BIO-115 Lab#2 -Mitosis + Interphase
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Interphase
- During this stage, replication of chromatin material (DNA) occurs.
- Comprises of three stages; G1, S, and G2
- G1 = cells start to grow larger, starts to duplicate organelles, and starts to get ready for the rest of the stages
- S = The cell copies all of the existing DNA in the nucleus so that there are two copies. The centrosomes starts to create the microtubules that attaches on to the kinetochore of the centromere later in mitosis and separates the chromosomes.
- G2 = The cell grows some more, finishes creating organelles and the proteins needed, and starts to prepare for mitosis.
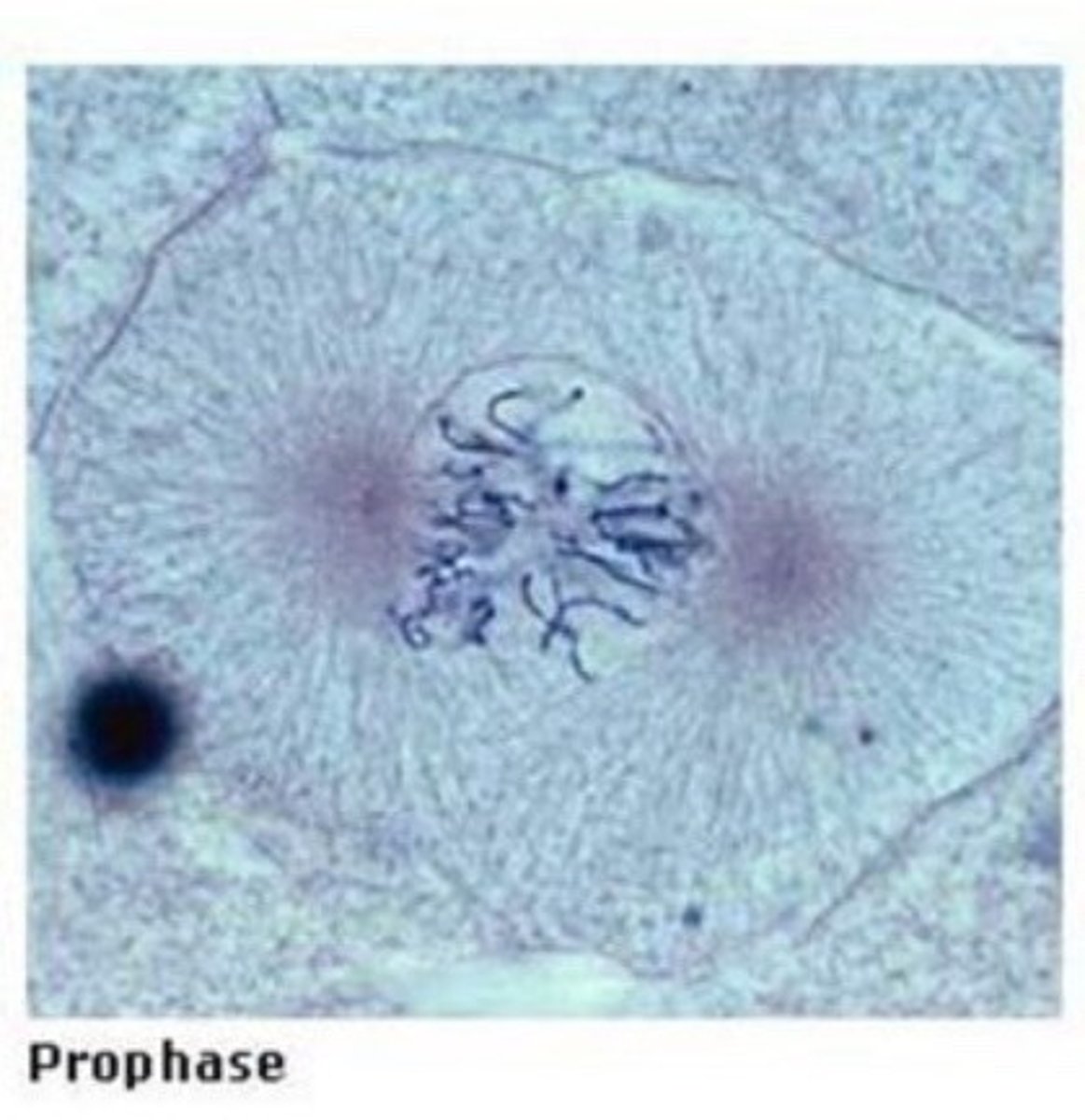
Prophase
- The nuclear envelope is in the process of disappearing as a spindle apparatus appears. DNA coils tightly to form visible chromosomes which appear rod shaped. The nucleolus disappears. In animal cells, a pair of centrioles (not visible on the slides) separate and with their newly formed asters (visible) move to each pole
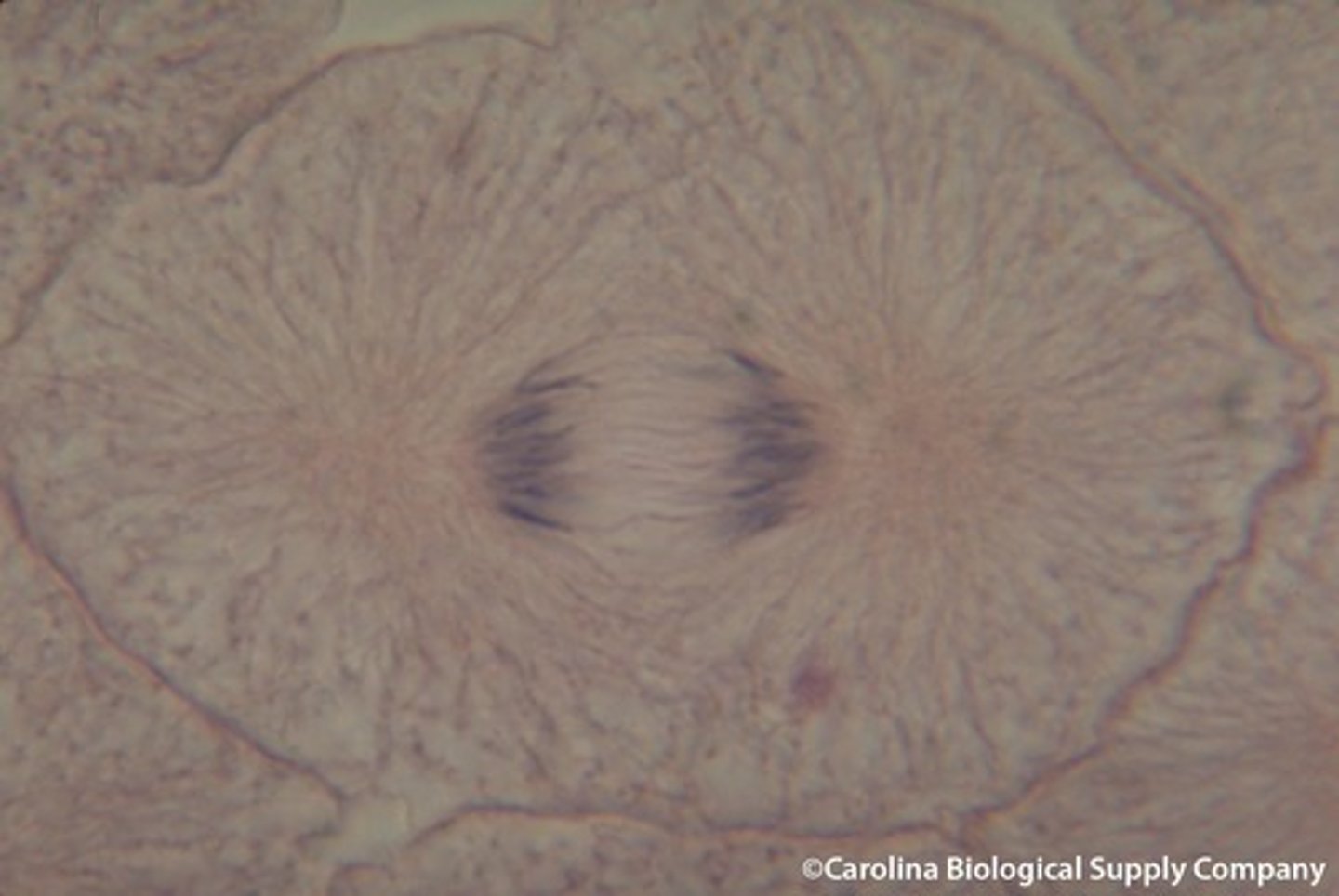
Metaphase
- A fully formed spindle is visible which stretches from pole to pole. Each chromosome is attached to a spindle fiber at the centromere (kinetochore), and all the chromosomes are lined up in the equator.
