Meiosis vs Mitosis phases
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Mitosis vs Meiosis
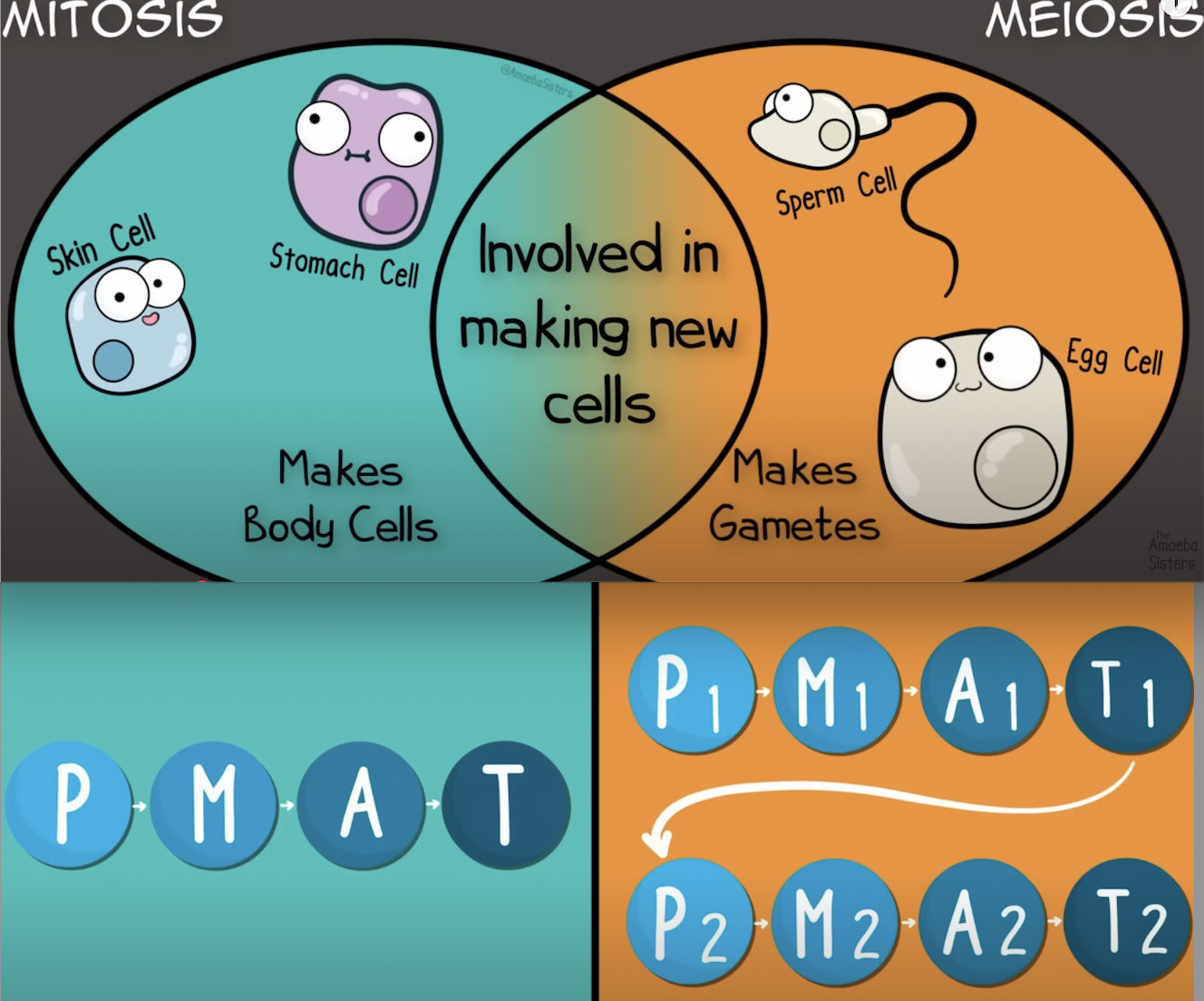
Mitosis is the process of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells, while meiosis leads to four genetically diverse gametes with half the chromosome number.
