MEA 449 Review - Fisheries, Detrital Food Web, Carbon Pump and Geoengineering, Deep Ocean Habitats, Hydrothermal Vents and Hydrocarbon (Cold) Seeps, and Mesopelagic and Bioluminescence
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Food Chain Type, Primary Productivity, # Trophic Levels, Food Chain Efficiency, and Potential Fish Production
Oceanic (90%) - 50, 5, 10, 0.5
Shelf (9%) - 100, 3, 15, 340
Upwelling (1%) - 300, 1.2, 20, 36000
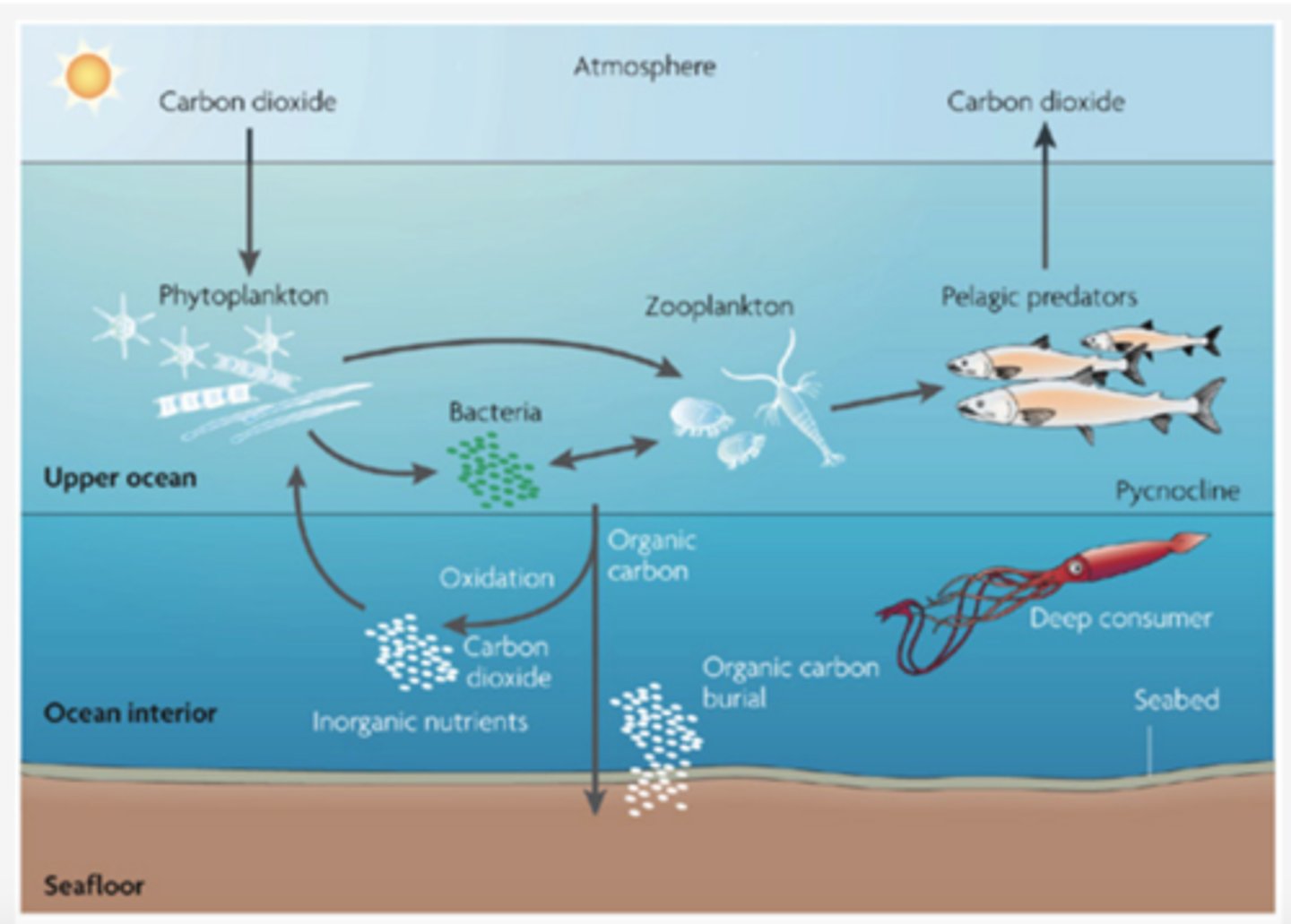
Biological Carbon Pump
Process of surface carbon reaching the deep ocean, mediated by biology
hydrothermal vents
spots on the ocean floor where hot gases and minerals escape from earth's interior into the water, high biomass and most organisms endemic, organisms here are extremophiles, short lived environment
