Art History Quiz 1
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Proto-Renaissance
Transitional period in Italy (12th-14th century) from middle ages to Renaissance. Art evolved from Byzantine to more realistic and humanistic styles.
Renaissance
Period in European history, from the 14th to 17th century, characterized by a revival of art, architecture, and culture inspired by classical antiquity. Artists focused on realism, perspective, and humanism, leading to significant advancements in art.
Humansim
An outlook or thought that attaches prime importance to human rather an divine holy power
Common human needs
Trust in humans to solve issues, saw humanity as inherently good
Major shift from middle ages’ focus on divine
(Protestant) Reformation
16th-century movement led by Martin Luther challenging the practices of the Catholic Church, resulting in the creation of Protestantism.
(Catholic) Counter-Reformation
Effort by Catholic Church to respond to Protestant Reformation, emphasizing spiritual renewal, education, and enforcing Catholic doctrine. decided art must be compiling, emotional, dramatic, and motivate religious devotion
Iconoclasm
The destruction of religious images or symbols, often due to a belief that they are idolatrous or against religious teachings.
Protestant sects did this a lot in 16th century
Mannerism
Artistic style characterized by distortion of proportions, vivid colors, and exaggerated poses. Emerged in the late Renaissance period as a reaction against the harmonious ideals of the High Renaissance. Dominant stylistic movement of 16th century
Baroque
deliberately evokes intense emotional responses from viewers, Meant as an insult by classical theorists who wanted a return to values
dramatic lighting, highlight technical skill, against mannerist
Arose from rulers’ economic strength slipping, artists finding patrons in church and secular state, and in newly confident and prosperous middle classes
Developed after the protestant reformation, during counter-reformation
Fundamentally naturalistic style
altarpiece
a painted or sculpted panel set above an altar
diptych
two panels
triptych
three panels
polyptych
multiple panels
fresco
____ is a painting technique where pigments are applied to wet plaster on a wall or ceiling, becoming a permanent part of the surface as it dries.
Buon ____
Occurs when plaster is still wet
Pigment applied to plaster before it dries
More durable and preferred
However you cant paint chunks and could only work on a small part at a time and had to be quick with no mistakes
____ Secco
Paint applied to a dry plastered wall
Color flakes off over time
tempera
Painting technique using pigments mixed with a water-soluble binder such as egg yolk. Known for its quick drying time and matte finish.
oil paint
_____ is a type of paint made with pigments suspended in drying oils, like linseed oil. It is known for its rich colors, smooth texture, and slow drying time.
modeling
Technique for creating the illusion of three-dimensionality on a two-dimensional surface using light and shadow, or shaping materials in sculpture to create depth.
sfumato
Painterly technique that gives haze effect in image
Gives blackish brown tone to all of his paints in Mona Lisa
chiaroscuro
Extreme contrasts of light and dark to give illusion of depth/volume
impasto
A painting technique where paint is applied thickly, creating texture and allowing brush or palette knife strokes to be visible.
venus pudica pose
covers private parts w/hands, exemplifying modesty and chastity

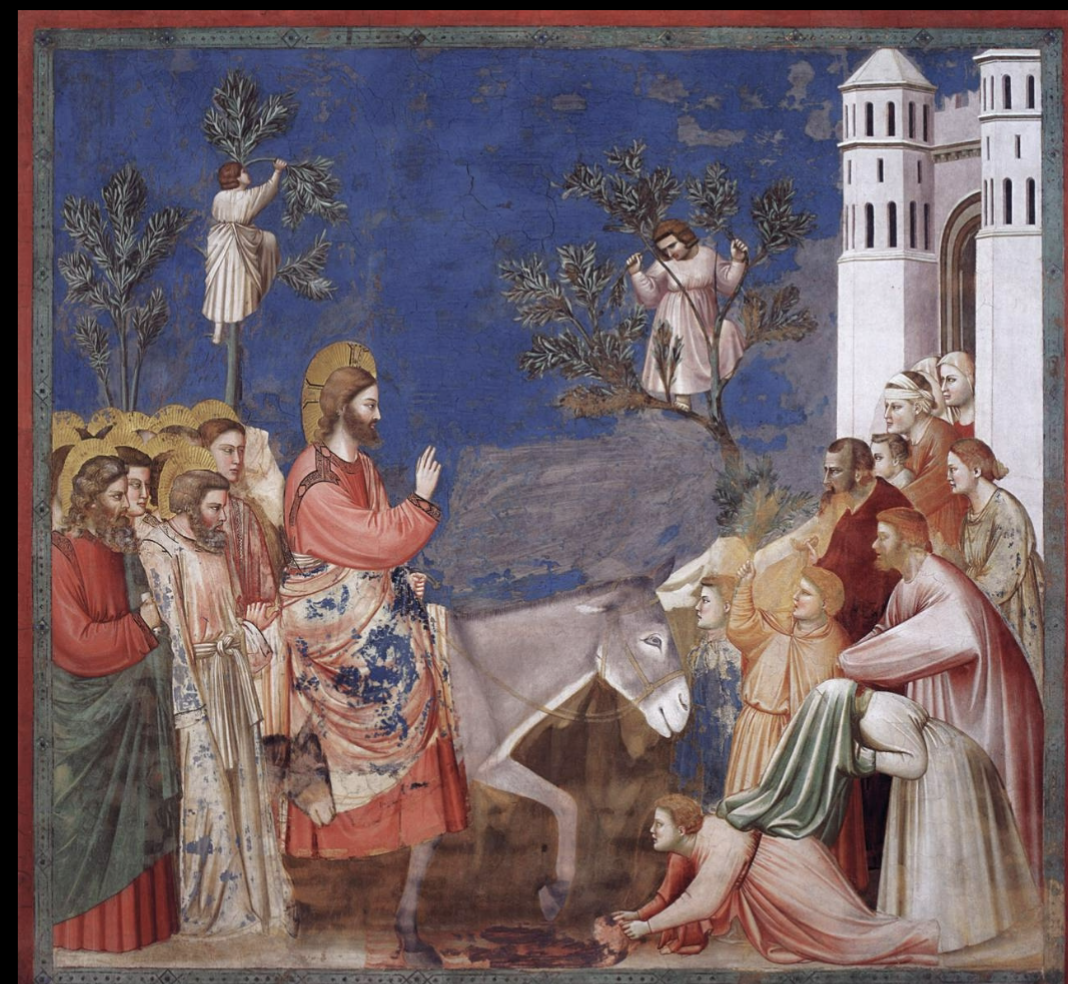
Giotto, Scrovegni Chapel, Christ’s Entry into Jerusalem
Blue sky for naturalism
Jesus is in focus against blue sky, elevated above crowd
Puts more emphasis on the figures
this artist scales it back since he’s more interested in clearly conveying the story (don’t need huge crowd to how story)

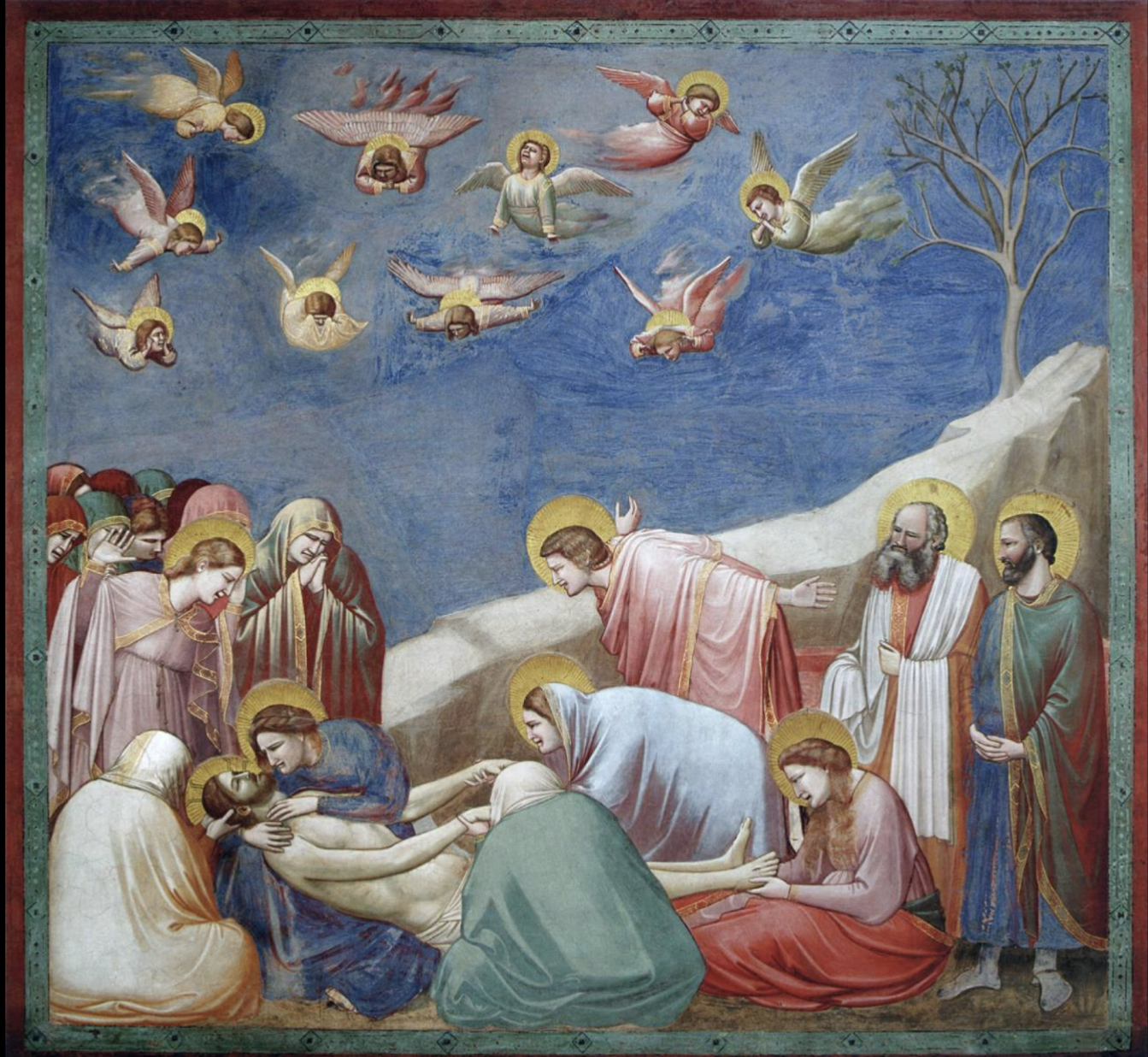
Giotto, Scrovegni Chapel, Lamentation of the Death of Christ
Back-facing people draw attention to Jesus
Everyone facing christ draws attention to him
Blurred strokes behind the angels in the sky show movement
Giotto added heightened emotionality instead of depicted stoicism of previous holy figures

