Labour Markets (include theory)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
2 Main ways information asymmetry manifests
adverse selection, moral hazard
Adverse selection
consumers only willing to spend a certain amount, but the supplier knows it is worth more causing the good firms to leave the market - unravelling of the market
Moral hazard
people may shirk their job as the employer can’t perfectly monitor their employees
What is the problem with unemployment rate
masks the large flows of employment
Quits
workers leaving their jobs for better employment
Layoffs
come from changes in employment levels across firms
What is the average duration of unemployment
three months
What is path dependence
the longer they remain unemployed, the more likely they are to remain unemployed
Discouraged workers
classified as out of the labour force but they would take a job if they found it
What is the standard relationship between wages and unemployment
wage is the outcome of bargaining, when in a tight labour market, workers have more bargaining power
How long until firms will not hire anymore workers
When the marginal productivity of labour equals the wage rate
Why does the labour supply curve slope upwards
the price of leisure is higher when wages are higher
Backward bending labour supply curve
when the wage is so high that the income effect dominates the substitution effect
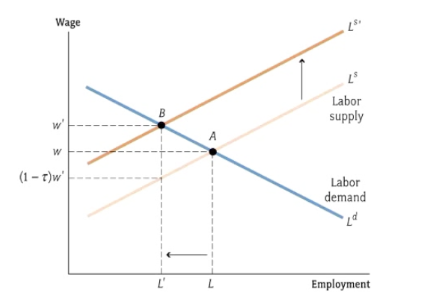
What does this show
increase in income tax
Monopsony
firm has pricing power over the price it pays for production factors
Supply shocks
changes in social norms, changes in technology for managing fertility, changes in immigration
Demand shocks
reduced discrimination against women, emergence of new technology enhancing productivity
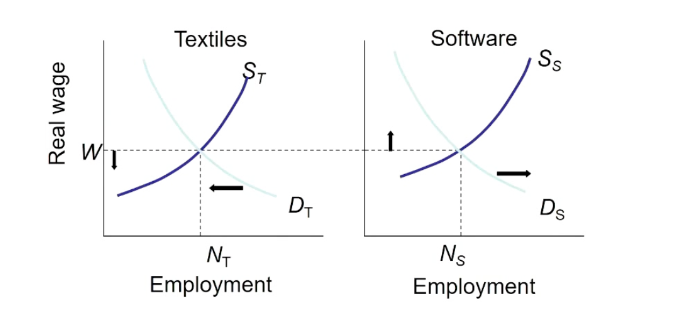
What is this
Effects of globalisation
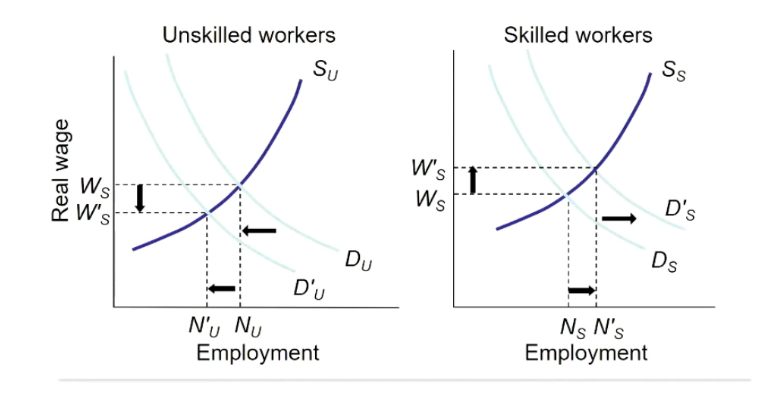
What is this
Skill-biased technological change
Natural rate of unemployment
rate that would happen if the economy did not have any boom or busts
Cyclical unemployment formula
the difference between the actual rate and the natural rate
the natural rate of unemployment includes two components
frictional unemployment, structural unemployment
Actual unemployment formula
frictional + structural + cyclical
Unemployment insurance - benefits
allows consumption smoothing, reduces stress associated with unemployment
Unemployment insurance - costs
provides disincentive to search for work, costly
Wage determination
collective bargaining, awards, individual agreements
How much bargaining power a worker has depends on
how costly it would be for the firm to replace the worker, how hard it would be for the worker to find another job