Key Drugs Guy/Study Tip Gal from RxPrep 2020
1/188
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
189 Terms
Common resistant pathogens
Klebsiella pneumoniae (ESBL, CRE)
Escherichia coli (ESBL, CRE)
Acinetobacter baumanii
Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium (VRE)
Staphylococcus aureas (MRSA)
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
CYP inducers
PS PORCS: phenytoin, smoking, phenobarbital, oxcarbazepine, rifampin, carbamazepine, St. John's wort
CYP inhibitors
G PACMAN: grapefruit, protease inhibitors, azole antifungals, cyclosporine (also cimetidine, cobicistat), macrolides (clarithro, erythro), amiodarone, non-DHP CCBs (diltiazem and verapamil)
List of approved drugs that can be interchanged with generics based on therapeutic equivalence
Orange Book (FDA)
Information on epidemiology and vaccine-preventable diseases
Pink Book (CDC)
News reports on regulatory, legislative, legal and business developments
Pink Sheet (Pharma Intelligence)
List of biological drug products, including biosimilars
Purple Book (FDA)
Drug pricing information
Red Book, Pharmacy
Summaries of pediatric infectious diseases, antimicrobial treatment and vaccinations
Red Book, Pediatrics (AAP)
Information of the health risks of international travel, required vaccines and prophylaxis medications
Yellow Book (CDC)
Information on approved animal drug products
Green Book (FDA)
Drugs with leaching/adsorption issues with PVC containers
Lorazepam, Amiodarone, Taxanes, Tacrolimus, Insulin, Nitroglycerin
Only compatible in saline
("A DIAbetic Can't Eat Pie")
Ampicillin, Daptomycin, Infliximab, Amp/Sulbactam, Caspofungin, Ertapenem, Phenytoin
Only compatible in dextrose
("Obese Bakers Avoid Salt")
Oxaliplatin, Bactrim, Amphotericin B, Synercid
Common drugs with filter requirements
Pushy Guys (and gals) in LA LA land
Phenytoin
Golimumab
Lipids (1.2 micron - larger pore size filter required)
Amphotericin B (lipid formulations - prepare using 5 micron filter)
Lorazepam
Amiodarone
Most require 0.22 micron filter during administration
Additional drugs: Isavuconazonium
Do not refrigerate
(Dear Sweet Pharmacist, Freezing Makes Me Edgy)
Dexmedetomidine, SMX/TMP, Phenytoin, Furosemide, Moxifloxacin, Metronidazole, Enoxaparin
Protect from light during administration
(Protect Every Necessary Med from Daylight)
Phytonadione, Epoprostenol, Nitroprusside, Micafungin, Doxycycline
Others: Ampho B Deoxycholate, Anthracyclines, Dacarbazine, Pentamidine, Thiotepa
Continuous data
ratio or interval data:
ratio - age, height, weight, time BP
interval - Celsius or F temp scales
Discreet data
also categorical data:
nominal - gender, ethnicity, marital status, mortality
ordinal - NYHA Functional Class, pain scale
Type I error
false positive, the incorrect rejection of a null hypothesis, related to alpha level
found a difference when there actually is not one
Type II error
false negative, incorrectly accept the null hypothesis
not finding a difference when there actually is one
study power
The ability to detect a difference btw study groups if one actually exists.
Indirectly related to the likelihood of making a Type II (b) error...As power increases, chance of type II error decreases
interpretation of 95% confidence interval
We are 95% confident that the true population value lies somewhere between ___ and ___ (range).
interpretation of NNT 45
For every 45 patients who receive [treatment] for [one year], [outcome (e.g. HF progression)] is prevented in one patient
(ROUND UP NNT so you don't overestimate benefit)
interpretation of NNH 90
One additional case of [major bleeding] is expected to occur for every 90 patients taking [drug] instead of [placebo/other drug].
(ROUND DOWN NNH so you don't underestimate harm)
What kind of statistical analysis should be performed for continuous data that is normally distributed between a single group compared to known data from the population?
one-sample t-test
What kind of statistical analysis should be performed for before and after continuous data that is normally distributed between a single group?
dependent/paired t-test
What kind of statistical analysis should be performed for continuous data that is normally distributed between two groups (e.g. treatment and control comparison for BP reduction)?
unpaired student t-test
What kind of statistical analysis should be performed for continuous data that is normally distributed between three or more groups?