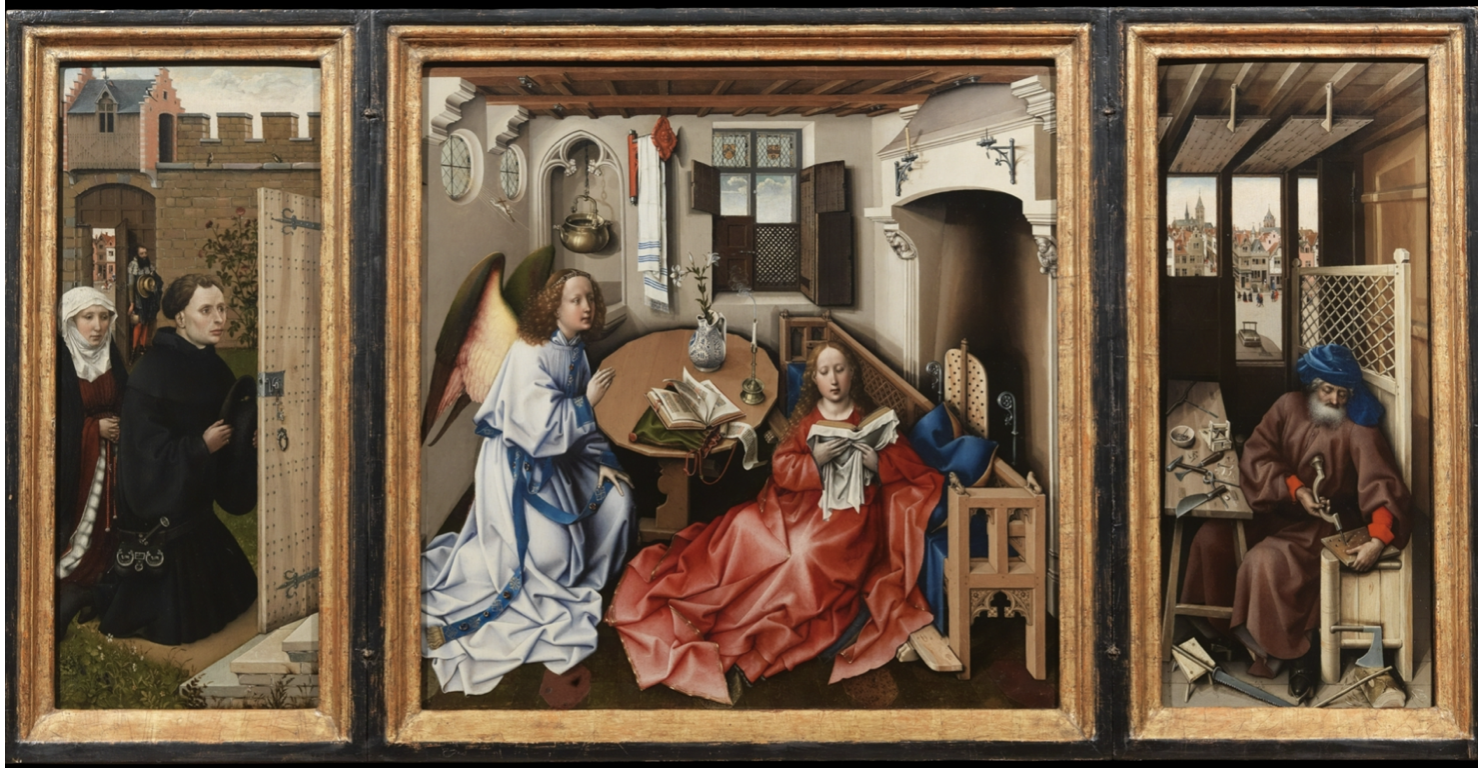
Robert Campin, Merode Altarpiece (Annunciation Triptych)
- Workshop involved, parts painted by assistants
- Center: Annunciation scene
- Left: Portrait of the commissioner
- Small altarpieces popular in 15th century for home prayer
- Minute attention to detail, maintains viewer interest
- Visible knees under clothes, but garments prioritized over anatomy
- Down-to-earth holy scene, similar to Giotto
- Tiny spirit flying through window symbolizes Mary's conception while maintaining her purity
- Right panel: St. Joseph as a carpenter
- Familiar setting for contemporary viewers
- Drilling holes references wine/blood of Christ
- Mouse traps reference St. Augustine, giving ordinary objects religious meaning
- Woodworking tools foreshadow Christ’s death/sacrifice
- No one-point perspective, uses warped and up-tilted floor for immersion
- Angled table to clearly display contents
- Uses tempera, not oil paint

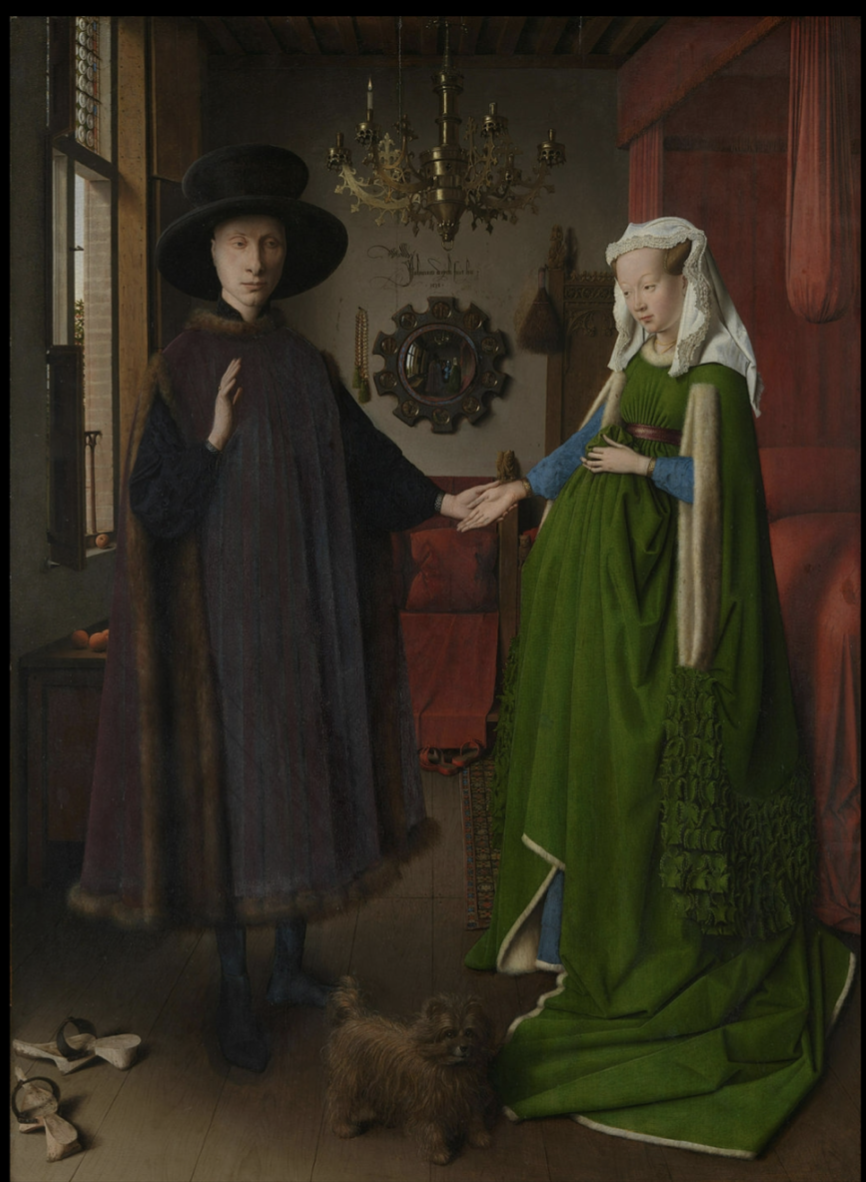
Jan Van Eyck, Arnolfini Portrait, 1434
Not pregnant, shows wealthy class and desire to be pregnant
Consistently interested in high degree of detail, but figures are elongated to appear more graceful
Hidden symbolism
Artist’s signature on wall in BG
Self-portrait in mirror on wall in BG
Represented a shift in recording the world around them realistically in Renaissance, equal attention is being applied to all elements throughout
Oil on wood

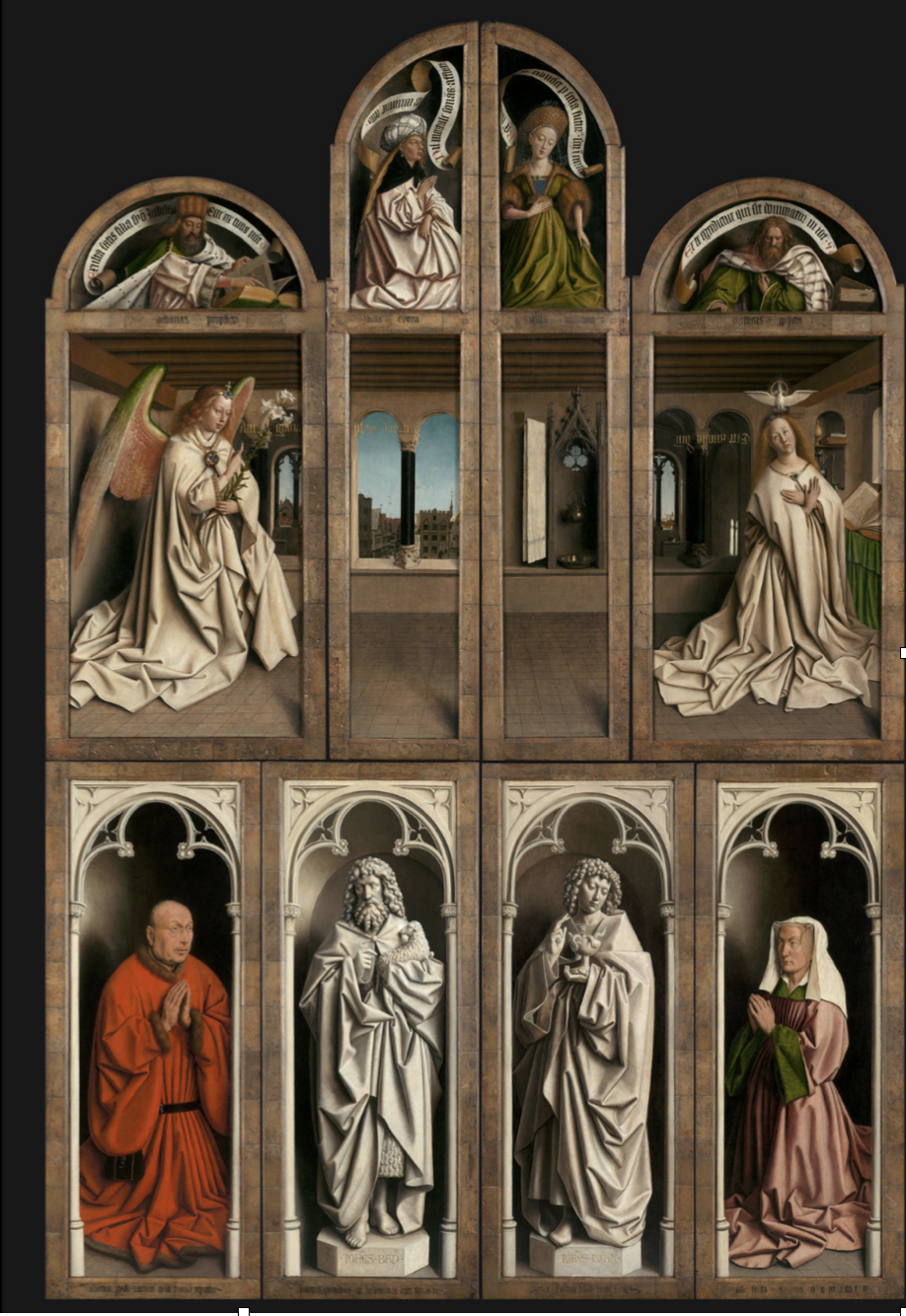
Hubert and Jan Van Eyck, Ghent Altarpiece, 1420-32,Closed Ver.
oil on wood
Mult-panel altarpiece
Polyptych altar
Commissioned to show wealth and penance/salvation
Almost burned by Calvinists
Stolen many times
Top part
Gabriel come to virgin Mary
grisaille or something
Early mother European
Donors on bottom far left/right
Common donor pose
Words going across panels to Mary again
Too large for space they’re in, shows interest in light for revealing different textures
The clock thing is symbolic of Mary’s purity

