Normal Labor & Delivery
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
what is labor?
contractions that cause cervical change
- most occurs spontaneously, but it can be induced or augmented
induced labor =
attempt to begin labor in a non-laboring patient
- using misoprostol in cervix & IV oxytocin
augmented labor =
intervening to increase already present contractions by use of oxytocin or artificial rupture of membranes
what is the Bishop Score?
a method of evaluating the cervix to predict if induction or augmentation is likely to succeed in vaginal delivery
- another option is "cesarean section delivery probability" score on Epocrates
patients are advised to report to the hospital for delivery if one of the following is true:
- contractions have been occurring every 5 mins or less for 1 hour
- rupture of membranes
- significant decrease in fetal movement in late pregnancy
what would initial evaluation of the patient include?
- time of onset & frequency of contractions
- GA: full-term or pre-term delivery?
- review of records: indication that vaginal delivery should not be attempted?
- maternal vitals
- external fetal monitor to evaluate fetal HR, movement, & frequency of contractions (technically monitors strength of contractions too, but not very accurate)
- determination of fetal lie & presentation by abdominal palpation
- determination of ruptured vs. intact membranes
- cervical/digital exam
what are Leopold Maneuvers?
abdominal palpation technique which helps determine the "lie" or presentation of the baby
what is the occiput?
back of head or skull
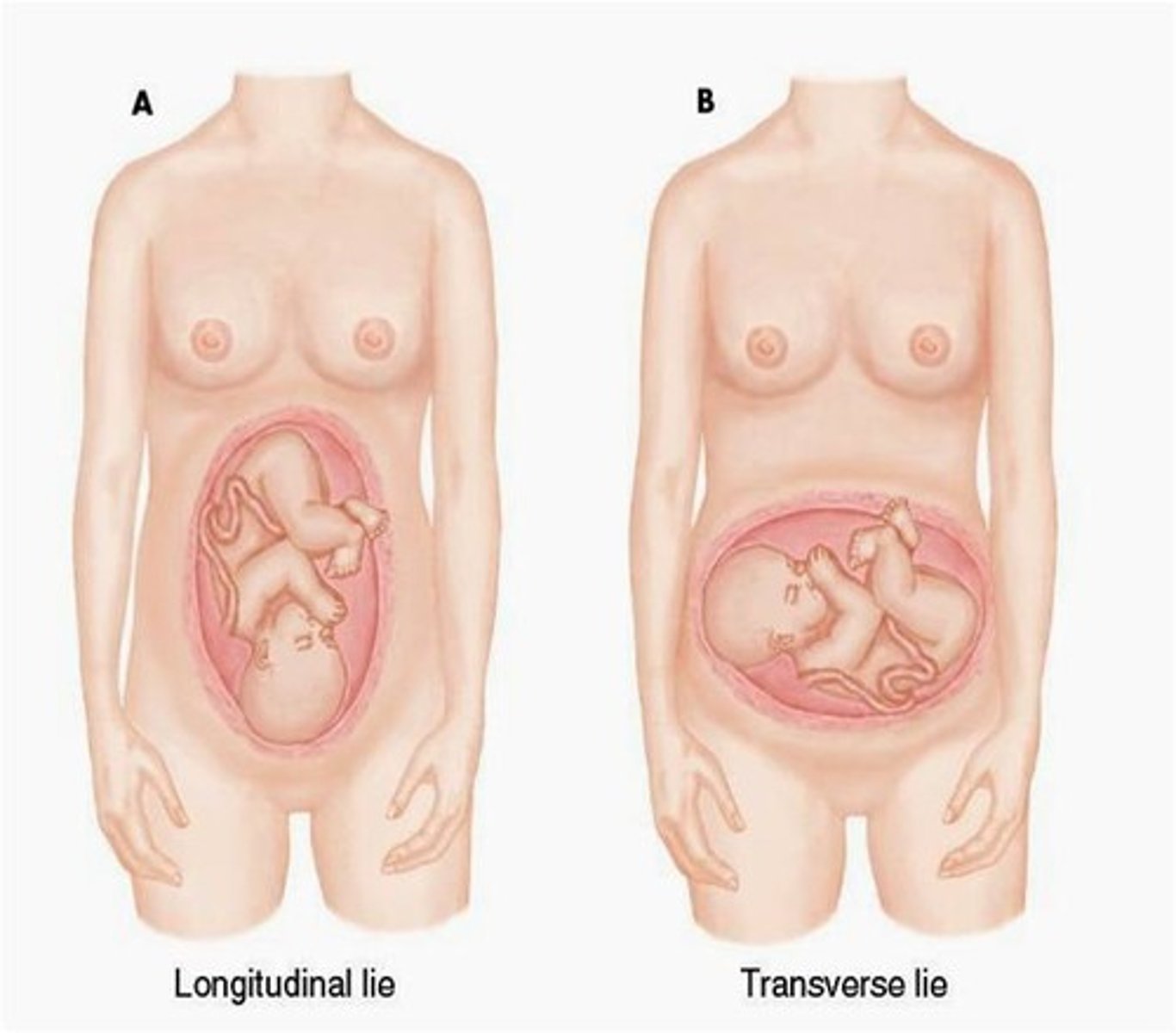
lie =
longitudinal or transverse
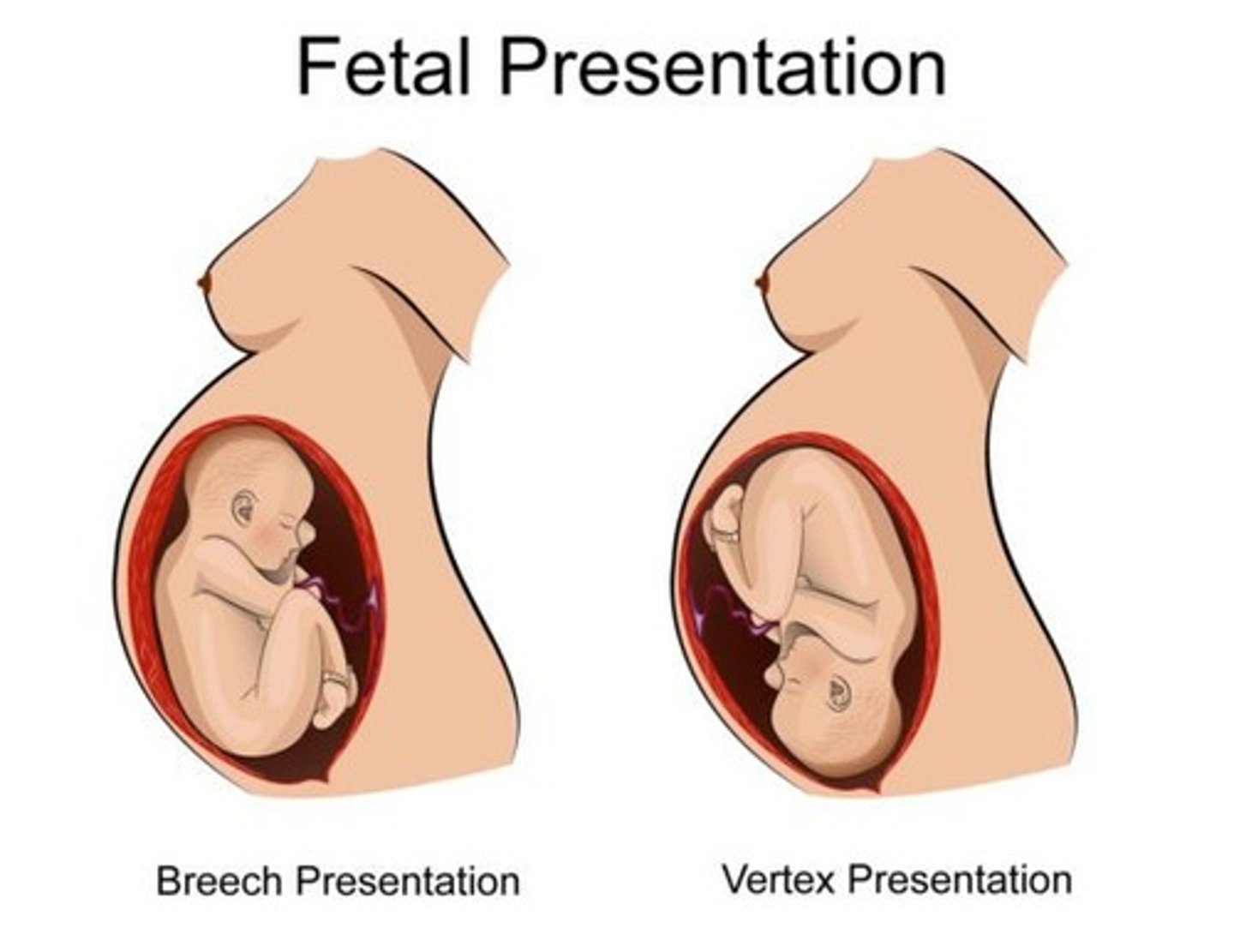
presentation =
- vertex/cephalic (head down)
- breech (buttocks down)
- transverse
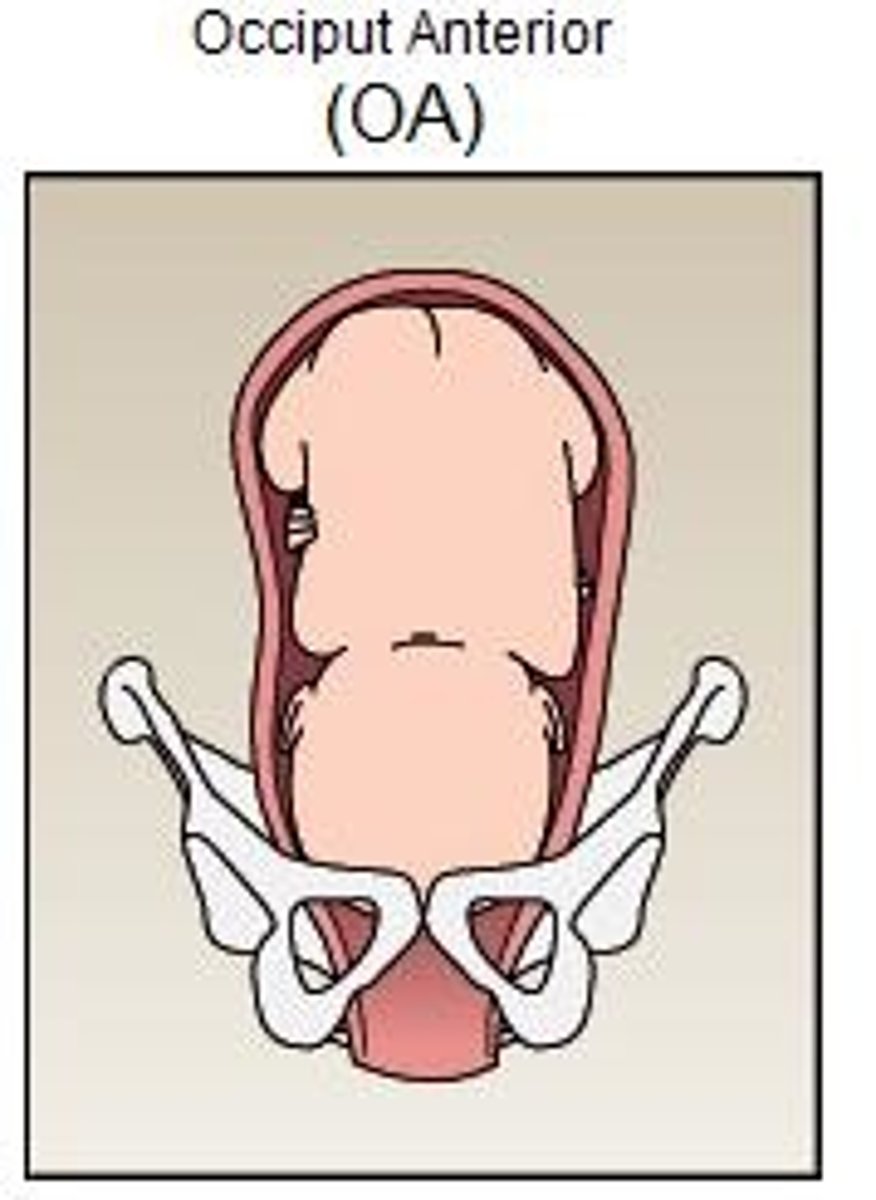
what is considered the easiest presentation for delivery?
