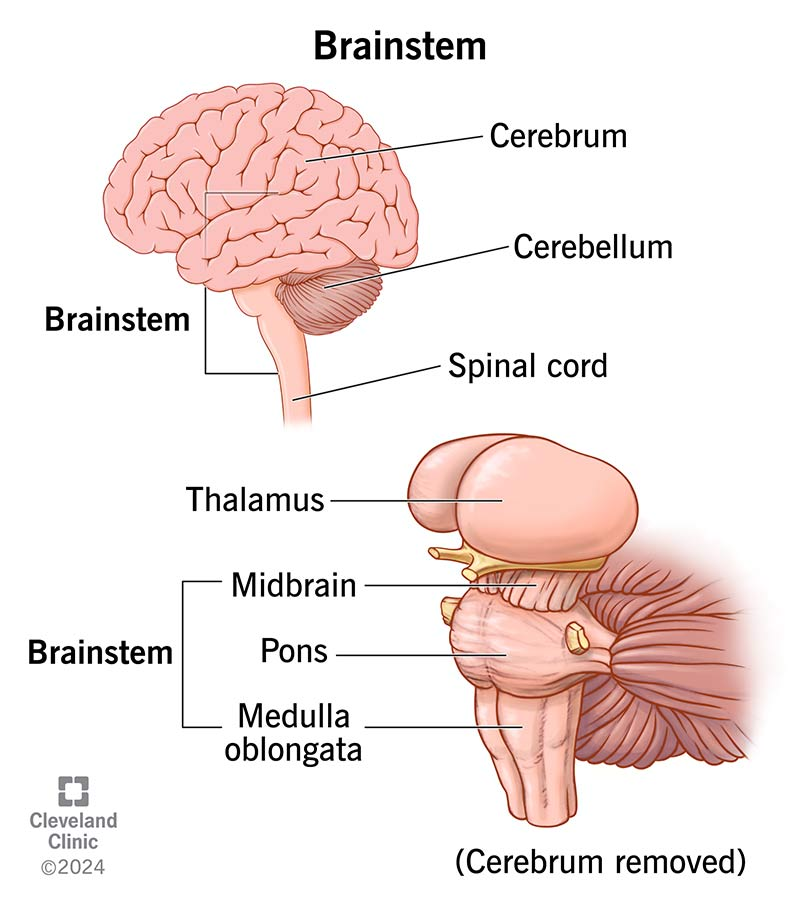
pons
controls breathing, balance, + coordination
reticular formation
controls arousal, attention, wakefulness
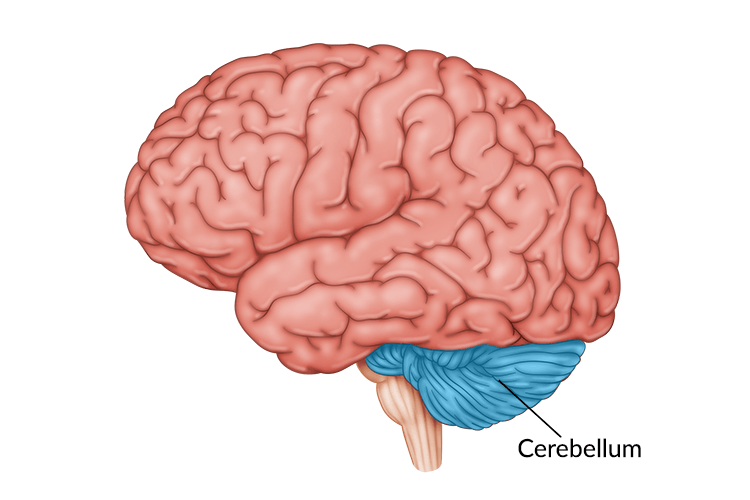
cerebellum
controls coordination, balance, precise movements + accurate timing
limbic system
known as the emotional brain (includes hypothalamus, thalamus, amygdala, hippocampus, basal ganglia)
hypothalamus
interface between brain + body, homeostatic regulation, fight-or-flight, directs autonomic nervous system + endocrine system
thalamus
relay station for all sensory signals (but smell), alertness + consciousness
amygdala