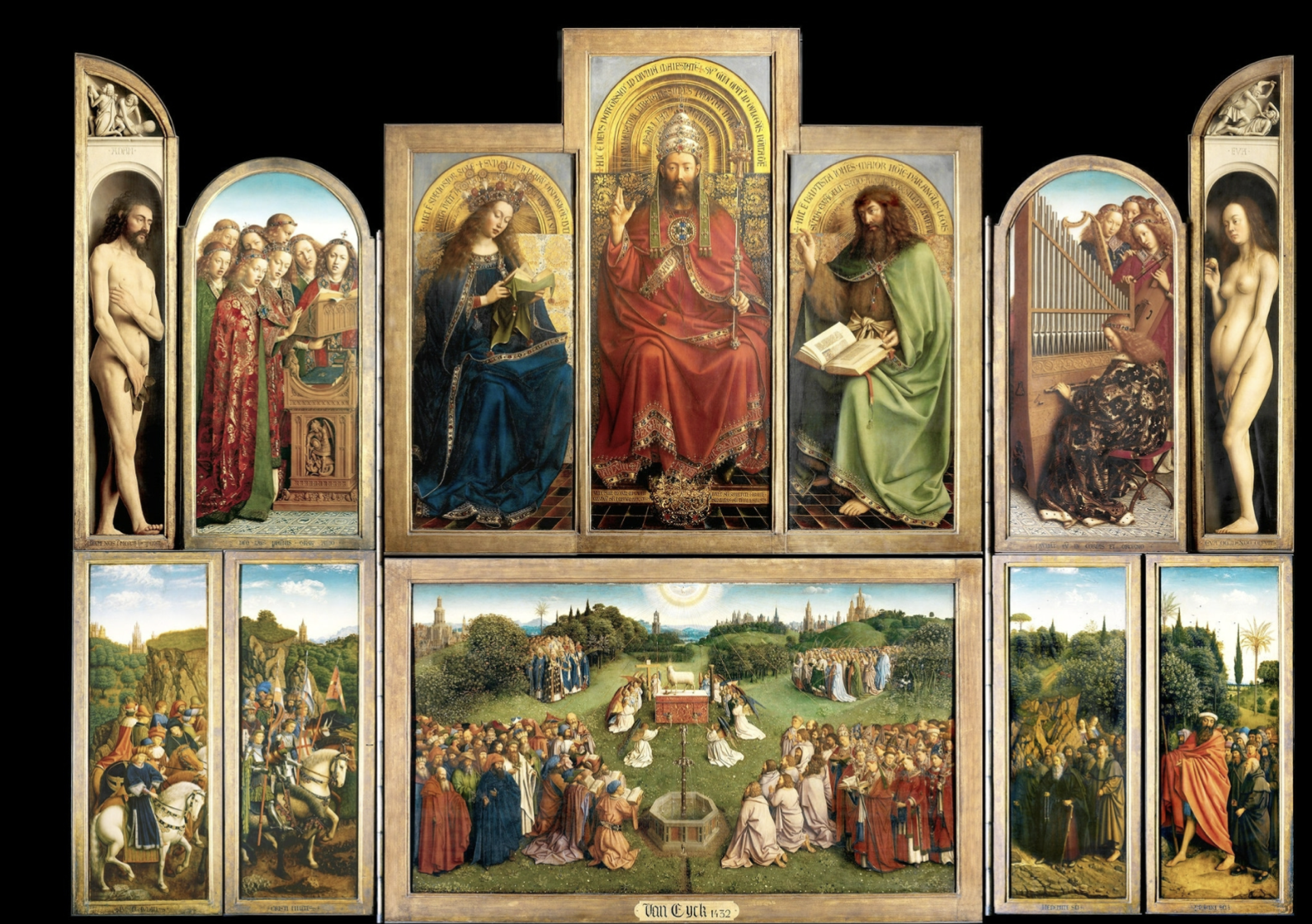
Hubert and Jan Van Eyck, Ghent Altarpiece, 1420-32,Open Ver.
oil on wood
Open version of thing
Adam and Eve on right/left of top register
Looks more human due to model that posed for him
Earlier international gothic style
Rounded stomach, holding forbidden fruit
Not much expression
Figures in between panels are more extravagant ig
Halos behind show virgin Mary god and pearls on crown show purity
Don the baptist on right middle green
Bottom register crows of people coming to altar, “Adoration of the Mystic Lamb”
Lamb represents Christ, bleeding into chalice representation of passion and catholic mass
Humanoid eyes reflect this
Musical subject matter and textures and variety appeals to viewer’s various senses
Making trenatarian message since he’s showing father son holy spirit or something

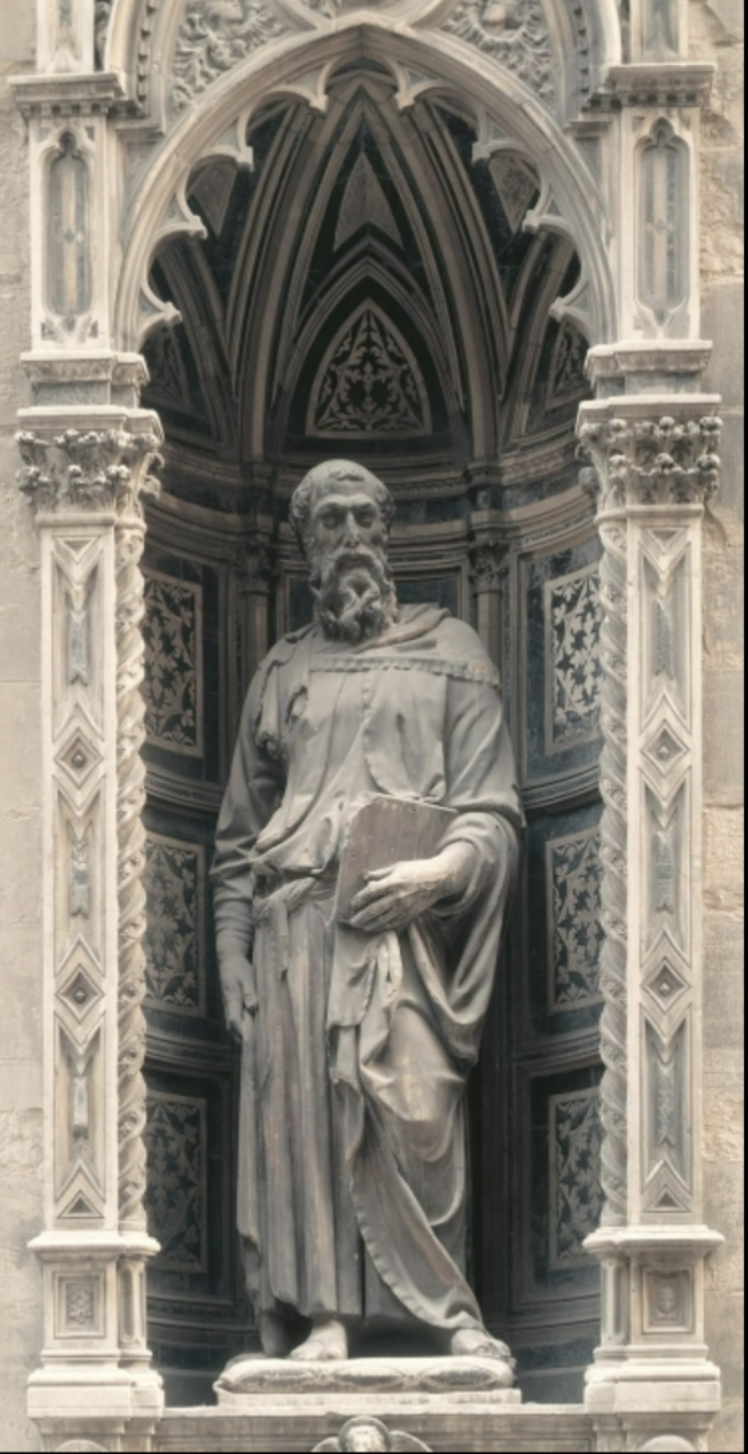
Donatello, St. Mark, 1411-1413
Marble, Florence
More detail in face
Contrapasto pose
Right arm engaged but right leg relaxed, left arm engaged left leg relaxed
Commission of this was a competition between the guide
Competition led to high output of art in the renaissance
this artist altered it so that it looks better when looking at it from below since it was on an upper niche
Neck longer, etc.

Masaccio, The Holy Trinity, 1425
fresco
Florence
Utilizes linear perspective to emphasize the sense of naturalism and create a relationship w/ the viewer
Leads to highly organized piece w/ clear foreground, midground, etc.
Furthest away from most divine figures
Organized in order of importance
Mary st. John Holy sprint, God
W example of one-point perspective
Memento mori is a reminder of impermanence of life
Focus not on pleasures of here and now but be aware of the afterlife w/heaven/hell type stuff

