Genetics Exam 3: Study Guide
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What are the three types of transposition?
Cut-and -paste
Replicative transposition
Retrotransposition
What is cut-and-paste transposition?
An element is cut out of one site in a chromosome and pasted into a new site
What is replicative transposition?
An element is replicated, and one copy is inserted at a new site; one copy also remains at original site
What is retrotransposition transposition?
An element’s RNA is used as a template to synthezie DNA molecules, which are inserted into new chromosomal sites
When a particular IS element is found on both a plasmid and a chromosme, what may occur?
Homologous recombination may occur
Insertion of an IS element causes what?
Insertion of an IS element causes target site duplication
Within the anterior-posteripor axis, bicoid and nanos proteins are morphogens. What does this mean?
Substances that control developmental events in a concentartion-dependent manner
When does zygotic gene expression occur?
Expression of genes from the embryo’s genome begins after fertilization
The initial wave of zygotic gene expression is a response of what?
It is a response to maternally synthesized factors. As development proceeds, activation of zygotic genes leads to complex cascades of gene expression
What is apoptosis?
This is a part of the normal developmental program in animals and is important in the prevention of cancer
What is caspases?
This is a family of proteolytic enzymes, and are involved inapoptosis and cleave many target proteins
What occurs if apoptosis is impaired?
A cell that should be killed can survive and proliferate, potentially forming a clone that could become canverous
What are tumor suppressor genes?
These are genes that when mutated, they fail to repress cell division. They are typically DNA repair genes
What are the two cancer genes?
Oncogenes
Tumor suppressor genes
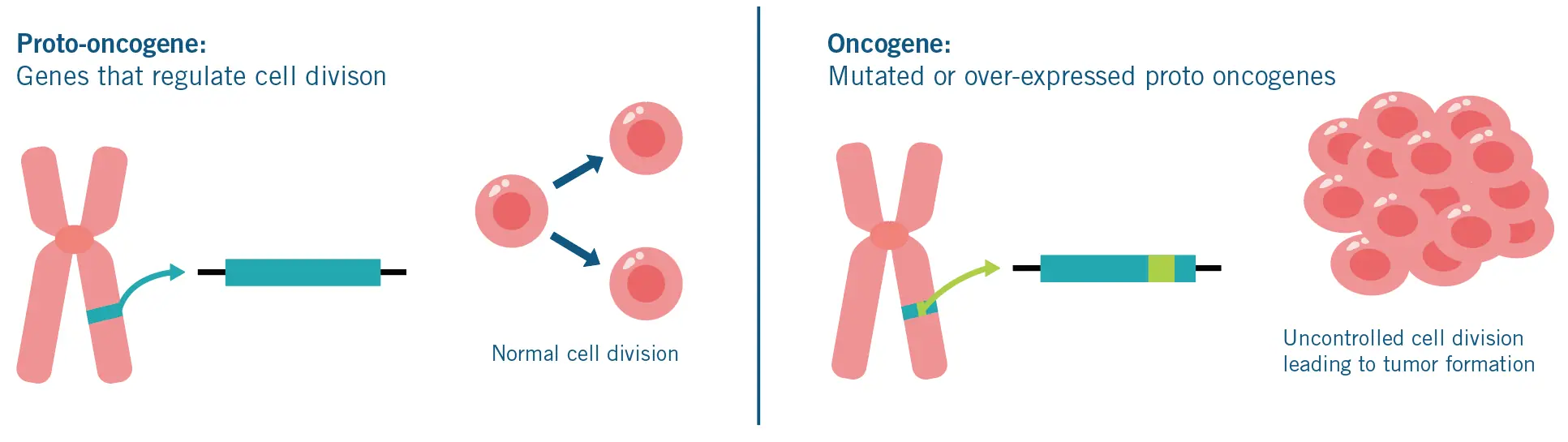
What occurs to oncogenes when mutated?
When mutated, they actively promote cell division
v-onc and c-onc
What are oncogenes?
Oncogenes are mutated genes that cam lead to uncontrolled cell growth and potentially cancer
What are cell cycle checkpoints?
A checkpoint is a mechanism that halts progression through the cycle until a critical process is completed.
What is regulated at cell cycle checkpoints?
Transitions between different phases of the cell cycle (G1, S, G2, and M)
What is responsible for cancer?
Mutations in genes that control cell growth and division are responsible for cancer
What are the 3 common methods of production of transgenic plants?
Microprojectile bombardment
Electroporation
Agrobacterium tumefacins-mediated transformation
In genome engineering, what is case9 endonuclease purpose?
This endonuclease derived from bacteria can be used to cleave genomic DNA in a wide vairety of cells and organisms (scissors)
In genome engineering, what guides RNA?
crRNA (targeting guide)
What are the 2 types of deliveries of transgenes for somatic-cell gene therapy?
