6- cornea 2
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Arcus Senilis
cholesterol deposits being at 6 and 12 o'clock and eventually for a ring
-occurs in corneal stroma
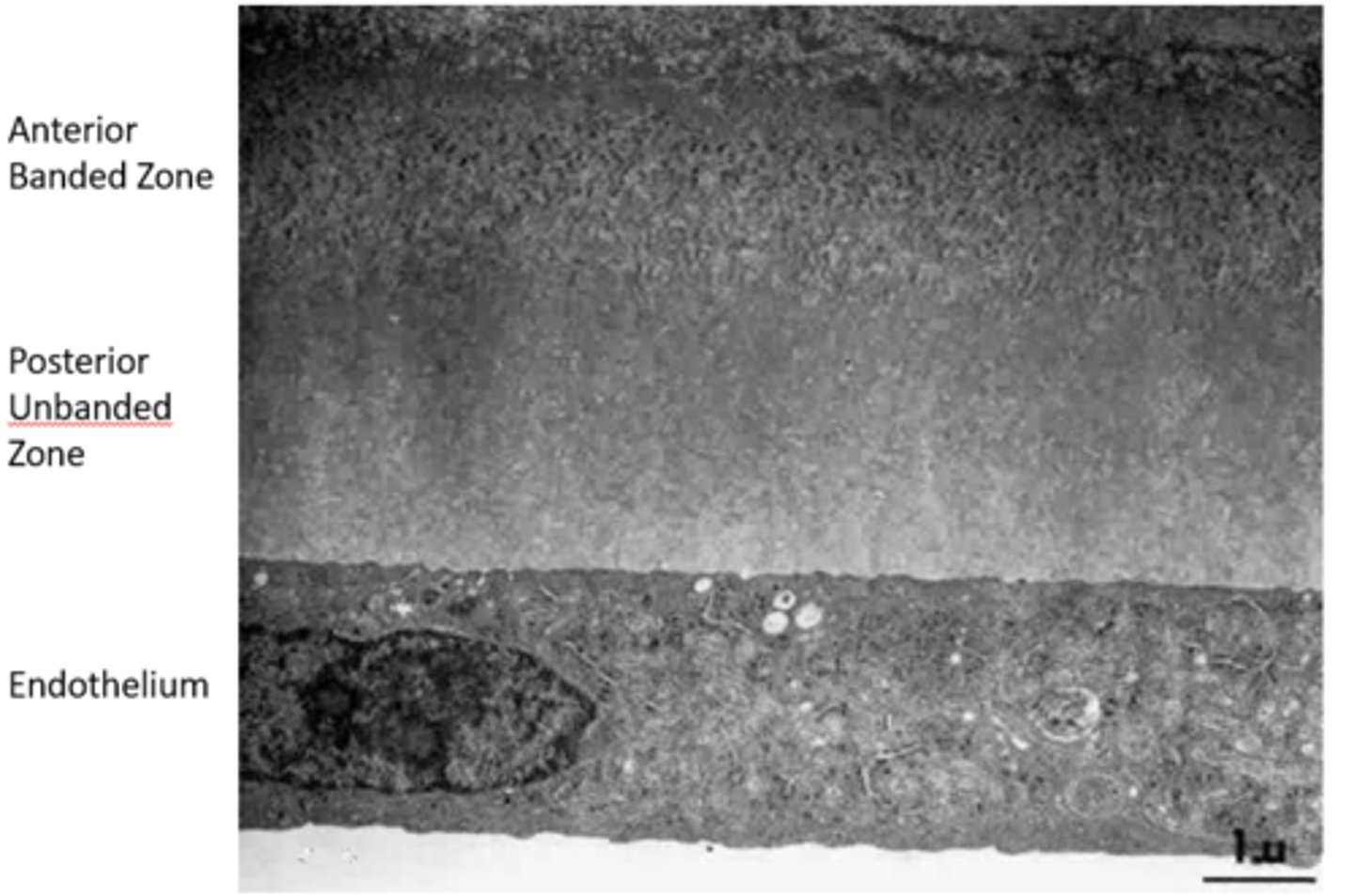
Descemet's Membrane
-Basement membrane of Endothelium
-Thickens throughout life from 3 um to 15 um
-Regenerates if damaged
-Anterior banded zone laid down before birth
-Posterior unbanded zone laid down after birth
-Terminates abruptly at Schwalbe's line

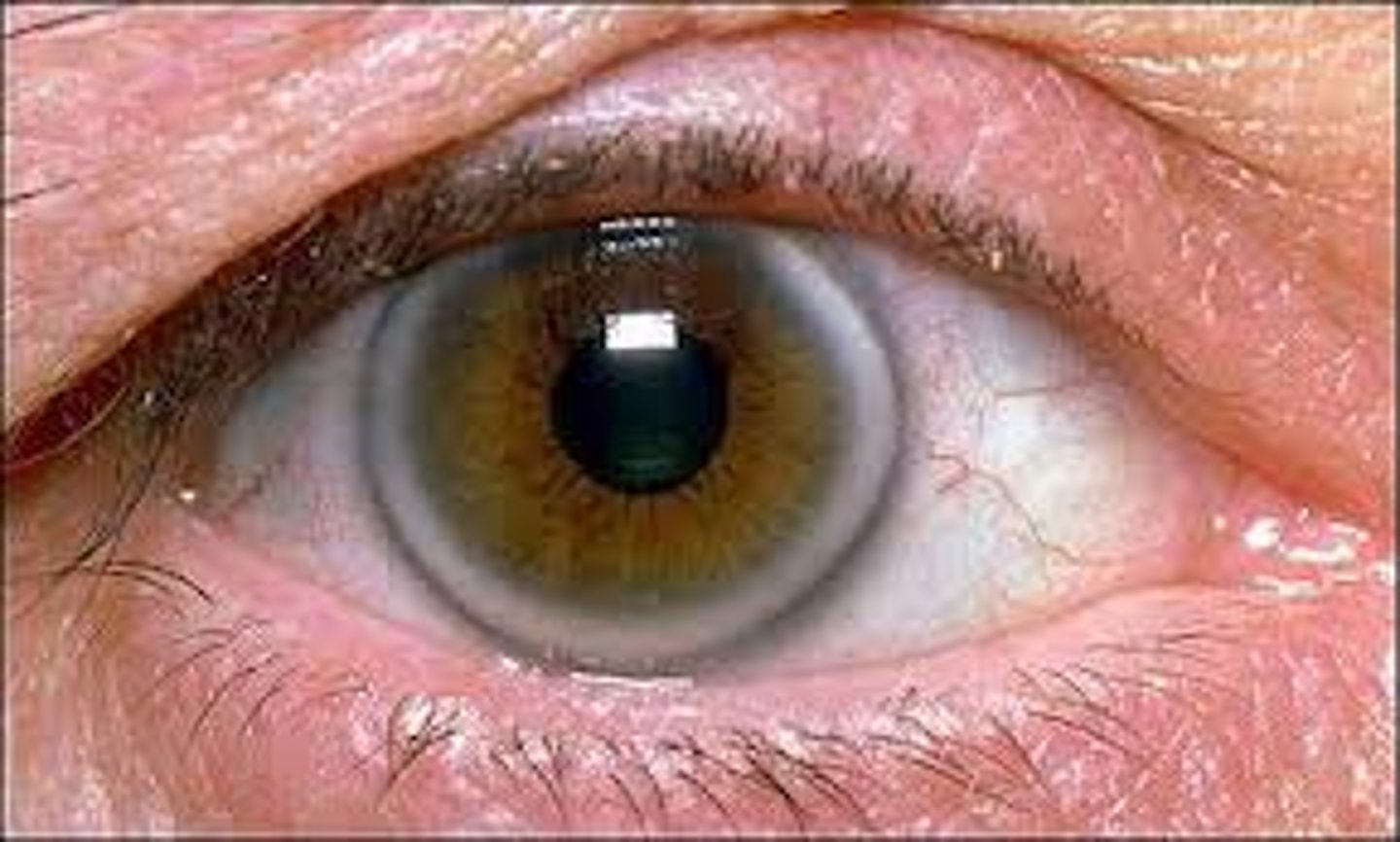
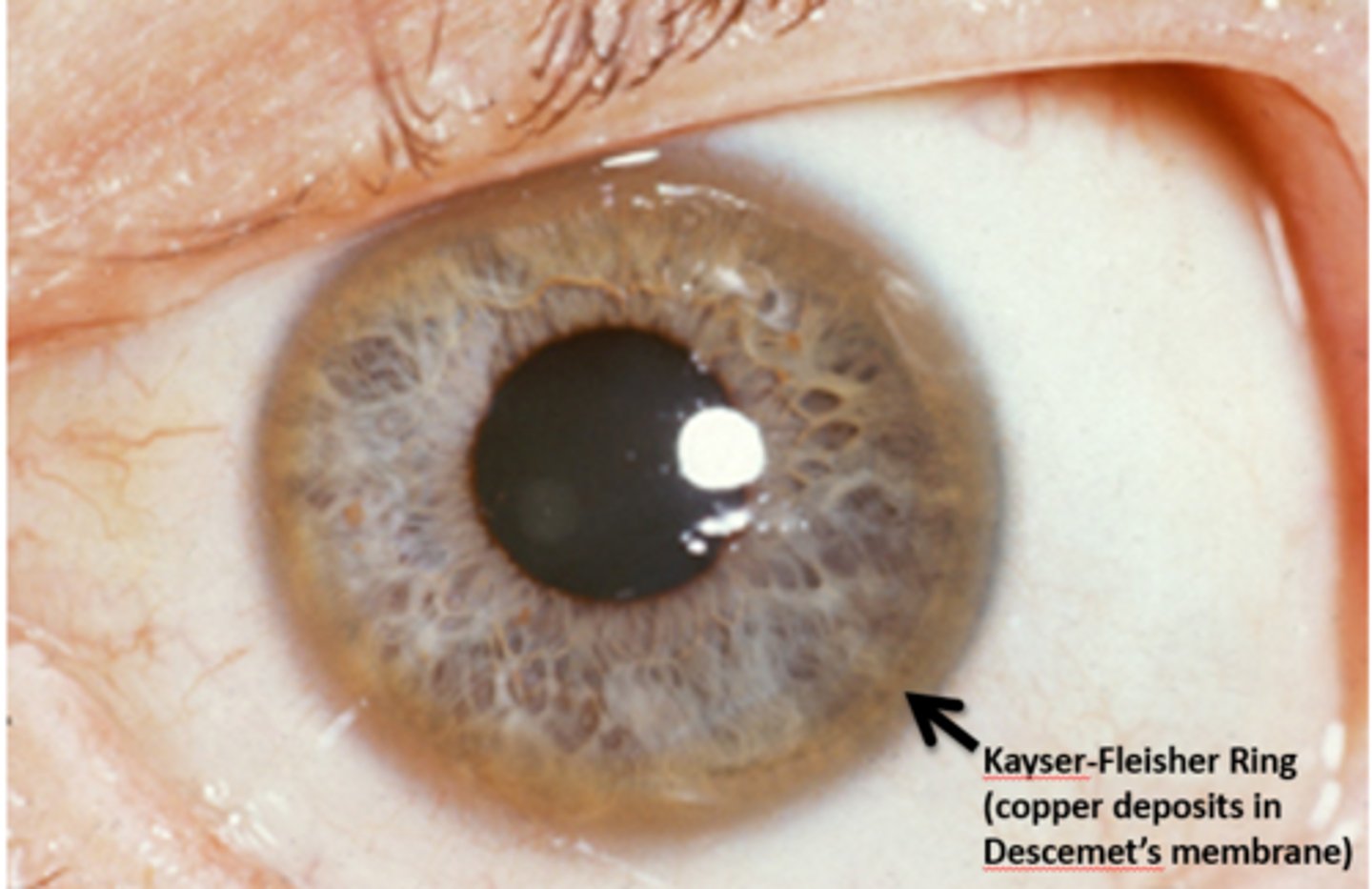
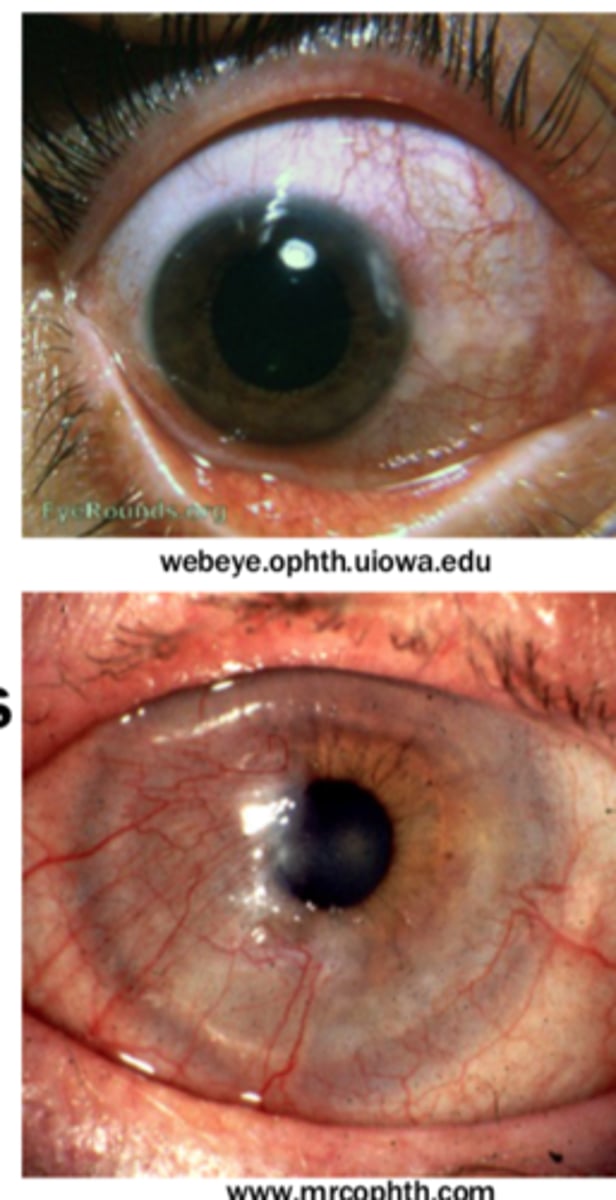
Wilson's disease
Kayser-Fleisher ring (copper deposits in Descemet's Membrane)