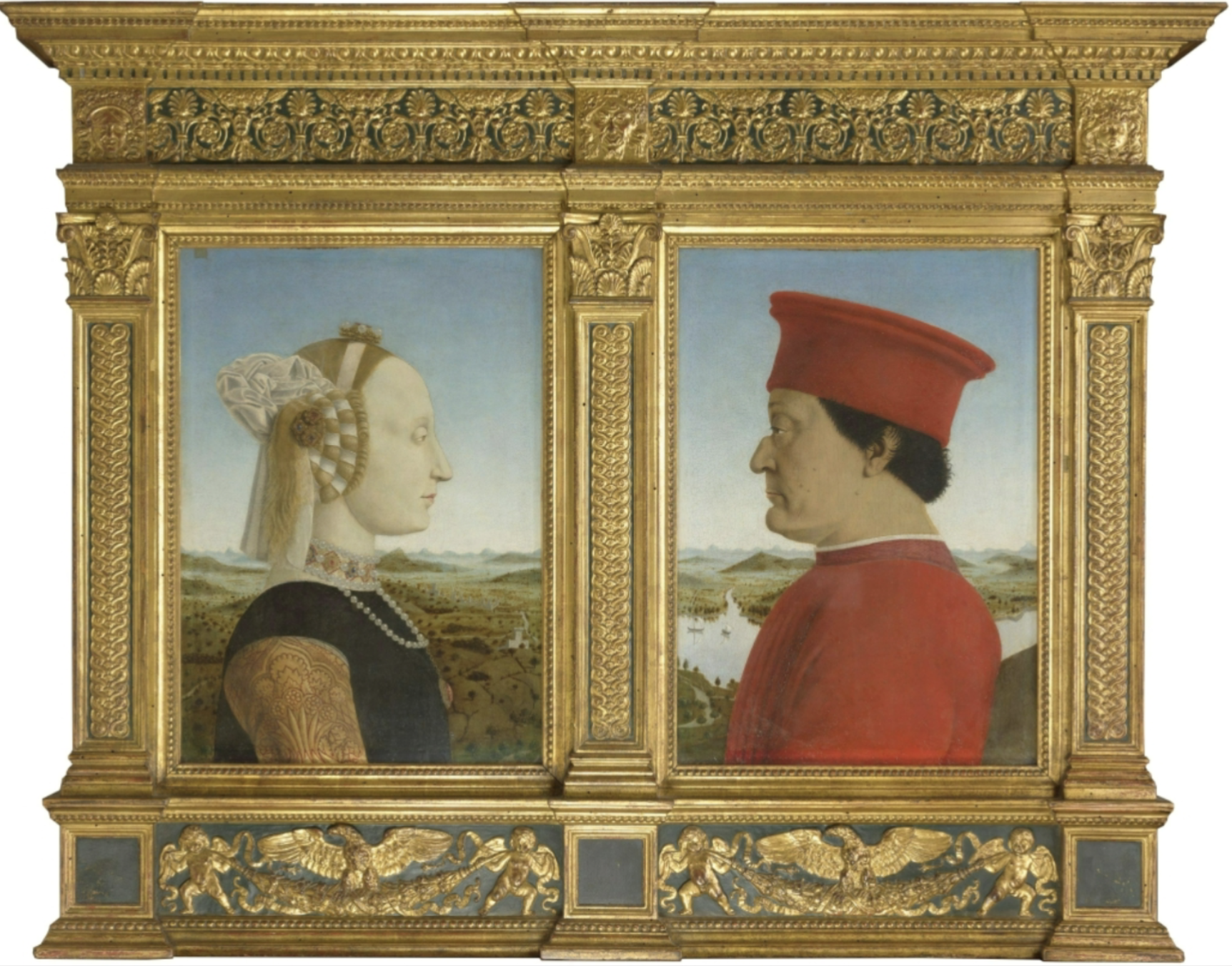
Della Francesca, The Duke and Duchess of Urbino, 1473-1475
oil on wood, Florence
Portraiture depicts individual human subjects
Concerned w/ capturing physical likeness of person
Artists start to engage with personality of their models
Wealthy use portraiture to further their goals
Has memorial function as well, stand in for person in their absence
Use of profile views like this were common in renaissance portraiture
Women’s stayed as side profiles for longer than men’s
Although on two-different panels, there is connections
Shown as relative equals since on same height
Landscape connects them across panels
River and ships suggest worldliness and duty for the dutch
Lack of emotion is common for early renaissance portraiture
More about display of social status and strong traits
Jewelry and fancy clothes display wealth and social status
Purity is reflected w/ pearls
Women are shown in profile view to objectify them because straight on portrait w/eyes to viewer shows agency

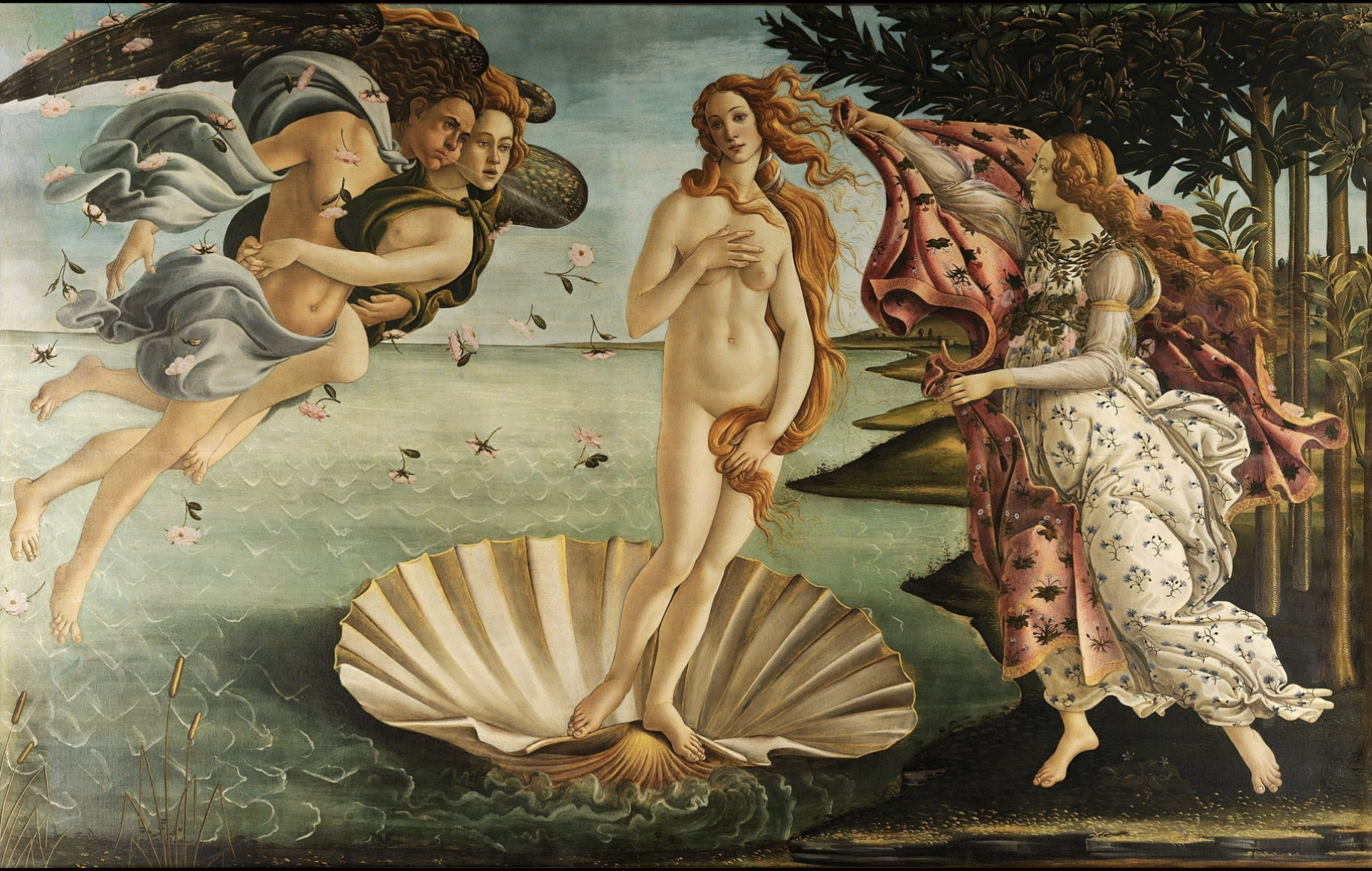
Sandra Botticelli, The Birth of Venus, 1485,
Tempera on canvas
Florence
Pagan subject matter
Burned many of his paintings due to religious stuff or sm
Made for humanist education of major ruling family of Florence
Would’ve taught young child of greco-roman values of beauty
Paining is allegory of beauty
Symbolizes and ideal concept or principle
Venus is beauty personified
Figure in seashell implying pearl
Venus pudica pose
Unusual stylistic approach
Botticelli uses black outlines for clear contour lines
Emphasizing/exaggerating curvature of her body (no shoulders)
Uses golden hue for hair
Patterning across robe, canvas, and ocean
More stylized piece not trying to hide the flatness of a painting
Bottecelli is interested in interesting values/colors more than forms
Emphasize graceful poetic qualities
Departing from direct observation
Using a more stylized approach
Although he still makes religious works
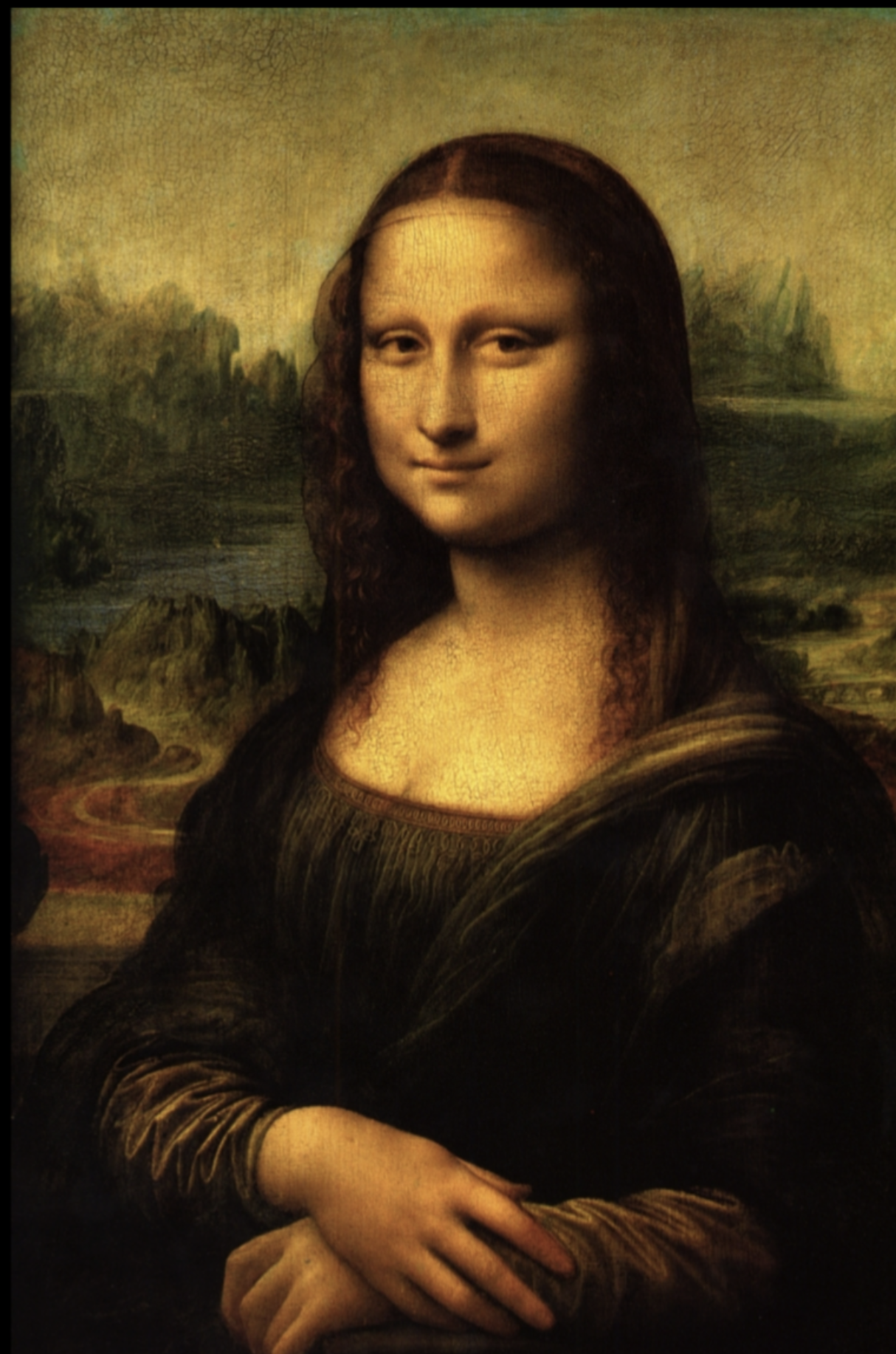
Leonardo da Vinci, Mona Lisa, 1503-1505
oil on panel
Florence
Commissioned to paint this, was supposed to be madonna scene
Smile is a way to identify her, since last name is basically “smile”
Compositionally breaks tradition by having woman with direct gaze and slight smile
Leonardo interested in emotionality not just wealth/status
Sfumato
Painterly technique that gives haze effect in image
Gives blackish brown tone to all of his paints in this painting
Chiaroscuro
Extreme contrasts of light and dark
Painting intentionally mysterious
After this painting, DaVinci only did inventions and stuff

