Eukaryotic Cells and Organelles
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cell structure (cgp)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Cell-surface (Plasma) Membrane
The membrane is found on the surface of animal cells and just inside the cell wall of other cells. its in all cells
It regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell. It also has receptor molecules on it, which allow it to respond to chemicals like hormones.
made from phospholipid bilayer
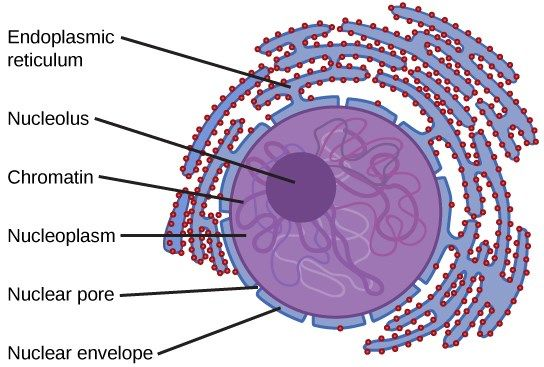
Nucleus
A large organelle surrounded by a nuclear envelope (double membrane), which contains many pores. The nucleus contains chromosomes (which are made from protein-bound linear DNA) and one or more structure(s) called a nucleolus
The nucleus controls the cell’s activities (by controlling the transcription of DNA). DNA contains instructions to make proteins. The pores allow substances (e.g. RNA) to move between nucleus and cytoplasm.
The nucleolus makes ribosomes
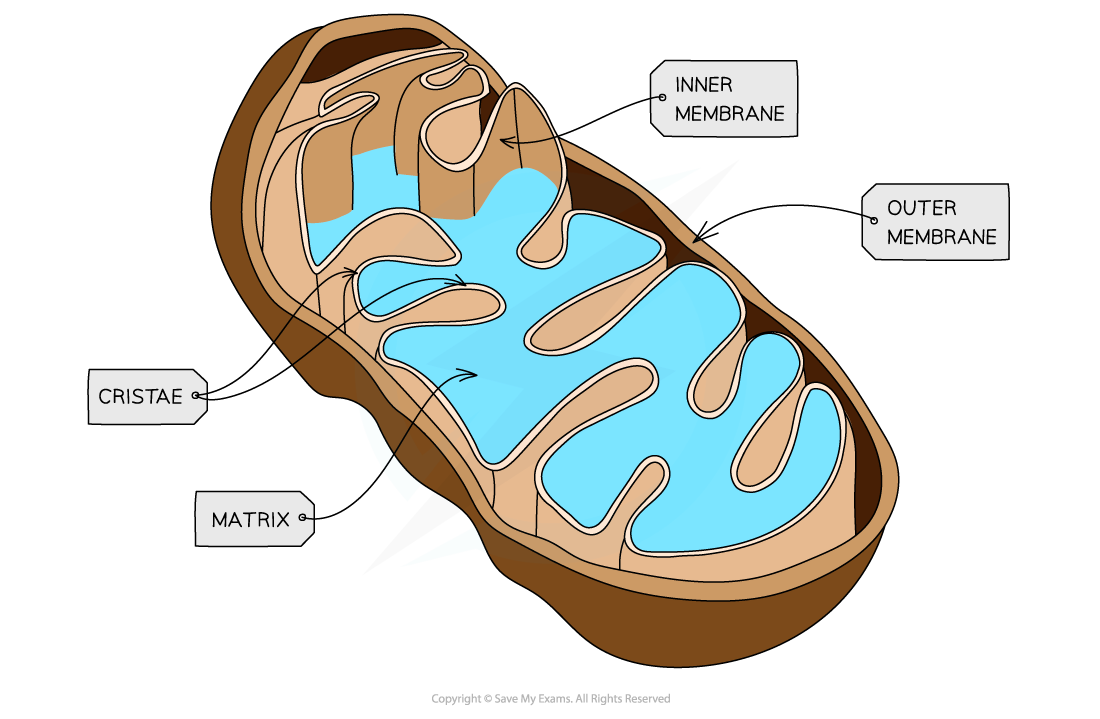
Mitochondrion
They are usually oval-shaped. They have a double membrane- the inner one is folded to form structures called cristae. Inside is the matrix, which contains enzymes involved in respiration
The site of aerobic respiration, where ATP is produced. They are found in large numbers in cells that are very active and require a lot of energy
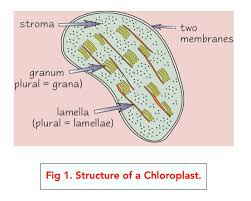
Chloroplast
a small, flattened structure found in plant algal cells. It’s surrounded by a double membrane, and also has membranes inside called thylakoid membranes. These membranes are stacked up in some parts of the chloroplast to form grana. Grana are linked together by lamellae— thin, flat pieces of thylakoid membrane.
The site where photosynthesis takes place. Some parts of photosynthesis happen in the grana, other parts happen in the stroma (thick fluid found in chloroplasts
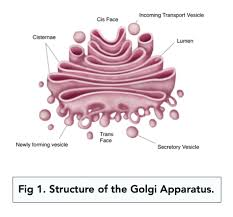
Golgi Apparatus
A group of fluid filled, membrane-bound flattened sacs. Vesicles are often seen at the edges of the sacs. Its a folded membrane.
Vesicles from rough and smooth ER arrive at it and bind to the Golgi
the Golgi modifies these molecules, ensuring they are transported to the next location in the cell.
It then packages them to vesicles to be transported
It processes and packages new lipids and proteins, it also makes lysosomes when it fills vesicles with enzymes
Lysosome
A round organelle surrounded by a membrane, with no clear internal structure. It’s a type of Golgi vesicle
contains digestive enzymes called lysozymes. These are kept separate from the cytoplasm by the surrounding membrane, and can be used to digest the invading cells or to break down worn out components of the cell.
Ribosome
A very small organelle that either floats free in the cytoplasm or is attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. It’s made up of proteins and RNA. It’s not surrounded by a membrane
The site where proteins are made/synthesised
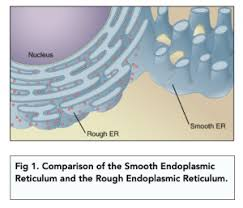
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
A system of membranes enclosing a fluid-filled space. The surface is covered with ribosomes.
Folds and processes proteins that have been made at the ribosomes
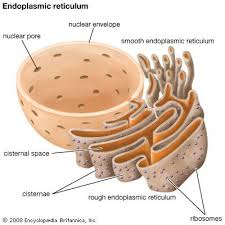
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Similar to rough endoplasmic reticulum but with no ribosomes
Synthesises and processes lipids
Cell Wall
A rigid structure that surrounds cells in plants, algae and fungi. In plants and algae it is made mainly of the carbohydrate cellulose. In fungi it’s made from chitin.
Supports cells and prevents them from changing shape.
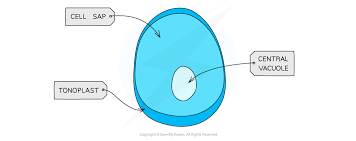
Cell vacuole
A membrane-bound organelle found in cytoplasm of plant cells. It contains cell sap— a weak solution of sugar and salts. The surrounding membrane is called the tonoplast.
Helps maintain pressure inside the cell and keep the cell rigid. This stops plants wilting. Also involved in isolation of unwanted chemicals inside the cell.