ANOVA
What kind of statistical analysis should be performed for discreet/categorical data between a single group or two groups (e.g. mortality data)?
Chi-square test
(Fisher's exact for a very small trial)
Cost-minimization analysis
used when two or more interventions have already demonstrated equivalency in outcomes and the costs of each intervention are being compared
cost-benefit analysis
compares the costs and benefits between unrelated or related programs, as long as the outcome is monetary
cost-effectiveness analysis
outcomes are measured in natural units (e.g. life years gained, mmHg blood pressure, % at treatment goal)
cost-utility analysis
measured in QALY
What is the focus of USP <797>?
minimize the risk of microorganisms or other contaminants in sterile preparations
What is the focus of USP <800>?
keep the compounder safe and reduce risk of exposure to the HD
What are the physical space basics for non-sterile compounding?
*needs to be separate and distinct from any sterile compounding
*can be performed in ambient (room) air
*must have adequate space for orderly work with shelving and storage & no storage on the floor
*needs to be adequate plumbing and 2 types of water: potable (tap water) to wash hands (along with soap and single-use towels or a hand dryer) and purified/distilled water for compounding and rinsing equipment
*well-lit, controlled HVAC, with temperature and humidity monitoring
What are the physical space basics for sterile compounding?
*anteroom, buffer area and a PEC (hood) with specific ISO air requirements
*all surfaces must be smooth, impervious, free from cracks or crevices and non-shedding so they are easy to clean
*walls - locked, sealed panels
*floors overlaid with wide, sheet vinyl flooring with heat-welded seams
*buffer area cannot contain sinks or floor drains
*required air and surface sampling, temp and humidity requirements to test for contaminants
What are the physical space basics for hazardous drugs?
Containment-PEC or SEC (vertical flow hood)
*permissible to perform both sterile and non-sterile HD compounding in same area as long as ISO 7 air is maintained, kept 1 meter apart, no HD powders at the same time as sterile compounding
negative air pressure in C-SEC and C-PEC & externally exhausted or use redundant HEPA filters ( if non-sterile HD ONLY*)
*non-sterile HD ACPH 12/sterile 30
Air quality for sterile compounding
*PEC/hood/isolator/glove box is ISO 5 air: < 3,520 particles/m^3
*SEC/buffer area/room where the hood is located is ISO 7 air: < 352,000 particles & anteroom if open to negative pressure SEC
*anteroom/where you garb & wash hands is ISO 8 if open to positive pressure: < 3,520,000 particles (7 if negative)
HEPA filters
>99.97% efficient at removing particles 0.5 microns or larger (including bacteria, viruses, fungi, dust)
-located at the top in a vertical biological safety cabinet
-located at the back in a horizontal LAFW
-must be recertified by a specialist every 6 months or any time a PEC is moved
Non-HD sterile compounding: working inside the hood/PEC
-always work 6 inches from the front edge of the hood
-wipe off the outside of vials, syringes, etc with 70% IPA before bringing them inside the hood
-line up items side by side in a horizontal LAFW to protect critical sites exposed to first air and avoid creating turbulence
-NO external vent for non-HDs
-waste buckets are red for sharps and non-hazardous waste
HD sterile compounding: working inside the Class II BSC/CACI
-will be externally vented
-negative air pressure, vertical flow
-do not block first air coming from the top; hold horizontal or underneath
-waste buckets are yellow for trace HD waste, such as empty vials and syringes
-garb: 2 pairs ASTM-rated gloves (powder free, 1 pair under gown cuff 1 pair over gown cuff, change every 30 mins or if punctured), head/hair covers, 2 pairs of shoe covers, disposable, impermeable gown closed to the back with closed cuffs, face shield, goggles
Personnel training requirements for sterile compounding
-initial training (didactic + hands-on), any time work is new or different must have additional training
-PRIOR to compounding, must demonstrate adequate aseptic technique in hand hygiene, garbing and gloving by passing the gloved fingertip test and in sterile drug preparation by passing the media-fill test
-if compounding low-medium risk CSPs: initially + annually
-high-risk CSPs: initially + every 6 months
What is considered passing a gloved fingertip test?