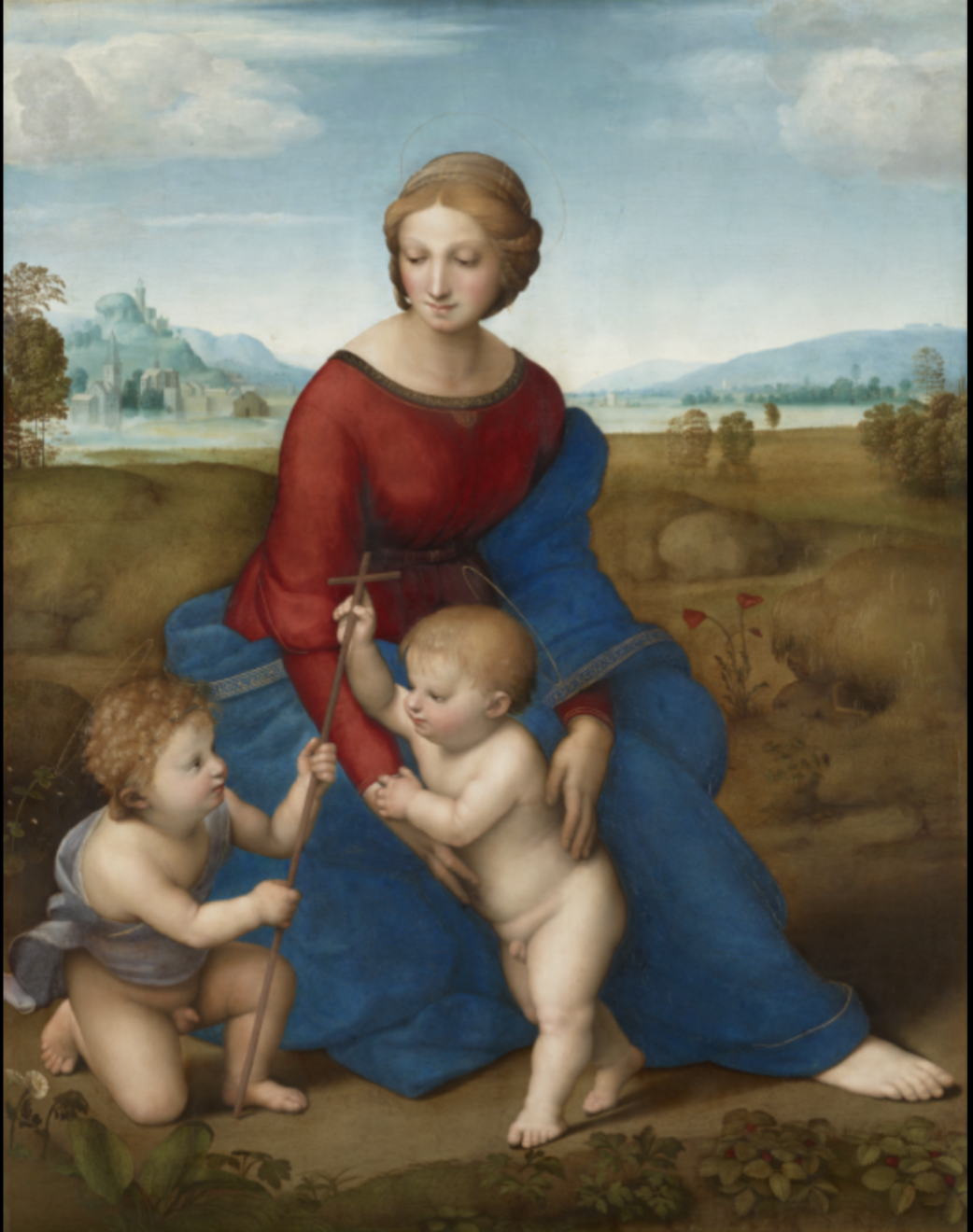
Raphael, Madonna of the Meadow (Madonna del Prato), 1505-1506
this artist more natural and organic babies actions than da Vinci’s version of this scene
More evenly lit paintings than Leonardo
Increasing naturalism and engagement between the Madonna and baby, this artist studies babies and moms for this

contrapposto
Right arm engaged but right leg relaxed, left arm engaged left leg relaxed

istoria (narrative)
historical painting
To qualify as history painting according to Alberti:
At least a few life-size characters
Clearly articulated feelings and expressions
Postures need to be appropriate to their reactions
Demonstrate expert knowledge of anatomy and scale
Clear foreground mid ground and background
Contrasting human types should be depicted
Dead/living, men/women, young/old
Variety of elements in painting like landscape, humans or something
Various movements
Gazes to lead viewers eye to important stuff
portraiture
Portraiture depicts individual human subjects
Concerned w/ capturing physical likeness of person

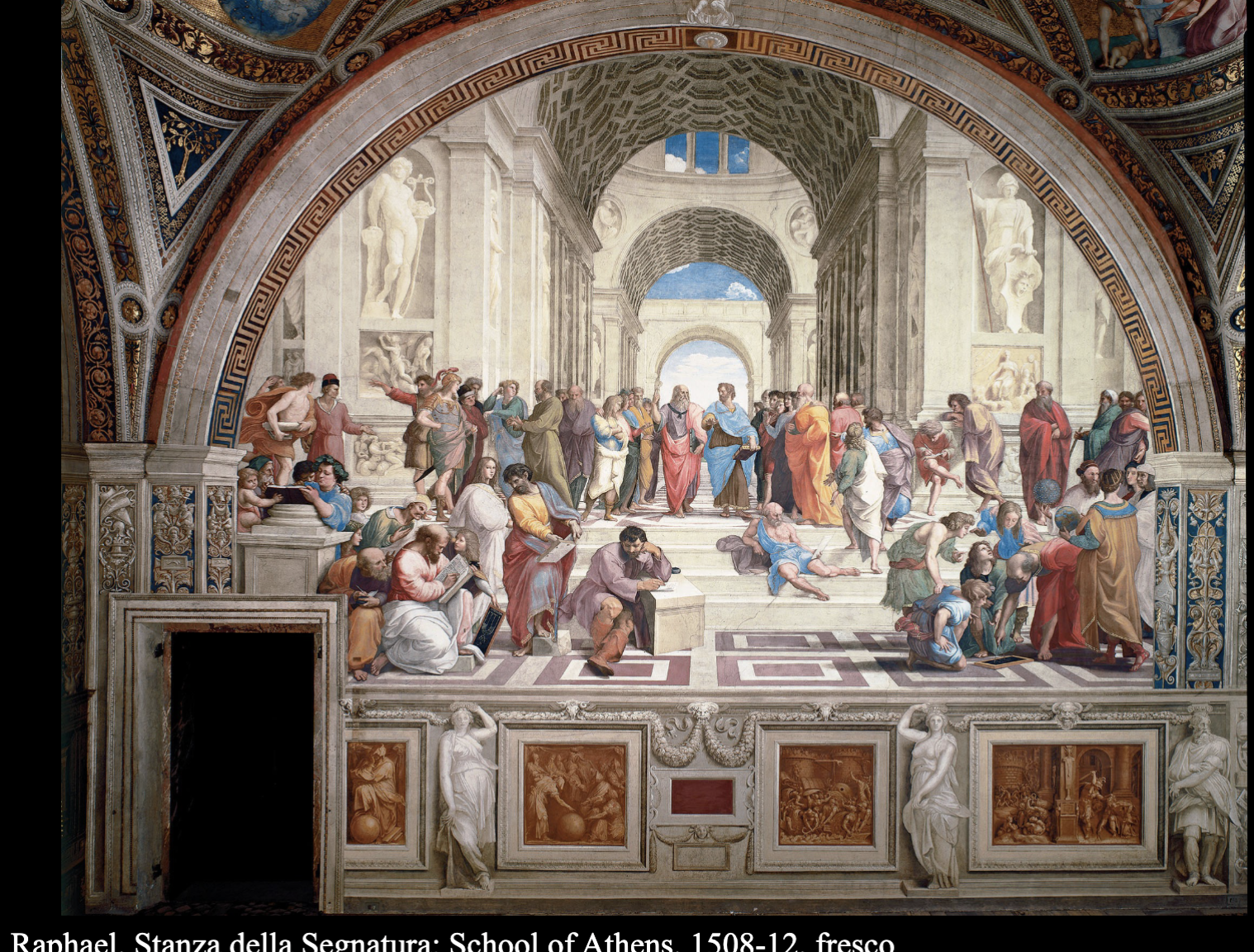
Raphael, School of Athens, Stanza della Segnatura, 1508-1512
Fresco, Rome
- Uses one-point linear perspective
- Positioned below the horizon line to depict the earthly realm, no holy figures
- Foreground, midground, and background separated by stairs
- Euclid in right foreground, Pythagoras opposite
- Emphasizes importance of mathematics in art, depicted by Raphael's presence amongst them
- Philosophers centered, elevated both literally and figuratively
- Plato points upward (importance of ideas), Aristotle gestures to ground (understanding through nature)
- Reflects ancient Greek and Roman architecture
- Features illusionistic statues of Apollo and Minerva/Athena
- Heraclitus in bottom middle, representing Michelangelo, added later

Michelangelo, Pieta, 1498-1499
Marble, Rome
Dead christ being comforted by mother Mary
More popular in northern renaissance art making it more French ig
Reduces pieta down to two essential figures, Mary and Christ
Fluid yet weighty figures
Mary open hand is grief + acceptance
Both have ideal beauty
Christ is not shown with injuries he’s endured
Slight smile read as implying is upcoming resurrection
Mary cloak reference to transubstantiation since its used to handle eucharist thing
Michelangelo signs this which is unusual for him

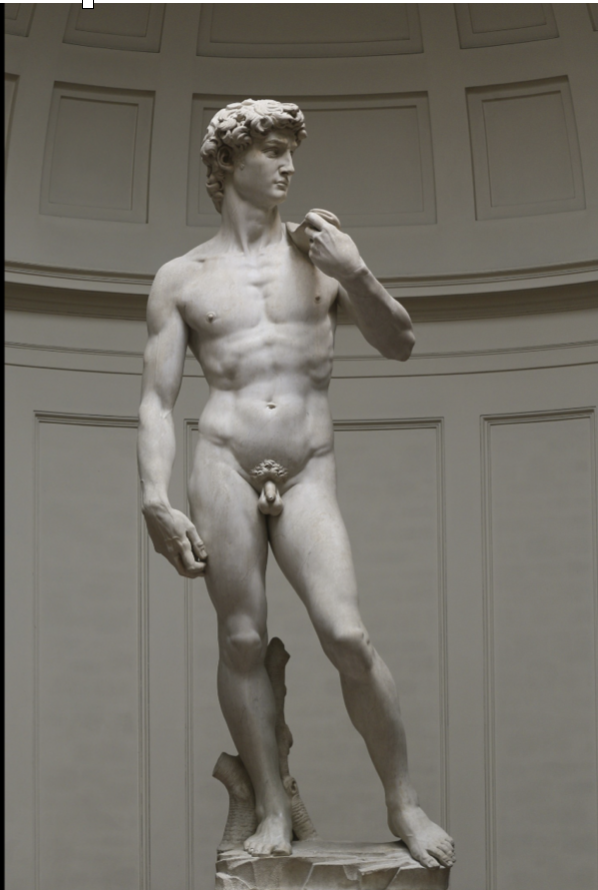
Michelangelo, David
1501 - 1504
Florentine, which became a republic at this time
As a republic called “Florentine commune” governed by elected official who wanted ppl to give back to Florence
Wanted this sculpture to become civic icon of giving back
Debate over where to place finished sculpture due to beauty/political significance
Placing it in Palazzo Vecchio would be dope for civic icon, putting in Loggia die Lanzi would neutralize political stuff since it would just be another sculpture among others
From David and Goliath
Shown moment before he shoots rock with sling in contrast to Donatello and Verrocchio’s version where it’s after
Shown nude since its associated with Heroism
Classic contraposto pose
Hands are big to account for being on top of cathedral
Meant to embody classical ideal of the male body
First example since antiquity of nude male sculpture for public outdoor viewing