vertex/cephalic (head down)
- w/ occiput anterior (back of the baby's head toward front of mom's body & baby's body facing toward mom's back)
shoulder presentation
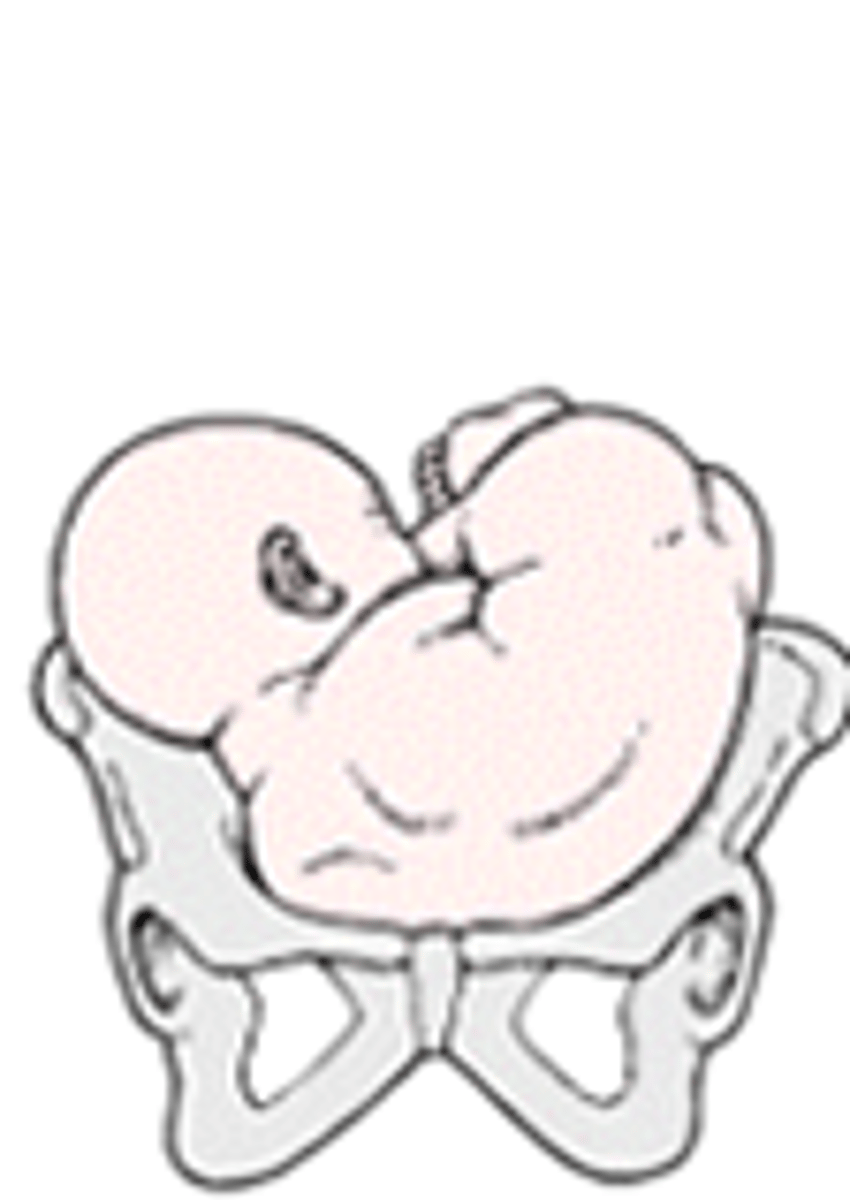
breech presentation
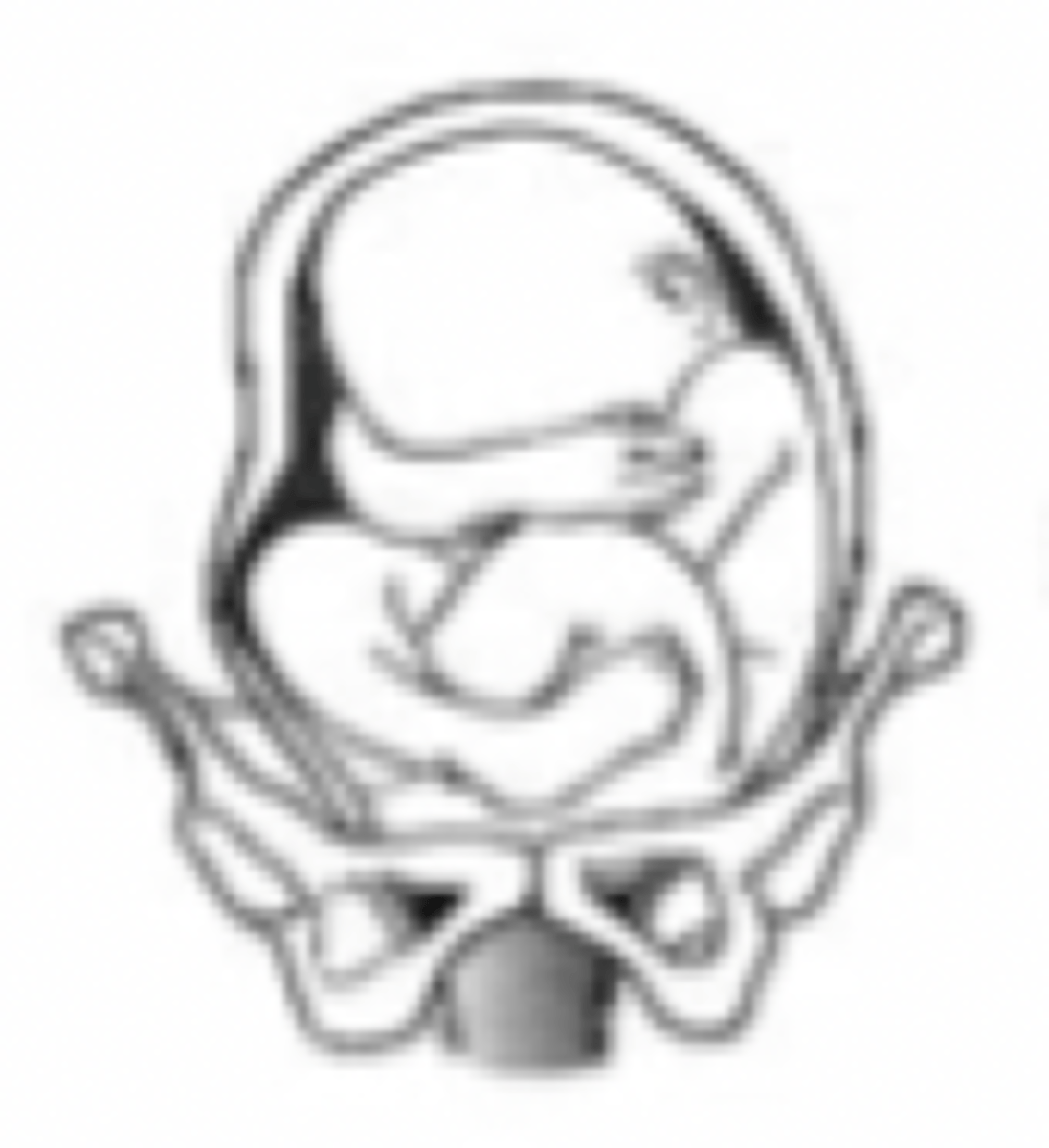
footing breech position
when is rupture of membranes (ROM) suspected?
when the patient reports a gush of fluid from the vagina
what is prelabor rupture of membranes (PROM)?
membrane rupture > 1 hr before labor began
what should be done if the PROM patient is >/= 36 wks gestation?
prompt induction of labor
- unless c-section is indicated
risk of __________ increases once the membranes have ruptured
infection
what is preterm prelabor rupture of membranes (PPROM)?
membrane rupture before 36/37 wks gestation
w/ PPROM (membrane rupture @ < 36/37 wks) decision to deliver is dictated by risks. what do these include?
- infection
- GA
- quantity of remaining amniotic fluid
w/ PPROM, what does use of prophylactic antibiotics reduce?
neonatal morbidity
what can infections lead to?
- tachycardia
- fetal distress & death
w/ PPROM, what should be done if infection is determined?
labor should be induced
how can ROM, PROM, or PPROM be confirmed?
initial testing usually includes:
- pooling
- US
then further testing can include:
- commerical test
- nitrazine
- fern
what is pooling?
vaginal exam using a sterile speculum & sterile gloves
+ test = fluid pooling in vaginal vault, speculum, or visualization of amniotic fluid coming from cervical canal
often ultrasound (US) will follow the pooling test.
if AFI = < 5 cm (oligohydraminos), what is assumed?
that the membranes have ruptured (ROM)
often ultrasound (US) will follow the pooling test.
if AFI = 5 to 20-25 (normal), what does this indicate?
further testing
often ultrasound (US) will follow the pooling test.
if AFI = > 20 to 25 cm (polyhydraminos), what does this indicate?
membranes have not ruptured
- rules out ROM
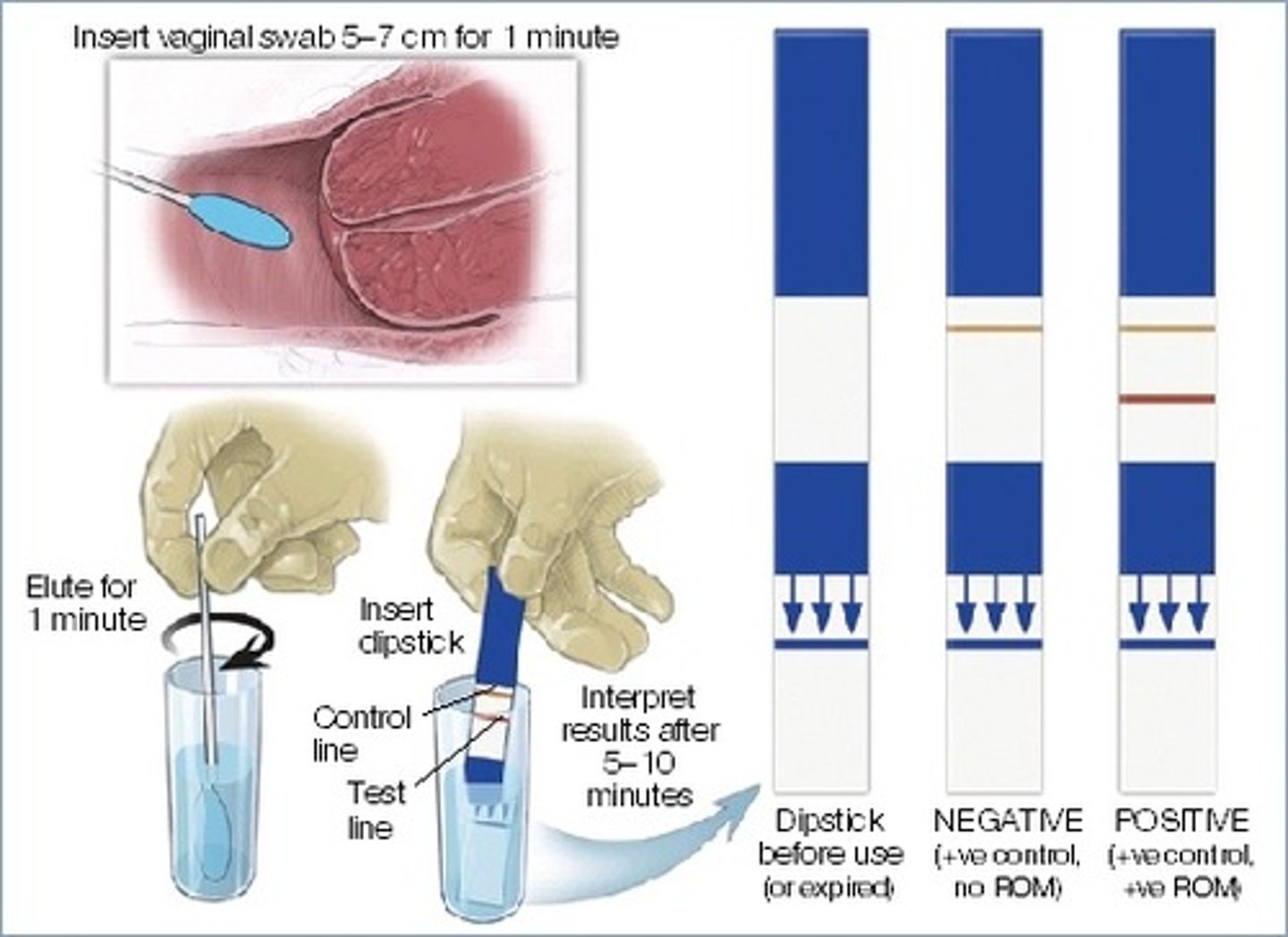
what is a commerical test?