Retroviral vectors
Adenoviral vectors
What are retroviral vectors?
the wild-type transgene and retroviral DNA are intergrated into the DNA of the host cell and transmitted to all progeny cells
What are adenoviral vectors?
These vectors do not integrate into the host cell genome. Thus, transgene expression is transient, and most humans exhibit immune responses to these viruses.
Adenoviral vectors are modified adenoviruses used to deliver genetic material, like a new gene or a normal copy of a mutated gene, into cells. They are double-stranded DNA viruses that don't integrate into the host genome, meaning they don't cause permanent changes to the cell's DNA. Adenoviral vectors are often used in gene therapy and vaccine development.
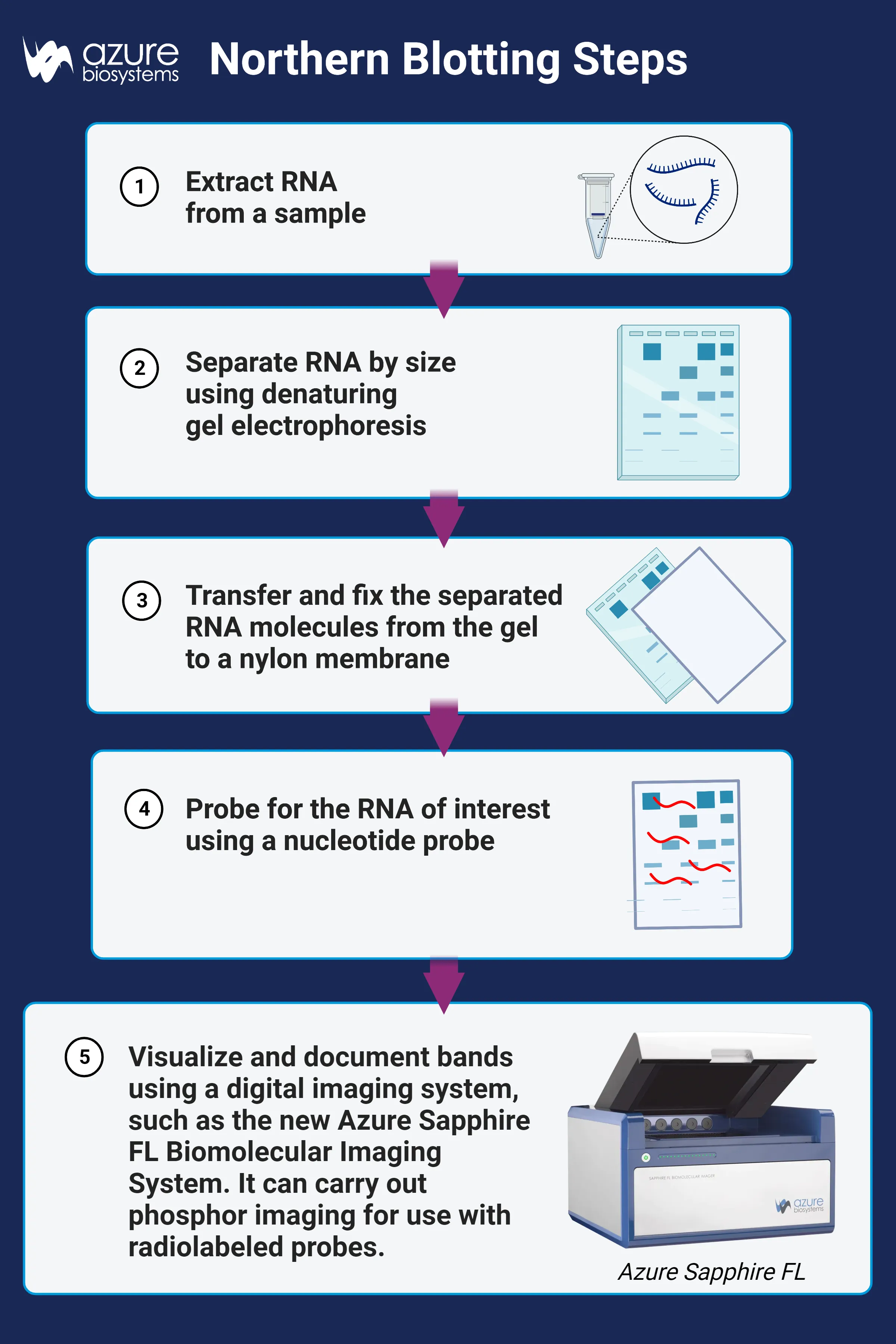
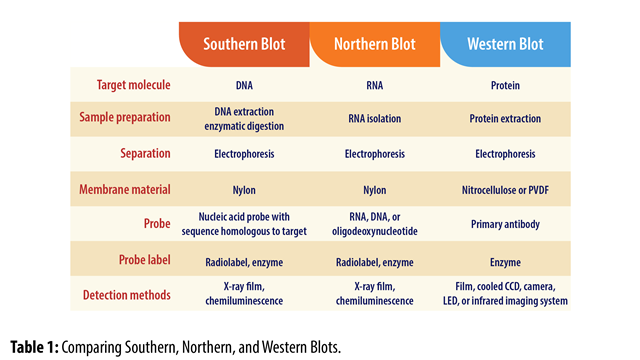
A northern blot is used for what?