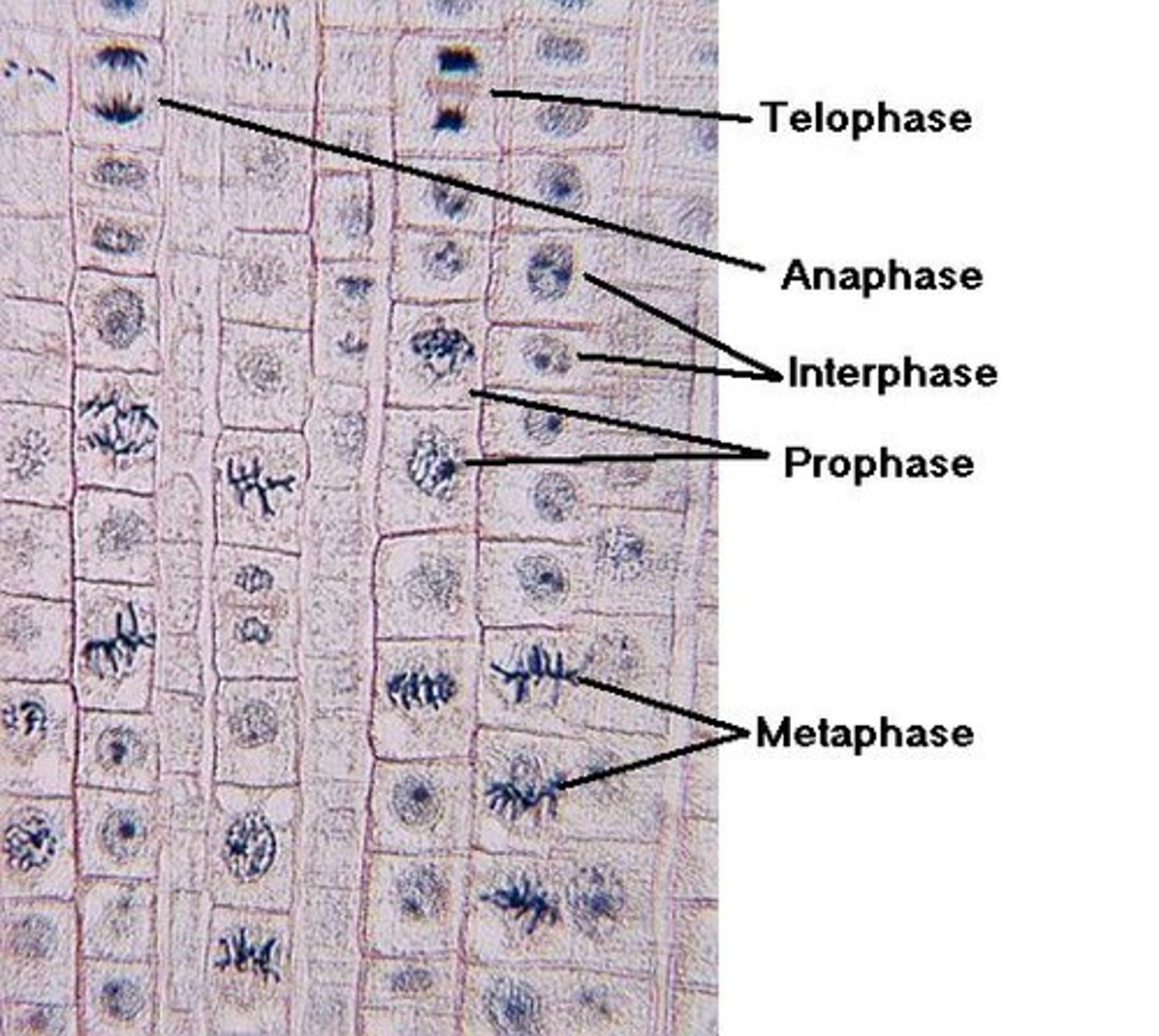
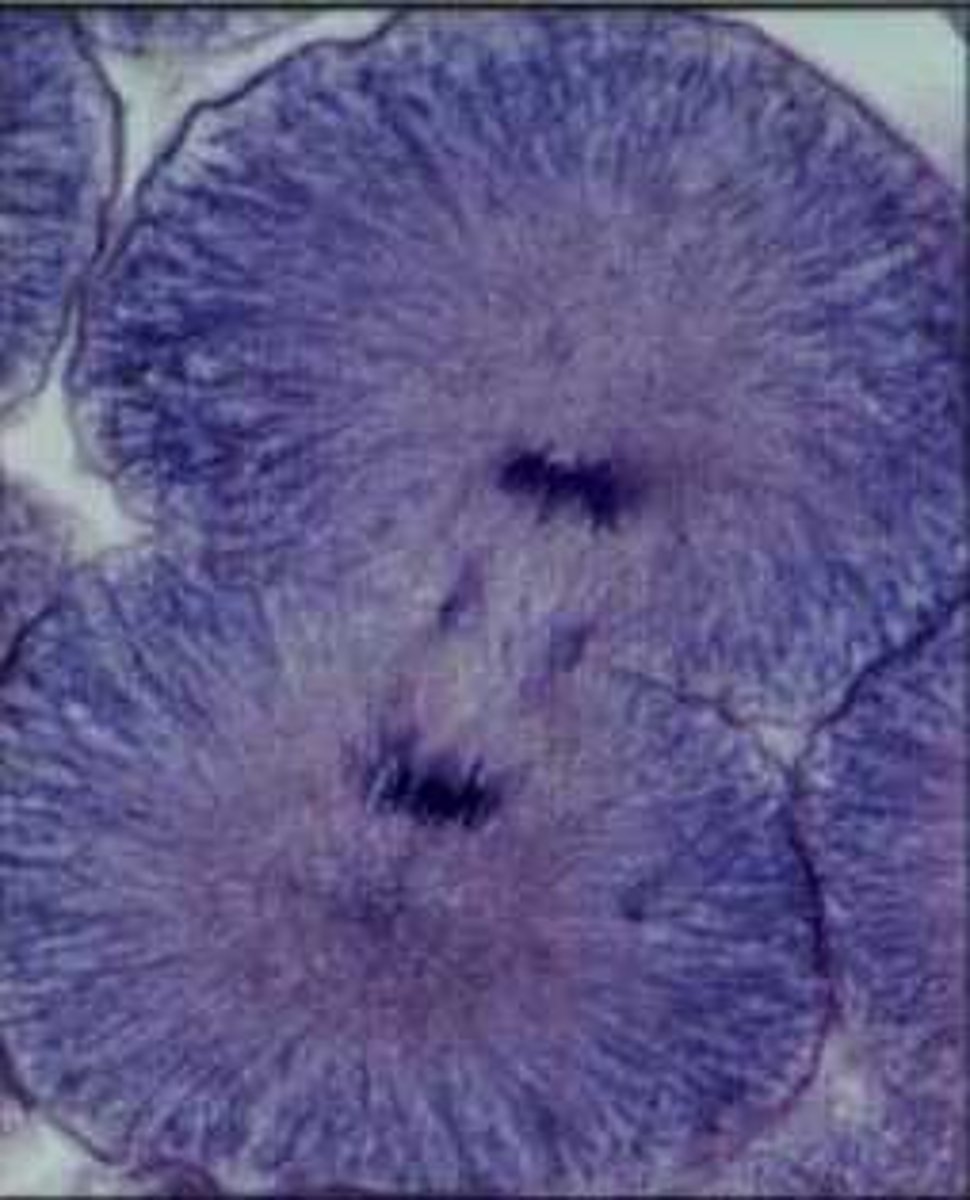
Onion Root Tip
Cells in mitotic phases:
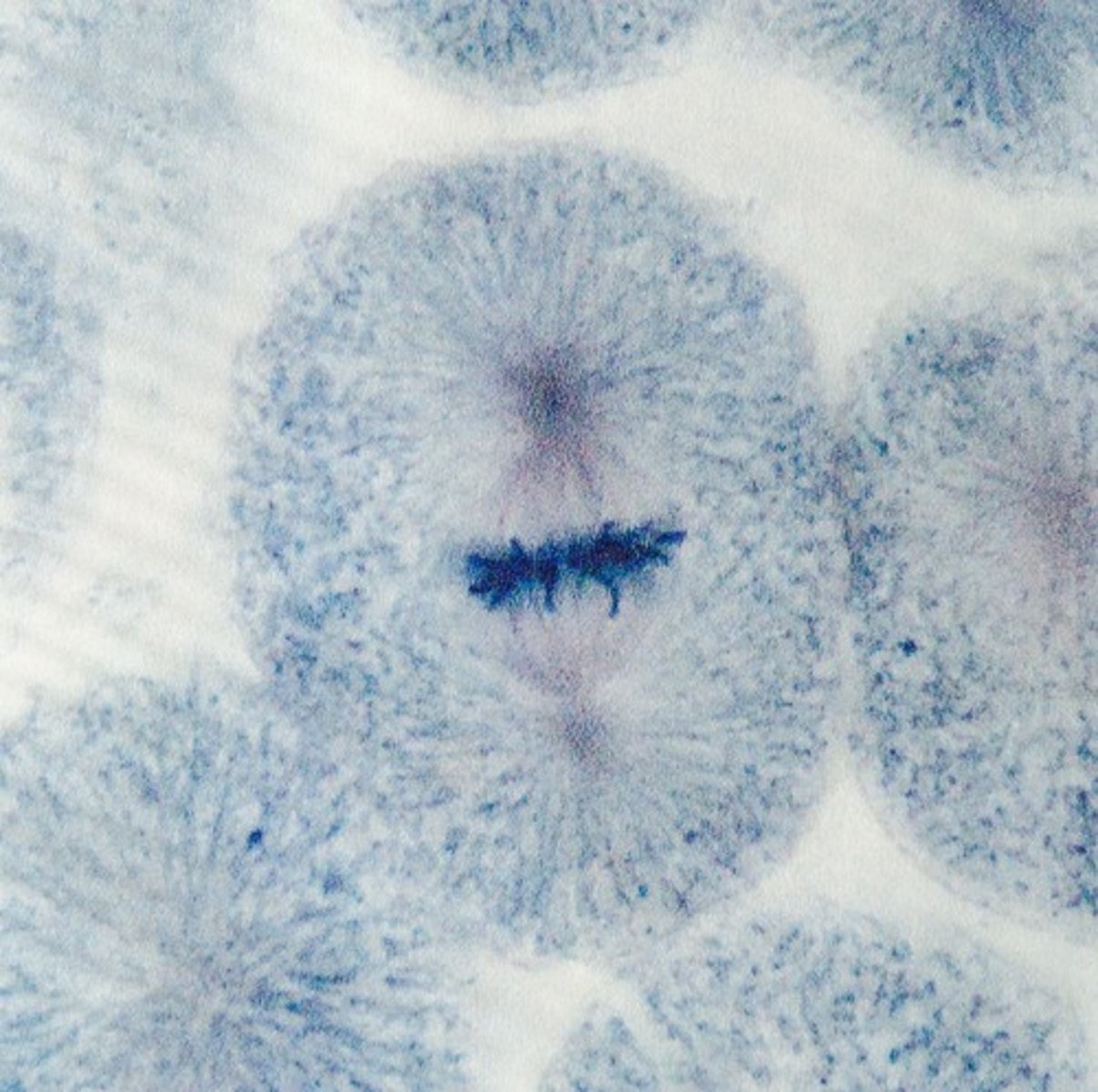
Anaphase
- The centromeres divide; the chromatids separate (now consisting of one DNA molecule each) and a set moves towards each pole
Telophase
- The chromosomes have clustered together near the spindle poles, where new nuclear envelope develop around them. The spindle slowly dissolves. In animal cells, cytokinesis occurs with a cleavage furrow dividing one cell into two cells