uses vaginal swabs (ex: Amnisure)
- has a "control" & a "positive" line
- requires trained staff to perform
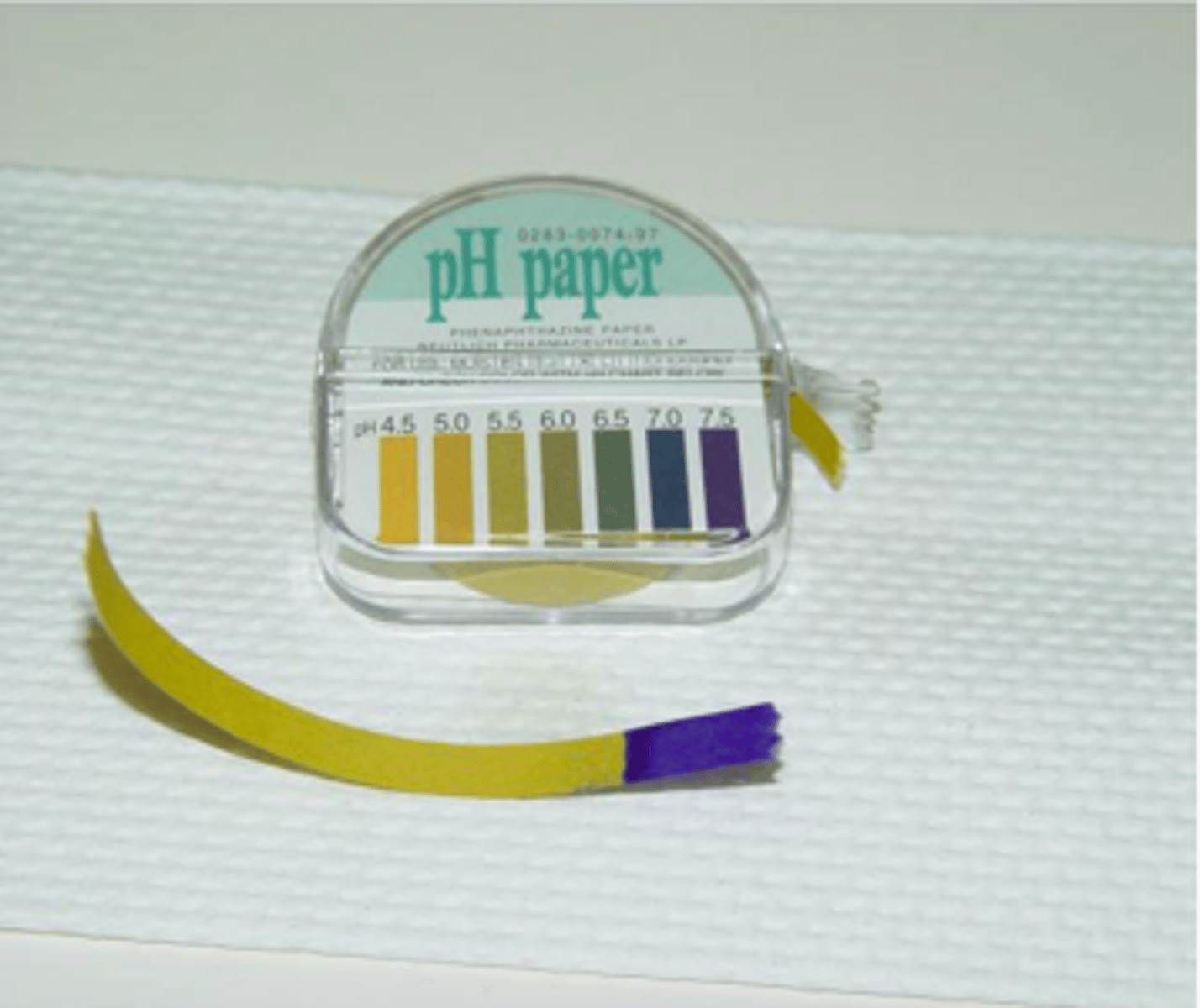
what is the nitrazine test?
place a piece of nitrazine paper on fluid collected w/ speculum
+ = paper turns blue
(which indicates alkaline fluid)
false positives can result from semen
what is the fern test?
place a drop of fluid on a dry microscope slide & allow it to dry completely
+ = "fern" like pattern that can be viewed under the microscope
false positives occur when sample is taken directly from the cervix (cervical mucus will also form a fern pattern)

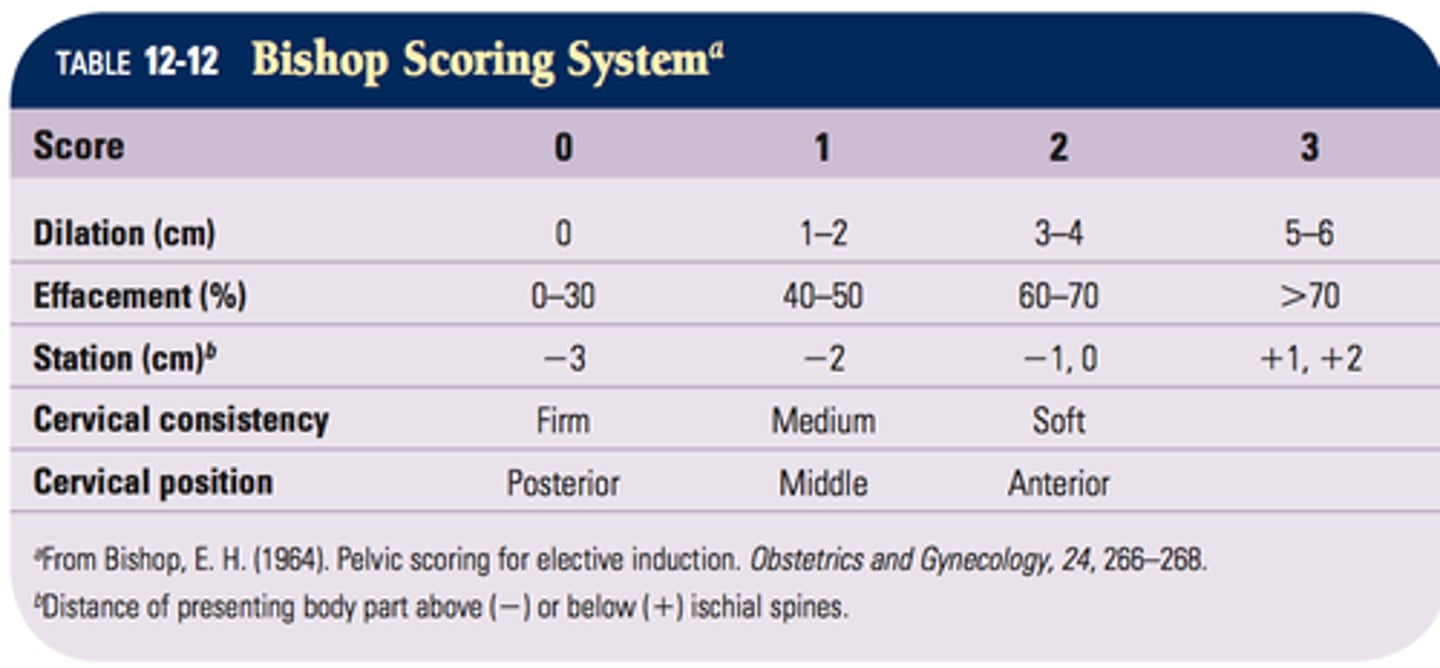
what things are evaluated during a cervical/digital exam?
- effacement
- dilation
- station
- cervical position
- cervical consistency
*these 5 things can be scored to create a Bishops Score (which can then guide decisions to proceed)
digital exam should NOT be performed after ________ w/o knowing the position of the placenta first
20 wks
what is effacement?
thickness or length of cervix
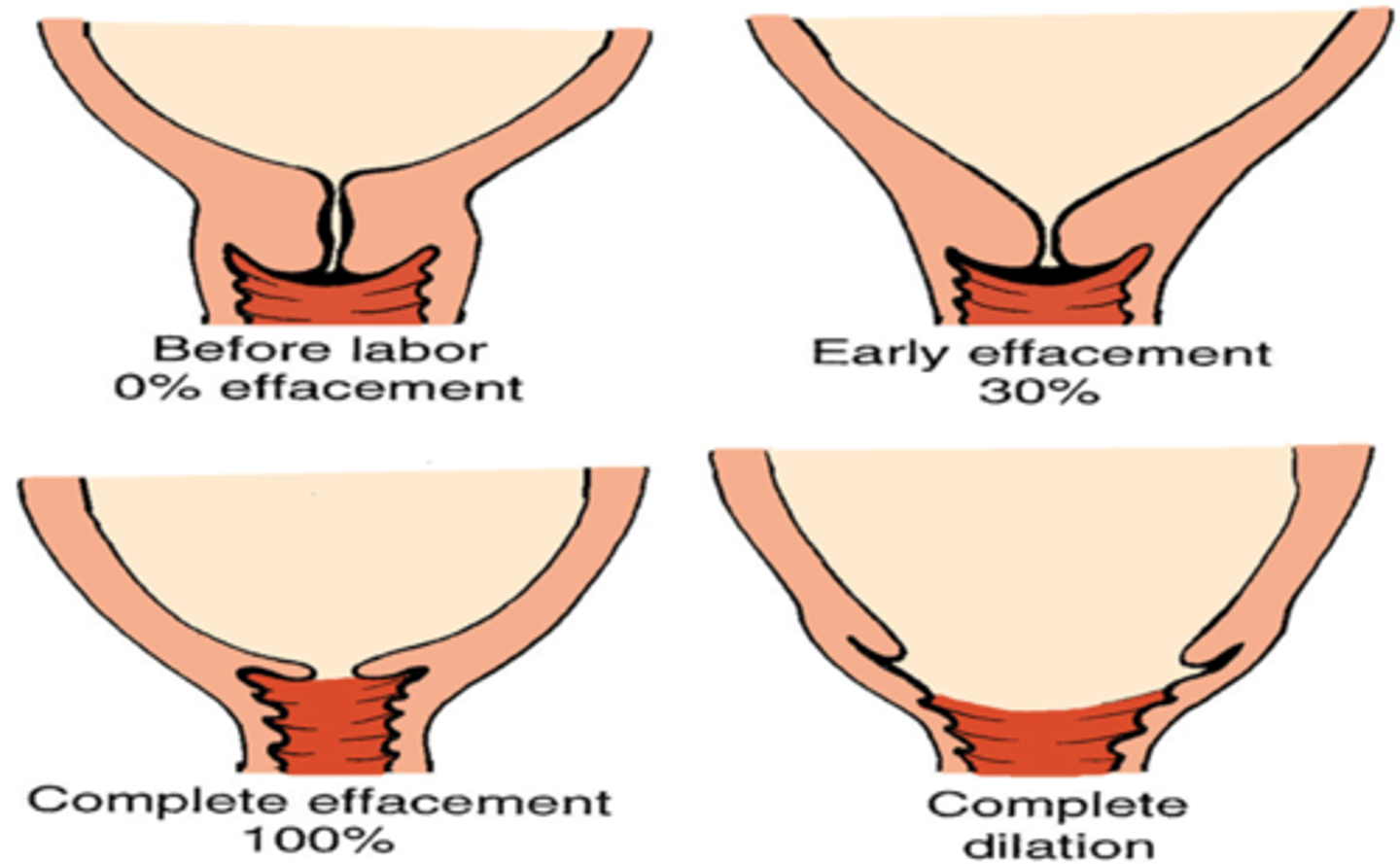
full thickness is about 4 cm or ____ effaced
0%
2 cm thickness is about ____ effaced
50%
very thin, membrane-like cervix =
100% effaced
what is dilation?