Mitosis is essential for growth and tissue repair, whereas meiosis is crucial for sexual reproduction.
Mitosis; Prophase
initial stage of mitosis where chromatin condenses into chromosomes and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
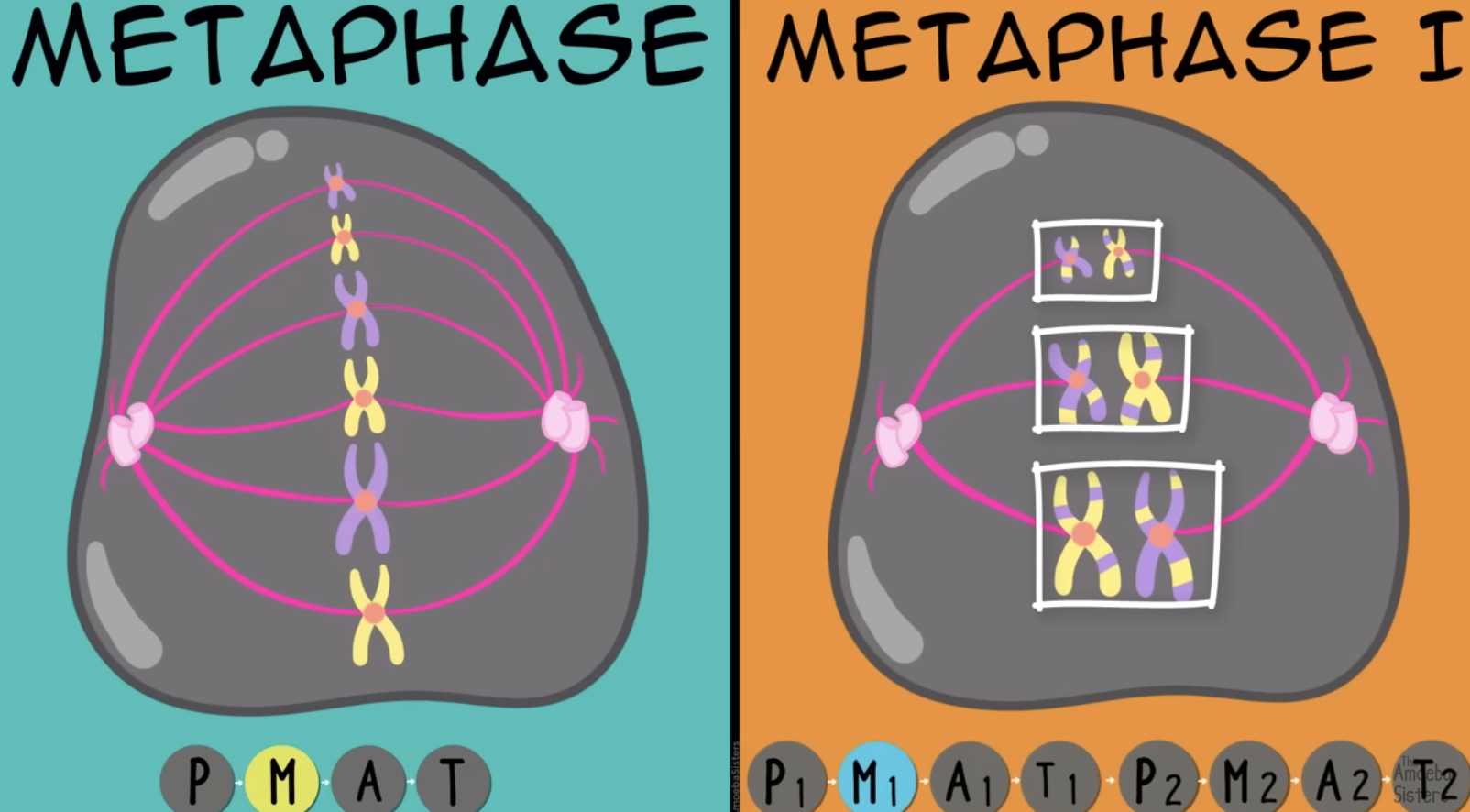
Mitosis; Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle in a single file line.
