Interpreting ECGs
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
How do you systematically interpret an ECG?
is it regular?
what is the heart rate?
are there P waves?
what is the length of the PR interval?
Is the QRS duration narrow or broad?
What is the relationship between the P waves and the QRS complex?
Which leads show ST elevation?
Which leads show ST depression?
How do you assess regularity?
On a piece of paper mark where the the R wave is, move the piece of paper along to line up with the next R wave and see if if the lines on paper match the R waves on the rhythm strip
What are the options of regularity?
regular, regularly irregular, irregularly irregular
How do you see if an ECG shows regularly irregular rhythm?
the lines on the paper sometimes match the R waves on the rhythm strip
How do you see if an ECG shows irregularly irregular rhythm?
The lines on the paper never match with the R waves on the rhythm strip
How do you calculate rate of regular rhythms?
300 divided by the number of big squares between 2 consecutive R waves, or
1500 divided by the number of little squares between consecutive R waves
How do you calculate rate of an irregular rhythm?
number of QRS complexes in 10 second (30 big squares) rhythm strip x 6
What is a flutter wave?
Multiple P waves before the QRS complex
What are the types of Acute Coronary Syndrome?
STEMI, NSTEMI, Unstable angina
What is a STEMI caused by?
The plaque in coronary arteries ruptures, the material exposed by this rupture causes the blood to clot, leading to a blockage
How is STEMI identified?
S and T is elevated on the ECG, J point is elevated
Pain and breathlessness
Increased troponin levels
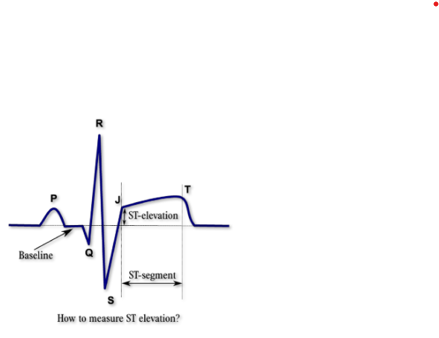
What happens when a STEMI is identified?
Patient needs immediate revascularisation
Attend a specialist hospital for pPCI
What is an NSTEMI?
They are having an MI but does not show ST elevation, will still have increased troponin levels
What is unstable angina?
May occur when sitting at rest, then go away again
Not as predictable as stable angina
No ST elevation
What is stable angina?
Fatty deposits in coronary arteries restrict blood flow, meaning pain may appear when the heart is under stress
Not shown on ECG