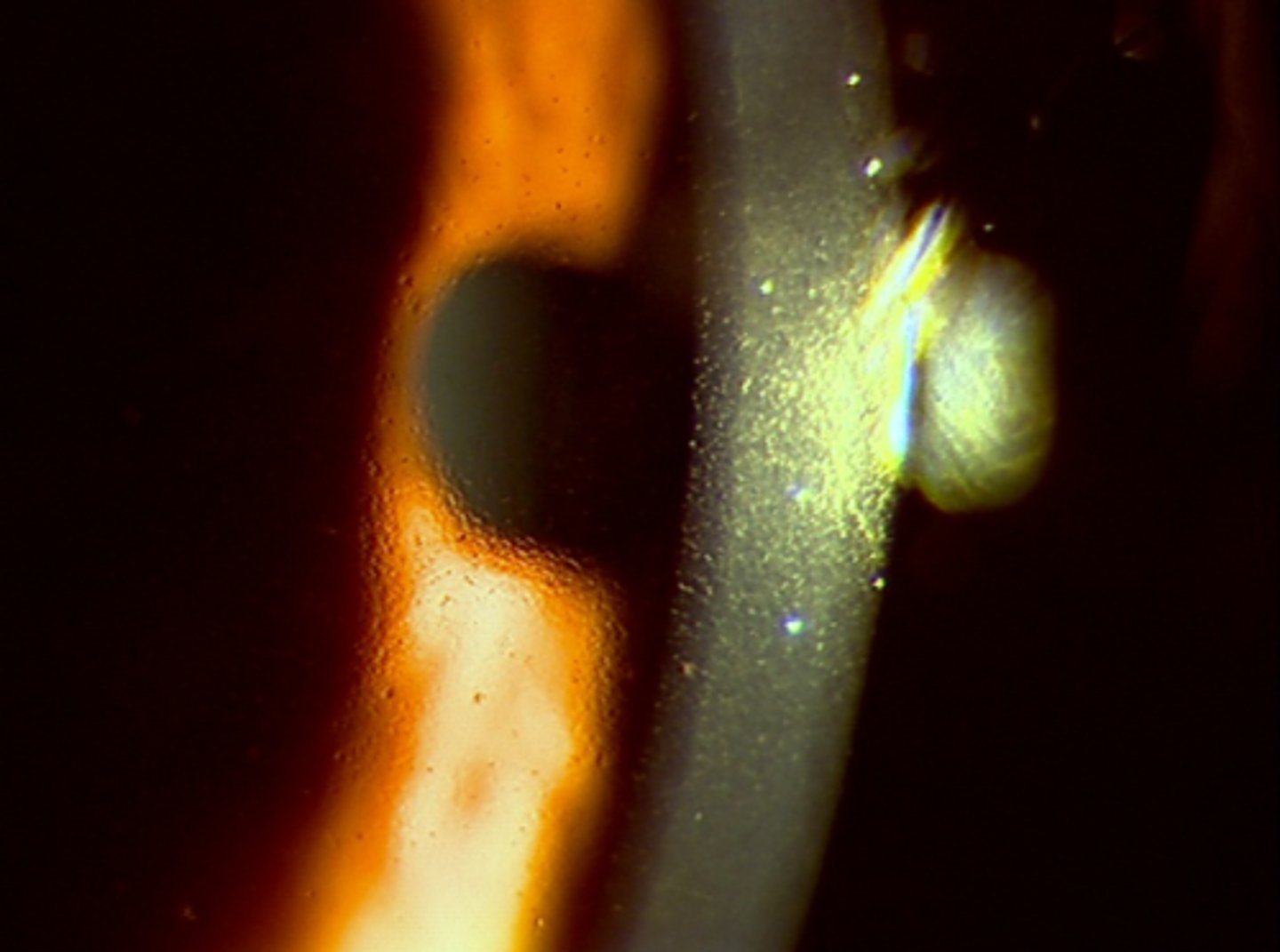
Corneal Guttae
occur in central cornea and indicate abnormal function of endothelium. Indicate endothelial dystrophy
-Hassall-Henle warts can resemble corneal guttae but occur in peripheral cornea and is a normal occurrence with age
What is the thickness of the corneal endothelium?
About 4-6 um thick
How many cells are typically in the corneal endothelium?
About 400,000 to 500,000 cells
What shape do the cells of the corneal endothelium appear?
Flat and hexagonal in shape
Which part of the corneal endothelium faces the anterior chamber?
Apex
What does the basal portion of the corneal endothelial cell secrete?
Descemet's membrane
What type of junctions do corneal endothelial cells form with adjacent cells?
Gap junctions
What is the function of the corneal endothelium in relation to aqueous humor?
Pumps aqueous humor out of cornea to maintain hydration
What is the typical cell density in the corneal endothelium?
2500 to 3000 cells/mm2
What is the minimum cell density required for normal corneal endothelial function?
400-700 cells/mm2
What changes can occur due to loss of corneal endothelial cells?
Polymegathism (changes in size) and pleiomorphism (changes in shape)
What happens if there is no pump action in the corneal endothelium?