processing emotional significance of sensory info, works with hippocampus to create vivid memories
psychic blindness
normal vision but visual stimuli lose their emotional signficance (caused by damage to the amygdala)
hippocampus
memory, spatial recognition, mental time traval
basal ganglia
planning, executing + controlling voluntary movement, suppression of unwanted movement (substantia nigra), reward + pleasure (nucleus accumbens)
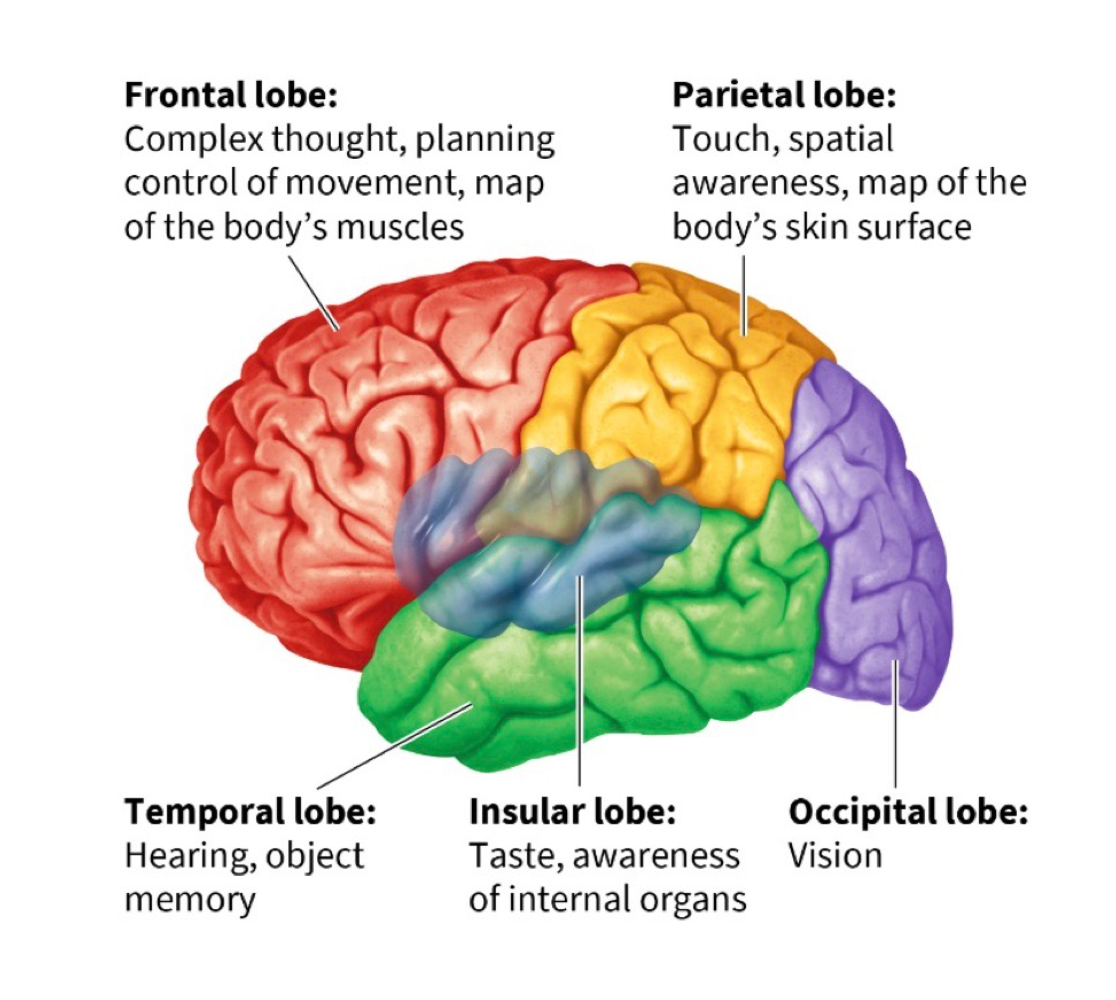
cerebral cortex
largest + outermost part of the human brains, further divided into lobes
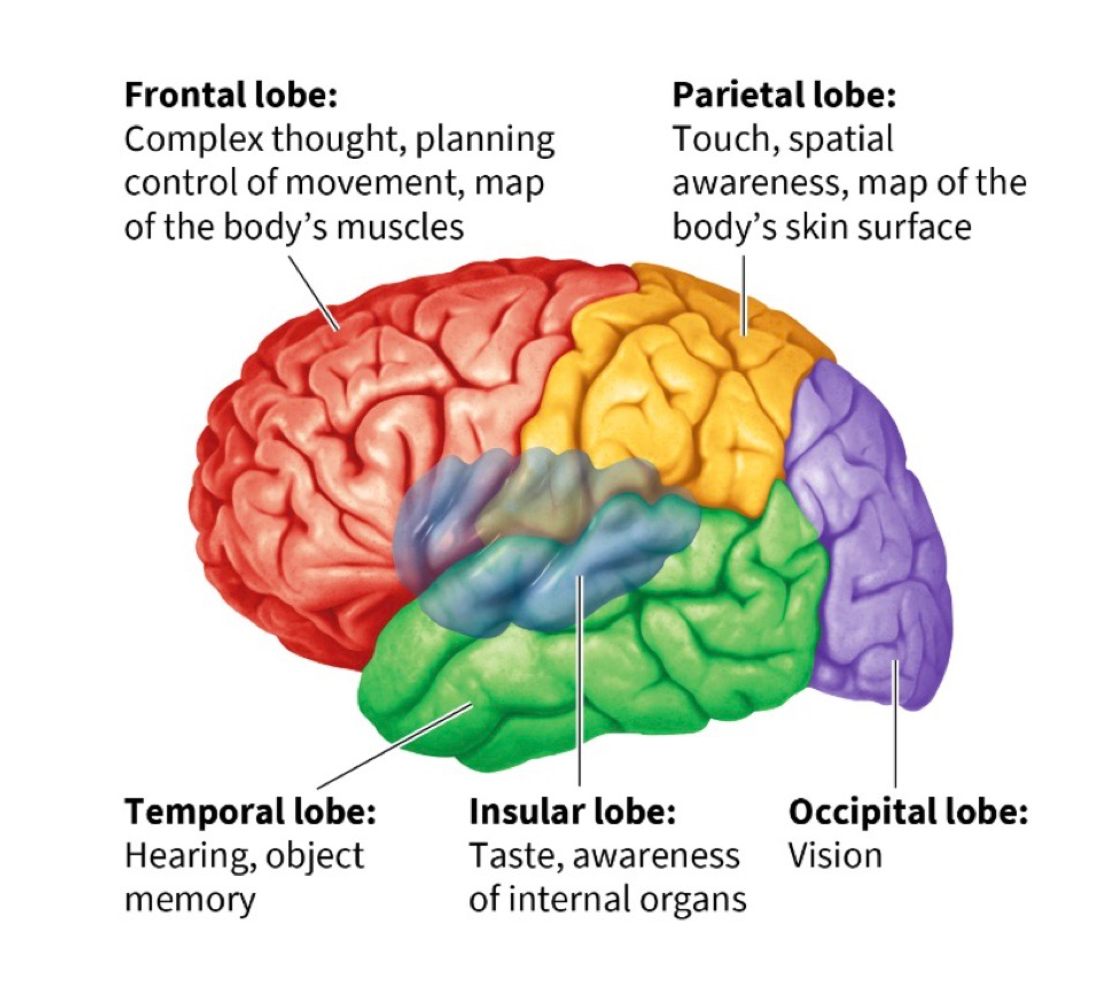
frontal lobe