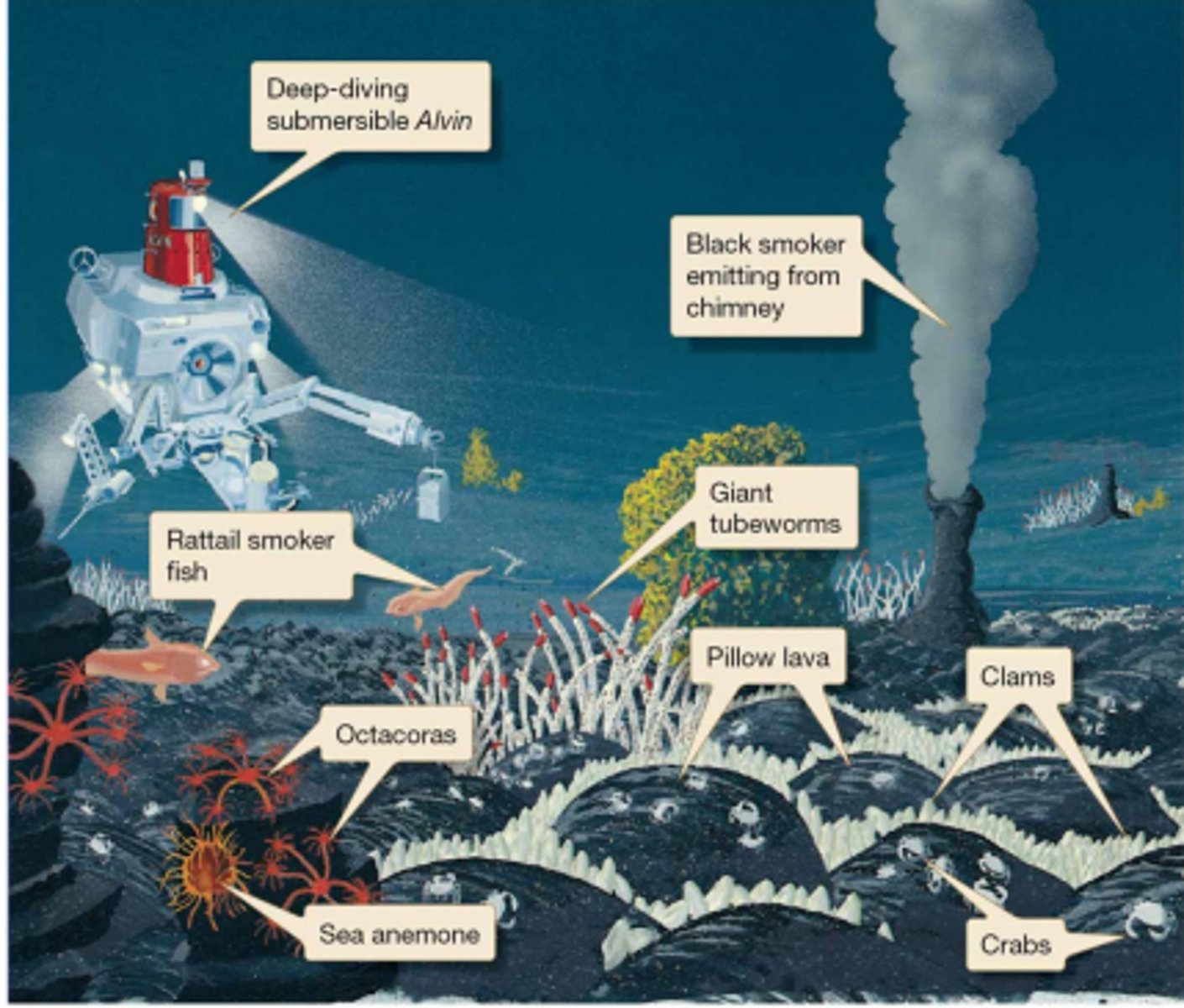
Organisms found at vents
Worms - vestimentiferan (riftia) worm, Pompeii worm
Giant clams
Mussels
Sulfide reducing bacteria
Chemosynthesis
6 CO2 + 3 H2S + 6 H2O --> C6H12O6 + 3 H2SO4
process in which chemical energy is used to produce carbohydrates
Luciferin-Luciferase Reaction
Luciferin + O2 --> Oxyluciferan + light
Co-factors: Ca^2+ and NADPH
Occurs in photocytes and photophores
Current patterns and particle concentrations along the continental shelf to depths of ~3000m in contrast to the abyssal plains favor __ over __.
suspension feeders, deposit feeders
What is Growth Overfishing?