Perform garbing and gloving, then must have three consecutive gloved fingertip samples with zero CFUs for both hands (6 total plates with TSA)
How do you pass a media fill test?
TSB takes place of the drug being prepared. The growth medium must stay clear after 14 days of incubation
How often should the temperature be monitored?
daily for the cleanroom/SEC (20 C/68 F or colder)
twice daily, minimum daily for the fridge (2-8 C) and freezer (-50 to -15 C)
How often should air and surface testing be performed?
-air sampling: at least every 6 months
-surface sampling: periodically; TSA plates with polysorbate 80 and lecithin cannot have > 3 CFUs in ISO 5 or > 5 CFUs in ISO 7, preferably -zero CFUs
-air pressure: every SHIFT or daily at a minimum
When can you shut down the hood/PEC?
Ideally it should be kept running at all times
-if power outage, all compounding must STOP and all hoods will need to be cleaned with germicidal detergent THEN disinfected with 70% IPA and allowed to run for 30 mins prior to resuming compounding
-C-PECs will need to be sanitized 1 & 2. deactivation and decontamination with bleach or peroxide 3. clean 4. disinfect with IPA
What is the cleaning schedule for the sterile compounding area?
DAILY: clean and disinfect counters, floors & carts; for HDs sanitize the work area at the end of each shift
WEEKLY: walls, windows, shelving, bins, chairs
MONTHLY: ceiling
How often should you clean ISO 5 PECs?
-before each shift
-every 30 minutes while working
-before and after each batch of CSPs
-whenever needed, including after spills
What do the different colors of waste bins mean?
RED: infectious waste, including IV tubing and culture dishes
YELLOW: trace hazardous waste, including sharps
BLACK: bulk hazardous waste with a visible amount of HD drug left, supplies used to administer HDs or clean up HD spills
Steps for garbing
Outside the ante area: remove all jewelry, make up, coat
Ante area: put on shoe covers, head and facial hair covers, and face mask (eye shield if preparing HDs), wash hands with soap and warm water for 30 seconds, scrubbing in circular motions up to elbows and cleaning under fingernails, dry hands with a lint-free disposable towel, put on non-shedding gown and enter the buffer area
Buffer area: apply chlorhexidine scrub or povidone-iodine, put on sterile gloves, sanitize with 70% IPA and wait until dry before compounding
BUD for nonaqueous formulations
Not later than the time remaining until the earliest expiration date of any API or 6 months, whichever is earlier
BUD for water-containing oral formulations
14 days refrigerated
BUD for water-containing topical/dermal and mucosal liquid and semisolid formulations
30 days at room temperature
BUD for hazardous drugs compounded in a segregated compounding area
12 hours at room temp or fridge
BUD for low risk CSPs
48 hrs room temp
14 days fridge
45 days freezer
