Cycle 5
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Scalar
Quantity with only magnitude
Vector
Quantities that have both magnitude and direction
Weight
Vector Quantity
Weight is sometimes used as a synonym for force. Your weight, in Newtons, is your mass, in kilograms, multiplied by the acceleration due to gravity, which is 9.8m/s~ downward on Earth. Although your mass remains constant, your weight would be different on another planet because gravity is different on other planets.
Fg = mg
Geometric vector
Directed line segment
Tail (initial point)
Head (terminal point)
Direction is from head to tail
Equivalent vectors
have the same length/magnitude and the same direction
Opposite Vectors
Vectors with the same magnitude, but opposite directions
Quadrant Bearings
compass measurements between 0° and 90° east or west of the north-south line. (Always start at N or S)
True Bearings
are compass measurements between 0° and 360° beginning at the north and rotating clockwise.
Resultant
add two or more vectors, you are finding a single vector
Adding Same Direction Parallel
Vectors a and b are parallel and have the same direction
Place vectors tip to tail and add, the direction of resultant will be the same as original vectors
Adding Opposite Direction Parallel Vectors
Vectors c and d are parallel but are in opposite directions.
Place tail of d and head of c
Resultant is same direction as c
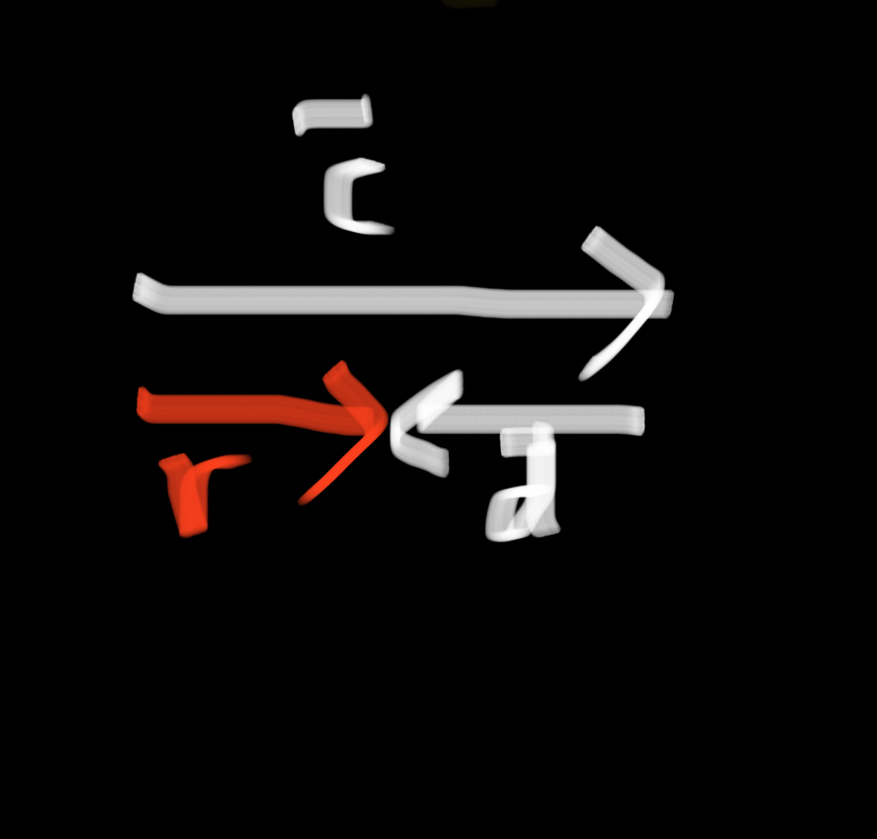
Subtracting parallel vectors
The relationship between addition and subtraction with vectors is similar to the relationship between addition and subtraction with scalars. To subtract u - v, add the opposite of v to u.
In other words, i - vis equivalent tou + (-v).
The Zero Vector
When you add two opposite integers, the result is zero. A similar result occurs when you add two opposite vectors.
The zero vector is written as 0 (with vector sign) It has no specific direction.
Multiply Vector by a Scalar
The magnitude is multiplied by the scalar and the vectors are parallel
k > 0
kv has the same direction as v
k < 0
kv has the opposite direction of v
Distributive Property
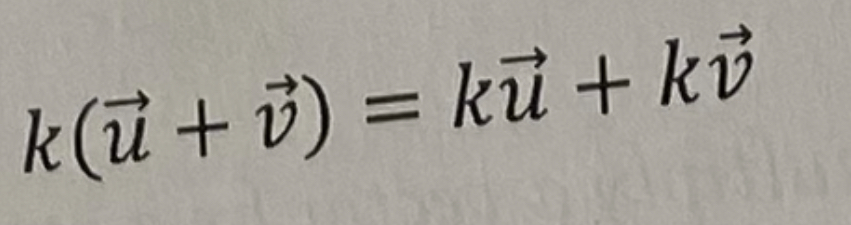
Associative Property
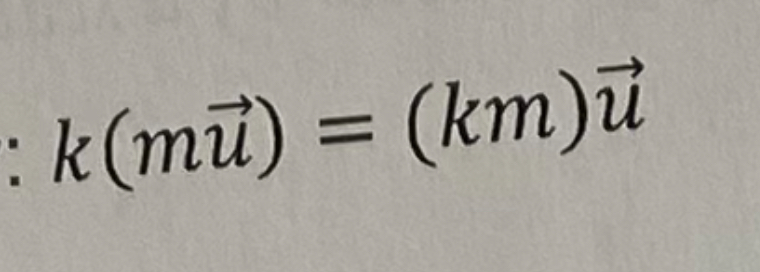
Identity Property
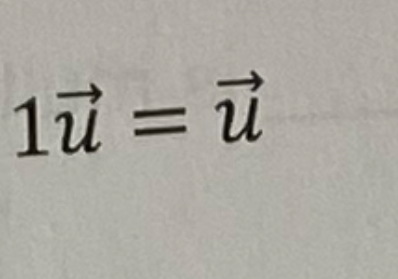
Collinear Vector
If they lie on a straight line when arranged tail to tail.
Are scalar multiples of another, which means they are parallel