Results in stromal edema
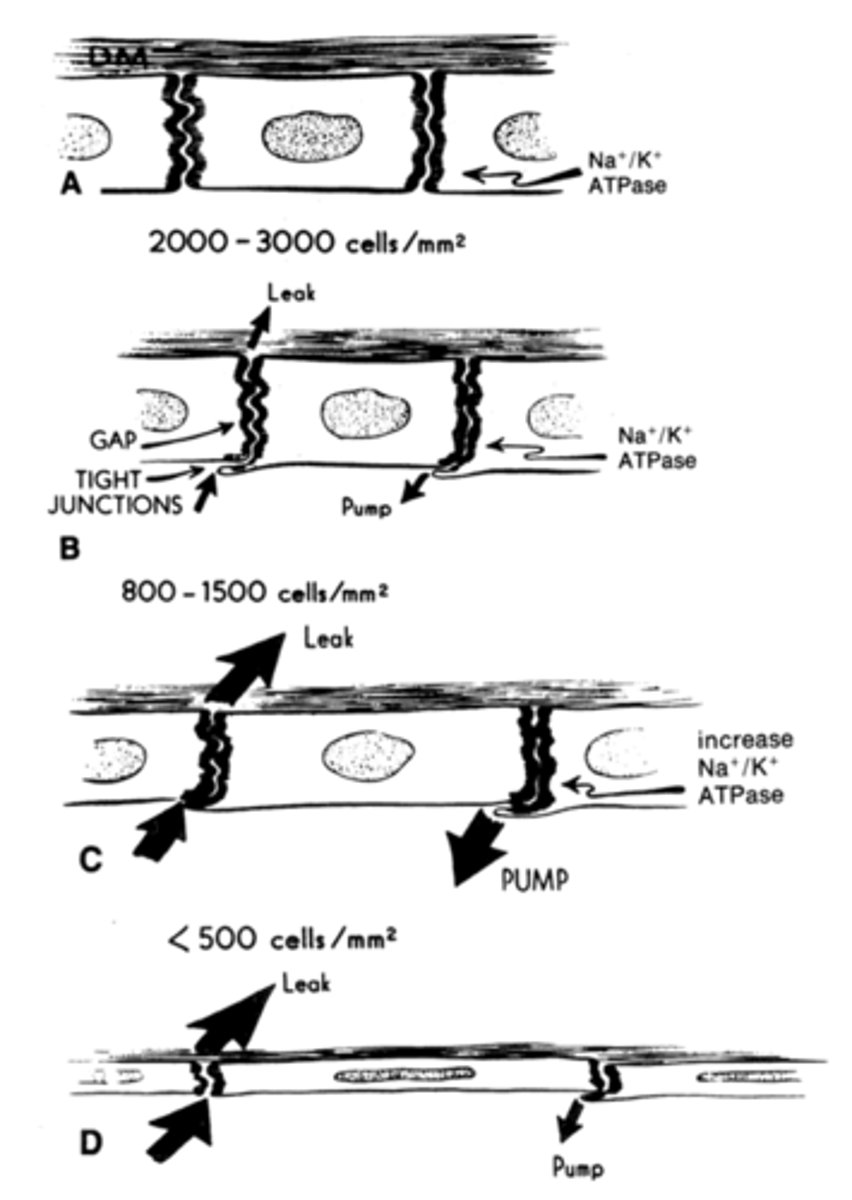
Breakdown of Pump Leak system
As corneal endothelial cells become stressed they dropout. Remaining cells expand in size and shape to compensate. Less pump available to counterbalance leak of aqueous humor into corneal stroma
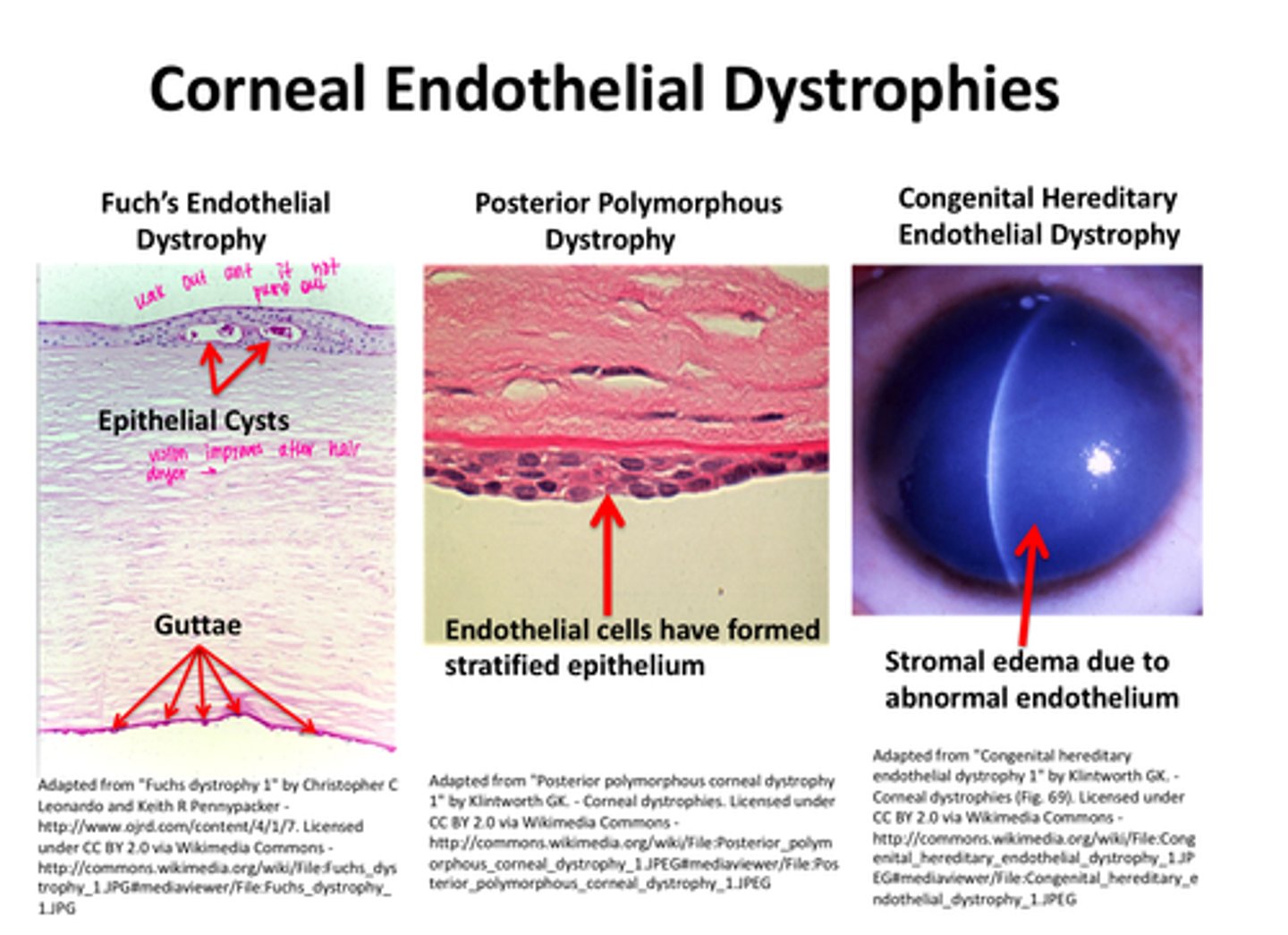
Corneal Endothelial Dystrophies
-Fuch's Endothelial dystrophy - epithelial cysts and guttae
-Posterior Polymorphous Dystrophy - endothelial cells have formed stratified epithelium