The average weight of fish decreases over time due to increased harvest of younger fish, requiring more fish to reach weight quotas.
What is Recruitment Overfishing?
The spawning stock is reduced to too low a level to ensure adequate production of young fish, which can lead to population collapse.
Which type of overfishing is more severe?
Recruitment overfishing because it can collapse the population of fish
List four components of overfishing and provide an example of each.
1. Uncontrollable effort - Bristol Bay, AK salmon fishing, recreational fishing
2. Over capitalized, overly efficient fishery - highly efficient gear (fish finder + gps)
3. Bycatch (non target species, destroying habitats) - shrimp trawls catching other species
4. Increased demand - sushi, Tokyo fish market
Why does overfishing happen?
Greed & politics
Politics & science disagreeing
Natural variation masks overfishing
Shifting baselines
solutions to overfishing
1. Catch shares (economists & sociologists)
2. Stock assessments & EBFM & MPAs (fishery scientists)
3. Educate on sustainability
4. Enforcement
5. Political pressure by voters
6. Economic pressure by consumers
What is the "key to success" to ending overfishing?
Enforcement - increasing cooperation among local, national, regional, and global levels
What are catch shares?
A type of management system that dedicates a secure share of fish or fishing area, to individual fishermen, communities or fishery associations
What are the effects of overfishing?
Growth overfishing -> reduced size at age -> reduced egg output
What are the population effects of overfishing?
Crab pots size-selective
Selects for early maturity
Decrease in mature female size, increased occurrence of pigmy females, less egg production
Ecosystem phase shift (coral reef)
Coral larvae need a clean substrate to settle on and grow
Herbivores "clean" substrate by grazing the algae
Overfishing -> Massive urchin die off, herbivorous fish overfished
Increased nutrients fuel algal growth
50:50 coral/algal ratio 200 years ago, dominated by large vertebrates
10:90 coral/algal ratio 1990s, loss of small fish and few urchins
Ecosystem phase shift (kelp forest)
Sea otters eat urchins
Kelp forests grow large in presence of otters
Orcas prey on sea lions and seals offshore
As fish stocks in AK declined, so have seals and sea lions, orcas switched from more favorable prey to otters
Sea otter populations wiped out by orcas, urchin populations explode and overgraze the kelp forest
What is Ecosystem-Based Fisheries Management (EBFM)?
Protects ecosystem structure, functioning, and key processes (eg key trophic links)
Recognizes interconections within and among systems (land use, trophic links, environmental stress)
Integrates ecological, social, economic and institutional perspectives
Place based or area based
Benefits of EBFM
More effective governance
Improved science for decision making
Strengthened educational programs
What is the fate of phytoplankton biomass?
Zooplankton grazing
Remineralization in microbial loop
Benthic-pelagic coupling (exchange of nutrients btwn. water column and benthic system)
Export flux to depth (passive & active transport)
What happens to carbon biomass that leaves the surface layers?
Most carbon remineralized at depth is eventually brought back to surface via physical mixing and upwelling
Sinking algal biomass, zooplankton migration, consumption & remineralization
1% of carbon reaches deep sediments
What happens to carbon in the surface mixed layer?
Physical mixing of water, phytoplankton production, zooplankton consumption, remineralization of dissolved carbon and nutrients
What is marine snow?
Detrital non-living organic particles visible to the naked eye (>0.5 mm)
Why is marine snow important?
1. Microhabitats for microorganisms, provides a food source
2. Transport of surface derived organic matter to depth
Where does marine snow come from?
Dead organisms (plankton, kelp, pollen, ash)
Fecal pellets (crustaceans)
Mucus products (pteropod feeding webs, larvacean houses)
Secretions from organisms (cell walls, cyanobacteria colonies)
Physical formation of marine snow
Small scale: Brownian movement
Shear forces, turbulence in surface layer
Differential settlement (mucus catches small particles)
DOC bubbles
Adsorption of dissolved molecules to aggregate surfaces
Biological formation of marine snow
Substances that enhance stickiness of particles
PER - photosynthetic extracellular release by algae pycosphere
Algae contents like proteins or DNA released from lysis
Polymers and exoenzymes released from bacteria
Brownian Movement
random movement of particles suspended in a fluid
Phycosphere
area immediately surrounding algal cells
Stoke's Law
describes the sinking behavior of a particle with a size of 1 micrometer to 1 millimeter
What variables are needed for Stoke's Law
particle radius, gravity, particle density, density of seawater, viscosity of seawater, shape factor
Explain the 2 main processes that make up the Biological Pump
Diel Vertical Migration (active)
Sinking of Marine Snow (passive)
What is the fate of marine snow as it sinks through the water column?
