Chapter 5 - Ionic and Covalent Bonding
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
A Compound
A substance that is made up of two or more different elements combined together chemically i.e NaCl
molecule
a group of atoms joined together. It is the smallest particle of an element or compound that can exist independently i.e Cl2
How can you tell and ionic compound from covalent compound
- Ionic compound consists of a metal and a non metal
Octet Rule
When Bonding occurs, atoms tend to reach an electron arrangement with eight electrons in the outermost energy level.
Exceptions: of octet rule
1.Transition metals don't obey the Octet Rule.
2.Hydrogen, Lithium and beryllium tend to achieve two electrons in the outer energy level rather than eight electrons.
Ion
A charged ion is a charged atom or group of atoms
Ionic bond
force of attraction between oppositely charged ions in a compound. Ionic bonds are always formed between the complete transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
Ionic bonding: diagram
Bohr type circle diagram
How to do Bohr type circle diagram
Give one electron away and represent it by a cross
Ionic bonding: diagram
Dot and Cross diagram
Writing the formulas OF Ionic compounds
- Group 1 = 1+
- Group 2 = 2+
- Group 3 = 3+
- Group 4 = 4+ or 4-
- Group 5 = 3 -
- Group 6 = 2 -
- Group 7 = 1 -
- Group 8 = No ion
Write the formula of calcium chloride
1. Write down the letters
2. Write down the charge numbers corresponding to each element
3. find the ions of each respective atom by bondingCross each element with the opposite charge
4. Don't represent the 1
5. Don't represent a negative
Common Group Ions with two negative charge
- Hydroxide #
- Nitrate
- Hydrogencarbonate
- Permangenate
Common Group Ions with two negative charge
- Carbonate
- Chromate
- Dichromate
- Sulfate Ion
- Sulfite
- Thiosulfate
-
Formula writing with polyotomic ions
Use the cross method Barium and Phosphate
Barium has a charge of 2 Ba2 Phosphate has a charge of Po 43
- Cross them
- Give Barium 3
- Give the two to phosphate, but put it on the outaide in parentheses like Ba3(Po4)2
Common Group Ions with three negative charge
phosphate
Common Group Ions with one positive charge
ammonium
diatomic molecule
A molecule consisting of two atoms
diatomic molecules examples
H2 - Hydrogen
N2 Nitrogen
F2 -Fluorine
O2 Oxygen
I2 Iodine
Cl2 Chlorine
Br2 Bromine
Transition metals
A transition metal is one that forms at least one ion with a partially filled d sublevel.
Transition metals features
- Transition metals have variable valency.
- Transition metals are widely used as catalysts.
- Transition metals usually form coloured compounds.