BUD for medium risk CSPs
30 hrs room temp
9 days fridge
45 days freezer
BUD for high risk CSPs
24 hrs room temp
3 days fridge
45 days freezer
Binders
acacia, starch paste, sucrose syrup
diluent or fillers
-tablets/capsules: lactose, mannitol, sorbitol, starches, calcium salts, gelatin, bentonite
powdered cellulose (also a thickener, adsorbent, disintegrant, suspending agent)
-liquid: water, glycerin, alcohol
-topical: mineral oil, petrolatum, lanolin, waxes
Disintegrants
alginic acid/alginates, polacrillin potassium (Amberlite), cellulose products, starches, compressible sugar (Nu-Tab)
lubricant/glidant/anti-adherent
magnesium stearate, calcium, PEG, glycerin, mineral oil, stearic acid, talc, colloidal silica
preservatives
"benz" "cetyl" "phenyl/ols" "parabens"
chlorhexidine
topical/nasal: alcohols, acids, chlorhexidine
sorbic acid/potassium sorbate, thimerosal
sodium benzoate, benzoic acid
buffers
potassium phosphate/metaphosphate
sodium acetate/citrate
hydrochloric acid/sodium hydroxide
boric acid/potassium chloride
potassium (biphthalate or phosphate)/water
hydrophilic solvents
-purified water: distilled, deionized, reverse osmosis, carbon-filtered
-sterile water for injection (SWFI)
-bacteriostatic water for injection (SWFI + preservatives)
-sterile water for irrigation
hydrophobic solvents
-alcohols: ethanol (grain alcohol, ethyl alcohol, drinking alcohol), isopropyl alcohol
-oils and fats: almond, borage, canola, castor coconut, mineral oils, omega-3, omega-6
-glycols: glycerin, propylene glycol, PEG, Polybase
-emollients (moisturizers): petroleum jelly/white petrolatum, theobroma oil/cocoa butter, beeswax, paraffin, lanolin, dimethicone
Lipoderm , Eucerin, Cetaphil creams
ointments
-Versabase lotion
-gels: poloxamer 407NF, PLO gel
-pastes: zinc oxide (also a desiccant)
suppository bases: cocoa butter, hydrogenated vegetable oils (palm, palm kernal, coconut oils), PEG polymers, glycerinated gelatin
humectants
glycerin, glycerol, propylene glycol, PEG, urea, hyaluronic acid
-draw water into the skin, less greasy but can feel sticky
hydrocarbon base ointments
white petrolatum, white ointment (Vaseline)
-forms occlusive barrier, feels greasy
-oleaginous, no water
adsorption base ointments
hydrophilic petrolatum, lanolin
-used for water-in-oil emulsions or as emollients
water-removable bases
oil-in-water emulsions, hydrophilic
-more easily diluted, washed off the skin more easily
-per USP, more correctly called creams
water-soluble bases
polyethylene glycol ointment
-do not contain petrolatum
-per USP, more correctly called gels
adsorbants
magnesium oxide/carbonate, kaolin
anti-foaming agents
Simethicone, dimethicone
Coatings (regular)
shellac, gelatin, gluten
enteric-coating
cellulose acetate phthalate, shellac
Gelling (thickening) agent, stabilizer