-Congenital Hereditary Endothelial Dystrophy - stromal edema due to abnormal endothelium
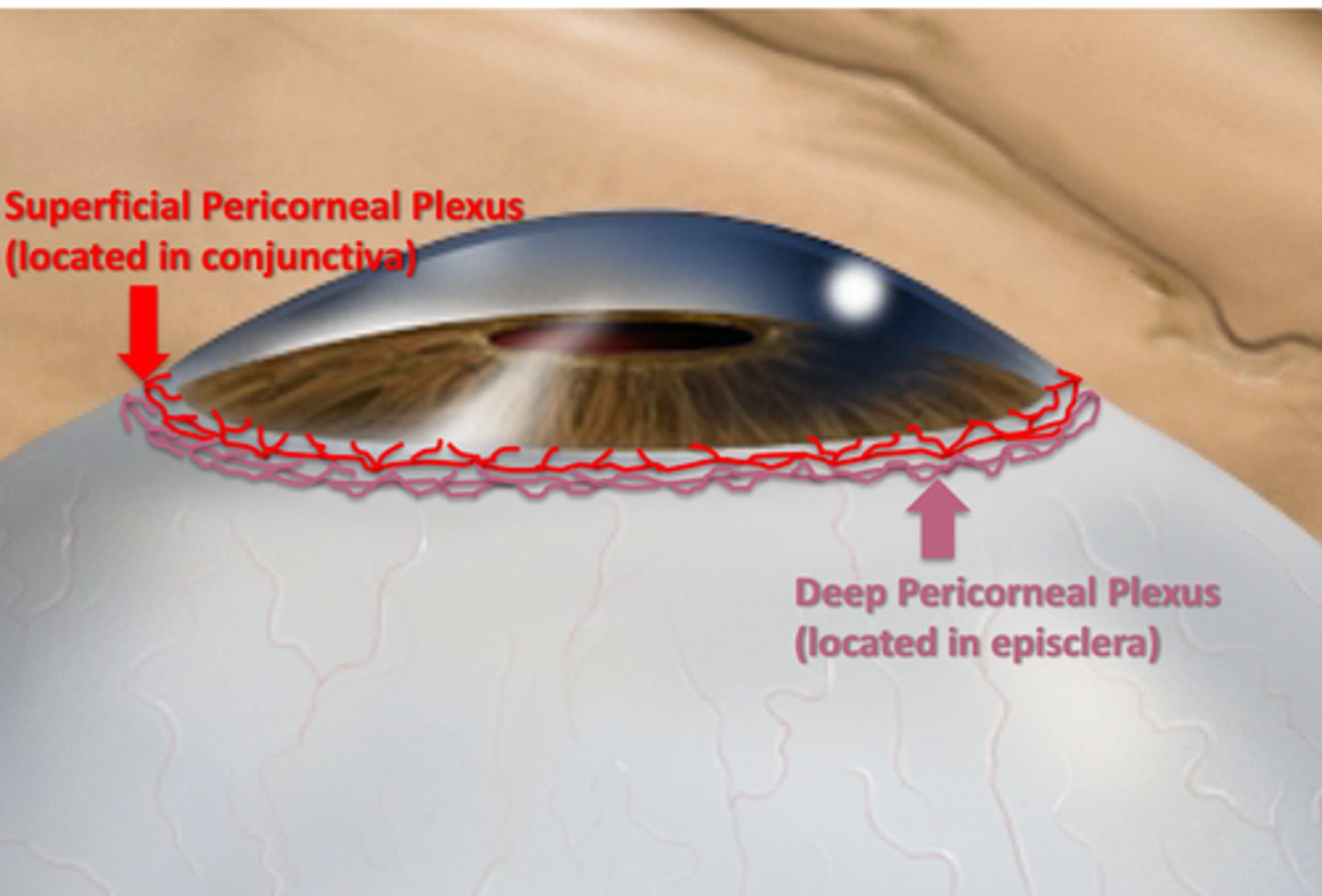
Is the cornea vascular or avascular?
Avascular
Where do corneal nutrients primarily come from?
Tear film and aqueous humor
What is the source of additional nutrients for the cornea?
Vasculature at the peripheral cornea
What is the name of the plexus associated with the conjunctiva that supplies the cornea?
Superficial Pericorneal Plexus
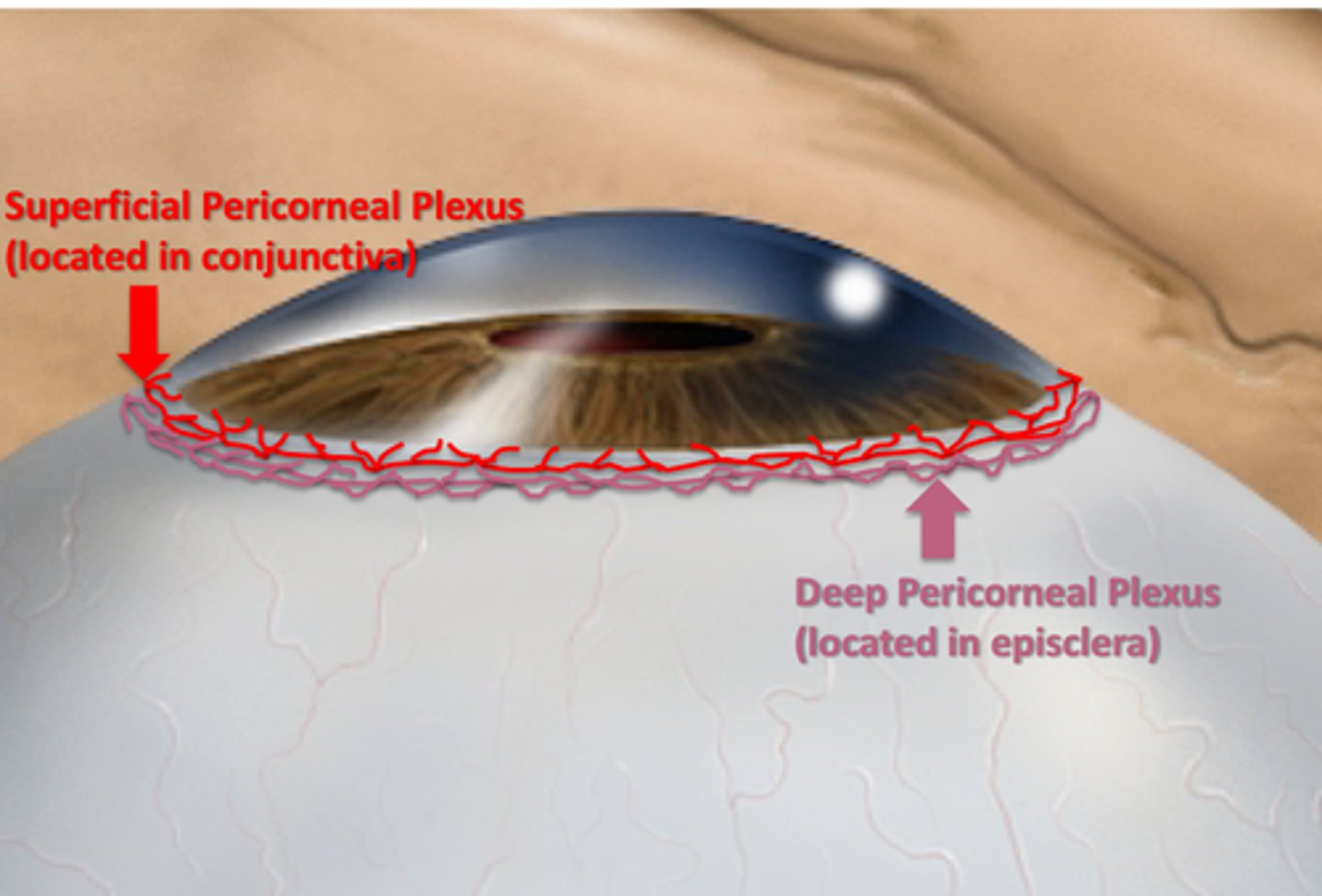
What is the name of the plexus associated with the episclera that supplies the cornea?