a measure of how open the cervix is
- ranges from 0 to 10 cm (if you can insert 1 finger all the way through the cervix to the baby's head = 1 cm dilated; if you can insert 2 fingers = 2 cm dilated; then start spreading fingers apart to gauge; when spreading fingers as far apart as you can = 10 cm dilated)
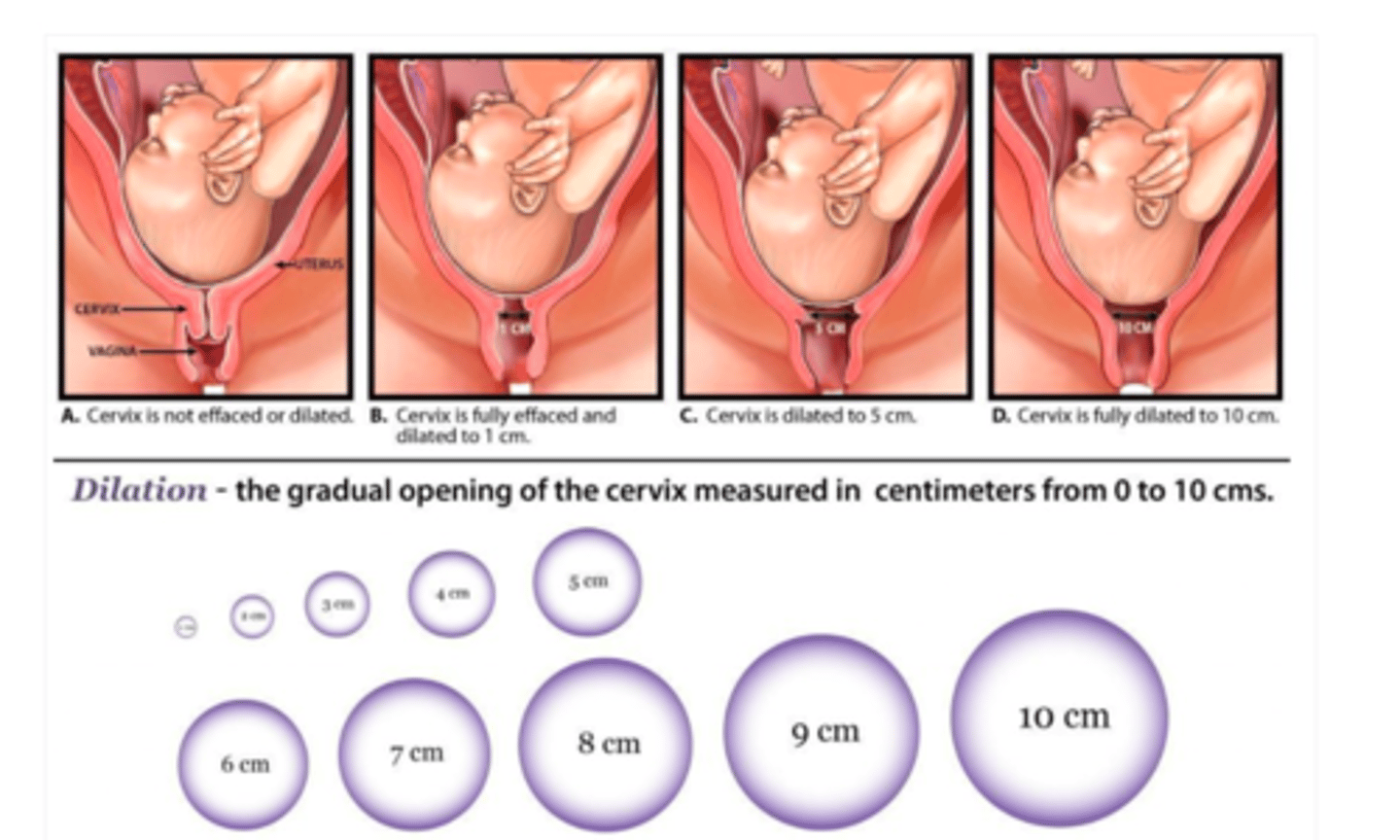
full dilation =
10 cm
what is station?
relation of the fetal head to the ischial spines of the mother
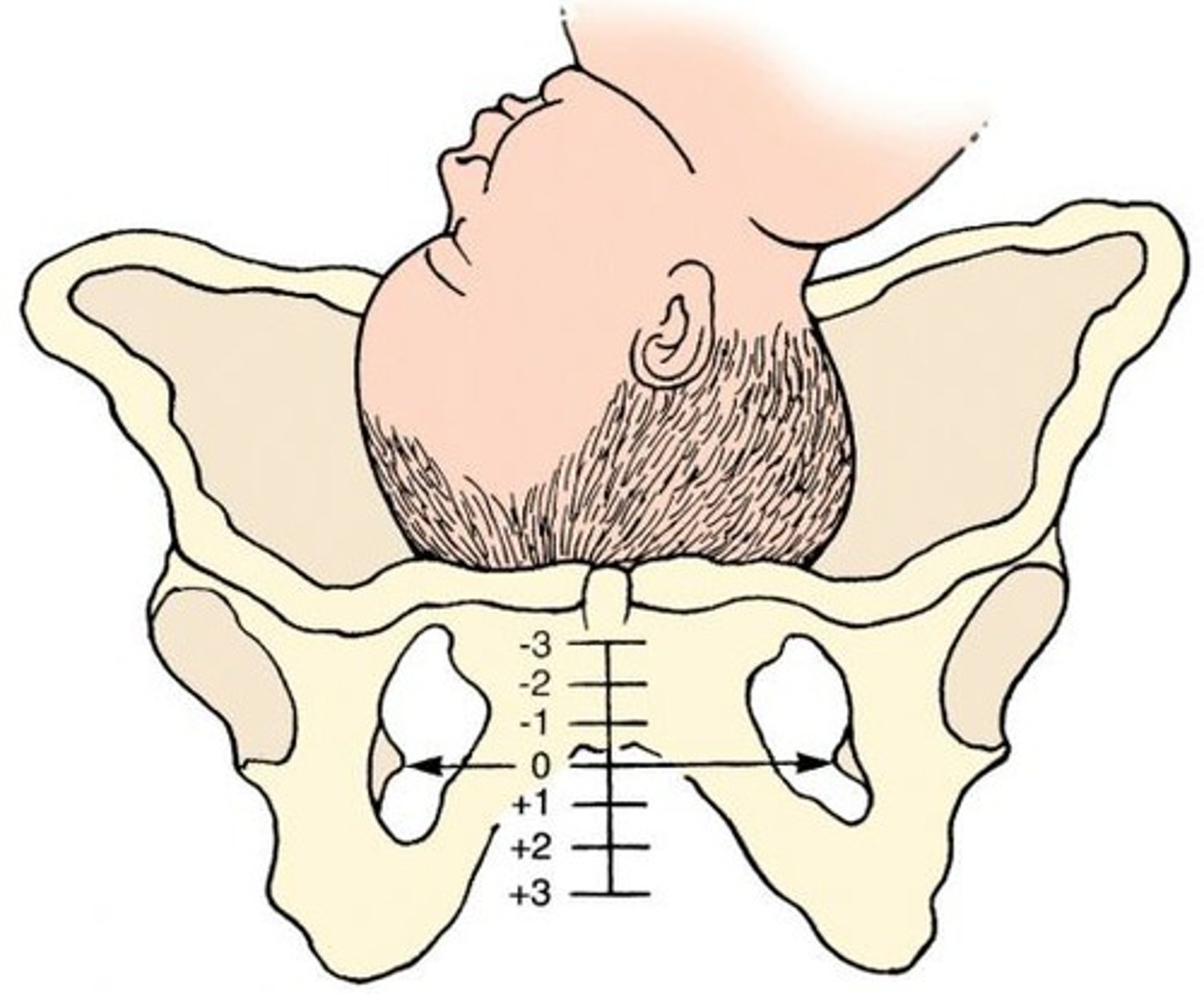
station 0 =
fetal head is level w/ mother's ischial spines
when the station is a negative number =
fetal head is above mother's ischial spines
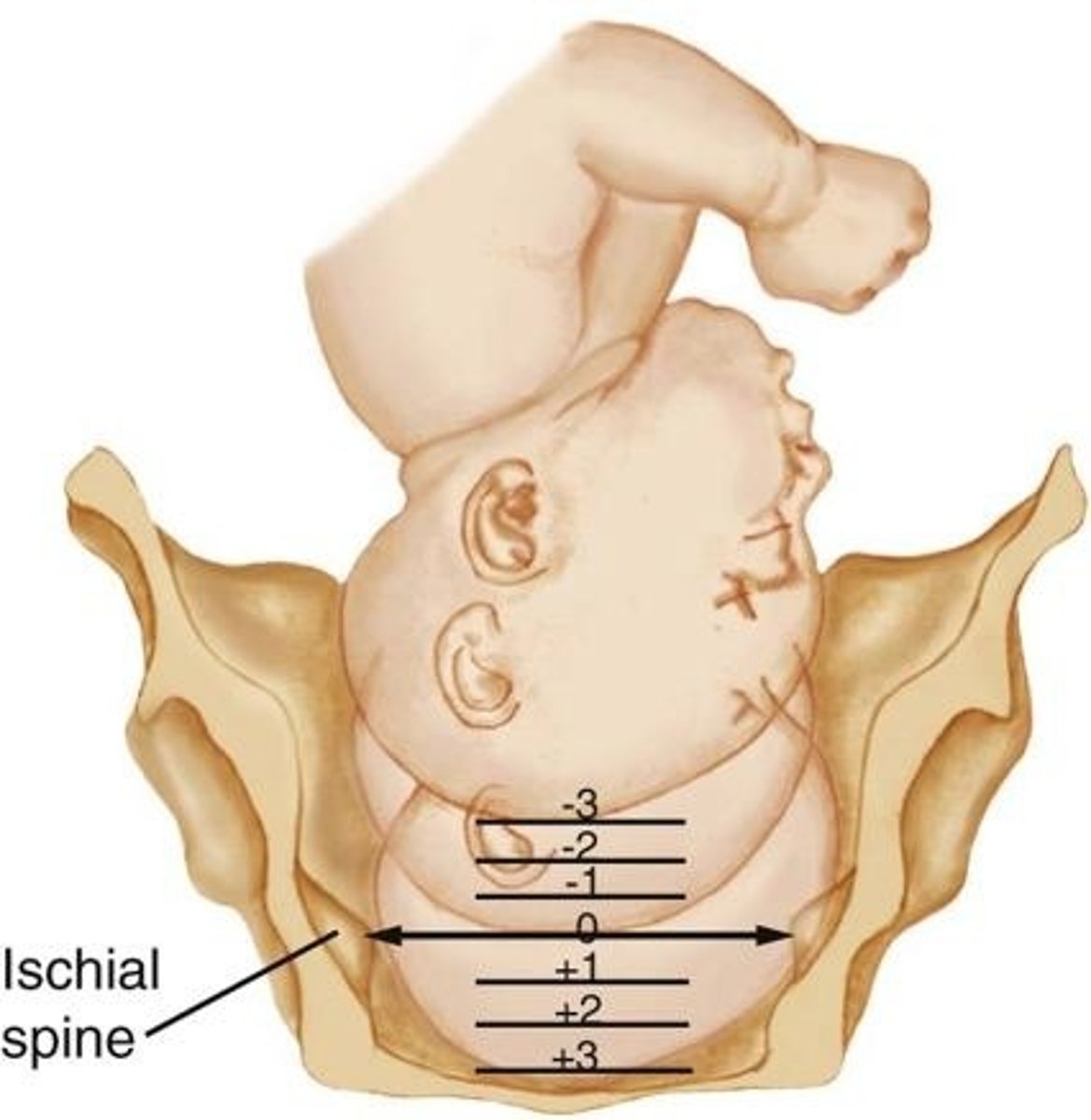
when the station is a positive number =
fetal head is below mother's ischial spines
as labor progresses, how does the position of the cervix change?