To detect specific RNA molecules among a mixture of RNA
What is a southern blot used for?
To detect DNA sequences within a complex mixture of DNA fragments
What is electrophoresis?
This is the migration of electricity charged molecules under the effect of the electical field. These are used for biomolecules: proteins, peptides, nucleic acids
What are the 6 steps to nucleic acid analyses (southern or northern blot)?
Seperate DNA or RNA by length using gel electrophoresis
transfer DNA/RNA to nylon membrane
Immoblize DNA/RNA
Hybridize with radioactive probe specific to nucleotide sequence
Expose membrane to X-ray film
Observe bands on X-ray film
What are the 3 steps to PCR?
Denaturation
Annealing
Elongation
What hormone needs a second messenger and a receptor complex due to it being too latge to cross the membrane?
Peptide hormones (human growth hormone or insulin)
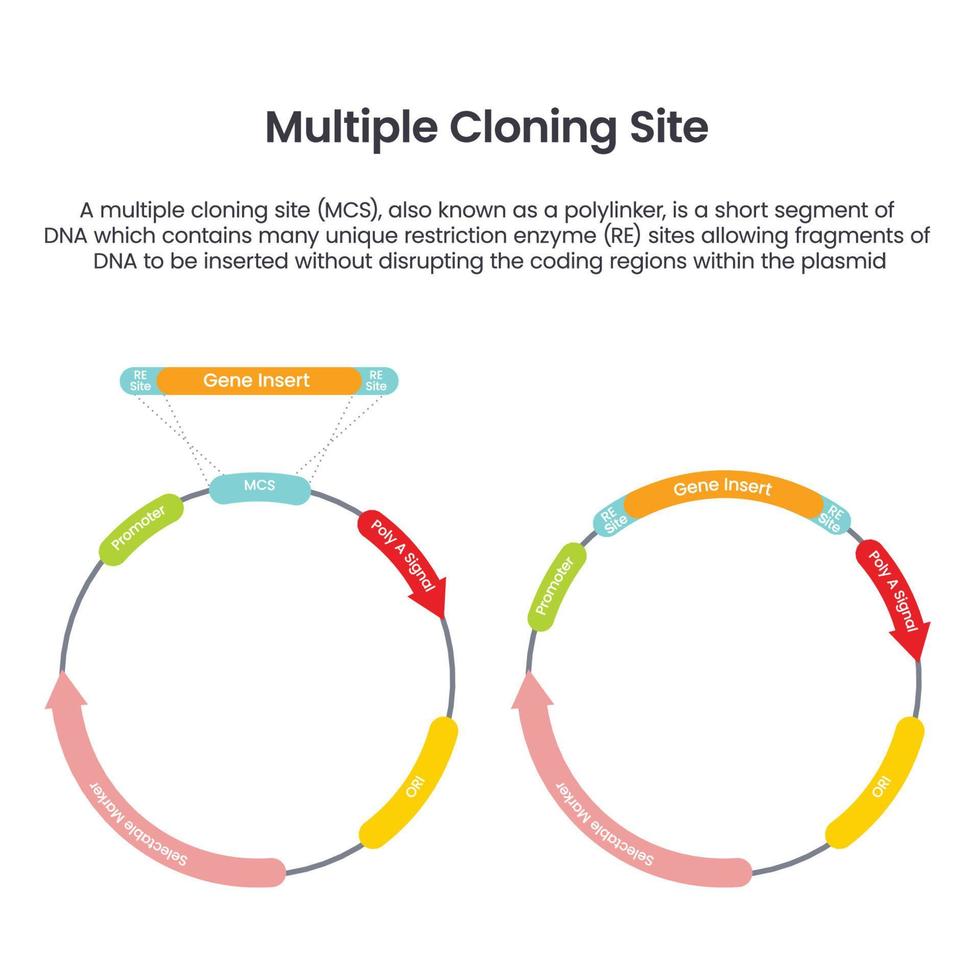
What is a polycloning site in a cloning vector?
AKA multiple cloning site (MCS) or polylinker, it is a short DNA sequence within a cloning vector that contains multiple unique restriction enzyme sites. These sites allow for the easy insertion of foregn DNA fragments into the vector for cloning purposes