Zooplankton grazing - trophic link
Decomposition by micro organisms
Fragmentation
Lateral advection - export of marine snow in coastal or shelf areas
Settlement - <1% gets buried in sediments
Geoengineering definition
the deliberate large-scale manipulation of earth's climate system to counteract climate change
Iron Fertilization Experiments
Iron added to areas of high nutrients but low productivity (iron is limiting)
Based on the biological pump, stimulated higher surface productivity results in higher carbon export to depth
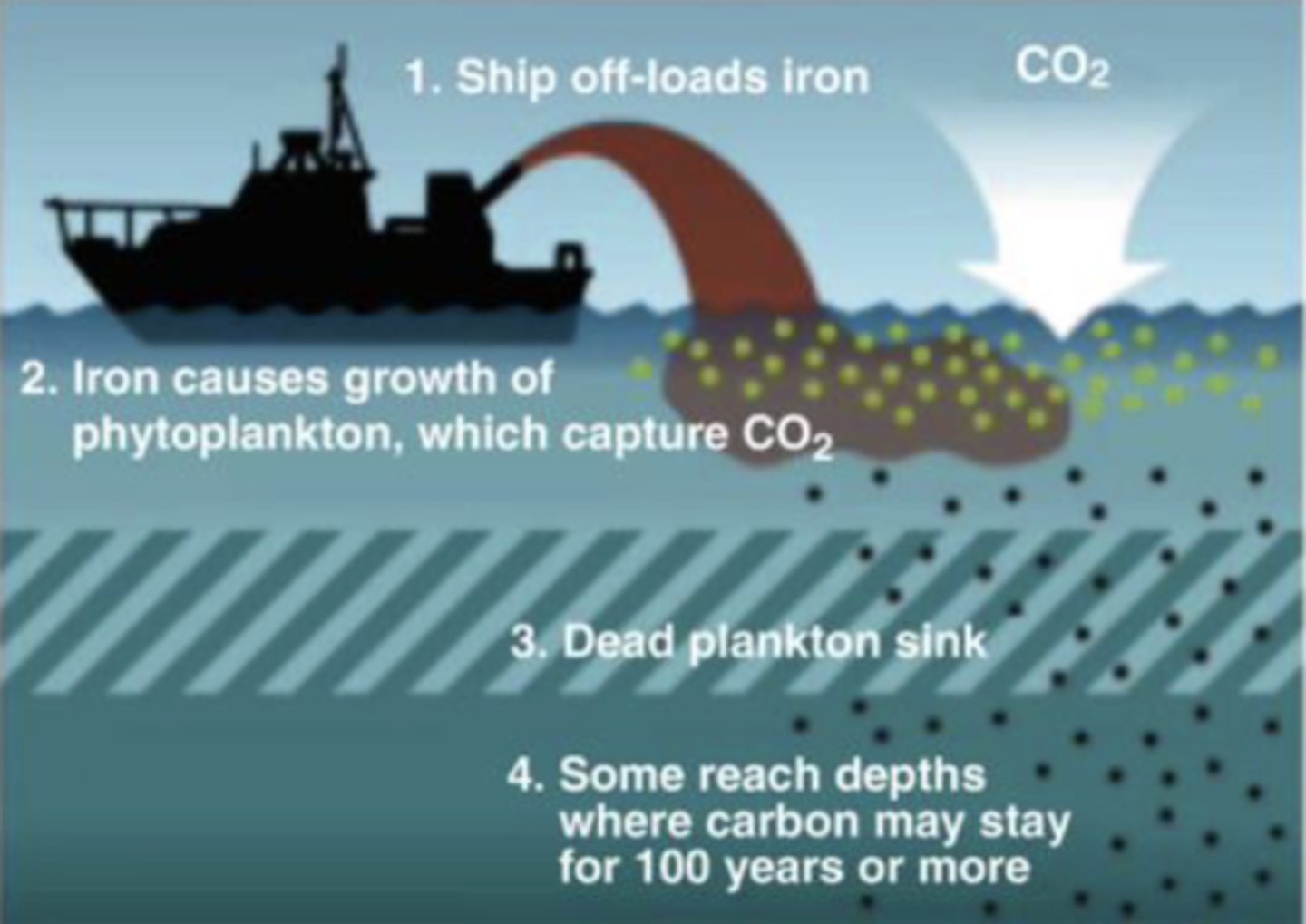
Iron Fertilization Hypothesis
The hypothesis that iron added to surface ocean enhances the productivity of the surface ocean, sends CO2 into the deep ocean, and reduces the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere
Should cause an increase in algae populations
Potential consequences of iron fertilization
may cause toxic algae to propagate, doesn't actually change the rate of deep ocean transport, may increase dead zones, no way to guarantee iron will stay in the area it is needed in because of storms/mixing/etc
List approaches to carbon management / Geoengineering strategies
1. Radiation Management - space mirrors or reflective aerosols let out by airplanes or cloud seeding
2. CO2 air capture and storage underground, directly injected to bottom of ocean or by afforestation
3. Iron fertilization
Physicochemical Properties of Deep Ocean
cold, dark, high pressure, nutrient limited
What percent of marine species are benthic?