posterior --> mid --> anterior
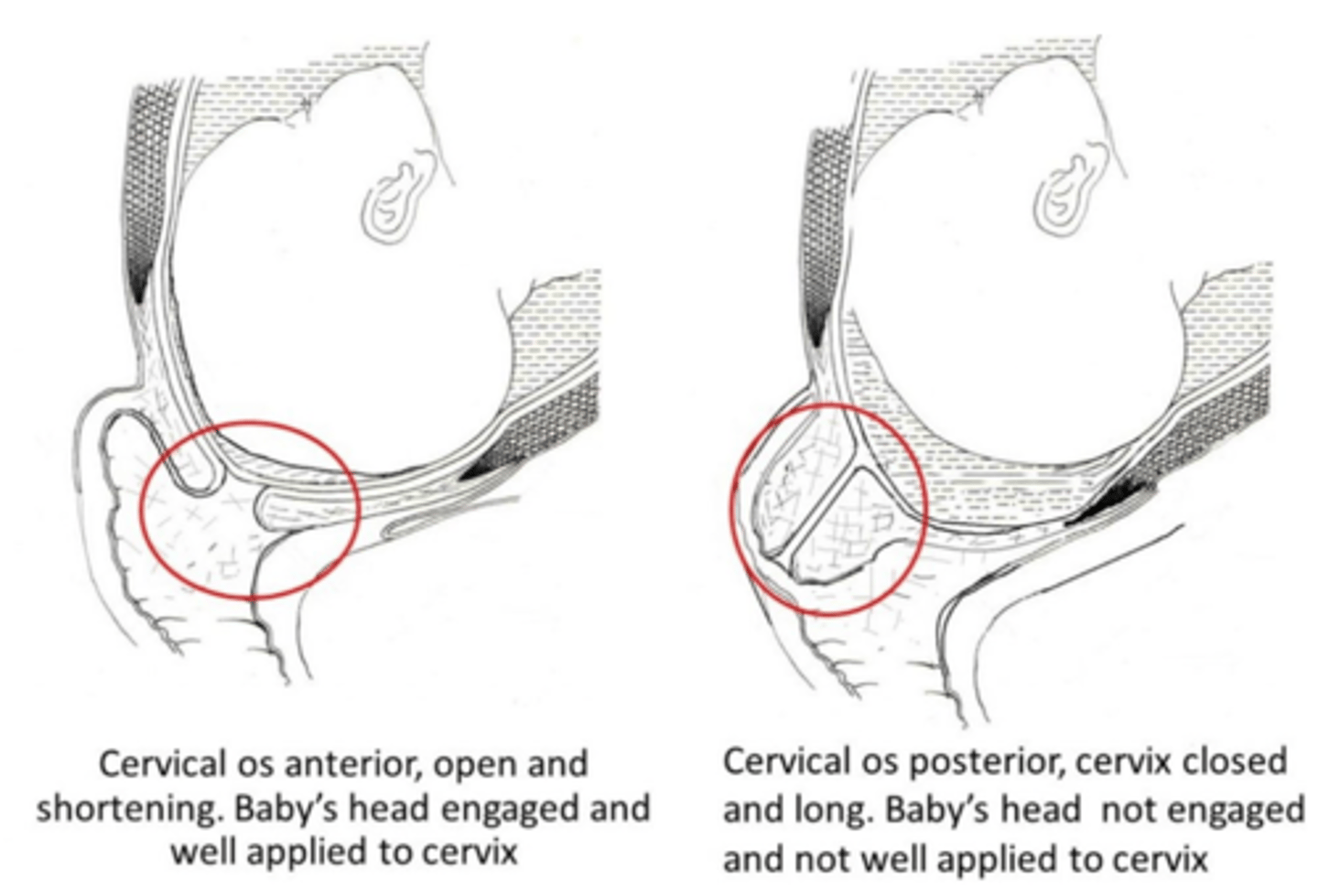
as labor progresses, how does the consistency of the cervix change?
firm --> medium --> soft
Bishops Score ___ is favorable for vaginal delivery
> 8
who is given antibiotic prophylaxis?
- all pts who tested positive for group B strep
- membranes ruptured > 18 hrs
- premature
- maternal fever >/= 100.4
- previously delivered a baby w/ group B strep
what is the antibiotic of choice for GBS prophylaxis (for most deliveries >/= 34 wks)?
Penicillin G
- unless PPROM < 34 wks gestation
what is the antibiotic of choice for GBS prophylaxis w/ PPROM < 34 wks?
combo of amoxicillin (or ampicillin) + erythromycin
what things are usually monitored throughout all stages of labor?
- maternal vitals
- fluid input & output
- fetal HR
during which stages of labor are maternal uterine contractions monitored?
1st & 2nd stages
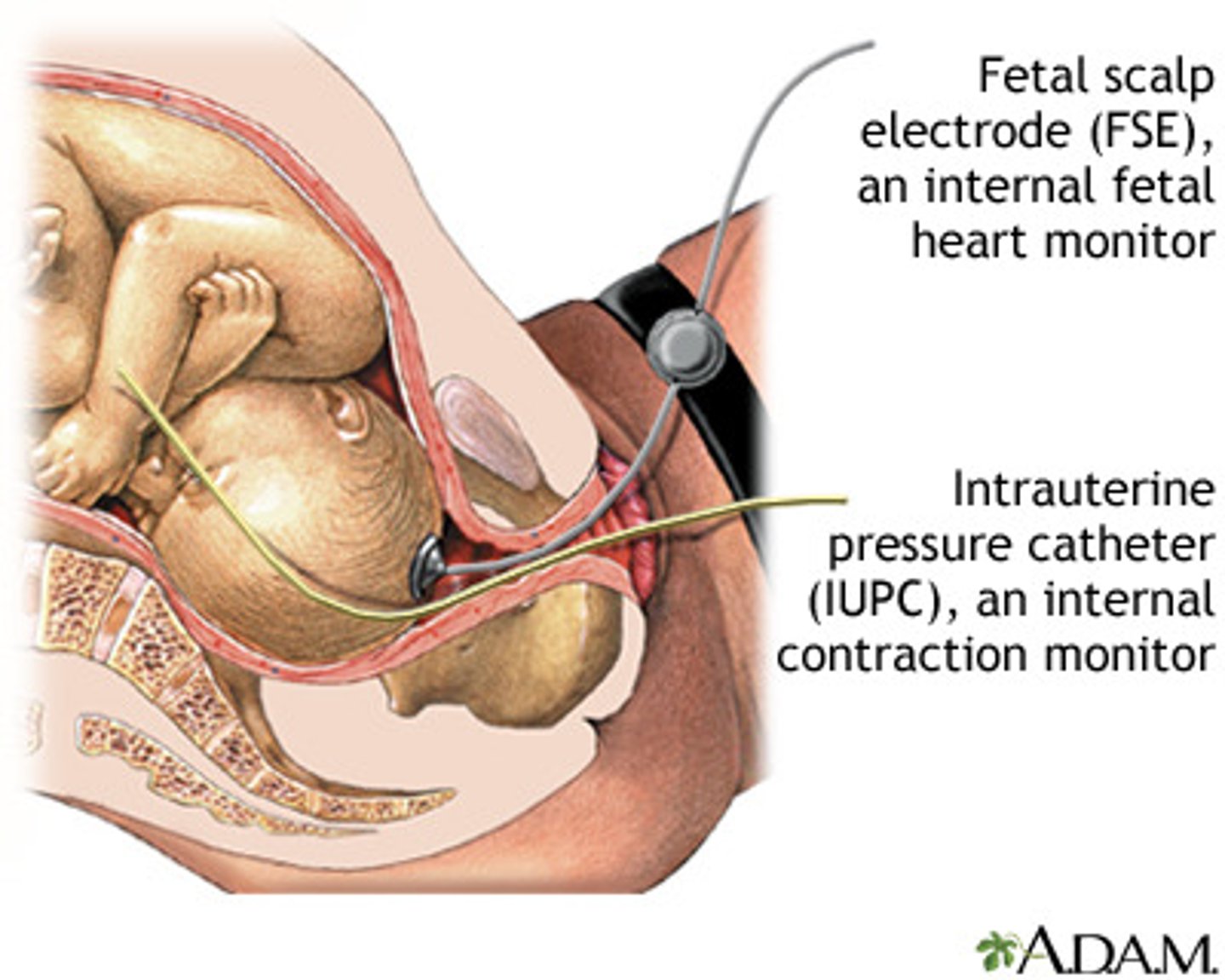
what can be used for continuous fetal heart monitoring?
external electronic monitors
- fetal scalp electrode can be used if more sensitive monitoring is needed
what can be used to (most accurately) monitor the strength of the uterine contractions?