Deep Pericorneal Plexus
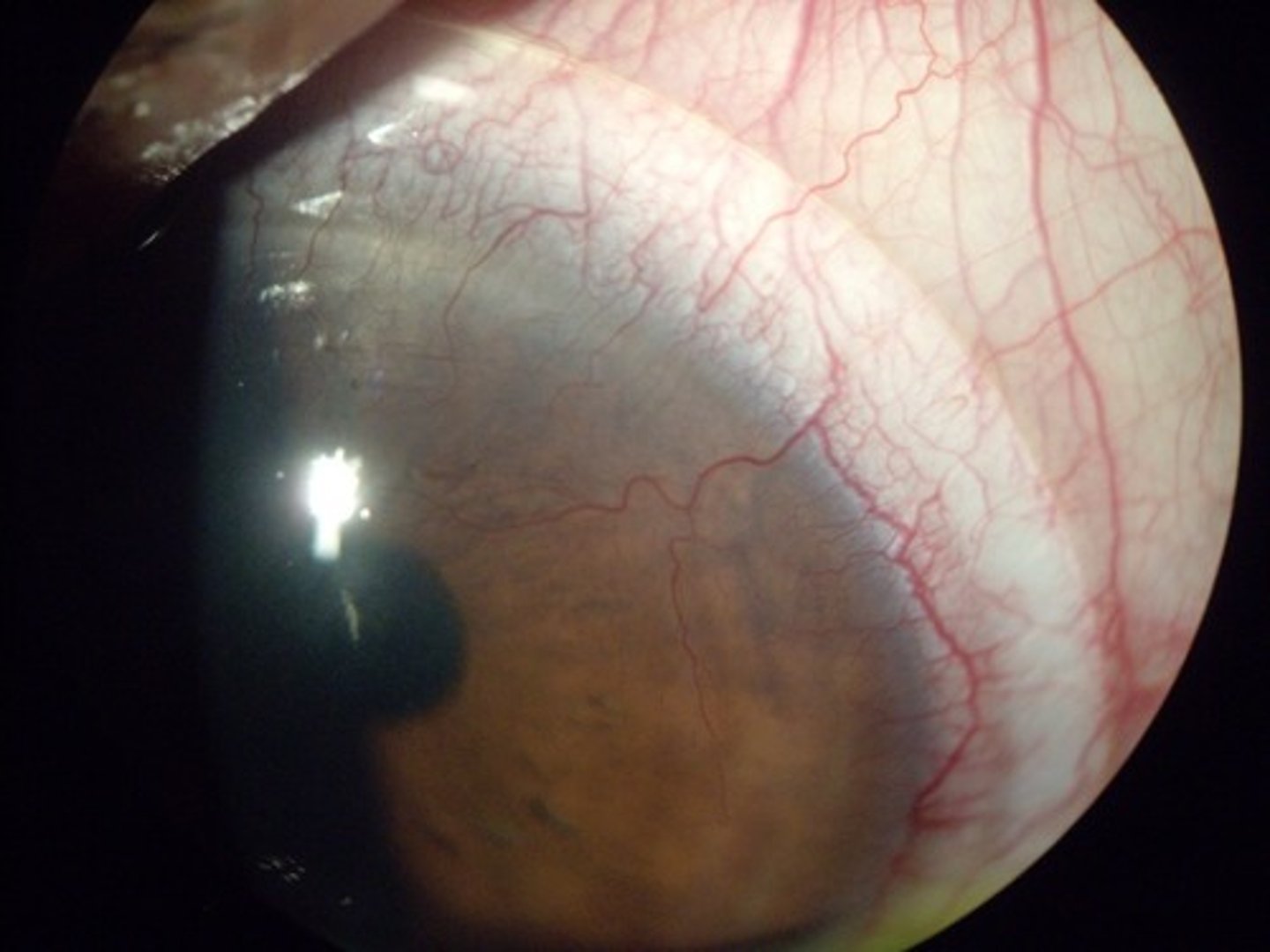
Corneal neovascularization
excessive growth of blood vessels from the limbal vascular plexus into cornea, caused by low reception of oxygen
Rosacea Keratitis
a condition where the cornea becomes inflamed due to rosacea, a skin and eye condition
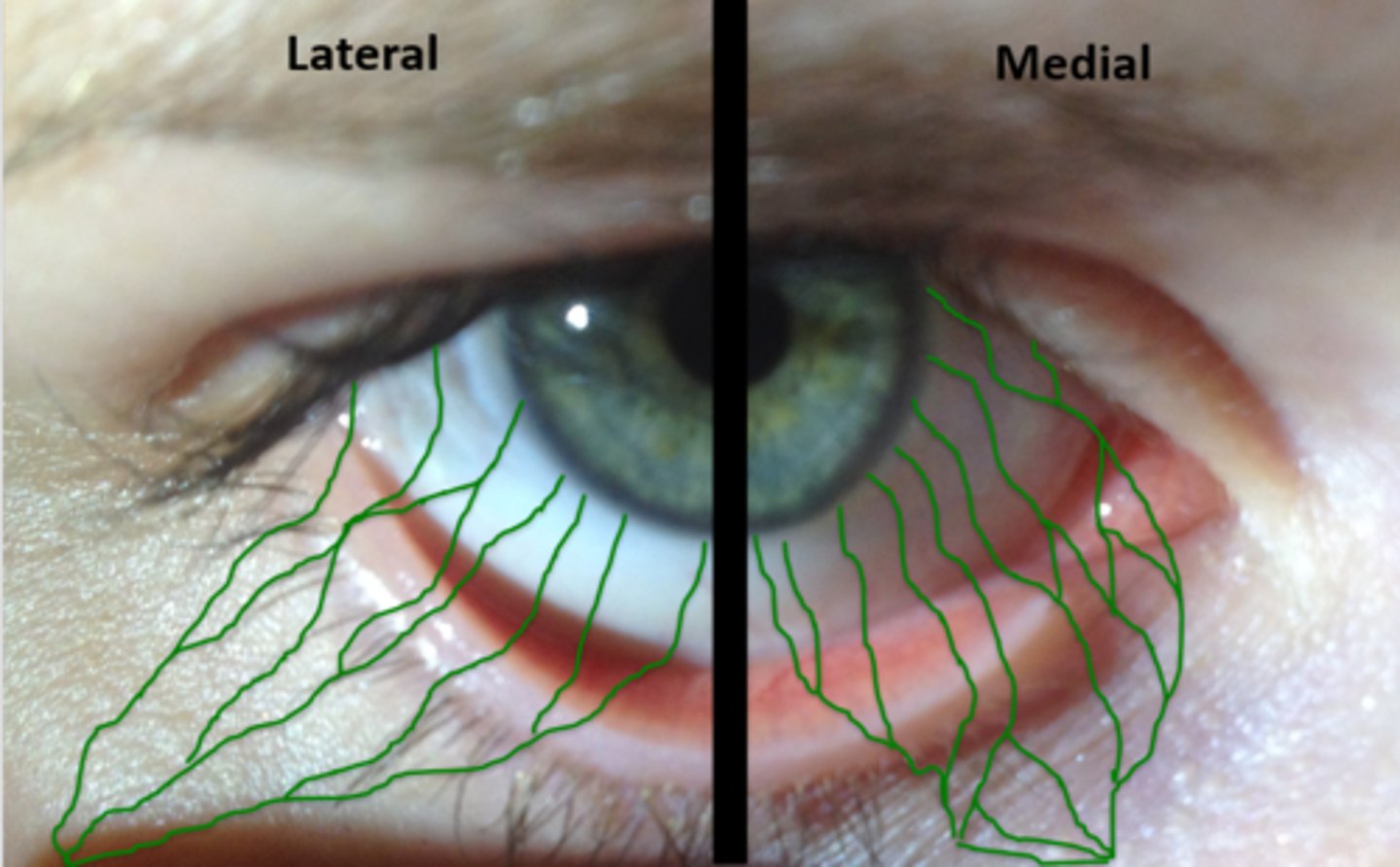
Lymphatic drainage from the conjunctiva
involved lymph will drain to the preauricular lymph nodes (lateral) or submandibular lymph nodes (medial).
