Understanding Series and Parallel Circuits
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Current
Flow of electrons in a circuit.
What kills
Voltage
Force that drives current through a circuit. quantity
not deadly
Deadly Current Threshold
4mA can induce ventricular fibrillation. ( irregular heart beat)
Lethal Current Level
80-100 mA can cause death.
What is a fuse?
A fuse is a thin wire enclosed in a casing that plugs into a circuit.
What happens to a fuse when a circuit is closed?
The fuse experiences the same current as any other point along the circuit.
What is the purpose of a fuse?
To disintegrate when it heats up above a certain level to protect the circuit.
What happens if the current climbs too high in a fuse?
The fuse burns up the wire, opening the circuit.
How does a fuse protect building wiring?
By opening the circuit before excess current can damage it.
How does an electromagnet in a circuit breaker prevent short circuits?
As current increases, the magnetism around the circuit increases. If the current becomes too high, the magnet pulls itself out of the circuit, opening it before damage occurs.
What is one method used by some circuit breakers to prevent short circuits?
Some circuit breakers use a small explosive charge that ignites at a lower level than a fire would start.
What happens when the explosive charge in a circuit breaker ignites?
It pushes the breaker away from the other end, opening the circuit.
What is an electrical circuit?
A pathway that permits electrons to move in a complete circle from their source.
What material is commonly used for electrical circuits?
Copper wire
What do electrical circuits allow electrons to do?
Move in a complete circle from their source, through resisting electrical devices and back to the source.
What is a series circuit?
A circuit in which all parts are connected end to end to provide a single path of current.
How does the total potential difference of a series circuit compare to parallel circuits when all other factors are the same?
Series circuits supply greater total potential difference than parallel circuits.
What happens to the total voltage in a series circuit as more resistance is added?
The total voltage increases.
What happens to total resistance in a parallel circuit as more resistors are added?
Total resistance drops.
What happens to total amperage in a parallel circuit as more resistors are added?
Total amperage increases.
What happens to total voltage in a parallel circuit when more resistors are added?
Total voltage remains the same.
What is a characteristic of parallel circuits regarding total resistance?
Parallel circuits offer less total resistance to electrical current when all other factors are the same.
What is a disadvantage of parallel circuits?
Increased amperage may cause a short circuit, which can cause a fire.
Short Circuit
Excessive current flow causing potential hazards.
Siemens (S)
A reciprocal ohm, as in 1/R. ac and dc
Total Voltage in Series
Sum of voltages across each component.
Vt = V1 + V2 + V3
Total Voltage in Parallel
Voltage remains constant across all components.
Vt = V1 = V2 = V3
Power in Series Circuit
Calculated as P=IV, where I is current.
Total Resistance in Parallel
1/Rt = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3
Total Current in Series
It = I1 = I2 = I3
Total Current in Parallel
It = I1 + I2 + I3
Total Resistance in Series
Rt = R1 + R2 + R3
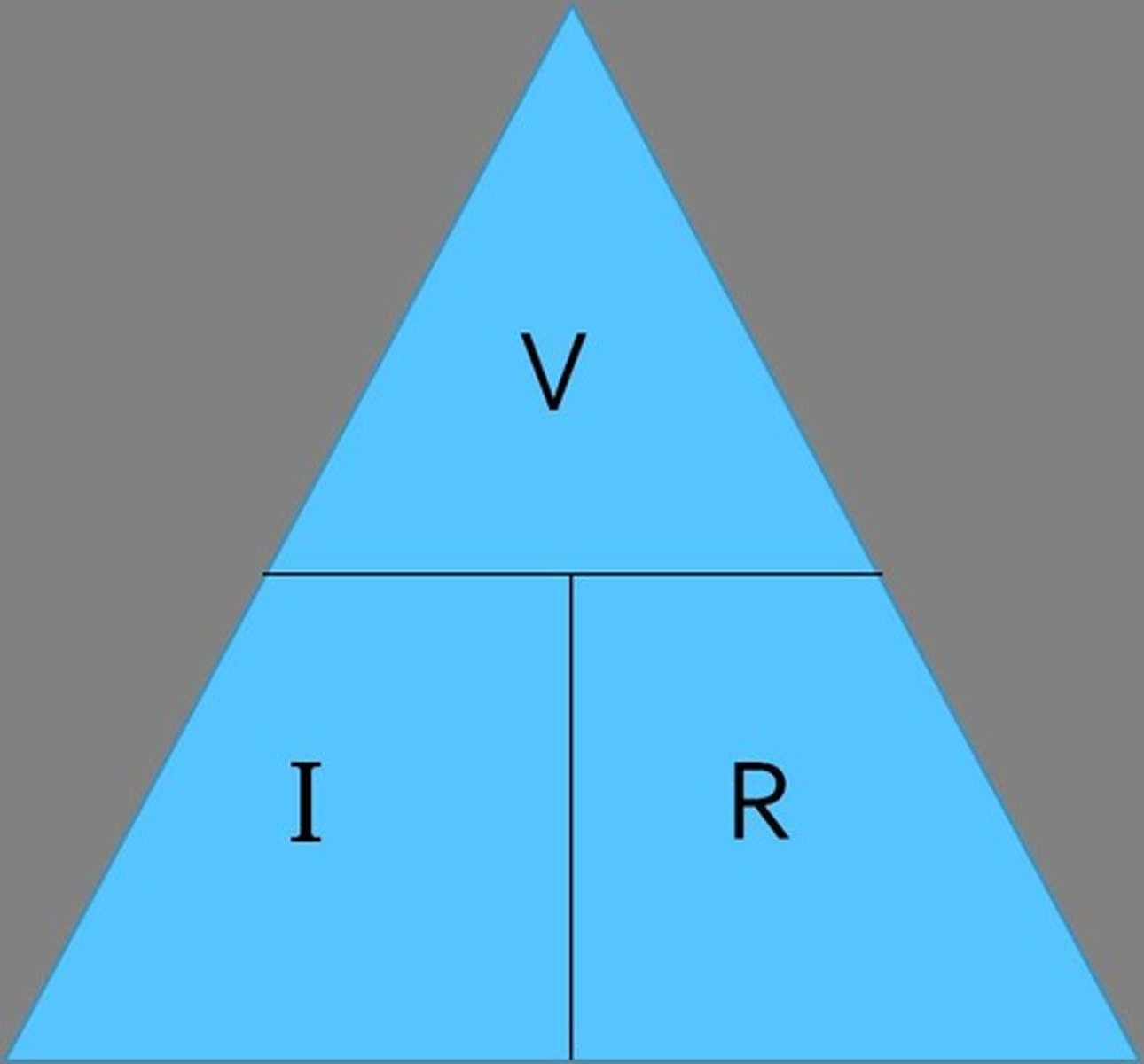
Ohm's Law
V=IR; relationship between voltage, current, resistance.
Amperage Increase in Parallel
Adding resistors increases total current.
Power Calculation
Power is the product of voltage and current.
Conductance
Reciprocal of resistance, measured in siemens.
P
E
P
SI
VOLTS- PLUS
(I)CURRENTAMPS-EQUALS
RESISTANCE OHMS- PLUS
SI- SERIES
E
P
I
PEN
VOLTS- EQUALS
I CURRENTS AMPS- PLUS
RESISTANCE- INVERSE
PARALLEL