movement + planning, contains primary motor cortex + prefrontal cortedx
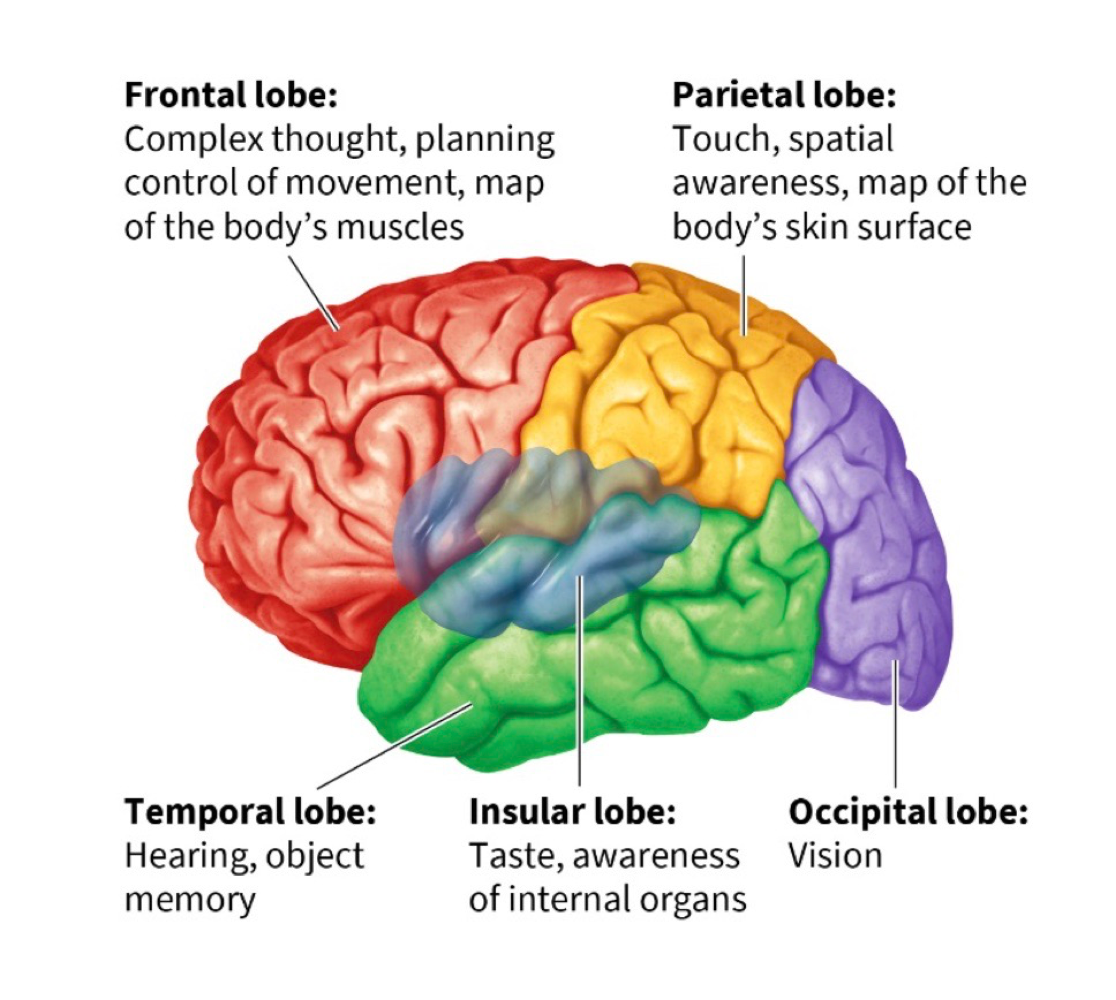
primary motor cortex
a map of the body’s muscles
prefrontal cortex
conscious experience of emotions
executive function
planning, judgement, decision making
primary somatosensory cortex
map of the body’s skin surface that lets us process touch
parietal lobe
helps us pay attention to and locate objects + navigate surroundings, contains primary somatosensory cortex
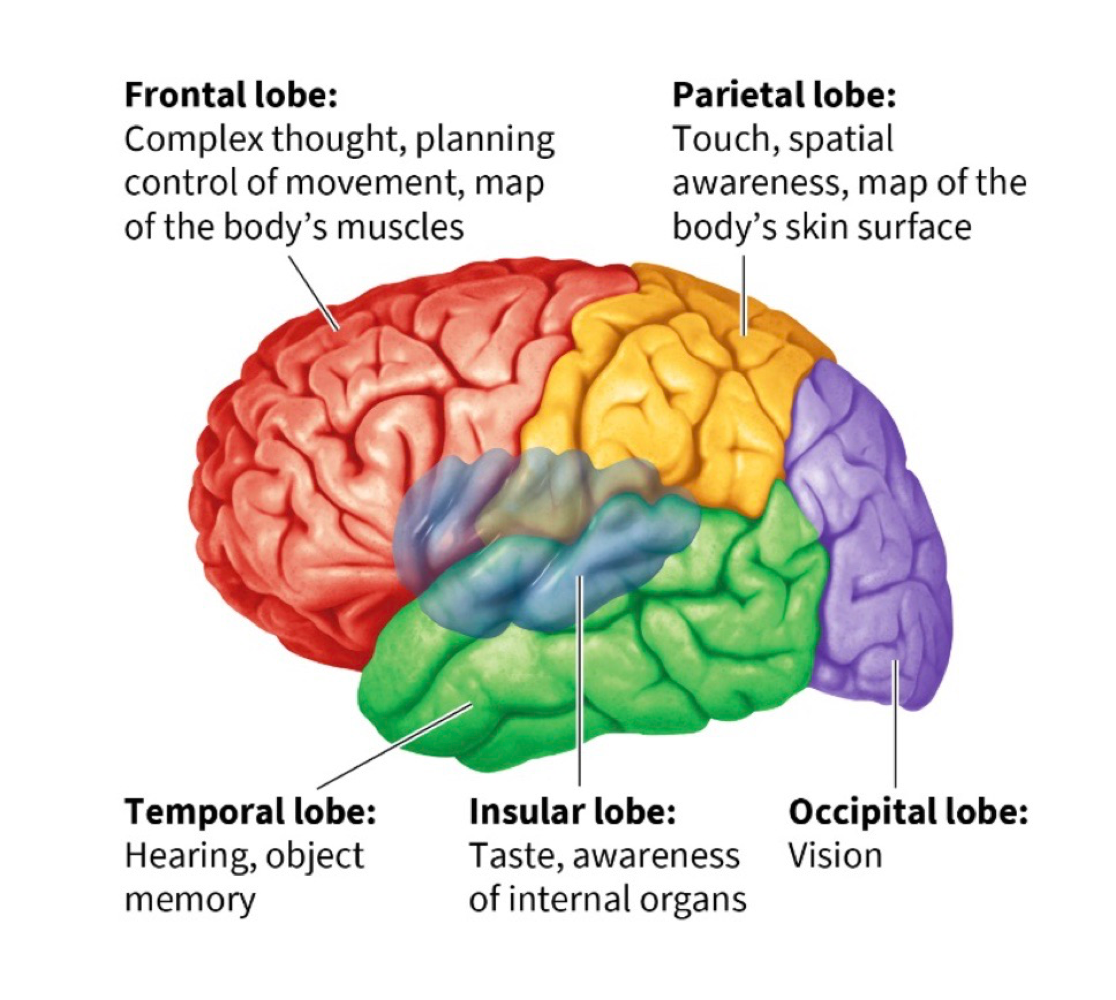
occipital lobe
links to temporal + parietal lobes let us recognize objects + process their movement, contains primary visual cortex