an intrauterine catheter can be threaded into the uterine cavity
stages of labor
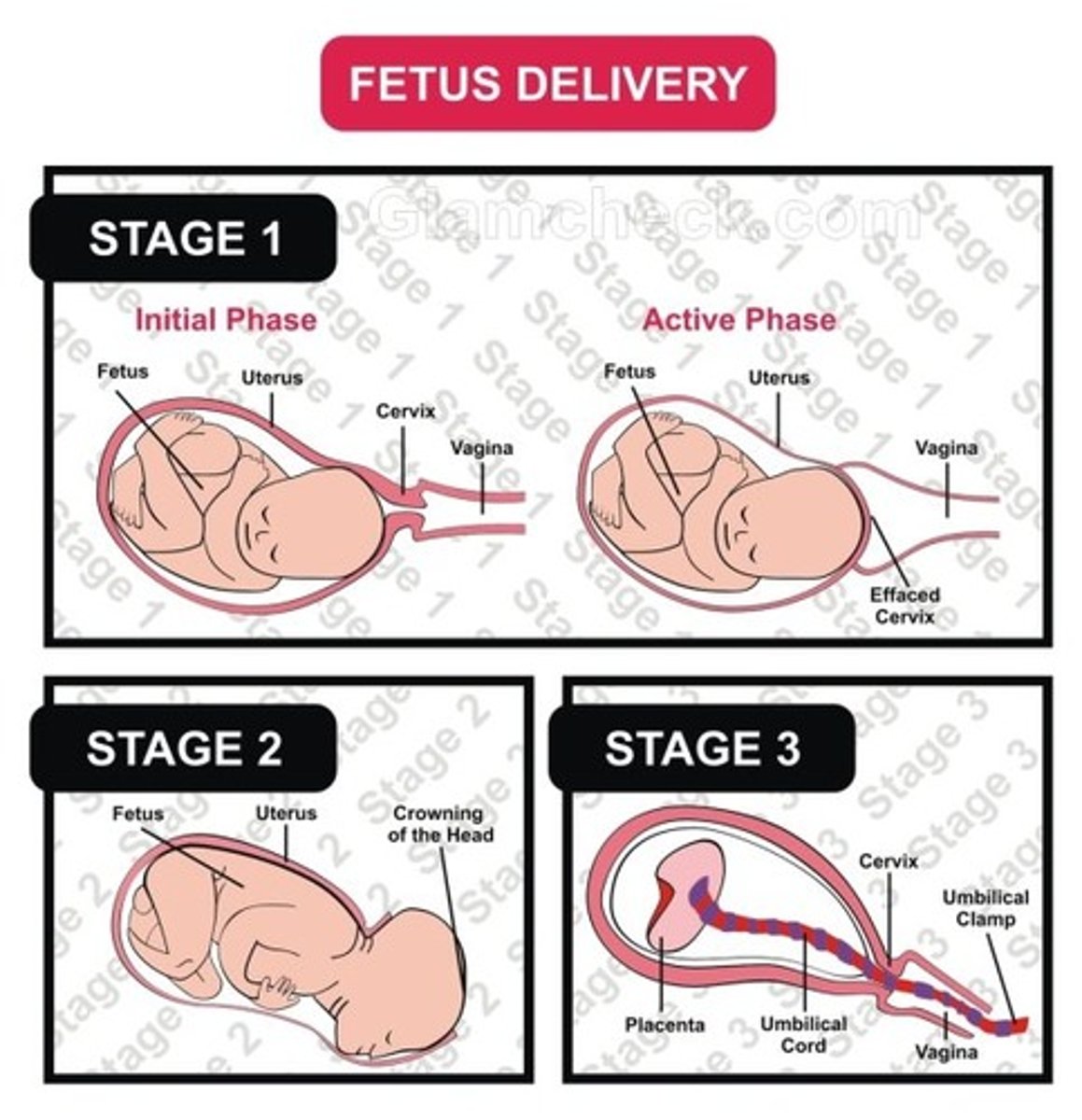
what is the first stage of labor?
from onset to full dilation & effacement of the cervix
- divided into latent & active
what is latent labor?
time period of early labor up to dilation of 6 cm
- cervix softens & becomes more effaced, but the contractions are moderate & the fetus has not descended into the pelvis
- narcotics are sometimes used at this point to relax pts & decrease pain
what is the maximum length of latent labor?
20 hrs
when may an attempt be made to prevent contractions & the progression of labor (tocolysis)?
if labor begins before 36 wks gestation
- only if pt is in the latent stage of labor
what are tocolytics?
medications used for the purpose of preventing contractions & progression of labor
- usually only succeed in prolonging labor by 48 hrs
common tocolytics =
- terbutaline
- magnesium sulfate
- nifedipine
- indomethacin
what do the 48 hrs (provided by tocolytics) allow for?
steroid treatment (betamethasone or dexamethasone)
- to enhance fetal lung maturity & reduce risk of respiratory distress syndrome & other complications (such as, intracranial hemorrhage, sepsis, & neonatal death)
betamethasone or dexamethasone is always used from _____________ gestation
24-34 wks
- use after 34 wks is controversial
administration of ____________________ can also be considered in premature labor (can reduce the risk of cerebral palsy, & work w/ steroid to reduce hemorrhage associated w/ hydrocephalus)
magnesium sulfate
common risks for preterm delivery =
- previous preterm delivery
- PPROM
- uterine abnormalities
- polyhydraminos
- bacterial vaginosis
patients w/ a hx of previous preterm delivery should be given supplemental _________________ to reduce the risk of a subsequent preterm delivery
progesterone
what is the 1st leading cause of neonatal death?
congenital anomalies
- 2nd = preterm delivery
what is the most common cause for hospitalization during pregnancy?
preterm delivery
what is active labor?
labor when the cervix is dilated beyond 6 cm
- contractions become more intense & the fetus descends
- regional analgesia (either epidurals or spinal analgesia) can be given during this time
average time of active labor is ____________.
2-4 hrs
what is a "walking epidural?"
combo of epidural & spinal analgesia that allows the patient to walk
if active labor stops for 2 hrs, think:
the 3 Ps!!
1. power
2. passage
3. passenger
*these can determine if vaginal delivery efforts should be continued or if c-section should be performed*
power =
strength of contractions as determined by intrauterine pressure catheter
passage =
easy downward movement of fetus w/ fundal pressure
- indication is not too large to pass through the pelvis
passenger =
presentation of the head
what is the second stage of labor?
from full dilation of cervix to delivery of the baby
- usually involves 25 to 50 mins of pushing
- includes cardinal movements of labor
when is the 2nd stage of labor considered prolonged?
if longer than:
- 2 hrs in a nulliparous patient
- 1 hr in a multiparous patient
**add 1 more hour to each if pt had epidural
in what stage of labor do the cardinal movements occur?
a. 1st
b. 2nd
c. 3rd
b. 2nd
2 multiple choice options
what are the cardinal movements of labor?
*don't need to know
- head engages in the pelvis (may have occurred before labor began)
- fetus starts its decent & flexion occurs
- then the fetus internally rotates (usually resulting in the head being in occiput anterior position)
- then as the head delivers, extension occurs, followed by external rotation of the head
- allowing expulsion of anterior shoulder, then posterior shoulder, then torso
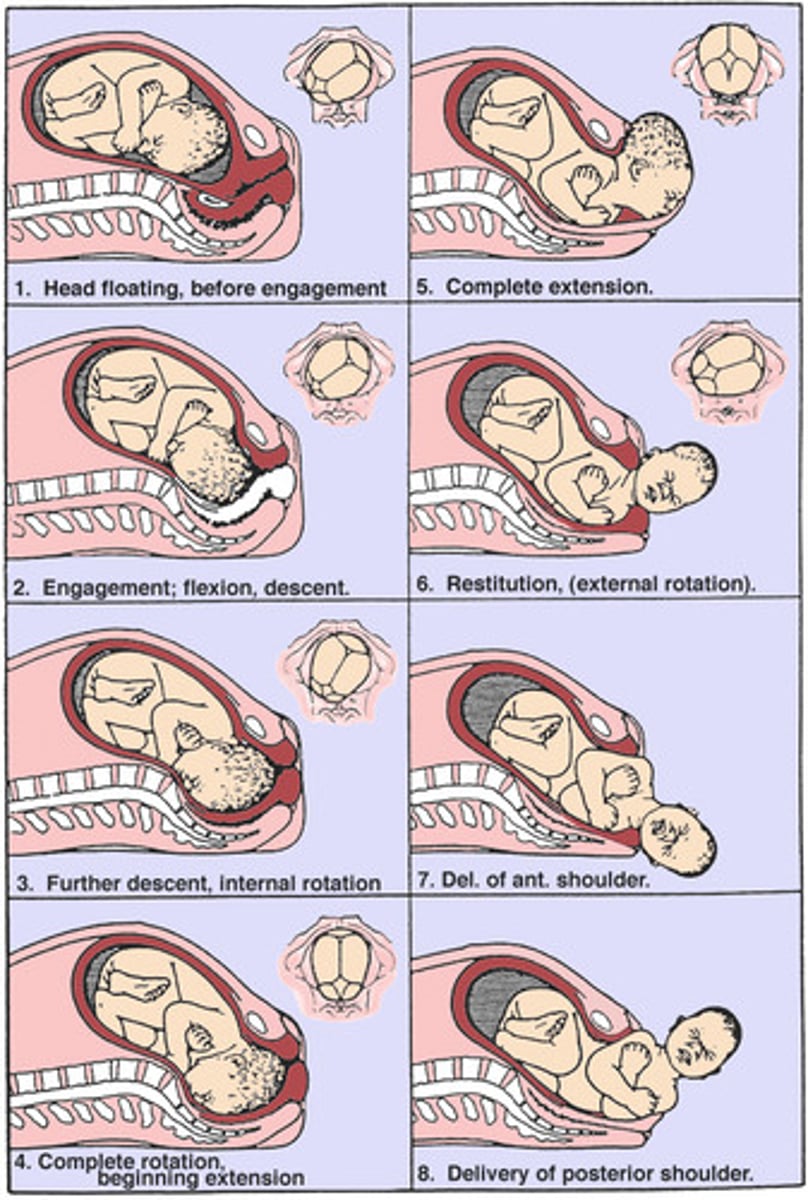
what is done once the head is delivered?
- the oropharynx is bulb suctioned or wiped w/ a towel & the umbilicial cord is assessed
- if cord is around neck, attempt to reduce it over the baby's head
- use gentle downward traction to deliver anterior shoulder, then gentle upward traction for posterior shoulder
what is done once the shoulders are delivered?
torso & legs deliver easily
- cord is clamped
- baby can be placed on mother's abdomen while the cord is cut
- baby will then be handed to a nurse or pediatrician
what is an episiotomy?
incision made in the perineum (midline or mediolateral) to facilitate delivery
- may be done to hasten delivery
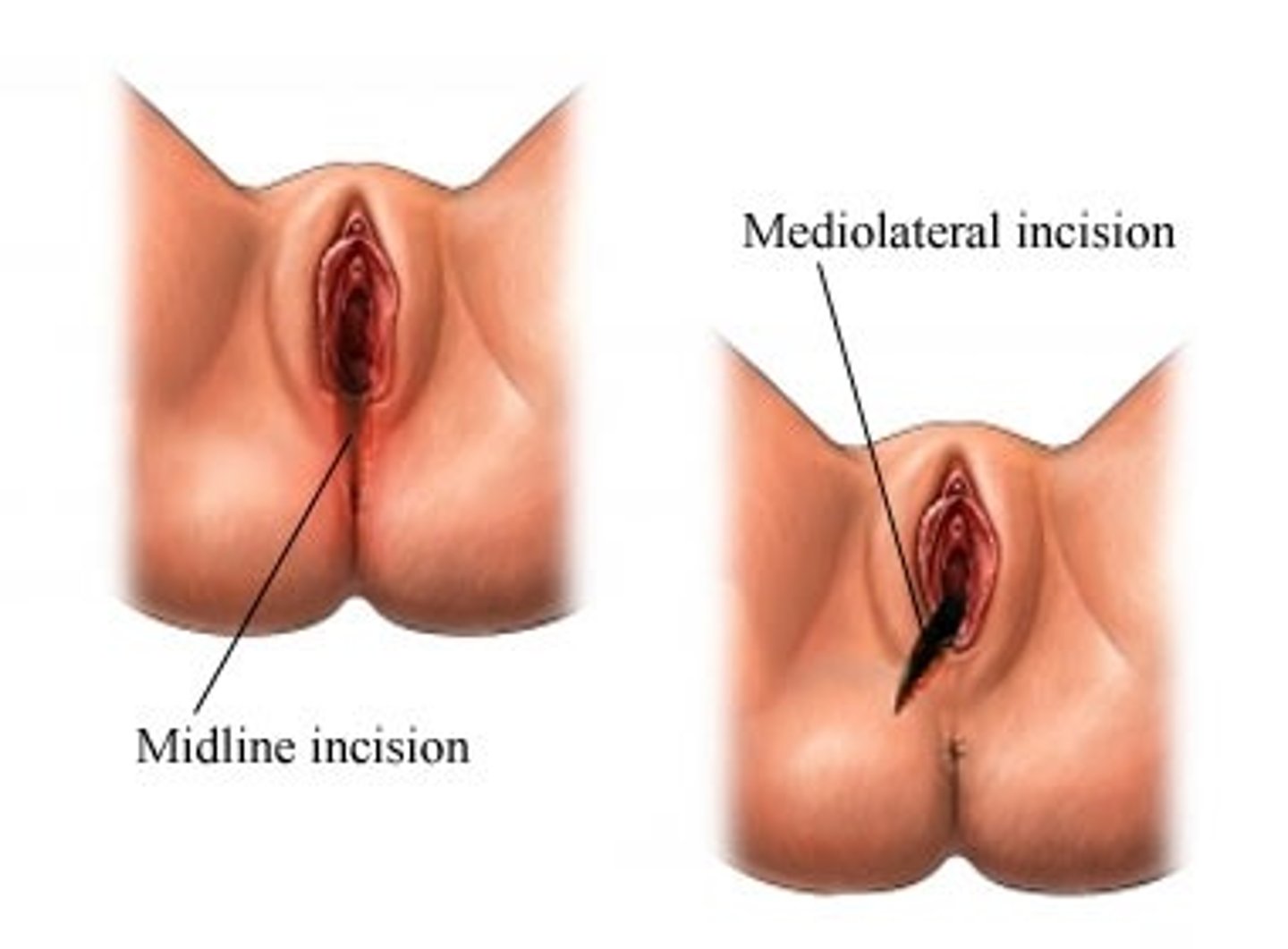
why is great care needed to support perineum after episiotomy during delivery (whether incision is midline or mediolateral)?