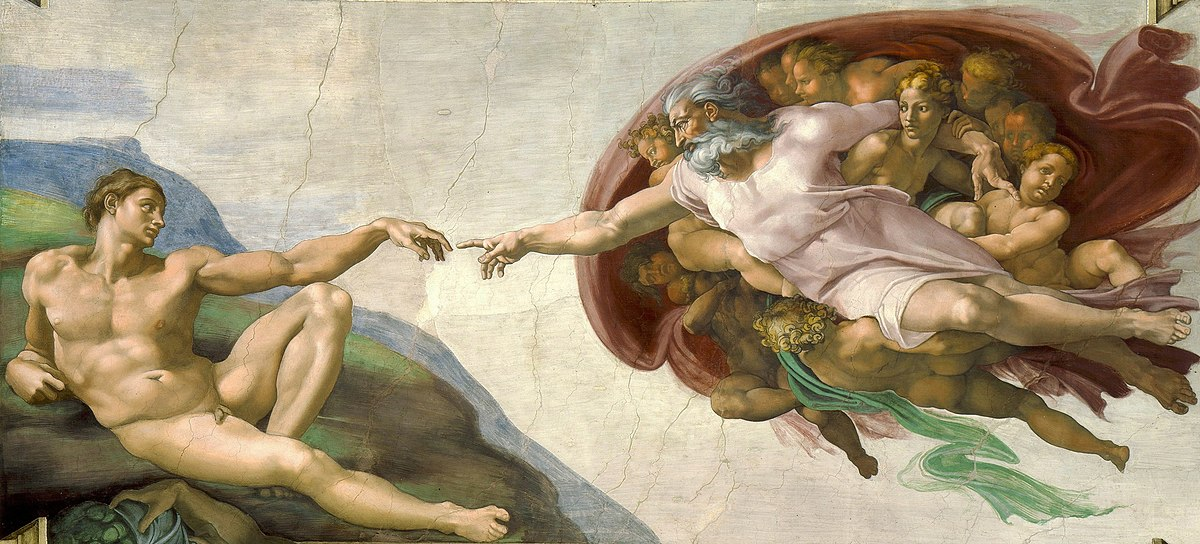
Michelangelo, Creation of Adam, Sistene Chapel Ceiling
1509-1510, Rome
Location: Sistine Chapel ceiling
Completed: 1512
Depicts: God creating Adam (Book of Genesis)
Iconic image: God reaching out to Adam
Symbolism: Divine (right arm) and humanity (left arm)
Anatomical accuracy
Famous gesture: Almost-touching hands
Part of a larger work: 9 scenes from Book of Genesis

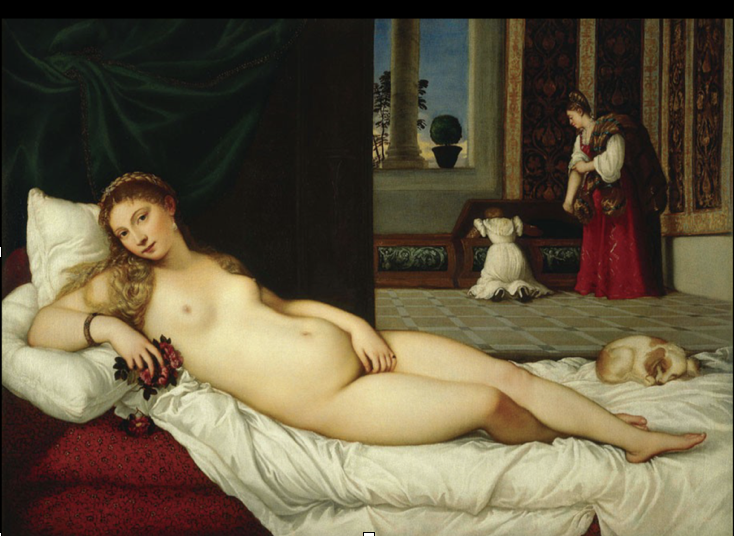
Titian, Venus of Urbino
1538, Rome, Oil on Canvas
Roses in her hand are iconography
Associated with godddess Venus
Dog by feet is sign of fidelity
Cassone (marriage trunks)
Large furniture chests made for couples after being married
Thus is not just erotic love, but marriage
Does look at viewer though coyly
Venetian painting values
Sensual subject matter
Rich and complex colors
Softness + sensuality of brushwork

Titian, Portrait of Laura Dianti [with a Black Page]
1520 - 1525, Venice
Page Noire portraiture
Wealthy start to have African servants
Her status portrayed in domination of composition
Notably older compared to page who is a child
Self-possessed meditative gaze
Elaborate attire + accessories show wealth
Page is smaller, in profile, and looking up in wonder
Attire is supposed to be comical

Sofonisba Anguissola
Father was not an artist, so she studied under other artists
Women cant enter into the guild system and apprentice under them since they would have to live with a man
12 self-portraits
Uncommon for renaissance artsits
Anguissola, Bernardino Campi Painting Sofonisba Anguissola
1559, oil on Canvas, Cremona (Northern Italy)
Double portrait painted by Anguissola
Depicts herself as wealthy
Campi (her teacher) shown holding tools of their shared trade
Female artists try to represent themselves, but not show as objects
Which is being commentated on here since her portrait is larger than Campi’s
Anguissola’s style vs. her teacher
Stating she’s surpassed her instructor since he uses tool deemed weak/ amateur
Could be homage to her teacher, but also pushes against limitations of being a woman artists and surpasses some thing
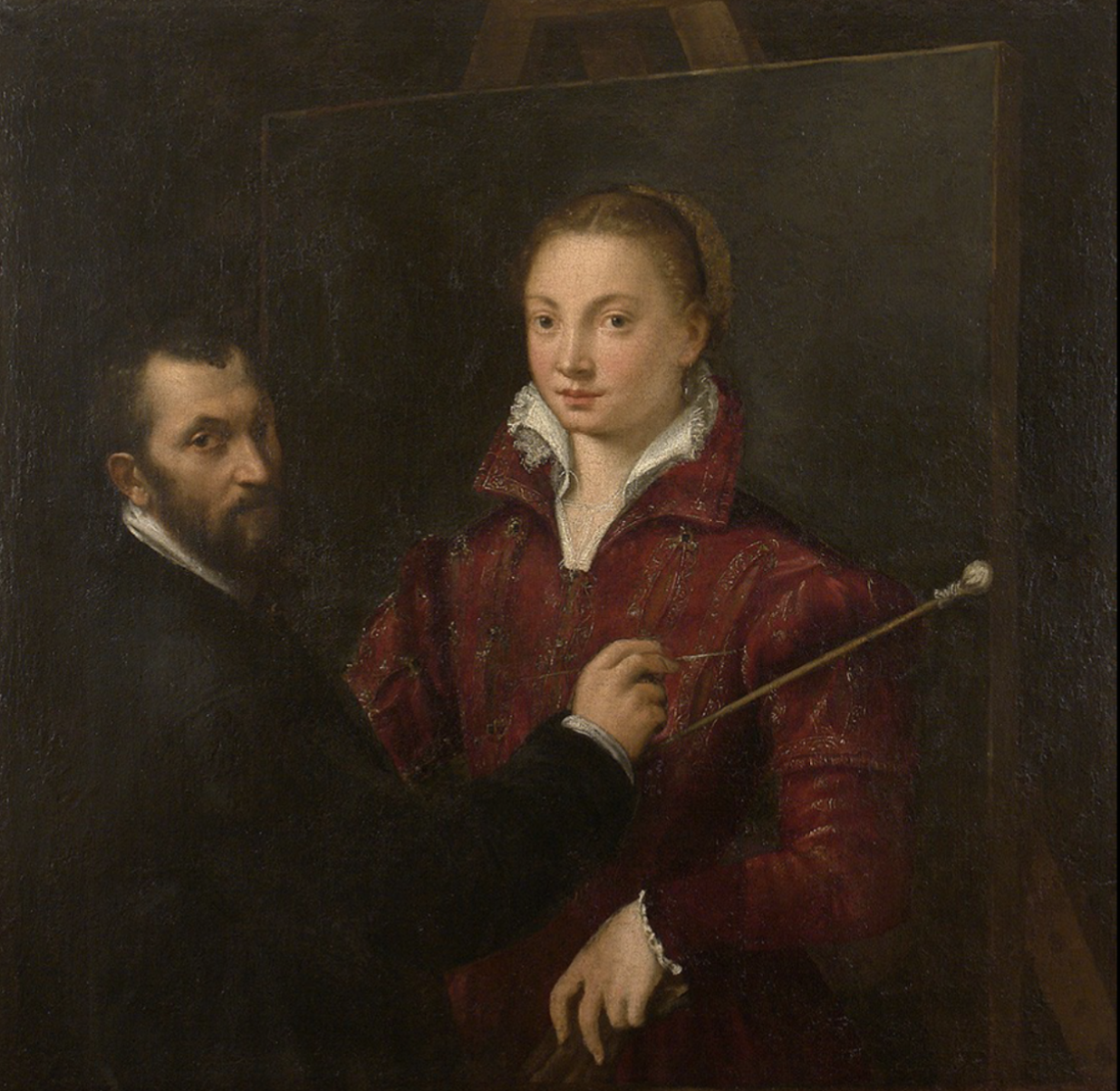

Albrecht Durer, Self Portrait
1500, Oil on wood, Germany
Likens himself to Jesus
Front-facing pose reserved for Jesus paintings
Claim artist as intellectual
Someone blessed with ability to create
Use of shadows/highlights draw attention to tools of artists
Eyes and hands
Puts his own signature on his work
he’s not racist btw
Humanist influnce reveal influence of Italy
Combining northern renaissance that he escaped from with this outside Italy culture

Albrecht Durer, Adam and Eve
1504, engraving, Germany
Contrapasto pose, statue-like
Northern artistic tradition is where detailed background comes from
Hidden symbolism
Four animals represent four bodily humors
Rabbit (glut/lust), elk (melancholy), ox (lazy), cat (angry)
First print artwork
Make it possible to produce multiples of an original artwork
Durer known for his printwork
Wood-block prints have less detail than engraving
This thing is an engraving