Exceptions - d Block Elements
- Sc3+ or Zn2+ don't have partially filled d sublevel.
- Sc3+ = 1s2, 2s2, 2p6,3s2, 3p6
- Zn2+ = 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d10
valence electrons
electrons in the outermost shell
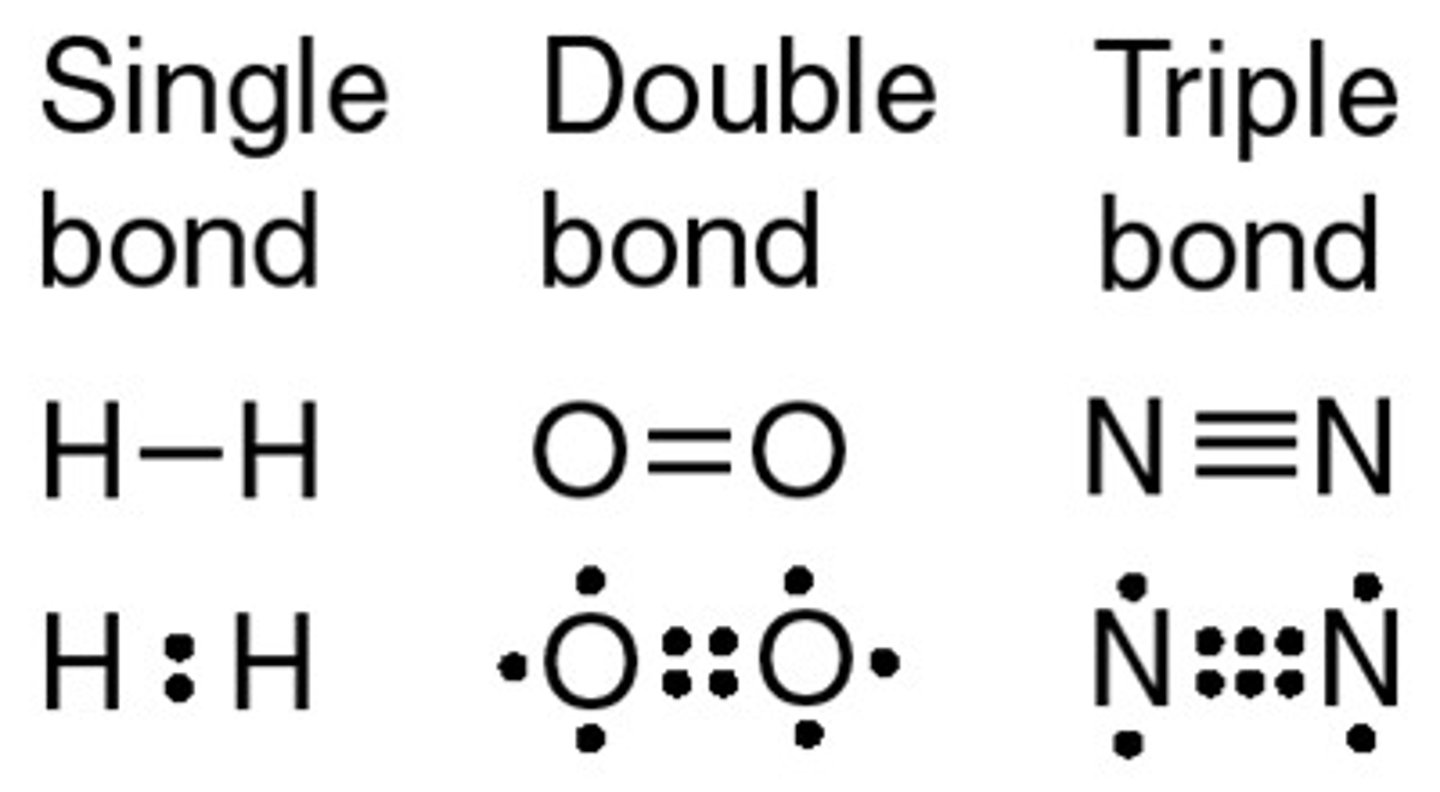
single bond
A single bond is formed when one pair of electrons is shared between two atoms.
double bond
A is formed when two electrons are shared between two atoms.
triple bond
A triple bond is formed when three pairs of electrons are shared two atoms
What shape Double and triple bonds
All double and triple bonds are linear in shape.
Bond energies between single, double and triple bonds
Bond energies for double are stronger than single and triple is the strongest. This is due to the sigma bonds being stronger than pi bonds.
Double bond and tripple bonds
What is a sigma bond
A sigma bond is formed by the head-on overlap of two orbitals.
Pi Bond
A pi bond is formed by the sideways overlap of p orbitals.
How many sigma bonds does one single bond have
one Single Bond: one sigma bond.
How many sigma bonds and pi bonds does A DOUBLE bond have
a Double Bond: one sigma, one pi bond.
How many sigma bonds and pi bonds does one double bond have
How many sigma bonds and pi bonds does one tripple bond have
a tripple Bond: one sigma, two pi bond.
lone pair electrons
Electrons that are not occupied with a bond
How can one element be partial positive and the other negative
The two electrons in HCL bond the electron from H is more attracted to CL and the electron from CL too. Since the H electron is moving away from H it gives the latter a slight positive charge. this happens when an element is more electronegaive
What happens with elements with 4.5.6.7 valence electrons as compared to elements with 1,2,3 valence electrons in terms of pairs
- Elements with 4 valence electrons like to have eight electrons in the outer shell. so they form 4 more bonds
- Elements with 5 valence electrons like to have eight electrons in the outer shell. so they form 3 more bonds
- However Elements with 3 valence electrons prefer to give away their free electrons
VSEPR
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
What is Valency
The valency of an element is defined as the number of atoms of hydrogen or any other monovalent element with which each atom of the element combines.
What does VESPR theory state
This theory states that the shape of a molecule depends on the numbers of pairs of electrons around the central atom. Since electrons are negatively charged, the electron pairs repel each other and arrange themselves in space so that they are as far apart as possible.