bc episiotomy is associated w/ risk of severe perineal laceration
once the head is delivered, you have _________ to deliver the rest of the body
5 mins
- due to risks w/ compression of umbilical cord
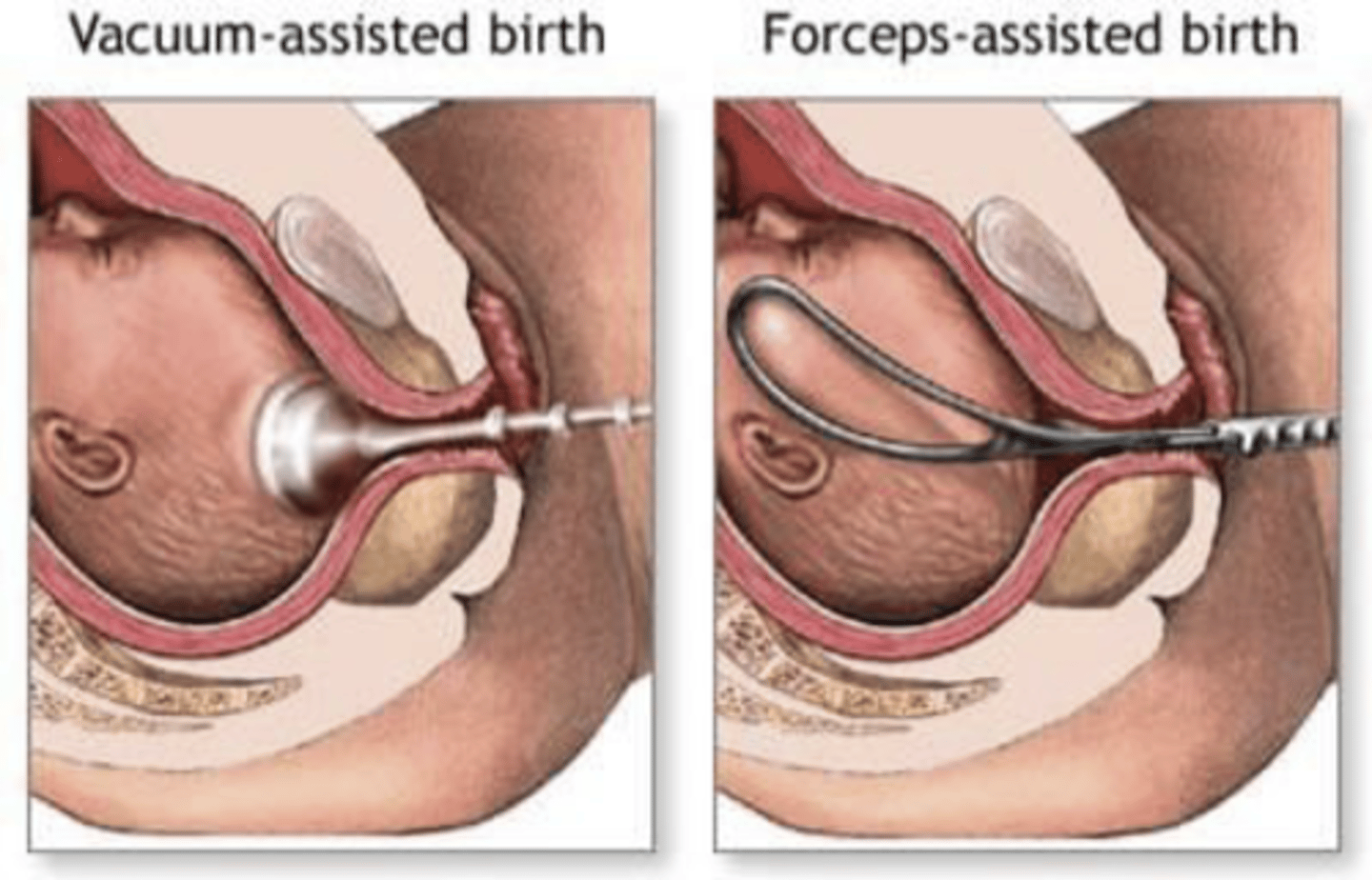
what can be considered if delivery becomes prolonged?
use of forceps or vacuum to assist birth
what is dystocia?
when labor increases in difficulty due to obstruction or constriction of the birth canal, or abnormal size, shape, or position of the fetus
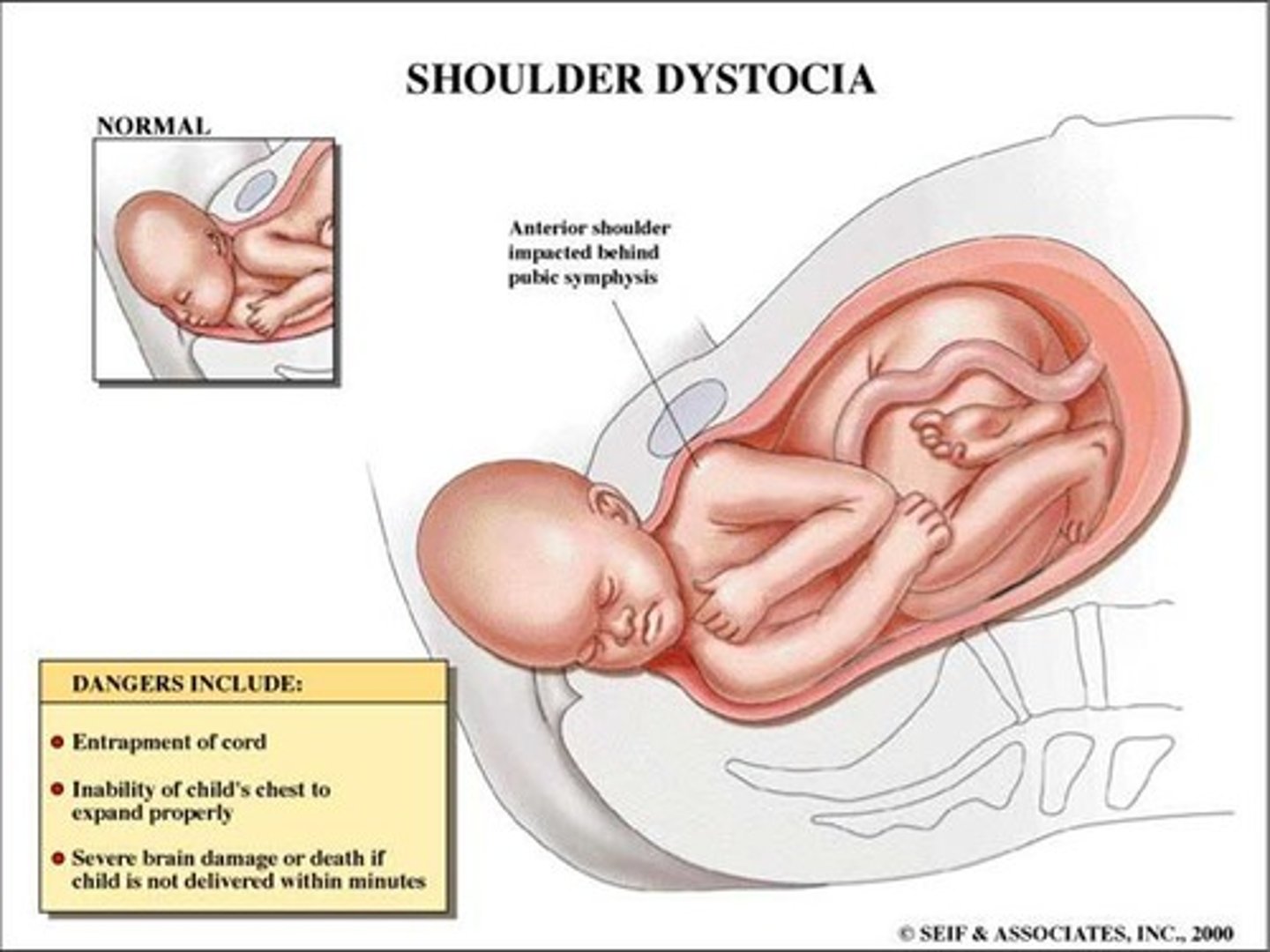
what is shoulder dystocia?