agar, alginates, guar gums, acacia, gelatins, tragacanth, bentonite, carbomer, cellulose, starches, acrylates, cetyl alcohol, magnesium aluminum silicate (Veegum), poloxamer (pluronic) gels, polyvinyl alcohol
-increases the viscosity of a substance; stabilizes the mixture
levigating agents
glycerin/glycerol, mineral oil, glycols, PEG, propylene glycol
comminution
reducing particle size by grinding, crushing, milling, vibrating, or other processes
-trituration
-levigation and spatulation
-pulverization by intervention
trituration
"mix thoroughly" or make product homogenous
-grinding tablets in a mortar with a pestle
-shaking/triturating an emulsion
levigation
triturating a powder with mortar and pestle and incorporating a small amount of liquid/levigating agent/wetting agent to help with the grinding process
-turns the solid into a uniform paste
spatulation
similar to levigation, performed on an ointment slab with a spatula instead of with a mortar and pestle
Pulverization by intervention
the reduction of a solid (crystalline powders that will not crush easily) by combining it with a solvent (alcohol) that will evaporate after pulverization is complete
types of solutions
-syrups: contain sucrose or other sugars
-elixirs: sweet hydroalcoholic solutions used for drugs that would be insoluble in aqueous formation
-tinctures: plant or animal extracts dissolved in alcohol or hydroalcohol
-spirits: alcohol or hydroalcohols of volatile, aromatic compounds (camphor)
-solute dissolved in a solvent; homogenous
emulsifiers
acacia, agar, carbomers, glyceryl monostearate, pectin, PEG, sodium laurel sulfate, sorbitan liphophlic ester (Arlacel, Span), sorbitan hydrophilic esters (Myrj, Tween)
Continental Gum Method
-also called the dry gum method uses 4 parts oil, 2 parts water, and 1 part emulsifier (acacia or other gum-type emulsifier)
-the gum is levigated with the oil, then the water is added all at once
-the mixture is triturated by shaking it until a cracking sound is heard and the mixture looks creamy white
-add other ingredients by dissolving them in the solution and QS water to final volume
-make the emulsion uniform with a homogenizer
English Gum Method
-also called the wet gum method also uses 4:2:1 oil, water, emulsifier
-triturate the gum and water to form a mucilage then add the oil slowly while triturating to form the emulsion
-add other ingredients by dissolving in the solution and QS water to final volume
-make the emulsion uniform with a homogenizer
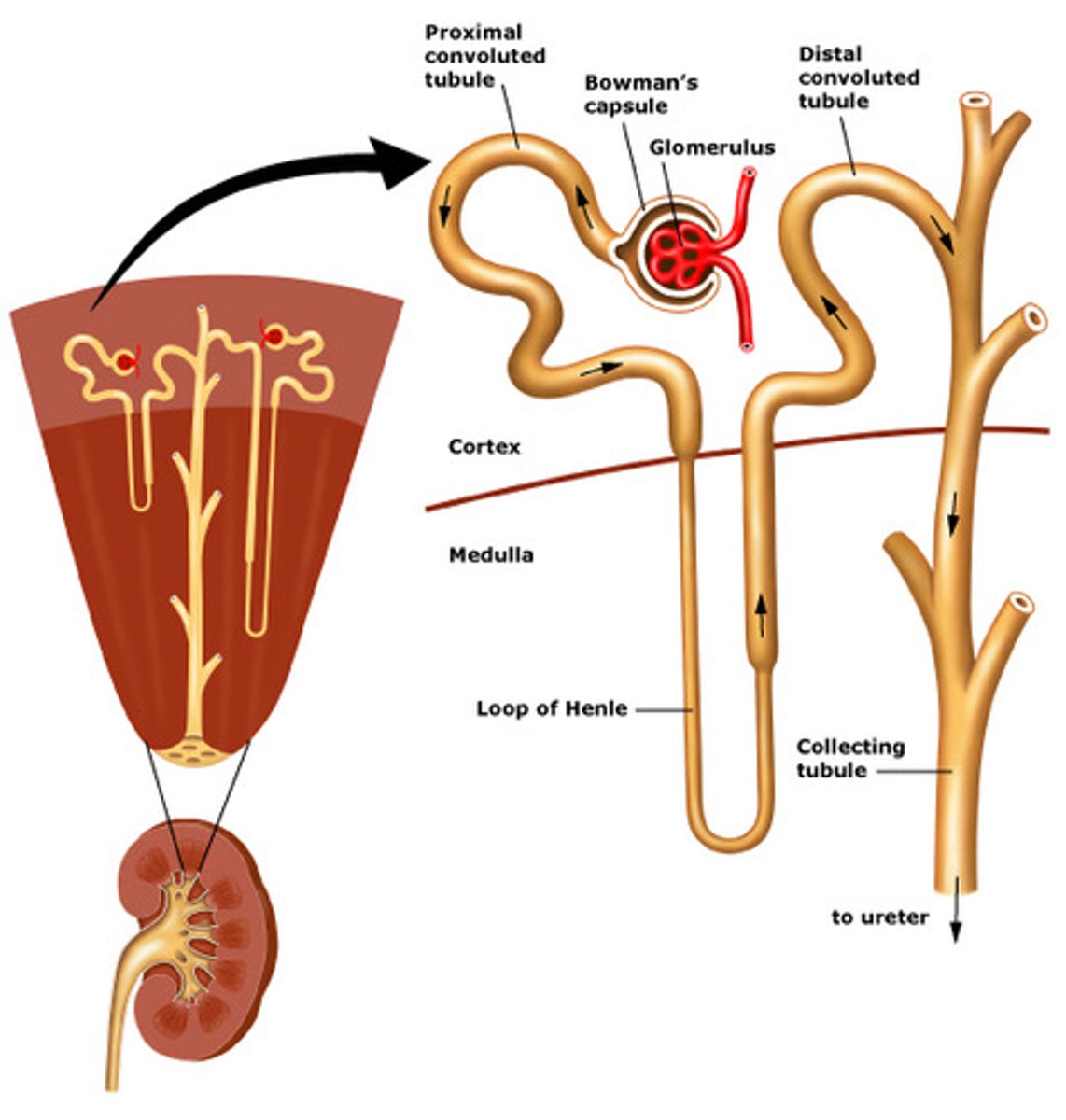
Nephron: hot spot diagram
PCT: SGLT2 inhibitors, acetazolamide (filters bicarb)
thick ascending Loop of Henle: loop diuretics
DCT: thiazides, K-sparing diuretics
CD: K-sparing diuretics (amiloride, triamterene)
Select drugs that cause kidney disease
aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, cisplatin, cyclosporine, loop diuretics, NSAIDs, polymyxins, contrast dye, tacrolimus, vancomycin
Key drugs that require dose reduction or increasing the interval in CKD