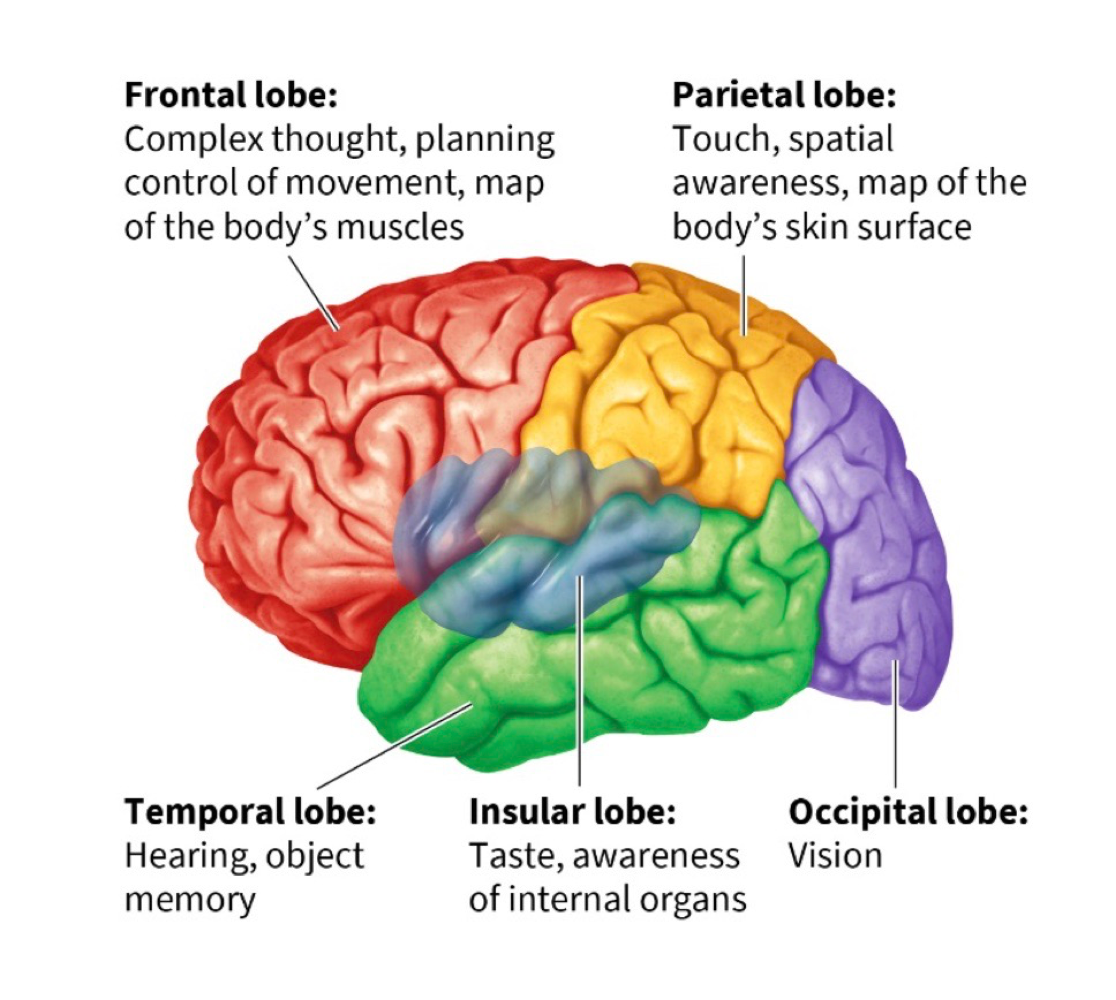
primary visual cortex
necessary for sight
temporal lobe
contains primary auditory + olfactory cortex, allows you to hear/understand language, allows you to recognize objects + people
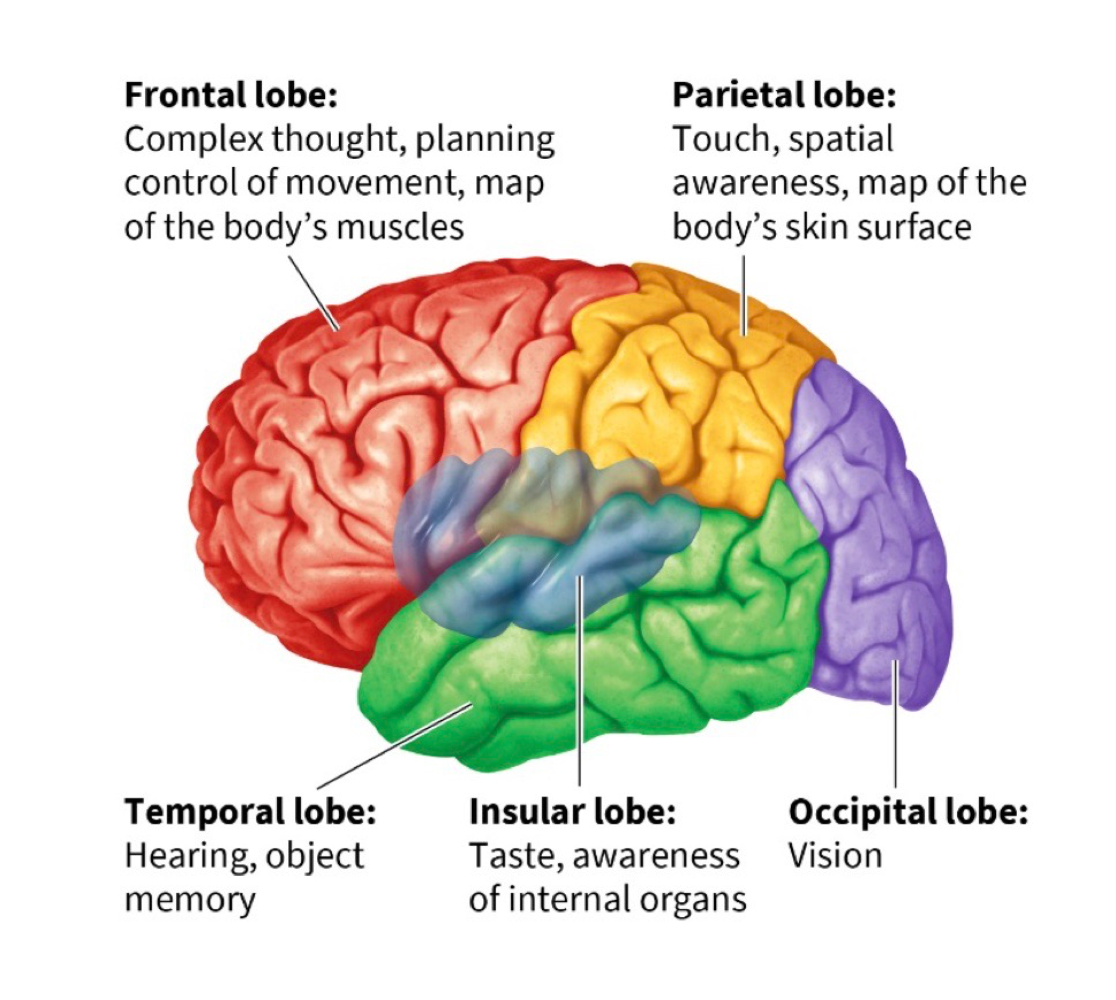
insular lobe
allows us to perceive our inner world + state of internal organs, includes the primary taste cortex
primary taste cortex
responsible for taste
association cortex
integrates incoming information from sensory areas with existing knowledge to produce meaningful experiences of the world
corpus callosum