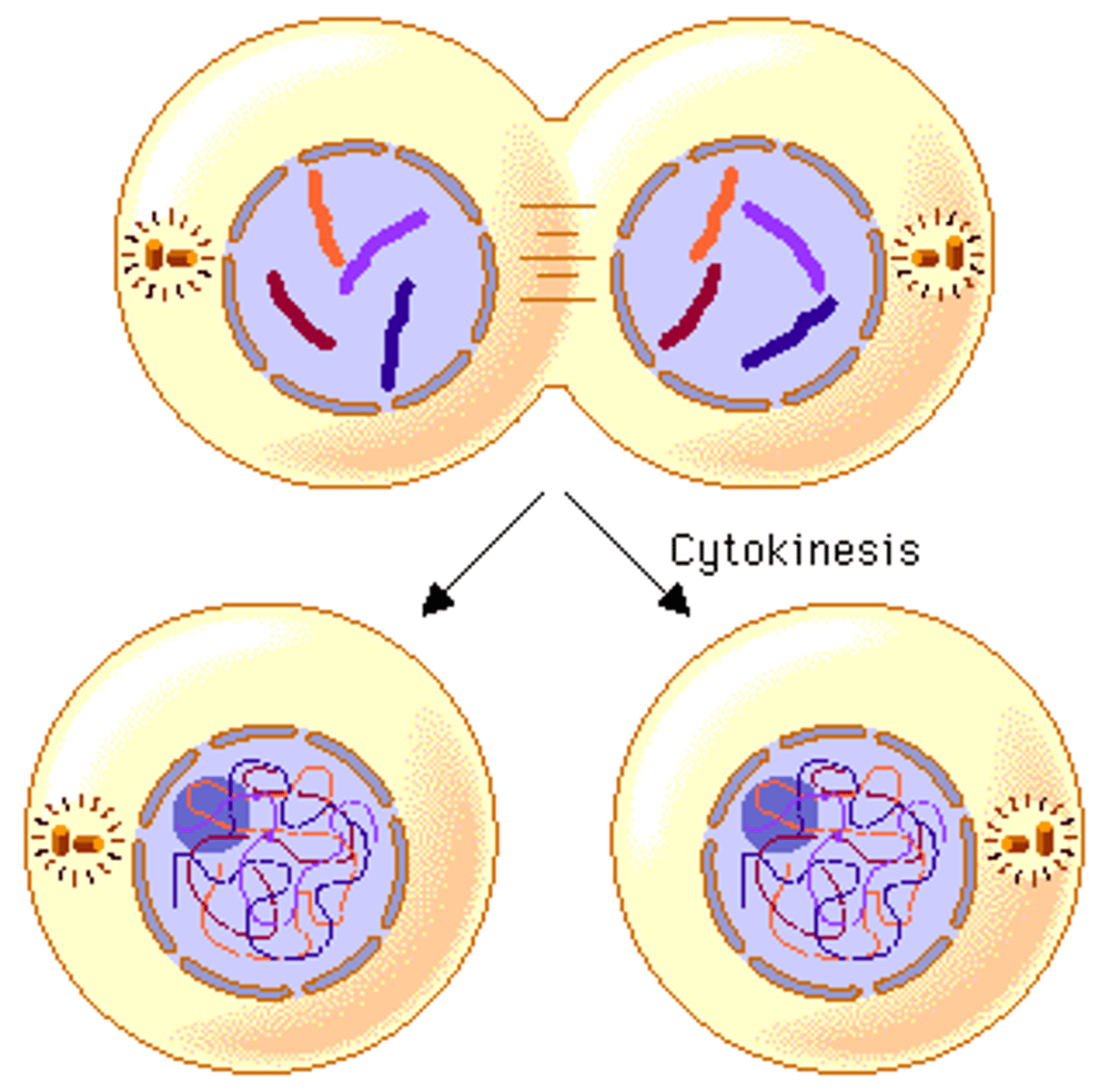
Cytokinesis
- Occurs in animal cells and forms a cleavage furrow which divides one cell into two cells.
What is the genetic significance of mitosis?
- Plays an important role in the growth of embryos - growth and development
- Helps replace skin cells.
- Creates two genetically identical cells.
Why are whitefish blastula and onion root tips used to study mitosis?
- Whitefish blastula are used because they are embryos and currently in the process of growing and duplicating cells (mitosis)
- Onion root tip cells are used because the roots are the part of the onion that has the most mitosis occuring. The roots anchor the plant into the ground so they must grow and growth = mitosis
Where is DNA located in the cell?
- The DNA is located inside the nucleus of each cell and it is wrapped around proteins called histones which allows it to easily regulate gene expression. In this form chromatin is more easily accessible. During mitosis, the chromatin condenses into chromosomes. There is also some DNA found in mitochondria.
Why is DNA considered to be such an important molecule?
- DNA contains the instructions to create all types of cells and proteins throughout the body which are useful for our growth, development, and health.
Why must the quantity of DNA in cells remain the same from one generation to the next?
- If we had different amounts of DNA from one generation to the next it would cause a disruption in the normal development and cellular processes. By keeping the quantity of the DNA the same, we can ensure that there is a correct amount of every protein and cell to function properly and maintain species stability.