Mitosis; Anaphase
Sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell.

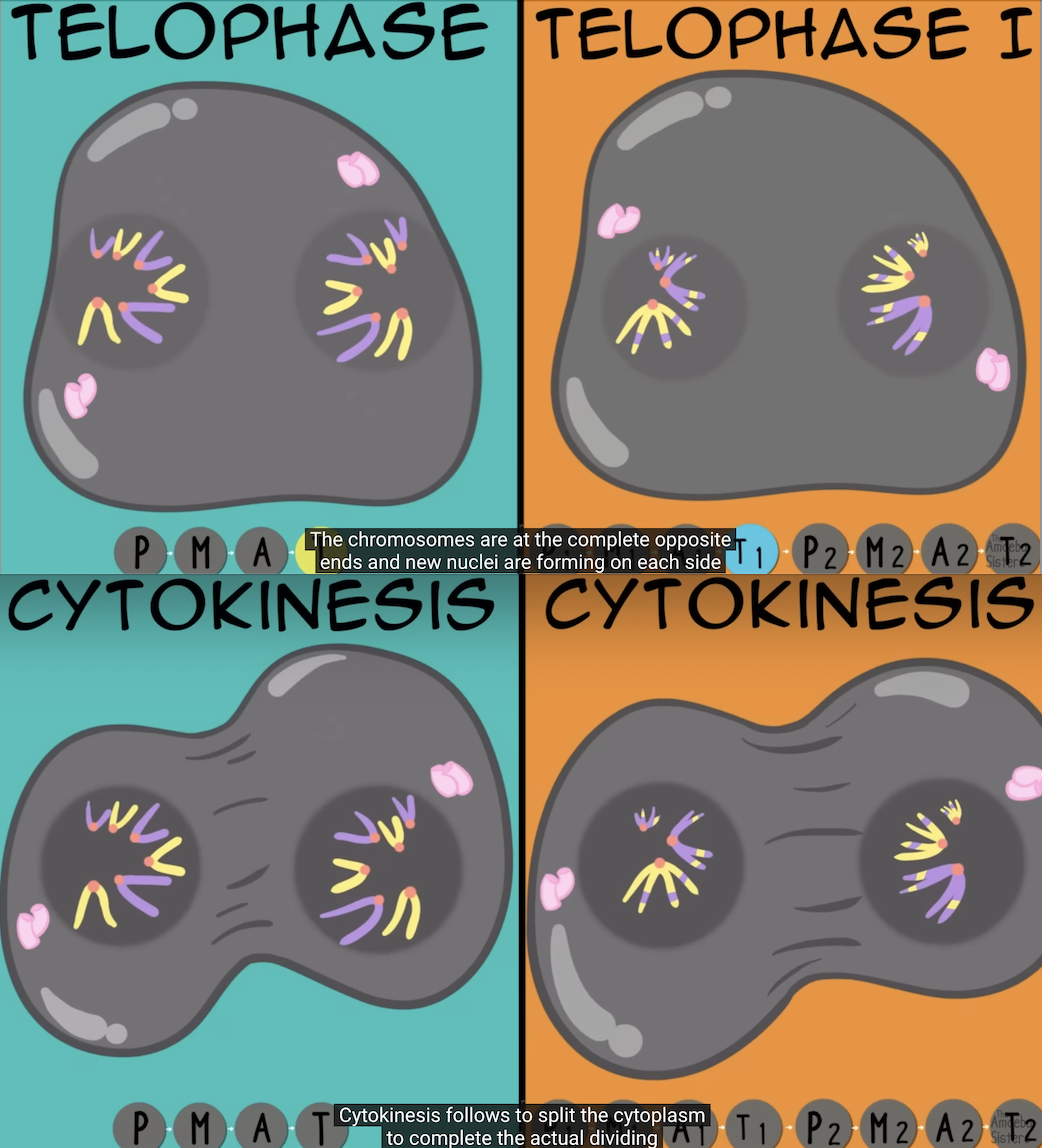
Mitosis; Telophase + Cytokinesis
Two identical copies of DNA are separated into two distinct daughter cells.