95%
Benthic organisms
Attach itself to a substrate

2 types of substrates
Hard rock (uncommon)
Sediments (common)
Types of hard rock
spreading centers (vents)
active faults
sides of seamounts
on top of another organism
offshore banks
manganese modules
Types of sediment
terrigenous/lithogenic - nearshore
biogenic - skeletal remains
aeolian - atmosphere
cosmic - meteors
Epifauna
Benthic animals that move about the surface of the sea bottom or are firmly attached to it

Infauna
Benthic animals that burrow in the substrate, dominant in deep sea
Snails, ciliates, worms, protozoa, bacteria
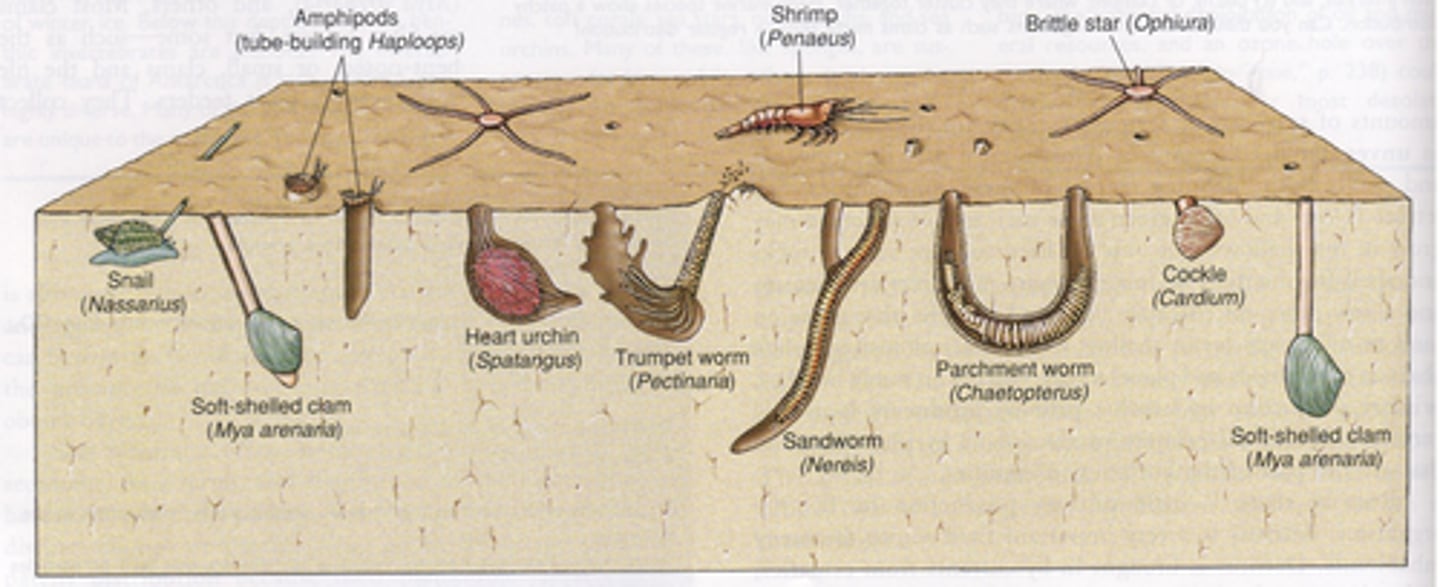
Sessile species
These are species that do not move; usually organisms attached to something.