bridge of fibers that connect the hemispheres and allows the hemispheres to talk to each other
interhemispheric transfer
2 hemispheres talking to each other
contralateral organization
each hemisphere controls primary sensory + motor functions for the opposite side of the body
lateralization
some brain functions being located on one of the two sides of the brain
what is the left side of the brain specialized for
language
what is the right side of the brain specialized for
nonverbal processing of info
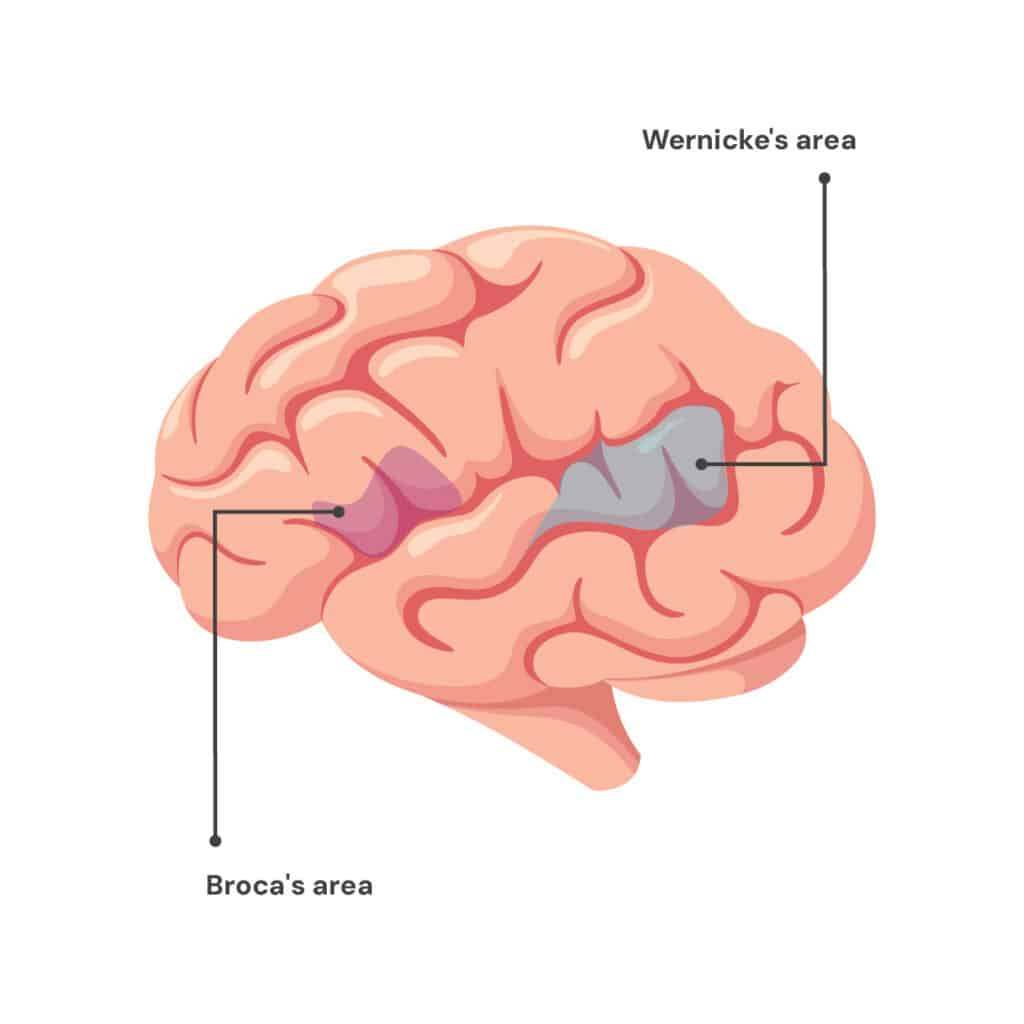
broca’s area
speech production + articulation, in left frontal lobe, damage causes telegraphic speech