Meiosis; Prophase 1
Mitotic spindle forms, chromosomes condense, and nuclear envelope disappears.
Crossing over occurs at chiasmata, parts of one chromosomes exchange between homologous chromosomes.
Chiasmata is the location where non sister chromatids intersect.
Microtubules (centrosome) attach to kinetochores at the centromere.

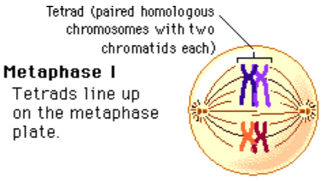
Meiosis; Metaphase 1
Chromosomes line up in the middle, on the metaphase plate but are still together in an X so it’s not a single file line.
Chromatids of one homologous pair is attached to microtubules on one pole, chromatids of other homolog is attached to microtubules at opposite pole.
Meiosis; Anaphase 1
Instead of sister chromatids being pulled apart, proteins that hold homologous chromosomes together are degraded and homologous chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles.

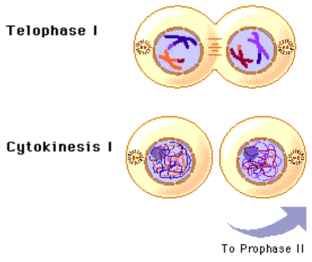
Meiosis; Telophase 1 + Cytokinesis 1
Telophase 1= The final phase of meiosis where the chromosomes arrive at the poles, the nucleus divides, spindles disappear, and the nuclear envelope reforms.
Cytokinesis 1: Cytoplasm divides, dividing the cell into two haploid daughter cells.
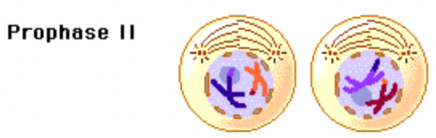
Meiosis; Prophase 2
Mitotic spindle forms, chromosomes condense into two cells, and nuclear envelope disappears.
Microtubules (centrosome) attach to kinetochores at the centromere
No crossing over occurs at this point.
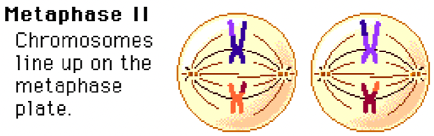
Meiosis; Metaphase 2
Chromosomes line up on metaphase plate.
Remember due to crossing over sister chromatids are not identical.
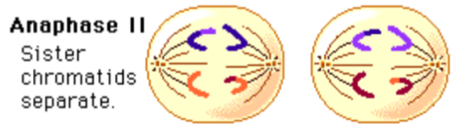
Meiosis; Anaphase 2
Breakdown of proteins that hold sister chromatids together.
Sister chromatids separate and are pulled to opposite poles.
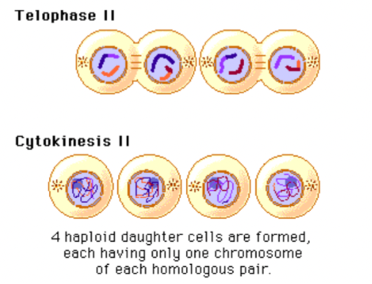
Meiosis; Telophase 2 + Cytokinesis 2
Telophase: Nuclear envelope reappears, chromosomes become less condense and microtubules disassemble.
Cytokinesis: Chromosomes are on complete opposite ends and nucleus is formed. 4 chromosomes are now created.