Errant species
These are species that move across the seafloor

Benthic boundary layer
layer of water above floor, slow flow so sediments may gather, favorable for suspension feeders
How is food limited in the deep ocean
Detritus (marine snow)
Ladder of vertical migration
Chemosynthesis at hydrothermal vents
How do organisms save energy
Movement: increase water content of body, non-ossified skeleton, gas filled area of body
Colors: counter shading, red, clear
Vision: large eyes, eye placement
Metabolism: very slow, specialized enzymes (10-100x slower)
Dominant feeding modes in deep ocean
Suspension feeding, deposit feeding
Suspension feeding
capture food particles suspending in the water that passes through them
crinoids, polychaet worms, molluscs
Deposit feeding
feeding on particulate organic matter that settles on the bottom
holothurians, worms
How do organisms at hydrothermal vents get energy?
Chemosynthesis
Pompeii worm (Alvinella pompejana)
Most heat tolerant animal in the world, has a bacterial fleece
How do Riftia / vestimentiferan worms survive without mouths and digestive tracts?
Symbiotic chemosynthetic bacteria pass nutrients to capillaries and they get distributed in the host, they also have special hemoglobin for O2 and H2S transport
If vents are 100s of kilometers apart, how do organisms get to the next vent after they disappear?
Whale falls as step stones, succession of organisms
Cold seeps
areas that produce lower temperature fluids where natural gas and methane gas seep into the water in the deep ocean, long lived environment, no extremophiles, bacterial mats

Difference of organisms at cold seeps vs. hydrothermal vents
Similar taxa, different species
No extremophiles in cold seeps
Difference of bacteria at cold seeps vs. hydrothermal vents
Bacteria at cold seeps reduce methane
Bacteria at vents reduce sulfide
Bioluminescence
the production of light by living organisms, 90% of all meso and bathypelagic organisms are bioluminescent, only light found below 1000 meters

Types of bioluminescence
Luciferin and photoproteins, extracellular and intracellular
Photoproteins
Stable enzyme substrate complexes, protein emits light
Does not need O2 because it can react with other molecules like calcium or iron
Luciferin vs. photoproteins
photoprotein bioluminescence does not require O2 and is extracellular
luciferin bioluminescence requires O2 and is intracellular
Extracellular bioluminescence
Glands produce luminescent photoproteins, associated with escape responses, found in coastal waters
Crustaceans, squid, medusae
Intracellular bioluminescence
Occurs in photocytes/photophores, under control of nervous system
More complex, utilizes lenses, shutters, filters, reflectors
Squids, ctenophores, dinoflagellates
Symbiotic photobacteria
Continuous light, shutters evolved to control light emission
Located in specialized organs
Bacteria nourished by blood supply but population is limited by the fish
How are photobacteria systems started in young fish
Consuming feces of older members of species that have bacteria in their guts
Why do organisms use bioluminescence?
Lure - anglerfish
Vision - barrel fish
Species recognition / communication - fish schooling
Startling predators - squids, medusae
Burglar alarm - dinoflagellate
Toxin warning - dinoflagellate
Camouflage - squids, octopus
What are biogenic sediments made of
foraminifera shells, diatom frustules, radiolarian ooze
Strategies to save energy as a mesopelagic and bathypelagic zooplankton can include the following:
lack of ossified skeleton, transparent or red pigmentation, ambush feeding and extendable stomachs in fish, slow growth and long reproduction cycles, diel vertical migration
open ocean
small primary producers (e.g., cyanobacteria), low export flux, food webs with many trophic levels
The following processes can contribute to fragmentation of marine snow in the twilight zone.
Zooplankton feeding
Potential sources of marine snow include the following:
phytoplankton, fecal pellets, mucous structures, molts
Applying what you know about trophic interactions and food webs from Ryther (Table discussed in lecture) answer this question. Assuming you measured an average value for primary production with 50 gC per m2 per year over a continental shelf region. How much yield would you predict for fish production in this system?
~170 mg C per m2 per year
Based on the Iron Fertilization Hypotheses stimulating growth in surface waters through the addition of iron is expected to result in increased carbon export to depth
True
Organisms mentioned in tipping point documentary
Limpets, coral reefs, oysters
Current patterns and particle concentrations along the continental shelf to depths of ~3000m in contrast to the abyssal plains favor _ over _
suspension feeders, deposit feeders