What is closest to the nucleus
bond angle of linear
180 (straight)
bond angle of tetrahedral
109.5 (4 bond pairs - no lone pairs)
bond angle of trigonal planar
120 degrees no lone pairs
bond angle of pyramidal
107 (one lone pairs)
Difference between trigonal and pyrimidal
Pyrimidal has lone pairs
bond angle of v shaped molecule
104.5 (2 lone pairs)
Difference between v shaped and pyramidal
v shaped has two lone pairs two bond pairs
What do lone pairs do?
lone pairs repel more than bonding pairs
How tp draw electrons around central molecule
Fill them in singly
Repelling power
Lone pair , Lone pair > Lone pair, Bond pair > Bond pair, Bond pair
Ionic bonding properties
- Contains a network of ions in the crystal d
- Usually hard and brittle
- Have high melting points and boiling points
- Usually solid at a room temperature
- Conduct electricity in molten state or when dissolved in water
Covalent bonding properties
- Contain individual molecules
- Usually soft
- Have low melting and boiling points
- Usually liquids, gases or soft solids at room temperature
- Do no conduct electricity
Electronegativity
Electronegativity is the relative attraction that an atom in a molecule has for the shared pair of electrons in a covalent bond.
Uses of electronegativity
1. To predict the polarity of covalent bonds.
2. To predict which compounds are ionic and which are covalent.
Polar covalent bond
A polar covalent bond is a bond in which there is unequal sharing of the pair (or pairs) of electrons. This causes one end of the bond to be slightly positive (δ+) and the other end slightly negative (δ-). one side attracts more the other less
non-polar covalent
A non-polar covalent bond is a bond in which there equal sharing of electrons
what indicates ionic bonding
An electronegaitivy difference greater than 1.7 indicates ionic bonding in a compund
what indicates covalent bonding
An electronegaitivy difference less than or equal to 1.7 indicates ionic bonding in a compund
what indicates polar bond
An electronegaitivy difference greater than .4 or less than1.7 indicates indicates a polar bond
what indicates non polar bond
An electronegaitivy difference less than or equal to .4 indicates non polar
Predict bonding type based on electronegativity/location on periodic table.
Precit bonding
Exceptions to polar covalent bonds
There are some molecules which, even though they have polar covalent bonds are not polar molecules as the centre of the positive charge and the negative charge coincide (Symmetry).
What type of bonding is always polar
Hydrogen bond
The following shapes are automatically non-polar molecules
1. Linear
2. Trigonal Planar
3.Tetrahedral
What is intramolecular bonding
Intramolecular bonding is bonding that takes places within a molecule i.e. it holds the atoms together i.e. Ionic and covalent bonding.
What are Intermolecular forces
Intermolecular forces are the forces of attraction that exist between molecules i.e. Van der Waals forces, dipole-dipole forces and hydrogen bonding.
Van Der Waals Forces
- Van der Waals forces are weak attractive forces between molecules resulting from the formation of temporary dipoles.
- They are the only forces of attraction between non-polar - molecules.
The boiling point of van der walls is high and the bigger the molecule the higher the boiling point
Temporary dioples
Electrons moving around in the electron cloud of a non polar molecule cause one side do be polarized creating temporary diopoles one negative and the other positive
What is proof of van der walls existing
Gases that consist of non polar molecules can be liquified
What are Dipole -Dipole forces
Dipole-dipole forces are forces of attraction between the negative pole of one polar molecule and the positive pole of another polar molecule. A permanent dipole is formed between two polar molecules.
Hydrogen bonding
- Hydrogen bonds are types of dipole-dipole attractions between molecules in which hydrogen atoms are bonded to nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine.
-
The strongest forces, therefore, the highest boiling points. Because there are stron intermolecular forces so cosniderable energy must be used to break the bonding
How can you tell if a molecule is in a hydrogen bond
When hydrogen is bonded to an atom of fluorine nitrogen or oxygen
What are Boiling points affected by
Boiling points are affected by intermolecular bonding and molecular mass.
What happens when two molecules exhibit the same type of bonding
If two molecules exhibit the same type of bonding, then it is the larger the molecular mass that will have the higher boiling point.
How is solu
- Solubility is affected by intramolecular bonding.
"Like Dissolves like"
Polar substances can only dissolve in other polar substances.
Non- polar substances can only dissolve in other non-polar substances.
Why wont water dissolve in oil
Water is polar and oil is non-polar this is why water and oil don't dissolve in one another.
What is the polar/non polar rod experiment
If the liquid is polar then then the stream f liquid is attracted to the negatively charged rod. It doesnt matter if the negatively charged rod is turned into a positive rod as the water molecules will turn so that the negative side is facing the positive rod
What happens to non polar substances in the rod experiment
Nothing happens they are not attracted to any side
Whats always automatically non polar
- Diatomic molecules
= Hydrocarbons
Is water a solvent
Yes most ionic and covalent substances dissolve in water