How does corneal sensitivity compare to that of the integument?
Corneal sensitivity is 300 to 600 times that of the integument.
Which nerves convey sensory innervation from the cornea?
Sensory innervation from the cornea is conveyed via the long posterior ciliary nerves.
Where do the long posterior ciliary nerves course?
The long posterior ciliary nerves course in the suprachoroidal space.
What structure do the long posterior ciliary nerves form within the corneoscleral limbus?
They form an annular plexus of smaller branches within the region of the corneoscleral limbus.
What do small radial branches of the corneal nerves extend into?
Small radial branches extend into the middle and anterior stroma.
What plexus is formed just below Bowman's layer?
A subepithelial plexus is formed just below Bowman's layer.
What happens to nerve fibers as they course within the basement membrane?
Nerve fibers turn 90 degrees and course within the basement membrane as a subbasal plexus.
What happens to nerve fibers in the subbasal plexus?
Nerve fibers in the subbasal plexus lose their myelin sheath and become naked.
Where do naked nerve fibers enter in the cornea?
They enter the corneal epithelium where they form an intraepithelial plexus.
Are sensory nerve fibers present in the posterior stroma, Descemet's membrane, and corneal endothelium?
No, sensory nerve fibers are not present in these areas.
What type of nerve fibers are also present in the cornea?
Some sympathetic nerve fibers are also present in the cornea.
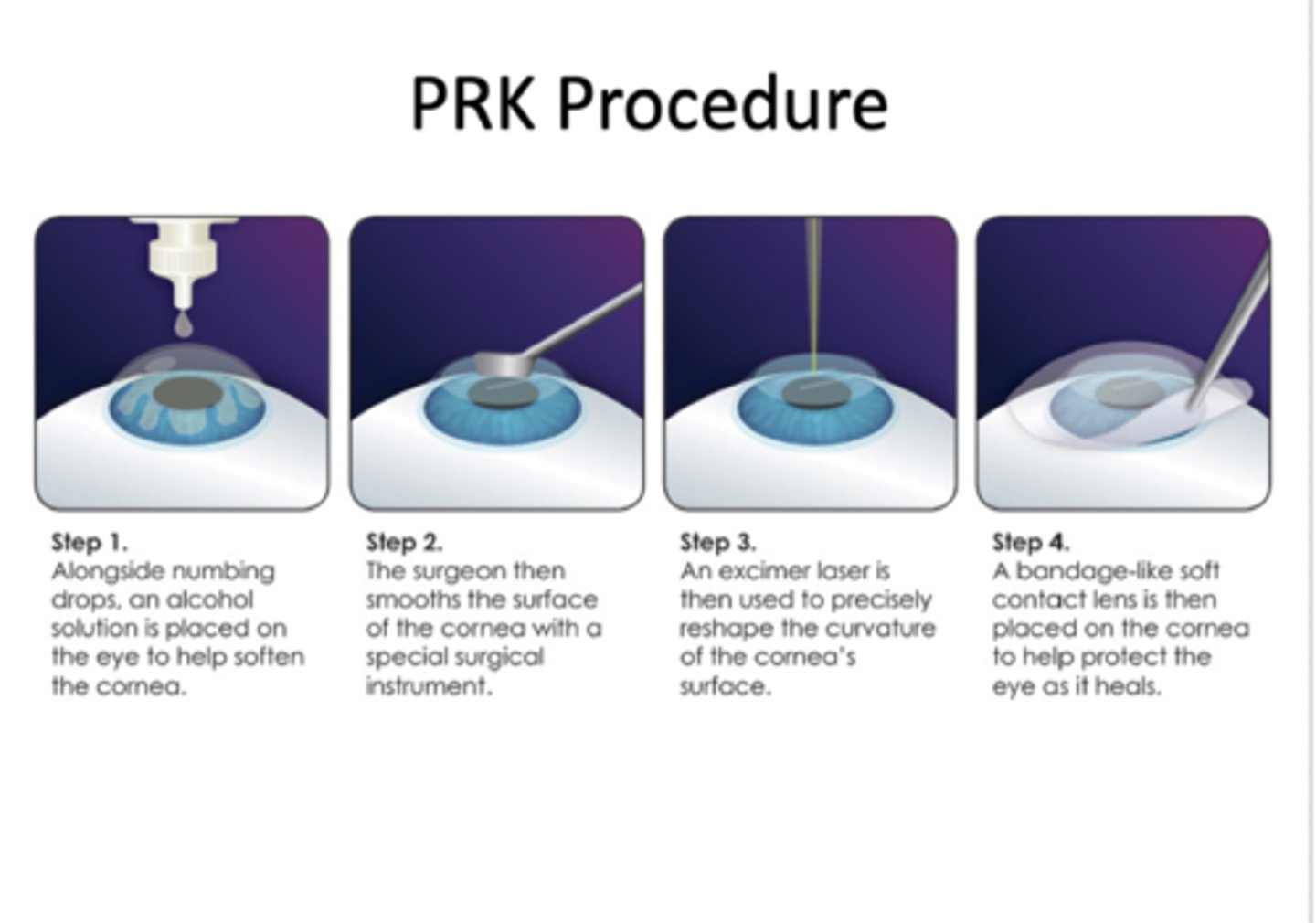
Photorefractive keratectomy (PRK)
Corneal epithelium is debrided with surgical tool
-193-nm argon fluoride excimer laser used to ablate anterior stroma
-Bandage contact lens placed over the cornea
-Re-epithelialization of cornea over ablated region
-Can be painful during the first 24 hours
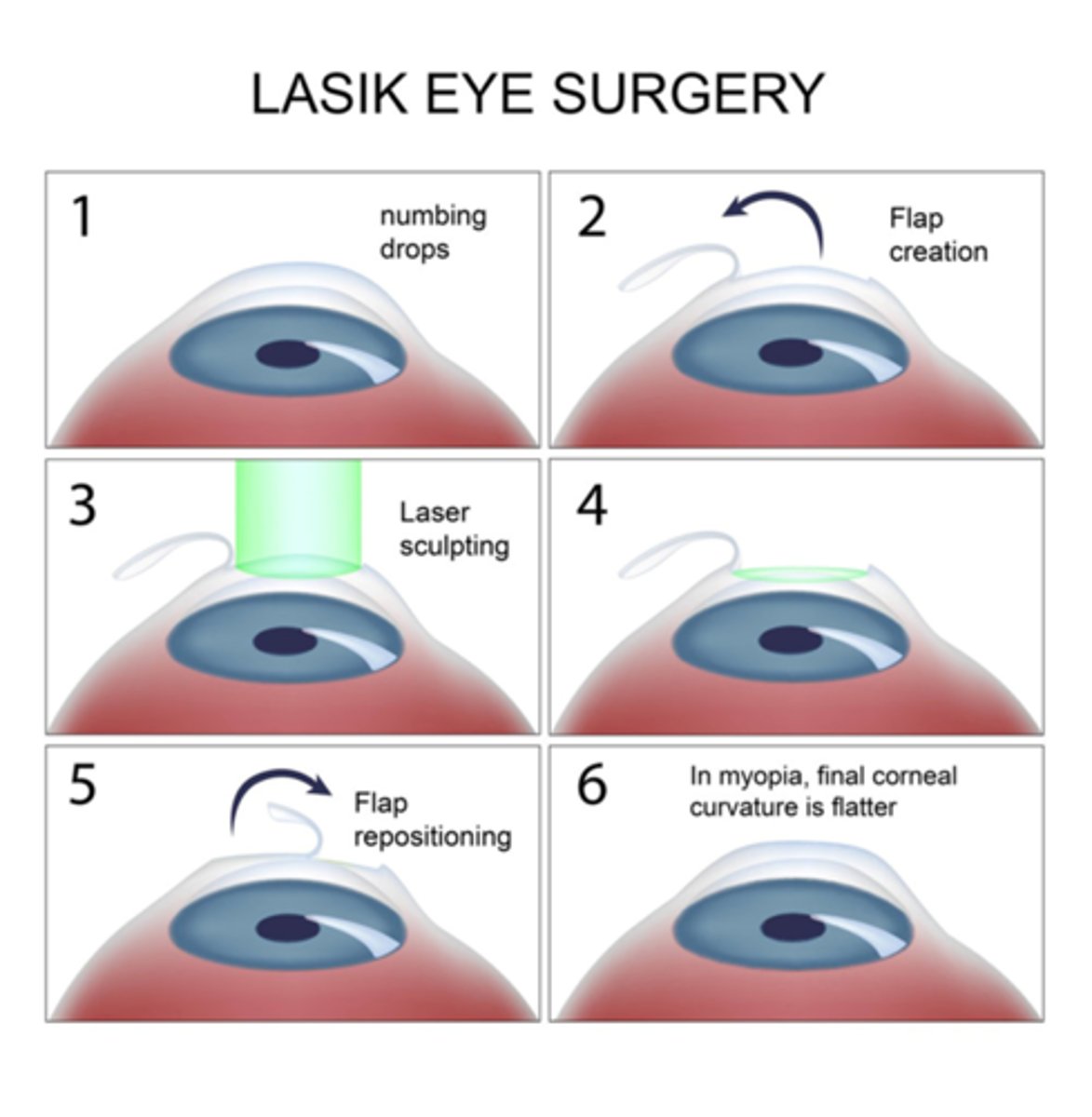
Laser-Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis (LASIK)
•Keratomileusis comes from Greek words for "cornea" and "to carve"
•Flap created and folded back
•Anterior stroma ablated using laser
•Flap replaced
Radial Keratotomy (RK)
Radial incisions cut into stroma to flatten the cornea
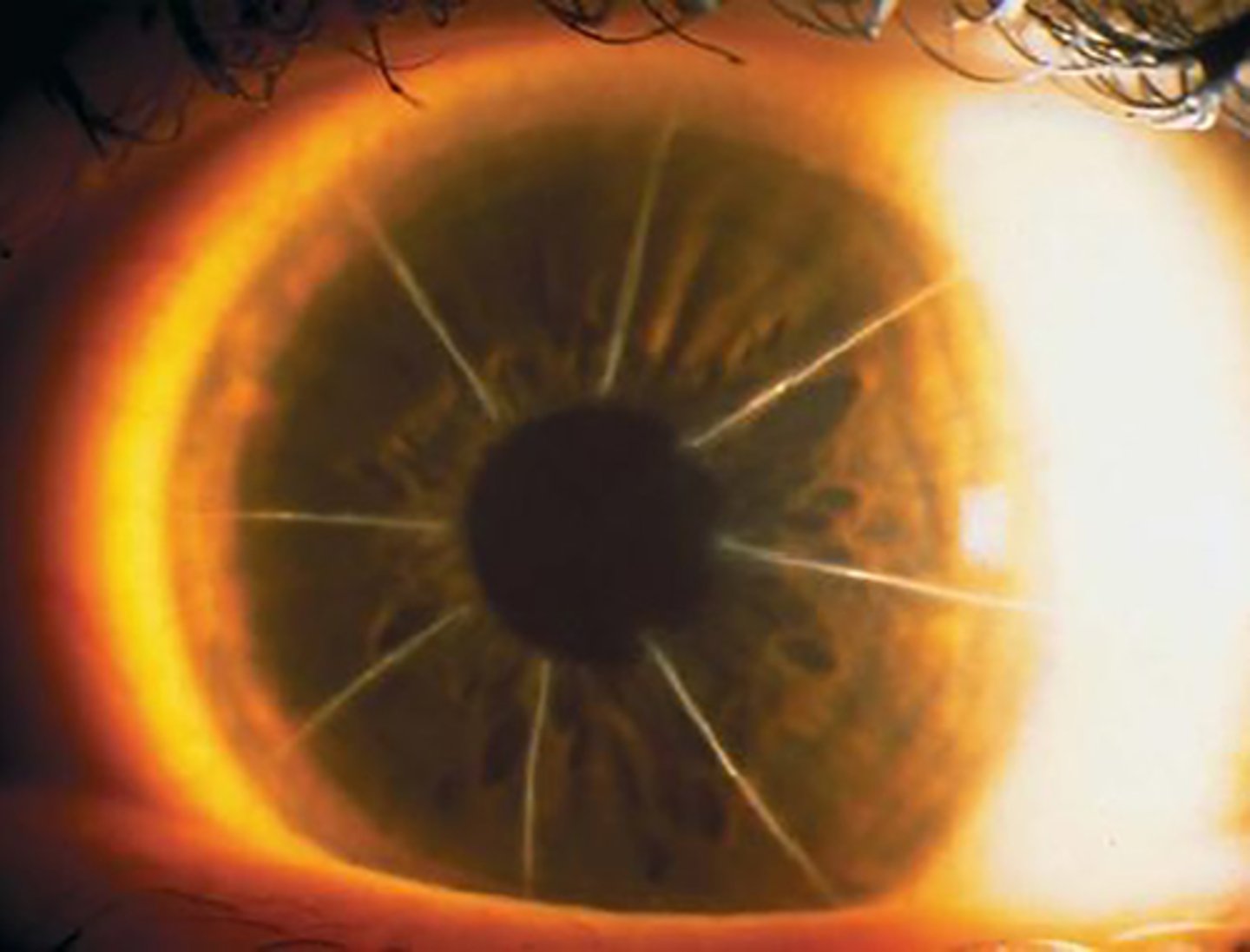
Penetrating keratoplasty (PK)
option for corneal dystrophy patients when lamellar graft not desirable; recurrence of dystrophic findings in corneal transplant are common (full thickness transplant)