Catharina van Hemessen, Self-portrait
1548, Tempra on Wood, Flanders
Shows herself holding tools of their trade
Gazes directly outward at viewer, giving her sense of agency
Testament/proof of her ability to make art
Shows herself in finery to show her social status

Bosch, Garden of Earthly Delights
1505, Netherlands
Left: Adam seeing Eve, sexual awakening
Center: Humans doing sins and stuff
Right: nightmarish depiction of hell
Controversy over intended meaning
Only shows hell, not heaven
Black bodies associated with barbarism

Pastoral
Landscape painting whose subject matter is based on idealized lives of shepherds
Disegno vs. Colore (line vs. Color) debate
A Renaissance art argument between the Florentine emphasis on design and drawing (disegno) and the Venetian focus on color and emotional impact (colore)

Poesia
Emphasizes secular over religious subject matter
Evoke emotional sensation within viewer
Poetry inspired
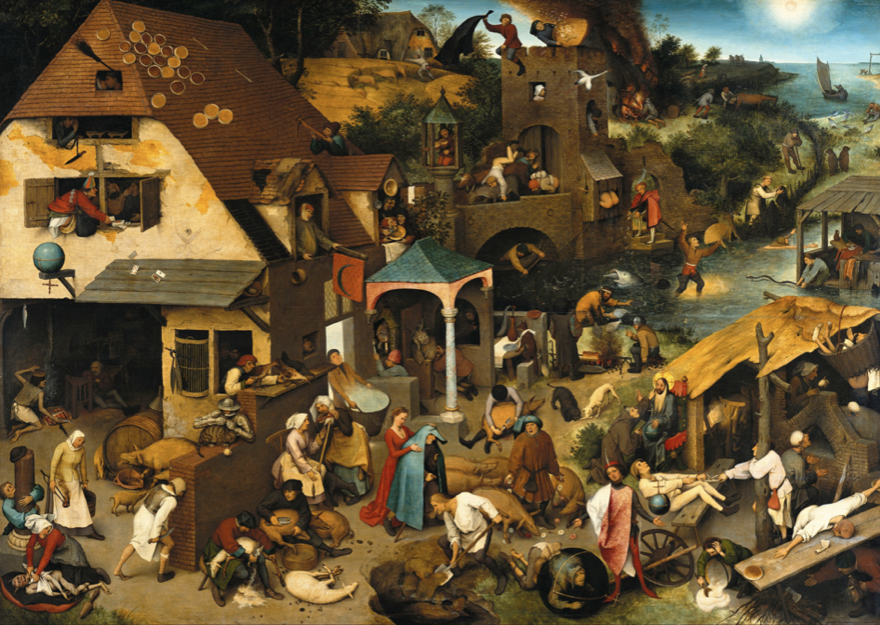
Netherlandish Proverbs
Pieter Bruegel the elder
Doing his own thing over high renaissance artists
Non-religious popular subject

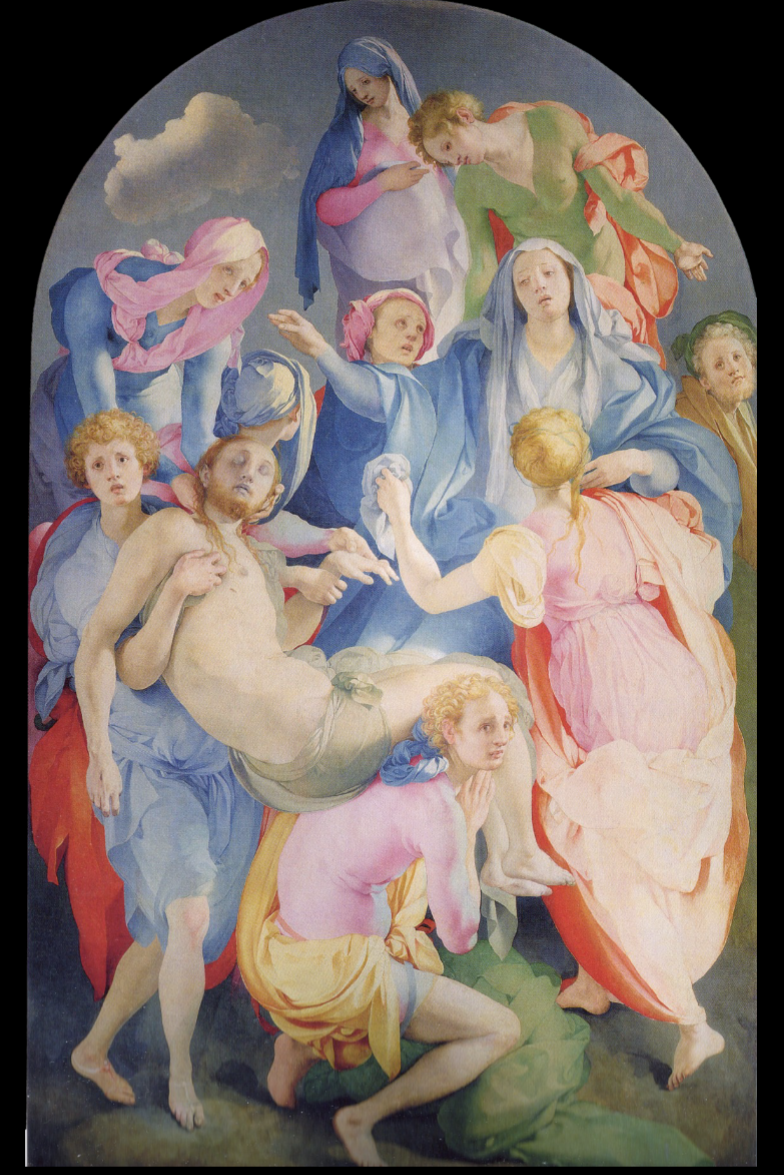
The Deposition [or Descent] from the Cross
Pontormo, (Mannerism), 1528, Florence
Crowded composition, some near front of picture frame
Placed around the frame, unusually creating void at center of frame
Bright & jarring colors, different from darker tones used by other artists like Raphael

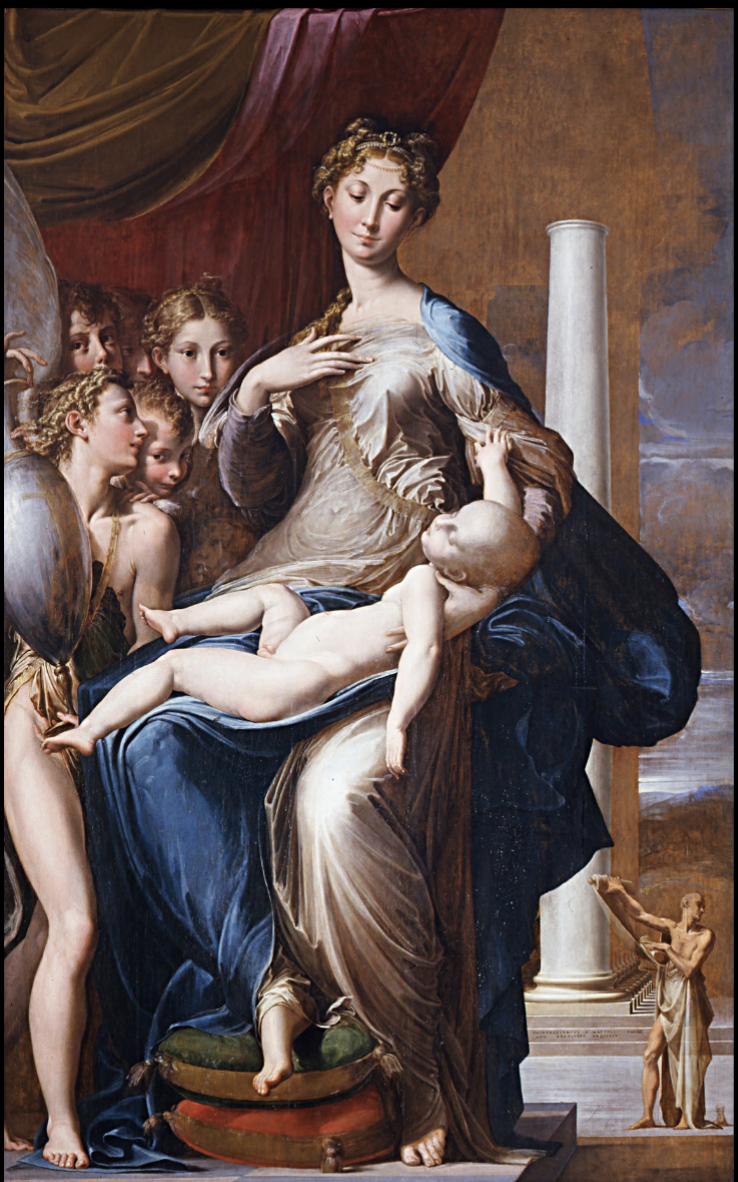
Madonna with the Long Neck
Parmagianino
Exaggerated features to give greater sense of grace/elegance
Both have elongated bodies
Foreshadow Christ’s sacrifice
Curvilinear and graceful
No one-point linear perspective, not interested in a naturalistic image
rejecting Renaissance art ideas
Artists like breaking standards to push into new boundaries

