PE450 SPORTS SCIENCE QUIZ
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Principles of H2F
Optimizations, individualization, immersion
H2F Domains
Physical, Mental, Nutritional, Spiritual, Sleep
Type 1 (muscle)
Slow twitch
ENDURANCE
High fatigue resistance
<65% resistance
Aerobic (energy source)
Running, cycling
Type 2a (muscle)
Fast twitch
Moderate strength and endurance (aerobic & anaerobic)
Moderate fatigue resistance
60-85% resistance
IOCT, middle distance cardio
Hypertrophy
Type 2x (muscle)
Fast twitch
STRENGTH
Short bursts of power and speed
Low fatigue resistance
Anaerobic (energy source)
Sprinting, weight lifting, jumping
15% of all muscle
Phosphagen / Phosphocreatine Pathway (ATP-PC System)
provides energy for short term (5-10 seconds)
Glycolytic Pathway (Anaerobic Glycolysis)
predominant energy source for high intensity activity lasting up
to approximately 90 seconds
Oxidative Phosphorylation (Aerobic Respiration)
is the predominant source of energy for low-intensity,
sustained activity lasting more than three minutes
Physical Components
Muscular strength, muscular endurance, aerobic endurance, anaerobic endurance, power
Hypertrophy
is the increase in muscle size, which can be achieved through a blending of muscular strength and muscular endurance training
Consistent aerobic training
more capillary density
Muscular strength
lift, drag, carry
Muscular endurance
sustained bouts of low intensity resistance
aerobic endurance
sustained bouts of low intensity movement
anaerobic endurance
short duration, high intensity movement
power
short duration, explosive movements with heavy loads
Movement skills
Agility, coordination, dynamic balance, kinesthesia, pace, perception, reaction time
Movement Skills
At Chas’s Diner: Knee Pain Problems, ReTrain
Agility
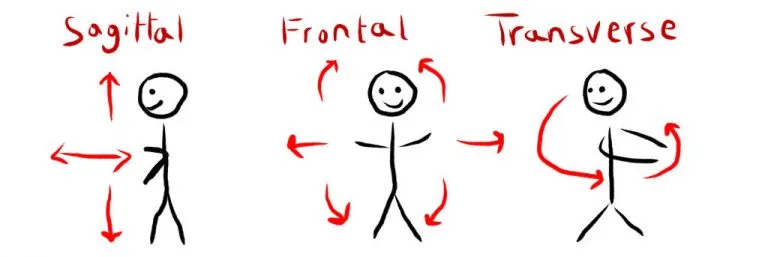
The ability to bend, rotate and twist in the frontal, transverse, and sagittal planes and use that ability to change direction.
Coordination
The ability to synchronize limb, torso and head movements at varying speeds of motion.
Dynamic balance
The ability to move under control at speed and under load.
Kinesthesia
The perception of the body’s position in space during movement.
Pace
The ability to set the correct speed of an activity to manage fatigue.
Perception
The understanding of correct technique and effort that builds skill.
Reaction time
The interval between an external stimuli and the Soldier’s response.
Structural capabilities
load tolerance, flexibility, static balance, body composition, bone density
load tolerance
The ability of the skeletal system to bear weight.
flexibility
The range of motion across single or multiple joints that allows the body to be positioned for optimal movement.
static balance
The ability to maintain a stable position over a base of support.
body composition
The percentage of lean muscle and other body tissues.
bone density
The thickness and quality of the bone that provides its strength.
Carbohydrates
4cal per gram
Proteins
4cal per gram
Fats
9 cal per gram
Optimal sleep duration
7-9 hours
Optimal sleep timing
Get as many cycles as possible
Sleep continuity
uninterrupted period of sleep
Movement planes
Sagittal, frontal, transverse