occurs after the head has delivered & it becomes difficult to deliver the shoulders
- after the head is delivered, it is imperative that the rest of the body delivers w/i 5 mins due to possible compression on the cord
- should be handled by an obstetrician
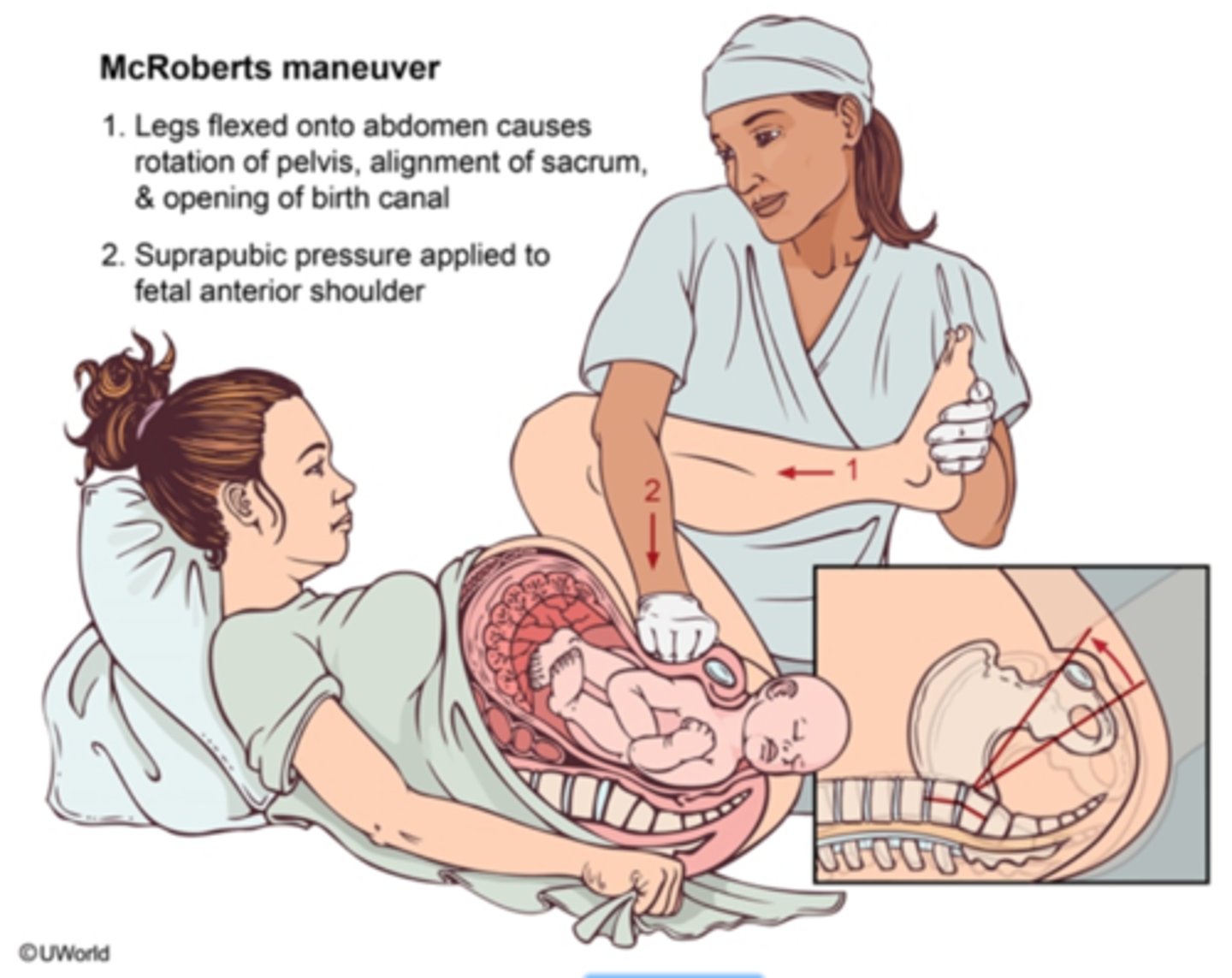
what is the McRoberts Maneuver?
used for delivery of an infant w/ shoulder dystocia
- knees of the mother are brought to her chest to increase the diameter of the pelvis
- then apply suprapubic pressure in an effort to dislodge the anterior shoulder from behind the pubic symphysis
possible complications of shoulder dystocia:
- humerus or clavicle fractures
- brachial plexus nerve injuries
- phrenic nerve palsy
- hypoxic brain injury
- death
what is the third stage of labor?
after delivery of the baby to the completed delivery of the placenta
placental delivery usually occurs w/i _____________ of delivery of the baby, w/ the operator applying gentle traction on the cord
5-30 mins
inspect the placenta to confirm that it is complete & that the cord has..
2 arteries & 1 vein
retained placenta or products of conception will require __________ for removal
curettage
- if any amount of placenta is left, the woman will continue to bleed
monitor blood loss.
it should not exceed _____
500 cc (mL)
during the third stage of labor, "active management" is recommended.
what does this include? why?
- uterine massage
- IV or IM oxytocin
- bimanual umbilical cord traction
*these steps increase uterine contractions, decrease blood loss & protect the uterus from prolapse or inversion
what is bimanual umbilical cord traction?
one hand very gently applies traction to the umbilical cord & the other applies suprapubic pressure
how are episiotomies & lacerations repaired?
absorbable sutures after placental delivery
how are suturing requirements determined?
by degree of tear
first-degree tear
involves only the mucosa & skin
- repaired w/ interrupted sutures

second-degree tear
extends subcutaneously into the perineal body, but does not involve the sphincter
- layered suturing is required
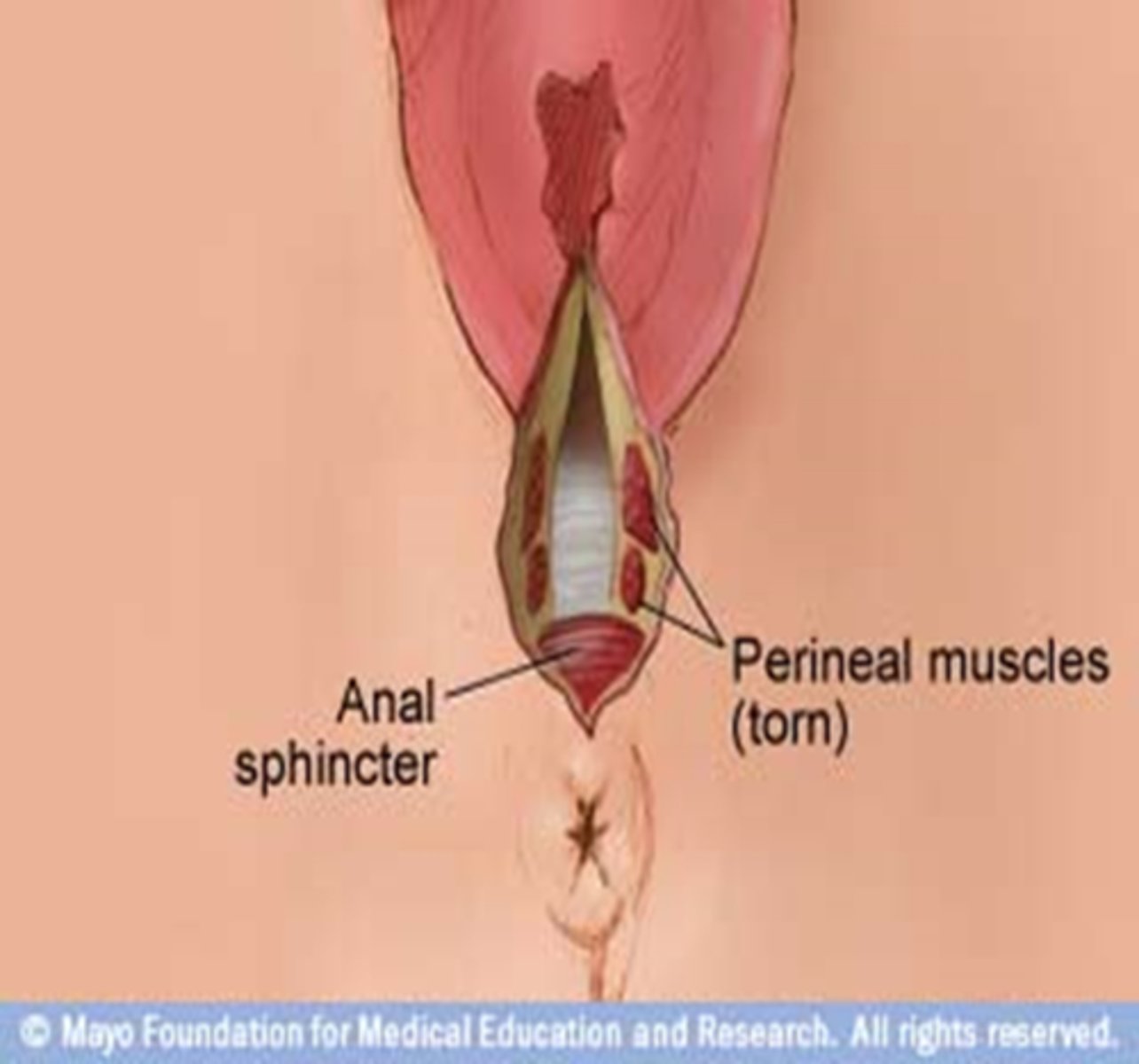
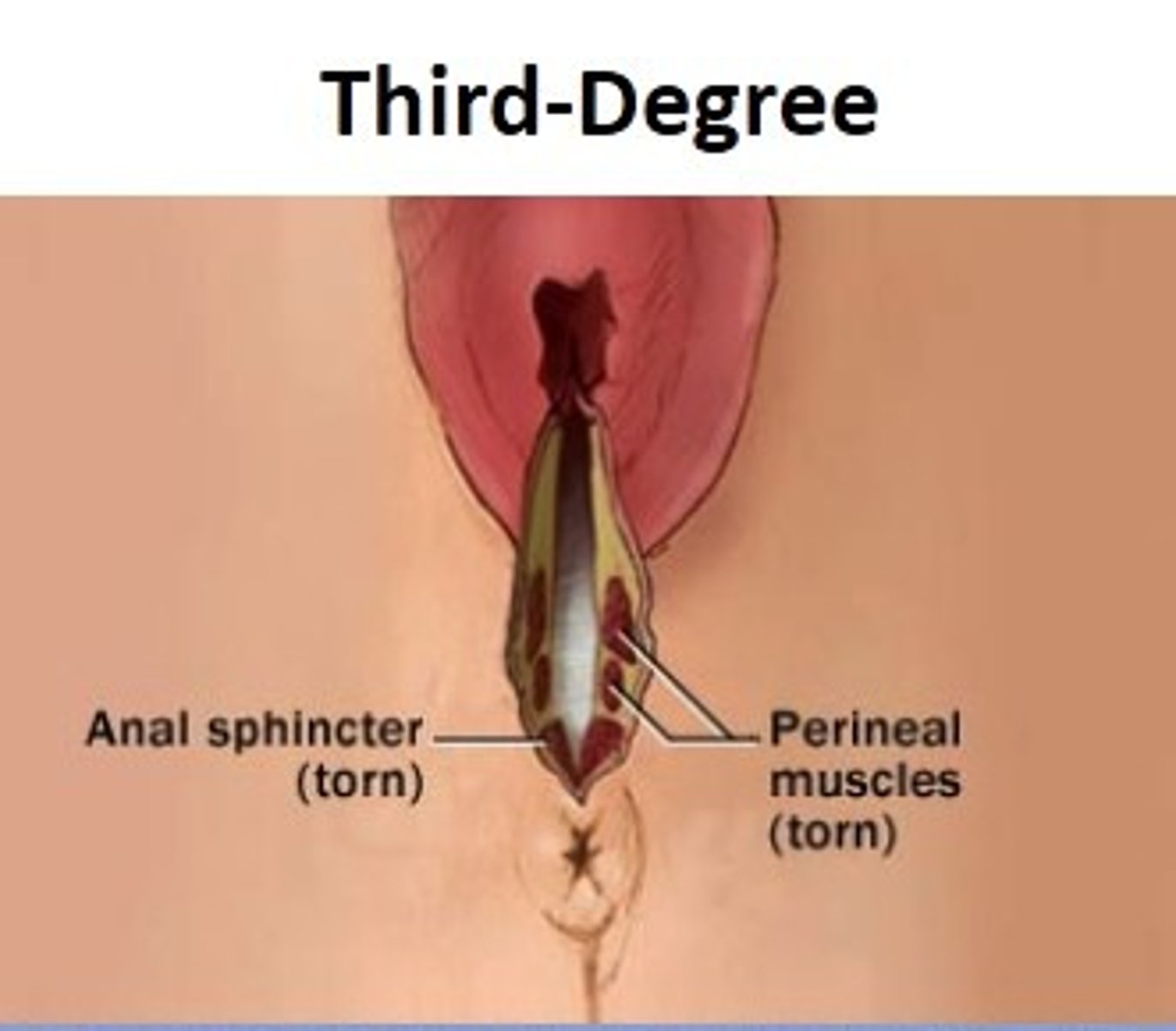
third-degree tear
extends into the muscle of the anal sphincter, but does not extend completely into the rectum
- requires repair of anal sphincter, followed by multiple layered suturing