-anti-infectives: aminoglycosides, beta-lactams (most), fluconazole, quinolones (except moxi), vancomycin
-CV drugs: LMWHs (enoxaparin), rivaroxaban (for AFib)
-GI drugs: metoclopramide, H2RAs
-Others: bisphosphonates, lithium
Other drugs that require dose reduction or interval increase in CKD
anti-infectives: amphotericin B, ethambutol, pyrazinamide, acyclovir, (valacyclovir, ganciclovir, valganciclovir), oseltamivir, aztreonam, NRTIs, polymyxins, sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim
CV drugs: antiarrhythmics (digoxin, disopyramide, dofetilide, procainamide, sotalol), apixaban, dabigatran, statins
pain/gout drugs: allopurinol, colchicine, gabapentin, pregabalin, morphine, codeine, tramadol ER
others: cyclosporine, tacrolimus, topiramate
Drugs contraindicated with CrCl < 60
-nitrofurantoin
-do not initiate TDF if < 70
-glyburide not recommended in CKD
Drugs contraindicated with CrCl < 50
-tenofovir disoproxil fumarate: Stribild, Complera, Symfi/Symfi Lo, Atripla, Truvada (during treatment)
-voriconazole IV
-meperidine (reduce dose to avoid accumulation of toxic metabolites)
Drugs contraindicated with CrCl < 30
-tenofovir alafenamide: Genvoya, Odefsey, Descovy, Biktarvy, Symtuza
-NSAIDs
-dabigatran (DVT/PE)
-rivaroxaban (DVT/PE)
-Others: bisphosphonates, duloxetine, fondaparinux, K-sparing diuretics, tadalafil, tramadol ER, avanafil
-sotalol (Betapace AF) at < 40
Drugs contraindicated with GFR < 30
-SGLT2 inhibitors
-metformin
Treatment for CKD induced hyperphosphatemia
1. calcium-based phosphate binders
2. aluminum-free, calcium-free phosphate binders (expensive) or sevelamer carbonate/HCl
3. aluminum-based phosphate binders LAST LINE and duration limited to 4 weeks due to toxicity ("dialysis dementia")
Treatment for CKD induced Vitamin D deficiency and secondary hyperparathyroidism
-vitamin D2 (dietary) or D3 (synthesized in the skin after sunlight) supplementation in CKD stage 3 or 4
-vitamin D analogs (calcitriol - active D3) for later stages of CKD or ESRD to increase calcium absorption from the gut and inhibit PTH secretion
-calcimimetics (cinacalcet) increase the sensitivity of the calcium-sensing receptor on the parathyroid gland, causing a further reduction in PTH and is only used in dialysis patients
Key drugs that raise potassium levels
ACE inhibitors, ARBs, aliskiren, aldosterone-receptor antagonists, canagliflozin, drospirenone-containing COCs, Bactrim, calcineurin inhibitors (cyclosporine, tacrolimus, everolimus)
Others: glycopyrrolate, heparin (chronic use), NSAIDs, IV fluids, K supplements, pentamidine
Steps for treating severe hyperkalemia
1. Stabilize the heart - prevent arrhythmias with calcium gluconate
2. Move it - shift excess K intracellularly with albuterol. bicarb, insulin/dextrose
3. Remove it - enhance K elimination with Kayexalate/SPS, dialysis, loop diuretics