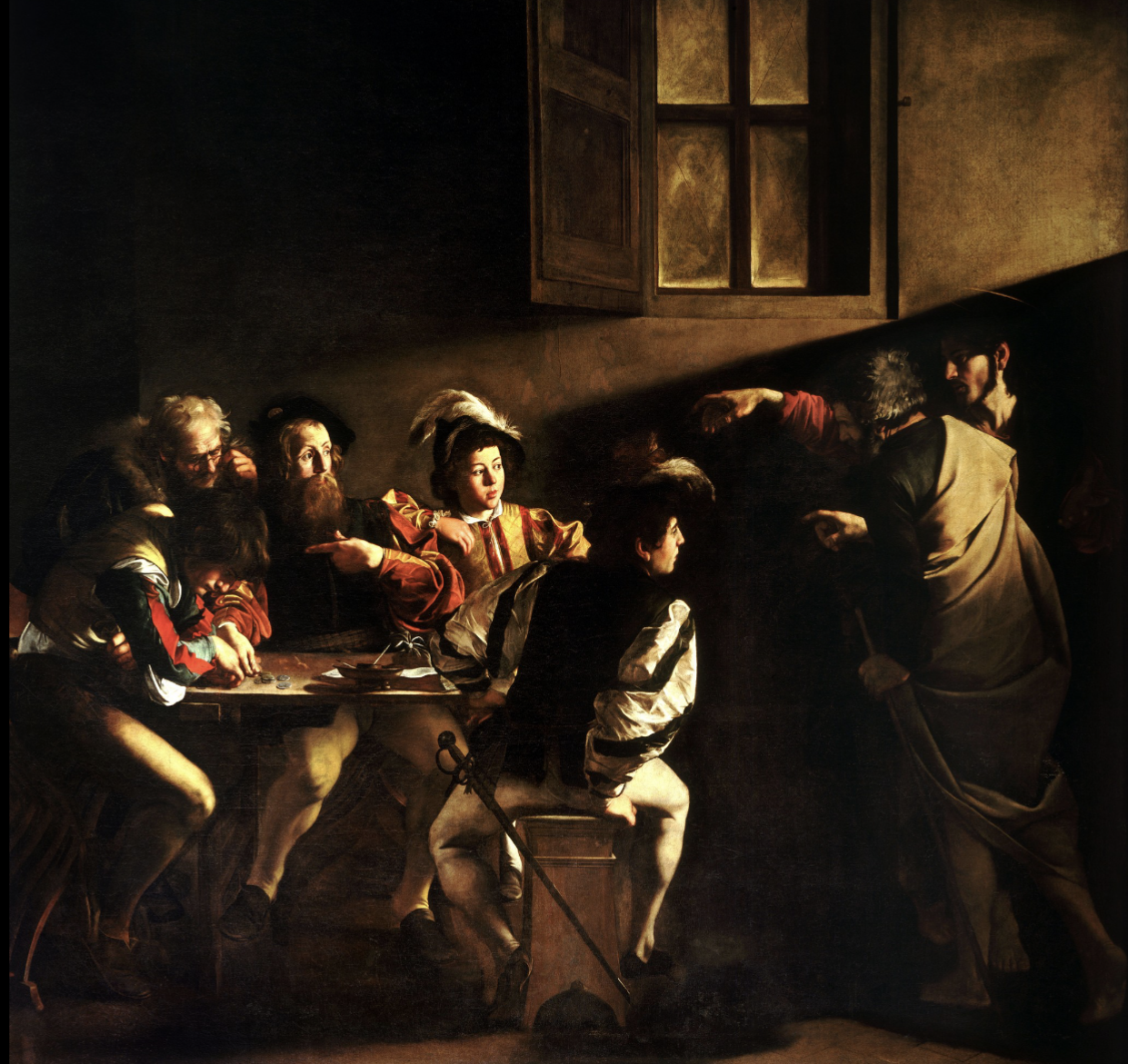
Caravaggio
- Italian baroque artist
- Rebellious
- Introduced new type of frank naturalism
- Rejected ideals of antiquity like geometry and rational ideas
- Doesn’t idealize his models
Calling of Saint Matthew
Caravaggio, 1600, oil on canvas, Rome
Due to his use of naturalism and lack of idealization, most of his church-commissioned pieces end up going to private collectors since church didn’t want non-idealized figures
Individual being called to convert to Christianity
But unusually set in dark alleyway with Christ shown in red in shadow
Anti-mannerist, thus very dark
Christs hand recalls Adam’s in Creation of Adam, christ aka second Adam
Sees natural world as vehicle for spiritual meaning, trying to bring viewers into painting
More accessible since doesn’t require advanced knowledge and shows It more achievable to everyday person
Matthew is either guy pointing at himself or guy hunched over counting coins
Reinvents biblical narrative with tenebrism, grittiness, baroque diagonal, and naturalism/humanism

Tenebrism
Light plays an active role in the work
Exaggerated form chiaroscuro
Stark contrasts of light and dark that create depth
Paintings with this often appear to have a spotlight within them
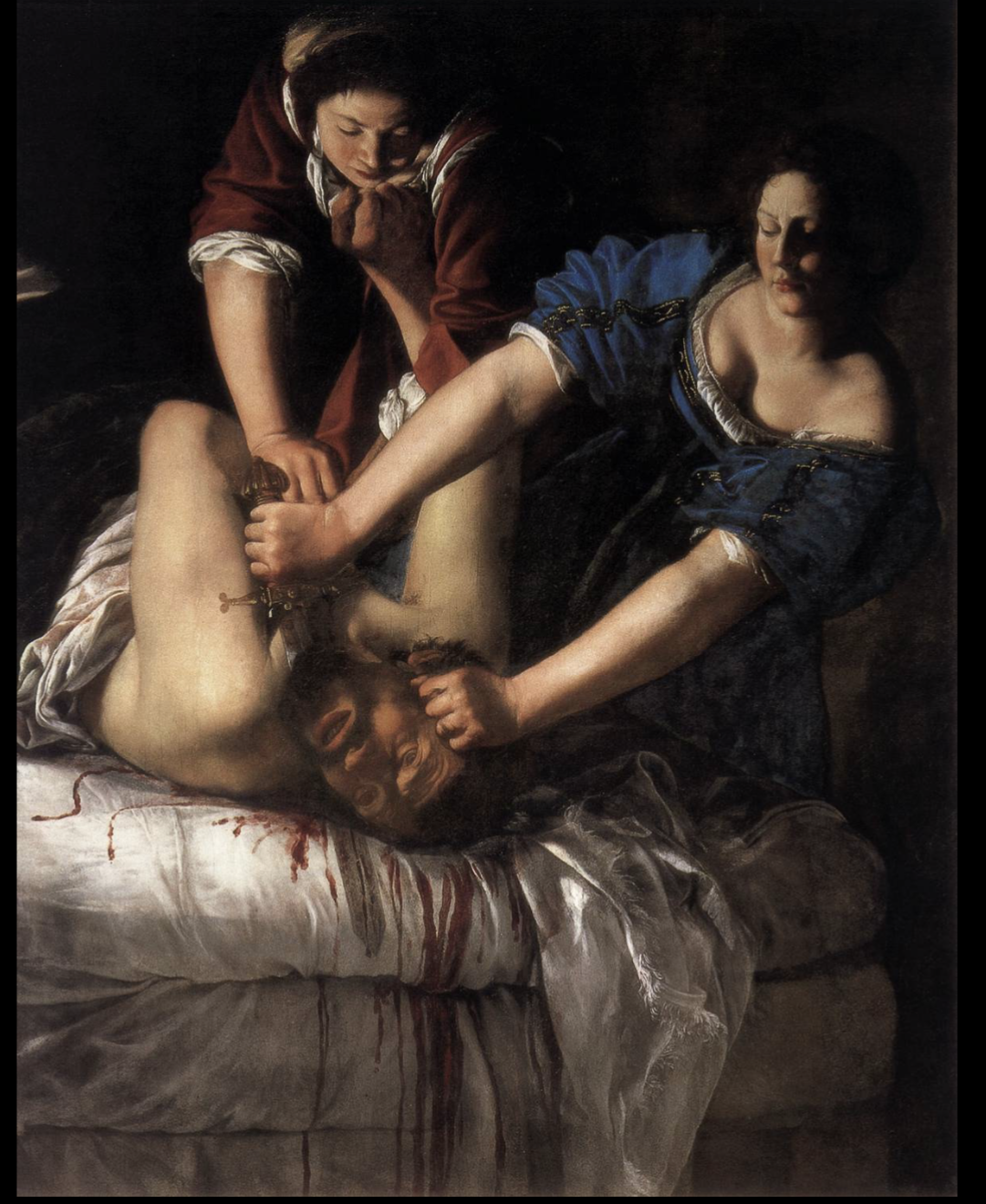
Artemisisa Gentilsechi
Went to some academy for painters, was first woman there
History paintings centering on female protagonists
Judith and Holofernes
Artemisia Gentileschi, 1620
More typical to show moment after beheading, instead shows them during violence
Bernini
Learned to sculpt from father and from looking at ancient sculptures
Figures idealized and idealistic
Attention to anatomic details, capture bodies in complex movements
Meant to walk around sculpture and view different figures/continue story
Hellenistic greek sculpture
More dynamic and naturalistic
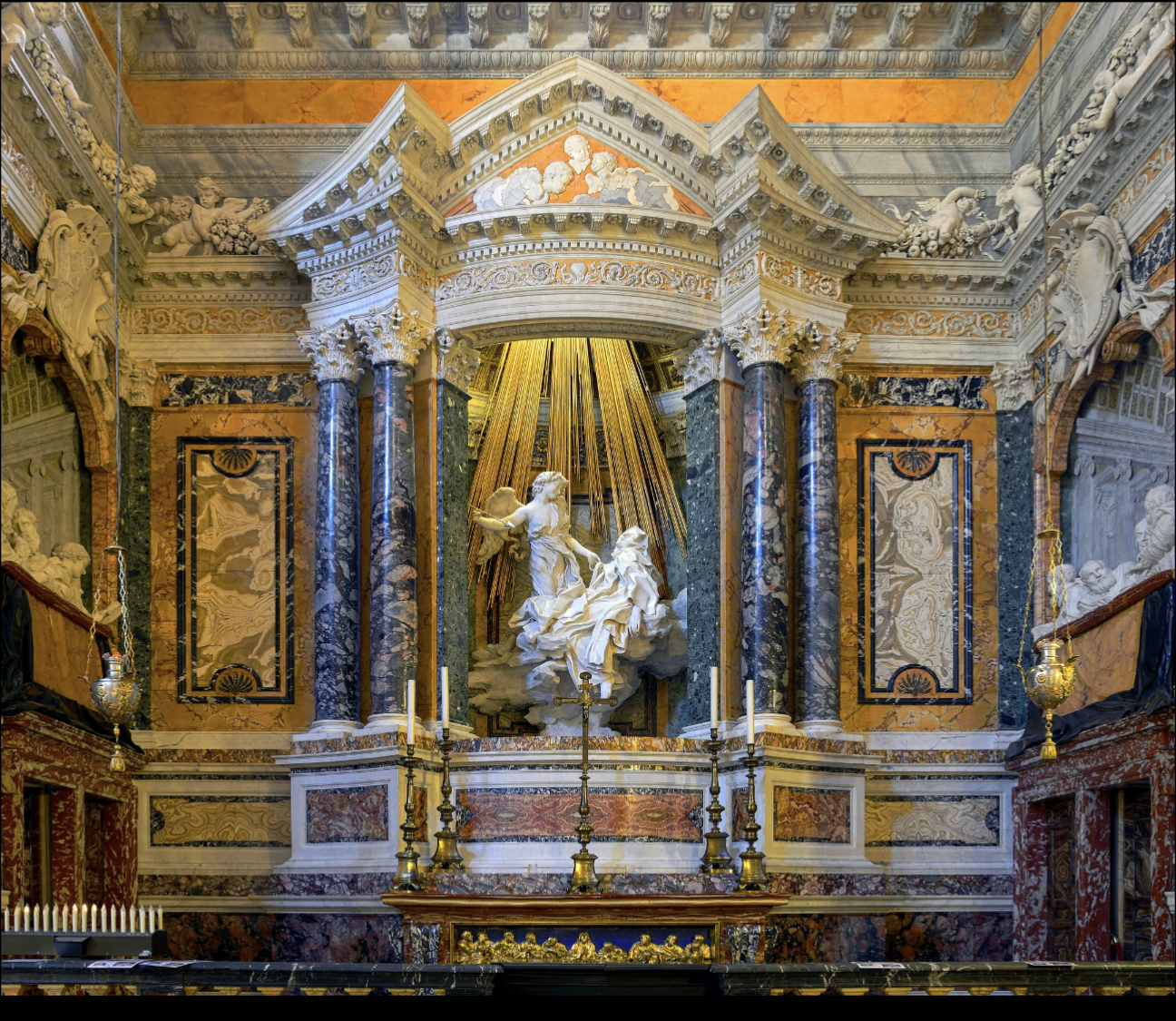
The Ecstasy of St. Teresa
Bernini, 1650, Rome
Spiritual vision in art would increase piety and devotion
Capturing St. Teresa’s vision would do this
Space around it was also designed by him, enhancing her vision story thing
Gilded rays as if godrays are emanating down onto teresa
Showing moment of cupid about to pierce her
Finely carved, whereas Teresa is dematerializing under the cloths showing spirituality stuff
Both figures appear weightless
Relief sculptures appear like windows on right/left
Cornaro Family who commissioned the work