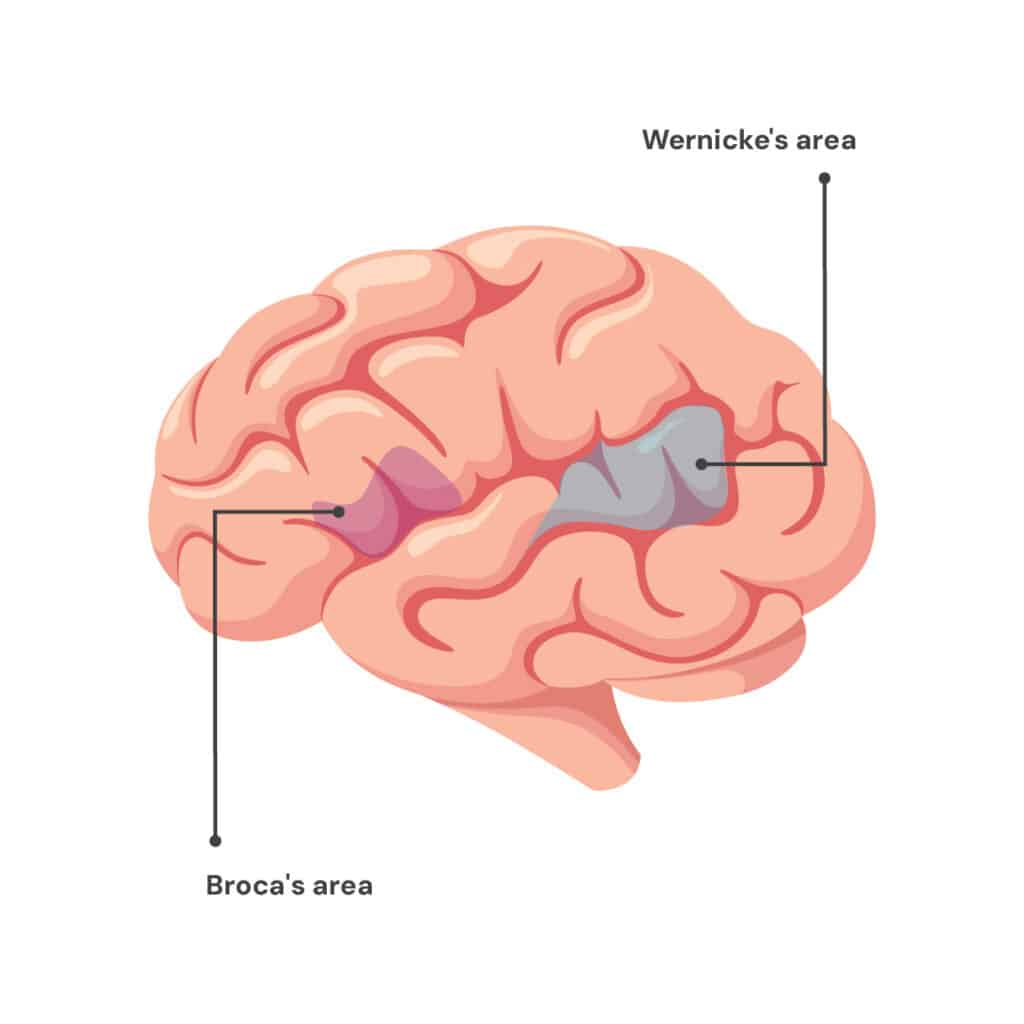
wernicke’s area
understanding/processing of words, in temporal lobe, damage causes fluent but nonsensical speech
phrenology
19th century belief that mental faculties + characteristics are located in specific brain regions + can be inferred from shape of the skull
neuropsychology
study of brain function by examining functional alterations
lesion
abnormal tissue from disease or trauma
single dissociation
lesion to brain structure A disrupts function X but not function Y
double dissociation
lesion to brain structure A disrupts function X but not function Y, lesion to structure B disrupts function Y but not X
deep-brain stimulation
stimulating specific parts of the brain with implanted electrodes
transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
exposure to magnetic field to create temporary disruption or enhancement of cortical brain function
transcranial direct current stimulation (TDCS)
low levels of direct current delivered via electrodes on the head to stimulate brain function
types of brain-stimulation study
deep-brain stimulation, transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), transcranial direct current stimulation (TDCS)
single-cell recording
measurement of the electrical activity of a single neuron
electroencephalography (eeg)
recording of electrical waves from thousands of neurons using electrodes on the scalp, shows synchronized electrical response to a sensory, cognitive or motor event that lets. us see how the brain responds to specific stimuli
magnetoencephalography (emg)
recording of magnetic fields produced by the brains electrical currents
limitations of eeg/emg
tells us when brain activity happens (temporal resolution) but not where (spacial resolution)
neural plasticity
brain’s ability to change and adapt through life